Precise identification of land-subsiding layers and reconstruction of subsid-ence process in Tianjin Binhai New Area
-
摘要:
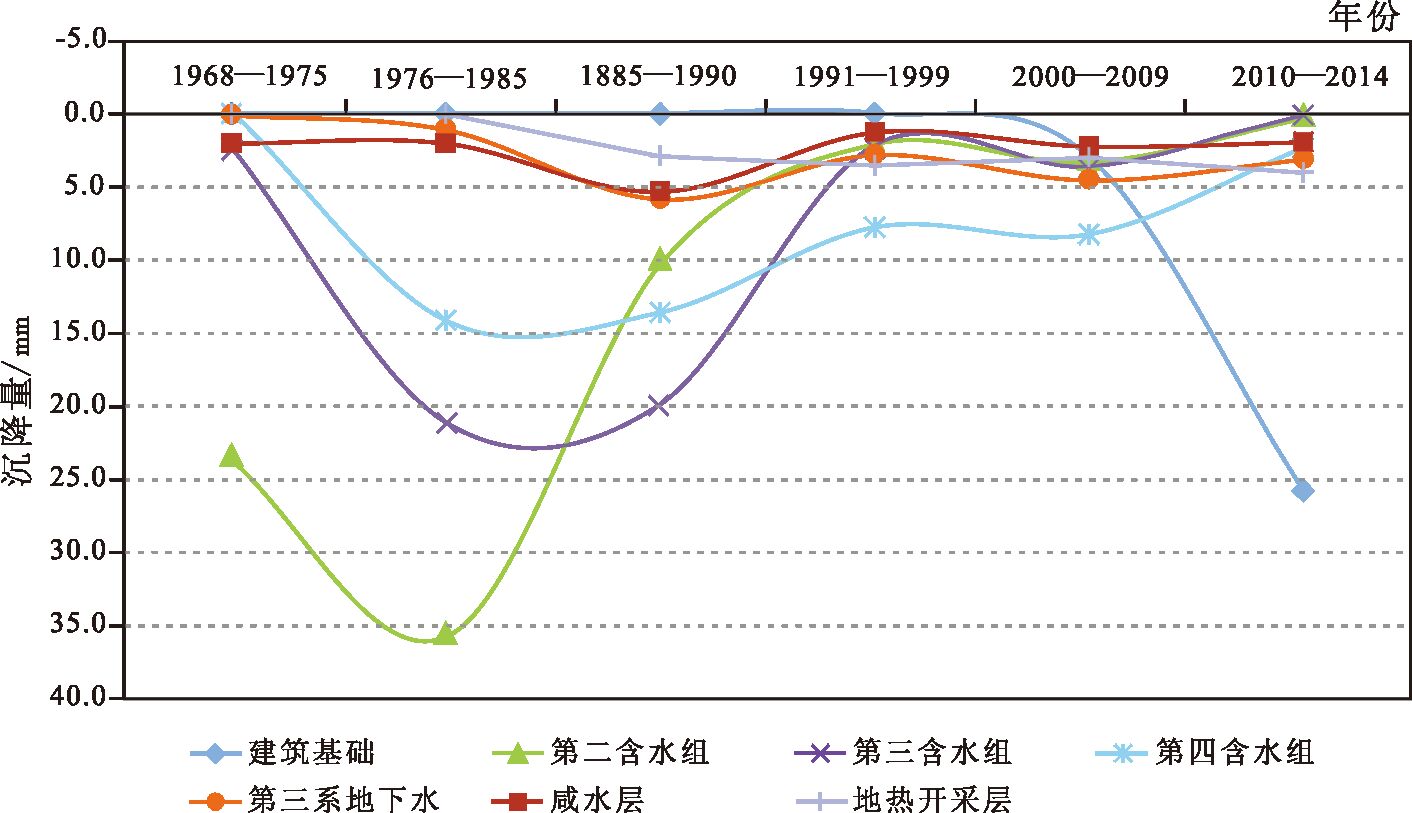
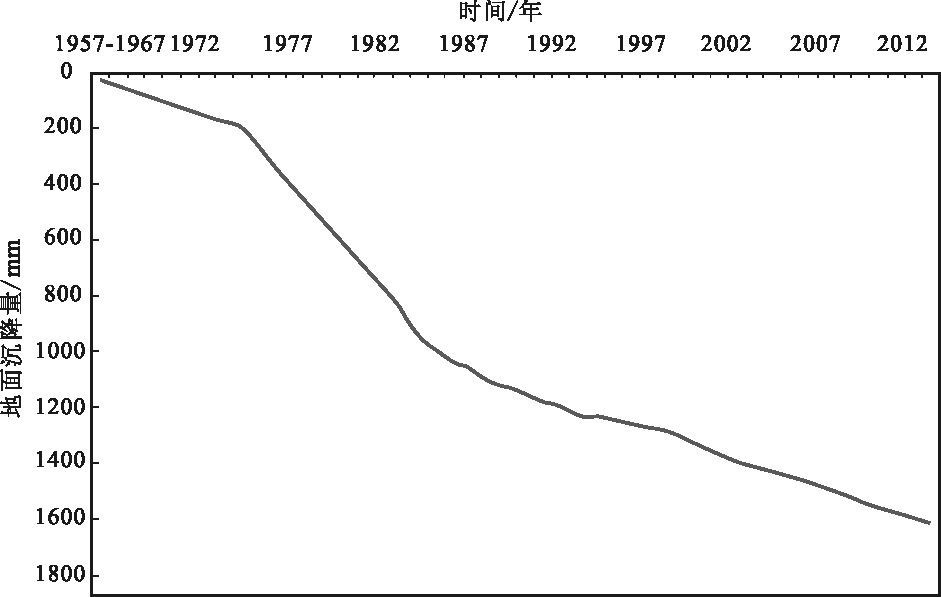
塘沽地区地面沉降是新生代松散沉积物多层位沉降叠加的结果,精准识别各层位的沉降贡献是该区地面沉降防控的关键。利用塘沽G2地面沉降分层标组2011-2014年观测数据,对新生代沉积物不同层位的地面沉降进行了精准识别;结合以前的分层标观测资料,重建了1960年以来不同层位的地面沉降过程。结果显示,在1960-1970年地下水开发初期,地面沉降主要层位是浅部粘性土自然固结和第二含水组地下水开采;1970-1980年深层地下水开采高峰期,主沉降层位由二组逐渐加深到三、四组;1985年以后实施了地面沉降控制措施后,第四系地下水开采引起的地面沉降逐渐减小;2000年之后,随着滨海新区的成立和大规模的城市建设,城市建设引起的建筑基础沉降逐渐成为主要的沉降层。通过对不同时期主要地面沉降层位的转换过程分析,提出地面沉降精准防治新思路。
Abstract:Land subsidence of Tanggu results from multi-layers subsidence of Cenozoic unconsolidated sediments, so accurate identification of each layer's contribution is s key problem for the prevention and control of land subsidence. In this paper, based on the land subsidence monitoring data of Tanggu G2 borehole extensometer during 2011~2014, the authors identified land subsidence of different layers of Cenozoic sediments precisely. Combined with previous data, the land subsidence process since 1960s was reconstructed, and the result shows that during the early stage groundwater mining of 1960~1970, land subsidence resulted mainly from shallow clayey soil layers of natural consolidation and second aquifer groundwater exploitation; during deep groundwater mining peak of 1970~1980, the main subsidence layers gradually deepened from two groups into three or four groups; after the beginning of the land subsidence control measures in 1985, land subsidence caused by Quaternary groundwater exploitation decreased; from 2000 to the present, with the establishment of Tianjin Binhai New Area and large-scale urban construction, the land subsidence caused by building foundation of urban construction has gradually become a major subsidence layer. In this paper, a new thinking for precise land subsidence prevention and control is proposed on the basis of the analysis of major land subsidence layers during different periods.
-
-
表 1 G2 孔各含水组厚度及粘性土厚度统计
Table 1 Statistics of the thickness for each aqueous stratum and the clay layers, Borehole G2

表 2 G2 分层标地面沉降监测层位
Table 2 Monitoring layers of G2 Borehole extensometer

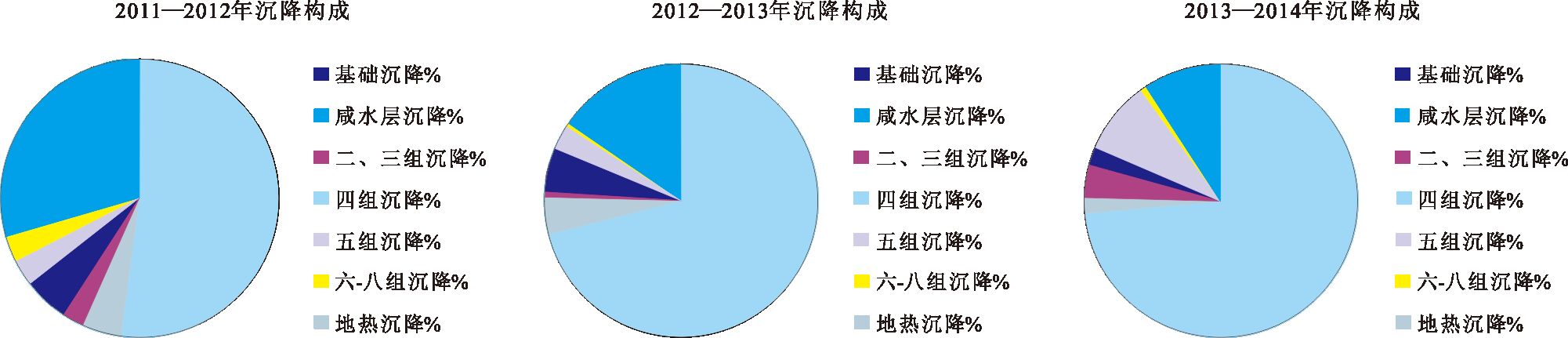
表 3 G2分层标2011—2014 年地面沉降监测结果
Table 3 Monitoring results of G2 Borehole extensometer from 2011 to 2014
时间/年 基础沉降/mm 咸水层沉降/mm 二、三组沉降/mm 四组沉降/mm 五组沉降/mm 六—八组沉降/mm 地热沉降/mm 总沉降量/mm 2011—2012 -28.79 -2.44 1.34 -2.94 -1.6 1.71 -16.2 -48.92 2012—2013 -23.29 -1.43 0.19 -1.74 -0.96 0.11 -5.12 -32.24 2013—2014 -34.02 -0.82 -1.77 -1.01 -3.95 0.42 -4.25 -45.4 2011—2014 -86.1 -4.69 -0.24 -5.69 -6.51 2.24 -25.57 -126.56 表 4 1985 年以来不同沉降层位的沉降量变化
Table 4 Land subsidence changes in different layers since 1985
沉降层 1985 年沉降量/mm 占比/% 1989 年沉降量/mm 占比/% 1999 年沉降量/mm 占比/% 2014 年沉降量/mm 占比/% 基础沉降 3.5 9.2 7.2 27.3 34.02 74.93 Ⅰ组 0.82 1.81 Ⅱ组 36 36 6.6 17.3 +0.5 +1.9 1.77 3.90 Ⅲ组 23 23 13.3 34.9 0.7 2.7 4.54 9.99 Ⅳ组以下 38 38 14.7 38.6 19.0 72.0 4.25 9.36 地热沉降 合计 100 38.1 26.4 45.4 -
徐恒力. 环境地质学[M]. 北京:地质出版社, 2009:1-66. 张人权, 梁杏, 靳孟贵, 等. 水文地质基础(第六版)[M]. 北京:地质出版社, 2011:1-151. 董克刚, 王威, 于强, 等. 天津市地面沉降防治历史的调查研究及启示[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2008,19(3):54-59. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH200803014.htm 王家兵. 天津深层地下水资源持续利用研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2006. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-11415-2006065340.htm 吴铁钧, 崔小东, 牛修俊, 等. 天津市地面沉降研究及综合治理[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 1998, 5:17-20. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG805.004.htm 林黎, 赵苏民, 李丹, 等. 深层地热水开采与地面沉降的关系研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2006, 3:34-36. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200603007.htm 张百鸣, 金爱善. 天津市滨海地区地热资源开发对地面沉降的影响[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 1998, 9(2):112-117. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH802.019.htm 马凤如, 林黎, 王颖萍, 等. 天津地热资源现状与可持续性开发利用问题[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2006, 29(3):222-228 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ200603008.htm 夏大平, 王心义, 林健旺, 等. 天津地热开发对环境地质条件的影响[J]. 山东科技大学学报, 2008, 27(5):14-18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDKY200805005.htm 白晋斌, 牛修俊. 天津新生界固结特征与地面沉降[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2010, 21(1):42-46. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201001011.htm 刘泓伶, 李波, 樊艳云, 等. 简述地面沉降的研究进展[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护, 2012, 23(1):16-20. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZHB201201004.htm 王荣, 贾三满, 赵立新. 北京市地面沉降监测标设计与施工技术[J]. 技术应用, 2012, 7(1):46-50. 张阿根, 顾为栋. 上海市地面沉降监测标的设计原理与施工技术[J]. 探矿工程, 2000, 5:67-69. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TKGC200005027.htm 张永强, 杨新爱, 张海涛. 天津市海岸带地面沉降影响因素分析[J]. 地下水, 2013, 35(3):58-59. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU201303020.htm 吴铁钧, 金东锡. 天津地面沉降防治措施及效果[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 1998, 9(2):6-12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH802.001.htm 肖国强. 深部粘性土高压固结机理与地面沉降过程研究——以天津滨海新区G2孔为例[D]. 中国地质大学(武汉)博士学位论文, 2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10491-1015661025.htm 花向红, 邹进贵. 高层建筑沉降监测技术及应用研究[J]. 矿山测量, 2002, 3(1):8-11. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KSCL200201002.htm



 下载:
下载: