Geochemical characteristics, chronology and geological significance of the dacite in the Mazhala deposit, southern Tibet
-
摘要:
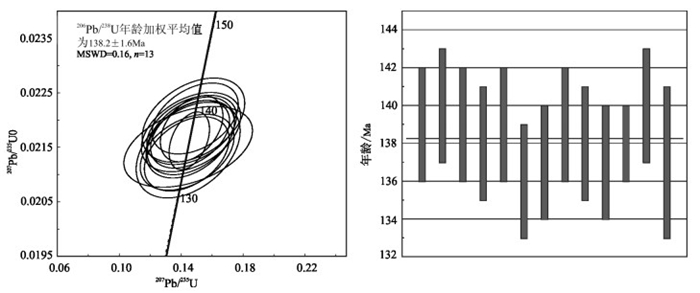
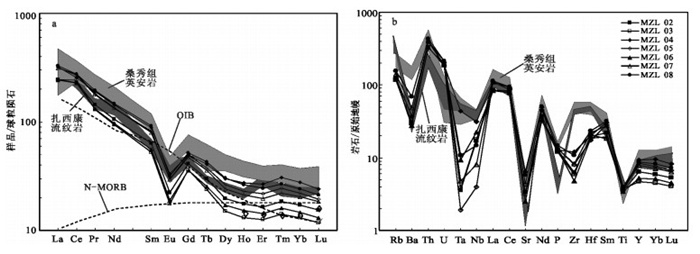
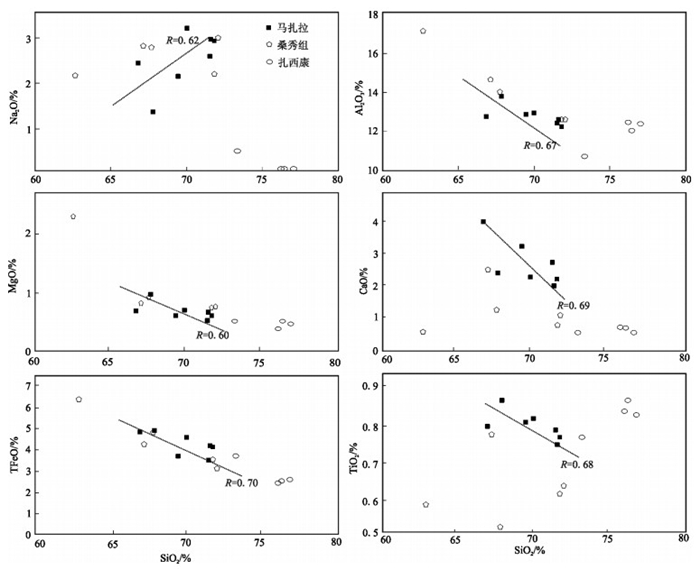
马扎拉金(锑)矿位于西藏北喜马拉雅金锑铅锌多金属成矿带,是扎西康整装勘查区发现的最早并最具代表性的金矿。对马扎拉矿区广泛出露的英安岩进行了锆石U-Pb年代学和岩石地球化学研究。全岩主量和微量元素地球化学特征显示,英安岩具有富硅(SiO2=66.86%~71.84%)、低碱(Na2O+K2O=3.79%~4.60%)、低Mg(MgO=0.50%~0.94%)、强过铝质(A/CNK=1.55~2.23)的特征,强烈富集Rb、U等大离子亲石元素(LILEs),相对亏损Ta、Ti、Zr等高场强元素(HFSEs);稀土元素总量较高(ΣREE=283.74×10-6~380.04×10-6),轻稀土元素富集,且轻、重稀土元素分馏明显(LREE/HREE=10.57~15.22),中等负Eu异常(δEu=0.39~0.48),无明显Ce异常。英安岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年获得206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为138.2±1.6Ma,表明马扎拉矿区英安岩形成于早白垩世。结合区域地质资料,初步认为马扎拉矿区英安岩形成于被动大陆边缘构造环境,可能是Comei-Bunury大火成岩省形成早期的产物。
-
关键词:
- 马扎拉 /
- 英安岩 /
- LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年 /
- 地球化学 /
- 藏南
Abstract:Located in Northern Himalaya metallogenic belt, the Mazhala deposit is the most representative gold deposit in the Zhaxikang integrated exploration area. In this study, the authors carried out comprehensive researches including petrochemistry and zircon U-Pb dating analysis of the dacite in the Mazhala deposit, Comei County, southern Tibet. Chemical analyses show that the dacite is characterized by high Si (SiO2=66.86%~71.84%), low alkali (Na2O+K2O=3.79%~4.60%), low Mg (MgO=0.50%~0.94%), strong peraluminous nature (A/CNK=1.55~2.23), enrichment of LILE such as Rb, U and depletion of HFSE such as Ta, Ti and Zr. The rocks also exhibit high total REE content (ΣREE=295.71×10-6~343.82×10-6), enrichment of LREE and obvious differentiation (LREE/HREE=10.5~15.22), with moderately negative Eu anomalies (δEu=0.39~0.48) and no cerium anomaly. LA-ICP-MS zircon UPb chronology indicates that the Mazhala dacite was emplaced at 138.2±1.6Ma, being the product of the Early Cretaceous magmatic activity. According to regional geology and related data, it is considered that the dacite was formed on the Himalayan passive continental margin and may be a part of Comei-Bunbury large igneous province.
-
Keywords:
- Mazhala deposit /
- dacite /
- LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating /
- geochemistry /
- southern Tibet
-
随着地球科学家对地球系统研究的不断深入,人们发现新元古代时地球系统发生了一系列的剧烈变化。在地球地质历史的这一时期,地球从较稳定的古-中元古代(17~7.5亿年)[1],进入剧烈变动的中-晚新元古代时期(7.5~5.4亿年)。中-晚新元古代地球上出现多期极冷事件[2-7],条带状铁矿也在消失十多亿年后,在新元古代中期又重新出现[1, 8],大洋与大气圈的氧含量快速增加[9-11]。地球系统这一系列的剧变很可能发生在Rodinia超大陆裂解的背景下。因此,重建这一时期的古地理古板块位置对于理解这些剧变至关重要。然而,由于这一时期(7.5~5.4亿年)全球不同块体古地磁数据的缺乏和可靠性问题,其古地理重建一直存在较大的争议[12-20]。
影响这一时期古地磁数据可靠性的因素,除了考虑剩磁的获得时间外,近年来越来越多的学者注意到非偶极子场及磁倾角偏低对古地磁数据的影响[21-26],特别是红层中存在普遍的磁倾角偏低现象[27-28]。
最近,Jing等[29]报道了湖北宜昌三峡地区莲沱组红层可靠的古地磁极,并根据Lan等[30]最新的SIMS锆石U-Pb定年研究,确定这一古地磁极年龄应为720Ma。虽然这一古地磁极通过了Van der Voo[31]的6项Q检验,确保其剩磁获得的原生性,但这一结果是否受到后期压实作用的影响并产生磁倾角偏低,以及影响程度的大小等问题,都需要进一步研究。在长阳地区,由于古城冰碛岩覆盖在莲沱组之上,因此准确确定莲沱组的磁倾角,对确定华南这一时期的古纬度及“雪球地球”的研究都具有重要意义。另外,目前华南地块莲沱组古地磁极与南沱组古地磁极相似的问题,一直没有得到可信的解释,本文通过磁倾角偏低的研究,对这一问题进行探讨。
1. 区域地质概况及采样
采样区位于华南新元古代地层典型剖面区,湖北三峡地区(图 1)。研究区出露的新元古代沉积地层包括莲沱组、南沱组、陡山沱组、灯影组等。莲沱组一般不整合覆盖于黄陵花岗岩之上,主要为厚层的紫红色砂岩和砾岩,可分为2个大的沉积旋回(图 2),每个旋回底部为砾石或粗粒石英砂岩,向上逐渐变为粉砂岩、泥质砂岩,含多层凝灰岩或凝灰质碎屑岩。在区域上,西北部地层厚度较大,向西南变薄。本区南沱组与莲沱组平行不整合接触或低角度不整合接触,南沱组主要为暗绿色冰碛砾岩,部分为红色冰碛岩[32]。
![]() 图 2 本次研究获取的采点(下划线标注TLS编号)在地层上的分布(TL编号为Jing等[29]采点)Figure 2. Stratigraphic column of the Liantuo Formation and detailed sampling layer positions of three sub-sections at Yichang
图 2 本次研究获取的采点(下划线标注TLS编号)在地层上的分布(TL编号为Jing等[29]采点)Figure 2. Stratigraphic column of the Liantuo Formation and detailed sampling layer positions of three sub-sections at Yichang在三峡地区南部的长阳地区,莲沱组之上覆盖古城组冰碛岩和大塘坡组页岩,而不是直接与南沱组接触[33]。古城组冰碛岩应与扬子西南部广泛发育的长安组冰碛岩一致[33],属于Sturtian冰期的产物。古城组沉积时间应始于715Ma左右[33]。
三峡地区从埃迪卡拉纪开始长期沉积碳酸盐岩,早寒武世有一次沉积间断,直到志留纪宜昌地区大规模抬升,沉积间断接受剥蚀,随后沉陷到早三叠世再次抬升[34-35]。本地区经历了3次主要的构造运动:加里东期、印支期和燕山期构造运动。同时中扬子地区存在与这3次构造运动相关的3期油气生成和排烃过程[36]。区域内构造变形较弱。
本次在宜昌花鸡坡、头顶石及田家院子3个剖面共采集了17块手标本样品(TLS1-17),对莲沱组是否存在磁倾角偏低现象进行检验(图 2)。样品在野外用罗盘测量层面的走向和倾角,并标记在层面上。
2. 实验方法
在室内用台式钻机垂直手标本层面钻取2根以上岩心,并加工出1~2块高2.2cm、直径2.5cm的标准岩心样品。每根岩心选取1~2块,共31块标准样品进行系统热退磁实验。同时对应选择了30块样品进行Hodych等[23]磁倾角偏低校正实验。所有实验工作均在中国地质科学院地质力学研究所国土资源部古地磁与古构造重建重点实验室完成。使用美国ASC Scientific Inc.公司生产的IM-10-30脉冲充磁仪对样品进行充磁,样品系统热退磁由TD-48大型热退磁仪完成,样品剩磁测量在ARGICO-JR6A旋转磁力仪上完成。另外,对部分样品利用KLY-3 Kappabridges进行了氮气环境下磁化率随温度变化实验(K-T),获取连续加热-冷却曲线分析样品磁化率的变化。
3. 实验结果
3.1 逐步热退磁结果
宜昌三峡地区花鸡坡、头顶石及田家院子剖面莲沱组样品的岩石磁学实验结果显示,岩石的特征剩磁载磁矿物为赤铁矿[29]。因此,系统热退磁温度区间在低温段以50~100℃为间隔,高温段温度区间以20℃为间隔,热退磁温度达到680℃(图 3)。样品使用主向量分析法[37]进行剩磁组分分析。
逐步热退磁结果显示,样品中共可以分离出3个剩磁方向(图 3):低温分量一般在小于等于300℃的情况下分离出来, 共有15块样品分离出此分量,其在地理坐标系下的统计方向(Dg=5.9°,Ig=60.1°,kg=81.3, ɑ95=4.3°)与采样点现代地磁场方向接近,应为现代地磁场的热粘滞剩磁;中温分量的温度区间一般在300~600~640℃之间,共有6块样品分离出此分量,其平均方向在地理坐标系下为Dg=34.5°,Ig=78.1°,kg=244.2,ɑ95=4.3°,在地层坐标系下为Ds=78.9°,Is=78.4°,ks=243.5,ɑ95=4.3°。另外,从11块样品中分离出了与宜昌剖面得到的特征分量相似的高温分量(600~680℃),其平均方向在地理坐标系下为Dg=67.0°,Ig=71.6°,kg=124.7,ɑ95=3.9°,在地层坐标系下为Ds=95.3°,Is=67.8°,ks=196.0,ɑ95=3.1°。
3.2 等温剩磁各向异性实验结果
对12个样品,在与其层面呈45°方向,从低到高逐步增加等温直流磁场,获得平行于层面IRMx和垂直于层面IRMz的等温剩磁,直流磁场大小由20、40、60、100、225、315、415、510、510、710、810、950、1200mT依次递增。在每步施加直流场后使用JR6旋转磁力仪对样品进行剩磁测试。然后用TD48大型热退磁炉对所有样品进行系统热退磁,相关数据结果列于表 1中。
表 1 宜昌地区剖面莲沱组样品等温热剩磁各向异性及磁倾角偏低值Table 1. Anisotropy of isothermal remnant magnetization for Liantuo Formation red beds in Yichang areaID Iobs IRMz/IRMx
(610~1200mT)IF1 ΔI1(=IF1-Iobs) IRMz/IRMx
(600°C以上)IF2 ΔI2(=IF2-Iobs) 15 64.4 0.7796 69.518 5.118 0.8542 67.7425 3.3425 15-2c 71.5 0.8414 74.277 2.777 0.8513 74.1009 2.6009 15-5b 65 0.899 67.256 2.256 0.8757 67.7876 2.7876 17-1 72.1 0.831 74.976 2.876 0.8118 75.3075 3.2075 3-1 73 0.87 75.105 2.105 0.8859 74.8452 1.8452 4-2b 66.3 0.6147 74.899 8.599 0.901 68.4206 2.1206 5-2b 64.2 0.8472 67.728 3.528 0.9117 66.2153 2.0153 5-4b 66 0.7989 70.420 4.420 0.872 68.7818 2.7818 7-1 61.9 0.8579 65.389 3.489 0.8731 65.0054 3.1054 8-3 70 0.8737 72.359 2.359 0.856 72.6951 2.6951 8-4 66.8 0.8701 69.548 2.748 0.8977 68.9555 2.1555 平均值 67.8 0.8258 71.377 3.577 0.8719 70.4146 2.6146 注:ID为样品号,Iobs为热退磁实验所得样品磁倾角,IRMz/IRMx(610~1200mT)为610~1200mT之间垂直层面方向和平行层面方向等温剩磁大小的比值,IRMz/IRMx(600°C以上)为600 °C以上垂直层面方向和平行层面方向等温剩磁大小的比值,IF为校正后磁倾角,ΔI为校正值 考虑到实验过程中样品的等温剩磁方向可能受天然剩磁的影响,以及载磁矿物主要为赤铁矿,所以施加外部直流场在200~1200mT之间及系统热退磁温度在600~680℃之间的IRMz/IRMx拟合线反映了赤铁矿的剩磁各向异性特征。
由于垂直于层面的IRMz值大部分在500mT之后略小于平行于层面的IRMx值(图 4-a、d),所以从磁场强度方面考虑,选取在500mT之后的610~1200mT区间的IRMz/IRMx拟合线的斜率作为磁倾角偏低校正因子,其大小为0.8258,对应的沉积压实为18%。另外,从热退磁的方面考虑,选取600~680℃区间的IRMz/IRMx热退磁结果拟合线的斜率作为磁倾角偏低校正因子,其大小为0.8719,对应的沉积压实为13%。利用公式IRMz/ IRMx=tan (Iobs)/tan (IF)进行校正后得到莲沱组磁倾角分别为71.4°和70.4°,两者的磁倾角值差别不大。
![]() 图 4 45°方向加场后平行于层面方向(IRMx)和垂直于层面方向(IRMz)等温剩磁获得曲线图(a, d),IRMz/IRMx关系图(b, e)和IRMz/IRMx的热退磁结果(c, f)Figure 4. Plots of IRMx (parallel to bedding) and IRMz (perpendicular to bedding) acquisitions produced by applying magnetic field at 45° to bedding as function of increasing field (a, d), plots of IRMZ/IRMX(b, e), the thermal demagnetization results of IRMZ/IRMX(c, f)
图 4 45°方向加场后平行于层面方向(IRMx)和垂直于层面方向(IRMz)等温剩磁获得曲线图(a, d),IRMz/IRMx关系图(b, e)和IRMz/IRMx的热退磁结果(c, f)Figure 4. Plots of IRMx (parallel to bedding) and IRMz (perpendicular to bedding) acquisitions produced by applying magnetic field at 45° to bedding as function of increasing field (a, d), plots of IRMZ/IRMX(b, e), the thermal demagnetization results of IRMZ/IRMX(c, f)3.3 岩石磁学实验结果
为了排除样品在加热过程中可能存在的磁性矿物的变化,对几个代表性样品进行了磁化率随温度变化实验(K-T,图 5)。结果表明,部分样品在加热和冷却过程中样品磁化率明显不同(图 5,TLS11),可能是因为样品在加热过程中生成了一部分磁铁矿。但580~680℃之间的加热曲线与冷却曲线一致,表明加热过程中磁性矿物的变化并未影响到样品中赤铁矿的剩磁变化(图 5,TLS11),因此,不影响磁倾角偏低实验的结果。另一部分样品的K-T曲线显示,在加热与冷却过程中,样品的磁化率没有明显的差异,因此样品中不存在明显的磁性矿物的改变(图 5,TLS4)。
由于加热过程并未影响到高温分量载磁性矿物赤铁矿,再考虑到赤铁矿较大的矫顽力,因此,选用600~680℃区间的IRMz/IRMx值作为磁倾角偏低校正因子,利用公式IRMz/IRMx=tan (Iobs)/tan(IF)计算得到校正后的莲沱组磁倾角大小为70.4°,与热退磁实验所得莲沱组磁倾角67.8°比较,莲沱组的磁倾角偏低大小为2.6°。
4. 磁倾角偏低对莲沱组古纬度及古地磁极的影响
利用本研究得到的莲沱组磁倾角偏低校正因子,对Jing等[29]所得高温分量进行磁倾角偏低校正,利用校正后的高温分量求得的三峡地区莲沱组沉积古纬度为47.7°±5.1°,比校正前的43.7°±4.8°向高纬度地区运动了3.9°±6°。
校正后古地磁极(LT-corr)为14.7°N, 153.9°E, dp/dm=4.9/6.0,与未校正的莲沱组古地磁极(LT:12.7°N,157.4°E,dp/dm=4.5/5.8)相比更偏西北。虽然校正前后,莲沱组古地磁极在统计分析上不能显著区分,但校正后的莲沱组古地磁极与现有华南南沱组古地磁极(Nantuo)[38]明显不同(图 6)。
5. 讨论
由于Evans等[39]得到的莲沱组古地磁极与南沱组古地磁极重合,使得一些学者认为莲沱组古地磁结果可能比以前认为的更年轻[40],或是南沱期重磁化的结果。然而,Jing等[29]对宜昌莲沱组的古地磁研究表明,莲沱组中下部到顶部至少存在5个正负极性时,因此现有的莲沱组古地磁结果应该不是重磁化的结果。另外,Jing等[29]通过总结前人在三峡地区对莲沱组大量的定年结果[41-45],认为现有华南莲沱组古地磁极年龄应在720Ma左右,比之前认为的750Ma年轻,但仍老于635Ma的南沱组古地磁结果。
Jing等[29]得到的莲沱组古地磁极与南沱组古地磁极相差不大。Yang等[46]认为,莲沱组采样区可能发生过局部构造旋转作用;Zhang等[38]则认为,没有证据表明莲沱组采样区发生过局部旋转。
排除以上各方面的影响因素,笔者认为,造成莲沱组与南沱组古地磁极相似的原因应该与莲沱组岩石受压实作用影响、发生微弱的磁倾角偏低现象有关。由于目前未对南沱组取得高温分量的古地磁样品进行磁倾角偏低实验,两者真实的差别还不能确定,需要进一步研究。
经磁倾角偏低校正后的华南板块在720Ma时应位于中纬度地区(图 6)。这一时期扬子地块多处发育冰碛岩沉积,从该时期华南板块上发育的冰碛岩分布看[40],当时整个地球应处于较寒冷的气候阶段。但由于这一时期华南板块位于中纬度地区,对于地球这一时期是否处于“雪球地球”的环境,仅从莲沱组的古地磁结果不能做出明确的判定。
为此,笔者重建了华南板块及与华南关系较紧密的澳大利亚-东南极板块720Ma的古地理位置(图 6)。图 6中,将莲沱组古地磁极通过欧拉极(34.4°N、100°E,98.6°)旋转到地理北极。MDS、YF及EF分别为澳大利亚755Ma,640Ma和635Ma古地磁极[22, 47-48],位于同一大圆弧上(虚线),利用内插法求出其720Ma的古地磁极位置,通过欧拉极(-0.4°N、53.7°E,44.1°)旋转使其与莲沱组古地磁极重合。通过这一古地理重建,可以清楚地看到,这一时期有大量冰川从中纬度地区一直延续到赤道地区。这一证据直接证明,当时地球处于“雪球地球”的环境。
6. 结论
对华南三峡地区莲沱组的等温剩磁各向异性研究表明,通过磁倾角偏低校正后的莲沱组古地磁极与南沱组古地磁极存在明显差别,这表明造成莲沱组与南沱组古地磁极相似的一个重要原因是地层压实引起的磁倾角偏低。利用720Ma古地磁数据对华南和澳大利亚进行古地理重建,并对比这一时期冰碛岩的分布,结果表明,当时地球确实处于“雪球地球”的环境中。
致谢: 野外工作和室内工作中得到成都地质调查中心张林奎、黄勇高级工程师及曹华文博士的大力支持,再此一并表示诚挚的感谢。 -
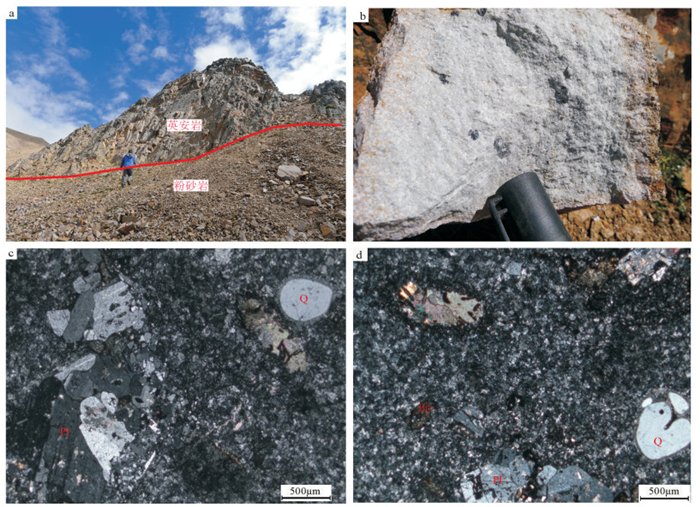
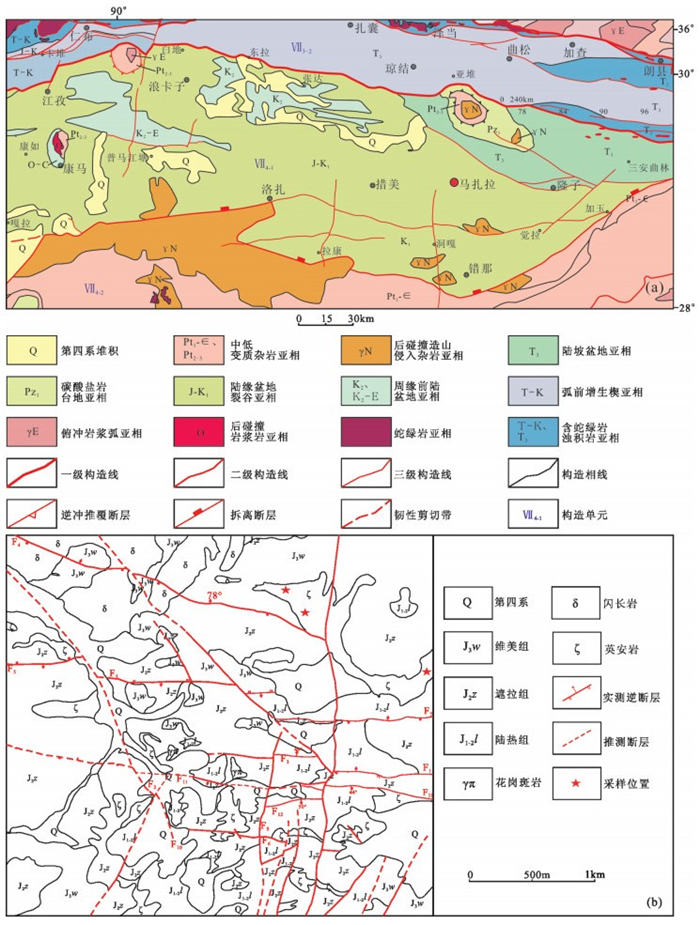
图 1 西藏措美马扎拉矿床大地构造位置(a,据参考文献[17]修改)和马扎拉矿区地质图及采样位置(b)
Figure 1. Tectonic location(a)and geological map (b) of the Mazhala deposit, southern Tibet
表 1 马扎拉矿区英安岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb分析结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb data for dacite in the Mazhala deposit
样品号 Th/10-6 U/10-6 Pb/10-6 Th/U 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 238U/232Th 206Pb/238U
年龄/Ma1σ 207Pb/235U
年龄/Ma1σ 207Pb/206Pb
年龄/Ma1σ MZL01-01 77.53 123.54 3.09 0.63 0.02174 0.00041 0.1458 0.0168 0.04862 0.00567 1.59 139 3 138 15 130 221 MZL01-02 73.76 98.69 2.59 0.75 0.02200 0.00051 0.1480 0.0219 0.04878 0.00727 1.34 140 3 140 19 137 264 MZL01-03 159.44 187.46 4.91 0.85 0.02184 0.00040 0.1468 0.0133 0.04875 0.00448 1.16 139 3 139 12 136 169 MZL01-04 63.11 115.69 2.82 0.55 0.02168 0.00045 0.1463 0.0186 0.04892 0.00628 1.83 138 3 139 17 144 241 MZL01-05 66.2 155.52 3.72 0.43 0.02182 0.00042 0.1468 0.0192 0.04880 0.00641 2.35 139 3 139 17 138 245 MZL01-06 78.47 115.02 2.89 0.68 0.02138 0.00045 0.1437 0.0181 0.04872 0.00619 1.47 136 3 136 16 134 237 MZL01-07 104.68 116.91 3.06 0.90 0.02151 0.00049 0.1446 0.0274 0.04874 0.00930 1.12 137 3 137 24 135 314 MZL01-08 81.28 126.9 3.19 0.64 0.02178 0.00048 0.1464 0.0212 0.04873 0.00711 1.56 139 3 139 19 135 260 MZL01-09 65.81 140.41 3.37 0.47 0.02168 0.00049 0.1459 0.0189 0.04881 0.00639 2.13 138 3 138 17 139 242 MZL01-10 55.38 154.73 3.52 0.36 0.02141 0.00046 0.1439 0.0200 0.04874 0.00683 2.79 137 3 137 18 135 254 MZL01-11 84.5 232.78 5.33 0.36 0.02162 0.00035 0.1453 0.0086 0.04872 0.00294 2.75 138 2 138 8 134 104 MZL01-12 75.04 128.24 3.17 0.59 0.02203 0.00043 0.1491 0.0184 0.04909 0.00610 1.71 140 3 141 16 152 238 MZL01-13 55.47 78.7 2.02 0.70 0.02145 0.00058 0.1446 0.0222 0.04888 0.00759 1.42 137 4 137 20 142 267 表 2 马扎拉矿区英安岩主量元素分析数据及相关系数
Table 2 Major element composition and parameters for the dacite in the Mazhala deposit
编号 MZL 02 MZL 03 MZL 04 MZL 05 MZL 06 MZL 07 MZL 08 SiO2 71.84 70.04 66.86 71.55 71.64 69.48 67.84 Al2O3 12.2 12.89 12.71 12.37 12.56 12.84 13.76 Fe2O3 1.22 1.78 2.17 3.16 1.09 1.04 0.99 FeO 2.93 2.88 2.79 0.57 3.13 2.68 3.94 CaO 2.18 2.23 3.98 2.71 1.96 3.21 2.37 MgO 0.58 0.68 0.66 0.5 0.64 0.58 0.94 K2O 1.58 1.48 1.86 1.79 1.56 2.12 2.5 Na2O 2.85 3.12 2.36 2.51 2.88 2.06 1.29 TiO2 0.76 0.81 0.79 0.78 0.74 0.8 0.86 P2O5 0.28 0.26 0.28 0.29 0.28 0.29 0.32 MnO 0.044 0.064 0.1 0.061 0.054 0.06 0.047 烧失量 3.34 3.38 5.05 3.55 2.96 4.44 4.61 总量 99.80 99.61 99.61 99.84 99.49 99.6 99.47 Q 44.59 41.55 38.37 45.69 44.4 43.25 45.2 An 9.32 9.73 18.95 12.01 8.18 14.74 10.19 Ab 25 27.43 21.12 22.09 25.24 18.32 11.51 Or 9.68 9.09 11.62 11 9.55 13.17 15.58 C 2.6 2.83 0.26 2.15 3.36 2.12 5.68 Hy 4.81 4.46 4.08 2.3 5.51 4.52 7.83 Tl 1.5 1.6 1.59 1.54 1.46 1.6 1.72 Mt 1.83 2.68 3.33 2.51 1.64 1.58 1.51 Ap 0.67 0.63 0.69 0.7 0.67 0.71 0.78 TFeO 4.03 4.48 4.74 3.41 4.11 3.62 4.83 Mg# 20.43 21.29 19.88 20.70 21.72 22.24 25.75 AR 1.89 1.87 1.68 1.8 1.88 1.69 1.38 DI 79.27 78.07 71.11 78.78 79.19 74.74 72.29 A/CNK 1.18 1.20 0.97 1.13 1.26 1.11 1.51 A/NK 1.91 1.91 2.16 2.04 1.95 2.26 2.85 注:Q—石英;An—钙长石;Ab—钠长石;Or—钾长石;C—刚玉;Hy—紫苏辉石;Tl—钛铁矿;Mt—磁铁矿;Ap—磷灰石;TFeO=FeO+0.8998 × Fe2O3;Mg#=molar MgO/(MgO+TFeO);A/CNK=n(Al2O3)/[n(CaO)+n(Na2O)+n(K2O)];A/NK=n (Al2O3)/[n(Na2O)+n(K2O)];AR—莱特碱度率;DI—分异系数;主量元素含量单位为% 表 3 马扎拉矿区英安岩微量及稀土元素分析数据及相关参数
Table 3 Trace and rare earth element composition and parameters for dacite in the Mazhala deposit
编号 MZL02 MZL03 MZL04 MZL05 MZL06 MZL07 MZL08 La 57.9 58.5 76.4 74.8 57.3 74.6 77.7 Ce 141 148 156 164 140 168 168 Pr 13.6 12.4 18.2 17 12.5 17.1 18.6 Nd 49.7 44 67.1 62.2 45.2 62.7 69 Sm 9.79 8.05 13.5 12.6 8.54 12.2 14.1 Eu 1.29 1.02 1.92 1.71 1.1 1.72 1.83 Gd 8.43 7.49 10.3 10.1 7.34 9.72 10.7 Tb 1.12 0.89 1.53 1.41 0.95 1.34 1.61 Dy 5.02 3.8 7.61 6.66 4.35 6.14 7.66 Ho 0.99 0.74 1.56 1.3 0.86 1.2 1.5 Er 2.73 2.08 4.4 3.6 2.36 3.24 4.02 Tm 0.47 0.36 0.78 0.62 0.41 0.56 0.68 Yb 2.9 2.21 4.73 3.76 2.5 3.48 4.1 Y 29.2 21.1 42.8 38.2 23.7 35.6 40.2 Lu 0.39 0.3 0.61 0.49 0.33 0.47 0.54 Ba 215 204 258 259 193 340 485 Sc 6.9 6.42 11.1 8.72 6.58 8.23 9.96 V 42.5 43.5 41.5 39.7 41.4 45.2 48.5 Cr 18.4 19.5 15.4 17.8 16.8 19.3 20.7 Co 7.88 8.06 7.57 6.54 7.41 7.66 7.17 Ni 10.8 9.31 9.23 8.15 9.35 8.53 11.1 Ga 24.4 24.9 25.8 23.2 23.1 24.9 27.4 Rb 73.3 73.7 80.3 78.9 76.6 88.9 99.1 Sr 70.4 65.9 134 90.9 53.3 92.3 122 U 3.85 4.11 3.98 3.96 3.93 4.52 4.45 Th 28 27.5 34.8 33 27.9 34.2 36.9 Nb 12.2 12.6 22.5 2.83 16 5.8 10.5 Ta 0.15 0.16 1.85 0.081 0.39 0.2 0.45 Zr 228 241 220 202 208 250 265 Hf 6.08 6.43 6.25 5.43 5.76 6.78 7.17 Cs 22.5 26.8 20 23.2 23.9 40.6 8.09 ∑REE 295.33 289.84 364.64 360.25 283.74 362.47 380.04 LREE 273.28 271.97 333.12 332.31 264.64 336.32 349.23 HREE 22.05 17.87 31.52 27.94 19.10 26.15 30.81 LREE/HREE 12.39 15.22 10.57 11.89 13.86 12.86 11.33 (La/Yb)N 14.32 18.99 11.59 14.27 16.44 15.38 13.59 δEu 0.42 0.39 0.48 0.45 0.41 0.47 0.44 δCe 1.19 1.28 0.99 1.08 1.23 1.11 1.05 注:δEu=2×ω(Eu)N/[w(Sm)N+w(Gd)N];δCe=2×CeN/(LaN+PrN);微量、稀土元素含量单位为10-6 -
杜光树, 冯孝良, 陈福忠.西藏金矿地质[M].四川:西南交通大学出版社, 1993. 张建芳, 郑有业, 张阳刚, 等.西藏北喜马拉雅马扎拉金锑矿床地质特征及成矿作用[J].黄金, 2011, 1(32):20-24. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ201101008.htm 杨竹森, 侯增谦, 高伟, 等.藏南拆离系锑金成矿特征与成因模式[J].地质学报, 2006, 80(9):1377-1391. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200609013.htm 聂凤军, 胡朋, 江思宏, 等.藏南地区金和锑矿床(点)类型及其时空分布特征[J].地质学报, 2005, 79(3):373-385. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1577852124&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn 王军, 张均, 郑有业.西藏南部马扎拉金锑矿成矿规律初探[J].黄金科学技术, 2001, 9(3/4):5-11. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ2001Z1001.htm 王军, 张均.西藏南部马扎拉金锑矿成矿特征及找矿方向[J].黄金地质, 2001, 7(3):15-20. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJDZ200103002.htm 郑有业, 多吉, 马国桃, 等.藏南查拉普金矿床特征、发现及时代约束[J].地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 2007, 32(2):185-192. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200702004.htm 郑有业, 孙祥, 田立明, 等.北喜马拉雅东段锑多金属成矿作用、矿床类型与成矿时代[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2014, 38(1):108-118. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201401010.htm Garzanti E,Le Fort P,Sciunnach D.First report of lower Permian basalts in south Tibet:Tholeiitic magmatism during break-up and incipient opening of Neotethys[J].J Asian Earth Sci.,1999,17(4):533-546. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(99)00008-5 Garzanti E, Le Fort P, Sciunnach D.First report of lower Permian basalts in south Tibet:Tholeiitic magmatism during break-up and incipient opening of Neotethys[J].J Asian Earth Sci., 1999, 17(4):533-546. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(99)00008-5
朱弟成, 王立全, 潘桂棠, 等.藏南特提斯喜马拉雅带中段中侏罗统遮拉组OIB型玄武岩浆的识别及其意义[J].地质科技情报, 2004, 23(3):15-24. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200403004.htm 朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 等.藏南特提斯喜马拉雅带中段二叠纪-白垩纪的火山活动(Ⅰ):分布特点及其意义[J].地质通报, 2004, 23(7):645-654. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=200407118&journal_id=gbc 朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 等.特提斯喜马拉雅带中段桑秀组玄武岩的地球化学和岩石成因[J].地质通报, 2005, 34(1):7-19. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQHX200501001.htm 朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 等.特提斯喜马拉雅桑秀组英安岩锆石SHRIMP年龄及其意义[J].地质通报, 2005, 50(4):375-379. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KXTB20050400C.htm 钟华明, 童劲松, 夏军, 等.藏南羊卓雍错南部桑秀组火山岩的特征及构造环境[J].地质通报, 2005, 24(1):72-79. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20050112&journal_id=gbc 朱弟成, 夏瑛, 裘碧波, 等.为什么要提出西藏东南部早白垩世措美大火成岩省[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(11):3659-3670. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201311001.htm Zhu D C,Chung S L,Mo X X,et al.The 132 Ma Comei-Bunbury large igneous province:Remnants identified in present-day southeastern Tibet and southwestern Australia[J].Geology,2009,37(7):583-586. doi: 10.1130/G30001A.1 Zhu D C, Chung S L, Mo X X, et al.The 132 Ma Comei-Bunbury large igneous province:Remnants identified in present-day southeastern Tibet and southwestern Australia[J].Geology, 2009, 37(7):583-586. doi: 10.1130/G30001A.1
潘桂棠, 王立全, 张万平, 等.青藏高原及邻区大地构造图及说明书(1:1500000)[M].北京:地质出版社, 2013. Andersen T.Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J].Chemical Geology,2002,192(1/2):59-79. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2022859730&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Andersen T.Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J].Chemical Geology, 2002, 192(1/2):59-79. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2022859730&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Ludwig K R.User's Manual for Isoplot 3.00:A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J].Berkeley:Berkeley Geochronology Center,Special Publication,2003,4:1-70. https://books.google.com.pg/books/about/User_s_Manual_for_Isoplot_3_00.html?id=OutNAQAAIAAJ Ludwig K R.User's Manual for Isoplot 3.00:A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J].Berkeley:Berkeley Geochronology Center, Special Publication, 2003, 4:1-70. https://books.google.com.pg/books/about/User_s_Manual_for_Isoplot_3_00.html?id=OutNAQAAIAAJ
Hoskin P W O,Black L P.Metamorphic zircon formation by solid-state recrystallization of protolith igneous zircon[J].Journal of Metamorphic Geology,2000,18(4):423-439. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1521262137&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Hoskin P W O, Black L P.Metamorphic zircon formation by solid-state recrystallization of protolith igneous zircon[J].Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2000, 18(4):423-439. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1521262137&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Middlemost E A K.Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J].Earth-Science Reviews,1994,37(3/4):215-224. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2019034794&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Middlemost E A K.Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J].Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37(3/4):215-224. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2019034794&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Maniar P D,Piccoli P M.Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J].Geological Society of America Bulletin,1989,101(5):635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2 Maniar P D, Piccoli P M.Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J].Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5):635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
Le Maitre R W.Igneous rocks:a classification and glossary of terms[M].Cambridge University press,2002. Le Maitre R W.Igneous rocks:a classification and glossary of terms[M].Cambridge University press, 2002.
Wringht J B.A simple alkalinity ratio and its application to questions of non-orogenic granite genesis[J].Geological Magazine,1969,106(4):370-384. doi: 10.1017/S0016756800058222 Wringht J B.A simple alkalinity ratio and its application to questions of non-orogenic granite genesis[J].Geological Magazine, 1969, 106(4):370-384. doi: 10.1017/S0016756800058222
林彬, 唐菊兴, 郑文宝, 等.藏南扎西康矿区流纹岩的岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb测年和Hf同位素组成[J].地质论评, 2014, 60(2):178-189. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGKD201304001292.htm Sun S S,McDonough W F.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and processes[J].Geological Society,1989,42:313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19 Sun S S, McDonough W F.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and processes[J].Geological Society, 1989, 42:313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Molzahn M,Reisberg L,Worner G.Os,Sr,Nd,Pb,O isotope and trace element data from the Ferrar flood basalts,Antarctica:evidence for an enriched subcontinental lithospheric source[J].Earth Planet.Sci.Lett.,1996,144:529-546. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(96)00178-1 Molzahn M, Reisberg L, Worner G.Os, Sr, Nd, Pb, O isotope and trace element data from the Ferrar flood basalts, Antarctica:evidence for an enriched subcontinental lithospheric source[J].Earth Planet.Sci.Lett., 1996, 144:529-546. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(96)00178-1
孙赛军, 张丽鹏, 丁兴, 等.西藏那曲中酸性火山岩的锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素和地球化学特征及岩石成因[J].岩石学报, 2015, 31(7):2063-2077 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=755920307&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn 张德江, 郭福生, 周万蓬, 等.江西潭港流纹英安岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及地球化学特征[J].中国地质, 2014, 41(3):784-796. http://www.cnki.com.cn/article/cjfdtotal-dizi201403008.htm 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 邓晋福, 等.印度-亚洲大陆主碰撞过程的火山作用响应[J].地学前缘, 2003, 10(3):135-147. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/DXQY200303019.htm 余光明, 王成善.西藏特提斯沉积地质[M].北京:地质出版社, 2009:10-49. 王根厚, 梁定益, 刘文灿, 等.藏南海西期以来伸展运动及伸展作用[J].现代地质, 2000, 14(2):133-139. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ200002003.htm Zhu D C,Pan G T,Mo X X et al,.Petrogenesis of volcanic rocks in the Sangxiu Formation,central segment of Tethyan Himalaya:A probable example of plume-lithosphere interaction[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2007,29(2/3):320-335. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2022810466&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Zhu D C, Pan G T, Mo X X et al, .Petrogenesis of volcanic rocks in the Sangxiu Formation, central segment of Tethyan Himalaya:A probable example of plume-lithosphere interaction[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2007, 29(2/3):320-335. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2022810466&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
任冲, 刘顺, 朱立东, 等.藏南古堆地区中基性脉岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年、地球化学特征及构造意义[J].四川地质学报, 2014, 34(4):496-500. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/SCDB201404004.htm 任冲, 马飞宙, 朱振华, 等.藏南哲古基性岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J].中国地质, 2015, 42(4):881-890. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DIZI201504007.htm 童劲松, 刘俊, 钟华明, 等.藏南洛扎地区基性岩墙群锆石U-Pb定年、地球化学特征及构造意义[J].地质通报, 2007, 26(12):1654-1664. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=200701218&journal_id=gbc 裘碧波, 朱弟成, 夏瑛, 等.藏南措美残余大火成岩省的西延及意义[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(7):2207-2216. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201007022.htm 夏瑛, 朱弟成, 赵志丹, 等.藏东南措美大火成岩省中OIB型镁铁质岩的全岩地球化学和锆石Hf同位素[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(5):1588-1602. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201205023.htm




 下载:
下载: