Local 137Cs reference profile on Bohai Bay:Implications, methods and initial results
-
摘要:
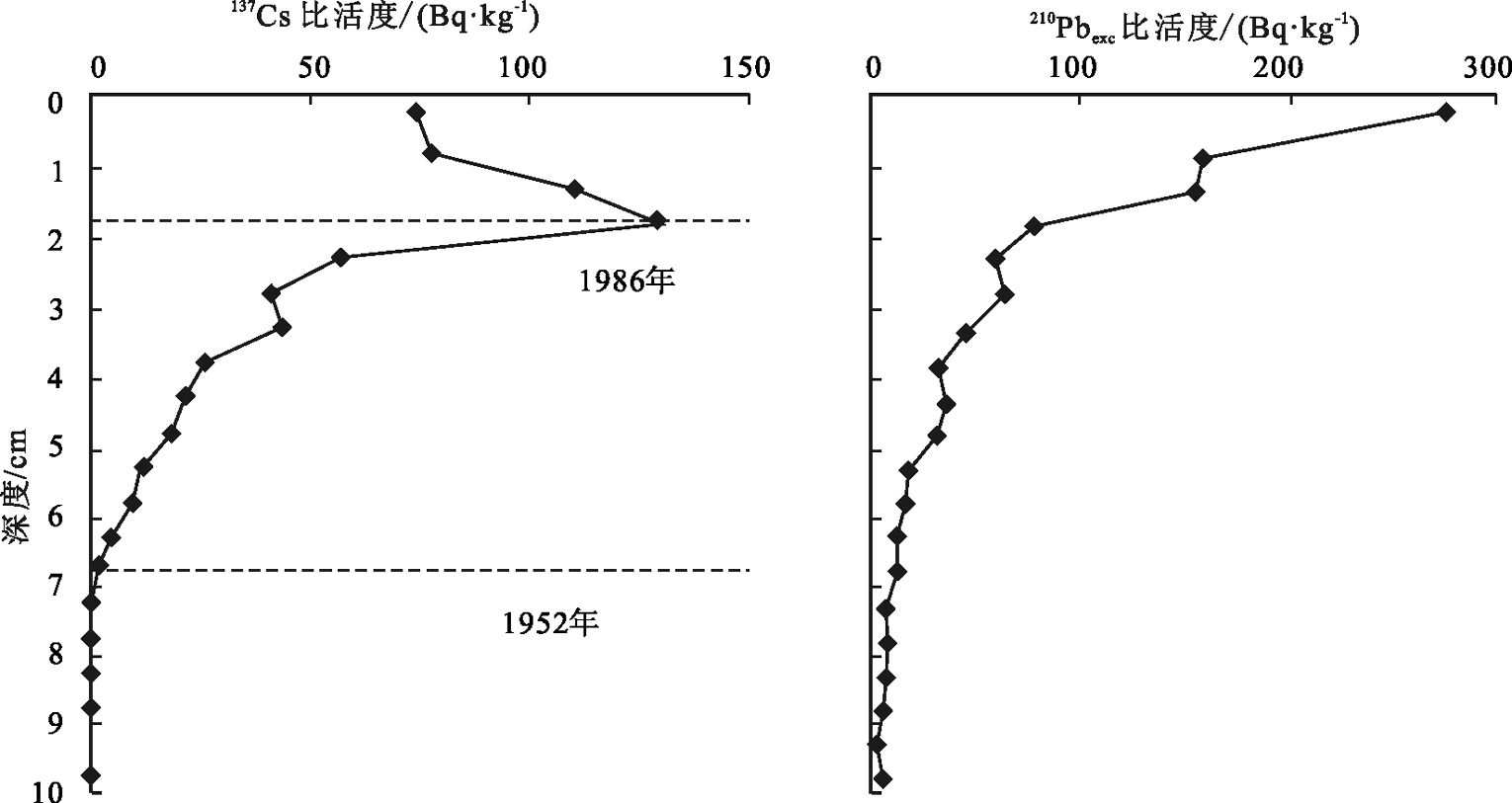
海岸带地区近百年来的现代地质过程重建必须以精确的年代学研究为基础,137Cs时标法和210Pbexc测年法是目前广泛应用的方法。由于易受到河流沉积物供给变化、潮位状况、极端天气事件等的影响,海岸带现代过程的定量研究一直是高分辨率研究的瓶颈。区域性参考剖面可以提升现代沉积物测年方法在海岸带应用中的可靠性。因此,建立区域性的210Pbexc和137Cs比活度-深度参考剖面,将改善对海岸带及邻近海区实测数据的解释。以渤海湾海岸带为研究区,选取沉积环境相对稳定、水平搬运作用较小的地区,采用人工探坑、Eijkelkamp槽型取样器获取了2个柱状岩心,通过γ能谱仪对样品进行210Pb、226Ra及137Cs比活度测试,绘制剖面图,结合研究区已有数据,总结出6类海岸带常见的210Pbexc和137Cs比活度-深度剖面类型,并重建了渤海湾海岸带137Cs区域性参考剖面。结果显示,137Cs在渤海湾地区的最大峰值指示1963年,可以作为区域性主要参考时标。但是,最大峰值上部的次峰在不同区域指示不同的时标,S4和S5两个站位该峰值指示的并非1986年时标。
Abstract:Reconstruction of geological processes during the last hundred years needs accurate dating methods. 137Cs and 210Pb dating methods are widely used at present. As coastal areas are vulnerable to the changes of river sediment supply, the local tidal conditions, and the effects of extreme weather events, the quantitative descriptions of their modern processes have been a bottleneck for the highresolution studies. Regional reference- profiles can help improve the precision of modern sediments dating. If regional 210Pbexc and 137Cs reference-profiles could be established, they will play a very positive role in the interpretation of the dating results of modern sediments. In this paper, the relatively stable salt-marsh sites with little transported activity were selected along the coastal areas of Bohai Bay. Based on systematic sampling of trench walls and Eijkelkamp cores, the authors measured the 210Pb, 226Ra and 137Cs activities of subsamples by γ spectrometer, combined with the existing data in the study area. Consequently, the local reference-profiles were established, six types of 210Pbexc and 137Cs activity-depth profiles were summarized, and the 137Cs regional reference-profiles were prelimiarily obtained. 137Cs maximum peak in the Bohai Bay is correlated with 1963, which could be used as the main time-marker of the coastal area. However, the second peak above the maximum peak detected in some cores can not be correlated with 1986 but is actually controlled by local environmental factors such as those indiacated at sites S4 and S5.
-
Keywords:
- Pbexc /
- 137Cs /
- reference profiles /
- coast /
- Bohai Bay
-
随着地球科学家对地球系统研究的不断深入,人们发现新元古代时地球系统发生了一系列的剧烈变化。在地球地质历史的这一时期,地球从较稳定的古-中元古代(17~7.5亿年)[1],进入剧烈变动的中-晚新元古代时期(7.5~5.4亿年)。中-晚新元古代地球上出现多期极冷事件[2-7],条带状铁矿也在消失十多亿年后,在新元古代中期又重新出现[1, 8],大洋与大气圈的氧含量快速增加[9-11]。地球系统这一系列的剧变很可能发生在Rodinia超大陆裂解的背景下。因此,重建这一时期的古地理古板块位置对于理解这些剧变至关重要。然而,由于这一时期(7.5~5.4亿年)全球不同块体古地磁数据的缺乏和可靠性问题,其古地理重建一直存在较大的争议[12-20]。
影响这一时期古地磁数据可靠性的因素,除了考虑剩磁的获得时间外,近年来越来越多的学者注意到非偶极子场及磁倾角偏低对古地磁数据的影响[21-26],特别是红层中存在普遍的磁倾角偏低现象[27-28]。
最近,Jing等[29]报道了湖北宜昌三峡地区莲沱组红层可靠的古地磁极,并根据Lan等[30]最新的SIMS锆石U-Pb定年研究,确定这一古地磁极年龄应为720Ma。虽然这一古地磁极通过了Van der Voo[31]的6项Q检验,确保其剩磁获得的原生性,但这一结果是否受到后期压实作用的影响并产生磁倾角偏低,以及影响程度的大小等问题,都需要进一步研究。在长阳地区,由于古城冰碛岩覆盖在莲沱组之上,因此准确确定莲沱组的磁倾角,对确定华南这一时期的古纬度及“雪球地球”的研究都具有重要意义。另外,目前华南地块莲沱组古地磁极与南沱组古地磁极相似的问题,一直没有得到可信的解释,本文通过磁倾角偏低的研究,对这一问题进行探讨。
1. 区域地质概况及采样
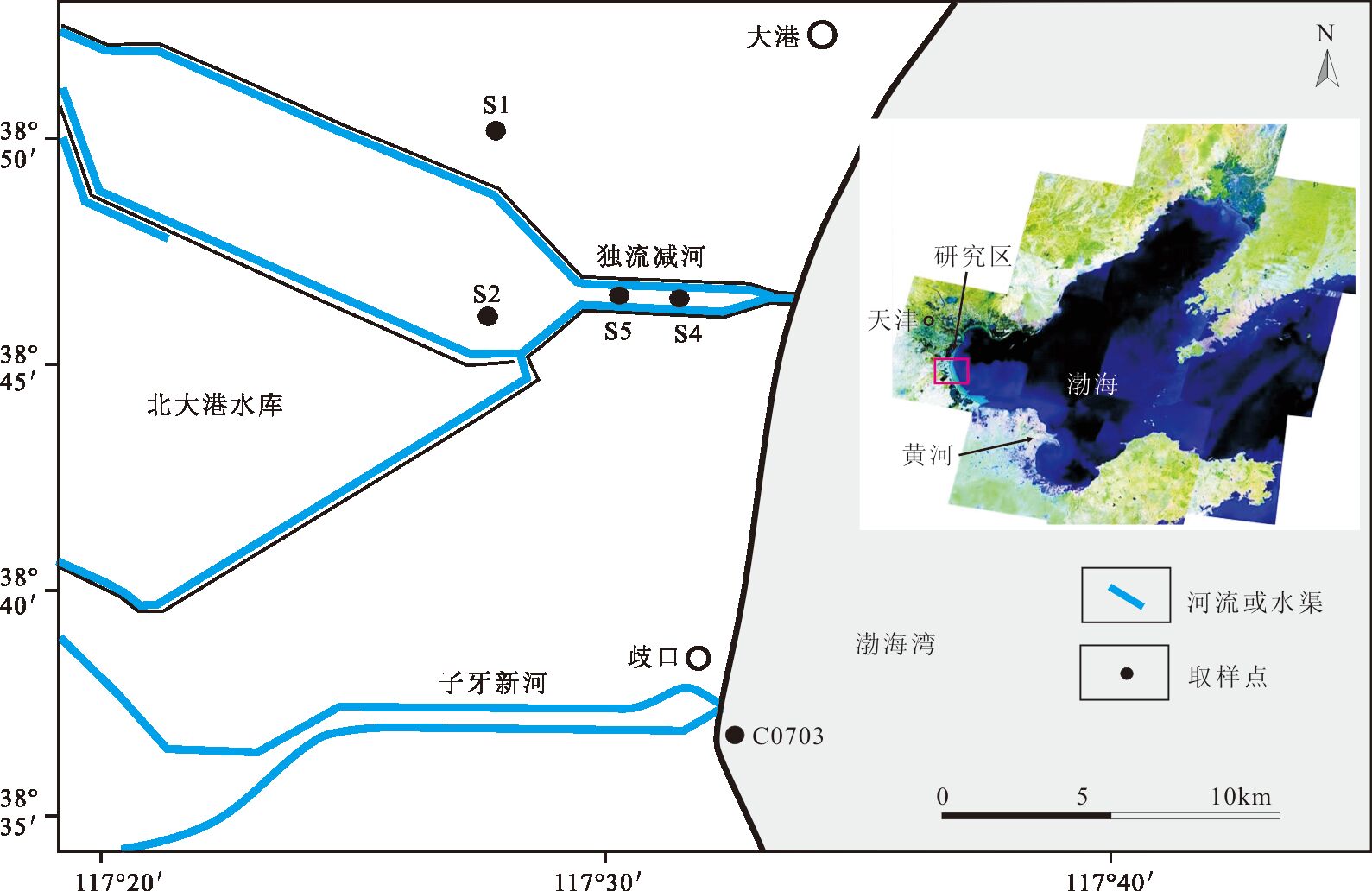
采样区位于华南新元古代地层典型剖面区,湖北三峡地区(图 1)。研究区出露的新元古代沉积地层包括莲沱组、南沱组、陡山沱组、灯影组等。莲沱组一般不整合覆盖于黄陵花岗岩之上,主要为厚层的紫红色砂岩和砾岩,可分为2个大的沉积旋回(图 2),每个旋回底部为砾石或粗粒石英砂岩,向上逐渐变为粉砂岩、泥质砂岩,含多层凝灰岩或凝灰质碎屑岩。在区域上,西北部地层厚度较大,向西南变薄。本区南沱组与莲沱组平行不整合接触或低角度不整合接触,南沱组主要为暗绿色冰碛砾岩,部分为红色冰碛岩[32]。
![]() 图 2 本次研究获取的采点(下划线标注TLS编号)在地层上的分布(TL编号为Jing等[29]采点)Figure 2. Stratigraphic column of the Liantuo Formation and detailed sampling layer positions of three sub-sections at Yichang
图 2 本次研究获取的采点(下划线标注TLS编号)在地层上的分布(TL编号为Jing等[29]采点)Figure 2. Stratigraphic column of the Liantuo Formation and detailed sampling layer positions of three sub-sections at Yichang在三峡地区南部的长阳地区,莲沱组之上覆盖古城组冰碛岩和大塘坡组页岩,而不是直接与南沱组接触[33]。古城组冰碛岩应与扬子西南部广泛发育的长安组冰碛岩一致[33],属于Sturtian冰期的产物。古城组沉积时间应始于715Ma左右[33]。
三峡地区从埃迪卡拉纪开始长期沉积碳酸盐岩,早寒武世有一次沉积间断,直到志留纪宜昌地区大规模抬升,沉积间断接受剥蚀,随后沉陷到早三叠世再次抬升[34-35]。本地区经历了3次主要的构造运动:加里东期、印支期和燕山期构造运动。同时中扬子地区存在与这3次构造运动相关的3期油气生成和排烃过程[36]。区域内构造变形较弱。
本次在宜昌花鸡坡、头顶石及田家院子3个剖面共采集了17块手标本样品(TLS1-17),对莲沱组是否存在磁倾角偏低现象进行检验(图 2)。样品在野外用罗盘测量层面的走向和倾角,并标记在层面上。
2. 实验方法
在室内用台式钻机垂直手标本层面钻取2根以上岩心,并加工出1~2块高2.2cm、直径2.5cm的标准岩心样品。每根岩心选取1~2块,共31块标准样品进行系统热退磁实验。同时对应选择了30块样品进行Hodych等[23]磁倾角偏低校正实验。所有实验工作均在中国地质科学院地质力学研究所国土资源部古地磁与古构造重建重点实验室完成。使用美国ASC Scientific Inc.公司生产的IM-10-30脉冲充磁仪对样品进行充磁,样品系统热退磁由TD-48大型热退磁仪完成,样品剩磁测量在ARGICO-JR6A旋转磁力仪上完成。另外,对部分样品利用KLY-3 Kappabridges进行了氮气环境下磁化率随温度变化实验(K-T),获取连续加热-冷却曲线分析样品磁化率的变化。
3. 实验结果
3.1 逐步热退磁结果
宜昌三峡地区花鸡坡、头顶石及田家院子剖面莲沱组样品的岩石磁学实验结果显示,岩石的特征剩磁载磁矿物为赤铁矿[29]。因此,系统热退磁温度区间在低温段以50~100℃为间隔,高温段温度区间以20℃为间隔,热退磁温度达到680℃(图 3)。样品使用主向量分析法[37]进行剩磁组分分析。
逐步热退磁结果显示,样品中共可以分离出3个剩磁方向(图 3):低温分量一般在小于等于300℃的情况下分离出来, 共有15块样品分离出此分量,其在地理坐标系下的统计方向(Dg=5.9°,Ig=60.1°,kg=81.3, ɑ95=4.3°)与采样点现代地磁场方向接近,应为现代地磁场的热粘滞剩磁;中温分量的温度区间一般在300~600~640℃之间,共有6块样品分离出此分量,其平均方向在地理坐标系下为Dg=34.5°,Ig=78.1°,kg=244.2,ɑ95=4.3°,在地层坐标系下为Ds=78.9°,Is=78.4°,ks=243.5,ɑ95=4.3°。另外,从11块样品中分离出了与宜昌剖面得到的特征分量相似的高温分量(600~680℃),其平均方向在地理坐标系下为Dg=67.0°,Ig=71.6°,kg=124.7,ɑ95=3.9°,在地层坐标系下为Ds=95.3°,Is=67.8°,ks=196.0,ɑ95=3.1°。
3.2 等温剩磁各向异性实验结果
对12个样品,在与其层面呈45°方向,从低到高逐步增加等温直流磁场,获得平行于层面IRMx和垂直于层面IRMz的等温剩磁,直流磁场大小由20、40、60、100、225、315、415、510、510、710、810、950、1200mT依次递增。在每步施加直流场后使用JR6旋转磁力仪对样品进行剩磁测试。然后用TD48大型热退磁炉对所有样品进行系统热退磁,相关数据结果列于表 1中。
表 1 宜昌地区剖面莲沱组样品等温热剩磁各向异性及磁倾角偏低值Table 1. Anisotropy of isothermal remnant magnetization for Liantuo Formation red beds in Yichang areaID Iobs IRMz/IRMx
(610~1200mT)IF1 ΔI1(=IF1-Iobs) IRMz/IRMx
(600°C以上)IF2 ΔI2(=IF2-Iobs) 15 64.4 0.7796 69.518 5.118 0.8542 67.7425 3.3425 15-2c 71.5 0.8414 74.277 2.777 0.8513 74.1009 2.6009 15-5b 65 0.899 67.256 2.256 0.8757 67.7876 2.7876 17-1 72.1 0.831 74.976 2.876 0.8118 75.3075 3.2075 3-1 73 0.87 75.105 2.105 0.8859 74.8452 1.8452 4-2b 66.3 0.6147 74.899 8.599 0.901 68.4206 2.1206 5-2b 64.2 0.8472 67.728 3.528 0.9117 66.2153 2.0153 5-4b 66 0.7989 70.420 4.420 0.872 68.7818 2.7818 7-1 61.9 0.8579 65.389 3.489 0.8731 65.0054 3.1054 8-3 70 0.8737 72.359 2.359 0.856 72.6951 2.6951 8-4 66.8 0.8701 69.548 2.748 0.8977 68.9555 2.1555 平均值 67.8 0.8258 71.377 3.577 0.8719 70.4146 2.6146 注:ID为样品号,Iobs为热退磁实验所得样品磁倾角,IRMz/IRMx(610~1200mT)为610~1200mT之间垂直层面方向和平行层面方向等温剩磁大小的比值,IRMz/IRMx(600°C以上)为600 °C以上垂直层面方向和平行层面方向等温剩磁大小的比值,IF为校正后磁倾角,ΔI为校正值 考虑到实验过程中样品的等温剩磁方向可能受天然剩磁的影响,以及载磁矿物主要为赤铁矿,所以施加外部直流场在200~1200mT之间及系统热退磁温度在600~680℃之间的IRMz/IRMx拟合线反映了赤铁矿的剩磁各向异性特征。
由于垂直于层面的IRMz值大部分在500mT之后略小于平行于层面的IRMx值(图 4-a、d),所以从磁场强度方面考虑,选取在500mT之后的610~1200mT区间的IRMz/IRMx拟合线的斜率作为磁倾角偏低校正因子,其大小为0.8258,对应的沉积压实为18%。另外,从热退磁的方面考虑,选取600~680℃区间的IRMz/IRMx热退磁结果拟合线的斜率作为磁倾角偏低校正因子,其大小为0.8719,对应的沉积压实为13%。利用公式IRMz/ IRMx=tan (Iobs)/tan (IF)进行校正后得到莲沱组磁倾角分别为71.4°和70.4°,两者的磁倾角值差别不大。
![]() 图 4 45°方向加场后平行于层面方向(IRMx)和垂直于层面方向(IRMz)等温剩磁获得曲线图(a, d),IRMz/IRMx关系图(b, e)和IRMz/IRMx的热退磁结果(c, f)Figure 4. Plots of IRMx (parallel to bedding) and IRMz (perpendicular to bedding) acquisitions produced by applying magnetic field at 45° to bedding as function of increasing field (a, d), plots of IRMZ/IRMX(b, e), the thermal demagnetization results of IRMZ/IRMX(c, f)
图 4 45°方向加场后平行于层面方向(IRMx)和垂直于层面方向(IRMz)等温剩磁获得曲线图(a, d),IRMz/IRMx关系图(b, e)和IRMz/IRMx的热退磁结果(c, f)Figure 4. Plots of IRMx (parallel to bedding) and IRMz (perpendicular to bedding) acquisitions produced by applying magnetic field at 45° to bedding as function of increasing field (a, d), plots of IRMZ/IRMX(b, e), the thermal demagnetization results of IRMZ/IRMX(c, f)3.3 岩石磁学实验结果
为了排除样品在加热过程中可能存在的磁性矿物的变化,对几个代表性样品进行了磁化率随温度变化实验(K-T,图 5)。结果表明,部分样品在加热和冷却过程中样品磁化率明显不同(图 5,TLS11),可能是因为样品在加热过程中生成了一部分磁铁矿。但580~680℃之间的加热曲线与冷却曲线一致,表明加热过程中磁性矿物的变化并未影响到样品中赤铁矿的剩磁变化(图 5,TLS11),因此,不影响磁倾角偏低实验的结果。另一部分样品的K-T曲线显示,在加热与冷却过程中,样品的磁化率没有明显的差异,因此样品中不存在明显的磁性矿物的改变(图 5,TLS4)。
由于加热过程并未影响到高温分量载磁性矿物赤铁矿,再考虑到赤铁矿较大的矫顽力,因此,选用600~680℃区间的IRMz/IRMx值作为磁倾角偏低校正因子,利用公式IRMz/IRMx=tan (Iobs)/tan(IF)计算得到校正后的莲沱组磁倾角大小为70.4°,与热退磁实验所得莲沱组磁倾角67.8°比较,莲沱组的磁倾角偏低大小为2.6°。
4. 磁倾角偏低对莲沱组古纬度及古地磁极的影响
利用本研究得到的莲沱组磁倾角偏低校正因子,对Jing等[29]所得高温分量进行磁倾角偏低校正,利用校正后的高温分量求得的三峡地区莲沱组沉积古纬度为47.7°±5.1°,比校正前的43.7°±4.8°向高纬度地区运动了3.9°±6°。
校正后古地磁极(LT-corr)为14.7°N, 153.9°E, dp/dm=4.9/6.0,与未校正的莲沱组古地磁极(LT:12.7°N,157.4°E,dp/dm=4.5/5.8)相比更偏西北。虽然校正前后,莲沱组古地磁极在统计分析上不能显著区分,但校正后的莲沱组古地磁极与现有华南南沱组古地磁极(Nantuo)[38]明显不同(图 6)。
5. 讨论
由于Evans等[39]得到的莲沱组古地磁极与南沱组古地磁极重合,使得一些学者认为莲沱组古地磁结果可能比以前认为的更年轻[40],或是南沱期重磁化的结果。然而,Jing等[29]对宜昌莲沱组的古地磁研究表明,莲沱组中下部到顶部至少存在5个正负极性时,因此现有的莲沱组古地磁结果应该不是重磁化的结果。另外,Jing等[29]通过总结前人在三峡地区对莲沱组大量的定年结果[41-45],认为现有华南莲沱组古地磁极年龄应在720Ma左右,比之前认为的750Ma年轻,但仍老于635Ma的南沱组古地磁结果。
Jing等[29]得到的莲沱组古地磁极与南沱组古地磁极相差不大。Yang等[46]认为,莲沱组采样区可能发生过局部构造旋转作用;Zhang等[38]则认为,没有证据表明莲沱组采样区发生过局部旋转。
排除以上各方面的影响因素,笔者认为,造成莲沱组与南沱组古地磁极相似的原因应该与莲沱组岩石受压实作用影响、发生微弱的磁倾角偏低现象有关。由于目前未对南沱组取得高温分量的古地磁样品进行磁倾角偏低实验,两者真实的差别还不能确定,需要进一步研究。
经磁倾角偏低校正后的华南板块在720Ma时应位于中纬度地区(图 6)。这一时期扬子地块多处发育冰碛岩沉积,从该时期华南板块上发育的冰碛岩分布看[40],当时整个地球应处于较寒冷的气候阶段。但由于这一时期华南板块位于中纬度地区,对于地球这一时期是否处于“雪球地球”的环境,仅从莲沱组的古地磁结果不能做出明确的判定。
为此,笔者重建了华南板块及与华南关系较紧密的澳大利亚-东南极板块720Ma的古地理位置(图 6)。图 6中,将莲沱组古地磁极通过欧拉极(34.4°N、100°E,98.6°)旋转到地理北极。MDS、YF及EF分别为澳大利亚755Ma,640Ma和635Ma古地磁极[22, 47-48],位于同一大圆弧上(虚线),利用内插法求出其720Ma的古地磁极位置,通过欧拉极(-0.4°N、53.7°E,44.1°)旋转使其与莲沱组古地磁极重合。通过这一古地理重建,可以清楚地看到,这一时期有大量冰川从中纬度地区一直延续到赤道地区。这一证据直接证明,当时地球处于“雪球地球”的环境。
6. 结论
对华南三峡地区莲沱组的等温剩磁各向异性研究表明,通过磁倾角偏低校正后的莲沱组古地磁极与南沱组古地磁极存在明显差别,这表明造成莲沱组与南沱组古地磁极相似的一个重要原因是地层压实引起的磁倾角偏低。利用720Ma古地磁数据对华南和澳大利亚进行古地理重建,并对比这一时期冰碛岩的分布,结果表明,当时地球确实处于“雪球地球”的环境中。
-
图 2 取自吉林小龙湾湖心的柱样137Cs 比活度-深度剖面[23]
Figure 2. Activity-depth profiles taken from Xiaolongwan in Jilin Province
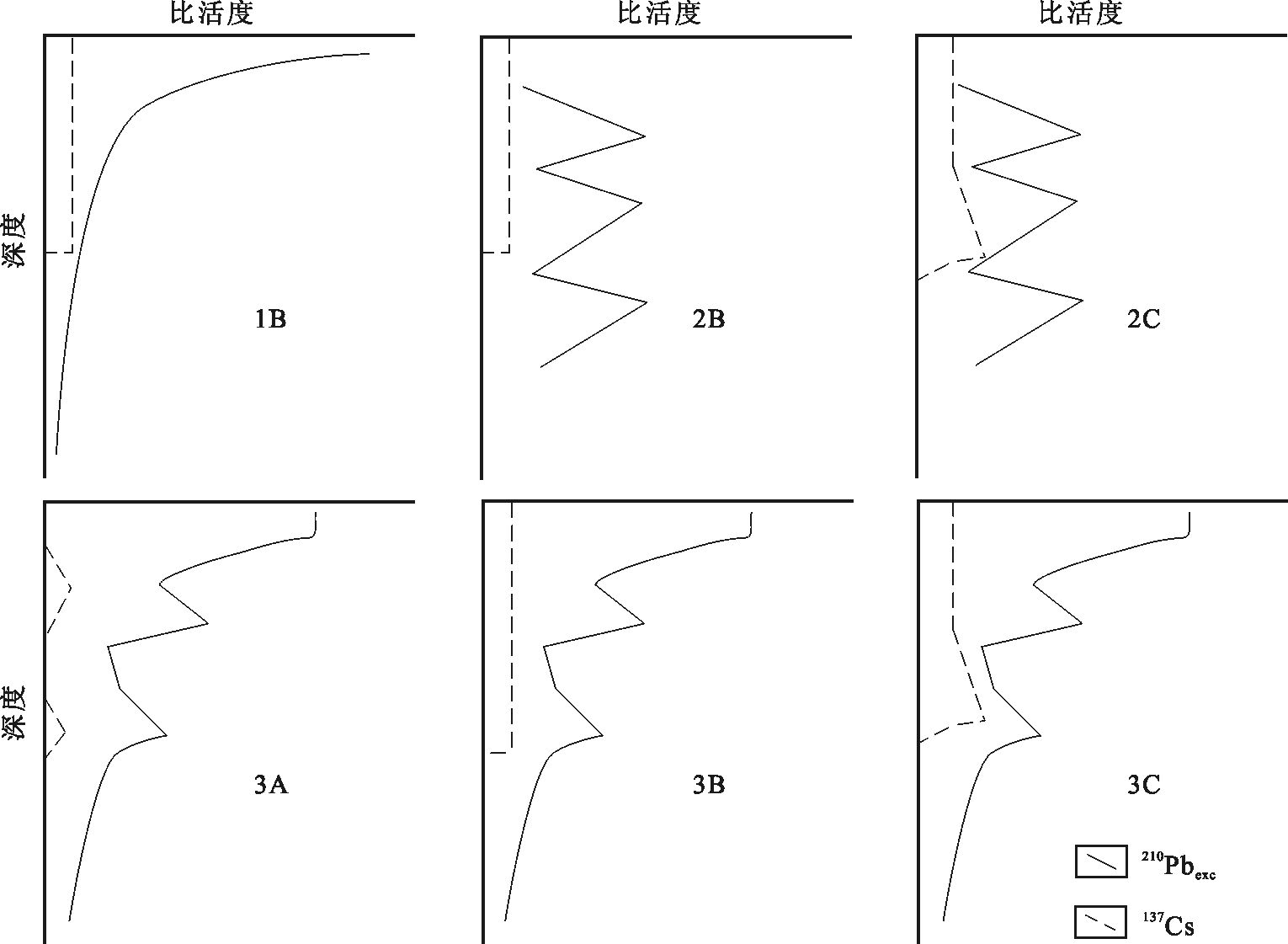
图 3 不同类型的210Pbexc和137Cs 曲线组合[28]
Figure 3. Different types of 210Pbexc and 137Cs activity-depth profiles
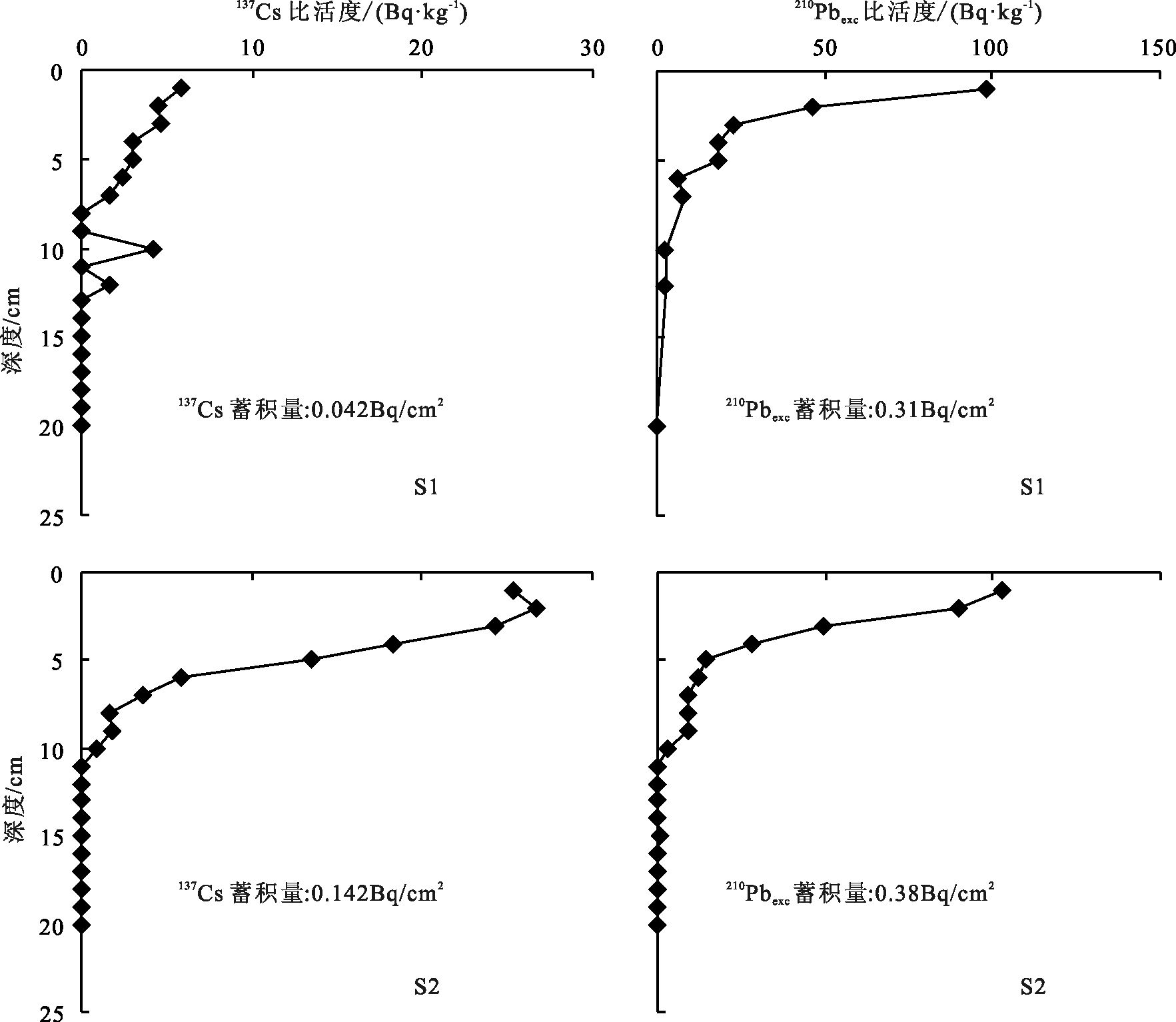
图 4 S1、S2 孔现代沉积物测年比活度-剖面[26]
Figure 4. Activity-depth profiles of Cores S1 and S2
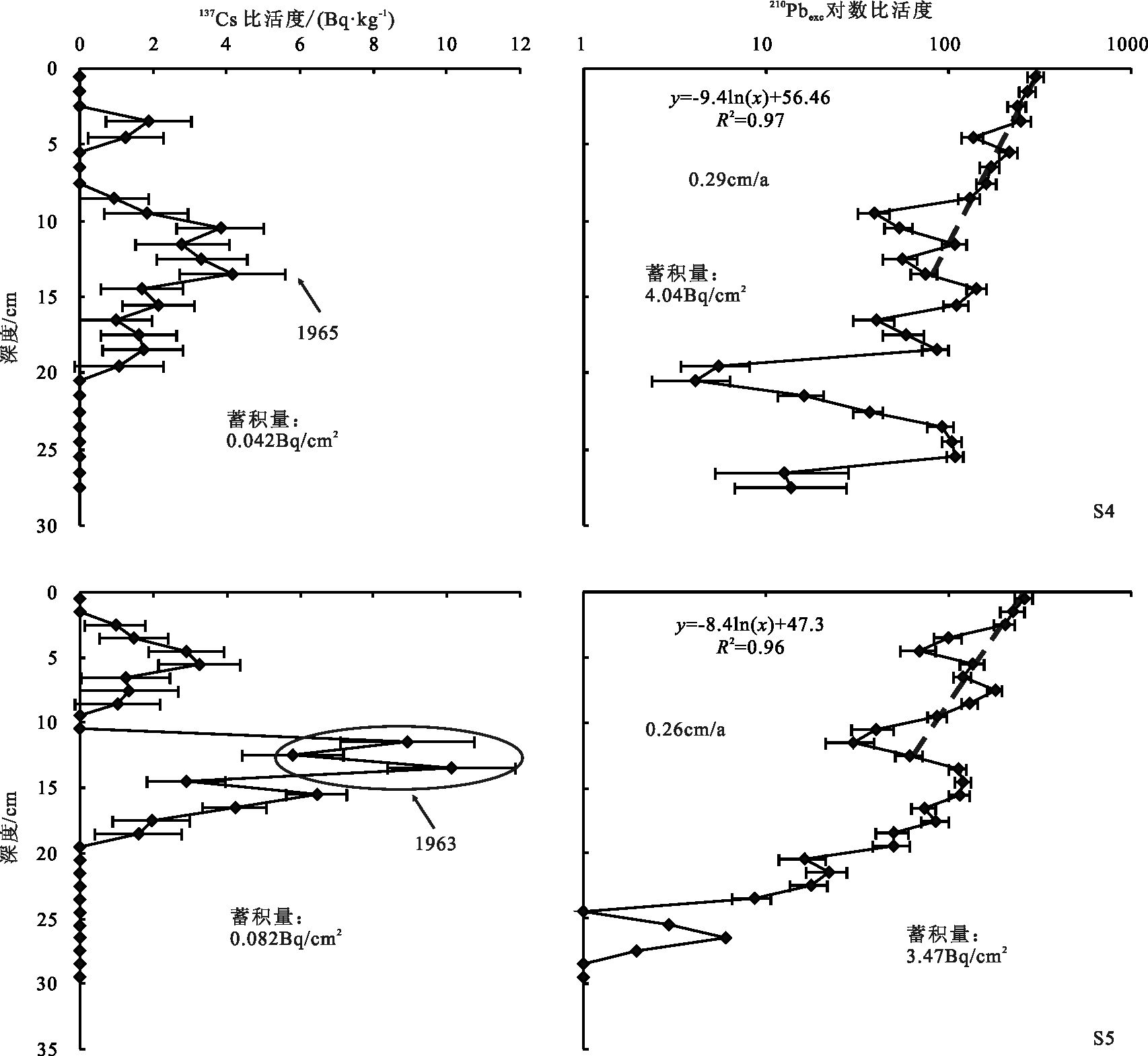
图 5 S4、S5 比活度-深度剖面[24]
Figure 5. Activity-depth profiles of Cores S4 and S5
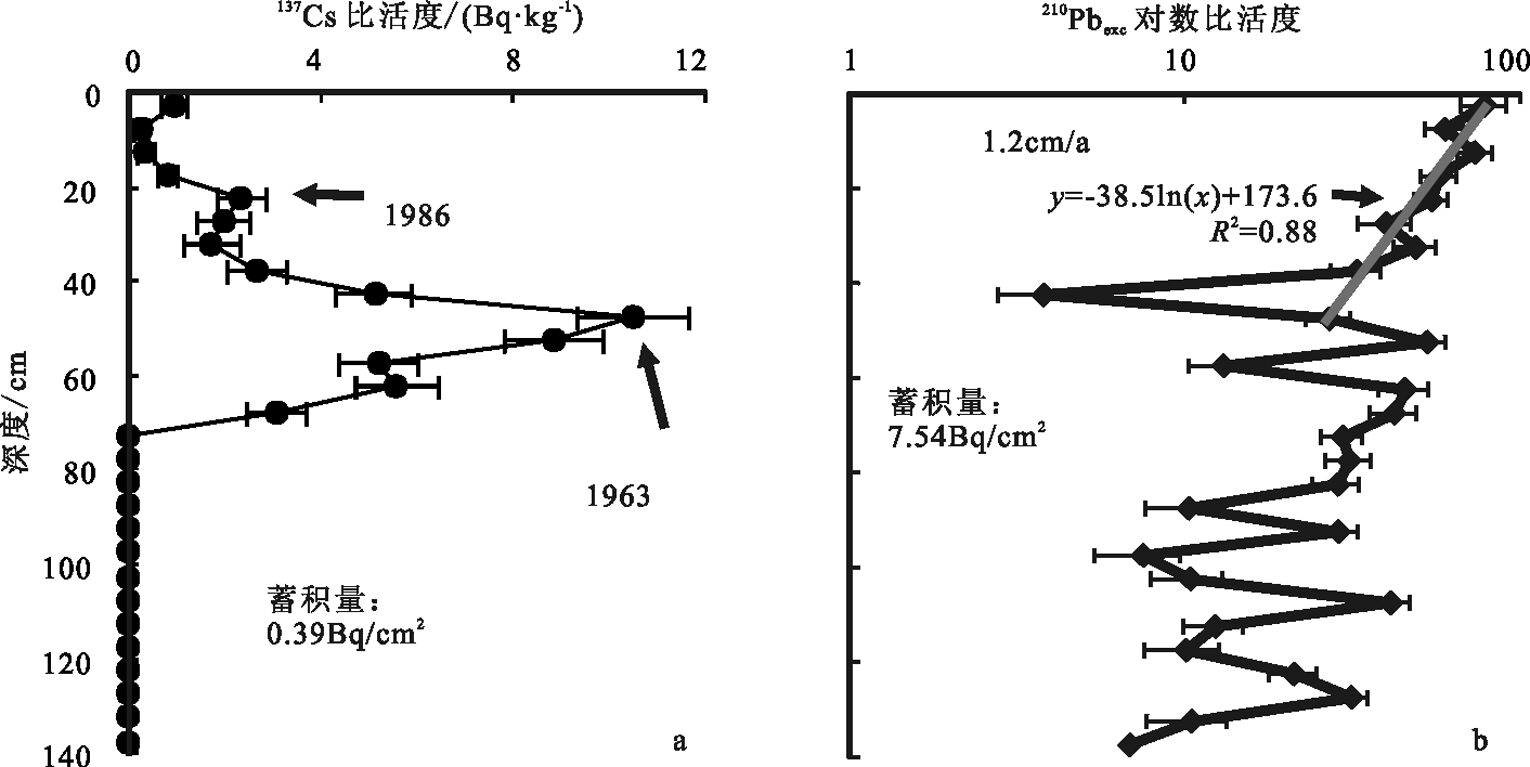
图 6 C0703 孔比活度-深度综合剖面[30]
Figure 6. Age profiles of Core C0703 given by activity-depth profile
表 1 渤海湾西岸典型盐沼沉积速率和蓄积量
Table 1 Sedimentation rates and inventory of salt marsh on the west coast of Bohai Bay
-
Pennington W, Tutin T G. Observation on Lake Sediments using Fallout 137Cs as a Tracer[J]. Nature, 1973, 242:324-326. doi: 10.1038/242324a0 Pennington W, Tutin T G. Observation on Lake Sediments using Fallout 137Cs as a Tracer[J]. Nature, 1973, 242:324-326. doi: 10.1038/242324a0
DeLaune R D, Patrick Jr, W H, Buresh R J. Sedimentation rates de-termined by 137Cs dating in a rapidly accreting salt marsh[J]. Nature, 1978, 275:532-533. doi: 10.1038/275532a0 DeLaune R D, Patrick Jr, W H, Buresh R J. Sedimentation rates de-termined by 137Cs dating in a rapidly accreting salt marsh[J]. Nature, 1978, 275:532-533. doi: 10.1038/275532a0
Milan C S, Swenson E M, Turner R E, et al. Assessment of the 137Cs method for estimating sediment accumulation rates:Louisiana salt marshes[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 1995, 11(2):296-307. Milan C S, Swenson E M, Turner R E, et al. Assessment of the 137Cs method for estimating sediment accumulation rates:Louisiana salt marshes[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 1995, 11(2):296-307.
Goodbred S L, Kuehl S A. Floodplain processes in the Bengal Basin and the storage of Ganges-Brahmaputra River sediment:An accre-tion study using 137Cs and 210Pb geochronology[J]. Sedimentary Geol-ogy, 1998, 121(3):239-258. Goodbred S L, Kuehl S A. Floodplain processes in the Bengal Basin and the storage of Ganges-Brahmaputra River sediment:An accre-tion study using 137Cs and 210Pb geochronology[J]. Sedimentary Geol-ogy, 1998, 121(3):239-258.
Callaway J C, Delaune R D, Patrick W H. Chernobyl Cs-137 used to determine sediment accretion rates at selected north European coastal wetlands[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 1996, 41(3):444-450. doi: 10.4319/lo.1996.41.3.0444 Callaway J C, Delaune R D, Patrick W H. Chernobyl Cs-137 used to determine sediment accretion rates at selected north European coastal wetlands[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 1996, 41(3):444-450. doi: 10.4319/lo.1996.41.3.0444
Mishra U C, Lalit B Y, Sethi S K, et al. Some observations based on the measurements on fresh fallout from the recent Chinese and French nuclear explosion[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1975, 80(36):5045-5049. doi: 10.1029/JC080i036p05045 Mishra U C, Lalit B Y, Sethi S K, et al. Some observations based on the measurements on fresh fallout from the recent Chinese and French nuclear explosion[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1975, 80(36):5045-5049. doi: 10.1029/JC080i036p05045
Jha S K, Chavan S B, Pandit G G, et al. Geochronology of Pb and Hg pollution in a coastal marine environment using global fallout 137Cs[J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2003, 69(1/2):145-157. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2084022307&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Jha S K, Chavan S B, Pandit G G, et al. Geochronology of Pb and Hg pollution in a coastal marine environment using global fallout 137Cs[J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2003, 69(1/2):145-157. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2084022307&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Krishnaswamy S, Lal D, Marin J M, et al. Geochronology of lake sediments[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1971, 11(1/5):407-414. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2127015504&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Krishnaswamy S, Lal D, Marin J M, et al. Geochronology of lake sediments[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1971, 11(1/5):407-414. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2127015504&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Appleby P G, Oldfield F. The calculation of 210Pb dates assuming a constant rate of supply of unsupported 210Pb to the sediment[J]. Cate-na, 1978, 5(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/S0341-8162(78)80002-2 Appleby P G, Oldfield F. The calculation of 210Pb dates assuming a constant rate of supply of unsupported 210Pb to the sediment[J]. Cate-na, 1978, 5(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/S0341-8162(78)80002-2
Meng W, Lei K, Zheng B H, et al. Modern sedimentation rates in the intertidal zone on the west coast of the Bohai Gulf[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2005, 24(3):46-53. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1558128271&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Meng W, Lei K, Zheng B H, et al. Modern sedimentation rates in the intertidal zone on the west coast of the Bohai Gulf[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2005, 24(3):46-53. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1558128271&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Andersen T J, Svinth S, Pejrup M. Temporal variation of accumula-tion rates on a natural salt marsh in the 20th century-The impact of sea level rise and increased inundation frequency[J]. Marine Ge-ology, 2011, 279(1/4):178-187. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1998205286&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Andersen T J, Svinth S, Pejrup M. Temporal variation of accumula-tion rates on a natural salt marsh in the 20th century-The impact of sea level rise and increased inundation frequency[J]. Marine Ge-ology, 2011, 279(1/4):178-187. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1998205286&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Teasdale P A, Collins P E F, Firth C R, et al. Recent estuarine sedi-mentation rates from shallow inter-tidal environments in western Scotland:implications for future sea-level trends and coastal wet-land development[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2011, 30:109-129. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2010.08.002 Teasdale P A, Collins P E F, Firth C R, et al. Recent estuarine sedi-mentation rates from shallow inter-tidal environments in western Scotland:implications for future sea-level trends and coastal wet-land development[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2011, 30:109-129. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2010.08.002
Gehrels W R, Callard S L, Moss P T, et al. Nineteenth and twenti-eth century sea-level changes in Tasmania and New Zealand[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2012, 315/316:94-102. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2011.08.046 Gehrels W R, Callard S L, Moss P T, et al. Nineteenth and twenti-eth century sea-level changes in Tasmania and New Zealand[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2012, 315/316:94-102. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2011.08.046
Goldberg E D, Koide M. Rates of sediment accumulation in the In-dian Ocean[C]//Geiss J, Goldberg E D. Earth Science and Meteor-itics. Amsterdam:North-Holland publishing company, 1963:90-102. Goldberg E D, Koide M. Rates of sediment accumulation in the In-dian Ocean[C]//Geiss J, Goldberg E D. Earth Science and Meteor-itics. Amsterdam:North-Holland publishing company, 1963:90-102.
Koide M, Bruland K W, Goldberg E D. 228Th/232Th and 210Pb geo-chronologies in marine and lake sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cos-mochimica Acta, 1973, 37:1171-1187. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(73)90054-9 Koide M, Bruland K W, Goldberg E D. 228Th/232Th and 210Pb geo-chronologies in marine and lake sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cos-mochimica Acta, 1973, 37:1171-1187. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(73)90054-9
苏贤泽, 马文通, 徐胜利, 等. 海洋沉积物的铅-210地质年代学方法[J]. 1984, 3(1):50-58. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TWHX198401006.htm 康兴伦. 210Pb测年法的数据处理问题[J]. 海洋科学, 1986, 10(6):13-17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYKX198606002.htm 业渝光, 和杰. 现代黄河三角洲210Pb剖面的标准化方法——粒度相关法[J]. 地理科学, 1992, 12(4):379-386. 万国江. 现代沉积的210Pb计年[J]. 第四纪地质, 1997, 3:230-239. 范德江, 杨作升, 郭志刚. 中国陆架210Pb测年应用现状与思考[J]. 地球科学进展, 2000, 15(3):297-302. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ200003010.htm Wright S M, Howard B J, Strand P. Prediction of 137Cs deposition from atmospheric nuclear weapons tests within the Arctic[J]. Envi-ronmental Pollution, 1999, 104:131-143. doi: 10.1016/S0269-7491(98)00140-7 Wright S M, Howard B J, Strand P. Prediction of 137Cs deposition from atmospheric nuclear weapons tests within the Arctic[J]. Envi-ronmental Pollution, 1999, 104:131-143. doi: 10.1016/S0269-7491(98)00140-7
王福, 王宏. 海岸带地区137Cs沉积剖面类型划分及其意义[J]. 地质通报, 2011, 30(7):1009-1110. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20110712&journal_id=gbc 夏威岚, 薛滨. 吉林小龙湾沉积速率的210Pb和137Cs年代学方法测定[J]. 第四纪研究, 2004, 24(1):124-125. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200401016.htm 杨彪, 王福, 田立柱, 等. 独流减河盐沼210Pbexc和137Cs剖面记录的现代洪水事件沉积[J]. 海洋学研究, 2016, 34:25-34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DHHY201602004.htm Wang F, Wang H, Zong Y, et al. Sedimentary dynamics along the West Coast of Bohai Bay, China, during the 20th century[J]. Jour-nal of coastal research, 2014, 30(2):379-388. Wang F, Wang H, Zong Y, et al. Sedimentary dynamics along the West Coast of Bohai Bay, China, during the 20th century[J]. Jour-nal of coastal research, 2014, 30(2):379-388.
李建芬, 王宏, 夏威岚, 等. 渤海湾西岸210Pbexc和137Cs测年与现代沉积速率[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2003, 26(2):114-128. Wang F, Wang H, Li J F, et al. 210Pb and 137Cs measurement on the Circum Bohai Sea (CBS) Region:sedimentation and implication[J]. Frontiers of Earth Science in China, 2008, 2(3):276-282. doi: 10.1007/s11707-008-0046-5 Wang F, Wang H, Li J F, et al. 210Pb and 137Cs measurement on the Circum Bohai Sea (CBS) Region:sedimentation and implication[J]. Frontiers of Earth Science in China, 2008, 2(3):276-282. doi: 10.1007/s11707-008-0046-5
王福. 渤海湾海岸带210Pb、137Cs示踪与测年研究:现代沉积及环境意义[D]. 中国地质科学院博士学位论文, 2009:1-101. Wang F, Zong Y, Li J F, et al. Recent sedimentation dynamics in-dicated by 210Pbexc and 137Cs records from the subtidal area of Bohai Bay, China[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2015, 32(2):416-423. Wang F, Zong Y, Li J F, et al. Recent sedimentation dynamics in-dicated by 210Pbexc and 137Cs records from the subtidal area of Bohai Bay, China[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2015, 32(2):416-423.
王福, 杨彪, 田立柱, 等. 开放潮坪地区210Pbexc测年CIC和CRS计算模式的选择[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(6):971-981. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201606005.htm 王宏, 姜义, 李建芬, 等. 渤海湾老狼坨子海岸带14C、137Cs、210Pb测年与现代沉积速率的加速趋势[J]. 地质通报, 2003, 22(9):658-664. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=200309126&journal_id=gbc




 下载:
下载: