Geochemical characteristics and LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age of the trachytic volcanic rocks in Zhushan area of Southern Qinling Mountains and their significance
-
摘要:
南秦岭竹山地区广泛分布的北西-南东向展布的基性岩-粗面岩带,主要赋存于志留纪地层中。竹山地区粗面质火山岩地球化学研究表明,该区粗面质火山岩全碱Na2O+K2O含量较高,为碱性岩系列;大离子亲石元素(Ba、Th、U)和高场强元素(Nb、Ta等)相对富集,Sr、Ti、Yb等元素相对亏损;稀土元素总量(ΣREE)较高,明显富集轻稀土元素,亏损重稀土元素;结合微量元素构造环境判别分析认为,该区粗面质火山岩形成于大陆裂谷环境。采用LA-ICP-MS方法测得该区粗面质火山碎屑岩中锆石的U-Pb年龄为430.6±2.7Ma,该年龄应代表粗面质火山岩主体的结晶年龄。研究结果表明,南秦岭竹山地区在早志留世发生了强烈的裂解活动,并形成一富硅质和炭质岩组合的深水盆地,该洋盆可能为南秦岭勉略洋向东的延伸。南秦岭竹山地区粗面质火山岩岩石化学及锆石U-Pb同位素定年研究,为了解南秦岭早古生代构造演化提供了重要依据。
Abstract:Basic rock-trachyte belts, trending in NW-SE direction, are widely distributed in Zhushan area of Southern Qinling Mountains, intruding in Silurian strata. Previous researchers conducted detailed studies focused on basic rocks. Compared with the ba-sic rocks, the research on trachytic volcanic rocks seems very insufficient, and hence accurate data forming chronologic data are espe-cially lacking. The dating of trachytic volcanic rocks from Zhushan area in Southern Qinling Mountains shows that the trachytic vol-canic rocks are alkaline series rocks with relatively high Na2O+K2O. Lithophile elements(Ba, Th, U)and high field strength elements (Nb, Ta)are relatively abundant, but the elements such as Sr, Ti and Yb are relatively poor. Rare earth elements(ΣREE, which are rich in light REE and deficient in heavy REE)are relatively high. Combined with the trace element characteristics, it is shown that the trachytic volcanic rocks were formed in a continental rifting environment. The crystallization of trachytic volcanic rocks took place at 430.6±2.7Ma, as shown by the LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of trachytic pyroclastic rocks in Zhushan area. The studies show that a strong cleavage activity occurred in the period of early Silurian and formed a deep water basin with rich siliceous and car-bonaceous rock combination in the Zhushan area of Southern Qinling Mountains. Combined with the discovery of ocean island ba-salts as well as island arc and oceanic basalts, the authors hold that this region might have developed a small finite ocean basin after Si-lurian, and the ocean basin was probably the eastward extension of the Mianlue Ocean in Southern Qinling Mountains. The study of the geochemical characteristics and zircon U-Pb age of the trachytic volcanic rocks provides an important basis for early Paleozoic tectonic evolution in Zhushan area of Southern Qinling Mountains.
-
横亘于中国中部的秦岭造山带经过了20多年的研究已经取得了丰硕的成果[1-6],但关于南秦岭造山带早古生代的构造演化历史还存有争议[7-12]。在南秦岭造山带的北大巴山地区,发育一套呈北西—南东向展布的基性岩-粗面岩带,该套岩系对揭示秦岭造山带早古生代构造演化具有重要意义。前人对该区的基性岩类进行了不同程度的岩石学、矿物学及地球化学研究,取得了丰富的成果[13-19]。与基性岩的研究程度相比,粗面质火山岩的研究明显不足,特别是缺少可靠的形成时代的年龄数据,前人大多利用与粗面质火山岩共生的地层中古生物化石,或上覆地层中的碎屑锆石年龄限定该套粗面岩的形成时代[20-21],这些年代学信息在一定程度上制约了对秦岭造山带构造演化历史的认识。湖北竹山、竹溪地区广泛发育该套基性岩-粗面岩组合,前人对其研究较少。本文在1∶5万区域地质填图的基础上,展开详细的岩石学、岩石地球化学和同位素年代学研究,以确定南秦岭竹山地区粗面质火山岩的性质与形成时代,并结合已有的研究成果,探讨南秦岭地区粗面质火山岩的大地构造意义。
1. 地质背景
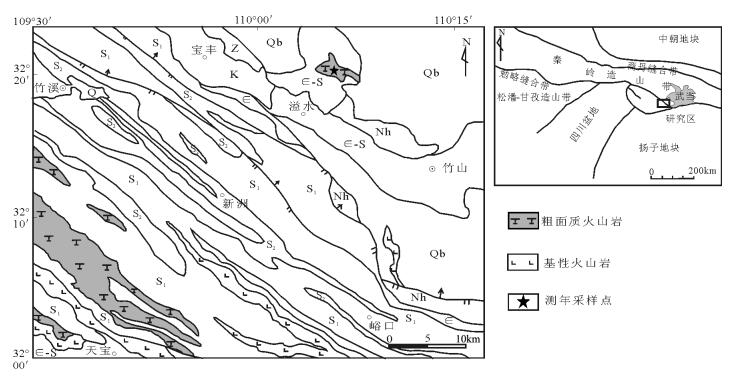
南秦岭大巴山基性岩-粗面岩带发育于陕西安康、紫阳、平利和镇坪,向东延伸至湖北竹溪、竹山等地,呈北西—南东向展布,与区域构造线方向一致。研究区位于北大巴山弧形构造带内(图 1),区内地层主要出露震旦纪—志留纪海相碎屑岩-碳酸盐岩,局部出露青白口纪中浅变质岩系(武当岩群)[22]。其中志留纪地层分布广泛,主要为一套碎屑岩系及碳酸盐岩,区域上划分为大贵坪组、梅子垭组和竹溪组。本文研究的粗面质火山岩赋存于大贵坪组和梅子垭组中,与基性侵入岩、基性火山岩及少量超基性侵入岩共生,总体呈北西向展布,延伸长度大于40km,宽度最大可达6km。受区域性主干断裂安康-竹山断裂和红椿坝-曾家坝断裂影响,研究区发育一系列北西—南东向断层,岩石不同程度发生褶皱和片理化,并显示多期剪切变形的构造特征。受区域变质作用影响,岩石普遍遭受低绿片岩相低级变质作用。
研究区粗面质火山岩主要分布于天宝一带,在溢水附近也有小面积出露(图 1)。区内粗面质火山碎屑岩与熔岩共同发育,以粗面质火山碎屑岩为主,粗面质熔岩(粗面岩)次之,见少量粗面质次火山岩(粗面斑岩)。本次工作对区内发育的粗面质火山碎屑岩、粗面岩和粗面斑岩分别采集了样品,进行了系统的岩石学、岩石地球化学分析,并对粗面质火山碎屑岩进行LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素定年。
2. 岩石学特征
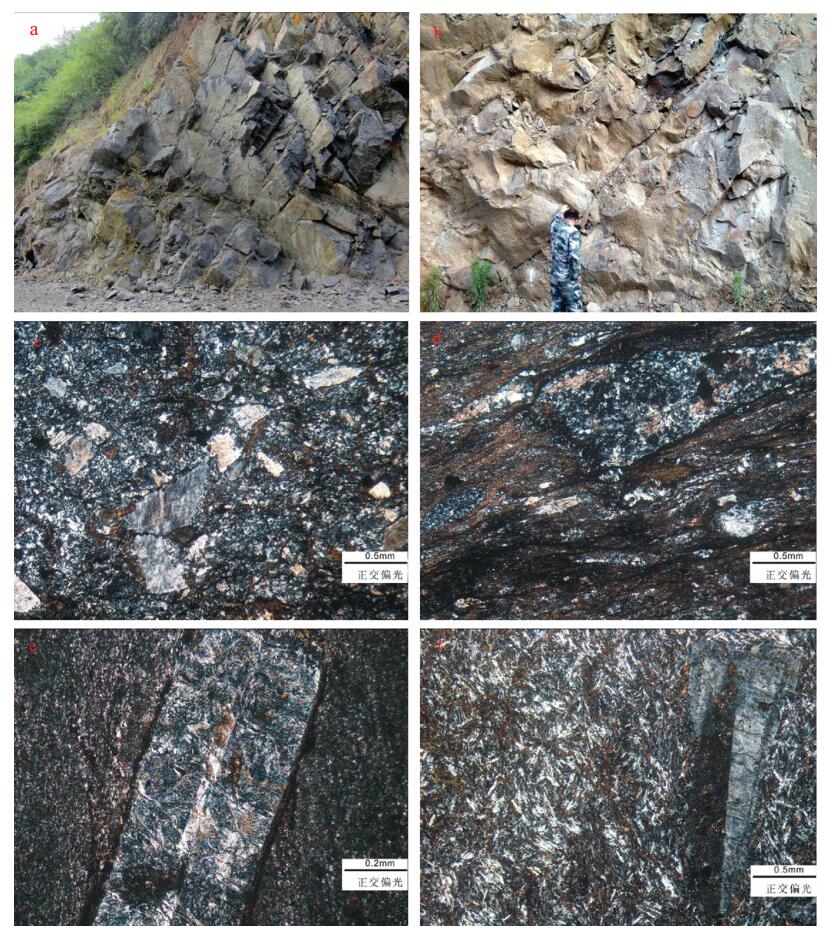
粗面质岩屑晶屑凝灰岩:野外露头上多呈深灰色-灰黑色,具变余凝灰质结构,块状构造(图版Ⅰ-a)。显微镜下观察,岩石由碎屑物(约15%)和胶结物(约85%)组成。碎屑物又分为岩屑和晶屑(图版Ⅰ-c),岩屑主要为凝灰质岩屑、粗面岩岩屑,以及少量基性岩和灰岩岩屑;晶屑主要为钾长石,见少量榍石、黄铁矿,钾长石以正长石为主,多呈次棱角状或半自形板状。碎屑物在岩石中往往呈带状或透镜状分布。胶结物由凝灰物质组成,粒度极细,在高倍显微镜下可见到条纹长石的晶粒及黑云母鳞片。
粗面岩:呈深灰色-灰黑色,具斑状结构,总体呈块状构造,部分见流动构造和枕状构造(图版Ⅰ-b、d),发育柱状节理;斑晶主要为钾长石(约95%)和黑云母(约5%)。钾长石多呈自形板状晶,粒径较粗大,0.3~3.5mm,且长轴方向大致相同,与岩石的流动构造相一致;钾长石以正长石为主,部分是条纹长石,可见卡氏双晶和条纹双晶。大部分样品基质为微晶结构,微晶矿物有微晶板条状钾长石、绢云母等,具弱粗面结构,部分发生绿泥石蚀变,少量白钛石、褐铁矿、磁铁矿化。粗面岩具块状和枕状构造,发育柱状节理,表明为水下溢流喷发环境。
粗面斑岩:呈灰黑色,具斑状结构(基质具粗面结构)(图版Ⅰ-e、f),块状构造。岩石主要由斑晶(约10%)和基质(约90%)组成;斑晶主要为钾长石,自形程度高,以正长石为主,见卡式双晶,斑晶较粗,可达2mm;基质具典型的粗面结构,细长的钾长石板条呈木排状分布,其间分布有鳞片状的黑云母或他形微粒状方解石。个别岩石中见石英脉,方解石脉穿切。
3. 岩石地球化学特征
本次对区内发育的粗面质火山碎屑岩、粗面岩和粗面斑岩分别采集了样品(表 1)。其中粗面质火山碎屑岩样品5件(样品编号101-33YQ、101-35YQ、203-20YQ、203-37YQ、205-3YQ),粗面岩3件(样品编号205-8YQ、205-24YQ、306-19YQ),粗面斑岩2件(样品编号305-16YQ、305-92YQ)。
表 1 竹山地区粗面质火山岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果Table 1. Major, trace and rare earth element data for trachytic pyroclastic rocks in Zhushan area样号 101-33YQ 101-35YQ 203-20YQ 203-37YQ 205-3YQ 205-8YQ 205-24YQ 305-16YQ 305-92YQ 306-19YQ 岩性 粗面质 粗面质岩屑 粗面质晶屑 粗面质晶屑 粗面质 粗面岩 粗面岩 粗面斑岩 粗面斑岩 粗面岩 凝灰岩 晶屑凝灰岩 凝灰岩 凝灰岩 凝灰岩 SiO2 63.11 61.67 58.84 66.29 54.16 59.80 64.48 58.82 59.29 64.09 TiO2 0.33 1.61 2.14 1.13 1.06 1.16 1.09 1.72 1.19 1.04 Al2O3 :0.66 14.95 14.12 14.12 19.85 17.60 15.35 15.26 18.49 15.96 Fe2O3 1.79 1.41 3.24 1.42 1.58 1.24 0.94 1.67 1.49 1.91 FeO 0.33 4.65 4.78 3.27 3.05 2.75 3.53 5.03 2.73 2.37 MnO 0.22 0.14 0.21 0.14 0.35 0.32 0.28 0.27 0.31 0.24 MgO 0.21 1.82 2.64 1.70 2.67 2.06 1.00 1.85 1.27 0.90 CaO 0.27 2.63 2.44 1.12 2.52 1.55 0.93 2.35 2.02 0.42 Na2O 8.87 3.25 4.64 4.58 4.47 6.09 7.34 5.78 6.74 5.68 K2O 1.85 4.24 3.96 4.03 6.70 5.20 3.43 4.72 4.58 5.91 P2O3 0.06 0.29 0.31 0.18 0.10 0.23 0.16 0.46 0.17 0.18 烧失 1.40 2.43 1.62 1.45 2.89 1.46 0.99 1.27 0.96 0.61 总量 99.10 99.09 98.94 99.43 99.40 99.46 99.52 99.20 99.24 99.31 La 21.58 92.52 110 124 234.6 170.0 201.4 122.6 218.5 163.2 Ce 45.53 183.3 216 224 607.01 293.76 360.96 246.77 414.43 286.27 Pr 5.48 22.57 23.46 24.28 70.57 34.00 43.53 30.52 48.33 33.58 Nd 17.46 80.79 82.43 84.52 199.31 109.92 139.27 105.63 156.56 111.63 Sm 3.97 14.43 15.39 15.50 31.25 18.49 24.68 19.36 25.98 18.68 Eu 1.28 3.21 3.74 3.85 3.97 4.84 5.03 5.48 6.61 4.10 Gd 3.81 15.25 13.46 13.68 23.92 14.37 19.34 14.52 19.69 14.13 Tb 0.67 2.22 2.33 2.37 3.80 2.21 3.00 2.29 2.94 2.13 Dy 3.98 11.42 11.67 12.04 21.50 11.26 15.49 11.80 14.78 11.29 Ho 0.86 2.17 2.26 2.33 3.94 1.97 2.72 2.00 2.55 1.98 Er 2.63 5.20 6.40 6.61 11.26 5.14 7.13 5.11 6.53 5.15 Tm 0.41 0.73 0.95 0.98 1.83 0.77 1.08 0.75 0.99 0.75 Yb 2.65 4.32 5.32 5.71 11.42 4.60 6.43 4.42 5.73 4.27 Lu 0.42 0.53 0.54 0.64 1.70 0.69 0.96 0.65 0.85 0.64 Y 21.57 52.72 60.62 61.06 116.80 55.75 75.27 55.52 66.80 54.22 1REE 110.73 438.66 494.55 520.51 1226.09 672.00 831.01 571.89 924.46 657.80 LREE 95.29 396.81 451.62 476.15 1146.71 631.01 774.87 530.36 870.41 617.45 HREE 15.43 41.85 42.93 44.36 79.39 41.00 56.14 41.53 54.05 40.34 LREE/HREE 6.18 9.48 10.52 10.73 14.44 15.39 13.80 12.77 16.11 15.30 (La/Yb)N 5.50 14.48 14.02 14.67 13.88 25.00 21.15 18.75 25.78 25.82 Rb 13.60 132.40 127.65 101.43 185.20 77.93 56.29 61.70 42.26 75.57 Ba 8155 1549 1063 268 268 1304 272 2062 1917 143 Th 15.53 16.66 16.19 10.48 57.41 13.57 15.49 11.72 17.49 7.11 U 8.61 2.66 2.40 2.40 16.38 2.63 2.19 2.20 3.35 1.35 Ta 19.36 7.43 7.94 5.52 35.52 13.47 16.29 10.15 15.77 10.35 Nb 613.6 147.8 138 103 638.4 237.2 296.5 177.5 273.7 190.4 Sr 84.54 140.2 244 113 353.4 176.2 123.4 272.6 2250.7 49.7 Zr 1541 659 697 621 2503 830 1388 806 1014 780 Hf 24.66 17.91 16.90 15.37 53.51 16.83 26.68 18.14 20.57 15.61 注:主量元素含量单位为%;微量和稀土元素含量为10-6;数据由国土资源部武汉矿产资源监督检测中心完成 3.1 主量元素特征
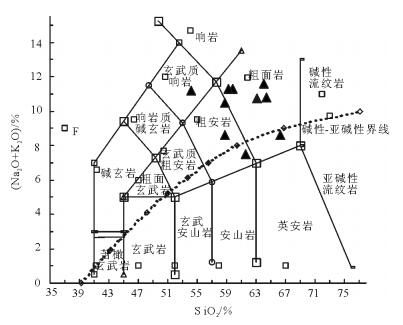
竹山地区粗面质火山岩样品主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果见表 1。岩石中SiO2含量为54.16%~ 66.29%,平均值为61.06%;TiO2含量普遍较低,介于0.33%~2.14%之间,平均值为1.25%,显示出低钛的特征;Al2O3含量较高,变化于14.12%~20.66%之间,平均值为16.64%,反映长石含量较高;TFeO介于1.49%~ 7.70%之间;CaO含量在0.27%~2.36%之间;MgO含量在0.21%~2.67%之间,平均值为1.61%;Na2O含量为3.25%~8.87%,平均值为5.74%;K2O含量在1.85%~ 6.70%之间,平均值为4.46%。各主量元素含量与世界上代表性粗面岩平均成分值接近[23];全碱含量较高,平均值为5.10%。在SiO2-(Na2O+K2O) (TAS)图解(图 2)中,研究区粗面质火山岩类主要落于碱性系列粗面岩-粗面安山岩,个别样品点落于亚碱性系列,可能是岩浆侵位结晶过程中混入地壳物质所致。
在Harker图解(图 3)中,随SiO2增加,各氧化物变化的相关性不好,但存在弱的变化趋势。随SiO2增加,MgO、TFeO显示下降的趋势;TiO2对SiO2的变化不明显;CaO、MnO与SiO2呈负相关性;Al2O3和P2O5也表现出与SiO2的负相关性;K2O、Na2O表现出与SiO2的正相关性。这些特征表明,岩浆分异在粗面质岩浆演化过程中起主导作用。
3.2 稀土元素特征
竹山地区粗面质火山岩稀土元素总量(∑REE)较高,变化范围为110.73×10-6~1226.09×10-6,平均值为644.77×10-6,其中LREE平均含量为599.07×10-6,HREE平均含量为45.70×10-6;LREE/HREE值为6.18~16.11,(La/Yb)N为5.50~25.82。数据结果表明,该区粗面质火山岩明显富集轻稀土元素,亏损重稀土元素;δEu为0.44~1.00,平均为0.80。在球粒陨石标准化配分模式(图 4-a)上,10个样品的稀土元素配分模式均呈轻稀土元素富集的平滑右斜模式,除1个样品外(101-33YQ),其余9个样品的配分模式基本一致,且均出现负Eu异常,这种稀土元素配分模式与造山带内大陆裂谷双峰式火山特征相似[24]。101-33YQ样品配分模式与其他样品略微不同,其主要原因是该样品采自构造带中,强烈的变质变形对其影响较大。
3.3 微量元素特征
在原始地幔标准化的微量元素蛛网图(图 4-b)上,样品的不相容元素分布趋势基本一致,均表现为大离子亲石元素(Ba、Th、U)和高场强元素(Nb、Ta等)相对富集,而Sr、Ti、Yb等元素相对亏损,与前人在大巴山地区所做的板内玄武岩微量元素蛛网图形态一致[25-26],暗示二者具有同源性;二者微量元素蛛网图形态有所不同的是,粗面质火山岩类明显存在Sr、Ti元素的低谷,可能是钛铁矿的分离结晶及后期热液活动的影响所致。
4. 锆石U-Pb年龄
4.1 测试方法
本次工作采集质量3.5kg的粗面质火山碎屑岩样品,采用常规方法粉碎,将粉末淘洗,进行电磁选和重液分选,最后在双目镜下挑选锆石晶体。选择晶形完好的颗粒制成样靶,用于可见光和阴极发光(CL)照相及U-Pb同位素分析。锆石阴极发光(CL)照相在中国地质大学(武汉)地质过程与矿产国家重点实验室完成,锆石U-Pb同位素分析在激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(LA-ICP-MS)上完成。激光剥蚀系统配有193nmAr-excimer激光器Geolas 200M,激光剥蚀斑束直径为32μm,剥蚀深度为20~ 40μm,采用标准锆石91500作为外标,使用的LAICP-MS为Agilent7500a型,仪器参数和分析流程见参考文献[27]。同位素比值和元素含量数据处理采用Glitter (4.0版)软件,采用Anderson[28]编制的软件对测试数据进行普通铅校正,采用Isoplot (3.23)程序进行加权平均计算和U-Pb谐和图绘制[29]。
4.2 测试结果
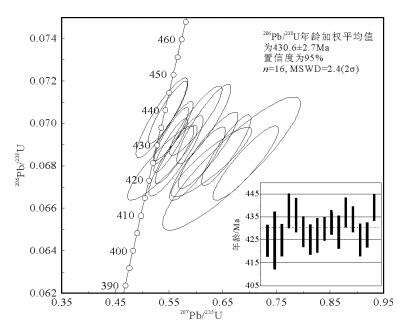
样品中的锆石大多数阴极发光图像(图 5)具有较好的条带结构,部分具有岩浆韵律环带,属于岩浆结晶产物。共测得22个数据(表 2;图 5)。从数据表可看出,锆石的206Pb/238U年龄介于416.3±7.8~ 445.3±5.4Ma之间,其中有16个点的年龄值集中在424.7±7.0~439.3±5.8Ma,即420~440Ma范围内,有2个点的年龄小于420Ma (分析号205-3、205-21),还有4个点年龄大于440Ma(分析号205-2、205-4、205-7、205-18)。考虑到仪器测试和数据分析时的误差,采用16组优势年龄计算年龄加权平均值,获得206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为430.6±2.7Ma (MSWD=2.4,置信度为95%)(图 6),该年龄代表研究区粗面质火山岩主体的结晶年龄。
表 2 竹山地区粗面质火山碎屑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果Table 2. LA-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb isotope composition of zircons in trachytic volcanic rocks of Zhushan area分析号 元素含量/10-6 232Th/238U 同位素比值 同位素年龄/Ma Total Pb 232Th 238U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 205-1 81.5 381 178 2.14 0.0663 0.0041 0.603 0.034 0.0681 0.0011 816.7 130 479.2 21.8 424.7 7.0 205-2 56.8 261 157 1.66 0.0626 0.0037 0.604 0.034 0.0708 0.0011 694.5 130 479.7 21.3 440.7 6.6 205-3 89.4 418 235 1.78 0.0746 0.0049 0.684 0.043 0.0667 0.0013 1057.4 130 529.4 26.2 416.3 7.8 205-4 109.7 544 252 2.15 0.0618 0.0032 0.593 0.030 0.0707 0.0010 733.3 110 473.0 18.9 440.4 6.0 205-5 28.9 127 102 1.24 0.0710 0.0092 0.666 0.085 0.0681 0.0021 966.7 270 518.5 51.7 424.8 12.5 205-6 57.0 232 170 1.36 0.0761 0.0048 0.693 0.040 0.0681 0.0012 1098.2 130 534.6 24.2 424.9 7.0 205-7 72.9 328 193 1.70 0.0595 0.0044 0.576 0.044 0.0711 0.0013 587.1 160 461.9 28.4 442.5 7.8 205-8 148.5 741 337 2.20 0.0553 0.0033 0.537 0.032 0.0703 0.0012 433.4 140 436.2 21.0 437.8 7.5 205-9 51.4 231 144 1.61 0.0659 0.0039 0.615 0.033 0.0700 0.0012 803.4 130 486.6 21.0 436.0 7.5 205-10 155.8 693 317 2.18 0.0701 0.0032 0.657 0.031 0.0687 0.0011 931.5 93 512.7 18.7 428.6 6.6 205-11 112.2 542 265 2.04 0.0656 0.0044 0.629 0.050 0.0682 0.0011 794.4 140 495.5 30.9 425.2 6.5 205-12 52.7 246 142 1.74 0.0618 0.0042 0.563 0.033 0.0685 0.0013 664.8 140 453.5 21.7 427.0 7.5 205-13 152.8 749 408 1.84 0.0582 0.0022 0.553 0.021 0.0690 0.0008 538.9 81 446.9 13.5 429.9 5.0 205-14 183.0 893 400 2.23 0.0584 0.0023 0.554 0.021 0.0694 0.0009 546.3 87 447.5 14.0 432.7 5.3 205-15 87.6 406 205 1.98 0.0668 0.0042 0.623 0.037 0.0687 0.0012 831.5 140 491.6 23.1 428.5 7.2 205-16 96.7 449 225 2.00 0.0615 0.0032 0.600 0.032 0.0701 0.0011 657.4 110 477.2 20.5 437.0 6.5 205-17 123.9 565 322 1.76 0.0588 0.0027 0.558 0.025 0.0696 0.0009 561.1 100 450.2 16.0 434.0 5.5 205-18 224.1 998 675 1.48 0.0597 0.0019 0.587 0.019 0.0715 0.0009 590.8 70 469.2 12.4 445.3 5.4 205-19 72.8 339 174 1.95 0.0579 0.0046 0.538 0.043 0.0682 0.0012 527.8 180 437.0 28.3 425.0 7.1 205-20 167.7 842 387 2.18 0.0598 0.0025 0.560 0.024 0.0685 0.0009 594.5 93 451.8 15.6 427.2 5.4 205-21 142.9 758 304 2.49 0.0588 0.0047 0.547 0.048 0.0668 0.0014 566.7 180 443.3 31.5 416.8 8.2 205-22 70.2 243 388 0.63 0.0569 0.0026 0.548 0.024 0.0705 0.0010 487.1 100 443.7 16.0 439.3 5.8 注:数据由中国地质大学(武汉)地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室完成 5. 构造环境分析及地质意义
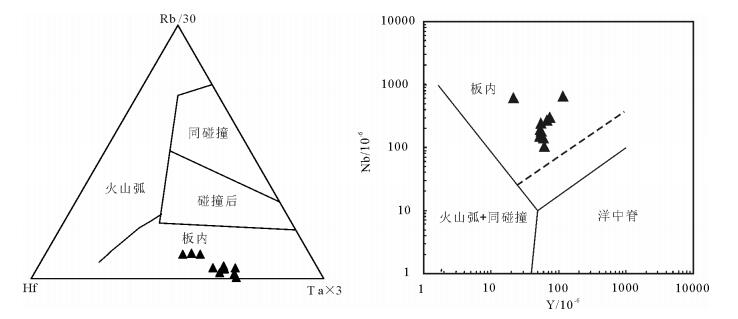
微量元素在溶液中强烈的不活泼性,使其组合能反映岩石形成的构造环境[30]。这些元素主要为Zr、Hf、Nb、Ta、Rb、Y、Yb等。因此,本次选择能够区分火山弧、同碰撞、碰撞晚期-碰撞后、板内花岗岩类的Rb/30-Hf-Ta×3图解和能够区分板内、火山弧+同碰撞、洋中脊花岗岩类的Y-Nb图解对其形成环境进行判断。在Rb/30-Hf-Ta×3图解和Y-Nb图解(图 7)中,所有样品点均投在板内构造环境。
秦岭造山带大巴山地区发育一套基性岩-粗面岩组合,前人对其做过较详细的研究,并提出该基性岩-粗面岩组合具有双峰式火山岩特征[20]。从本文研究的粗面质火山岩地球化学特征看,主量元素显示全碱含量较高,为碱性岩系列;微量元素蛛网图形态特征与前人研究该区的基性岩一致,暗示二者具有同源性;稀土元素配分模式与造山带内大陆裂谷双峰式火山岩特征相似。结合微量元素构造环境判别分析认为,该区粗面质火山岩形成于大陆裂谷,与前人研究的基性岩形成于大陆裂谷环境结论一致[25-26, 31]。
黄月华等[20]在陕西蒿坪地区的研究指出,粗面岩与晚奥陶世—早志留世地层共生,结合辉绿岩成岩年龄认为,该套粗面岩形成于晚奥陶世—早志留世之间;王刚等[21]通过对陕西岚皋地区粗面质火山碎屑岩上覆地层中碎屑锆石U-Pb定年及古生物化石证据推测,该套粗面质火山岩形成于早泥盆世。本次研究获得了粗面质火山碎屑岩锆石U-Pb年龄为430.6±2.7Ma,该年龄为粗面质火山岩成岩的直接年龄数据,与前人获得的大巴山地区基性岩年龄431.1±3.0Ma[20]、431.0±3.2Ma[26]、433.3±4.1Ma[32]基本一致。结合该区粗面质火山岩赋存于早志留世地层分析,笔者认为研究区粗面质火山岩的形成时代应为早志留世。
前人研究表明,南秦岭早古生代时期为扬子大陆北缘被动大陆边缘[33]。本文通过对粗面质火山岩岩石化学及锆石U-Pb同位素定年研究表明,南秦岭竹山地区早志留世被动大陆边缘发生过强烈的裂解活动。结合本次1∶5万填图工作认为,该裂解作用在该区形成了一套富硅质和炭质岩组合的裂谷相深水盆地沉积,同时伴有双峰式火山岩岩浆侵位,形成研究区具枕状构造的粗面质熔岩。
值得指出的是,本次工作在竹山官渡地区发现洋岛玄武岩[22],并在竹山断裂带中发现具岛弧和洋脊性质的玄武岩(内部资料)。结合本文研究认为,南秦岭竹山地区在早志留世大规模伸展活动之后可能发展成为一小规模的有限洋盆,该洋盆可能为南秦岭勉略洋向东的延伸,关于该洋盆的演化特征有待进一步研究。南秦岭竹山地区粗面质火山岩岩石化学及锆石U-Pb同位素定年分析,为了解南秦岭早古生代构造演化提供了重要依据。
6. 结论
(1)岩石学、地球化学研究表明,南秦岭竹山地区粗面质火山岩为碱性岩系列,以粗面质火山碎屑岩为主,粗面质熔岩(粗面岩)次之,见少量粗面质次火山岩(粗面斑岩);岩石微量元素构造环境判别图表明,竹山地区粗面质火山岩处于板内构造环境;主量、微量和稀土元素特征表明,该区的粗面质火山岩与前人研究的大巴山地区板内玄武岩具有同源性,共同构成大陆裂谷双峰式火山岩组合。
(2)竹山地区粗面质火山碎屑岩锆石U-Pb年龄为430.6±2.7Ma,代表了该区粗面质火山岩主体的结晶年龄,表明南秦岭竹山地区早志留世被动大陆边缘发生过强烈的裂解活动,并形成富硅质和炭质岩组合的深水盆地。
(3)综合分析认为,南秦岭竹山地区在早志留世大规模伸展活动之后可能发展成为一小规模的有限洋盆,该洋盆可能为南秦岭勉略洋向东的延伸。
致谢: LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年得到中国地质大学(武汉)地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室相关工作人员的帮助,锆石U-Pb同位素数据分析得到湖北省地质调查院郭盼、江苏省地质调查院贺新星的帮助,审稿专家对论文初稿提出了宝贵的建设性的修改意见,在此一并表示感谢。 -
表 1 竹山地区粗面质火山岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 1 Major, trace and rare earth element data for trachytic pyroclastic rocks in Zhushan area
样号 101-33YQ 101-35YQ 203-20YQ 203-37YQ 205-3YQ 205-8YQ 205-24YQ 305-16YQ 305-92YQ 306-19YQ 岩性 粗面质 粗面质岩屑 粗面质晶屑 粗面质晶屑 粗面质 粗面岩 粗面岩 粗面斑岩 粗面斑岩 粗面岩 凝灰岩 晶屑凝灰岩 凝灰岩 凝灰岩 凝灰岩 SiO2 63.11 61.67 58.84 66.29 54.16 59.80 64.48 58.82 59.29 64.09 TiO2 0.33 1.61 2.14 1.13 1.06 1.16 1.09 1.72 1.19 1.04 Al2O3 :0.66 14.95 14.12 14.12 19.85 17.60 15.35 15.26 18.49 15.96 Fe2O3 1.79 1.41 3.24 1.42 1.58 1.24 0.94 1.67 1.49 1.91 FeO 0.33 4.65 4.78 3.27 3.05 2.75 3.53 5.03 2.73 2.37 MnO 0.22 0.14 0.21 0.14 0.35 0.32 0.28 0.27 0.31 0.24 MgO 0.21 1.82 2.64 1.70 2.67 2.06 1.00 1.85 1.27 0.90 CaO 0.27 2.63 2.44 1.12 2.52 1.55 0.93 2.35 2.02 0.42 Na2O 8.87 3.25 4.64 4.58 4.47 6.09 7.34 5.78 6.74 5.68 K2O 1.85 4.24 3.96 4.03 6.70 5.20 3.43 4.72 4.58 5.91 P2O3 0.06 0.29 0.31 0.18 0.10 0.23 0.16 0.46 0.17 0.18 烧失 1.40 2.43 1.62 1.45 2.89 1.46 0.99 1.27 0.96 0.61 总量 99.10 99.09 98.94 99.43 99.40 99.46 99.52 99.20 99.24 99.31 La 21.58 92.52 110 124 234.6 170.0 201.4 122.6 218.5 163.2 Ce 45.53 183.3 216 224 607.01 293.76 360.96 246.77 414.43 286.27 Pr 5.48 22.57 23.46 24.28 70.57 34.00 43.53 30.52 48.33 33.58 Nd 17.46 80.79 82.43 84.52 199.31 109.92 139.27 105.63 156.56 111.63 Sm 3.97 14.43 15.39 15.50 31.25 18.49 24.68 19.36 25.98 18.68 Eu 1.28 3.21 3.74 3.85 3.97 4.84 5.03 5.48 6.61 4.10 Gd 3.81 15.25 13.46 13.68 23.92 14.37 19.34 14.52 19.69 14.13 Tb 0.67 2.22 2.33 2.37 3.80 2.21 3.00 2.29 2.94 2.13 Dy 3.98 11.42 11.67 12.04 21.50 11.26 15.49 11.80 14.78 11.29 Ho 0.86 2.17 2.26 2.33 3.94 1.97 2.72 2.00 2.55 1.98 Er 2.63 5.20 6.40 6.61 11.26 5.14 7.13 5.11 6.53 5.15 Tm 0.41 0.73 0.95 0.98 1.83 0.77 1.08 0.75 0.99 0.75 Yb 2.65 4.32 5.32 5.71 11.42 4.60 6.43 4.42 5.73 4.27 Lu 0.42 0.53 0.54 0.64 1.70 0.69 0.96 0.65 0.85 0.64 Y 21.57 52.72 60.62 61.06 116.80 55.75 75.27 55.52 66.80 54.22 1REE 110.73 438.66 494.55 520.51 1226.09 672.00 831.01 571.89 924.46 657.80 LREE 95.29 396.81 451.62 476.15 1146.71 631.01 774.87 530.36 870.41 617.45 HREE 15.43 41.85 42.93 44.36 79.39 41.00 56.14 41.53 54.05 40.34 LREE/HREE 6.18 9.48 10.52 10.73 14.44 15.39 13.80 12.77 16.11 15.30 (La/Yb)N 5.50 14.48 14.02 14.67 13.88 25.00 21.15 18.75 25.78 25.82 Rb 13.60 132.40 127.65 101.43 185.20 77.93 56.29 61.70 42.26 75.57 Ba 8155 1549 1063 268 268 1304 272 2062 1917 143 Th 15.53 16.66 16.19 10.48 57.41 13.57 15.49 11.72 17.49 7.11 U 8.61 2.66 2.40 2.40 16.38 2.63 2.19 2.20 3.35 1.35 Ta 19.36 7.43 7.94 5.52 35.52 13.47 16.29 10.15 15.77 10.35 Nb 613.6 147.8 138 103 638.4 237.2 296.5 177.5 273.7 190.4 Sr 84.54 140.2 244 113 353.4 176.2 123.4 272.6 2250.7 49.7 Zr 1541 659 697 621 2503 830 1388 806 1014 780 Hf 24.66 17.91 16.90 15.37 53.51 16.83 26.68 18.14 20.57 15.61 注:主量元素含量单位为%;微量和稀土元素含量为10-6;数据由国土资源部武汉矿产资源监督检测中心完成 表 2 竹山地区粗面质火山碎屑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果
Table 2 LA-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb isotope composition of zircons in trachytic volcanic rocks of Zhushan area
分析号 元素含量/10-6 232Th/238U 同位素比值 同位素年龄/Ma Total Pb 232Th 238U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 205-1 81.5 381 178 2.14 0.0663 0.0041 0.603 0.034 0.0681 0.0011 816.7 130 479.2 21.8 424.7 7.0 205-2 56.8 261 157 1.66 0.0626 0.0037 0.604 0.034 0.0708 0.0011 694.5 130 479.7 21.3 440.7 6.6 205-3 89.4 418 235 1.78 0.0746 0.0049 0.684 0.043 0.0667 0.0013 1057.4 130 529.4 26.2 416.3 7.8 205-4 109.7 544 252 2.15 0.0618 0.0032 0.593 0.030 0.0707 0.0010 733.3 110 473.0 18.9 440.4 6.0 205-5 28.9 127 102 1.24 0.0710 0.0092 0.666 0.085 0.0681 0.0021 966.7 270 518.5 51.7 424.8 12.5 205-6 57.0 232 170 1.36 0.0761 0.0048 0.693 0.040 0.0681 0.0012 1098.2 130 534.6 24.2 424.9 7.0 205-7 72.9 328 193 1.70 0.0595 0.0044 0.576 0.044 0.0711 0.0013 587.1 160 461.9 28.4 442.5 7.8 205-8 148.5 741 337 2.20 0.0553 0.0033 0.537 0.032 0.0703 0.0012 433.4 140 436.2 21.0 437.8 7.5 205-9 51.4 231 144 1.61 0.0659 0.0039 0.615 0.033 0.0700 0.0012 803.4 130 486.6 21.0 436.0 7.5 205-10 155.8 693 317 2.18 0.0701 0.0032 0.657 0.031 0.0687 0.0011 931.5 93 512.7 18.7 428.6 6.6 205-11 112.2 542 265 2.04 0.0656 0.0044 0.629 0.050 0.0682 0.0011 794.4 140 495.5 30.9 425.2 6.5 205-12 52.7 246 142 1.74 0.0618 0.0042 0.563 0.033 0.0685 0.0013 664.8 140 453.5 21.7 427.0 7.5 205-13 152.8 749 408 1.84 0.0582 0.0022 0.553 0.021 0.0690 0.0008 538.9 81 446.9 13.5 429.9 5.0 205-14 183.0 893 400 2.23 0.0584 0.0023 0.554 0.021 0.0694 0.0009 546.3 87 447.5 14.0 432.7 5.3 205-15 87.6 406 205 1.98 0.0668 0.0042 0.623 0.037 0.0687 0.0012 831.5 140 491.6 23.1 428.5 7.2 205-16 96.7 449 225 2.00 0.0615 0.0032 0.600 0.032 0.0701 0.0011 657.4 110 477.2 20.5 437.0 6.5 205-17 123.9 565 322 1.76 0.0588 0.0027 0.558 0.025 0.0696 0.0009 561.1 100 450.2 16.0 434.0 5.5 205-18 224.1 998 675 1.48 0.0597 0.0019 0.587 0.019 0.0715 0.0009 590.8 70 469.2 12.4 445.3 5.4 205-19 72.8 339 174 1.95 0.0579 0.0046 0.538 0.043 0.0682 0.0012 527.8 180 437.0 28.3 425.0 7.1 205-20 167.7 842 387 2.18 0.0598 0.0025 0.560 0.024 0.0685 0.0009 594.5 93 451.8 15.6 427.2 5.4 205-21 142.9 758 304 2.49 0.0588 0.0047 0.547 0.048 0.0668 0.0014 566.7 180 443.3 31.5 416.8 8.2 205-22 70.2 243 388 0.63 0.0569 0.0026 0.548 0.024 0.0705 0.0010 487.1 100 443.7 16.0 439.3 5.8 注:数据由中国地质大学(武汉)地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室完成 -
张国伟, 孟庆任, 于在平, 等.秦岭造山带的造山过程及其动力学特征[J].中国科学(D辑), 1996, 3:193-200. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199603000.htm Hsu K J, Wang Q, Li J. Tectonic evolution of Qingling Mountains, China[J]. Eclogae. Geol. Helv., 1987, 80:735-752. Hsu K J, Wang Q, Li J. Tectonic evolution of Qingling Mountains, China[J]. Eclogae. Geol. Helv., 1987, 80:735-752.
Mattauer M, Matte Ph, Malavieille J. Tectonics of Qingling Belt:build-up and evolution of Eastern Asia[J]. Nature, 1985, 317:496-500. doi: 10.1038/317496a0 Mattauer M, Matte Ph, Malavieille J. Tectonics of Qingling Belt:build-up and evolution of Eastern Asia[J]. Nature, 1985, 317:496-500. doi: 10.1038/317496a0
杜远生, 盛吉虎, 韩欣, 等.南秦岭勉(县)略(阳)构造混杂岩带的泥盆纪-石炭纪古海洋演化[J].古地理学报. 1999, 1(4):54-60. http://www.cnki.com.cn/article/cjfdtotal-gdlx199904007.htm 杨志华, 苏生瑞.秦岭造山带发展演化阶段的新认识[J].地质力学学报, 1995, 3:38-45. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX503.005.htm 裴先治, 张国伟, 赖绍聪, 等.西秦岭南缘勉略构造带主要地质特征[J].地质通报, 2002, 21(8):486-494. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2002Z2005.htm 张宗清, 唐索寒, 张国伟, 等.勉县-略阳蛇绿混杂岩带镁铁质-安山质火山岩块年龄和该带构造演化的复杂性[J].地质学报, 2005, 4:531-539. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/dzxe200504016.htm 王宗起, 闫臻, 王涛, 等.秦岭造山带主要疑难地层时代研究的新进展[J].地球学报, 2009, 30(5):561-570. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200905001.htm 王宗起, 闫全人, 闫臻, 等.秦岭造山带主要大地构造单元的新划分[J].地质学报, 2009, 11:1527-1546. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200911003.htm 张传林, 董永观, 杨志华.秦岭晋宁期的两条蛇绿岩带及其对秦岭-大别构造演化的制约[J].地质学报. 2000, 74(4):313-324. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/dzxe200004002.htm 闫全人, 王宗起, 闫臻, 等.秦岭勉略构造混杂带康县-勉县段蛇绿岩块-铁镁质岩块的SHRIMP年代及其意义[J].地质论评, 2007, 6:755-764. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/dzlp200706010.htm 陈友章, 刘树文, 李秋根, 等.南秦岭岚皋基性火山岩的地质学、地球化学及其构造意义[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 46(4):607-619. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ201004016.htm 董云鹏, 周鼎武, 张国伟, 等.秦岭造山带南缘早古生代基性火山岩地球化学特征及其大地构造意义[J].地球化学, 1998, 5:432-441. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX199805003.htm 张成立, 高山, 张国伟, 等.南秦岭早古生代碱性岩墙群的地球化学及其地质意义[J].中国科学(D辑), 2002, 10:819-829. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200210004.htm 邱家骧, 李昌年, 喻学惠.秦巴碱性岩[M].北京:地质出版社, 1993:147-153. 黄月华, 杨建业.北大巴山笔架山-铜洞湾碱性镁铁质熔岩的岩石学研究[J].中国地质科学院西安地质矿产研究所刊, 1990, 28:15-24. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/ExternalResource-dzkjqb200903004%5e5.aspx 夏祖春, 夏林圻, 张诚.北大巴山碱质基性-超基性潜火山杂岩的辉石矿物研究[J].西北地质科学, 1992, 2(13):22-30. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/xbfk199202003.htm 晏云翔.陕西紫阳-岚皋地区碱-基性岩墙群的岩石地球化学及Sr、Nd、Pb同位素地球化学研究[D].西北大学硕士学位论文, 2005. 张欣.南秦岭紫阳-镇巴地区基性侵入体动力学机制及地质意义讨论[D].长安大学硕士学位论文, 2010. 黄月华, 任有祥, 夏林圻, 等.北大巴山早古生代双模式火成岩套:以高滩辉绿岩和蒿坪粗面岩为例[J].岩石学报, 1992, 3:243-256. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB199203004.htm 王刚.北大巴山紫阳-岚皋地区古生代火山岩浆事件与中生代成矿作用[D].中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2014. 刘成新, 胡正祥, 毛新武, 等.南秦岭竹山地区洋岛型玄武岩的发现及构造意义[J].资源环境与工程, 2013, 27(2):109-118. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK201302002.htm 桑隆康, 马昌前.岩石学(第二版)[M].北京:地质出版社, 2012:72-73. 邓晋福, 肖庆辉, 苏尚国, 等.火成岩组合与构造环境:讨论[J].高校地质学报, 2007, 13(3):392-402. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200703004.htm 邹先武, 段其发, 汤朝阳, 等.北大巴山镇坪地区辉绿岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年和岩石地球化学特征[J].中国地质, 2011, 2:282-291. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/dizi201102006.htm 王存智, 杨坤光, 徐扬, 等.北大巴基性岩墙群地球化学特征、LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及其大地构造意义[J].地质科技情报, 2009, 28(3):19-26. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/dzkq200903003.htm 袁洪林, 吴福元, 高山, 等.东北地区新生代侵入体的锆石激光探针U-Pb年龄测定与稀土元素成分分析[J].科学通报, 2003, 48(14):1511-1520. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/kxtb200314007.htm Andersen T. Correlati on of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192:59-79. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X Andersen T. Correlati on of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192:59-79. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X
Ludwig K R. User's manual for Isoplot 3.00. A geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley Geochronology Center, Special Publication No. 4a, 2003. 赵振华.关于岩石微量元素构造环境判别图解使用的有关问题[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2007, 31(1):92-103. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200701012.htm 丁宇.南秦岭中段亚碱性-碱性岩板块构造环境及岩浆演化[J].桂林冶金地质学院学报, 1993, 1:34-44. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/glgx199301003.htm 张成立, 高山, 袁洪林, 等.南秦岭早古生代地幔性质:来自超镁铁质、镁铁质岩脉及火山岩的Sr-Nd-Pb同位素证据[J].中国科学(D辑), 2007, 37(7):857-865. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/jdxk200707000.htm 张国伟, 张宗清, 董云鹏.秦岭造山带主要构造岩石地层单元的构造性质及其大地构造意义[J].岩石学报, 1995, 2:101-114. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB199502000.htm



 下载:
下载: