Monitoring the tidal topography of the north Yellow River Delta with LIDAR data
-
摘要:
调查潮滩的演化对海岸保护和开发非常重要。随着人为活动的增强,即使过去认为稳定的潮滩也在发生着显著变化。利用航空激光测高(LIDAR)数据和实测剖面数据对黄河三角洲北部潮滩的地形特征和变化进行了分析。这段海岸的西段海岸平直,潮滩坡降小于1/1000,不发育潮沟,潮间有人工开挖的沟道。海岸的东段为老黄河刁口流路岸段。老黄河口岸段突出海岸,同时在两侧形成2个小海湾。LIDAR数据揭示了本段潮滩的三维地形和剖面特征。老黄河口突出岸段西北侧潮滩剖面为平直斜坡,坡度1/1000。而其东侧小海湾湾底的剖面呈上凸的形态,该特征与平面的地形分布、潮间茂密的盐地碱蓬一起,指示淤积。再向东在大堤围成的岬湾内,潮滩受波浪作用形成潮间坝。因此,黄河三角洲北部潮滩受局部地形影响大,局部岸段呈侵蚀状态或淤积状态。LIDAR数据还揭示了潮沟的特征。顺着潮沟的走向,沟底的坡度比潮间带的坡度小,近乎水平,说明涨潮时为何潮沟水位会迅速上升。
Abstract:Tidal flat of the north Yellow River Delta has been strongly influenced by human activities. In this study, the LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) data and in-situ topographic data were used to study the characteristics and changes of the tidal flat in this area. The west section of the area is characterized by straight, featureless tidal flat with tidal slope less than 1/1000. The east section is the coast of the abandoned Yellow River section. LIDAR data show the topographic characteristics of the tidal flat. In the northwest of the abandoned Yellow River section, the tidal flat profiles are straight slope with a gradient of about 1/1000. However, a tidal profile in the bay in the east of the abandoned river mouth exhibits upward convex. The profile, along with the plan view of topography and the growing saline seepweed (Suaeda salsa), indicates that the tidal flat is accretional. A strong eroded tidal profile is located in a small bay formed by seawalls. The different patterns of profiles show that the local factors such as local morphology, hydrodynamic conditions, and human activities influence the topography of tidal flats. LIDAR data also show that the bottom of a tidal channel is almost flat. Therefore, through the tidal channels, the sea water rapidly enters the tidal flat when the tide comes in.
-
Keywords:
- LIDAR /
- tidal flat profile /
- tidal channel /
- human activities /
- Yellow River Delta
-
致谢: 感谢山东正元航空遥感技术有限公司冯幼贵经理和青岛海洋地质研究所王飞飞、徐刚副研究员及刘森博士在工作中给予帮助。
-
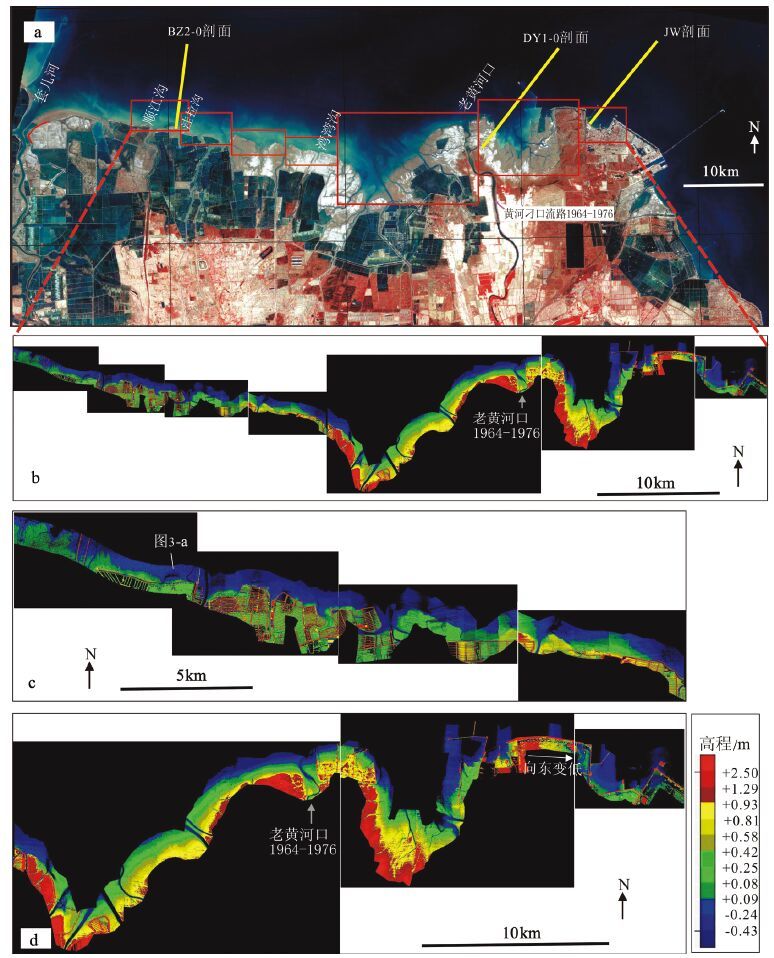
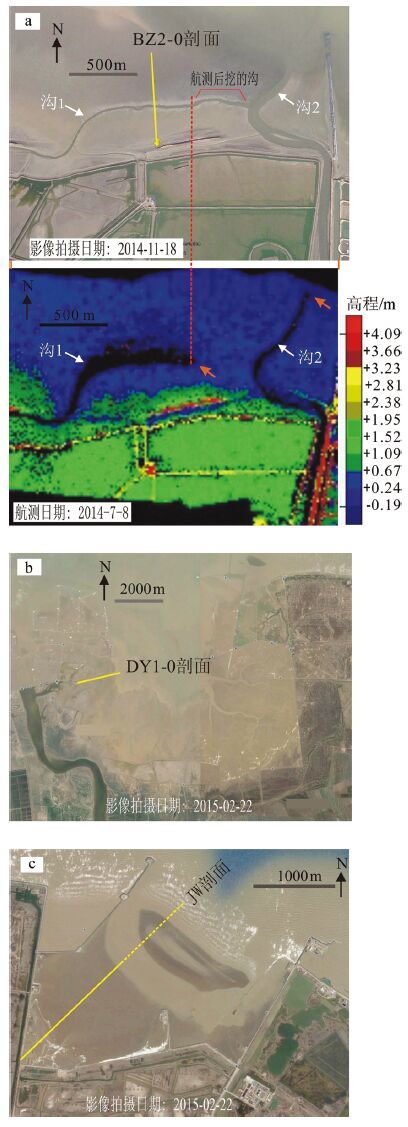
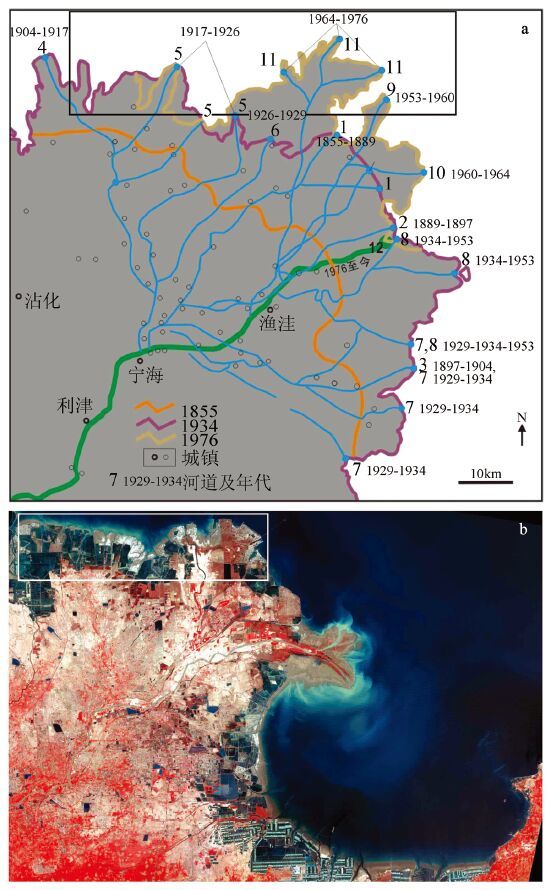
图 1 黄河河道变迁[1] (a) 与研究区位置(b)
Figure 1. Channel migrations of Yellow River (a) and the 2009 satellite image (ETM+) of the study area (b)
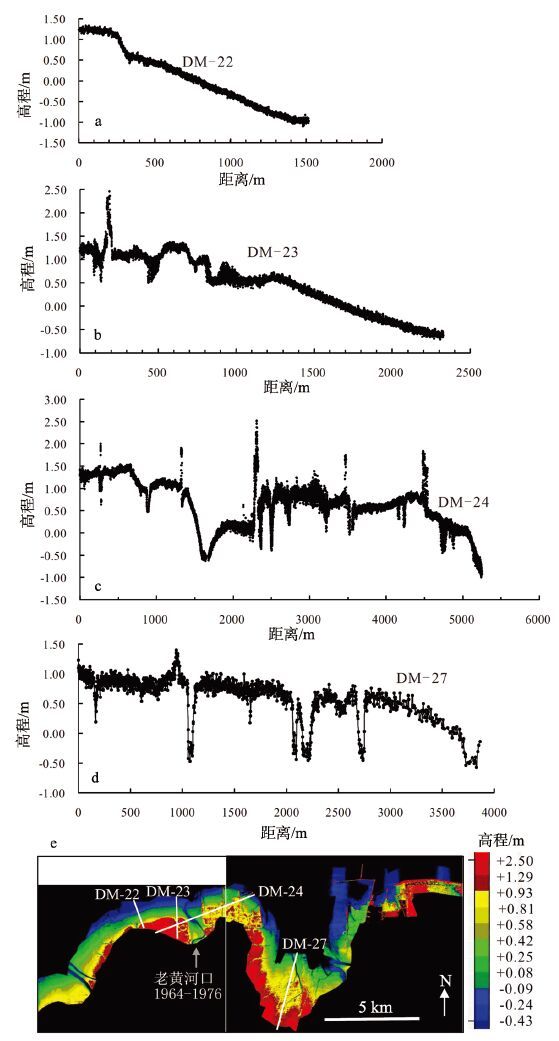
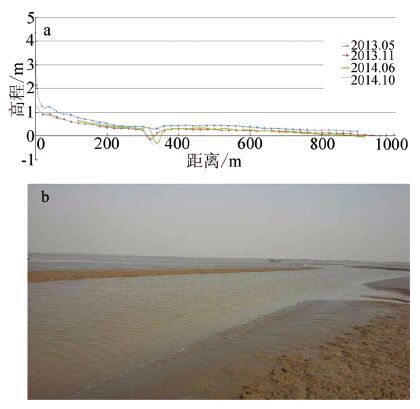
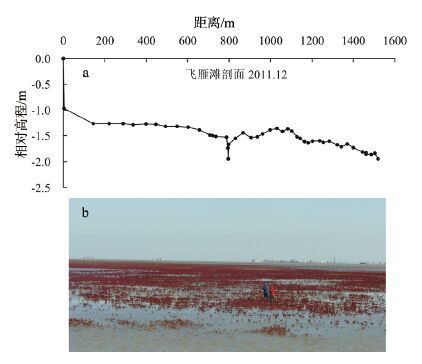
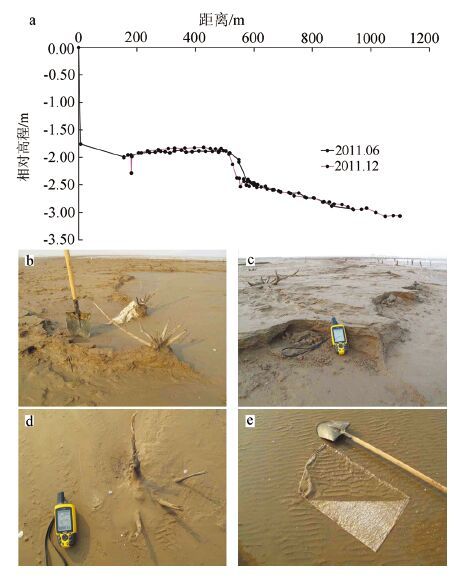
图 5 黄河三角洲沾化潮滩监测剖面对比(a)及剖面上的沟(b)
(2013 年5 月测量时没有沟,2013 年11 月测量时出现一条浅沟(b),2014 年11 月18 日,沟向东延伸,(见图 4-a)
Figure 5. The Zhanhua profiles in the Yellow River Delta (a) and a photo of a channel in the profile (b)
-
庞家珍, 司书亭. 黄河河口演变I近代历史变迁[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1979, 10(2):136-141. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYFZ197902005.htm 黄世光, 王志豪. 黄河1964-1976年刁口流路泥沙冲淤及其分布特点[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1991, 11(1):15-28. 燕峒胜, 蒲高军, 张建华, 等. 黄河三角洲胜利滩海油区海岸蚀退与防护研究[M]. 郑州:黄河水利出版社, 2006. 成国栋, 薛春汀. 黄河三角洲沉积地质学[M]. 北京:地质出版社, 1997. 尹延鸿. 潮沟研究现状及进展[J]. 海洋地质动态, 1997, 13(7):1-4. 周良勇, 刘健, 刘锡清, 等. 现代黄河三角洲滨浅海区的灾害地质[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2004, 24(3):19-27. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200403003.htm 黄海军, 樊辉. 黄河三角洲潮滩潮沟近期变化遥感监测[J]. 地理学报, 2004, 59(5):723-730. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLXB200405010.htm Ottinger M, Kuenzer C, Liu G H, et al. Monitoring land cover dy-namics in the Yellow River Delta from 1995 to 2010 based on Land-sat 5 TM[J]. Applied Geography, 2013, 44:53-68. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeog.2013.07.003 Ottinger M, Kuenzer C, Liu G H, et al. Monitoring land cover dy-namics in the Yellow River Delta from 1995 to 2010 based on Land-sat 5 TM[J]. Applied Geography, 2013, 44:53-68. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeog.2013.07.003
Chu Z X, Sun X G, Zhai S K, et al. Changing pattern of accretion/erosion of the modern Yellow River (Huanghe) subaerial delta, Chi-na:Based on remote sensing images[J]. Marine Geology, 2006, 277(1/2):13-30. Chu Z X, Sun X G, Zhai S K, et al. Changing pattern of accretion/erosion of the modern Yellow River (Huanghe) subaerial delta, Chi-na:Based on remote sensing images[J]. Marine Geology, 2006, 277(1/2):13-30.
栗云召, 于君宝, 韩广轩, 等. 基于遥感的黄河三角洲海岸线变化研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2012, 36(4):99-106. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYKX201204016.htm 任于灿, 丁东, 董万, 等. 黄河三角洲的蚀退[C]//成国栋.黄河三角洲现代沉积作用及模式. 北京:地质出版社, 1991:70-71. 周良勇, 李广雪, 刘健, 等. 黄河三角洲潮滩剖面特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(2):1-8. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200602000.htm Morton R A, Miller T L, Moore L. National Assessment of Shore-line Change:Part 1 Historical Shoreline Change and Associated Coastal Land Loss along the U.S. Gulf Mexico[M]. USGS Center for Coastal and Watershed Studies. St. Petersburg, Florida, 2004. Morton R A, Miller T L, Moore L. National Assessment of Shore-line Change:Part 1 Historical Shoreline Change and Associated Coastal Land Loss along the U.S. Gulf Mexico[M]. USGS Center for Coastal and Watershed Studies. St. Petersburg, Florida, 2004.
任于灿, 周永青. 废弃的黄河三角洲的地貌特征及演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1994, 14(2):19-28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ402.001.htm



 下载:
下载: