Zircon U-Pb age, geochemistry and Hf isotopic compositions of quartzdiorite from the Xinliaodong Cu polymetallic deposit in eastern Guangdong Province
-
摘要:
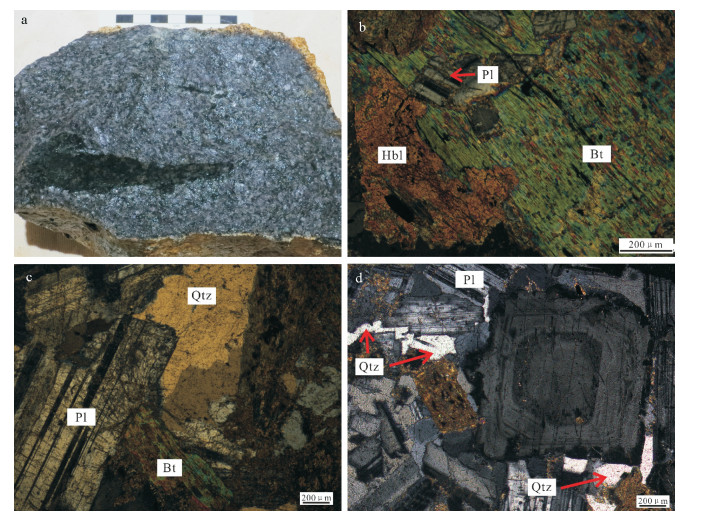
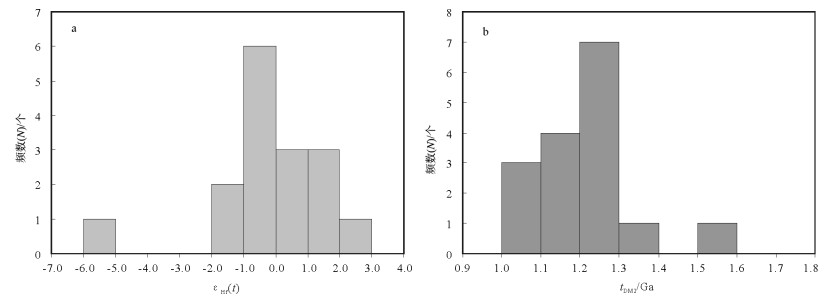
新寮岽铜多金属矿是近年来在粤东地区新发现的一个铜矿床。对该矿床中与成矿关系密切的石英闪长岩进行了锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学、Hf同位素研究,以约束其形成时代和岩石成因。测得石英闪长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为161±1Ma(n=25,MSWD=0.57),被解释为岩体的成岩年龄。地球化学数据显示,石英闪长岩具有碱含量中等(Na2O+K2O=3.99%~5.05%),高镁(MgO=4.53%~4.91%)的特征,属准铝质钙碱性系列。稀土和微量元素特征表明,其富集轻稀土元素和大离子亲石元素(K、Rb、Ba、Th、U),亏损重稀土元素和高场强元素(Nb、Ta、Ti、P),具弱负Eu异常(δEu=0.68~0.76)。电子探针分析结果表明,石英闪长岩中黑云母为镁质黑云母,具环带结构,斜长石为拉长石。锆石Hf同位素分析结果表明,石英闪长岩εHf(t)为-5.8~2.7,tDM2=1.03~1.58Ga。岩石地球化学和锆石Hf同位素组成特征表明,石英闪长岩源区较复杂,为壳幔混合源,可能为俯冲板片部分熔融并与楔形地幔橄榄岩相互作用形成,且岩浆上侵过程中有古老地壳物质的混染。综合岩石地球化学、矿物化学及Hf同位素特征,结合区域构造演化史和前人研究成果,推测岩体形成于俯冲背景下的活动大陆边缘环境。
-
关键词:
- 石英闪长岩 /
- LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄 /
- Hf同位素 /
- 岩石成因 /
- 粤东地区
Abstract:The Xinliaodong Cu polymetallic deposit is a newly-discovered copper ore deposit in eastern Guangdong Province. In this paper, zircon U-Pb age, geochemistry and zircon Hf isotope of the ore-related quartz-diorite from the Xinliaodong Cu polymetallic ore district were studied to constrain its geochronology and petrogenesis. The zircon LA-ICP-MS dating yielded a concordant age of 161±1Ma (n=25, MSWD=0.57), which is interpreted as the petrogenic age of quartz-diorite. Geochemical data show that the quartz-diorite is magnesium-enriched in composition (MgO=4.53%~4.91%) with moderate content of alkali (Na2O+K2O=3.99%~5.05%). It is a metaluminous granite and belongs to the calc-alkaline series. Its REE and trace elements are characterized by enrichment of LREE and large ion lithophile elements (K, Rb, Ba, Th and U) and depletion of HREE and high-field strength elements (Nb, Ta, Ti and P), with slightly weak negative anomalies of Eu (δEu=0.68~0.76). The results of the electron microprobe analysis show that the biotite from the quartz-diorite belongs to magnesian biotite, whereas the zoned plagioclase belongs to labradorite. The Hf isotope shows that the εHf (t) values of the quartze-diorite range from -5.8 to 2.7, with tDM2 ages between 1.03Ga and 1.58Ga. Geochemistry and zircon Hf isotopic compositions indicate that the parental magmas of the quartz-diorite are rather complex. The diagenetic mass of the pluton was derived from the source of crust-mantle mixture and it might have originated from partial melting of a subducted slab which reacted with mantle wedge peridotites. Besides, the magma was intermingled with ancient crustal material during magmatic ascent. According to petrogeochemistry, mineral chemistry and Hf isotope, combined with the tectonic evolution of the eastern Guangdong Province as well as previous achievements, the authors infer that the quartz-diorite was generated in an active continental margin setting triggered by slab subduction.
-
致谢: 成文过程中得到中国地质大学(北京)郑伟博士和中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所杨阳博士的指导,野外地质工作得到广东省地质局第二地质大队的大力支持和帮助,锆石U-Th-Pb同位素测定工作得到南京大学内生金属矿床成矿机制研究国家重点实验室武兵老师的热情指导,中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所电子探针室陈振宇和陈小丹老师在电子探针分析实验过程中给予了热情的指导和帮助,资料收集和数据分析过程中得到中国地质大学(北京)李伟、李正远、曹晶、姚通、张伟等同学的帮助,在此一并表示诚挚的谢意。
-
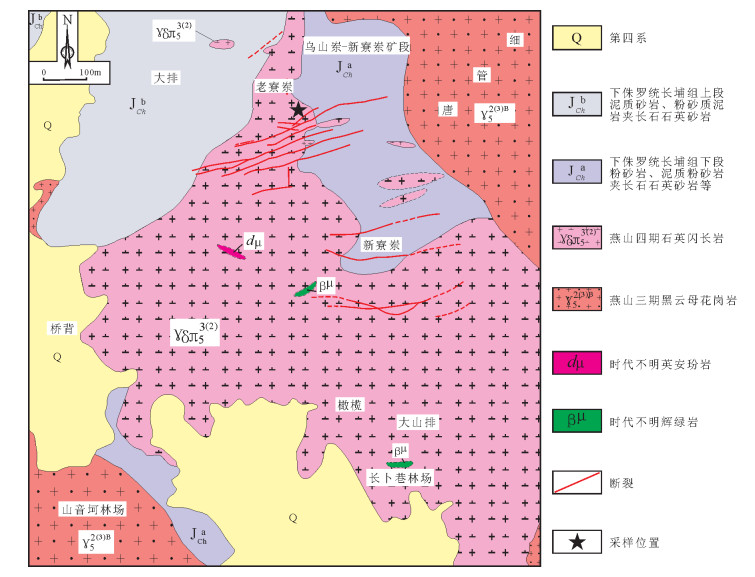
图 1 粤东地区地质略图(据参考文献[16]修改)
Figure 1. Schematic geological map of eastern Guangdong Province
图 7 新寮岽铜多金属矿区石英闪长岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化图解(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)(标准化值据参考文献[29])
Figure 7. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a)and primitive mantlenormalized trace-element spider diagram(b)of quartz-diorite in the Xinliaodong Cu polymetallic ore district
图 8 黑云母成分分类(底图据参考文献[32])
Figure 8. Classification of biotites
图 9 斜长石分类图解及环带状斜长石成分剖面(底图据参考文献[35])
Qtz—石英;Pl—斜长石
Figure 9. Classification of feldspar and electron microprobe analyses of zoned plagioclase
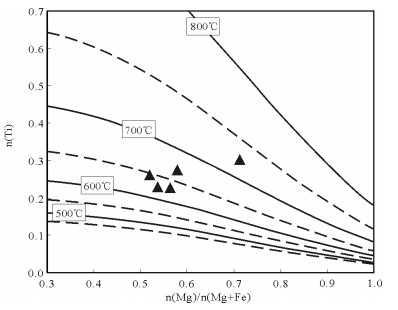
图 11 黑云母Mg/(Mg+Fe)-Ti图解(底图据参考文献[44])
Figure 11. Mg/(Mg+Fe)-Ti diagram of biotites
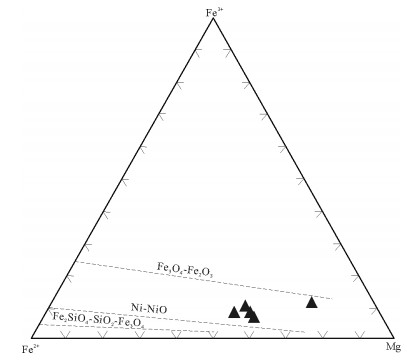
图 12 黑云母Fe3+-Fe2+-Mg图解(底图据参考文献[46])
Figure 12. Fe3+-Fe2+-Mg diagram of biotites
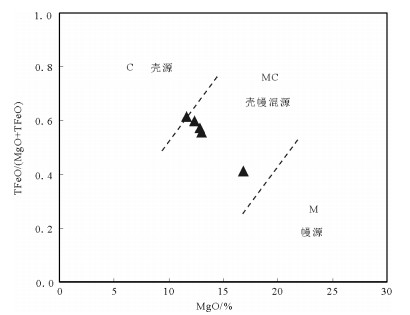
图 13 黑云母物质来源判别图(底图据参考文献[56])
Figure 13. Diagram for discrimination of material source of biotite
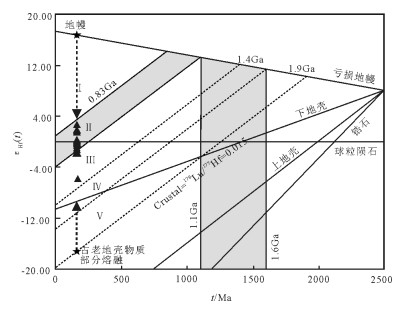
图 14 石英闪长岩的Hf同位素演化图解(底图据参考文献[57])
(地壳派生物的谐和线为通过假定的平均大陆地壳176Lu/177Hf值为0.015计算得到)
Figure 14. Hf isotope evolution diagram of quartz-diorite
Ⅰ—小于0.83Ga; Ⅱ—0.83~1.1Ga; Ⅲ—1.1~1.4Ga; Ⅳ—1.4~1.6Ga; Ⅴ—1.6~1.9Ga
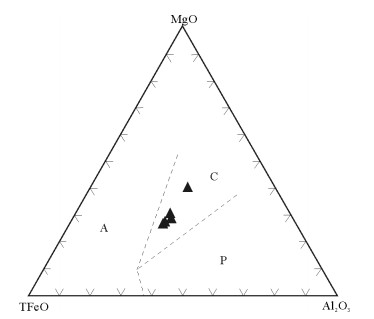
图 15 黑云母构造环境判别图(底图据参考文献[71])
A—非造山的碱性岩系;C—造山带钙碱性岩系;P—过铝质岩系
Figure 15. Discrimination diagram of tectonic settings for biotite
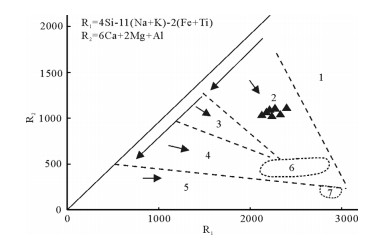
图 16 石英闪长岩R1-R2多阳离子图解(底图据参考文献[72])
1—地幔分异花岗岩;2—活动板块边缘花岗岩;3—碰撞后隆起花岗岩;4—造山晚期花岗岩;5—非造山花岗岩;6—同碰撞花岗岩;7—造山后的A型花岗岩
Figure 16. R1 versus R2 multicationic diagram for quartz diorites
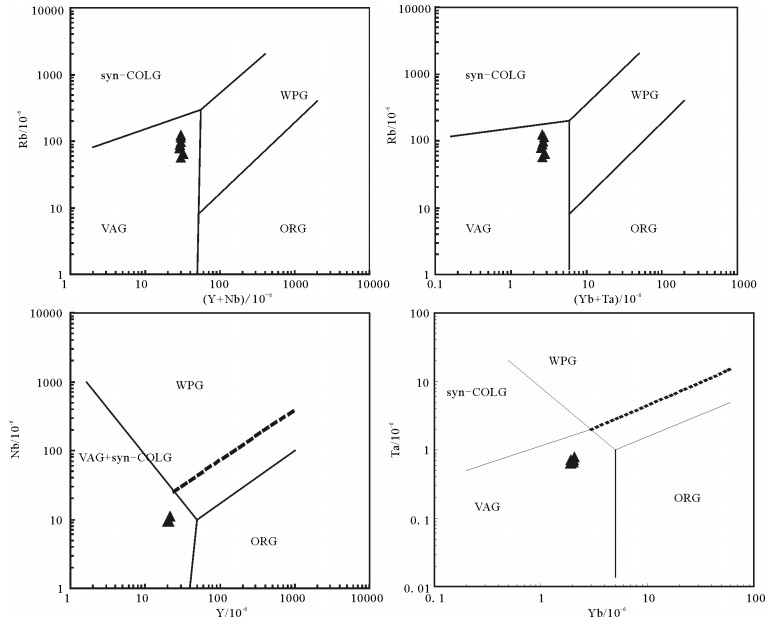
图 17 石英闪长岩构造环境判别图解(底图据参考文献[73])
syn-COLG—同碰撞花岗岩;VAG—火山弧花岗岩;WPG—板内花岗岩;ORG—洋脊花岗岩
Figure 17. Discrimination diagram for tectonic settings of quartz diorates
表 1 新寮岽铜多金属矿区石英闪长岩(XLDY-005)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素测定结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb isotopic data of the quartz-diorite (XLDY-005)from the Xinliaodong Cu polymetallic ore district
测点号 含量/10-6 Th/U 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 208Pb/232Th 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 208Pb/232Th Th U 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 1 1122 880 1.3 0.0491 0.0016 0.1749 0.0056 0.0258 0.0004 0.0077 0.0018 153 75 164 5 164 2 155 35 2 1112 1677 0.7 0.0508 0.0017 0.1737 0.0056 0.0248 0.0004 0.0130 0.0069 230 75 163 5 158 2 260 137 4 3523 2535 1.4 0.0494 0.0014 0.1727 0.0049 0.0253 0.0004 0.0126 0.0060 168 65 162 4 161 2 253 120 6 2730 2603 1.1 0.0495 0.0011 0.1726 0.0038 0.0253 0.0004 0.0110 0.0042 173 51 162 3 161 2 222 83 7 2810 1771 1.6 0.0491 0.0012 0.1746 0.0042 0.0258 0.0004 0.0092 0.0029 154 56 163 4 164 2 185 58 8 2918 1687 1.7 0.0496 0.0023 0.1719 0.0079 0.0251 0.0005 0.0110 0.0067 177 106 161 7 160 3 220 134 9 2231 1398 1.6 0.0492 0.0014 0.1680 0.0047 0.0248 0.0004 0.0093 0.0032 156 64 158 4 158 2 186 65 11 2717 2085 1.3 0.0496 0.0013 0.1713 0.0045 0.0251 0.0004 0.0078 0.0023 174 60 161 4 160 2 157 46 12 1756 1545 1.1 0.0494 0.0014 0.1742 0.0050 0.0256 0.0004 0.0080 0.0025 168 66 163 4 163 2 162 51 13 1502 1130 1.3 0.0499 0.0015 0.1726 0.0052 0.0251 0.0004 0.0077 0.0023 188 70 162 5 160 2 155 47 14 3708 2048 1.8 0.0497 0.0021 0.1707 0.0070 0.0249 0.0004 0.0078 0.0039 180 95 160 6 159 3 157 79 15 2575 1924 1.3 0.0512 0.0016 0.1799 0.0056 0.0255 0.0004 0.0114 0.0059 248 71 168 5 162 2 229 118 17 2354 1978 1.2 0.0499 0.0016 0.1721 0.0055 0.0250 0.0004 0.0099 0.0053 192 74 161 5 159 2 199 107 18 5470 2521 2.2 0.0501 0.0012 0.1741 0.0042 0.0252 0.0004 0.0080 0.0013 201 56 163 4 160 2 160 27 20 4248 2491 1.7 0.0501 0.0011 0.1740 0.0038 0.0252 0.0004 0.0089 0.0015 198 51 163 3 160 2 180 30 21 2369 1513 1.6 0.0512 0.0011 0.1785 0.0038 0.0253 0.0004 0.0089 0.0015 248 48 167 3 161 2 178 30 22 534 725 0.7 0.0487 0.0020 0.1725 0.0071 0.0257 0.0004 0.0084 0.0014 132 94 162 6 164 3 168 29 23 2953 1737 1.7 0.0507 0.0013 0.1772 0.0044 0.0253 0.0004 0.0087 0.0015 229 56 166 4 161 2 176 29 24 2223 2341 1.0 0.0503 0.0009 0.1777 0.0032 0.0256 0.0004 0.0089 0.0015 207 41 166 3 163 2 180 30 26 1512 1187 1.3 0.0509 0.0027 0.1790 0.0092 0.0255 0.0005 0.0095 0.0016 237 117 167 8 162 3 192 33 27 919 670 1.4 0.0501 0.0031 0.1741 0.0106 0.0252 0.0005 0.0087 0.0015 201 138 163 9 160 3 174 30 28 2931 1592 1.8 0.0521 0.0013 0.1793 0.0043 0.0249 0.0004 0.0087 0.0015 291 54 168 4 159 2 175 29 29 958 1096 0.9 0.0499 0.0014 0.1747 0.0049 0.0254 0.0004 0.0092 0.0016 188 65 163 4 162 2 184 31 30 4156 2260 1.8 0.0492 0.0010 0.1709 0.0035 0.0252 0.0004 0.0086 0.0014 158 48 160 3 160 2 172 29 31 1860 1615 1.2 0.0508 0.0011 0.1751 0.0039 0.0250 0.0004 0.0086 0.0015 232 50 164 3 159 2 173 29 表 2 新寮岽铜多金属矿区石英闪长岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果及锆石饱和温度
Table 2 Major, trace and rare earth elements data of the quartz-diorite from the Xinliaodong Cu polymetallic ore district and zircon saturation temperatures
样品号 XLD05001 XLD05002 XLD05003 XLD05004 XLD05005 XLD05006 XLD05007 SiO2 57.63 58.07 57.32 57.56 57.57 57.46 58.14 TiO2 0.88 0.95 0.99 0.92 0.98 0.92 0.94 Al2O3 16.30 16.53 15.88 16.21 16.40 16.06 16.23 TFe2O3 7.12 7.67 7.81 7.39 7.48 7.55 7.33 MnO 0.12 0.13 0.18 0.12 0.22 0.15 0.34 MgO 4.56 4.91 4.63 4.58 4.55 4.64 4.53 CaO 6.76 6.68 6.12 6.43 6.17 6.64 6.02 Na2O 2.52 2.61 2.36 2.56 2.56 2.39 2.40 K2O 2.01 1.38 2.69 2.29 1.62 2.35 2.45 P2O5 0.18 0.18 0.18 0.18 0.19 0.18 0.18 烧失量 1.19 1.82 1.23 0.99 1.73 0.89 0.92 总量 99.27 100.93 99.39 99.23 99.47 99.23 99.48 σ 1.40 1.06 1.78 1.62 1.20 1.55 1.55 A/CNK 0.88 0.92 0.89 0.88 0.95 0.87 0.93 A/NK 2.58 2.86 2.34 2.42 2.75 2.48 2.46 DI 45.13 43.39 46.72 45.45 45.28 46.11 47.20 Na 2O+K2O 4.53 3.99 5.05 4.85 4.18 4.74 4.85 K2O/Na2O 0.80 0.53 1.14 0.89 0.63 0.98 1.02 Li 17.49 27.38 20.19 19.87 22.01 17.91 25.99 Be 1.56 1.56 1.57 1.58 1.82 1.56 1.76 Sc 21.05 22.77 21.52 20.91 20.85 20.70 19.78 V 151.0 152.1 147.8 148.8 160.6 148.4 144.3 Cr 150.6 155.1 140.3 135.7 133.7 138.3 127.4 Co 24.06 26.02 22.25 22.70 26.46 23.51 19.62 Ni 45.27 41.05 37.90 36.77 41.77 40.95 33.57 Cu 17.53 21.80 22.81 22.84 40.28 20.89 9.30 Zn 112.0 99.63 164.5 106.7 196.6 125.6 171.3 Ga 20.18 21.06 20.25 20.31 21.70 19.71 19.43 Rb 78.85 56.33 122.6 112.8 63.67 96.68 89.78 Sr 361.6 374.8 349.1 336.0 398.5 300.0 298.9 Y 19.72 20.62 20.29 20.58 21.41 20.98 19.90 Zr 180.2 22.98 53.97 205.4 214.4 162.8 160.7 Nb 9.16 9.42 9.84 9.68 11.20 9.24 9.20 Cd 0.29 0.17 0.53 0.79 1.22 0.51 0.60 In 0.23 0.14 1.27 0.27 0.12 0.11 0.14 Cs 7.25 3.89 5.84 15.13 5.69 11.90 10.63 Ba 457.8 392.8 590.3 416.6 670.0 412.6 502.9 Hf 4.24 0.68 1.57 4.91 5.21 3.92 3.98 Ta 0.64 0.67 0.71 0.71 0.78 0.65 0.67 Pb 12.44 11.31 18.03 52.45 111.1 17.66 114.3 Bi 0.74 0.23 4.66 2.60 1.80 0.30 0.26 Th 8.61 10.31 8.86 9.95 9.76 9.43 9.53 U 2.56 2.78 2.78 3.20 3.00 2.68 3.16 La 23.59 26.73 24.49 26.56 27.15 25.03 21.34 Ce 50.13 54.87 51.94 56.28 56.92 53.19 45.80 Pr 5.89 6.62 6.16 6.59 6.75 6.28 5.49 Nd 23.45 25.93 24.76 25.92 26.82 25.04 22.65 Sm 4.58 5.04 4.90 4.93 5.13 4.84 4.56 Eu 1.16 1.17 1.25 1.14 1.20 1.14 1.14 Gd 4.83 5.25 5.13 5.17 5.42 5.14 4.83 Tb 0.67 0.73 0.72 0.71 0.75 0.72 0.68 Dy 3.78 4.05 3.98 3.99 4.16 4.02 3.83 Ho 0.75 0.79 0.78 0.79 0.82 0.80 0.76 Er 2.15 2.24 2.20 2.26 2.35 2.29 2.17 Tm 0.29 0.30 0.30 0.31 0.32 0.31 0.29 Yb 1.91 1.92 1.91 2.02 2.08 2.03 1.93 Lu 0.28 0.29 0.28 0.30 0.31 0.31 0.29 ΣREE 123.5 135.9 128.8 137.0 140.2 131.1 115.8 LREE 108.8 120.4 113.5 121.4 124.0 115.5 101.0 HREE 14.68 15.57 15.29 15.56 16.21 15.62 14.79 LREE/HREE 7.41 7.73 7.42 7.80 7.65 7.39 6.83 (La/Yb)N 8.84 9.98 9.21 9.43 9.38 8.84 7.93 δEu 0.75 0.69 0.76 0.68 0.69 0.69 0.74 δCe 1.01 0.98 1.01 1.01 1.00 1.01 1.01 T/℃ 748 610 660 759 775 738 747 表 3 石英闪长岩黑云母电子探针分析结果及相关参数(以11个氧原子为基准)
Table 3 Electron microprobe analyses of biotite from quartze-diorite(based on 11 oxygen atoms)
测点号 XLD XLD XLD XLD XLD 测点号 XLD XLD XLD XLD XLD 05001-4-1 05001-4-2 05007-1-1 05007-1-2 05007-1-3 05001-4-1 05001-4-2 05007-1-1 05007-1-2 05007-1-3 SiO2 38.57 37.48 37.81 38.23 38.52 ArⅣ 1.14 1.15 1.20 1.12 1.12 TiO2 4.08 3.98 5.44 4.62 4.88 AlⅣ 0.10 0.06 0.00 0.04 0.03 Al2O3 14.24 13.49 13.20 13.09 12.96 Ti 0.23 0.23 0.30 0.26 0.27 FeOT 17.28 18.48 11.80 18.51 16.32 Fe3+ 0.20 0.27 0.29 0.20 0.17 MnO 0.17 0.14 0.32 0.53 0.51 Fe2+ 0.91 0.95 0.46 1.01 0.89 MgO 12.90 12.36 16.85 11.64 13.01 Mn 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.03 CaO 0.02 0.00 0.06 0.05 0.03 Mg 1.43 1.40 1.86 1.31 1.45 Na2O 0.12 0.05 0.09 0.17 0.20 Ca 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 K2O 9.01 8.78 9.06 9.04 8.99 Na 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.03 Cr2O3 0.22 0.20 0.25 0.24 0.20 K 0.85 0.85 0.86 0.87 0.86 总量 96.61 94.97 94.87 96.11 95.62 Cr 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 Si 2.86 2.85 2.80 2.88 2.88 MF 0.61 0.59 0.79 0.56 0.61 注: TFeO为全铁;FeO3+和Fe2+采用郑巧荣[30]的方法校正;MF=n(Mg)/n(Mg+Fe2++Mn) 表 4 石英闪长岩中环带结构斜长石电子探针成分分析结果
Table 4 Electron microprobe analyses of zoned plagioclase from quartz-diorite
% 测点 XLD0500 XLD0500 XLD0500 XLD0500 XLD0500 XLD0500 6-2-1-1 6-2-1-2 6-2-1-3 6-2-1-4 6-2-1-5 6-2-1-6 边部→核部 SiO2 51.78 52.35 51.45 51.51 51.27 51.72 TiO2 0.06 0.11 0.10 0.05 0.07 0.02 Al2O3 32.12 31.02 30.31 30.62 30.93 29.83 FeO 0.14 0.30 0.24 0.32 0.36 0.35 MgO 0.03 0.01 0.02 0.00 0.01 0.00 Cr2O3 0.00 0.00 0.04 0.01 0.03 0.02 MnO 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.02 CaO 11.45 11.64 11.31 10.94 12.29 12.32 Na2O 4.84 4.81 4.70 5.12 4.32 4.32 K2O 0.22 0.30 0.27 0.35 0.28 0.21 P2O5 0.03 0.02 0.03 0.01 0.00 0.04 总量 100.72 100.59 98.48 98.96 99.57 98.92 Si 2.33 2.37 2.37 2.37 2.35 2.38 Al 1.71 1.65 1.65 1.66 1.67 1.62 Ca 0.55 0.56 0.56 0.54 0.60 0.61 Na 0.42 0.42 0.42 0.46 0.38 0.39 K 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.01 Ba 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 An 55.91 56.21 56.16 53.08 60.12 60.40 Ab 42.80 42.05 42.24 44.92 38.25 38.35 Or 1.29 1.74 1.60 2.00 1.64 1.25 注:数据处理采用Geokit软件计算得出 表 5 新寮岽铜多金属矿区石英闪长岩的锆石Hf同位素分析结果
Table 5 Lu-Hf isotopic data of zircon from quartz-diorite in the Xinliaodong Cu polymetallic ore district
测点号 t/Ma 176Yb/177Hf 176Lu/177Hf 176Hf/177Hf 2σ (176Hf/177Hf)i εHf(0) εHf(t) tDM1/Ma tDM2/Ma fLu/Hf 2 158 0.067067 0.001030 0.282631 0.000014 0.282627 -5.0 -1.6 881 1312 -0.97 6 161 0.075668 0.001280 0.282660 0.000013 0.282656 -4.0 -0.6 845 1245 -0.96 8 160 0.098102 0.001804 0.282678 0.000018 0.282672 -3.3 0.0 831 1210 -0.95 11 160 0.131231 0.002008 0.282756 0.000018 0.282750 -0.6 2.7 722 1033 -0.94 12 163 0.086784 0.001220 0.282664 0.000016 0.282660 -3.8 -0.4 838 1235 -0.96 13 160 0.050521 0.000718 0.282640 0.000017 0.282638 -4.7 -1.2 860 1288 -0.98 15 162 0.137709 0.001854 0.282669 0.000018 0.282664 -3.6 -0.3 844 1228 -0.94 17 159 0.114314 0.001635 0.282722 0.000018 0.282717 -1.8 1.5 764 1110 -0.95 20 160 0.116023 0.002127 0.282689 0.000021 0.282683 -2.9 0.4 822 1186 -0.94 21 161 0.096930 0.001492 0.282681 0.000015 0.282677 -3.2 0.2 819 1199 -0.96 22 164 0.034677 0.000682 0.282509 0.000033 0.282507 -9.3 -5.8 1042 1579 -0.98 23 161 0.125353 0.001983 0.282653 0.000014 0.282647 -4.2 -0.9 871 1266 -0.94 27 160 0.066417 0.001374 0.282672 0.000016 0.282668 -3.5 -0.2 829 1219 -0.96 29 162 0.119899 0.001741 0.282729 0.000016 0.282724 -1.5 1.9 755 1091 -0.95 30 160 0.161227 0.002218 0.282736 0.000019 0.282729 -1.3 2.0 756 1082 -0.93 31 159 0.061143 0.001105 0.282683 0.000015 0.282680 -3.1 0.2 808 1193 -0.97 注:εHf(t)={[(176Hf/177Hf)s-(176Lu/177Hf)s×(eλt-1)]/[(176Hf/177Hf)CHUR, 0-(176Lu/177Hf)CHUR×(et-1)]-1}×10000;TDM1=1/ λ×ln {1+[(176Hf/177Hf)s-(176Hf/177Hf)DM]/[(176Lu/177Hf)s-(176Lu/177Hf)DM]};TDM2=1/λ×ln{1+[(176Hf/177Hf)s, t-(176Hf/177Hf)DM, t]/[(176Lu/177Hf)C-(176Lu/177Hf)DM]}+t;s=sample, (176Hf/177Hf)CHUR, 0=0.282772, (176Lu/177Hf)CHUR=0.0332, (176Hf/177Hf)DM=0.28325, t为锆石结晶年龄,λ=1.867×10-11a-1, (176Lu/177Hf)C=0.015 -
毛景文, 谢桂青, 郭春丽, 等.华南地区中生代主要金属矿床时空分布规律和成矿环境[J].高校地质学报, 2008, 14(4):510-526. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200804007.htm 毛景文, 华仁民, 李晓波.浅议大规模成矿作用与大型矿集区[J].矿床地质, 1999, 18(4):291-299. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ199904000.htm 毛景文, 王志良.中国东部大规模成矿时限及其动力学背景的初步探讨[J].矿床地质, 2000, 19(4):289-296. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200004000.htm 毛景文, 谢桂青, 李晓峰, 等.华南地区中生代大规模成矿作用与岩石圈多阶段伸展[J].地学前缘, 2004, 11(1):45-55. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200401002.htm 毛景文, 谢桂青, 郭春丽, 等.南岭地区大规模钨锡多金属成矿作用:成矿时限及地球动力学背景[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(10):2329-2338. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200710003.htm 毛景文, 陈懋弘, 袁顺达, 等.华南地区钦杭成矿带地质特征和矿床时空分布规律[J].地质学报, 2011, 85(5):636-658. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201105006.htm 毛景文, 谢桂青, 张作衡, 等.中国北方中生代大规模成矿作用的期次及其地球动力学背景[J].岩石学报, 2005, 21(1):169-188. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200501018.htm 华仁民, 毛景文.试论中国东部中生代成矿大爆发[J].矿床地质, 1999, 18(4):300-308. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ199904001.htm 华仁民, 陈培荣, 张文兰, 等.华南中、新生代与花岗岩类有关的成矿系统[J].中国科学(D辑), 2003, 33(4):335-343. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200304005.htm 华仁民, 陈培荣, 张文兰, 等.论华南地区中生代3次大规模成矿作用[J].矿床地质, 2005, 24(2):99-107. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200502001.htm 华仁民, 李光来, 张文兰, 等.华南钨和锡大规模成矿作用的差异及其原因初探[J].矿床地质, 2010, 29(1):9-23. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201001004.htm 舒良树.华南构造演化的基本特征[J].地质通报, 2012, 31(7):1035-1053. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20120703&journal_id=gbc 程彦博, 童祥, 武俊德, 等.华南西部地区晚中生代与W-Sn矿有关花岗岩的年代学格架及地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(3):809-818. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/ysxb201003014.htm 杨明桂, 黄水保, 楼法生, 等.中国东南陆区岩石圈结构与大规模成矿作用[J].中国地质, 2009, 36(3):528-543. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200903006.htm 郑伟, 陈懋弘, 赵海杰, 等.广东鹦鹉岭钨多金属矿床中黑云母花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年和Hf同位素特征及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(12):4121-4135. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2314684786&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn 刘鹏, 程彦博, 毛景文, 等.粤东田东钨锡多金属矿床花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素特征及其意义[J].地质学报, 2015, 89(5):1244-1257. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201507008.htm 王小雨, 毛景文, 程彦博, 等.粤东新寮岽铜多金属矿床绿泥石特征及其地质意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2014, 33(5):885-905. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201405007.htm 徐晓春.粤东地区中生代岩浆作用和金属成矿的地球化学研究[D].合肥工业大学博士学位论文, 1993:1-198. 徐晓春, 岳书仓.粤东中生代火山-侵入杂岩的地壳深熔成因——Pb-Nd-Sr多元同位素体系制约[J].地质论评, 1999, 45(增刊):829-835. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4887255 黄卉, 马东升, 陆建军, 等.湘东邓阜仙二云母花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学及地球化学研究[J].矿物学报, 2013, 33(2):245-255. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/kwxb201302018.htm Ludwig K R.User's Manual for Isoplot 3.00:A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M].Berkeley:Geochronology Center Special Publication,2003:4-70. Ludwig K R.User's Manual for Isoplot 3.00:A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M].Berkeley:Geochronology Center Special Publication, 2003:4-70.
侯可军, 李延河, 邹天人, 等.LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石Hf同位素的分析方法及地质应用[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(10):2594-2604. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=584145679&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Elhlou S,Belousova E,Griffin W L,et al.Trace element and isotopic composition of GJ-red zircon standard by laser ablation[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2006,70(18):407-421. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/248431967_Trace_element_and_isotopic_composition_of_GJ_red_zircon_standard_by_Laser_Ablation Elhlou S, Belousova E, Griffin W L, et al.Trace element and isotopic composition of GJ-red zircon standard by laser ablation[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70(18):407-421. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/248431967_Trace_element_and_isotopic_composition_of_GJ_red_zircon_standard_by_Laser_Ablation
Qi L,Hu J,Gregoire D C.Determination of trace elements in granites by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Talanta,2000,51(3):507-513. doi: 10.1016/S0039-9140(99)00318-5 Qi L, Hu J, Gregoire D C.Determination of trace elements in granites by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Talanta, 2000, 51(3):507-513. doi: 10.1016/S0039-9140(99)00318-5
吴元保, 郑永飞.锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J].科学通报, 2004, 49(16):1589-1604. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/kxtb200416001.htm Compston W,Williams I S,Kirschvink I L.Zircon U-Pb ages for the Early Cambrian timescale[J].Geological society of London,1992,149(2):171-184. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.149.2.0171 Compston W, Williams I S, Kirschvink I L.Zircon U-Pb ages for the Early Cambrian timescale[J].Geological society of London, 1992, 149(2):171-184. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.149.2.0171
Maniar P D,Piccoli P M.Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J].Geological Society of America Bulletin,1989,101(5):635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2 Maniar P D, Piccoli P M.Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J].Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5):635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
Rollinson H R.Using Geochemical Data:Evaluation,Presentation,Interpretation[M].New York:Longman Scientific and Technical,1993:1-352. Rollinson H R.Using Geochemical Data:Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation[M].New York:Longman Scientific and Technical, 1993:1-352.
Sun S S,McDonough W F.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and process[C]//Saunders A D,Norry M J.Magmatism in the Ocean Basins.Geol.Soc.Spec.Publ.,1989,42(1):313-345. http://www.oalib.com/references/19049542 Sun S S, McDonough W F.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and process[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J.Magmatism in the Ocean Basins.Geol.Soc.Spec.Publ., 1989, 42(1):313-345. http://www.oalib.com/references/19049542
郑巧荣.由电子探针分析值计算Fe3+和Fe2+[J].矿物学报, 1983, (1):55-62. 马昌前, 杨坤光, 汤仲华, 等.花岗岩类岩浆动力学理论方法及鄂东花岗岩类例析[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1994:77-78. Foster M D.Interpretation of the composition of trioctahedral micas[J].U.S.Geol.Surv.Prof.Paper.,1960,354-B:11-49. http://pubs.usgs.gov/pp/0354b/report.pdf Foster M D.Interpretation of the composition of trioctahedral micas[J].U.S.Geol.Surv.Prof.Paper., 1960, 354-B:11-49. http://pubs.usgs.gov/pp/0354b/report.pdf
吴平霄, 吴金平, 肖文丁, 等.斜长石环带的成因机制[J].地质地球化学, 1997, 4:40-49. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ199704006.htm Wiebe R A.Plagioclase stratigraphy:a record of magmatic conditions and events in a granite stock[J].American Journal of Science,1986,266:690-703. doi: 10.2475/ajs.266.8.690 Wiebe R A.Plagioclase stratigraphy:a record of magmatic conditions and events in a granite stock[J].American Journal of Science, 1986, 266:690-703. doi: 10.2475/ajs.266.8.690
Holness M B.Spherulitie textures formed during crystallization of partially melted arkose[J].Rum,Scotland,Geol.Mag.,2002,139(6):651-663. http://journals.cambridge.org/production/action/cjoGetFulltext?fulltextid=143452 Holness M B.Spherulitie textures formed during crystallization of partially melted arkose[J].Rum, Scotland, Geol.Mag., 2002, 139(6):651-663. http://journals.cambridge.org/production/action/cjoGetFulltext?fulltextid=143452
梅芳.宁镇地区中酸性岩浆岩中斜长石的矿物学特征[J].科技信息, 2012, 17:11-17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJXX201217010.htm Watson E B,Harrison T M.Zircon saturation revisited:Temperature and composition effects in avariety of crustal magma types[J].Earth Planet.Sci.Lett,1983,64:295-304. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(83)90211-X Watson E B, Harrison T M.Zircon saturation revisited:Temperature and composition effects in avariety of crustal magma types[J].Earth Planet.Sci.Lett, 1983, 64:295-304. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(83)90211-X
Kinny P D,Mass R.Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd isotope systems in zircon[C]//Hanchar J M,Hoskin P W O.Zircon.Rev.Mineral.Geochem.,2003,53:327-341. Kinny P D, Mass R.Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd isotope systems in zircon[C]//Hanchar J M, Hoskin P W O.Zircon.Rev.Mineral.Geochem., 2003, 53:327-341.
吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 等.Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(2):185-220. http://www.cnki.com.cn/article/cjfdtotal-ysxb200702002.htm Vervoort J D,Pachelt P J,Gehrels G E,et al.Constraints on early Earth differentiation from hafnium and neodymium isotopes[J].Nature,1996,379(6566):624-627. doi: 10.1038/379624a0 Vervoort J D, Pachelt P J, Gehrels G E, et al.Constraints on early Earth differentiation from hafnium and neodymium isotopes[J].Nature, 1996, 379(6566):624-627. doi: 10.1038/379624a0
Amelin Y,Lee D C,Halliday A N.Early-Middle Archean crustal evolution deduced from Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotopic studies of single zircon grains[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2000,64(24):4205-4225. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00493-2 Amelin Y, Lee D C, Halliday A N.Early-Middle Archean crustal evolution deduced from Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotopic studies of single zircon grains[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(24):4205-4225. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00493-2
Watson E B,Harrison T M.Zircon thermometer reveals minimum melting conditions on earliest Earth[J].Science,2005,308(5723):841-844. doi: 10.1126/science.1110873 Watson E B, Harrison T M.Zircon thermometer reveals minimum melting conditions on earliest Earth[J].Science, 2005, 308(5723):841-844. doi: 10.1126/science.1110873
Miller C F,McDowell S M,Mapes R W.Hot and cold granites? Implications of zircon saturation temperatures and preservation of inheritance[J].Geology,2003,31(6):529-532. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2003)031<0529:HACGIO>2.0.CO;2 Miller C F, McDowell S M, Mapes R W.Hot and cold granites? Implications of zircon saturation temperatures and preservation of inheritance[J].Geology, 2003, 31(6):529-532. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2003)031<0529:HACGIO>2.0.CO;2
Henry D J,Guidotti C V,Thomson J A.The Ti saturation surface for low to medium pressure metapelitic biotites:Implications for geothemometry and Ti-substitution mechanisms[J].Am.Mineral.,2005,90:316-328. doi: 10.2138/am.2005.1498 Henry D J, Guidotti C V, Thomson J A.The Ti saturation surface for low to medium pressure metapelitic biotites:Implications for geothemometry and Ti-substitution mechanisms[J].Am.Mineral., 2005, 90:316-328. doi: 10.2138/am.2005.1498
高飞, 庞雅庆, 林锦荣, 等.诸广棉花坑铀矿床花岗岩中黑云母成分特征及其成岩成矿意义[J].高校地质学报, 2013, 19(增刊):274-275. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201403014.htm Wones D R,Eugster H P.Stability of biotite:experiment,theory,and application[J].Am.Mineral,1965,50:1228-1272. http://www.minsocam.org/ammin/AM50/AM50_1228.pdf Wones D R, Eugster H P.Stability of biotite:experiment, theory, and application[J].Am.Mineral, 1965, 50:1228-1272. http://www.minsocam.org/ammin/AM50/AM50_1228.pdf
Eugster H P,Wones D R.Stability relations of the ferruginous biotite,annite[J].J.Petrol.,1962,3(1):2648-2697. http://petrology.oxfordjournals.org/content/3/1/82.abstract Eugster H P, Wones D R.Stability relations of the ferruginous biotite, annite[J].J.Petrol., 1962, 3(1):2648-2697. http://petrology.oxfordjournals.org/content/3/1/82.abstract
Ishihara S.The magnetite-series and ilmenite-series granitic rocks[J].Mining Geology,1977,27:293-305. https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/shigenchishitsu1951/27/145/27_145_293/_article/-char/ja/ Ishihara S.The magnetite-series and ilmenite-series granitic rocks[J].Mining Geology, 1977, 27:293-305. https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/shigenchishitsu1951/27/145/27_145_293/_article/-char/ja/
吕志成, 段国正, 董光华.大兴安岭中南段燕山期三类不同成矿花岗岩中黑云母的化学成分特征及其成岩成矿意义[J].矿物学报, 2003, 23(2):177-184. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB200302014.htm Kelemen P B,Hangh K,Greenem A R.One view of the geochemistry of subduction-related magmatic arcs,with an emphasis on primitive andesite and lower crust[C]//Rudnick R L.Treatise On Geochemistry,2003,3:593-659. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2003TrGeo...3..593K Kelemen P B, Hangh K, Greenem A R.One view of the geochemistry of subduction-related magmatic arcs, with an emphasis on primitive andesite and lower crust[C]//Rudnick R L.Treatise On Geochemistry, 2003, 3:593-659. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2003TrGeo...3..593K
Li J W,Zhao X F,Zhou M F,et al.Origin of the Tongshankou porphyry-skarn Cu-Mo deposit,eastern Yangtze craton,Eastern China:geochronological,geochemical,and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints[J].Miner.Deposita.,2008,43:315-336. doi: 10.1007/s00126-007-0161-3 Li J W, Zhao X F, Zhou M F, et al.Origin of the Tongshankou porphyry-skarn Cu-Mo deposit, eastern Yangtze craton, Eastern China:geochronological, geochemical, and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints[J].Miner.Deposita., 2008, 43:315-336. doi: 10.1007/s00126-007-0161-3
Wu F Y,Jahn B M,Wilde S A,et al.Highly fractionated I-type granites in NE China (I):Geochronology and petrogenesis[J].Lithos,2003,66:241-273. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(02)00222-0 Wu F Y, Jahn B M, Wilde S A, et al.Highly fractionated I-type granites in NE China (I):Geochronology and petrogenesis[J].Lithos, 2003, 66:241-273. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(02)00222-0
Eby G N,Wooley A R,Din V,et al.Geochemistry and petrogenesis of nepheline syenite:Kasungu-Chipala,Homba,and Ulindi nepheline syenite intrusions,north Nyasa alkaline province,Malawi[J].J.Petrol.,1998,39:1405-1424. doi: 10.1093/petroj/39.8.1405 Eby G N, Wooley A R, Din V, et al.Geochemistry and petrogenesis of nepheline syenite:Kasungu-Chipala, Homba, and Ulindi nepheline syenite intrusions, north Nyasa alkaline province, Malawi[J].J.Petrol., 1998, 39:1405-1424. doi: 10.1093/petroj/39.8.1405
汪欢, 王建平, 刘家军, 等.南秦岭西坝花岗质岩体矿物学特征及成岩意义[J].现代地质, 2011, 25(3):489-502. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201103011.htm 丁孝石.西藏中南部花岗岩类中云母矿物标型特征及其地质意义[J].中国地质科学院矿床地质研究所所刊, 1988, 1:33-50. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ198800009005.htm 周作侠.湖北丰山洞岩体成因探讨[J].岩石学报, 1986, (1):59-70. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB198601007.htm Cheng Y B,Mao J W.Age and geochemistry of granites in Gejiu area,Yunnan province,SW China:Constraints ont their petrogenesis and tectonic setting[J].Lithos,2010,120:258-276. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2010.08.013 Cheng Y B, Mao J W.Age and geochemistry of granites in Gejiu area, Yunnan province, SW China:Constraints ont their petrogenesis and tectonic setting[J].Lithos, 2010, 120:258-276. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2010.08.013
邓晋福, 莫宣学, 赵海玲, 等.中国东部燕山期岩石圈-软流圈系统大灾变与成矿环境[J].矿床地质, 1999, 18(4):309-315. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/kcdz199904003.htm 王德滋, 沈渭洲.中国东南部花岗岩成因与地壳演化[J].地学前缘, 2003, 10(3):209-220. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200303031.htm 徐夕生, 谢昕.中国东南部晚中生代-新生代玄武岩与壳幔作用[J].高校地质学报, 2005, 11(3):318-334. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/gxdx200503004.htm 董树文, 张岳桥, 龙长兴, 等.中国侏罗纪构造变革与燕山运动新诠释[J].地质学报, 2007, 81(11):1449-1461. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200711002.htm 徐先兵, 张岳桥, 贾东, 等.华南早中生代大地构造过程[J].中国地质, 2009, 36(3):573-593. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200903009.htm 张岳桥, 董树文, 李建华, 等.华南中生代大地构造研究新进展[J].地球学报, 2012, 33(3):257-279. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201203001.htm 杨宗永, 何斌.华南侏罗纪构造体质转换:碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学证据[J].大地构造与成矿, 2013, 37(4):580-591. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/dgyk201304004.htm Xu X S,Dong C W,Li W X,et al.Late Mesozoic intrusive complexes in the coastal area of Fujian,SE China:The significance of the gabbro-diorite-granite association[J].Lithos,1999,46(2):299-315. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00087-5 Xu X S, Dong C W, Li W X, et al.Late Mesozoic intrusive complexes in the coastal area of Fujian, SE China:The significance of the gabbro-diorite-granite association[J].Lithos, 1999, 46(2):299-315. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00087-5
Zhou X M,Li W X.Origin of Late Mesozoic igneous rocks in southeastern China:Implications for lithosphere subduction and underplating of mafic magmas[J].Tectonophysics,2000,326(3/4):269-287. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195100001207 Zhou X M, Li W X.Origin of Late Mesozoic igneous rocks in southeastern China:Implications for lithosphere subduction and underplating of mafic magmas[J].Tectonophysics, 2000, 326(3/4):269-287. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195100001207
汪洋.湘南早中侏罗世花岗闪长岩的岩石化学特征、构造背景及地质意义[J].北京地质, 2003, 15(3):1-7. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBDZ200303000.htm 李晓峰, Watanabe Y, 华仁民, 等.华南地区中生代Cu-(Mo)-W-Sn矿床成矿作用与洋岭/转换断层俯冲[J].地质学报, 2008, 82(5):625-640. http://www.cnki.com.cn/article/cjfdtotal-dzxe200805007.htm 孙卫东, 凌明星, 杨晓勇, 等.洋脊俯冲与斑岩铜金矿成矿[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2010, 40(2):127-137. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201002001.htm 梁锦, 周永章, 李红中, 等.钦-杭结合带斑岩型铜矿的基本地质特征及成因分析[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(10):3361-3372. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/ysxb201210024.htm Abdel-Ralman M A.Nature of biotites from alkaline,calc-alkaline and peraluminous magmas[J].J.Petrol.,1994,35(2):525-541. doi: 10.1093/petrology/35.2.525 Abdel-Ralman M A.Nature of biotites from alkaline, calc-alkaline and peraluminous magmas[J].J.Petrol., 1994, 35(2):525-541. doi: 10.1093/petrology/35.2.525
Batchelor R A,Bowden P.Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series using multi-cationic parameters[J].Chemical Geology,1985,48(1):43-55. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0009254185900348 Batchelor R A, Bowden P.Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series using multi-cationic parameters[J].Chemical Geology, 1985, 48(1):43-55. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0009254185900348
Pearce J A,Harris N B W,Tindle A G.Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J].J.Petrol.,1984,25:956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956 Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G.Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J].J.Petrol., 1984, 25:956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
广东省地质局第二地质大队.广东省揭东县新寮岽铜多金属矿详查中间性地质报告(内部资料). 2012.




 下载:
下载: