Research on provenance using luminescence sensitivity of quartz grains: Progress and prospect
-
摘要:
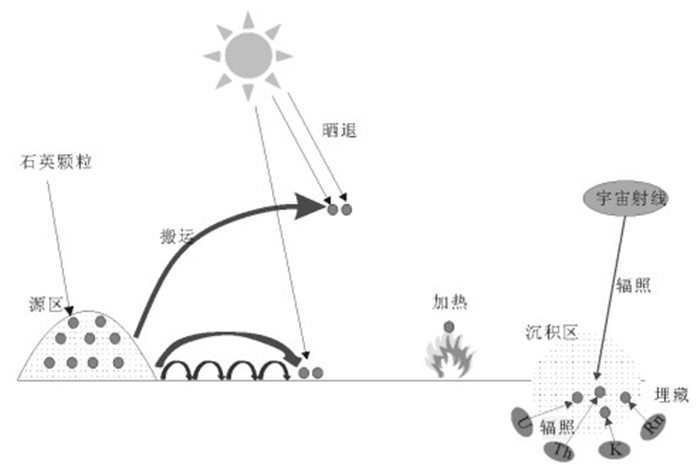
应用石英释光灵敏度进行物源研究是释光技术发展的新方向。回顾了石英释光灵敏度在测年研究中的发展现状,对其产生的机制、实验中的影响因素及其在测年中对灵敏度的监测、矫正等进行了介绍,详细介绍了空间尺度上不同沉积物(冰碛物、风成沉积物、水成沉积物)石英释光灵敏度的差异和时间序列上风成沉积物释光灵敏度的变化特征。据现有的研究成果分析,沉积历史和母岩来源对沉积物中石英的释光灵敏度的高低有重要的影响,因此可用它来追溯石英的物源。探讨该技术在物源研究领域存在的问题,对其发展前景进行了展望。
Abstract:The Thermoluminescence (TL) and Optically Stimulated Luminescence (OSL) sensitivity of quartz grains is a new indicator to trace the provenance of deposits. Many achievements have been obtained. This paper focuses on the development of the luminescence sensitivity of quartz grains, describing the production mechanism, the influencing factors for TL and OSL sensitivity changes in the laboratory, and the ways to monitor and to correct the luminescence sensitivity changes. Then various luminescence sensitivity characteristics of quartz grains from different deposits (glacigenic sediments, eolian deposits, and aqueous sediments) in different regions are recounted in detail. Meanwhile, various temporal luminescence sensitivity characteristics are also described for the eolian deposits. The parent rock and sedimentary history play important roles in the quartz luminescence sensitivity in nature, and hence luminescence sensitivity of quartz grains can be used to infer the origin and provenance of deposits. The challenges and chances in applying such a technique in tracing are also analyzed.
-
Keywords:
- luminescence /
- quartz /
- sensitivity /
- provenance /
- trace
-
致谢: 本次研究得到香港大学李盛华教授和中国地质大学(武汉)赖忠平研究员的悉心指导,在此一并表示感谢。
-
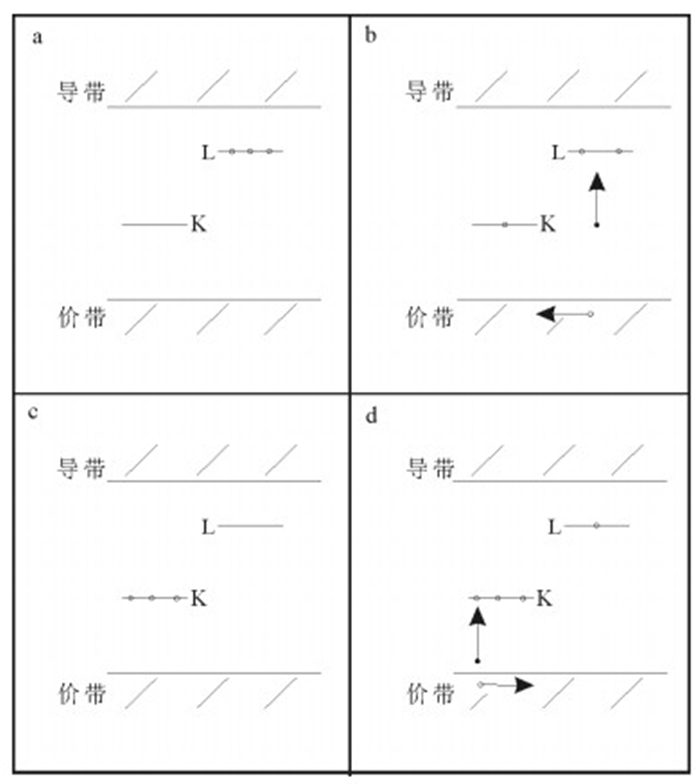
图 1 空穴“o”在释光中心(L)和非释光中心(K)的分布模型[31]
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of possible distribution of trapped holes (o) between luminescence centers L, and nonluminescence centers K
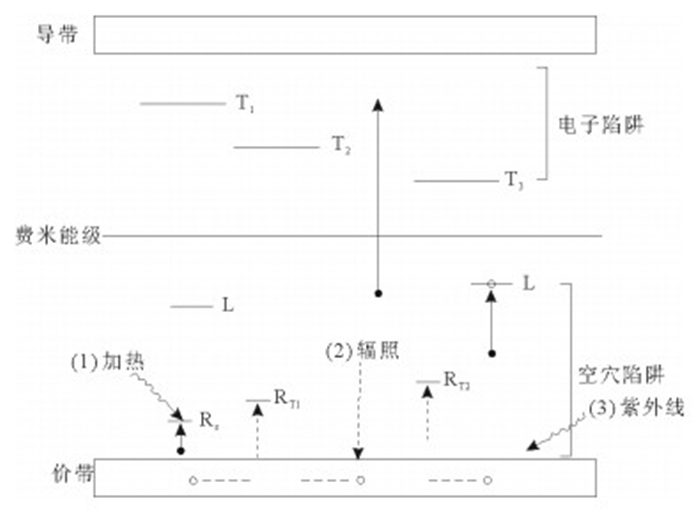
图 2 石英的OSL灵敏度变化机制模型[32](1~3代表不同能级的陷阱,4代表释光中心,5代表非释光中心)
Figure 2. The schematic band model used to explain the OSL sensitivity change
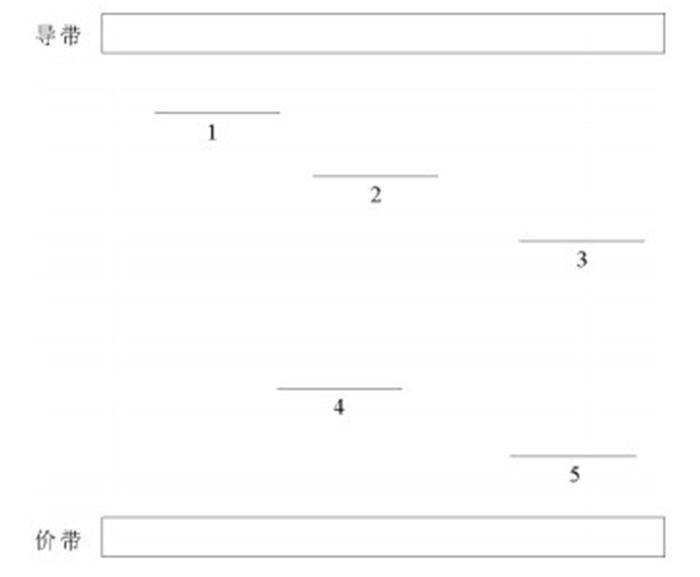
图 3 OSL和110℃ TL灵敏度变化模型(“·”代表电子,“o”代表空穴, T代表电子陷阱,R代表不同能量的空穴陷阱[29])
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of multiple levels of R traps applied
-
孙有斌, 安芷生.风尘堆积物中石英颗粒表面微结构特征及其沉积学指示[J].沉积学报, 2000, 18(4):506-509. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200004003.htm 黄求获, 徐文强.我国不同海区沉积物石英颗粒表面的微结构[J].海洋科学, 1997, 21(2):43-47. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYKX199702015.htm 李珍, 张家武.西宁黄土石英颗粒表面结构与黄土物质来源探讨[J].沉积学报, 1999, 17(2):221-225. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB902.009.htm 乔淑卿, 杨作升.石英物源示源研究进展[J].海洋科学进展, 2006, 24(2):266-274. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/91338a/200602/22101932.html 侯圣山, 杨石岭, 丁仲礼.风成沉积物4~16μm石英氧同位素记录及其物质来源意义[J].中国科学(D辑), 2003, 33(6):535-542. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200306005.htm Rink W J.Electron spin resonance (ESR) dating and ESR applications in Quaternary science and archaeometry[J].Radiation Measurements,1997,27(5/6):975-1025. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1979072884&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Rink W J.Electron spin resonance (ESR) dating and ESR applications in Quaternary science and archaeometry[J].Radiation Measurements, 1997, 27(5/6):975-1025. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1979072884&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
业渝光, 和杰, 刁少波.沉积物中石英的ESR测年研究[J].核技术, 1993, 16(4):222-224. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJSU199304006.htm 张绍平, 顿铁军.阴极发光显微镜在岩矿鉴定方面的应用[J].西安地质学院学报, 1989, 11(1):40-49. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX198901004.htm Huntley D J,Godfrey-Smith D I,Thewalt M L W.Optical dating of sediments[J].Nature,1985,313(5998):105-107. doi: 10.1038/313105a0 Huntley D J, Godfrey-Smith D I, Thewalt M L W.Optical dating of sediments[J].Nature, 1985, 313(5998):105-107. doi: 10.1038/313105a0
Aitken M J.ThermoluminescenceDating[M].Academic Press,1985:1-359. Aitken M J.ThermoluminescenceDating[M].Academic Press, 1985:1-359.
Aitken M J.An Introduction to Optical Dating[M].Oxford University Press,1998:1-263. Aitken M J.An Introduction to Optical Dating[M].Oxford University Press, 1998:1-263.
Wintle A G,Catt J A.Thermoluminescence dating of soils developed in late devensian loess at pegwell bay,Kent[J].Journal of Soil Science,1985,36(2):293-298. doi: 10.1111/ejs.1985.36.issue-2 Wintle A G, Catt J A.Thermoluminescence dating of soils developed in late devensian loess at pegwell bay, Kent[J].Journal of Soil Science, 1985, 36(2):293-298. doi: 10.1111/ejs.1985.36.issue-2
Wintle A G.A review of current research on TL dating of loess[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,1990,9(4):385-397. doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(90)90029-A Wintle A G.A review of current research on TL dating of loess[J].Quaternary Science Reviews, 1990, 9(4):385-397. doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(90)90029-A
Murray A S,Wintle A G.Luminescence dating of quartz using an improved single-aliquot regenerative-dose protocol[J].Radiation Measurements,2000,32(1):57-73. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(99)00253-X Murray A S, Wintle A G.Luminescence dating of quartz using an improved single-aliquot regenerative-dose protocol[J].Radiation Measurements, 2000, 32(1):57-73. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(99)00253-X
Derbyshire E.Aeolian sediments in the Quaternary record:An introduction[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,1995,14(7/8):641-643. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1971512052&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Derbyshire E.Aeolian sediments in the Quaternary record:An introduction[J].Quaternary Science Reviews, 1995, 14(7/8):641-643. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1971512052&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Chithambo M L,Preusser F,Ramseyer K,et al.Time-resolved luminescence of low sensitivity quartz from crystalline rocks[J].Radiation Measurements,2007,42(2):205-212. doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2006.07.005 Chithambo M L, Preusser F, Ramseyer K, et al.Time-resolved luminescence of low sensitivity quartz from crystalline rocks[J].Radiation Measurements, 2007, 42(2):205-212. doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2006.07.005
Lai Z P,Wintle A G.Locating the boundary between the Pleistocene and the Holocene in Chinese loess using luminescence[J].Holocene,2006,16(6):893-899. doi: 10.1191/0959683606hol980rr Lai Z P, Wintle A G.Locating the boundary between the Pleistocene and the Holocene in Chinese loess using luminescence[J].Holocene, 2006, 16(6):893-899. doi: 10.1191/0959683606hol980rr
Li S H,Chen Y Y,Li B,et al.OSL dating of sediments from deserts in northern China[J].Quaternary Geochronology,2007,2:23-28. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2006.05.034 Li S H, Chen Y Y, Li B, et al.OSL dating of sediments from deserts in northern China[J].Quaternary Geochronology, 2007, 2:23-28. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2006.05.034
Zheng C X,Zhou L P,Qin J T.Difference in luminescence sensitivity of coarse-grained quartz from deserts of northern China[J].Radiation Measurements,2009,44(5):534-537. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2045686346&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Zheng C X, Zhou L P, Qin J T.Difference in luminescence sensitivity of coarse-grained quartz from deserts of northern China[J].Radiation Measurements, 2009, 44(5):534-537. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2045686346&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Lü T Y,Sun J M.Luminescence sensitivities of quartz grains from eolian deposits in northern China and their implications for provenance[J].Quaternary Research,2011,76:181-189. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2011.06.015 Lü T Y, Sun J M.Luminescence sensitivities of quartz grains from eolian deposits in northern China and their implications for provenance[J].Quaternary Research, 2011, 76:181-189. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2011.06.015
郑辰鑫, 周力平.石英释光信号作为粉尘物源示踪手段的再研究[J].第四纪研究, 2012, 32(5):1036-1045. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201205022.htm Wintle A G,Murray A S.Luminescence sensitivity changes in quartz[J].Radiation Measurements,1999,30(1):107-118. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(98)00096-1 Wintle A G, Murray A S.Luminescence sensitivity changes in quartz[J].Radiation Measurements, 1999, 30(1):107-118. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(98)00096-1
李盛华.光释光信号灵敏度变化的模式, 验证和推论[J].核技术, 1995, 18(8):458-462. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJSU508.003.htm Aitken M J,Smith B W.Optical dating-recuperation after bleaching[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,1988,7:387-393. doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(88)90034-0 Aitken M J, Smith B W.Optical dating-recuperation after bleaching[J].Quaternary Science Reviews, 1988, 7:387-393. doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(88)90034-0
Bøtter-Jensen L,Duller G A T.A new system for measuring optically stimulated luminescence from quartz samples[J].International Journal of Radiation Apllications&Instrumentation.Part D.Nuclear Tracks&Radiation Measurements,1992,20(4):549-553. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2072295734&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Bøtter-Jensen L, Duller G A T.A new system for measuring optically stimulated luminescence from quartz samples[J].International Journal of Radiation Apllications & Instrumentation.Part D.Nuclear Tracks & Radiation Measurements, 1992, 20(4):549-553. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2072295734&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Huntley D J,Godfreysmith D I,Haskell E H.Light-induced emission-spectra from some quartz and feldspars[J].Nuclear Tracks&Radiation Measurements,1991,18(1):127-131. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1980874692&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Huntley D J, Godfreysmith D I, Haskell E H.Light-induced emission-spectra from some quartz and feldspars[J].Nuclear Tracks & Radiation Measurements, 1991, 18(1):127-131. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1980874692&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Stoneham D,Stokes S.An investigation of the relationship between the 110℃ TL peak and optically stimulated luminescence in sedimentary quartz[J].Nuclear Tracks&Radiation Measurements,1991,18(1/2):119-123. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/232359489_An_investigation_of_the_relationship_between_the_110C_TL_peak_and_optically_stimulated_luminescence_in_sedimentary_quartz Stoneham D, Stokes S.An investigation of the relationship between the 110℃ TL peak and optically stimulated luminescence in sedimentary quartz[J].Nuclear Tracks & Radiation Measurements, 1991, 18(1/2):119-123. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/232359489_An_investigation_of_the_relationship_between_the_110C_TL_peak_and_optically_stimulated_luminescence_in_sedimentary_quartz
Wintle A G,Murray A S.The relationship between quartz thermoluminescence,photo-transferred thermoluminescence,and optically stimulated luminescence[J].Radiation Measurements,1997,27(4):611-624. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(97)00018-8 Wintle A G, Murray A S.The relationship between quartz thermoluminescence, photo-transferred thermoluminescence, and optically stimulated luminescence[J].Radiation Measurements, 1997, 27(4):611-624. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(97)00018-8
Li S H.Luminescence sensitivity changes of quartz by bleaching,annealing and UV exposure[J].Radiation Effects and Defects in Solids,2002,157(3):357-364. doi: 10.1080/10420150212998 Li S H.Luminescence sensitivity changes of quartz by bleaching, annealing and UV exposure[J].Radiation Effects and Defects in Solids, 2002, 157(3):357-364. doi: 10.1080/10420150212998
Murray A S,Rorberts R G.Measurement of the equivalent dose in quartz using a regenerative-dose single-aliquot protocol[J].Radiation Measurements,1998,29(5):503-515. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(98)00044-4 Murray A S, Rorberts R G.Measurement of the equivalent dose in quartz using a regenerative-dose single-aliquot protocol[J].Radiation Measurements, 1998, 29(5):503-515. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(98)00044-4
Zimmerman J.The radiation-induced increase of the 100℃ thermoluminescence sensitivity of fired quartz[J].Journal of Physics C:Solid State Physics,1971,4:3265-3275. doi: 10.1088/0022-3719/4/18/032 Zimmerman J.The radiation-induced increase of the 100℃ thermoluminescence sensitivity of fired quartz[J].Journal of Physics C:Solid State Physics, 1971, 4:3265-3275. doi: 10.1088/0022-3719/4/18/032
Bøtter-Jensen L,Agersnap L N,Mejdahl V,et al.Luminescence sensitivity changes in quartz as a result of annealing[J].Radiation Measurements,1995,24:535-541. doi: 10.1016/1350-4487(95)00006-Z Bøtter-Jensen L, Agersnap L N, Mejdahl V, et al.Luminescence sensitivity changes in quartz as a result of annealing[J].Radiation Measurements, 1995, 24:535-541. doi: 10.1016/1350-4487(95)00006-Z
李虎侯.用石英110℃热释光峰灵敏度增高法测定年龄[J].核电子学与探测技术, 1984, 4(1):11-18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HERE198401002.htm 尹功明, 李盛华.石英的热释光前剂量特征及其在地学上的初步应用[J].地震地质, 2000, 12, 22(增刊):37-41 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ2000S1006.htm 王晓聆, 张慧军, 孙淼等.温度对细粒石英前剂量热释光响应的影响[J].中国医学物理学杂志, 1998, 15(2):116-117. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXWZ802.022.htm Roberts H M,Wintle A G.Luminescence sensitivity changes of polymineral fine grains during IRSL and[post-IR]OSL measurements[J].Radiation Measurements,2003,37(6):661-671. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(03)00245-2 Roberts H M, Wintle A G.Luminescence sensitivity changes of polymineral fine grains during IRSL and[post-IR]OSL measurements[J].Radiation Measurements, 2003, 37(6):661-671. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(03)00245-2
Wintle A G,Murray A S.Towards the development of a preheat procedure for OSL dating of quartz[J].Radiation Measurements,1998,29(1):81-94. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(97)00228-X Wintle A G, Murray A S.Towards the development of a preheat procedure for OSL dating of quartz[J].Radiation Measurements, 1998, 29(1):81-94. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(97)00228-X
Murray A S,Mejdahl V.Comparison of regenerative-dose singlealiquot and multiple-aliquot (SARA) protocols using heated quartz from archaeological sites[J].Quaternary science reviews,1999,18(2):223-229. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(98)00055-9 Murray A S, Mejdahl V.Comparison of regenerative-dose singlealiquot and multiple-aliquot (SARA) protocols using heated quartz from archaeological sites[J].Quaternary science reviews, 1999, 18(2):223-229. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(98)00055-9
Murray A S,Wintle A G.The single aliquot regenerative dose protocol:potential for improvements in reliability[J].Radiation Measurements,2003,37(4):377-381. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2052493774&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Murray A S, Wintle A G.The single aliquot regenerative dose protocol:potential for improvements in reliability[J].Radiation Measurements, 2003, 37(4):377-381. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2052493774&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Lu Y C,Wang X L,Wintle A G.A new OSL chronology for dust accumulation in the last 130,000yr for the Chinese Loess Plateau[J].Quaternary Research,2007,67(1):152-160. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2006.08.003 Lu Y C, Wang X L, Wintle A G.A new OSL chronology for dust accumulation in the last 130, 000yr for the Chinese Loess Plateau[J].Quaternary Research, 2007, 67(1):152-160. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2006.08.003
Murray A S,Roberts R G,WintleA G.Equivalent dose measurement using a single aliquot of quartz[J].Radiation Measurements,1997,27(2):171-184. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(96)00130-8 Murray A S, Roberts R G, WintleA G.Equivalent dose measurement using a single aliquot of quartz[J].Radiation Measurements, 1997, 27(2):171-184. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(96)00130-8
Singhvi A K,Stokes S C,Chauhan N,et al.Changes in natural OSL sensitivity during single aliquot regeneration procedure and their implications for equivalent dose determination[J].Geochronometria,2011,38(3):231-241. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2025522922&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Singhvi A K, Stokes S C, Chauhan N, et al.Changes in natural OSL sensitivity during single aliquot regeneration procedure and their implications for equivalent dose determination[J].Geochronometria, 2011, 38(3):231-241. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2025522922&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Rhodes E J.Quartz single grain OSL sensitivity distributions:Implications for multiple grain single aliquot dating[J].Geochronometria,2007,26(1):19-29. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2041694375&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Rhodes E J.Quartz single grain OSL sensitivity distributions:Implications for multiple grain single aliquot dating[J].Geochronometria, 2007, 26(1):19-29. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2041694375&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Pietsch T J,Olleya J M,Nanson GC.Fluvial transport as a natural luminescence sensitiser of quartz[J].Quaternary Geochronology,2008,3(4):365-376. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2007.12.005 Pietsch T J, Olleya J M, Nanson GC.Fluvial transport as a natural luminescence sensitiser of quartz[J].Quaternary Geochronology, 2008, 3(4):365-376. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2007.12.005
Tsukamoto S,Nagashima K,Murray A S,et al.Variations in OSL components from quartz from Japan sea sediments and the possibility of reconstructing provenance[J].Quaternary International,2011,234(1):182-189. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2019390988&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Tsukamoto S, Nagashima K, Murray A S, et al.Variations in OSL components from quartz from Japan sea sediments and the possibility of reconstructing provenance[J].Quaternary International, 2011, 234(1):182-189. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2019390988&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Duller G A T.Single grain optical dating of glacigenicdeposits[J].Quaternary Geochronology,2006,1(4):296-304. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2006.05.018 Duller G A T.Single grain optical dating of glacigenicdeposits[J].Quaternary Geochronology, 2006, 1(4):296-304. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2006.05.018
Fuchs M,Owen L A.Luminescence dating of glacial and associated sediments:review,recommendations and future directions[J].Boreas,2008,37(4):636-659. doi: 10.1111/bor.2008.37.issue-4 Fuchs M, Owen L A.Luminescence dating of glacial and associated sediments:review, recommendations and future directions[J].Boreas, 2008, 37(4):636-659. doi: 10.1111/bor.2008.37.issue-4
Rhodes E J,Pownall L.Zeroing of the OSL signal in quartz from young glaciofluvialsediments[J].Radiation Measurements,1994,23(2):581-585. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2114357977&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Rhodes E J, Pownall L.Zeroing of the OSL signal in quartz from young glaciofluvialsediments[J].Radiation Measurements, 1994, 23(2):581-585. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2114357977&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
RhodesE J,Bailey R M.The effect of thermal transfer on the zeroing of the luminescence of quartz from recent glaciofluvialsediments[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,1997,16(3):291-298. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2086045989&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn RhodesE J, Bailey R M.The effect of thermal transfer on the zeroing of the luminescence of quartz from recent glaciofluvialsediments[J].Quaternary Science Reviews, 1997, 16(3):291-298. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2086045989&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Rhodes E J.Observations of thermal transfer OSL signals in glacigenicquartz[J].Radiation Measurements,2000,32(5):595-602. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2058307254&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Rhodes E J.Observations of thermal transfer OSL signals in glacigenicquartz[J].Radiation Measurements, 2000, 32(5):595-602. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2058307254&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Richards B.Luminescence dating of Quaternary sediments in the Himalaya and High Asia:a practical guide to its use and limitations for constraining the timing of glaciation[J].Quaternary International,2000,65(99):49-61. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2067080216&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Richards B.Luminescence dating of Quaternary sediments in the Himalaya and High Asia:a practical guide to its use and limitations for constraining the timing of glaciation[J].Quaternary International, 2000, 65(99):49-61. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2067080216&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Richthofen B F.Ⅱ-On the Mode of Origin of the Loess[J].Geological Magazine (Decade Ⅱ),1882,9(7):293-305. doi: 10.1017/S001675680017164X Richthofen B F.Ⅱ-On the Mode of Origin of the Loess[J].Geological Magazine (Decade Ⅱ), 1882, 9(7):293-305. doi: 10.1017/S001675680017164X
Lukas S,Spencer J Q G,Robinson R A J,et al.Problems associated with luminescence dating of Late Quaternary glacial sediments in the NW Scottish Highlands[J].Quaternary Geochronology,2007,2(1):243-248. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2028802527&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Lukas S, Spencer J Q G, Robinson R A J, et al.Problems associated with luminescence dating of Late Quaternary glacial sediments in the NW Scottish Highlands[J].Quaternary Geochronology, 2007, 2(1):243-248. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2028802527&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Thrasher I M,Mauz B,Chiverrell R C,et al.Luminescence dating of glaciofluvial deposits:A review[J].Earth-Science Reviews,2009,97(1):133-146. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2091983811&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Thrasher I M, Mauz B, Chiverrell R C, et al.Luminescence dating of glaciofluvial deposits:A review[J].Earth-Science Reviews, 2009, 97(1):133-146. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2091983811&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Sawakuchi A O,Blair M W,DeWitt R,et al.Thermal history versus sedimentary history:OSL sensitivity of quartz grains extracted from rocks and sediments[J].Quaternary Geochronology,2011,6(2):261-272. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2010.11.002 Sawakuchi A O, Blair M W, DeWitt R, et al.Thermal history versus sedimentary history:OSL sensitivity of quartz grains extracted from rocks and sediments[J].Quaternary Geochronology, 2011, 6(2):261-272. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2010.11.002
Sawakuchi A O,Dewitt R,Blair M W,et al.Quartz OSL sensitivity as a proxy for storm activity on the southern Brazilian coast during the Late Holocene[J].Quaternary Geochronology,2012,13(6):92-102. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2038269904&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Sawakuchi A O, Dewitt R, Blair M W, et al.Quartz OSL sensitivity as a proxy for storm activity on the southern Brazilian coast during the Late Holocene[J].Quaternary Geochronology, 2012, 13(6):92-102. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2038269904&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Zular A,Sawakuchi A O,Guedes C C F,et al.Attaining provenance proxies from OSL and TL sensitivities:Coupling with grain size and heavy minerals data from southern Brazilian coastal sediments[J].Radiation Measurements,2015,81:39-45. doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2015.04.010 Zular A, Sawakuchi A O, Guedes C C F, et al.Attaining provenance proxies from OSL and TL sensitivities:Coupling with grain size and heavy minerals data from southern Brazilian coastal sediments[J].Radiation Measurements, 2015, 81:39-45. doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2015.04.010
Lü T Y,Sun J M,Li S H,et al.Vertical variations of luminescence sensitivity of quartz grains from loess/paleosol of Luochuan section in the central Chinese loess plateau since the last interglacial[J].Quaternary Geochronology,2014,22(3):107-115. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1999837643&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Lü T Y, Sun J M, Li S H, et al.Vertical variations of luminescence sensitivity of quartz grains from loess/paleosol of Luochuan section in the central Chinese loess plateau since the last interglacial[J].Quaternary Geochronology, 2014, 22(3):107-115. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1999837643&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Wintle A G,Murray A S.A review of quartz optically stimulated luminescence characteristics and their relevance in single-aliquot regeneration dating protocols[J].Radiation Measurements,2006,41(4):369-391. doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2005.11.001 Wintle A G, Murray A S.A review of quartz optically stimulated luminescence characteristics and their relevance in single-aliquot regeneration dating protocols[J].Radiation Measurements, 2006, 41(4):369-391. doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2005.11.001
McKeever S W S,BotterJensen L,Larsen N A,et al.Optically stimulated luminescence sensitivity changes in quartz due to repeated use in single aliquot readout:Experiments and computer simulation[J].Radiation Protection Dosimetry,1996,65:49-54. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.rpd.a031680 McKeever S W S, BotterJensen L, Larsen N A, et al.Optically stimulated luminescence sensitivity changes in quartz due to repeated use in single aliquot readout:Experiments and computer simulation[J].Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 1996, 65:49-54. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.rpd.a031680
Moska P,Murray A S.Stability of the quartz fast-component in insensitive samples[J].Radiation Measurements,2006,41(7):878-885. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2073168135&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Moska P, Murray A S.Stability of the quartz fast-component in insensitive samples[J].Radiation Measurements, 2006, 41(7):878-885. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2073168135&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Koul D K,Chougaonkar M P.The pre-dose phenomenon in the OSL signal of quartz[J].Radiation Measurements,2007,42(8):1265-1272. doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2007.04.001 Koul D K, Chougaonkar M P.The pre-dose phenomenon in the OSL signal of quartz[J].Radiation Measurements, 2007, 42(8):1265-1272. doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2007.04.001
Preusser F,Chithambo M L,Gotte T,et al.Quartz as a natural luminescence dosimeter[J].Earth-Science Reviews,2009,97(1):184-214. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2050881970&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Preusser F, Chithambo M L, Gotte T, et al.Quartz as a natural luminescence dosimeter[J].Earth-Science Reviews, 2009, 97(1):184-214. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2050881970&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Preusser F,Ramseyer K,Schluchter C.Characterisation of low OSL intensity quartz from the New Zealand Alps[J].Radiation Measurements,2006,41(7/8):871-877. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2068151697&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Preusser F, Ramseyer K, Schluchter C.Characterisation of low OSL intensity quartz from the New Zealand Alps[J].Radiation Measurements, 2006, 41(7/8):871-877. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2068151697&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Fitzsimmons K E,Rhodes E J,Barrows TT.OSL dating of southeast Australian quartz:A preliminary assessment of luminescence characteristics and behavior[J].Quaternary Geochronology,2010,5:91-95. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2009.02.009 Fitzsimmons K E, Rhodes E J, Barrows TT.OSL dating of southeast Australian quartz:A preliminary assessment of luminescence characteristics and behavior[J].Quaternary Geochronology, 2010, 5:91-95. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2009.02.009
Dennen W H,Blackburn W H,Quesada A.Aluminum in quartz as a geothermometer[J].Contribution to Mineralogy and Petrology,1970,27(4):332-342. doi: 10.1007/BF00389817 Dennen W H, Blackburn W H, Quesada A.Aluminum in quartz as a geothermometer[J].Contribution to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1970, 27(4):332-342. doi: 10.1007/BF00389817
Wark D A,Watson E B.TitaniQ:a titanium-in-quartz geothermometer[J].Contribution to Mineralogy and Petrology,2006,152(6):743-754. doi: 10.1007/s00410-006-0132-1 Wark D A, Watson E B.TitaniQ:a titanium-in-quartz geothermometer[J].Contribution to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2006, 152(6):743-754. doi: 10.1007/s00410-006-0132-1
Fitzsimmons K E.An assessment of the luminescence sensitivity of Australian quartz with respect to sediment history[J].Geochronometria,2011,38(3):199-208. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2007412053&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Fitzsimmons K E.An assessment of the luminescence sensitivity of Australian quartz with respect to sediment history[J].Geochronometria, 2011, 38(3):199-208. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2007412053&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn



 下载:
下载: