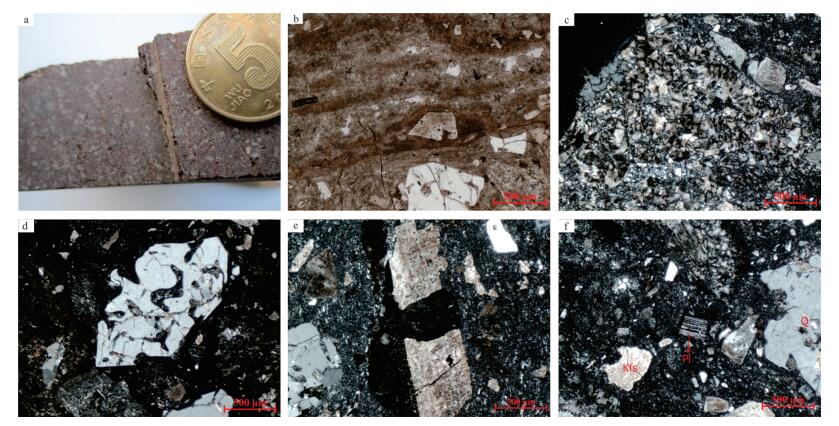
Geochronological and geochemical characteristics of the rhyolites in Taerqi of middle Da Hinggan Mountains and their geological significance
-
摘要:
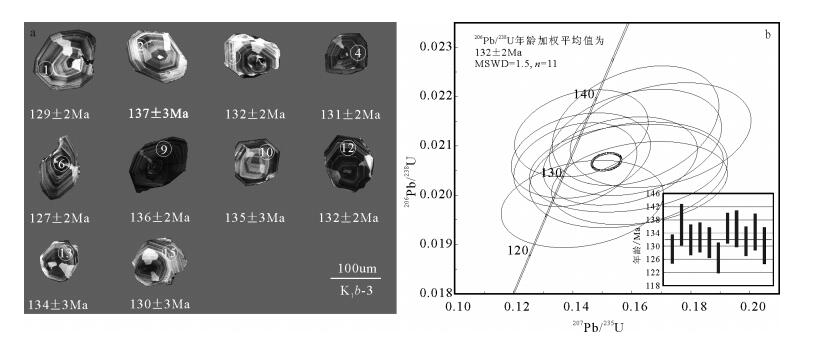
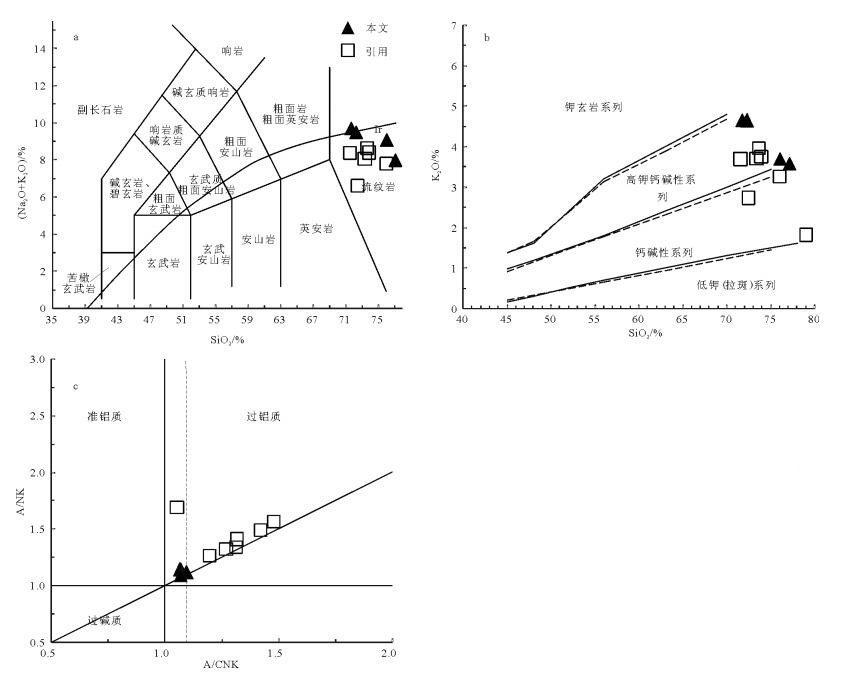
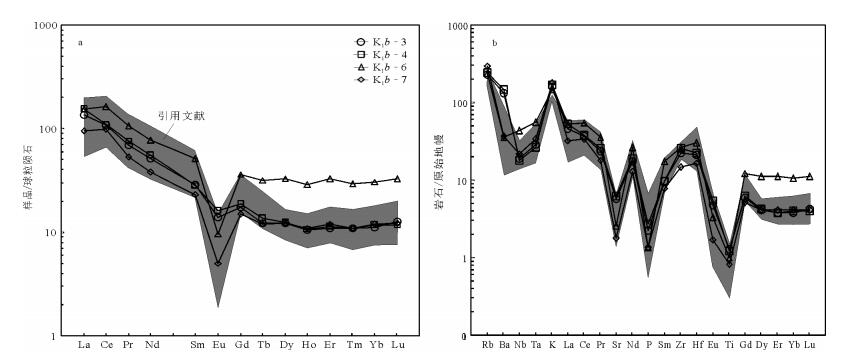
塔尔气地区位于大兴安岭主脊中段, 晚中生代广泛发育一套玄武岩、安山岩、英安岩、流纹岩及相应火山碎屑岩的岩石组合。以流纹岩为研究对象, 进行了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄、岩石地球化学研究。测年结果显示, 流纹岩形成于132±2Ma(MSWD=1.5, 2σ), 属早白垩世中期。岩石地球化学特征表明, 流纹岩属于典型的弱过铝质高钾钙碱系列岩石, 具有高硅(71.6%~77%)、富碱(Na2O+K2O=7.94%~9.64%)且富钾(K2O=4.5%~5.46%)的特征; 轻、重稀土元素分馏明显, 具中等Eu负异常(δEu=0.22~0.7), 亏损高场强元素Nb、Ta、P、Ti, 相对富Th、U、Zr、Hf, 富集大离子亲石元素K、Rb, 相对贫Ba、Sr, 显示A型流纹岩特征。岩浆源区与硬质砂岩相似, 具有较高的锆饱和温度, 可能为地壳部分熔融的产物, 形成于后碰撞伸展的大地构造环境。
Abstract:Taerqi area is located in the middle main ridge of Da Hinggan Mountains, where there is developed a suite of late Mesozo-ic volcanic rocks, which include basalt, andesite, dacite, rhyolite and tuff. In this paper, detailed LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb geochro-nological and element geochemical studies were carried out for the rhyolites. The zircon U-Pb dating yielded a weighted average age of 132±2Ma(MSWD=1.5, 2σ), indicating that the rhyolites were formed at the middle stage of the early Cretaceous. Rock geo-chemical characteristics show that the rocks are peraluminous cal-alkaline rhyolites, which are characterized by high SiO2(71.6%~77%), high potassium and alkali content (K2O=4.5%~5.46%, Na2O+K2O=7.94%~9.64%). Trace elements have a similar variation trend that systematic enrichment of LILE and depletion of HFSE as well as LREE fractionation are more obvious than that of HREE, and also show significant weak anomaly of Eu (δEu=0.22~0.7). In addition, there exist the depletion of Sr, Ba, P, Ti, Nb, Ta and en-richment of Rb, K, Th, U, Zr, Hf. The rocks belong genetically to A type with a high zirconium saturation temperature (TZr=842℃), and the magma source was probably similar to the metagrewacks. Accordingly, it is inferred that the A-type rhyolites were products of partial melting of the crust and formed in a post-collision environment and an extensional tectonic setting.
-
Keywords:
- middle Da Hinggan Mountains /
- Taerqi area /
- zircon U-Pb dating /
- A-type rhyolites /
- post-orogenic
-
火山岩TAS分类是IUGS(国际地质科学联合会)在1989年第28届国际地质大会上通过的,迄今已40年。该分类对推进岩石学和地球化学研究起到了积极的作用,规范了岩石(尤其火山岩)的命名,方便了学术界的交流。
岩浆岩分类是岩石学研究最基本的问题,是其出发点,也是岩石学的基础。20世纪70—90年代,IUGS火成岩分类学分会推荐了侵入岩的QAPF分类方案[1-14]。火山岩由于矿物颗粒细小,很难识别,许多是玻璃质的,显微镜下很难确定其成分,需要借助岩石化学分析加以判断。于是相应地推出了火山岩的TAS分类方案,随后在火山岩分类的基础上又提出了侵入岩的TAS分类。上述分类已经得到各国科学家的信赖,成为学术界一致的认识[13, 15-19],很少有人对这个方案提出异议。笔者认为,该方案确有明显的优点,但仔细考究,也有不足之处。
例如TAS图解的不同岩区是以直线和斜线分割的(图 1),这样的分割是否合理?直线和斜线虽然简单易行,但是,它是否能真实地反映岩石的自然组合和自然分布?又如,该方案规定SiO2=45%是超基性岩与基性岩之间的界线,也是苦橄质玄武岩与玄武岩之间的界线。可是,苦橄质玄武岩并非超基性岩,严格说属于基性岩类,不是超基性岩,这显然自相矛盾。再者,碱性岩部分划分的岩区很多,而实际上全球火山岩主要是亚碱性的,碱性岩很少,碱性岩的划分是否能够简化一些?还有,IUGS通过的TAS分类中玄武岩在B区,这是一个矩形区域(图 1),又规定B区可以细分为碱性玄武岩(有霞石标准矿物出现)和亚碱性玄武岩(无霞石标准矿物出现)2个亚类。B区原本就属于正常系列,现在又要从正常系列中划出碱性岩,是否自相矛盾?再有,TAS分类是以根名(root name)作为岩区名称的,在该分类中,basalt、andesite、dacite、rhyrolite属于根名很好理解,于是,picro-basalt、basalt-andesite应当属于亚类或亚根名。但是,该分类却把picrobasalt、basalt-andesite也当作根名,是否概念上混淆了?按照这个原则,andesite-basalt、dacite-rhyrolite、rhyrolite-dacite是否也可以作为根名?诸如此类的问题还有很多。
![]() 图 1 TAS火山岩分类命名图[20]Pc—苦橄玄武岩;B—玄武岩;O1—玄武安山岩;O2—安山岩;O3—英安岩;R—流纹岩;S1—粗面玄武岩;S2—玄武质粗面安山岩;S3—粗面安山岩;T—粗面岩、粗面英安岩;F—似长石岩;U1—碱玄岩、碧玄岩;U2—响岩质碱玄岩;U3—碱玄质响岩;Ph—响岩Figure 1. TAS volcanic rock classification and nomenclature diagram
图 1 TAS火山岩分类命名图[20]Pc—苦橄玄武岩;B—玄武岩;O1—玄武安山岩;O2—安山岩;O3—英安岩;R—流纹岩;S1—粗面玄武岩;S2—玄武质粗面安山岩;S3—粗面安山岩;T—粗面岩、粗面英安岩;F—似长石岩;U1—碱玄岩、碧玄岩;U2—响岩质碱玄岩;U3—碱玄质响岩;Ph—响岩Figure 1. TAS volcanic rock classification and nomenclature diagram地球上岩浆岩的出现应当是有一定条件的,而且可能有一定规律。例如,由地幔部分熔融形成的基性岩具有一定的特征,形成一个以玄武岩为主的岩石组合[2, 21-22]。地壳如果有来自地幔热的供给,使下地壳发生部分熔融,形成的是中酸性的岩浆组合。这样的组合可以很多,研究岩石的自然组合和分布,是岩石分类必然遇到的问题。笔者认为,是否属于一个组合,不是依据理论和模式,而是按照数据集中和分布的情况决定的,与成因无关,但是,很可能反映了成因的某些影响。TAS图解简洁实用,是它明显的优点,但是,随着科学的发展和数据的积累,也显示出一些不足。早先的研究,由于分析方法、分析技术、数据量及研究思路的限制,可能并不是非常完美[23]。目前,全球已经积累了海量的数据,有条件对TAS分类做新的研究。本次工作秉承这一宗旨对该问题进行了初步探索。
1. 火成岩分类的始末
岩石的分类问题早在岩石学成为地质科学中一门独立的学科时就引起了重视。早期地质学岩石命名很混乱,Trigor[24]为此专门收集了当时经过鉴定和有特定名词的火成岩计777种,其中深成岩275个,浅成岩(包括细晶岩、伟晶岩、煌斑岩及微粒脉岩等) 254个,喷出岩248个,再加上同义语、复合语、群体名和某些不通用和未采用的名词,共有1022个名词。Le Maitre等[7]在提交给IUGS的报告中,从786篇文献中检索出1534个岩石名词,足见岩石名词之复杂和混乱及统一岩石名词的必要性。因此,国际学术界对这个问题有很大兴趣并非偶然。早在一百多年前,欧美许多岩石学家就对火成岩的定量矿物分类提出了许多方案和建议[3, 5, 11, 15, 25-29]。在众多科学家的推动下,在1897年,于圣彼得堡举行的第7届国际地质大会上将岩石的分类和命名列入大会议程,并于会后成立了岩石命名国际委员会。在1899年第8届国际地质会议(1900,巴黎)的前夕,该委员会举行预备会议讨论了岩石的分类草案,认为在岩石分类中占首要地位的是矿物成分,岩石命名首先应考虑岩石组成中主要矿物的相对数量,其次才是化学的分类。1968年在布拉格召开的第23届国际地质大会上,瑞士地质学家Streckeisen提出了一份岩石分类的建议。1972年4月,分委会在伯尔尼举行了有13个国家代表参加的第一次会议,讨论了侵入岩总的分类原则。此后,分委会还分别在格勒诺布尔(1975年)、悉尼(1976年)、布拉格(1977年)、帕多瓦(1979年)、巴黎(1980年)、剑桥(1981年)和格拉纳达(1983年)举行了会议,反复讨论、修改该方案[7, 20]。
2. TAS火山岩分类的原则
国际地科联火成岩分类委员会在完成了深成岩的QAPF分类后,开始了火山岩分类的研究,并在多次国际会议上进行了广泛的讨论。分委会考虑到火山岩不同于侵入岩的情况,并提出以下建议[7, 20, 30]:①如果实际矿物成分可以用来分类,那么根据其在QAPF图中的位置对火山岩进行分类和命名,其他参数则可用来对火山岩作进一步的细分。②如果实际矿物成分不能用来分类,那么可以用化学参数作为分类的依据,但划分岩石类别应与QAPF矿物的分类相对应。于是分委会在1981年的剑桥会议上提出利用全碱-二氧化硅(TAS)图解作为火山岩分类的建议(图 1)。
同时,分委会也赞同下述原则:简单的分类比复杂的分类更可取,直线分界线比弯曲分界线更可取。一种岩石应当总是能够在不知道其产地或与其伴生的其他岩石的情况下进行分类,换句话说,该分类除要求所讨论的岩石是火山岩外,不应包含任何需要说明的内容[20]。鉴于此,Le Martre教授在帕多瓦建立了一个分类委员会工作小组,分析研究TAS图解作为分类依据的优越性,提出了一个火山岩TAS分类的建议。该建议被广为传阅,并成为格拉纳达会议讨论的基础。在这次会议上,这个建议稍作修改后,得到分类委员会正式通过[20]。
会议指出,使用TAS图进行分类必须注意以下四点:①该分类是纯描述性的,不一定意味着成因关系;②该分类是为利用新鲜火山岩的分析数据而设计的,为此,建议删去H2O大于2%和CO2大于0.5%的分析数据;③在使用之前,分析数据都必须在不计算H2O和CO2的情况下换算成100%;④已被风化、蚀变、交代、变质或经过晶体堆积作用的岩石,其分析数据在该分类中都不能使用,否则会得出虚假的结果。
3. TAS分类说明
TAS岩石分区的界线是怎样确定的,Le Matrai[7, 20]有详细的说明。
3.1 不同根名(root name)的命名
如图 1所示,TAS图共有15个根名(root name;邓晋福等[17]将其译为“基本名称”;“基本名称”是意译,“根名”是直译)。不同的根名分别用字母标示,并将火山岩划分为3个系列,描述其在CIPW标准矿物成分中二氧化硅的饱和度状况:O代表过饱和,U代表不饱和,S代表饱和(也可以代表弱过饱或弱不饱和)。
TAS分类规定苦橄玄武岩、玄武岩、玄武安山岩、安山岩和英安岩各区之间的界线为竖的直线,以与其他分类中已经使用的界线一致[20, 31]。分委会推荐SiO2=52%为玄武岩的上限,这个界线与通用的超基性、基性和中性岩石之间的区分一致。在Frolova等[31]和Peccerillo等[32]的分类方案中,英安岩与流纹岩的分界线定在一个不变的SiO2值上。
其他的分界线则是估量其在QPAF分类中的位置来描绘的。例如,把碧玄岩-碱玄岩、响质碱玄岩、碱玄响岩和响岩的区与粗面玄武岩、粗面安山岩和碱性粗面岩-粗面岩的区分开的斜线,要位于尽量靠近标准矿物QAPF图中的10%标准矿物似长石等值线的位置上(F区)。同样,碱性粗面岩-粗面岩区与碱性流纹岩区的斜线在QAPF图中靠近20%标准矿物石英的位置上(Q区)。把粗面安山岩和碱性粗面岩-粗面夏岩的区与玄武安山岩、安山岩和英安岩的区分开的斜线,是由2种岩石之间出现的间断来定位的。这2种岩石是文献中称为典型碱性的岩石和被认为属于钙-碱性的或拉斑玄武质的岩石。
TAS图共采用了数据库中的23937个数据[20]。该图中确定的S系列和U系列之间的分界线,分别平行于碱性粗面岩-粗面岩区与粗面安山岩区之间的分界线和响岩区与碱玄质响岩区之间的分界线。虽然这些分界线与某些其他分界线成直角,但是不一定要把这些分界线画成这样,因为这些分界线之间的交角取决于在2个坐标轴上选择的相对标尺。
3.2 TAS图的构成
(1)TAS图首先把全部火山岩分为3个系列,每个系列再划分为若干岩类。三大系列即钙碱性(CA)、拉斑玄武岩(TH)和碱性(A)系列。上述三大岩石系列由于历史的沿革和发展,经历过很大的变化。据邓晋福[33]研究,钙碱性(CA)术语至少有7种岩石学涵义,拉斑(玄武岩)系列(TH)术语至少有6种涵义,碱性系列(A)至少有4种涵义[17]。可见,相同的CA、TH、A术语可有不同的化学参数,尽管术语相同(英文,中文名称写法均相同),但它们的岩石学涵义可以不同。
(2)TAS分类B区的根名是玄武岩,按SiO2饱和度可进一步划分为碱性和亚碱性玄武岩,为此,必须进行CIPW标准矿物计算:出现霞石标准矿物者称为碱性玄武岩,无霞石标准矿物者称为亚碱性玄武岩。对于S1区(粗面玄武岩区)、S2区(玄武质粗面安山岩区)和S3区(粗面安山岩区),每个区均有2个根名,即按Na2O-2%大于或小于K2O划分为钠质或钾质。例如,粗面玄武岩区(S1区)有2个根名:钠质的为夏威夷岩(Hawaiite),钾质的为钾质粗面玄武岩(potassic trachybasalt)。同样,S2和S3也各有2个名称,分别为钠质的橄榄粗安岩和钾质的橄榄玄武粗安岩(还有译为钾玄岩的);钠质的歪长粗安岩和钾质的安粗岩。
对于U1区的命名,需要通过CIPW标准矿物计算来确定。当标准矿物Ol > 10时称为碧玄岩,01 < 10时称为碱玄岩。
TAS分类对于R区(流纹岩区)、T区(粗面岩区)和Ph区(响岩区)进一步划分的依据是过碱性指数(peralkaline index),即[(Na2O+K2O)/Al2O3]大于或小于1来确定的。具体步骤如下:对于R区(流纹岩区)和Ph区(响岩区),过碱性指数大于1者称为过碱性流纹岩和过碱性响岩。另外,在确认过碱性流纹岩和过碱性粗面岩之后,按Al2O3大于或小于1.33 (TFeO)+4.4%对过碱性岩石作更进一步划分,位于该坐标系中分界线上方的过碱性岩石称为钠闪碱流质粗面岩(comenditic trachyte)和钠闪碱流质流纹岩(comenditic rhyrite)(=钠闪碱流岩,comditite),位于分界线下方的则称为碱流质粗面岩(pantelleritic trachyte)和碱流质流纹岩(pantelleritic rhyrite)(=碱流岩,pantellerite)。
看来,TAS分类对过碱性岩石的划分十分繁琐[17, 20]。
4. TAS分类存在的问题
对于TAS分类,全球岩石学家和地球化学家已经研究、讨论了近百年,最终得出一个令全球科学家折服的方案,全球科学家按照该方案执行,这里面流淌着千千万万科学家的心血和汗水[1, 5-10, 30]。但是,科学是发展的,人类的认识是不断进步的。今天已经进入大数据时代,在大数据的眼光下,TAS图解是否最合适?葛粲等[34]利用GEOROC数据库资料对全碱对硅(TAS)的图解进行了研究。本次研究认为,目前的TAS分类可能并不完善,至少有下列几个问题值得思考。
4.1 为什么TAS图的分类以直线和斜线分割?
如上所述,这个原则是1984年作为TAS分类主持人的Le Martre[20]在向IUGS提交的报告中确定的,岩石命名分类委员会赞同下述原则:简单的分类比复杂的分类好,直的分界线比弯曲的分界线好。看来,以直线和斜线分割是40多年前当时学术界的共识。然而,从今天的角度看就不一定合适了。笔者采用全球数据库数据考察了多种岩石,发现没有几种是可以用直线加以区分的(图 2)。在图 2中,玄武岩、苦橄质玄武岩和苦橄岩数据的密集情况都是以曲线表示的,反映了自然界岩石的分布。
地球上的所有岩石都有自己的分布规律。出现在地球上的岩浆岩,不论是幔源的还是壳源的,都应当是在一定条件下形成的[13, 16, 19, 35-36]。岩浆形成以后还会经历各种各样的变化,如分离结晶作用、混合作用、混染作用、交代作用、蚀变作用等[16, 19, 35-36]。岩石成分也会发生一定的变化,这个变化具有一定的范围和规律,这也在岩石自然分布的范围内。尊重岩石的自然分布,反映岩石的自然分布,是火成岩分类学第一位重要的任务。
4.2 玄武岩SiO2的上限问题
Le Bas等[10]在提交给国际地科联火成岩分类学分委会关于火山岩分类命名的报告中确定了3条主要界线:超镁铁质岩与玄武岩的SiO2为45%,玄武岩与玄武安山岩的SiO2为52%,安山岩与英安岩SiO2为63%(图 1)。据Le Bas等[10]的解释,早先的方案将玄武岩与玄武安山岩的界线确定在SiO2=53%,后来火成岩分类学分委会一致同意将该界线调整为52%[37]。
实际情况如何呢?据王金荣等[38]的统计,全球MORB平均为50.14%,IAB为51.84%。也就是说,全球IAB的平均值已经接近52%,超过52%的数据可能不在少数。张旗等[37]在研究云南白马雪山蛇绿岩时遇到过一个火山岩剖面,其SiO2含量的变化大体在50%~54%之间,按照TAS的规定分别属于玄武岩和玄武安山岩2个岩区,可是野外和镜下均不存在明显差别,都是玄武岩的特征。镜下主要显示间粒结构、粗玄结构和斑状结构,野外SiO2含量大于52%和小于52%的岩石之间也没有明显的界线[35]。看来,在某些情况下,玄武岩的上限也是可以变化的。
4.3 苦橄质玄武岩与玄武岩之间的界线
IUGS将苦橄质玄武岩与玄武岩的界线定在SiO2=45%[10, 32, 37, 39],并且明确指出这也是基性岩与超基性岩的界线(图 1)。这个问题更麻烦,Jiao等[40]对该问题作了专门的研究[40],结论性意见如下。
(1)全球火山岩数据的研究揭示,SiO2=45%并非苦橄质玄武岩与玄武岩之间的界线,苦橄质玄武岩与玄武岩的SiO2含量有很大的重叠部分(图 2)。苦橄质玄武岩及其类似的岩石,如大洋岩(oceanite)及富辉橄玄岩(ankalamite)的SiO2也是变化的,基本上不受SiO2=45%的限制。
(2)苦橄质玄武岩不是超基性岩,从岩石名称上看属于基性岩类。按照岩石学教科书的规定,苦橄岩才是超基性的火山岩,而苦橄质玄武岩与苦橄岩的区分主要依靠橄榄石斑晶的含量。岩石学研究表明,橄榄石是否出现与火山岩冷却速度及橄榄石结晶速度有关,有些没有大量橄榄石出现的玄武岩其实也是苦橄质玄武岩甚至苦橄岩。因此,玄武岩、苦橄质玄武岩、苦橄岩可能是过渡的。一般来说,玄武岩是基性岩,但是,也不排除某些富镁玄武岩可能是超基性岩。在TAS图解上,玄武岩、苦橄质玄武岩和苦橄岩的SiO2含量是重叠的(图 2)。
(3)对全球侵入和喷出的超基性岩的统计表明,很少超基性岩受SiO2=45%限制(除幔源的纯橄岩和方辉橄榄岩外,连lherzolite和peridotite也不受SiO2=45%的限制[40]),把SiO2=45%作为基性岩与超基性岩的界线似乎并不合适。
(4)鉴于苦橄质玄武岩在TAS图上的表现,且全球大多数超基性岩似乎并不受SiO2=45%的限制,SiO2=45%并不是基性岩与超基性岩的界线,因此,建议TAS图删去对超基性岩的讨论,TAS图不适合超基性岩[40]。尤其是玄武岩,其为基性岩还是超基性岩,不能单由橄榄石含量决定,因此,SiO2=45%也不适用于作为玄武岩的下限。
4.4 B区玄武岩的问题
IUGS规定玄武岩的总碱量可高达5%(图 1)。而Yoder等[41]认为,玄武岩的总碱量通常不超过3%,某些富硅的玄武岩碱含量可以超过3%,而一些贫硅的碱性玄武岩总碱量可低于3%。McDonald等[21-22]在研究夏威夷地区的夏威夷岩时,确定拉斑玄武岩与夏威夷岩的界线约在Na2O+K2O=4%(当SiO2= 50%时)和Na2O + K2O=2%(当SiO2=45%时),与Yoder等[41]的见解大体一致,也与图 1中的Ir曲线大体一致。
此外,IUGS火山岩分类委员会在确定TAS作为火山岩的分类图时还明确一条:玄武岩(B区)可进一步细分为碱性玄武岩和亚碱性玄武岩2类,这取决于它们是否含有标准矿物霞石。这一方案早在1892年就被Iddings[1]确立,且一直被广泛使用。而这一划分在1985年伦敦的国际地质大会上再次得到确认。这是什么意思呢?有标准矿物霞石的玄武岩是碱性玄武岩,夏威夷岩就有霞石标准矿物[21-22],夏威夷岩应当是碱性玄武岩。但是,夏威夷岩的碱性玄武岩在S1区,而IUGS规定的碱性玄武岩在B区。同样是碱性玄武岩,却出现在2个不同的岩区,是否暗示S1区的夏威夷岩不同于B区的碱性玄武岩?
4.5 碱性岩问题
碱性岩是按照岩相学标志划分的,其基本特征是硅酸不饱和、碱质含量高、矿物成分出现似长石和碱性暗色矿物[2, 4, 7-8, 17, 22, 46]。这一点,学术界的认识大体一致。
TAS图解上碱性岩的分类很繁琐,需要一些较复杂的计算才能确定,操作起来太麻烦。实际上,碱性岩在地球上分布很少,据查瓦里茨基[42]的统计占岩浆岩的1%左右,而笔者统计的全球碱性岩数据量为8%左右(据GEOROC和PetDB数据库资料)。碱性岩的规模一般很小,但是,鉴于其在矿物学上的特殊性及具有磷酸盐及铌-钽矿床的远景,故对其研究较重视,认为碱性岩有重要的理论和现实意义[43-45]。因此,文献中碱性岩的数据量与碱性岩的实际分布是不匹配的。
5. 分类应当遵循的原则
上一节历数了TAS分类可能存在的问题,而如何解决上述问题,首先要明确分类应当遵循的原则。
5.1 岩石分类命名是描述性的,没有成因的含义
Le Matrai[7, 20]在对TAS图解说明时指出,TAS分类是纯描述性的,不一定意味着成因关系。他强调,该分类除要求所讨论的岩石是火山岩外,不应包含任何需要说明的内容[7, 20]。这是正确的,本文也遵循这一原则。
5.2 岩石分类应当反映岩石的自然组合和自然分布
火成岩是一种岩浆,喷出地表的称喷出岩或火山岩,固结在地壳浅部的为深成岩或侵入岩。最早的岩石分类具有强烈的地域性,如Iddings[1]和Harker[47]发现,产于大西洋(如亚速尔群岛)和太平洋(如安第斯山)的岩浆岩明显不同,前者是碱性的,后者是亚碱性的,分别称为大西洋型岩石系列和太平洋型岩石系列。2个系列反映了2种不同的成因、不同的组合。邓晋福等[48]指出,构造环境也是一种火成岩组合。例如,大洋中脊火成岩是一个岩石组合,岛弧的所有岩石也是一个组合,这是从大的构造背景来说的。
应当指出,IUGS的TAS分类遵循了岩石自然分布,许多岩区的界线选在不同岩石分布密度最小的地方[7]。可能由于某些原因,该分类在某些问题的处理上又没有遵循上述原则,例如对玄武岩、玄武安山岩、安山岩和英安岩各区的界线,选择了目前通用的垂直于SiO2横坐标的分界线[7]。又如S系列的S1、S2、S3与T之间,以及U系列的U1、U2、U3与Ph之间的界线为相互平行的斜线,各区范围大小差不多[7],这些均是人为规定的。再如对地球上出现频率最高的玄武岩,IUGS规定其为一个矩形(图 1,SiO2在45%~52%之间,Na2O+K2O在0%~5%之间)。
如图 2所示,自然界的岩石基本上都不可能是方方正正聚合在一起以直线和斜线分割的。本文收集了全球全部玄武岩数据(67715件),发现玄武岩在TAS图上极度分散(图 3),说明数据库的玄武岩数据是杂乱无章的,甚至可能包括一些分析错误、命名错误的数据等(图 3红色斜十字图例)。其次,较可靠的玄武岩数据(图 3中以不同颜色圆圈表示)也不呈矩形分布,而是一个不规则的近椭圆的多边形。此外,可靠的玄武岩数据也不受SiO2为45%或52%的下限和上限的制约(图 3)。
5.3 TAS分类中贯穿的岩石命名非此即彼的思路是否合适
TAS分类统一了岩石名称,例如,SiO2=52%是玄武岩和玄武安山岩之间的界线,超过了就不是玄武岩而是玄武安山岩。SiO2=51.6%属于玄武岩,而SiO2=52.3%则属于玄武安山岩。这样的命名符合TAS分类的原则,但不一定合理。例如前面介绍的笔者在云南研究的一个剖面[35],该剖面上火山岩的SiO2含量在52%~54%之间,属于一个系列,是玄武岩的一个自然组合,人为地把它们分割为玄武岩和玄武安山岩2个岩区显然不合适。
6. TAS分类调整
6.1 从数据出发,让数据发声
TAS分类需要调整,如何调整,可能不同学者有不同的见解。本文从数据出发,将全球全部火山岩(24万多个)数据投进TAS图解(图 4),发现全球火山岩主要属于基性岩,主要为正常系列的岩石,碱性岩很少。
![]() 图 4 全球火山岩在TAS图解中的分布密度(图中代号同图 1)Figure 4. Distribution density map of global volcanic rocks in the TAS diagram
图 4 全球火山岩在TAS图解中的分布密度(图中代号同图 1)Figure 4. Distribution density map of global volcanic rocks in the TAS diagram前文已经指出,全球碱性岩的数量很少,但分类很繁琐。从图 4看,碱性岩系列中碧玄岩(U1)的数据量最多,其次是响岩(Ph),而碧玄质响岩(U3)几乎很少有数据。响岩则相当复杂,分别集中在2个区域,且大部分响岩落入粗面岩区(T)。看来,Ph与T两个岩区之间的界线不合适(图 4)。
6.2 火山岩划分为3个系列
众所周知,全球火山岩分为3个系列,即正常系列、粗玄岩系列和碱性岩系列,这3个系列也是TAS图解采用的方案。本次研究表明,3个系列的区分也不容易,因为3个系列之间的重叠很大,尤其在基性岩部分。为此,笔者对数据库中的数据进行归并,例如对于正常系列,是从数据库中选取具有上述root name的数据,删去数据中标注有“碱性”作为附加名称的数据,如basalt, alkaline; basalt, shoshonitic; basalt, latitic; basalt, trachytic; basalt, trachydoleritic; andesite, alkaline; andesite, latitic; andesite, trachytic; dacite, alkaline; dacite, trachytic; rhyolite, alkaline; rhyolite, trachytic等,有些属于地方性的术语难以归类,则直接把数据投在TAS图中决定取舍。将删去的上述数据归入粗玄岩系列。其次,删去上述root name中含似长石类(白榴石、黄玉、霞石、黄长石、蓝方石等)和碱性暗色矿物(钠铁闪石、钠闪石、霓石、霓辉石等)的数据及过碱性岩石(如basalt, basanitic; basalt, nepheline; basalt, peralkaline; basalt, tephritic; rhyolite, comenditic; rhyolite, peralkaline; rhyolite, topaz; rhyolite, soda等),将删去的上述岩石并入碱性岩系列。对于粗玄岩系列,则将包含有似长石类和碱性暗色矿物的岩石及过碱性的岩石归入碱性岩系列。
(3)调整的过程即不断试错的过程。科学研究本身就是一个不断试错的过程,在不断试错中逼近真理。在试错过程中,笔者主要着眼于正常系列的研究,主要集中在2个方面:一是如何减少正常系列与粗玄岩系列之间的重叠;另一个是正常系列的不同岩区如何划分?图 5显示了全球正常系列岩石的自然分布。从图 5看,正常系列的数据主要集中在系列的两端:基性端员是玄武岩,数据量最多,主要集中在SiO2=50%左右,与图 4一致;酸性端员是流纹岩,数据量显著减少。正常系列数据量最少的部分在流纹岩与英安岩的界线附近(图 5)。
![]() 图 5 全球正常系列火山岩数据分布趋势图(图中代号同图 1)Figure 5. Distribution map of global normal series volcanic rocks
图 5 全球正常系列火山岩数据分布趋势图(图中代号同图 1)Figure 5. Distribution map of global normal series volcanic rocks正常系列之间不同岩区的界线如何确定?笔者考虑了多种方案,最后采用数据中出现basalt、andesite、dacite和rhyolite根名的术语(不考虑picrobasalt和basalt-andesite,它们不是根名)。上述岩区的界线与早先的界线基本一致,由于删去了玄武安山岩区,玄武岩与安山岩之间的界线大致在SiO2=55%(图 6)。
此外,经过上述处理,全球3个系列的数据仍然有很大的重叠(图 7)。为此,笔者开发了一个小软件(密度分布函数方法),以解决这个问题[49]。
7. 新的火山岩TAS分类
图 8是图 7的归纳,是本文提出的火山岩TAS分类图。新方案尽可能沿用早先的命名(只新增了一个碱流岩区),但范围有所改变,岩区数目有所减少。以下简要说明之。
7.1 正常系列
正常系列包括玄武岩、安山岩、英安岩和流纹岩4个岩区。早先的分类中还有玄武安山岩和苦橄玄武岩2个岩区(图 1),本文建议取消上述2个岩区(理由详见参考文献[40])。新TAS图玄武岩区大大扩展了,上限在SiO2=55%左右,且不设下限(涵盖了早先的苦橄质玄武岩区)。此外,安山岩和英安岩之间的界线大体不变(SiO2=63%),英安岩与流纹岩之间的界线从70%左右调整到68%左右(图 8)。
正常系列与粗玄岩系列的界线是根据2个系列之间的重叠最小程度拟合的(图 8),该界线在中酸性岩部分大体相当于O系列与S系列的分界线,在基性岩部分大体沿Ir曲线的方向(图 8)。早先的TAS图解对于流纹岩的Na2O+K2O没有限制(R岩区,对比图 1和图 8),本文将其限制在上述分界线(Ir)以下,以上为碱性岩系列的碱流岩。
7.2 粗玄岩系列
粗玄岩系列包括粗玄岩、粗安岩和粗面岩3个岩区,其与正常系列的界线前面已经介绍,二者的界线(包括与碱性岩系列)在基性岩部分重叠较多,很难准确区分。粗玄岩系列以基性岩部分数据最多,中性岩部分数据明显减少,酸性岩部分数据更少(对比图 1和图 8)。粗玄岩系列的粗玄岩岩区范围有很大的扩展,包括全部S1区、S2区的一部分和B区的一部分(大体与Ir界线重叠);粗安岩大体相当于早先的S3区,包括一部分S2区,粗面岩大体相当于早先的T区,但是范围大大缩小了,T区由开口变为封闭(图 8)。
7.3 碱性岩系列
碱性岩系列也分为3个区:碧玄岩区、响岩区和碱流岩区(pantellerite)。碱性岩系列与粗玄岩系列的界线以岩石中出现似长石和碱性暗色矿物为标志,与早先的TAS图解界线接近(图 8)。早先的TAS图解将碱性岩系列划分为5个岩区(图 1),由于似长石岩的数量很少(数据库仅有207件),且并不是以SiO2=45%作为界线与碧玄岩分开,故取消该岩区,将其合并入碧玄岩区(包括数量更少的响岩质碧玄岩和响岩质碱玄岩)。新TAS图解的碧玄岩区范围扩大了,包括早先的F区、部分Pc区和大部分U2区(图 8)。响岩区包括Ph、U3区和部分T区。碱性岩系列最大的变化是增加了一个碱流岩区,包括碱流岩(pantellerite)、钠闪碱流岩(comendite)、过碱性流纹岩(peralkaline-rhyolite)等,主要分布在早先R区的上部和T区的右部(图 8)。这个岩区在TAS图解中没有标出,是本文新设的。但是,Le Maitre等[7]早已指出,R区的根名是流纹岩,假若过碱性指数(Na2O+K2O)/Al2O3(分子比) > 1,则还可进一步分出过碱性流纹岩。看来,Le Maitre等有先见之明,可能由于某些原因没有在TAS图解上有所表示。本次研究从数据库检索出相当数量的碱流岩数据,使之可以构成一个岩区(对比图 1和图 8)。
8. 新的TAS图解的使用
早先的TAS图解使用是有严格规定的:①该图解只能应用于新鲜岩石,故要删去H2O+ > 2%和CO2 > 0.5%的岩石;所有分析均在无H2O和CO2的基础上重新计算为100%[10]。而使用新的TAS分类(图 8)则无上述限制,不论火山岩是否经历了蚀变、变质、也无需重新计算为100%。②早先的分类要把化学分析数据换算为CIPW标准矿物,再根据计算中霞石标准的有无确定所属的岩区,碱性岩的计算尤其麻烦。而使用本文推荐的方案,上述计算不再需要,只要将数据投在TAS图解上即可。③早先的分类命名原则是数据点投到哪个岩区即属于哪个名称,本文不这样规定。从图 7看,不同岩区的重叠是普遍的,尤其基性岩部分。因此,新的TAS图解的界线具有过渡性质,不存在岩石名称命名唯一性的规定。例如一个剖面或一套岩石组合的数据,投在TAS图解上可能出现跨岩区分布的情况,则不一定属于不同的岩石。因此,在使用本分类方案时,应根据岩石分布密度确定它们是否属于1个组合或2个不同的组合。如图 2-e所示,苦橄质玄武岩按照MgO含量的差异至少可以分为2个组合。对比图 7和图 8,碱流岩也明显可以分为2个亚类(图 8碱性岩系列蓝色线条圈定的酸性岩部分)。
9. 存在的问题
(1)本文提出的TAS分类方案,是以全球24万个火山岩数据作为基础的,是数据分析的结果。但是,由于方法上的局限,上述结果并不令人满意。今后的数据量会更多,如何对这些数据进行处理,方法学的突破是一个急待解决的问题。
(2)超基性岩与基性岩的界线定在SiO2=45%,它是什么来历?这是一个基本的问题,笔者几乎穷尽了全部超基性岩数据,仍然没有解决这个问题。
(3)碱性岩系列在TAS图解中呈“人”字形分布是早先想不到的,尤其在酸性岩部分,碱性岩系列与正常系列直接接触也令人费解。笔者曾经尝试查找粗玄岩系列的酸性岩,由于数据量少而无法表示。众所周知,火山岩3个系列主要是依据火山岩的硅是否饱和来划分的:硅过饱和为正常系列,硅饱和为粗玄岩系列,硅不饱和为碱性岩系列。而具体识别时的标志却是以是否出现标准矿物霞石(区分正常系列与粗玄岩系列)和是否出现实际碱性矿物作为标志(划分碱性岩系列的标志)。上述规定表现在TAS图解上,则是按照随着SiO2含量的变化总碱量(NaO+K2O)的变化来决定的,其含义是硅饱和程度与总碱量之间存在一定的相关关系:总碱量低,硅饱和程度高;反之总碱量高,硅饱和度低。但是,总碱量与硅饱和程度是2个不同的概念,总碱量与硅饱和度是否一一对应也不清楚。上述标志还要求:无霞石标准矿物的,总碱量低;有霞石标准矿物的,总碱量较高;有实际矿物霞石出现的,总碱量最高。岩石学自身是否有上述规律呢?霞石的化学成分为KNa3[AlSiO4]4,霞石的确富碱,但是,全岩总碱量并不是由霞石一种矿物决定的,霞石出现的岩石其总碱量并不一定是最高的。数据库有大量不含霞石的岩石,其总碱量甚至比含霞石的岩石还高。由此说明,有实际矿物霞石出现与总碱量之间并无一一对应的关系。看来,TAS图解的理论基础还需要进一步讨论。
10. 小结
(1)TAS图解是IUGS推荐的火山岩分类方案,已经使用40年了,已成为学术界的共识。在大数据时代,从大数据的眼光看,TAS图解存在一些问题,需要加以调整和改进。
(2)本文收集了全球火山岩数据,考察了这些数据在TAS图解上的表现,采用大数据方法对上述数据进行处理,得出了新的火山岩TAS分类方案。早先的TAS图解分为15个岩区,互相之间以直线和斜线分割;本文将其缩减为10个岩区,其间的界线按照数据分布的疏密分割。本文建议取消苦橄质玄武岩、玄武安山岩、玄武粗面岩、碱玄质响岩、响岩质碱玄岩、似长石岩6个岩区,增加1个碱流岩岩区。
(3)本文的研究是初步的,提出的方案可能还存在许多问题。新的TAS分类是根据大量的数据确定的,实际上本文的数据远远不够。如果能收集到更多的数据,将能够得到更好的分类。
(4)TAS图解的3个系列主要是依据火山岩的硅是否饱和来划分的,具体识别标志却是以是否出现标准矿物霞石(区分正常系列与粗玄岩系列)和是否出现实际碱性矿物作为标志(区分粗玄岩系列与碱性岩系列的标志),而表现在TAS图上则是按照随着SiO2含量的变化总碱量(Na2O+K2O)的变化来决定的。上述3个标志之间是什么关系?能否一一对应?看来,TAS图解的理论基础可能也需要进一步讨论。
本文只是抛砖引玉,希望能够引起大家的关注,开启利用大数据方法对TAS分类的重新研究。
后记:笔者开始只是感觉TAS图解可能存在一些不足,遂开启了对全球数据的研究。随着研究的进展,发现TAS图解存在的问题不少。对数据进行反复的琢磨,尝试各种方法,初步得出了一些结果。这些结果与早先的TAS分类大相径庭,是这些结果合理还是早先的分类合适?本文无法定论。研究的过程令人非常纠结,因为,早先的研究应当说是经过了千锤百炼的,但是,在全球数据基础上给出的结果却是令人震撼的。随着科学的发展,岩石命名已经很少有人关注了。笔者认为,火成岩分类命名可能需要重新认识,希望本次研究能够引起学术界的关注,揭开火成岩分类命名研究新的一页。
-
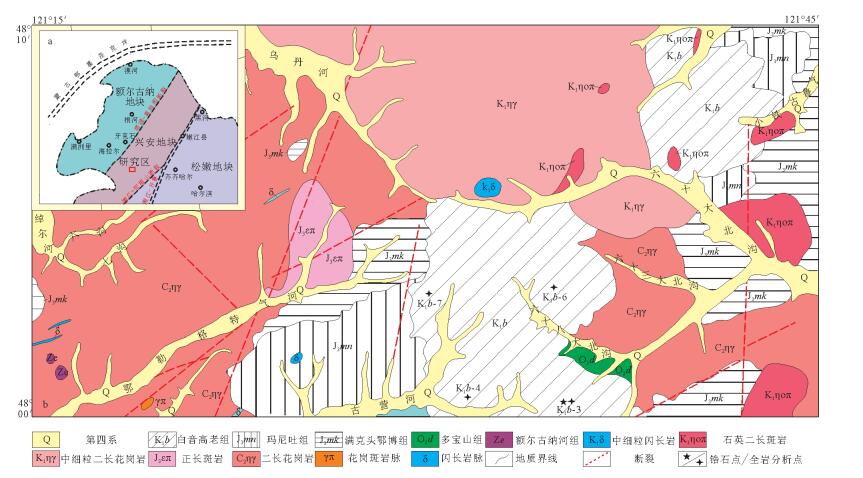
图 1 研究区大地构造位置(a)[19]和区域地质简图(b)①②
Figure 1. Sketch showing tectonic setting and regional simplified geological map of the study area
图 4 微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图及稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线图[34]
Figure 4. Primitive mantle-normalized trace element patterns and chondrite-normalized REE patterns
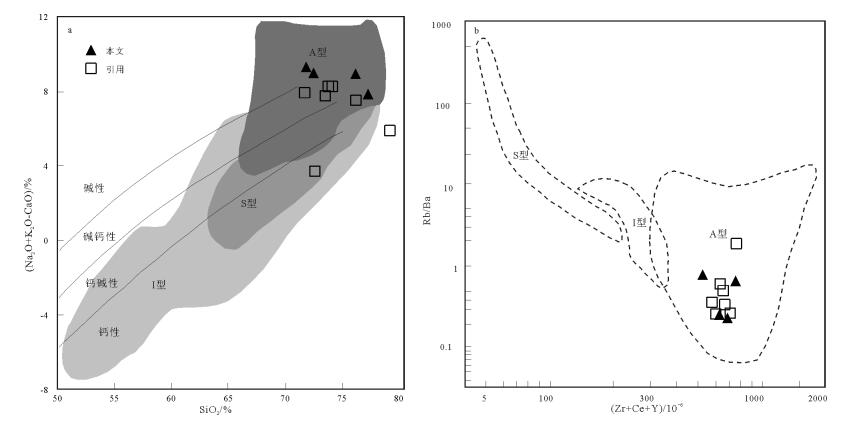
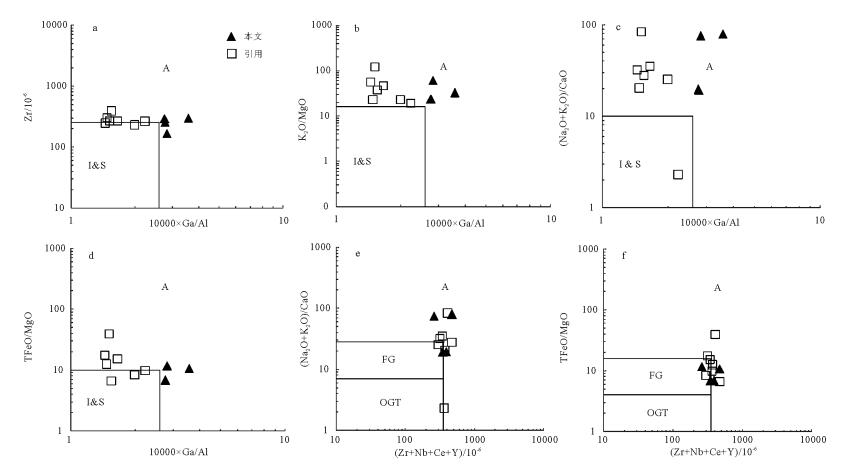
图 6 流纹岩岩石成因类型(A型、I型、S型)判别图[42]
I,S,A—I型,S型,A型花岗岩;FG—高分异I型花岗岩;OGT—未分异花岗岩
Figure 6. Discrimination diagram of Petrogenetic type (A type, I type, S type) for the rhyolite
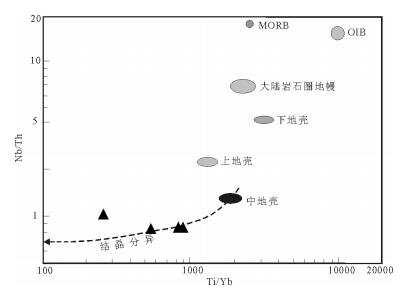
图 7 流纹岩的Ti/Yb-Nb/Th图解[49]
MORB—洋中脊玄武岩;OIB—岛弧玄武岩
Figure 7. Plot of Ti/Yb versus Nb/Th of the rhyolites
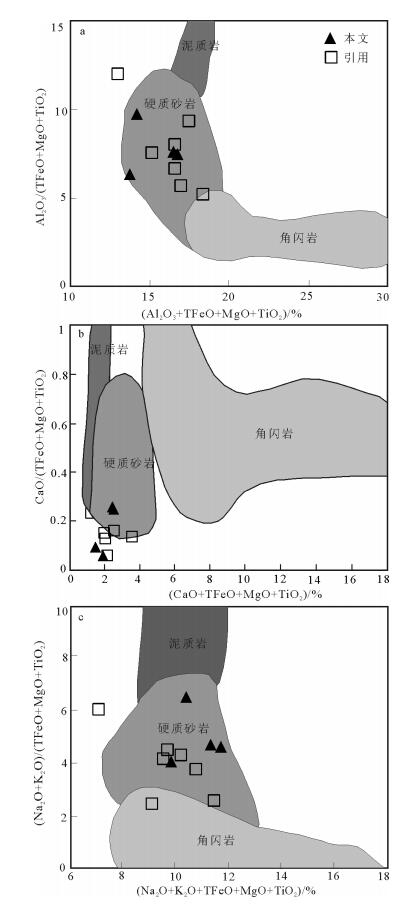
图 8 A型流纹岩源区判别图解[61]
Figure 8. Discrimination diagrams of source regions for the A-type rhyolites
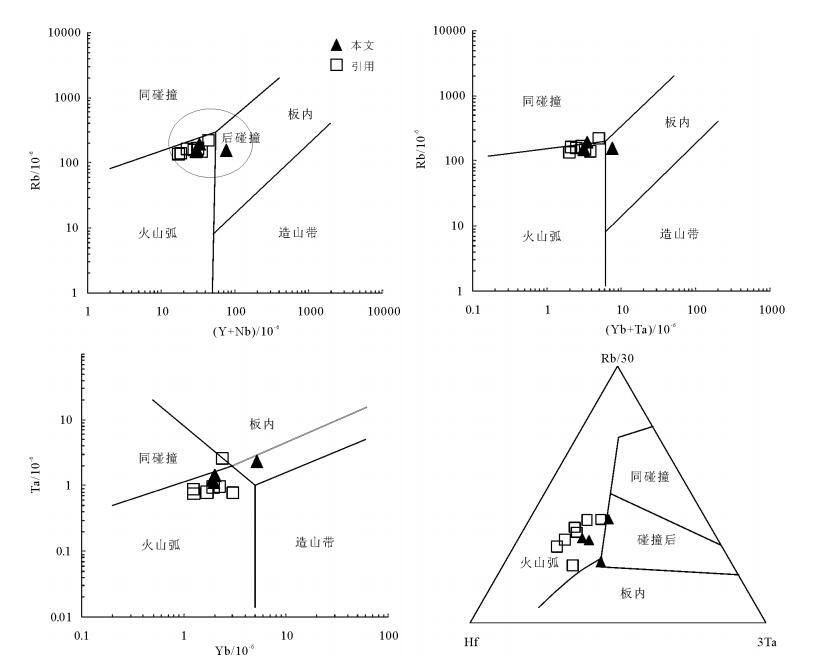
图 9 流纹岩形成构造环境判别[65]
Figure 9. Diagrams of tectonic environment discrimination of rhyolites
表 1 塔尔气流纹岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb测年结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb results of the Taerqi rhyolites
样品测点 Th/10-6 U/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 表面年龄/Ma 207Pb/206Pb 土1σ 207Pb/235U 土1σ 206Pb/238U 土1σ 207Pb/206Pb 土1σ 207Pb/235U 土1σ 206Pb/238U 土1σ K1b-3-1 1062 725 1.46 0.0583 0.0046 0.163 0.012 0.02025 0.00034 543 172 153 11 129 2 K1b-3-2 453 433 1.05 0.0567 0.0047 0.161 0.012 0.02141 0.00050 480 187 152 10 137 3 K1b3-3 765 738 1.04 0.0555 0.0040 0.156 0.011 0.02069 0.00037 432 161 147 9 132 2 K1b-3-4 441 707 0.62 0.0564 0.0048 0.158 0.013 0.02055 0.00036 478 158 149 12 131 2 K1b-3-5 1243 1092 1.14 0.0513 0.0037 0.143 0.0096 0.02080 0.00035 254 167 135 9 133 2 K1b-3-6 1134 933 1.22 0.0528 0.0040 0.143 0.011 0.01982 0.00036 320 142 136 10 127 2 K1b-3-9 649 734 0.88 0.0485 0.0032 0.143 0.0087 0.02125 0.00036 124 148 136 8 136 2 K1b-3-10 546 506 1.08 0.0580 0.0044 0.170 0.013 0.02122 0.00043 528 167 159 11 135 3 K1b-3-12 1342 1107 1.21 0.0496 0.0031 0.141 0.0085 0.02062 0.00035 176 142 134 8 132 2 K1b-3-13 641 596 1.08 0.0567 0.0043 0.161 0.012 0.02107 0.00044 480 167 152 10 134 3 K1b-3-15 498 443 1.12 0.0591 0.0054 0.159 0.014 0.02041 0.00044 572 200 150 12 130 3 表 2 塔尔气流纹岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 2 Major, trace and REE composition of the Taerqi rhyolites
样品号 K1b-3 K1b-4 K1b-6 K1b-7 MIN* MAX* VER* SiO2 72.20 71.60 77.00 75.90 71.48 78.90 74.41 TiO2 0.28 0.27 0.22 0.18 0.05 0.29 0.21 Al2O3 14.60 14.80 11.75 12.85 11.79 15.79 14.11 Fe2O3 0.22 0.23 0.23 0.16 0.67 2.05 1.23 MnO 0.05 0.06 0.06 0.05 0.05 0.16 0.07 MgO 0.21 0.22 0.14 0.09 0.04 0.21 0.13 CaO 0.49 0.49 0.10 0.12 0.10 2.83 0.56 Na2O 4.51 4.53 3.44 3.57 1.68 3.82 3.19 K2O 4.92 5.11 4.50 5.46 3.94 5.46 4.63 P2O5 0.05 0.06 0.03 0.03 0.01 0.15 0.10 LOI 0.46 0.59 0.39 0.44 0.50 1.49 0.63 σ43 3.05 3.25 1.85 2.48 1.04 2.48 1.99 A/CNK 1.07 1.07 1.10 1.07 1.05 1.48 1.27 A/NK 1.14 1.14 1.11 1.09 1.26 1.69 1.39 A.I 0.87 0.88 0.90 0.92 0.59 0.92 0.73 TZr/℃ 844 858 860 804 817 911 857 La 32.20 36.40 36.60 22.50 12.51 47.28 27.10 Ce 66.10 67.80 99.10 60.20 40.50 124.50 62.69 Pr 6.59 7.24 10.05 5.04 3.98 13.20 6.46 Nd 23.80 25.70 36.10 17.70 15.35 48.87 23.56 Sm 4.41 4.34 7.82 3.52 3.19 9.31 4.53 Eu 0.81 0.93 0.56 0.29 0.11 0.88 0.71 Gd 3.56 3.82 7.44 3.07 3.15 7.31 4.08 Tb 0.46 0.51 1.19 0.45 0.41 0.92 0.58 Dy 3.09 3.15 8.36 3.11 2.12 4.18 3.04 Ho 0.59 0.61 1.62 0.62 0.40 0.86 0.61 Er 1.82 1.86 5.40 1.99 1.21 2.89 1.89 Tm 0.28 0.28 0.75 0.28 0.17 0.42 0.27 Yb 1.90 1.98 5.22 2.03 1.26 3.05 1.99 Lu 0.32 0.30 0.83 0.31 0.19 0.50 0.31 ΣREE 145.93 154.92 221.04 121.11 84.63 264.17 137.83 LREE 133.91 142.41 190.23 109.25 75.64 244.04 125.05 HREE 12.02 12.51 30.81 11.86 8.99 20.13 12.78 LREE/HREE 11.14 11.38 6.17 9.21 8.41 12.12 9.85 (La/Yb)N 12.16 13.19 5.03 7.95 7.07 11.12 10.54 δEu 0.62 0.70 0.22 0.27 0.11 0.33 0.55 δCe 1.11 1.02 1.27 1.39 1.41 1.22 1.17 Y 16.00 17.90 44.40 17.20 6.62 21.41 14.14 Rb 147 155 153 191.50 132.61 217.60 159.32 Sr 124 133.50 55.20 38.30 26.00 141.22 94.53 Ba 923 1055 253 260 85.29 798.58 514.36 Nb 13.50 12.80 31.10 15.90 10.77 25.96 14.09 Ta 1.20 1.10 2.30 1.40 0.74 2.57 1.09 Zr 253 291 298 166 227 387 278 Hf 6.60 7.10 9.40 5.20 4.30 17.42 8.02 Th 17.20 16.40 29.80 21.50 - - - U 5.61 5.89 7.13 5.31 - - - V 12.00 16.00 16.00 7.00 3.52 28.61 9.27 Cr 50.00 50.00 60.00 50.00 2.97 6.35 4.37 Ga 21.40 21.60 22.20 19.20 9.69 17.01 12.82 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素为10-6 -
赵越, 杨振宇, 马醒华.东亚大地构造发展的重要转折[J].地质科学, 1994, 2:105-119. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX402.000.htm 李锦轶, 莫申国, 和政军, 等.大兴安岭北段地壳左行走滑运动的时代及其对中国东北及邻区中生代以来地壳构造演化重建的制约[J].地学前缘, 2004, 3:157-168. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200403022.htm Li J Y. Permian geodynamic setting of Northeast China and adjacent regions:closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean and subduction of the Pa-leo-Pacific Plate[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2006, 26(3/4):207-224. Li J Y. Permian geodynamic setting of Northeast China and adjacent regions:closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean and subduction of the Pa-leo-Pacific Plate[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2006, 26(3/4):207-224.
Wu F Y, Sun D Y, Ge W C, et al. Geochronology of the Phanero-zoic granitoids in northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sci-ences, 2011, 41(1):1-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.11.014 Wu F Y, Sun D Y, Ge W C, et al. Geochronology of the Phanero-zoic granitoids in northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sci-ences, 2011, 41(1):1-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.11.014
许文良, 王枫, 裴福萍, 等.中国东北中生代构造体制与区域成矿背景:来自中生代火山岩组合时空变化的制约[J].岩石学报, 2013, 2:339-353. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201302002.htm Wang F, Zhou X H, Zhang L C, et al. Late Mesozoic volcanism in the Great Xing'an Range (NE China):Timing and implications for the dynamic setting of NE Asia[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Let-ters, 2006, 251(1/2):179-198. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2054765896&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Wang F, Zhou X H, Zhang L C, et al. Late Mesozoic volcanism in the Great Xing'an Range (NE China):Timing and implications for the dynamic setting of NE Asia[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Let-ters, 2006, 251(1/2):179-198. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2054765896&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
张吉衡.大兴安岭地区中生代火山岩的年代学格架[D].吉林大学硕士学位论文, 2006. 张吉衡.大兴安岭中生代火山岩年代学及地球化学研究[D].中国地质大学博士学位论文, 2009. 苟军.满洲里南部白音高老组火山岩的形成时代与岩石成因[D].吉林大学硕士学位论文, 2010. Zhang J H, Gao S, Ge W C, et al. Geochronology of the Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Great Xing'an Range, northeastern China:Implications for subduction-induced delamination[J]. Chemical Geology, 2010, 276(3/4):144-165. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1988557437&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Zhang J H, Gao S, Ge W C, et al. Geochronology of the Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Great Xing'an Range, northeastern China:Implications for subduction-induced delamination[J]. Chemical Geology, 2010, 276(3/4):144-165. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1988557437&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
佘宏全, 李进文, 向安平, 等.大兴安岭中北段原岩锆石U-Pb测年及其与区域构造演化关系[J].岩石学报, 2012, 2:571-594. http://www.cnki.com.cn/article/cjfdtotal-ysxb201202019.htm 杨扬, 高福红, 陈井胜, 等.赤峰地区中生代火山岩锆石U-Pb年代学证据[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 2:257-268. http://www.cnki.com.cn/article/cjfdtotal-ccdz2012s2029.htm 苟军.满洲里南部中生代火山岩的时代、成因及构造背景[D].吉林大学博士学位论文, 2013. 董玉, 葛文春, 杨浩, 等.大兴安岭中段早白垩世白音高老组火山岩年代学与地球化学研究[C]//2014年中国地球科学联合学术年会, 2014. 张亚明, 杜玉春, 崔天日, 等.扎兰屯地区白音高老组火山岩特征及成因[J].金属矿山, 2014, 6:101-104. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS201406021.htm 秦涛, 郑常青, 崔天日, 等.内蒙古扎兰屯地区白音高老组火山岩地球化学、年代学及其地质意义[J].地质与资源, 2014, 2:146-153. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJSD201402012.htm 张乐彤, 李世超, 赵庆英, 等.大兴安岭中段白音高老组火山岩的形成时代及地球化学特征[J].世界地质, 2015, 1:44-54. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ201501007.htm 王雄, 陈跃军, 李勇, 等.大兴安岭中北段塔尔气地区早白垩世白音高老组火山岩地球化学特征及意义[J].世界地质, 2015, 1:25-33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ201501005.htm 王兴安, 徐仲元, 刘正宏, 等.大兴安岭中部柴河地区钾长花岗岩的成因及构造背景:岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb同位素年代学的制约[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(8):2647-2655. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/ysxb201208029.htm 刘建辉, 刘敦一, 张玉海, 等.使用SHRIMP测定锆石铀-铅年龄的选点技巧[J].岩矿测试, 2011, 3:265-268. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/ykcs201103010.htm 吴元保, 郑永飞.锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J].科学通报, 2004, 16:1589-1604. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/kxtb200416001.htm Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Gao S, et al. In situ analysis of major and trace el-ements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 257(1/2):34-43. http://medsci.cn/sci/show_paper.asp?id=4405145487 Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Gao S, et al. In situ analysis of major and trace el-ements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 257(1/2):34-43. http://medsci.cn/sci/show_paper.asp?id=4405145487
Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Zong K Q, et al. Reappraisement and refine-ment of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LAICP-MS[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(15):1535-1546. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4 Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Zong K Q, et al. Reappraisement and refine-ment of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LAICP-MS[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(15):1535-1546. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4
Ludwig K R.. User's Manual for Isoplot/Ex, Version 3.00. a geo-chronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J]. Berkeley Geochronolo-gy Center Special Publication, 2003, 4(2):1-70 Ludwig K R.. User's Manual for Isoplot/Ex, Version 3.00. a geo-chronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J]. Berkeley Geochronolo-gy Center Special Publication, 2003, 4(2):1-70
Gao S, Liu X M, Yuan H L, et al. Determination of Forty Two Major and Trace Elements in USGS and NIST SRM Glasses by La-ser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2002, 26(2):181-196. doi: 10.1111/ggr.2002.26.issue-2 Gao S, Liu X M, Yuan H L, et al. Determination of Forty Two Major and Trace Elements in USGS and NIST SRM Glasses by La-ser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2002, 26(2):181-196. doi: 10.1111/ggr.2002.26.issue-2
高剑峰, 陆建军, 赖鸣远, 等.岩石样品中微量元素的高分辨率等离子质谱分析[J].南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 6:844-850. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJDZ200306013.htm 钟玉芳, 马昌前, 佘振兵.锆石地球化学特征及地质应用研究综述[J].地质科技情报, 2006, 1:27-34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200601004.htm 李长民.锆石成因矿物学与锆石微区定年综述[J].地质调查与研究, 2009, 3:161-174. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ200903004.htm Le Bas M J, Le Maitre R W. A chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkali-silica diagram[J]. Journal of petrolo-gy, 1986, 27(3):745-750. doi: 10.1093/petrology/27.3.745 Le Bas M J, Le Maitre R W. A chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkali-silica diagram[J]. Journal of petrolo-gy, 1986, 27(3):745-750. doi: 10.1093/petrology/27.3.745
Irvine T N, Baragar W R A. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Scienc-es, 1971, 8(5):523-548. doi: 10.1139/e71-055 Irvine T N, Baragar W R A. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Scienc-es, 1971, 8(5):523-548. doi: 10.1139/e71-055
Peccerillo A, Taylor S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey[J]. Con-tributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1):63-81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745 Peccerillo A, Taylor S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey[J]. Con-tributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1):63-81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745
Le Maitre R W, Bateman P, A D. A classification of igneous rocks and glossary of terms:Recommendations of the International Union of Geological Sciences Subcommission on the Systematics of Igneous Rocks[M]. Oxford:Blackwell, 1989. Le Maitre R W, Bateman P, A D. A classification of igneous rocks and glossary of terms:Recommendations of the International Union of Geological Sciences Subcommission on the Systematics of Igneous Rocks[M]. Oxford:Blackwell, 1989.
Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5):635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2 Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5):635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1):313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19 Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1):313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
王中刚, 于学元, 赵振华.稀土元素地球化学[M].北京:科学出版社, 1989:133-246. 熊兴国, 岳龙, 徐安全, 等.西藏羌塘达尔应强过铝花岗岩地球化学特征及地球动力学意义[J].沉积与特提斯地质, 2006, 4:40-46. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD200604005.htm Wedepohl K H. The composition of the continental crust[J]. Geo-chimica et cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(7):1217-1232. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00038-2 Wedepohl K H. The composition of the continental crust[J]. Geo-chimica et cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(7):1217-1232. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00038-2
刘一鸣, 李才, 王明, 等.藏北羌塘盆地望湖岭组流纹岩地球化学特征及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2014, 30(11):1759-1767. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201411012.htm 陈根文, 邓腾, 刘睿, 等.西天山阿吾拉勒地区二叠系塔尔得套组双峰式火山岩地球化学研究[J].岩石学报, 2015, (01):105-118. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201501008.htm 李莉, 白云山, 牛志军, 等.藏北羌塘中部劳日特错花岗斑岩体的特征及构造意义[J].地质通报, 2004, 23(2/3):1040-1045. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2004Z2030.htm 李宁波, 单强, 张永平, 等.西天山阿吾拉勒地区A型流纹斑岩的初步研究[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2012, 4:624-633. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201204018.htm Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell B W. A-type granites:geo-chemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contri-butions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95(4):407-419. doi: 10.1007/BF00402202 Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell B W. A-type granites:geo-chemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contri-butions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95(4):407-419. doi: 10.1007/BF00402202
邱检生, 俆夕生.火成岩岩石学[M].北京:科学出版社, 2010:207-235. Frost B R, Barnes C G, Collins W J, et al. A geochemical classifica-tion for granitic rocks[J]. Journal of petrology, 2001, 42(11):2033-2048. doi: 10.1093/petrology/42.11.2033 Frost B R, Barnes C G, Collins W J, et al. A geochemical classifica-tion for granitic rocks[J]. Journal of petrology, 2001, 42(11):2033-2048. doi: 10.1093/petrology/42.11.2033
Loiselle M C, Wones D R. Characteristics and origin of anorogen-ic granites[J]. Geological Society of America Abstracts with Pro-grams, 1979, 11(7):468. Loiselle M C, Wones D R. Characteristics and origin of anorogen-ic granites[J]. Geological Society of America Abstracts with Pro-grams, 1979, 11(7):468.
吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等.花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J].岩石学报, 2007, 6:1217-1238. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/ysxb200706000.htm King P L, White A J R, Chappell B W, et al. Characterization and origin of aluminous A-type granites from the Lachlan Fold Belt, southeastern Australia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1997, 3(38):371-391. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2144081161&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn King P L, White A J R, Chappell B W, et al. Characterization and origin of aluminous A-type granites from the Lachlan Fold Belt, southeastern Australia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1997, 3(38):371-391. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2144081161&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Watson E B, Harrison T M. Zircon saturation revisited:tempera-ture and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983, 64(2):295-304. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(83)90211-X Watson E B, Harrison T M. Zircon saturation revisited:tempera-ture and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983, 64(2):295-304. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(83)90211-X
李献华, 周汉文, 李正祥, 等.川西新元古代双峰式火山岩成因的微量元素和Sm-Nd同位素制约及其大地构造意义[J].地质科学, 2002, 3:264-276. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/dzkx200203001.htm Mushkin A. The Petrogenesis of A-type Magmas from the Amram Massif, Southern Israel[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2003, 44(5):815-832. doi: 10.1093/petrology/44.5.815 Mushkin A. The Petrogenesis of A-type Magmas from the Amram Massif, Southern Israel[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2003, 44(5):815-832. doi: 10.1093/petrology/44.5.815
陈志洪, 邢光福, 姜杨, 等.华夏陆块古元古代A型流纹斑岩的发现及其地质意义[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2013, 3:499-510. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201303016.htm Wu F Y, Sun D Y, Li H M, et al. A-type granites in northeastern China:age and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 187(1):143-173. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1988317790&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Wu F Y, Sun D Y, Li H M, et al. A-type granites in northeastern China:age and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 187(1):143-173. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1988317790&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
丁烁, 黄慧, 牛耀龄, 等.东昆仑高Nb-Ta流纹岩的年代学、地球化学及成因[J].岩石学报, 2011, (12):3603-3614. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/ysxb201112009.htm Yang J H, Wu F Y, Chung S L, et al. A hybrid origin for the Qian-shan A-type granite, northeast China:Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic evidence[J]. Lithos, 2006, 89(1):89-106. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222426460_A_hybrid_origin_for_the_Qianshan_A-type_granite_northeast_China_Geochemical_and_Sr-Nd-Hf_isotopic_evidence Yang J H, Wu F Y, Chung S L, et al. A hybrid origin for the Qian-shan A-type granite, northeast China:Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic evidence[J]. Lithos, 2006, 89(1):89-106. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222426460_A_hybrid_origin_for_the_Qianshan_A-type_granite_northeast_China_Geochemical_and_Sr-Nd-Hf_isotopic_evidence
苟军, 孙德有, 赵忠华, 等.满洲里南部白音高老组流纹岩锆石U-Pb定年及岩石成因[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(1):333-344. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/YSXB201001038.htm Green T H. Significance of Nb/Ta as an indicator of geochemical processes in the crust-mantle system[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120(3):347-359. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1972337416&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Green T H. Significance of Nb/Ta as an indicator of geochemical processes in the crust-mantle system[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120(3):347-359. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1972337416&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Hofmann A W. Chemical differentiation of the earth:the relation-ship between mantle, continental crust, and oceanic crust[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1988, 90(3):297-314. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(88)90132-X Hofmann A W. Chemical differentiation of the earth:the relation-ship between mantle, continental crust, and oceanic crust[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1988, 90(3):297-314. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(88)90132-X
张玉涛, 张连昌, 英基丰, 等.大兴安岭北段塔河地区早白垩世火山岩地球化学及源区特征[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(11):2811-2822. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200711013.htm Kerrich R, Polat A, Wyman D, et al. Trace element systematics of Mg-, to Fe-tholeiitic basalt suites of the Superior Province:impli-cations for Archean mantle reservoirs and greenstone belt genesis[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46(1):163-187. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00059-0 Kerrich R, Polat A, Wyman D, et al. Trace element systematics of Mg-, to Fe-tholeiitic basalt suites of the Superior Province:impli-cations for Archean mantle reservoirs and greenstone belt genesis[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46(1):163-187. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00059-0
李昌年.火成岩微量元素岩石学[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1992:1-195. Douce A E P. What do experiments tell us about the relative con-tributions of crust and mantle to the origin of granitic magmas[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 1999, 168(1):55-75. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1999.168.01.05 Douce A E P. What do experiments tell us about the relative con-tributions of crust and mantle to the origin of granitic magmas[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 1999, 168(1):55-75. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1999.168.01.05
张本仁.大陆造山带地球化学研究:Ⅰ岩石构造环境地球化学判别的改进[J].西北地质, 2001, 3:1-17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI200103000.htm 林强, 葛文春, 吴福元, 等.大兴安岭中生代花岗岩类的地球化学[J].岩石学报, 2004, 3:403-412. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200403004.htm 葛文春, 吴福元, 周长勇, 等.大兴安岭中部乌兰浩特地区中生代花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2005, 3:749-762. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/ysxb200503016.htm Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. Trace element discrimina-tion diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4):956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956 Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. Trace element discrimina-tion diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4):956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
Eklund O, Konopelko D, Rutanen H, et al. 1.8 Ga Svecofennian post-collisional shoshonitic magmatism in the Fennoscandian shield[J]. Lithos, 1998, 45(1):87-108. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2019402209&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Eklund O, Konopelko D, Rutanen H, et al. 1.8 Ga Svecofennian post-collisional shoshonitic magmatism in the Fennoscandian shield[J]. Lithos, 1998, 45(1):87-108. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2019402209&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn




 下载:
下载: