LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb ages, geochemistry and Hf isotopic composition of Jinbaogou granite porphyry in eastern Hebei and their geological implications
-
摘要:
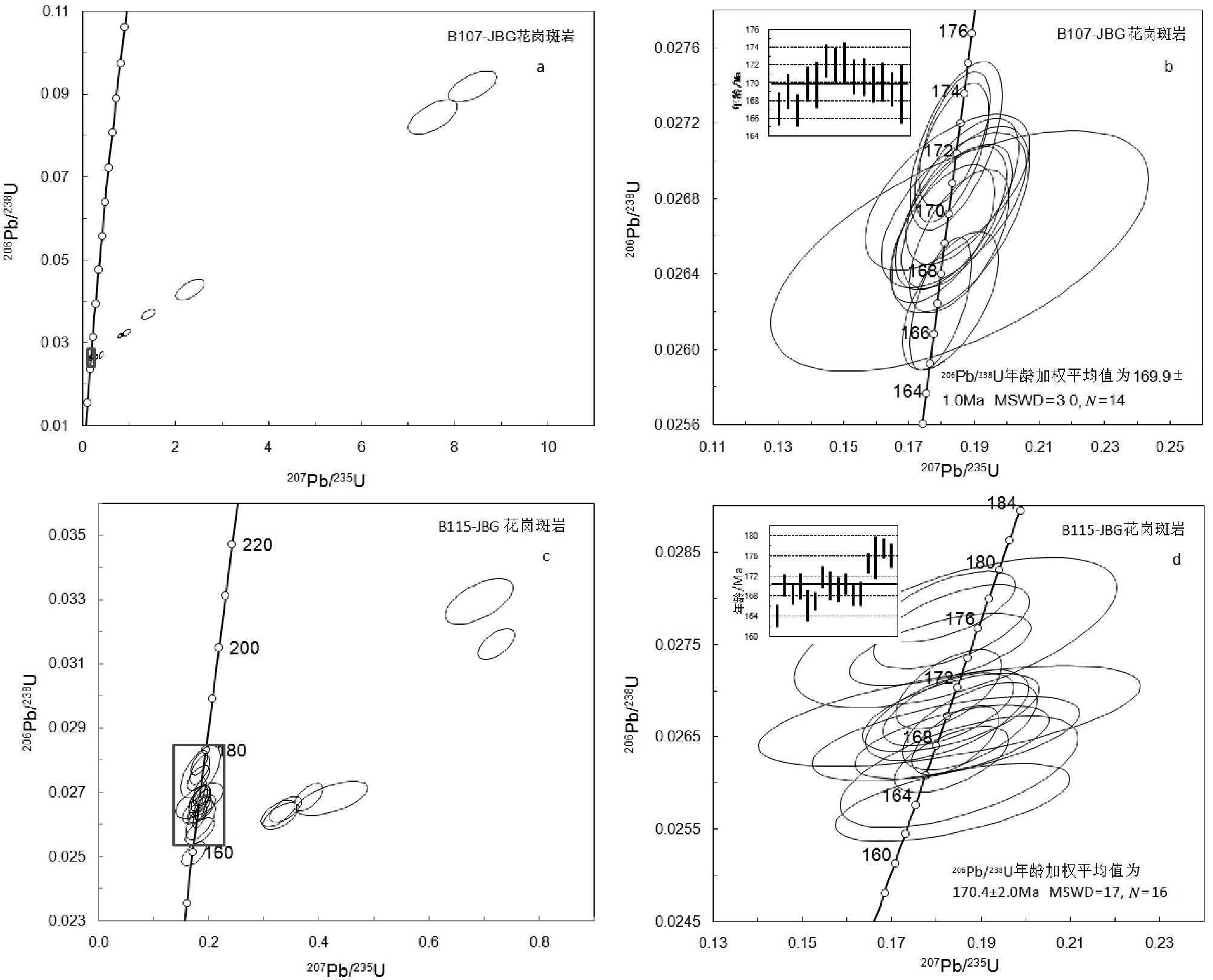
金宝沟金矿床是冀东地区近年查明的一个大型斑岩型金矿床,金矿体主要赋存于金宝沟花岗斑岩体及岩体与太古宙迁西群黑云角闪斜长片麻岩接触带中。为查明金宝沟含矿花岗斑岩体的成岩时代、岩石地球化学特征、岩浆源区特征及其与区域上峪耳崖、牛心山等成矿花岗岩体的关系,采用LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年方法,测得金宝沟2件花岗斑岩的成岩年龄分别为169.9±1.0Ma和170.4±2.0Ma,表明其形成于中侏罗世。金宝沟花岗斑岩属于过铝质钾玄岩系列岩石,ΣREE含量为38.17×10-6~136.51×10-6,岩石富集Rb、K等大离子亲石元素和Ba、Th、U,亏损Ta、Nb、Ti等高场强元素和P、Sr,显示出典型岛弧或活动大陆边缘岩浆岩的特征。锆石Hf同位素研究显示,2件花岗斑岩样品的锆石εHf(t)分别为-12.8~-7.4和-14.4~-8.8,两阶段模式年龄分别为1685~2028Ma和1773~2130Ma,暗示岩浆可能来源于古元古代地壳物质的部分熔融。金宝沟花岗斑岩岩浆形成的温度为788~834℃,岩浆形成压力为0.8~1.6GPa。结合区域地质资料认为,包括金宝沟花岗斑岩在内的冀东中侏罗世花岗岩及同时代的髫髻山组火山岩是在陆内收缩、地壳增厚、古太平洋板块向欧亚大陆俯冲的构造背景下,在挤压应力松弛的间隙环境侵位的。
Abstract:The Jinbaogou gold deposit in eastern Hebei has been recently identified as a large porphyry gold deposit. The orebodies mainly occur in Jinbaogou granite porphyry and the contact zone between the granite porphyry and the biotite-hornblende plagiogneiss of Archean Qian'xi Group. In order to confirm the age, geochemistry,magma source characteristics of Jinbaogou granite porphyry and its relationship with Yu'erya and Niuxinshan granites, the authors conducted LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of the two granite porphyries, which yielded ages of 169.9±1.0Ma and 170.4±2.0Ma, suggesting the products of Middle Jurassic. Jinbaogou granite porphyry falls into the peraluminous and shoshonite series, its total values of REE are 38.17×10-6~136.51×10-6; and the rock is characterized by enrichment of large lithophile elements (Rb, K) and Ba, Th, U but depletion of high-field strength elements (Ta, Nb, Ti) and P, Sr, displaying the characteristics of typical island arc or magmatic rocks of active continental margin. Zircon Hf isotope studies show that the εHf(t) values and TDM2 ages of two granite porphyry samples are -12.8~-7.4 and -14.4~-8.8, 1685~2028Ma and 1773~2130Ma, respectively, implying representatives of the Paleoproterozoic crustal reservoir. Integrated with the regional geological materials, it is considered that the Middle Jurassic granites in the eastern Hebei, including the Jinbaogou granite porphyry and volcanics of Tiaojishan, were under the tectonic settingsof crustal thickening and the subduction of ancient Pacific plate towards Eurasian plate, and were emplaced during the relaxation after extrusion stress.
-
哀牢山构造带是藏东(东南亚)地区最重要的一条线性构造和显著的地质地貌分界线[1],是印支地块与扬子地块的分界线,是印度-欧亚大陆碰撞过程中逃逸块体的西边界,同时也是川滇菱形块体的西南边界,在青藏高原的大陆逃逸地球动力学模型中具有重要的意义[2],长期以来被国内外地学界所关注。以往的研究主要侧重于对哀牢山-红河走滑剪切带运动学特征、运动时限、运动模式及转换机制的研究,而对构成哀牢山构造带主体的深变质岩系(哀牢山岩群)的时代和构造属性的研究较少,且存在争议。前人[3-4]依据相关同位素测年结果和区域地质资料,将哀牢山深变质岩系(哀牢山岩群)暂定为新元古代,认为其物质组成和成矿作用特点与扬子准地台间有更多联系,因此将其划为扬子准地台丽江台缘褶皱带内的一个三级构造单元,即扬子地台的结晶基底;但也有学者认为,该构造带构造延伸方向与唐古拉-昌都-兰坪-思茅褶皱系较一致,将哀牢山岩群划为唐古拉-昌都-兰坪-思茅褶皱系的第一结晶基底[5]。近年来,部分学者的研究结果对哀牢山岩群原岩形成时代及构造归属提出了挑战,认为哀牢山岩群不全形成于元古宙,也不全是扬子地台的结晶基底[6-8]。造成上述不同认识的主要原因之一是,基底岩石已有的年代学研究结果少且准确度低。此外,由于造山作用的强烈改造,大多数地层的原有序列遭受破坏,一些古生代或中生代岩体由于遭受高级变质作用而被误认为是前寒武纪基底岩石。哀牢山深变质岩系的形成时代、变质时代,以及哀牢山岩群的构造属性,这些关键性问题都关系着对该区地质构造特征及成矿规律的认识。为解决上述问题,本文选取哀牢山岩群花岗质片麻岩、花岗闪长质片麻岩及花岗质岩脉,以及哀牢山岩群西侧的变质粉砂岩为研究对象,采用LA-ICP-MS 锆石U-Pb 同位素测定技术,揭示和探讨哀牢山岩群的原岩形成时代、变质变形时代及哀牢山构造带构造属性。
1. 区域地质背景
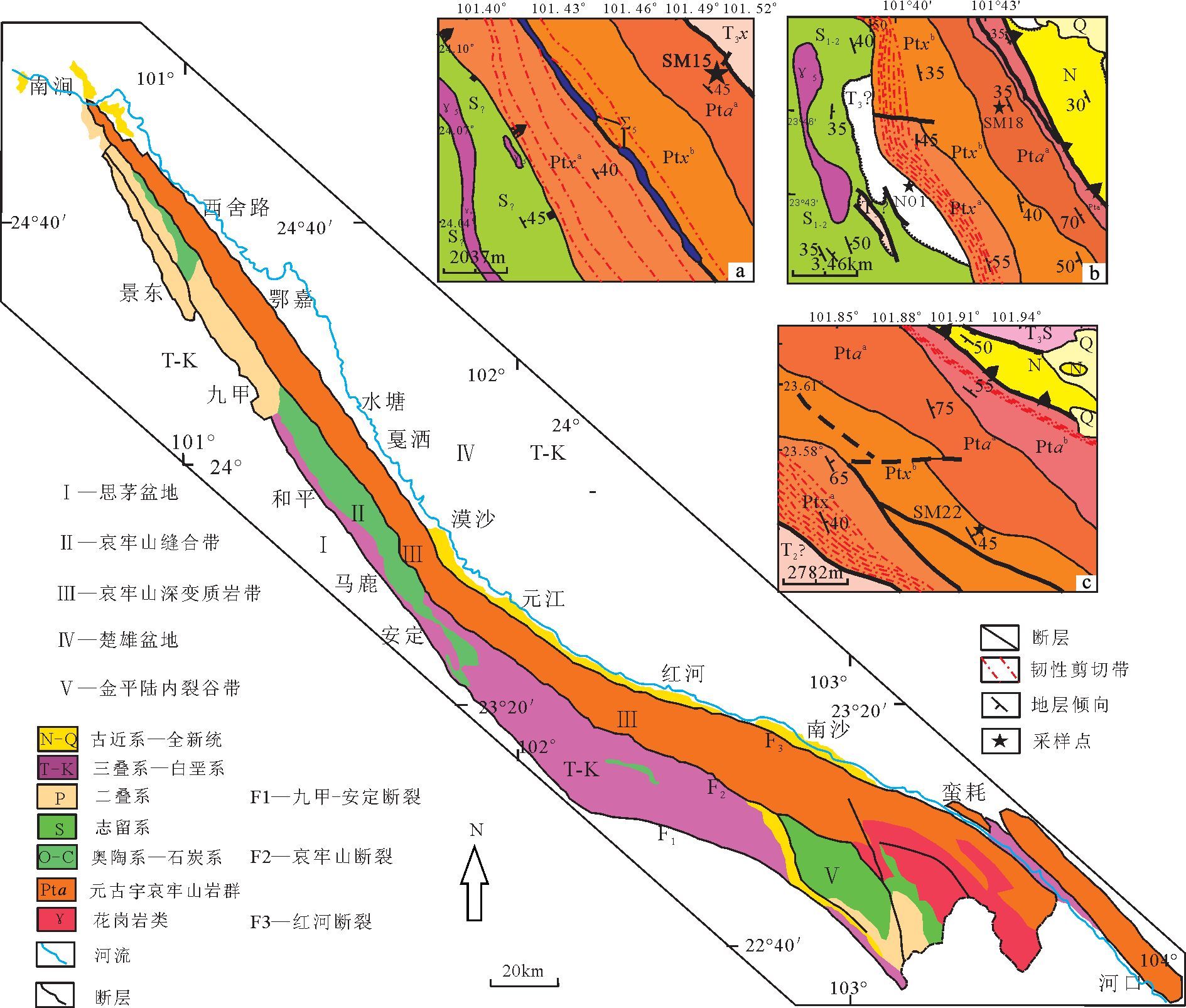
哀牢山构造带在大地构造上位于扬子准地台、松潘-甘孜褶皱系和唐古拉-昌都-兰坪-思茅褶皱系3 个一级构造单元,以及扬子准地台内丽江台缘摺皱带和滇东台褶带2 个二级构造单元的接触过渡带[2]。它被作为哀牢山板块缝合线,具备双变质带的特征,其中哀牢山岩群为低压高温带[9]。有的将其作为喜马拉雅期的陆内左行走滑平移剪切带[10],有的将其看作逆冲-推覆构造[11],为表达统一,本文暂将其称为哀牢山构造带,构造带由九甲-墨江断裂、哀牢山浅变质岩系、哀牢山断裂、哀牢山深变质岩杂岩(哀牢山岩群)、红河断裂,以及分布于带内的超基性、基性、酸性岩体共同构成(图 1)。
![]() 图 1 哀牢山构造带地质简图(据参考文献[1]修改)Figure 1. Simplified geological map of the Ailaoshan tectonic belt
图 1 哀牢山构造带地质简图(据参考文献[1]修改)Figure 1. Simplified geological map of the Ailaoshan tectonic belt哀牢山岩群为一套混合岩化强烈的中深变质岩系,因沿哀牢山脉分布而得名,两侧分别为哀牢山断裂和红河断裂所限,呈NW—SE 向条带状延伸,向北延至南涧县密滴附近,因上述2 条断裂相交而消失,向南延入越南,变质岩系延伸长度约500km,宽20~30km,厚度大于8500m,以中国境内分布为主。哀牢山断裂东侧红河断裂西侧为哀牢山深变质岩系(哀牢山岩群),一般达高绿片岩相-角闪岩相,局部具高角闪岩相的特点,主要由各类片岩、片麻岩、变粒岩、透辉大理岩等组成;哀牢山断裂西侧为一套低绿片岩相变质岩系,主要为岔河、大平坝、转马路及外麦地岩组,一般称为马邓岩群,岩性主要为千枚岩及千糜岩、片岩、板岩、变质砂岩等;深变质岩带因受剪切带活动影响,岩石局部发生糜棱岩化,同时由于该岩群岩石变质较深,混合岩化强烈,片理化或劈理化也强烈,加之多期构造运动的改造,使原岩面貌改变较大,岩石的结晶片理、片麻理已全面取代原生层理,难以建立确切的地层层序。1965 年云南省地质局区测队将该深变质岩系命名为哀牢山岩群[4],命名剖面位于云南元江县小羊街南满河( 小羊街组)、元阳县大文迷河( 凤港组、阿龙组)、个旧- 金平公路大平台(乌都坑组)。1973 年进一步将该群自下而上划分为小羊街组(Ptx)、阿龙组(Pta)、凤港组、乌都坑组,并作为一个向北东倾斜的单斜构造看待[4]。
2. 样品采集和分析方法
2.1 样品采集位置及岩石学特征
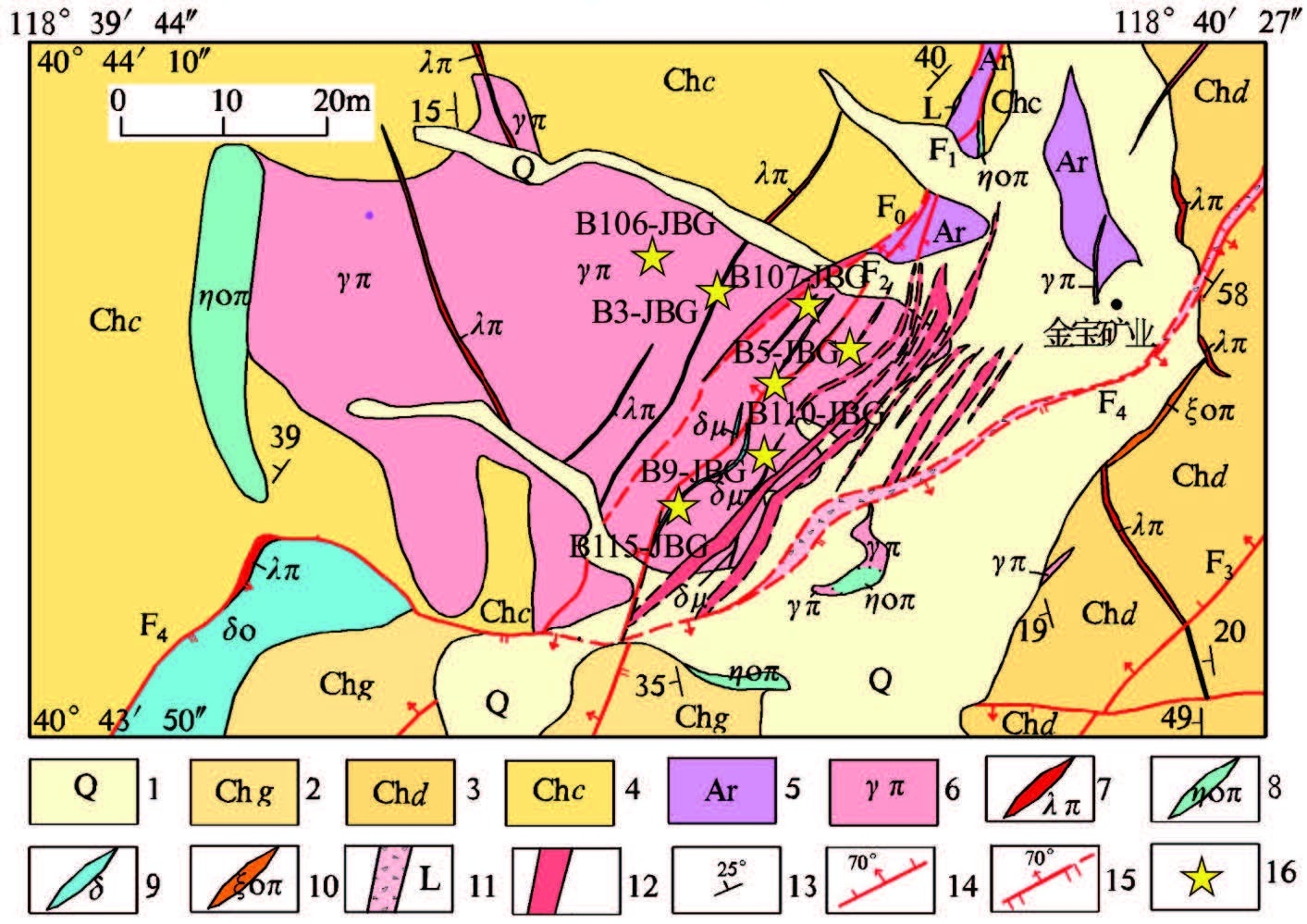
样品SM-15 为碎裂岩系,采于云南新平县水塘镇拉博村新房子社SSE900m,即N24°6.164′、E101°30.403′,位于1∶20万新平幅地质图上Pta(a 阿龙组下亚组)(图 1-a)。野外露头呈浅灰黄色,风化严重,风化面为黄褐色(图版Ⅰ-a),主要矿物有石英、长石,次要矿物为黑云母、角闪石,粒径大小不一,肉眼可见;石英、长石含量约85%,云母和角闪石含量较低,约占10%;石英、长石颗粒被碎裂化,具有不规则的撕碎边缘,呈锯齿状、棱角状,黑云母发生扭曲,为典型的碎裂结构;岩石中矿物无定向排列,为块状构造(图版Ⅰ-e),初步定名为花岗质片麻岩或碎裂岩。
样品SM-22 采自国道323 沿线,具体位置为元江镇咪哩乡土堆梁子新寨白岩浅沟处,即N23°33.063′、E101°55.019′,采样处位于1∶20 万墨江幅地质图中Ptx(b 小羊街组上亚组,图 1-c)。野外露头为灰白色,风化后颜色变化不大(图版Ⅰ-b),主要矿物有石英、长石,次要矿物为黑云母,石英、长石含量为60%左右,云母含量35%左右,为粒状鳞片花岗变晶结构,岩石以粒状矿物为主,片状矿物云母被长石、石英分开显得不连续,为典型的片麻状构造(图版Ⅰ-f),暂定名为花岗闪长质片麻岩。
样品SM-18 采自新平县漠沙镇红旗村中部,即N23°46.066′、E101°43.621′,位于1∶20 万墨江幅地质图中Pta(a 阿龙组的下亚组,图 1-b)。样品呈灰白色,风化面为黄色(图版Ⅰ-c),主要矿物有石英、长石,副矿物有云母等,其中长石含量50%,石英、长石为90%左右;粒径3mm 左右;石英与长石相互穿插排列,细粒变晶结构,矿物无定向排列,为典型的块状构造(图版Ⅰ-g),初步定名为浅变粒花岗岩,属于后期同变形变质作用下形成的长英质脉体。
样品NO-1 采自新平县建兴乡挖窖村奥特坡,即N23°43.093′、E101°40.416′,位于1∶20 万墨江幅地质图中T3?(图 1-b),紧邻哀牢山岩群西侧的浅变质岩系中,野外露头呈灰绿色,表面为土黄色(图版I-d),主要矿物成分为石英、云母;粒径较小,石英与云母定向性排列(图版Ⅰ-h),为典型的石英云母片岩或变质砂岩。
2.2 分析方法
用于锆石U-Pb 测年的样品粉碎至40~60 目,由河北省廊坊市区域地质调查研究院在双目镜下挑选出晶形完好、纯度在99%以上的锆石样品。将锆石样品置于环氧树脂中,制成样品靶,在样品靶改造固结后,打磨至约1/2 并抛光,使锆石中心部位暴露出来,用于锆石阴极发光(CL)照相。
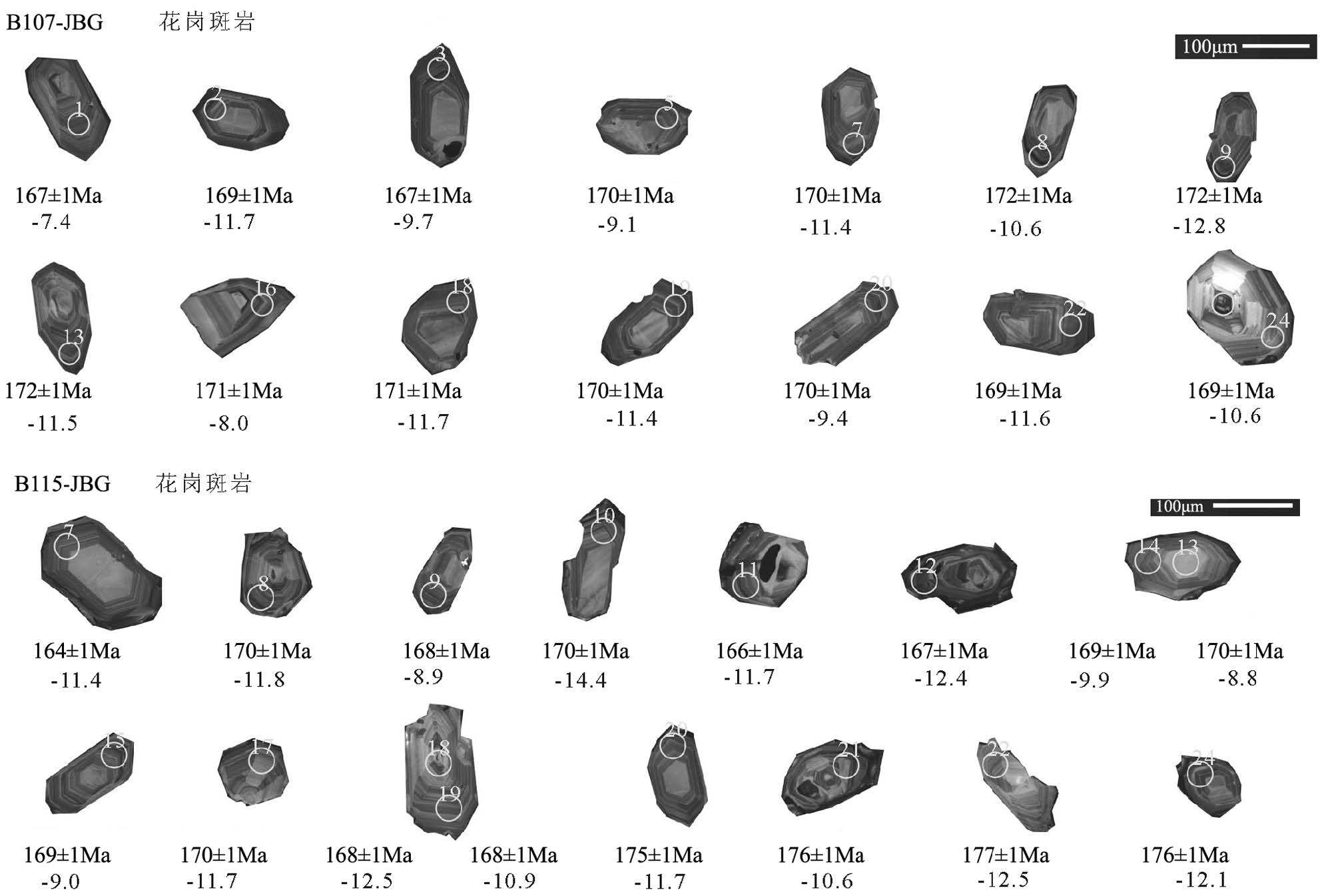
锆石的阴极发光照相(图 4)在中国地质科学院国土资源部成矿作用与资源评价重点实验室完成,用于锆石形态和内部结构研究。锆石原位U-Pb 同位素分析在中国地质科学院国家地质实验测试中心LA-ICP-MS 仪器上完成,测点的选取力求避开内部裂隙等区域,以获得较准确的年龄信息。实验中每个样品选取30 个点进行分析测试,分析仪器为Thermo ElementⅡ质谱仪和New Wave 193 型激光剥蚀系统,激光波长为193nm,激光剥蚀斑束直径为35μm,脉冲频率10Hz,脉冲能量0.155~0.160mJ,激光剥蚀样品的深度为20~40μm。等离子质谱参数:冷却气流速(Ar) 为16.92L/min,辅助气流速(Ar)为0.8 L/min,载气流速(He)为0.637 L/min,样品气流速(Ar)为0.769 L/min,射频发生器功率1090W。其他参数:采样时间202Hg、204Pb 是2ms,其他是5ms,每峰点数100,检测器模式238U、232Th 用模拟,其他是计数,剥蚀时间40s;单个样品点数据包括20s 空白信号及40s 样品信号;每分析10 个样品点,分析锆石标准样品GJ-1 及质量监控样品Plesovice 各2 次[12]。年龄加权平均值计算、U-Pb 谐和图等的绘制采用Isoplot(3.0 版)软件完成[13],单个数据的误差为1σ,年龄加权平均值误差为2σ,具95%的置信度。年轻锆石(寒武纪以后)采用206Pb/238U 年龄,古老锆石(前寒武纪)采用207Pb/206Pb 年龄[14] 。
3. 锆石特征及U-Pb 同位素测定结果
3.1 样品SM-15
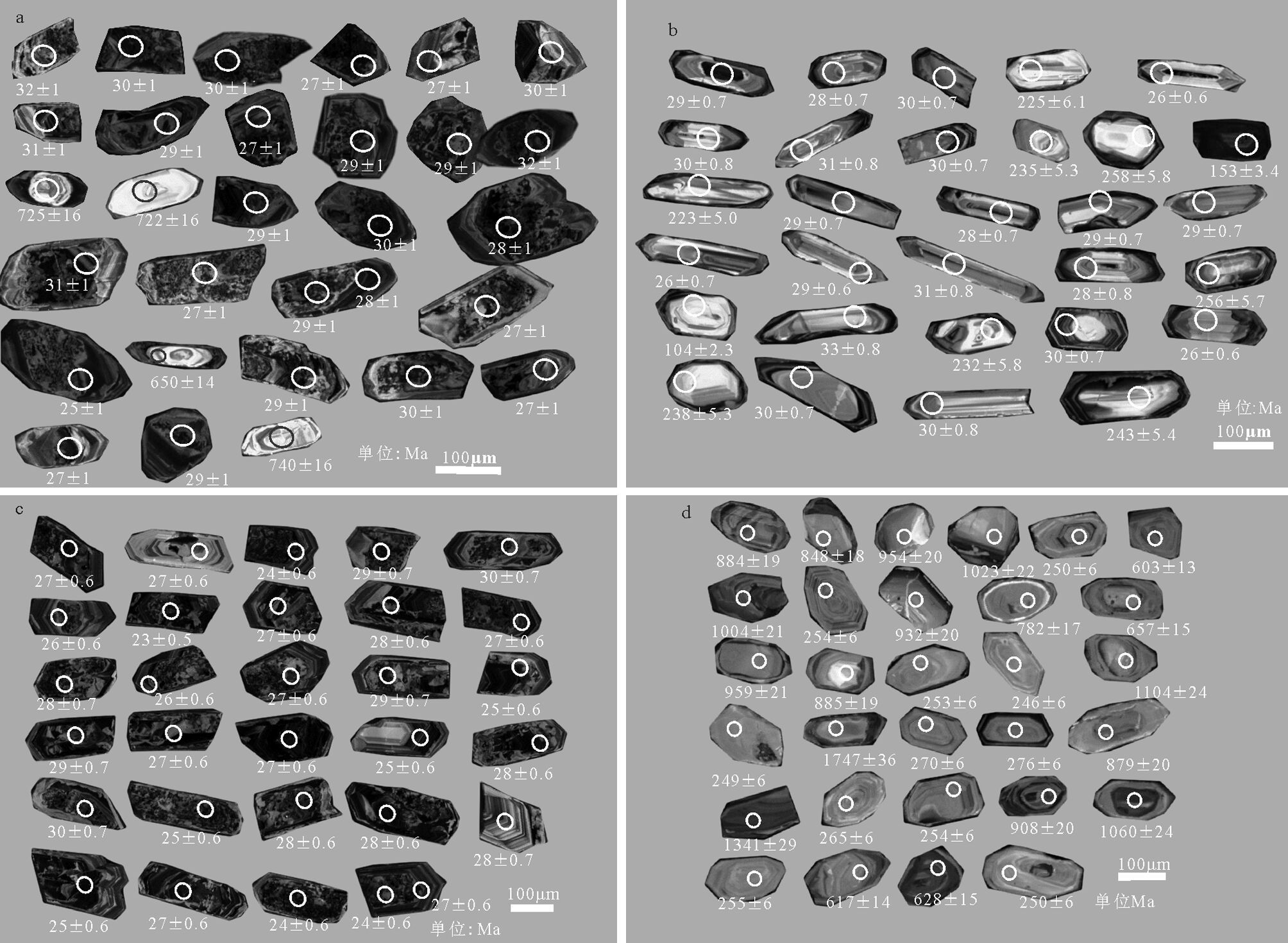
锆石CL 图像显示,锆石可分为2 类,第一类锆石(图 2-a,测点13、14、24、30)颗粒较小,具有明显的核-边结构,核部较宽,为50~120μm,发光明亮,有明显的岩浆结晶环带,边部较窄,一般小于15μm,极少数为30μm 左右(图 2-a,测点13),发光微弱,无明显的环带结构;第二类锆石无核-边结构,锆石颗粒较大,呈深灰色板状,隐约可见环带结构,边部环带清楚,其中锆石颗粒中部较脏,可能是后期热液溶蚀加上变质变形作用造成的。
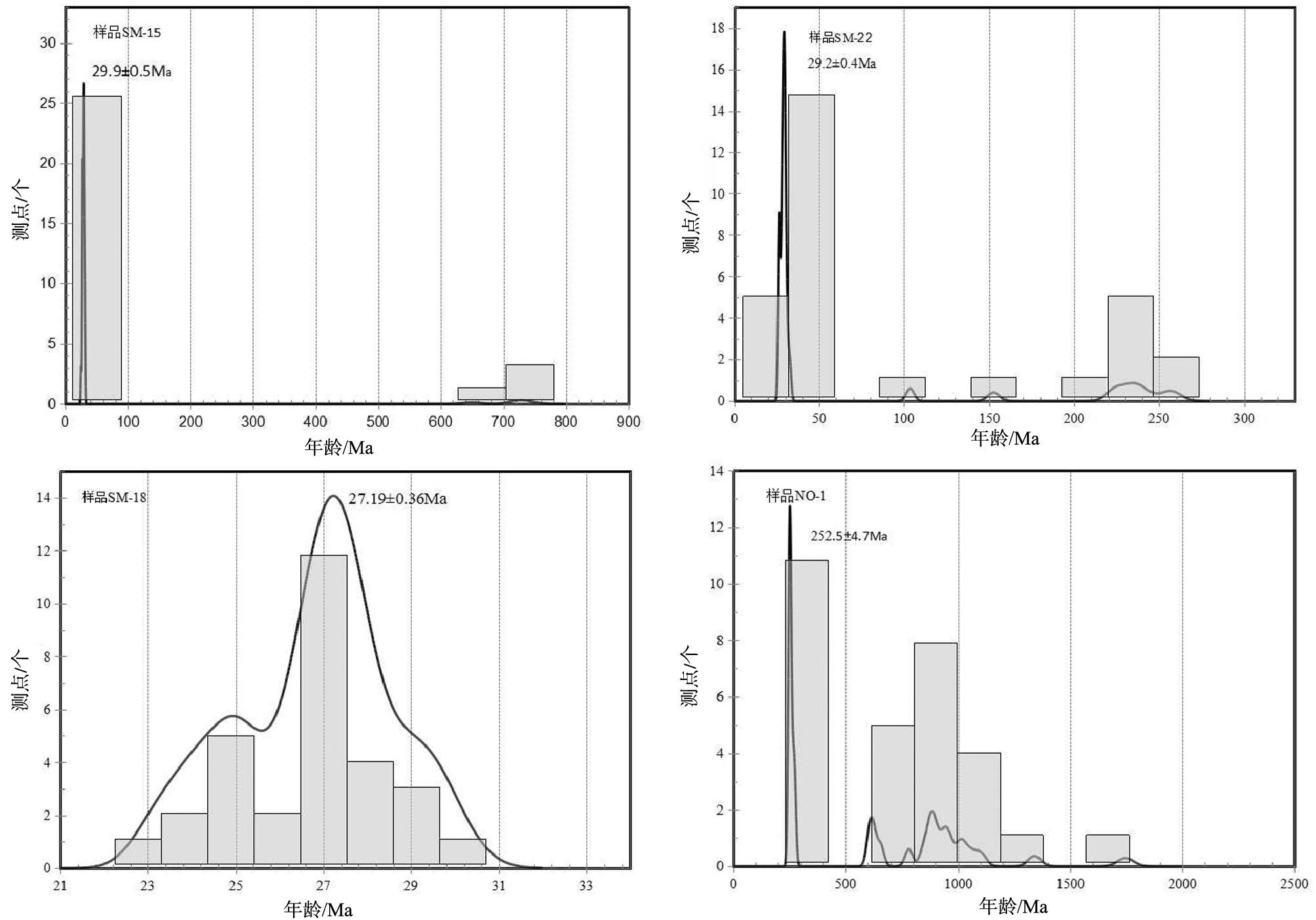
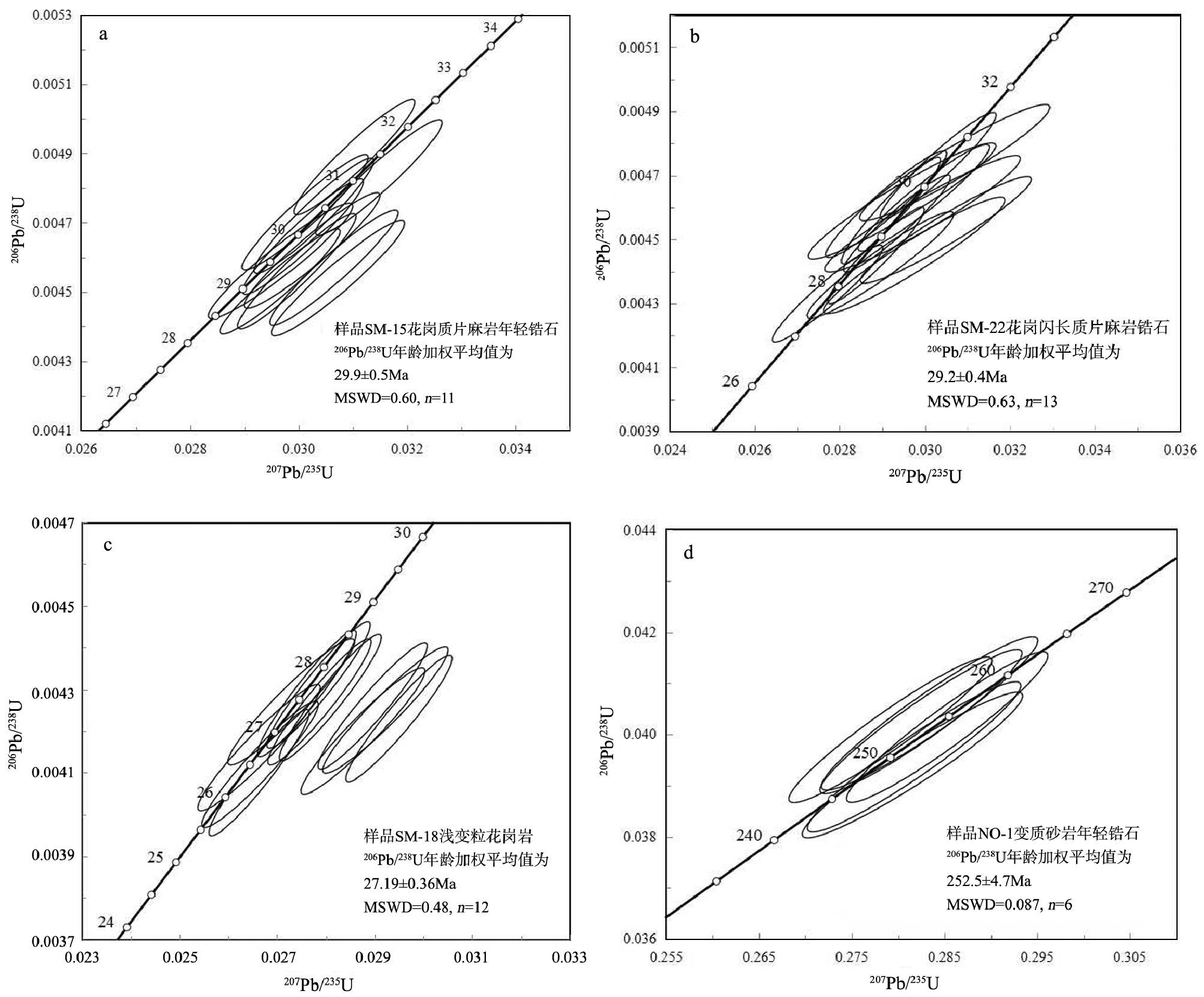
测年结果显示,其锆石年龄由2 组构成(图 3)。第一类锆石共计4 个点,其中点23 由于谐和度较差未参与计算,剩余3 个点中锆石的核部Th/U 值介于0.2~2.4 之间,为典型的岩浆锆石,年龄集中在722~740Ma 之间,具体的同位素比值及年龄结果见表 1和图 3-a;第二类锆石共计26 个点,其中15 个点的谐和度较差未参与计算,剩余11 个点锆石Th/U 值普遍介于0.01~0.1 之间(测点4 的Th/U 为0.16),Th/U<0.1,为典型的变质锆石,年龄集中于29Ma左右。
3.2 样品SM-22
根据锆石的CL 图像,可将锆石分为3 类:第一类锆石颗粒较大,大于100μm,具有较大的长宽比值,最大可达7∶1,外形特征为细长柱状或针状,晶棱尖锐,自形,平直棱柱面发育,具有亮色的阴极发光和窄的振荡环带(图 2-b)。研究表明,在低温条件下微量元素的扩散速度慢,易形成较窄的岩浆环带(如I 型和S 型花岗岩中的锆石)[15],说明该类锆石可能形成于后期相对较低的温度下;第二类锆石(测点9、12、21、25、30)除具备第一类锆石的特征外,还具有继承锆石的残留核,核部发光性强,边部具有环带结构,可能为后期变质重结晶作用形成的;第三类锆石为短柱状或圆饼状,具有明显的核-边结构,核部较宽,为50~60μm,发光明亮,有明显的岩浆环带,边部较窄,一般小于10μm(测点4、10、22、24、27),发光微弱,无环带结构。测年结果显示,其年龄由2 组构成(图 3),其中第一类锆石的19 个测点和第二类锆石中测点25 的边部可归为后期岩浆作用形成的,锆石的Th/U 值介于0.4~2.1 之间,为典型的岩浆锆石,锆石的UPb年龄集中在26~32Ma 之间;第二类锆石的核部(测点9、12、21、30)与第三类锆石的核部可归为早期岩浆作用形成的,锆石的Th/U 值介于0.11~0.97之间,也为岩浆锆石,由于测点10、11、21、22 谐和度较差,未参与计算,其余锆石的U-Pb 年龄集中在223~243Ma 之间,U- Pb 年龄加权平均值为232.3±4.3Ma,同位素比值及锆石U-Pb 定年结果见表 1 和图 3-b。
表 1 哀牢山变质岩系LA-ICP-MS 锆石U-Th-Pb 同位素测定结果Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb data of the metamorphic rocks in Ailaoshan area点号 锆石特征 分析部位 同位素比值 同位素年龄/Ma年龄/Ma 同位素含量/10-6 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/206U 1σ 206Pb/238U 207Pb/235U Th U 样品SM-15 花岗质片麻岩 1 环带 环带 0.1396 0.0029 0.00489 0.0001 0.09453 0.002 2222 35 32 1 92 2 110 3039 2 板状 板状 0.04799 0.0011 0.00473 0.0001 0.03012 0.001 98 54 30 1 30 1 123 4629 3 环带 环带 0.05104 0.0013 0.00462 0.0001 0.03025 0.001 243 57 30 1 30 1 296 4685 4 板状 板状 0.0482 0.0010 0.00412 0.0001 0.02675 0.001 109 48 27 1 27 1 3006 19032 5 环带 环带 0.04976 0.0011 0.00424 0.0001 0.02789 0.001 184 52 27 1 28 1 38 2357 6 环带 环带 0.04959 0.0014 0.00459 0.0001 0.02967 0.001 176 63 30 1 30 1 18 1594 7 环带 环带 0.04759 0.0010 0.00487 0.0001 0.03142 0.001 78 50 31 1 31 1 119 3540 8 环带 环带 0.04831 0.0011 0.00457 0.0001 0.03065 0.001 115 52 29 1 31 1 202 5860 9 环带 环带 0.059 0.0018 0.00425 0.0001 0.03855 0.001 567 65 27 1 38 1 41 2013 10 环带 环带 0.04876 0.0010 0.00453 0.0001 0.02966 0.001 136 50 29 1 30 1 600 6150 11 环带 环带 0.10675 0.0022 0.00452 0.0001 0.07903 0.002 1745 37 29 1 77 2 873 9742 12 环带 环带 0.04757 0.0010 0.00489 0.0001 0.03103 0.001 77 49 32 1 31 1 1006 13060 13 核-边 核 0.06678 0.0015 0.11896 0.0028 1.03685 0.030 831 47 725 16 722 15 536 217 14 核-边 核 0.06936 0.0015 0.11856 0.0027 1.21774 0.031 910 43 722 16 809 14 78 137 15 环带 环带 0.06986 0.0015 0.00455 0.0001 0.04518 0.001 924 42 29 1 45 1 179 4324 16 板状 板状 0.05399 0.0011 0.00472 0.0001 0.03028 0.001 370 47 30 1 30 1 790 13044 17 环带 环带 0.05121 0.0011 0.00436 0.0001 0.02802 0.001 250 49 28 1 28 1 426 6005 18 环带 环带 0.04835 0.0010 0.00483 0.0001 0.03148 0.001 116 49 31 1 32 1 146 5291 19 环带 环带 0.05107 0.0013 0.00422 0.0001 0.02892 0.001 244 59 27 1 29 1 79 3909 20 环带 环带 0.05122 0.0012 0.00454 0.0001 0.03073 0.001 251 53 29 1 31 1 186 5701 21 环带 环带 0.0488 0.0011 0.00426 0.0001 0.02893 0.001 138 53 27 1 29 1 305 6003 22 环带 环带 0.05414 0.0013 0.00385 0.0001 0.02749 0.001 377 54 25 1 28 1 99 3555 23 核-边 核 0.06407 0.0014 0.10607 0.0025 0.88689 0.023 744 45 650 14 645 12 35 267 24 环带 环带 0.04992 0.0011 0.00436 0.0001 0.02878 0.001 191 49 28 1 29 1 60 3502 25 环带 环带 0.04821 0.0010 0.00456 0.0001 0.02997 0.001 110 49 29 1 30 1 181 4426 26 环带 环带 0.04634 0.0010 0.00466 0.0001 0.03008 0.001 16 50 30 1 30 1 147 4676 27 环带 环带 0.05088 0.0012 0.00422 0.0001 0.02834 0.001 235 52 27 1 28 1 42 2940 28 环带 环带 0.04899 0.0012 0.00425 0.0001 0.02713 0.001 147 55 27 1 27 1 110 2924 29 环带 环带 0.04861 0.0011 0.00456 0.0001 0.03025 0.001 129 51 29 1 30 1 44 2002 30 核-边 核 0.0643 0.0013 0.12157 0.0028 1.07118 0.026 751 43 740 16 739 13 82 370 样品SM-15 花岗质片麻岩 1 环带 环带 0.05052 0.00131 0.00455 0.0001 0.02934 0.00083 219 59 29 0.7 29 0.8 588 1568 2 环带 环带 0.05027 0.00193 0.00442 0.00011 0.02895 0.00114 208 87 28 0.7 29 1.1 554 448 3 板状 板状 0.04948 0.00151 0.00461 0.00011 0.02909 0.00094 171 70 30 0.7 29 0.9 1810 1099 4 核-边 核 0.05322 0.00145 0.03554 0.00082 0.24853 0.00777 338 61 225 5.1 225 6.3 320 411 5 环带 环带 0.07895 0.0025 0.00409 0.0001 0.0449 0.00149 1171 61 26 0.6 45 1.4 1503 1977 6 环带 环带 0.04547 0.00222 0.00462 0.00012 0.02946 0.00146 0.1 83 30 0.8 30 1.4 358 411 7 环带 环带 0.05353 0.00255 0.00474 0.00012 0.0307 0.00148 351 104 31 0.8 31 1.5 494 431 8 环带 环带 0.05396 0.00175 0.00463 0.00011 0.02997 0.00102 369 71 30 0.7 30 1.0 206 1285 9 核-边 核 0.05327 0.00122 0.03715 0.00084 0.26139 0.00686 340 51 235 5.3 236 5.5 184 616 10 核-边 核 0.06448 0.00144 0.04087 0.00093 0.36533 0.00946 758 46 258 5.8 316 7.0 44 394 11 板状 板状 0.05086 0.00111 0.02395 0.00054 0.16319 0.00408 235 50 153 3.4 154 3.6 394 667 12 核-边 核 0.05077 0.00121 0.03522 0.00081 0.25138 0.00689 231 54 223 5.0 228 5.6 365 396 13 环带 环带 0.0517 0.00242 0.00445 0.00012 0.02975 0.00141 272 104 29 0.7 30 1.4 1154 961 14 环带 环带 0.0516 0.00151 0.00433 0.0001 0.02771 0.00086 268 66 28 0.7 28 0.9 4417 2035 15 环带 环带 0.04841 0.00114 0.00445 0.0001 0.02885 0.00075 120 54 29 0.7 29 0.7 431 902 16 板状 板状 0.05441 0.00234 0.00453 0.00011 0.03049 0.00133 388 93 29 0.7 31 1.3 299 344 17 环带 环带 0.05331 0.00239 0.00405 0.0001 0.02883 0.00131 342 98 26 0.7 29 1.3 623 560 18 环带 环带 0.05287 0.00189 0.0041 0.0001 0.02879 0.00107 323 79 26 0.6 29 1.1 938 535 19 环带 环带 0.05268 0.00225 0.00489 0.00012 0.03113 0.00135 315 94 31 0.8 31 1.3 2038 1086 20 环带 环带 0.06921 0.00404 0.00435 0.00013 0.03338 0.00193 905 116 28 0.8 33 1.9 365 321 21 核-边 核 0.05102 0.00108 0.04045 0.00092 0.28502 0.00696 242 48 256 5.7 255 5.5 93 439 22 核-边 核 0.05386 0.00121 0.01619 0.00037 0.11974 0.00305 365 50 104 2.3 115 2.8 66 552 23 环带 环带 0.05807 0.00231 0.0051 0.00013 0.03198 0.0013 532 85 33 0.8 32 1.3 659 606 24 核-边 核 0.0517 0.0013 0.03658 0.00084 0.25506 0.00735 272 56 232 5.3 231 5.9 184 348 25 核-边 边 0.05025 0.00139 0.00473 0.00011 0.03031 0.0009 207 63 30 0.7 30 0.9 879 1204 26 环带 环带 0.04825 0.00132 0.0041 0.0001 0.02599 0.00077 112 63 26 0.6 26 0.8 809 493 27 核-边 核 0.05038 0.00106 0.03753 0.00085 0.26436 0.00641 212 48 238 5.3 238 5.2 626 645 28 环带 环带 0.04729 0.00112 0.00459 0.00011 0.0292 0.00077 64 56 30 0.7 29 0.8 363 787 29 环带 环带 0.05123 0.00257 0.00458 0.00012 0.02995 0.00152 251 111 30 0.8 30 1.5 470 256 30 核-边 核 0.05572 0.00117 0.03845 0.00087 0.27808 0.00673 441 46 243 5.4 249 5.4 69 466 样品SM-18 变粒花岗岩 2 环带 环带 0.04677 0.00136 0.00416 0.0001 0.02663 0.00083 37 68 27 0.6 27 0.8 357 675 3 环带 环带 0.06102 0.00125 0.00375 0.00009 0.03299 0.00078 640 43 24 0.6 33 0.8 1601 8931 4 环带 环带 0.0488 0.00107 0.00452 0.0001 0.02867 0.00072 138 51 29 0.7 29 0.7 718 6249 5 环带 环带 0.04921 0.00108 0.00464 0.00011 0.02974 0.00074 158 50 30 0.7 30 0.7 1945 3916 6 环带 环带 0.04735 0.00107 0.0041 0.0001 0.02663 0.00068 66 53 26 0.6 27 0.7 117 2103 7 环带 环带 0.05221 0.00108 0.00358 0.00008 0.02598 0.00062 295 46 23 0.5 26 0.6 1631 16956 8 环带 环带 0.04609 0.00126 0.00412 0.0001 0.02665 0.00079 2 64 27 0.6 27 0.8 232 3025 9 环带 环带 0.0465 0.00102 0.00431 0.0001 0.02785 0.0007 23 51 28 0.6 28 0.7 377 4513 10 环带 环带 0.05727 0.00133 0.00419 0.0001 0.03066 0.0008 502 51 27 0.6 31 0.8 2003 4975 11 环带 环带 0.04685 0.00138 0.00427 0.0001 0.02729 0.00086 41 69 28 0.7 27 0.9 131 1810 12 环带 环带 0.0488 0.00105 0.00409 0.00009 0.02794 0.00069 139 50 26 0.6 28 0.7 1023 3242 13 环带 环带 0.04838 0.0011 0.00426 0.0001 0.02873 0.00074 118 53 27 0.6 29 0.7 120 2014 14 环带 环带 0.04815 0.00121 0.00443 0.0001 0.02953 0.00082 107 59 29 0.7 30 0.8 171 2804 15 环带 环带 0.04838 0.00106 0.00389 0.00009 0.0258 0.00064 118 51 25 0.6 26 0.6 688 5468 16 环带 环带 0.0478 0.00112 0.00456 0.00011 0.02957 0.00078 89 56 29 0.7 30 0.8 289 2244 17 环带 环带 0.04999 0.00133 0.00425 0.0001 0.02922 0.00085 195 61 27 0.6 29 0.8 125 2052 18 环带 环带 0.04851 0.0011 0.00426 0.0001 0.02896 0.00074 124 53 27 0.6 29 0.7 147 3449 19 环带 环带 0.04674 0.00103 0.00389 0.00009 0.02592 0.00065 36 51 25 0.6 26 0.6 2077 2723 20 环带 环带 0.04623 0.00102 0.00427 0.0001 0.02787 0.0007 10 52 28 0.6 28 0.7 510 5163 21 环带 环带 0.04937 0.00107 0.00459 0.00011 0.02906 0.00072 165 50 30 0.7 29 0.7 1508 3562 22 环带 环带 0.05438 0.00142 0.0039 0.00009 0.02967 0.00085 387 57 25 0.6 30 0.8 260 2813 23 环带 环带 0.04863 0.00103 0.00429 0.0001 0.02761 0.00067 130 49 28 0.6 28 0.7 1182 7621 24 环带 环带 0.04727 0.00101 0.00428 0.0001 0.02809 0.00069 62 50 28 0.6 28 0.7 308 4610 25 环带 环带 0.0475 0.00121 0.00441 0.0001 0.02842 0.00079 74 60 28 0.7 29 0.8 563 2820 26 环带 环带 0.04876 0.00109 0.00391 0.00009 0.02761 0.0007 137 52 25 0.6 28 0.7 1267 2411 27 环带 环带 0.04874 0.00104 0.00423 0.0001 0.0295 0.00072 136 50 27 0.6 30 0.7 156 2593 28 环带 环带 0.05642 0.00119 0.00369 0.00009 0.02973 0.00072 468 47 24 0.6 30 0.7 2017 15942 29 环带 环带 0.05087 0.0011 0.00378 0.00009 0.02871 0.00071 235 49 24 0.6 29 0.7 1058 8084 30 环带 环带 0.04761 0.00128 0.0042 0.0001 0.02876 0.00084 79 64 27 0.6 29 0.8 92 1604 样品NO-1 变质砂岩 1 环带 环带 0.0727 0.0015 0.14689 0.0033 1.39284 0.034 1006 41 884 19 886 14 445 469 2 核-边 核 0.07262 0.0015 0.14054 0.0032 1.30838 0.033 1003 42 848 18 849 14 99 254 3 板状 板状 0.07598 0.0017 0.1595 0.0037 1.56873 0.044 1095 44 954 20 958 18 101 122 4 核-边 核 0.07097 0.0016 0.17192 0.0039 1.72666 0.049 957 44 1023 22 1019 18 109 98 5 环带 环带 0.05159 0.0011 0.0395 0.0009 0.2812 0.007 267 48 250 6 252 6 455 426 6 环带 环带 0.06071 0.0013 0.09801 0.0022 0.80713 0.020 629 44 603 13 601 11 167 253 7 环带 环带 0.07411 0.0015 0.16848 0.0039 1.68381 0.041 1044 41 1004 21 1002 16 151 205 8 环带 环带 0.05232 0.0011 0.04025 0.0009 0.28247 0.007 300 49 254 6 253 6 307 244 9 环带 环带 0.06891 0.0015 0.15556 0.0036 1.51102 0.040 896 43 932 20 935 16 78 104 10 核-边 核 0.0673 0.0014 0.12892 0.0030 1.15945 0.029 847 42 782 17 782 13 324 243 11 环带 环带 0.06114 0.0013 0.10727 0.0025 0.89975 0.023 644 45 657 15 652 12 339 256 12 核-边 核 0.0675 0.0015 0.16031 0.0038 1.55939 0.047 853 46 959 21 954 19 275 78 13 核-边 核 0.06534 0.0014 0.1471 0.0035 1.38216 0.038 785 45 885 19 881 16 89 111 14 环带 环带 0.05161 0.0011 0.04009 0.0009 0.27918 0.007 268 50 253 6 250 6 161 165 15 环带 环带 0.05259 0.0012 0.03896 0.0009 0.27583 0.007 311 50 246 6 247 6 177 168 16 核-边 核 0.08024 0.0016 0.18676 0.0044 1.96238 0.049 1203 40 1104 24 1103 17 124 159 17 板状 板状 0.05095 0.0012 0.0394 0.0009 0.28155 0.008 239 54 249 6 252 6 65 101 18 核-边 核 0.11777 0.0024 0.31117 0.0073 4.56669 0.116 1923 36 1747 36 1743 21 230 252 19 环带 环带 0.05501 0.0012 0.04274 0.0010 0.30467 0.008 412 47 270 6 270 6 269 282 20 环带 环带 0.05568 0.0012 0.04366 0.0010 0.31236 0.008 439 46 276 6 276 6 214 308 21 环带 环带 0.07514 0.0016 0.14611 0.0035 1.39229 0.037 1072 41 879 20 886 16 137 305 22 板状 板状 0.08812 0.0018 0.23132 0.0055 2.74083 0.067 1385 38 1341 29 1340 18 60 406 23 环带 环带 0.05192 0.0011 0.04189 0.0010 0.29458 0.008 282 48 265 6 262 6 202 202 24 环带 环带 0.05189 0.0011 0.04014 0.0010 0.2853 0.007 281 47 254 6 255 6 251 294 25 环带 环带 0.07288 0.0015 0.15132 0.0036 1.44456 0.035 1011 40 908 20 908 14 269 664 26 核-边 核 0.07437 0.0015 0.17865 0.0043 1.8228 0.047 1052 41 1060 24 1054 17 2111 167 27 环带 环带 0.05105 0.0012 0.04041 0.0010 0.2834 0.008 243 52 255 6 253 6 498 303 28 环带 环带 0.06402 0.0013 0.10042 0.0024 0.83699 0.021 742 42 617 14 618 11 95 201 29 环带 环带 0.06176 0.0012 0.10227 0.0025 0.8603 0.021 666 42 628 15 630 11 141 480 30 环带 环带 0.05402 0.0012 0.03956 0.0010 0.28173 0.008 372 50 250 6 252 6 72 109 3.3 样品SM-18
花岗岩SM-18 的锆石粒度较大,CL 图像显示具典型的岩浆结晶环带,无继承性核、无变质增生边(图 2-c),属岩浆结晶产物。对样品进行了30 个点的U-Th-Pb 同位素测定,获得的同位素比值及年龄结果见表 1 和图 3-c,其中18 个点(点1、3、4、5、7、10、12~16、19、21、22、25、26、28、29)由于谐和度差,不参与计算,其余12 个点的投影均分布在U-Pb谐和线上(图 3-c),12 个分析点的206Pb/238U 年龄加权平均值为27.19±0.36Ma(MSWD=0.48),代表锆石结晶年龄。该年龄与样品SM-15、SM-22 中第一类锆石和第二类锆石的边部年龄接近,反映脉体形成可能与区域混合岩化有关。
3.4 样品NO-1
样品NO-1中锆石呈次圆状和次棱角状,多数保持较自形的棱柱状(图 2-d),其大小为50~150μm,具有振荡环带,其中少数几颗锆石具有均一的内部结构或核边结构(多为残留核)。选取30 个点进行测试,其同位素比值及年龄结果见表 1,其中测点22和29 的Th/U 值介于0.1~0.2 之间,可能为变质成因,其余锆石的Th/U 值均大于0.4。以上特征表明,锆石可能遭受了沉积作用的磨损,但仍为典型的岩浆锆石。对30 个点进行统计分析,其年龄可分为4 组(图 3):246~276Ma(n=11)、600~800Ma(n=5)、800~1000Ma(n=9)和1000Ma 以上(n=5);最老的锆石年龄测点18 的年龄值为1922.7Ma,其中第一组年龄较为集中,且投影点均分布在U-Pb 谐和线上(图 3-d),显示出很好的谐和度,锆石U-Pb 年龄加权平均值为252.5±4.7Ma(MSWD=0.087,n=6),其余的年龄值较为分散,且谐和度较差。
4. 讨论
4.1 哀牢山群原岩时代及邻区变质砂岩时代
关于哀牢山群的形成时代一直是地质界关注的热点,关系着区域地质构造演化等重大地质问题,但迄今为止,并未得到一致的看法。最早在1945 年黄汲清的《中国主要地质单位》[15]一书中,曾把哀牢山变质带称之为红河结晶片岩带,并推论其可能由太古宙花岗岩及片麻岩组成,但是并未获得确切的资料加以证实。云南区测队1965 年将沿哀牢山分布的一套混合岩化强烈的变质岩系命名为哀牢山岩群,并将其时代定为前奥陶纪,云南第二区测队1970 年将其归于元古宙[4];随后不同学者依据Sm-Nd、40Ar/39Ar、K-Ar 法等获得了一些年龄较大的数据,如斜长角闪岩Sm- Nd 模式年龄为1971.9Ma、1958.3Ma 和1672.2Ma,石榴辉石岩40Ar/39Ar 年龄为1710.3±2.4Ma[17-18]。中国科学院地质研究所用Rb-Sr 法测得年龄为839±73.9Ma,K-Ar 法年龄值为1360Ma 和1393Ma[19]。依据上述同位素测年结果,将哀牢山岩群的形成时间暂定为元古宙,并作为扬子板块的基底。但笔者认为,上述年龄值范围较宽,且精度较差,解释多样。此外,由于造山作用的强烈改造,加之强的混合岩化作用,岩石普遍片理化或劈理化,导致大多数地层的原有序列遭受破坏,一些岩体由于经历了高级变质作用而被误认为是前寒武纪基底岩石。最近也有部分学者依据锆石U-Pb 测年获得的相关数据,对哀牢山岩群的形成时代提出了质疑,认为其形成时代不全是元古宙,也不全属于扬子地台的结晶基底[6-8]。
本文采用锆石U-Pb 测年法对哀牢山岩群的原岩形成时代进行了研究,其中样品SM-15 中第一类锆石核部、样品SM-22 中第二类锆石和第三类锆石的核部年龄可代表哀牢山岩群原岩的形成时代。锆石U-Pb 测年结果显示,样品SM-15 中第一类锆石较少,仅有4 颗,其中测点23 由于谐和度较差,未参与计算,剩余3 点年龄集中于722~740Ma 之间,年龄加权平均值为729±18Ma(NSWD=0.34,n=3),可代表原岩的形成时代,属于新元古代;SM-22 中第二类锆石与第三类锆石的核部U-Pb 年龄加权平均值为235±10Ma,属于三叠纪。
样品NO-1 中碎屑锆石测年结果显示,其年龄可分为4 组:246~276Ma、600~800Ma、800~1000Ma、1000Ma 以上;最老锆石年龄为1922.7Ma,为古元古代。其中第一组年龄较为集中,其余各组年龄较为分散,不具有指示意义,只能说明NO-1 中可能存在元古宙的岩石。第一组锆石U-Pb 年龄加权平均值为252.5±4.7Ma,为晚二叠纪,而碎屑锆石的最小年龄可代表沉积岩的下限年龄,即沉积岩的沉积时代,因此252.5±4.7Ma 可代表变质砂岩的形成时代;而在1∶20 万墨江幅地质图上标注的是T3?(图 1-b),笔者认为该变质砂岩形成时代应早于晚三叠世,为晚二叠世—早三叠世;此外由于碎屑锆石呈次圆状和次棱角状,指示较差的分选磨圆和较近的源区,推断其可能来源哀牢山岩群,因此哀牢山岩群中也应包括NO-1 中锆石的4 组年龄。
综上可以看出,哀牢山岩群中既有元古宙,又有二叠纪—三叠纪的岩浆岩或地层,哀牢山深变质岩带(哀牢山岩群)至少在元古宙和二叠纪末—三叠纪初各发生一期构造-岩浆事件,其中又以235~255Ma 为主,这一年龄与最近一些学者在哀牢山构造带中获得的年龄较为接近[20-23],说明构造带在二叠纪末—三叠纪初受印支运动的影响,经历一期空间上广泛分布的构造-岩浆活动,同时可能导致哀牢山古特提斯洋盆或弧后盆地的基本闭合。此外,这一构造-岩浆活动时间(235~255Ma)与二叠纪2次生物灭绝事件在时间上存在耦合关系,其与生物灭绝间的关系有待进一步研究。
4.2 哀牢山岩群的主变质时代
前已述及,SM-15 中第二类锆石和SM-22 第一类与第二类锆石测点25 的边部年龄可指示哀牢山岩群的主变质时代,样品SM-18 采自同变形的长英质脉体中,其锆石年龄也指示变质变形时代,且上述3 件样品中该类锆石占各自全部锆石的比例较大,说明该期变质变形作用可能为哀牢山岩群的变质峰期或主变质期,其测年结果分别为SM-15 为29.9 ± 0.5Ma;SM- 22 为29.2 ± 0.4Ma;SM- 18 为27.19±0.36Ma,与近期研究成果较为符合[6-7],且这些变质年龄主要集中在27~32Ma 之间,与哀牢山-红河韧性剪切带左行走滑剪切的主要时代(30Ma 左右)较一致[24-26],同时也与喜山运动的第一幕发生间大致吻合(始新世末期—渐新世初期),说明喜山运动与哀牢山-红河剪切带的左行走滑运动之间存在必然联系,符合前人的观点[10]。综上笔者认为,哀牢山岩群的主变质时代发生在27~32Ma,现今所见的哀牢山岩群可能是由地质历史上浅变质或未变质的地层和岩浆岩在该时期发生强烈的变质变形作用而形成的[6],其变质变形作用可能归因于喜山运动。
5. 结论
(1)哀牢山岩群至少包括元古宙岩浆岩(722~740Ma)、二叠纪末—三叠纪初岩浆岩或地层(235~255Ma),以及古近纪—新近纪岩浆岩(27~32Ma),至少经历了3 期构造-岩浆活动,是一个复杂的变质岩带,而不是以往认为的全部属于元古宙。
(2)哀牢山岩群的主变质时代集中在27~32Ma之间,现今的哀牢山岩群面貌主要是由于地质历史上的浅变质或未变质的地层和岩浆岩在该时期发生强烈的变质变形作用而形成的,以往研究把哀牢山岩群全部归为前寒武纪扬子板块的变质结晶基底是不妥当的,其构造归属有待进一步研究。
(3)哀牢山岩群西侧浅变质岩系中的变质砂岩,最大沉积时代为252.5±4.7Ma,为晚二叠世—早三叠世,而不是1∶20万墨江幅地质图标注的晚三叠世。
致谢: 锆石Hf 同位素分析过程中得到中国地质科学院国土资源部成矿作用与资源评价重点实验室郭春丽副研究员的指导,成文过程中得到中国地质大学(北京)曹晶博士和王赛硕士的帮助与指导,在此一并表示衷心的感谢。 -
图 1 冀东地区区域地质及金矿床分布简图(据参考文献[2]修改)
1—中侏罗统;2—古生界;3—中、新元古界;4—太古宙遵化-青龙变质杂岩;5—燕山期花岗岩;6—印支期花岗岩;7—断裂;8、9、10、11—金矿床规模(大、中、小、矿点)
Figure 1. Simplified regional geological map showing distribution of gold deposits in eastern Hebei
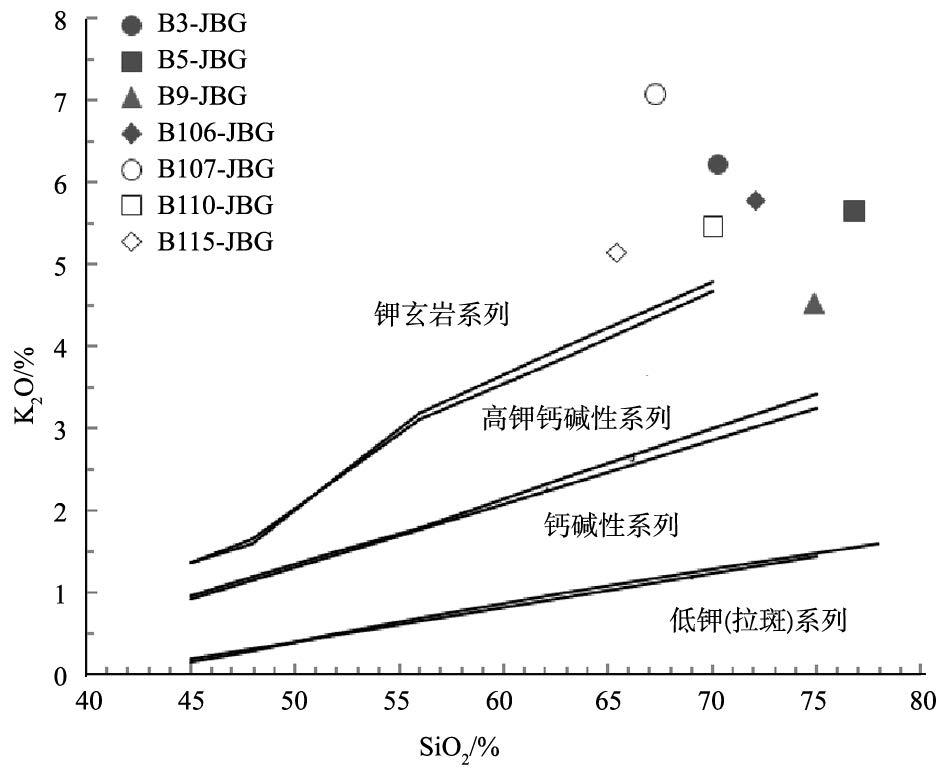
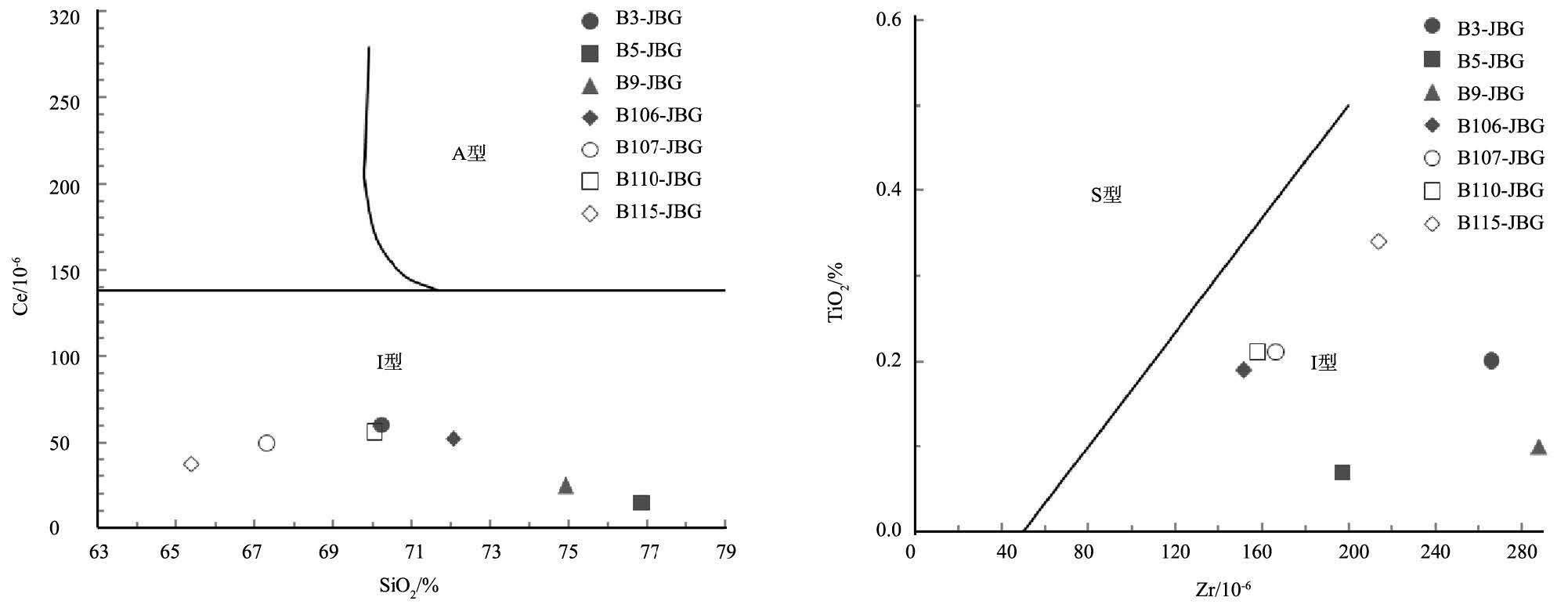
图 5 金宝沟花岗斑岩的SiO2-K2O 图解[23]
Figure 5. SiO2 versus K2O diagram of Jinbaogou granite porphyry
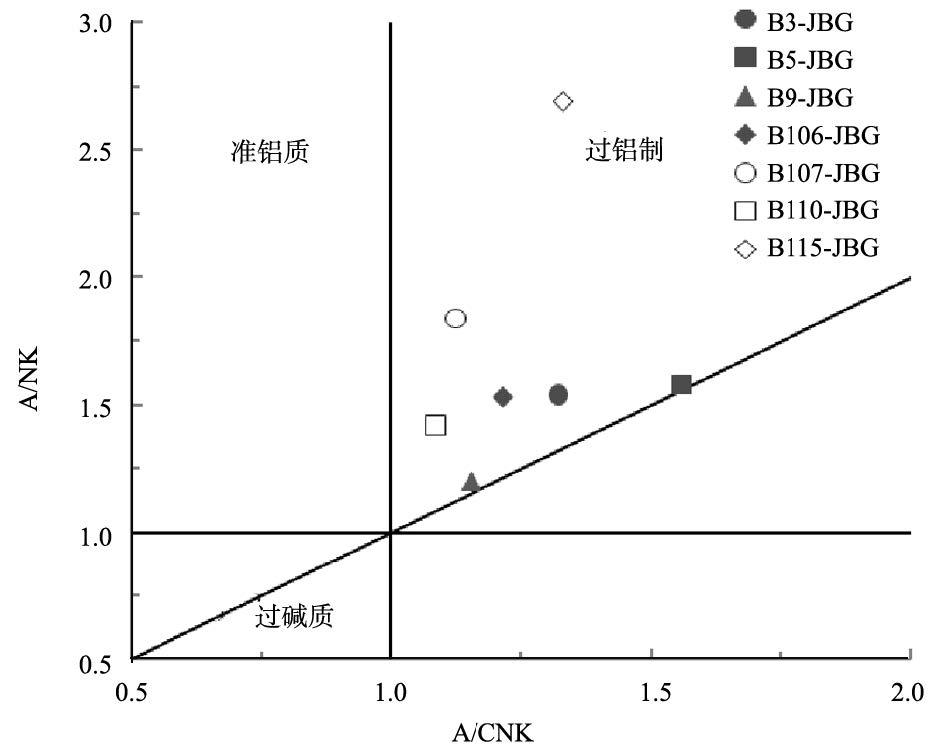
图 6 金宝沟花岗斑岩A/CNK-A/NK 图解[24]
Figure 6. A/CNK versus A/NK diagram of Jinbaogou granite porphyry
图 7 金宝沟花岗斑岩体稀土元素球粒陨石标准化分布型式图(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)(标准值据参考文献[22])
Figure 7. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spidergram (b) of Jinbaogou granite porphyry
图 10 金宝沟花岗斑岩t-176Hf/177Hf 和t-εHf (t) 图解[38]
Figure 10. 176Hf/177Hf versus t and εHf versus t diagrams of Jinbaogou granite porphyry
图 11 金宝沟花岗斑岩岩浆形成压力判别图解[47]
Figure 11. Discrimination diagram of pressure of Jinbaogou granite porphyry
图 12 金宝沟花岗斑岩构造环境判别图及Rb/30-Hf-3Ta 图解[71]
VAG—火山弧花岗岩;ORG—洋中脊花岗岩;WPG—板内花岗岩;syn-COLG—同碰撞花岗岩;
Figure 12. Tectonic setting discrimination diagram and Rb/30- Hf-3Ta diagram of Jinbaogou granite porphyry
表 1 金宝沟花岗斑岩LA-ICP-MS 锆石U-Th-Pb 同位素定年结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb dating of Jinbaogou granite porphyry
点号 元素含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 同位素年龄/Ma Th Pb U 206Pb/238U 207Pb/235U 207Pb/206Pb 206Pb/238U 207Pb/235U 207Pb/206Pb 样品B107-JBG 1 112 7 270 0.41 0.0263±0.0001 0.1827±0.0060 0.0505±0.0016 167±1 170±6 216±75 2 112 7 234 0.48 0.0266±0.0002 0.1854±0.0063 0.0506±0.0017 169±1 173±6 222±77 3 158 10 349 0.45 0.0262±0.0001 0.1798±0.0038 0.0497±0.001 167±1 168±4 180±49 4 120 18 220 0.54 0.0428±0.001 2.3059±0.1267 0.3906±0.0103 270±6 1214±67 3873±40 5 109 6 220 0.50 0.0267±0.0002 0.1847±0.0069 0.0502±0.0018 170±1 172±6 202±85 6 244 16 361 0.67 0.0318±00002 0.8190±0.0222 0.1865±0.0041 201±1 608±16 2712±36 7 120 6 220 0.55 0.0267±0.0002 0.1858±0.0086 0.0505±0.0021 170±1 173±8 218±97 8 200 10 344 0.58 0.0271±0.0001 0.1840±0.0044 0.0492±0.0012 172±1 171±4 157±56 9 258 9 322 0.80 0.0270±0.0002 0.1831±0.0046 0.0491±0.0012 172±1 171±4 153±55 10 70 8 175 0.40 0.0324±0.0003 0.9383±0.0394 0.2098±0.0071 206±2 672±28 2904±55 11 95 10 176 0.54 0.0369±0.0005 1.4153±0.0586 0.2784±0.0082 233±3 895±37 3354±46 12 159 42 204 0.75 0.0844±0.0017 7.5229±0.2155 0.6461±0.0086 523±11 2176±62 4615±19 13 189 7 270 0.70 0.0271±0.0002 0.1845±0.0057 0.0494±0.0015 172±1 172±5 168±70 14 78 7 164 0.47 0.0317±0.0002 0.8144±0.0230 0.1865±0.0046 201±1 605±7 2712±41 15 172 8 293 0.59 0.0270±0.0003 0.3926±0.0176 0.1054±0.0035 172±2 336±15 1721±60 16 136 7 245 0.55 0.0268±0.0002 0.1864±0.0070 0.0504±0.0019 171±1 174±7 213±87 17 165 69 294 0.56 0.0918±0.0015 8.3788±0.2124 0.6618±0.0082 566±9 2273±58 4650±18 18 107 5 202 0.53 0.0268±0.0002 0.1818±0.0103 0.0491±0.0027 171±1 170±10 154±131 19 118 7 242 0.49 0.0267±0.0002 0.1829±0.007 00497±0.0018 170±1 171±6 180±85 20 123 6 199 0.62 0.0267±0.0002 0.1838±0.0091 0.0499±0.0024 170±1 171±8 188±113 21 94 5 175 0.54 0.0265±00002 0.2473±0.0095 0.0678±0.0025 168±1 224±9 862±76 22 117 6 231 0.51 0.0266±0.0001 0.1803±0.0066 0.0491±0.0018 169±1 168±6 154±84 23 72 4 125 0.57 0.0266±0.0002 0.2951±0.0121 0.0803±0.029 169±1 2263±11 1206±71 24 164 5 147 1.12 0.0265±0.0003 0.1857±0.0236 0.0508±0.0065 169±2 173±22 231±195 样品B115-JBG 1 82 4 149 0.55 0.0263±0.0002 0.3305±0.0134 0.0913±0.0035 167±1 290±12 1452±73 2 136 5 177 0.77 0.0251±0.0002 0.1725±0.0091 0.0499±0.0025 160±1 162±8 189±117 3 132 6 194 0.68 0.0263±0.0002 0.3247±0.0124 0.0894±0.0032 168±1 286±11 1413±69 4 104 6 199 0.52 0.0265±0.0002 0.3393±0.0117 0.0930±0.0030 168±1 297±10 1488±60 5 116 8 236 0.49 0.0268±0.0002 0.4237±0.0265 0.1147±0.0059 171±1 359±22 1874±93 6 107 7 219 0.49 0.0268±0.0002 0.3807±0.0106 0.1029±0.0026 171±1 328±9 1676±46 7 70 4 155 0.45 0.0258±0.0002 0.1836±0.0107 0.0516±0.0029 164±1 171±10 269±128 8 140 6 225 0.62 0.0268±0.0002 0.1832±0.0081 0.0496±0.0020 170±1 171±8 178±92 9 114 5 193 0.59 0.0265±0.0002 0.1842±0.0040 0.0505±0.0010 168±1 172±4 217±47 10 122 5 182 0.67 0.0267±0.0002 0.1824±0.0075 0.0495±0.0017 170±1 170±7 170±82 11 125 6 237 0.53 0.0261±0.0002 0.1850±0.0109 0.0514±0.0024 166±2 172±10 258±105 12 207 9 327 0.63 0.0263±0.0001 0.1834±0.0052 0.0506±0.0013 167±1 171±5 225±61 13 80 4 162 0.49 0.0270±0.0002 0.1828±0.0048 0.0491±0.0011 172±1 170±5 152±54 14 37 2 76 0.49 0.0267±0.0002 0.1829±0.0175 0.0496±0.0048 170±1 171±16 177±224 15 93 5 179 0.52 0.0266±0.0002 0.1875±0.0062 0.0511±0.0015 169±1 174±6 245±66 16 368 11 229 1.61 0.0329±0.0003 0.6904±0.0252 0.1520±0.0045 209±2 533±19 2369±50 17 80 4 150 0.53 0.0268±0.0002 0.1827±0.0060 0.0495±0.0016 170±1 170±6 170±75 18 85 4 157 0.54 0.0264±0.0002 0.1834±0.0089 0.0503±0.0024 168±1 171±8 209±110 19 68 3 115 0.60 0.0265±0.0002 0.1821±0.0123 0.0499±0.0034 168±1 170±11 189±158 20 113 5 162 0.70 0.0274±0.0002 0.1808±0.0083 0.0478±0.0022 175±1 169±8 89±107 21 48 3 103 0.46 0.0276±0.0003 0.1842±0.0147 0.0484±0.0029 176±2 172±14 117±140 22 174 7 225 0.77 0.0279±0.0002 0.1826±0.0062 0.0474±0.0016 177±1 170±6 71±80 23 110 8 173 0.64 0.0316±0.0002 0.7218±0.0136 0.1656±0.0028 201±1 552±10 2514±28 24 154 7 208 0.74 0.0277±0.0002 0.1834±0.0072 0.0480±0.0017 176±1 171±7 100±86 表 2 金宝沟花岗斑岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 2 Major, trace and rare earth elements analyses of Jinbaogou granite porphyry
样品号 B3-JBG B5-JBG B9-JBG B106-JBG B107-JBG B110-JBG B115-JBG SiO2 70.25 76.88 74.92 72.08 67.33 70.04 65.4 Al2O3 14.9 13.23 13.95 13.74 14.14 14.24 15.05 CaO 0.87 0.07 0.27 1.06 0.96 0.38 1.33 Fe2O3 0.45 0.15 0.52 1.27 2.69 1.67 3.15 MgO 0.47 0.18 0.19 0.45 0.48 0.47 0.97 MnO 0.06 0.03 0.05 0.06 0.23 0.05 0.42 K2O 6.23 5.65 4.53 5.79 7.07 5.45 5.15 Na2O 1.79 1.37 4.07 1.65 0.02 2.53 0.01 P2O5 0.07 0.01 0.02 0.07 0.07 0.07 0.16 TiO2 0.2 0.07 0.1 0.19 0.21 0.21 0.34 LOI 2.45 1.08 0.72 2.98 4.49 3.31 5.82 Total 97.74 98.72 99.34 99.34 97.69 98.42 97.8 K2O/Na2O 2.29 2.71 0.73 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.03 K2O+Na2O 8.02 7.02 8.6 7.44 7.09 7.98 5.16 A/CNK 1.32 1.56 1.15 1.22 1.12 1.09 1.33 La 33.3 9.15 12.3 26.9 23.5 29.3 12.8 Ce 60.5 15.3 24.8 52.6 49.4 55.8 37.5 Pr 6.42 2.12 2.69 5.17 4.78 5.55 5.01 Nd 22.40 6.95 8.43 18.1 16.7 19 20.5 Sm 4.02 1.01 1.34 2.82 2.77 2.87 3.74 Eu 0.77 0.19 0.23 0.65 0.7 0.69 0.73 Gd 2.51 0.87 0.99 1.97 2.37 2.23 3.06 Tb 0.37 0.13 0.15 0.33 0.31 0.31 0.4 Dy 2.39 0.78 0.81 1.75 1.71 1.84 2.29 Ho 0.44 0.17 0.16 0.36 0.37 0.38 0.48 Er 1.29 0.52 0.48 1.01 1 1.01 1.28 Tm 0.22 0.11 0.09 0.15 0.16 0.16 0.2 Yb 1.63 0.73 0.63 1.13 1.24 1.23 1.39 Lu 0.25 0.14 0.09 0.19 0.21 0.2 0.23 Y 15.8 8.13 8.03 9.88 9.46 10.3 14 Rb 153 187 131 140 206 137 193 Ba 977 72.8 140 1022 1239 1033 255 Th 9.97 10.2 5.77 7.8 6.8 8.64 4.57 U 4.72 2.94 1.35 1.58 1.81 2.64 2.3 Ta 0.96 1.2 1.01 0.62 0.57 0.63 0.56 Nb 11.6 14.2 14.5 10.3 9.19 10 12.5 La 33.3 9.15 12.3 26.9 23.5 29.3 12.8 Ce 60.5 15.3 24.8 52.6 49.4 55.8 37.5 Sr 163 11.2 37.2 74 88.1 138 106 Nd 22.4 6.95 8.43 18.1 16.7 19 20.5 Zr 266 197 288 152 167 158 214 Hf 8.71 6.72 8.71 4.5 4.65 4.66 5.25 Sm 4.02 1.01 1.34 2.82 2.77 2.87 3.74 ΣREE 136.51 38.17 53.19 113.13 105.22 120.57 89.61 LREE/HREE 14 10.06 14.64 15.42 13.28 15.38 8.6 (La/Yb)N 14.65 8.99 14 17.08 13.59 17.09 6.61 δEu 0.69 0.60 0.58 0.8 0.81 0.8 0.64 δCe 0.95 0.82 1.01 1.02 1.08 1 1.15 注:LOI 为烧失量;Total 为主量元素总和;A/CNK=(Al2O3)/(CaO+K2O+Na2O)摩尔分数比; 里特曼指数δ=(K2O+Na2O)2/(SiO2-43);球粒陨石、原始地幔数据据参考文献[22];主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素为10-6 表 3 金宝沟花岗斑岩锆石Hf 同位素分析结果
Table 3 Zircon Hf isotopic composition of Jinbaogou granite porphyry
点号 年龄/Ma 176Yb/177Hf 176Lu/177Hf 176Hf/177Hf 2σ 176Hf/177Hf (t) εHf(0) εHf(t) TDM1/Ma TDM2/Ma fLu/Hf 样品B107-JBG 1 167 0.037843 0.001401 0.282463 0.000019 0.282459 -3938.3 -7.4 1127 1685 -0.96 2 169 0.039339 0.001444 0.282342 0.000020 0.282337 -3936.6 -11.7 1301 1956 -0.96 3 167 0.038144 0.001385 0.282398 0.000019 0.282394 -3937.4 -9.7 1219 1831 -0.96 5 170 0.035937 0.001283 0.282413 0.000021 0.282409 -3937.6 -9.1 1195 1796 -0.96 7 170 0.027297 0.001008 0.282347 0.000019 0.282344 -3936.6 -11.4 1277 1940 -0.97 8 172 0.034716 0.001261 0.282368 0.000020 0.282364 -3936.9 -10.6 1257 1894 -0.96 9 172 0.034333 0.001273 0.282308 0.000019 0.282304 -3936.1 -12.8 1342 2028 -0.96 13 172 0.029854 0.001116 0.282344 0.000017 0.282341 -3936.6 -11.5 1286 1946 -0.97 16 171 0.037994 0.001425 0.282444 0.000019 0.282439 -3938.0 -8.0 1155 1727 -0.96 18 171 0.027275 0.001036 0.282339 0.000019 0.282335 -3936.5 -11.7 1291 1959 -0.97 19 170 0.033228 0.001236 0.282349 0.000020 0.282345 -3936.7 -11.4 1283 1938 -0.96 20 170 0.034634 0.001280 0.282404 0.000018 0.282400 -3937.4 -9.4 1206 1814 -0.96 22 169 0.027790 0.001055 0.282341 0.000019 0.282338 -3936.6 -11.6 1288 1955 -0.97 24 169 0.045791 0.001652 0.282372 0.000021 0.282367 -3937.0 -10.6 1264 1889 -0.95 B115-JBG 7 164 0.030501 0.001163 0.282352 0.000023 0.282348 -3936.7 -11.4 1277 1935 -0.96 8 170 0.034451 0.001330 0.282337 0.000021 0.282333 -3936.5 -11.8 1303 1964 -0.96 9 168 0.031858 0.001236 0.282420 0.000024 0.282416 -3937.7 -8.9 1183 1780 -0.96 10 170 0.040754 0.001632 0.282264 0.000026 0.282259 -3935.5 -14.4 1417 2130 -0.95 11 166 0.037877 0.001443 0.282342 0.000021 0.282338 -3936.6 -11.7 1300 1957 -0.96 12 167 0.037739 0.001428 0.282322 0.000020 0.282318 -3936.3 -12.4 1327 2000 -0.96 13 172 0.024507 0.001004 0.282389 0.000018 0.282386 -3937.2 -9.9 1219 1846 -0.97 14 170 0.028499 0.001175 0.282422 0.000020 0.282419 -3937.7 -8.8 1178 1773 -0.96 15 169 0.031058 0.001282 0.282415 0.000019 0.282411 -3937.6 -9.0 1191 1790 -0.96 17 170 0.031301 0.001275 0.282340 0.000018 0.282336 -3936.5 -11.7 1297 1958 -0.96 18 168 0.021409 0.000862 0.282318 0.000019 0.282315 -3936.2 -12.5 1314 2006 -0.97 19 168 0.031610 0.001282 0.282364 0.000021 0.282360 -3936.9 -10.9 1263 1905 -0.96 20 175 0.033658 0.001384 0.282336 0.000019 0.282332 -3936.5 -11.7 1306 1964 -0.96 21 176 0.025831 0.001052 0.282368 0.000021 0.282364 -3936.9 -10.6 1251 1891 -0.97 22 177 0.027672 0.001135 0.282311 0.000019 0.282307 -3936.1 -12.5 1333 2017 -0.97 24 176 0.031711 0.001292 0.282326 0.000019 0.282322 -3936.3 -12.1 1318 1986 -0.96 注:εHf (t)={[(176Hf/177Hf)s-(176Lu/177Hf)s×(eλt-1)]/[(176Hf/177Hf)CHUR,0-(176Lu/177Hf)CHUR×(eλt-1)]-1}×10000;TDM1=1/λ×ln{1+[(176Hf/177Hf)s-(176Hf/177Hf)DM]/[(176Lu/ 177Hf)s-(176Lu/177Hf)DM];TDM2=1/λ×ln{1+[(176Hf/177Hf)s,t-(176Hf/177Hf)DM,t]/[(176Lu/177Hf)C-(176Lu/ 177Hf)DM]}+t;(176Lu/177Hf)s和(176Hf/177Hf)s为样品测定值;(176Hf/177Hf)CHUR,0=0.282772,(176Lu/177Hf)CHUR =0.0332,(176Hf/177Hf)DM=0.28325,(176Lu/177Hf)DM=0.0384;λ=1.867×10-11a-1,(176Lu/177Hf)C=0.015,t=锆石结晶年龄 -
赵海玲,邓晋福,徐立权,等.冀东地区中生代花岗岩、深部过程与金矿[J].桂林工学院学报,2001,21(1):20-26. 李俊健,沈保丰,翟安民,等.冀东地区金矿床类型及其地质特征[J]. 前寒武纪研究进展,2002,25(2):73-79. 康显桂,陈克荣,陈小明.河北峪耳崖花岗岩地球化学特征与成因[J].中山大学学报(自然科学版), 1996,35(2):137-141. Davis G A, Zheng Y, Wang C, et al. Geometry and geochronology of Yanshan Belt tectonics[C]//International Symposium on Geological Science,100thAnniversary Celebration of Peking University:Beijing, Peking University Department of Geology, 1998:275-292. Davis G A, Zheng Y, Wang C, et al. Geometry and geochronology of Yanshan Belt tectonics[C]//International Symposium on Geological Science,100thAnniversary Celebration of Peking University:Beijing, Peking University Department of Geology, 1998:275-292.
Deng J, Mo X, Zhao H, et al. Yanshanian magma-tectonic-metallogenic belt in east China of circum-Pacific domain (I):Igneous rocks and orogenic processes[J]. China University of Geosciences Journal, 1999, 10:21-24. Deng J, Mo X, Zhao H, et al. Yanshanian magma-tectonic-metallogenic belt in east China of circum-Pacific domain (I):Igneous rocks and orogenic processes[J]. China University of Geosciences Journal, 1999, 10:21-24.
罗镇宽,裘有守,关康,等.冀东峪耳崖和牛心山花岗岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年及其意义[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报,2001,20(4):278-285. 毛景文,谢桂青,张作衡,等.中国北方中生代大规模成矿作用的期次及其地球动力学背景[J].岩石学报,2005,21(1):169-188. 郭少丰,汤中立,罗照华,等. 冀东唐杖子、牛心山花岗岩体SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J].地质通报,2009,28(10):1458-1464. 陆继龙,石厚礼,赵玉岩,等.冀东罗文峪花岗岩体LA-MC-ICPMS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2012,42(3):179-188. 肖振,魏峰,刘铁侠,等.河北峪耳崖金矿成矿预测及找矿方向[J]. 地质找矿论丛,2010,25(3):217-222. 李伍平,路风香,李献华,等.北京西山署髻山组火山岩的地球化学特征与岩浆起源[J].岩石矿物学杂志,2001,20(2):123-133. Davis G A, Zheng Y D, Wang C, et al. Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the Yanshan fold and thrust belt, with emphasis on Hebei and Liaoning provinces, norther China[C]//Hendrix M S, Davis G A. Paleozoic and Mesozoic Tectonic Evolution of Central Asia:From Continental Assembly to Intra-continental Deformation. Boulder, Colorado:Geological Society of America Memoir, 2001:171-197. Davis G A, Zheng Y D, Wang C, et al. Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the Yanshan fold and thrust belt, with emphasis on Hebei and Liaoning provinces, norther China[C]//Hendrix M S, Davis G A. Paleozoic and Mesozoic Tectonic Evolution of Central Asia:From Continental Assembly to Intra-continental Deformation. Boulder, Colorado:Geological Society of America Memoir, 2001:171-197.
Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010,51(1/2):537-571. Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010,51(1/2):537-571.
Ludwig K R. User's manual for Isoplot/Ex, version 3.00:A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J]. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication,2003, 4:1-70. Ludwig K R. User's manual for Isoplot/Ex, version 3.00:A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J]. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication,2003, 4:1-70.
Anderson T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J].Chemical Geology,2002,192(1/2):59-79. Anderson T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J].Chemical Geology,2002,192(1/2):59-79.
李怀坤,朱士兴,相振群,等.北京延庆高于庄组凝灰岩的锆石U-Pb定年研究及其对华北北部中元古界划分新方案的进一步约束[J].岩石学报,2010,26(7):2131-2140. 侯可军,李延河,邹天人,等.LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石Hf同位素的分析方法及地质应用[J].岩石学报,2007,23(10):2595-2604. Jackson S E, Pearson N J, Griffin W L, et al. The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U-Pb zircon geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004,211(1/2):47-6. Jackson S E, Pearson N J, Griffin W L, et al. The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U-Pb zircon geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004,211(1/2):47-6.
Elhlou S, Belousova E, Griffin W L, et al. Trace element and isotopic composition of GJ-red zircon standard by Laser ablation[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70(19):A158. Elhlou S, Belousova E, Griffin W L, et al. Trace element and isotopic composition of GJ-red zircon standard by Laser ablation[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70(19):A158.
Connely J N. Degree of preservation of igneous zonation in zircon as a signpost for concordancy in U/Pb geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2000,172(1):25-39. Connely J N. Degree of preservation of igneous zonation in zircon as a signpost for concordancy in U/Pb geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2000,172(1):25-39.
Wu Y B and Zheng Y F. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004,49(15):1554-1569. Wu Y B and Zheng Y F. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004,49(15):1554-1569.
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition process[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society Special Publication, 1989, 42:313-345. Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition process[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society Special Publication, 1989, 42:313-345.
Rickwood P C. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides major and minor elements[J]. Lithos, 1989,22:247-263. Rickwood P C. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides major and minor elements[J]. Lithos, 1989,22:247-263.
Peccerillo R, Taylor S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calakaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey[J]. Mineral. Petrol, 1976,58:63-81. Peccerillo R, Taylor S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calakaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey[J]. Mineral. Petrol, 1976,58:63-81.
Griffin W L, Belousova E A, Shee S R, et al. Archean crustal evolution in the northern Yilgarn Craton:U-Pb and Hf-isotope evidence from detrital zircons[J]. Precambrian Research, 2004,131(3/4):231-282. Griffin W L, Belousova E A, Shee S R, et al. Archean crustal evolution in the northern Yilgarn Craton:U-Pb and Hf-isotope evidence from detrital zircons[J]. Precambrian Research, 2004,131(3/4):231-282.
Zheng Y F, Zhang S B, Zhao Z F, et al. Constrasting zircon Hf and O isotopes in the two episodes of Neoproterozoic granitoids in South China:Implications for growth and reworking of continental crust[J]. Lithos, 2007,96:127-150. Zheng Y F, Zhang S B, Zhao Z F, et al. Constrasting zircon Hf and O isotopes in the two episodes of Neoproterozoic granitoids in South China:Implications for growth and reworking of continental crust[J]. Lithos, 2007,96:127-150.
罗镇宽,关康,裘有守,等.冀东金厂峪金矿区钠长岩脉及青山口花岗岩体SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年及其意义[J].地质找矿论丛, 2001,16(4):226-231. 董传万,李武显.高钾钙碱性I型花岗岩类的成因[J].世界地质, 1994,13(4):8-11,73. Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell B W.A-type granites:Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987,95:407-419 Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell B W.A-type granites:Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987,95:407-419
Watson E B,Harrison T M. Zircon saturation revisited:temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983,64(2):295-304. Watson E B,Harrison T M. Zircon saturation revisited:temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983,64(2):295-304.
Miller C F, McDowell S M,Mapes R W. Hot and cold granites? Implications of zircon saturation temperatures and preservation of inheritance[J]. Geology, 2003,31:529-532. Miller C F, McDowell S M,Mapes R W. Hot and cold granites? Implications of zircon saturation temperatures and preservation of inheritance[J]. Geology, 2003,31:529-532.
King P L, White A J R, Chappell B W, et al. Characterization and origin of aluminous A-type granites from the Lachlan Fold belt, Southeastern Australia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1997,38(3):371-391. King P L, White A J R, Chappell B W, et al. Characterization and origin of aluminous A-type granites from the Lachlan Fold belt, Southeastern Australia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1997,38(3):371-391.
Scherer E E, Cameron K L,Blichert-Toft J. Lu-Hf garnet geochronology:closure temperature relative to the Sm-Nd system and the effects of trace mineral inclusions[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000,64:3413-3432. Scherer E E, Cameron K L,Blichert-Toft J. Lu-Hf garnet geochronology:closure temperature relative to the Sm-Nd system and the effects of trace mineral inclusions[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000,64:3413-3432.
Griffin W L, Pearson N J, Belousova E, et al. The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle:LA-MC-ICPMS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000,64:133-147 Griffin W L, Pearson N J, Belousova E, et al. The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle:LA-MC-ICPMS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000,64:133-147
徐平,吴福元,谢烈文,等.U-Pb同位素定年标准锆石的Hf同位素[J].科学通报,2004,49:1403-1410. Belousova E A, Griffin W L,O'Reilly S Y. Zircon crystal morphology, trace element signatures and Hf isotope composition as a tool for petrogenetic modelling:examples from eastern Australian granitoids[J]. Petrol.,2006,47:329-353. Belousova E A, Griffin W L,O'Reilly S Y. Zircon crystal morphology, trace element signatures and Hf isotope composition as a tool for petrogenetic modelling:examples from eastern Australian granitoids[J]. Petrol.,2006,47:329-353.
Patchett P J, Kouvo O, Hedge C E, et al. Evolution of continental crust and mantle heterogeneity:Evidence from Hf isotopes[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1982,78(3):279-297. Patchett P J, Kouvo O, Hedge C E, et al. Evolution of continental crust and mantle heterogeneity:Evidence from Hf isotopes[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1982,78(3):279-297.
孙立新,任邦方,赵凤清,等.内蒙古锡林浩特地块中元古代花岗片麻岩的锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素特征[J].地质通报,2013, Z1:327-340. 吴福元,李献华,郑永飞,等.Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J]. 岩石学报,2007,23(2):185-220. 任荣,韩宝福,张志诚,等.北京昌平地区基底片麻岩和中-新元古代盖层锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素研究及其地质意义[J].岩石学报,2011,27(6):1721-1745. 吴福元,李献华,杨进辉,等.花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J].岩石学报,2007,23(6):1217-1238. Watson E B, Harrison T M. Zircon saturation revisited:temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983,64(2):295-304. Watson E B, Harrison T M. Zircon saturation revisited:temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983,64(2):295-304.
张旗,王焰,李承东,等.花岗岩的Sr-Yb分类及其地质意义[J].岩石学报,2006,22(9):2249-2269. 张旗,金惟俊,李承东,等.再论花岗岩按照Sr-Yb的分类:标志[J]. 岩石学报,2010,26(4):985-1015. 张旗,金惟俊,李承东,等.三论花岗岩按照Sr-Yb的分类:应用[J]. 岩石学报,2010,26(12):3431-3455. 殷勇,殷先明.西秦岭北缘与埃达克岩和喜马拉雅型花岗岩有关的斑岩型铜-钼-金成矿作用[J].岩石学报,2009,25(5):1239-1252. 熊小林,刘星成,朱志敏,等.华北埃达克质岩与克拉通破坏:实验岩石学和地球化学依据[J].科学通报,2011,41(5):654-667. 李承东,张旗,苗来成,等.冀北中生代高Sr低Y和低Sr低Y型花岗岩:地球化学、成因及其与成矿作用的关系[J].岩石学报,2004, 20(2):269-284. 邓晋福,刘厚祥,赵海玲,等.燕辽地区燕山期火成岩与造山模型[J].现代地质,1996,2:137-148. 李俊健,沈保丰,翟安民,等.冀东地区金矿地质[M].北京:地质出版社,2004:1-133. 孙金凤,杨进辉.华北中生代岩浆作用与去克拉通化[J].岩石矿物学杂志,2013,5:577-592. 吴福元,徐义刚,朱日祥,等.克拉通岩石圈减薄与破坏[J].中国科学(D辑),2014,11:2358-2372. 邵济安,牟保磊,何国琦,等.华北北部在古亚洲域与古太平洋域构造叠加过程中的地质作用[J].中国科学(D辑),1997,27(5):390-394. 葛肖虹.华北板内造山带的形成史[J].地质评论,1989,35(2):254-261. 邓晋福,赵国春,苏尚国,等.燕山造山带燕山期构造叠加及其大地构造背景[J].大地构造与成矿学,2005,29(2):157-165. 郑伟,陈懋弘,徐林刚,等.广东天堂铜铅锌多金属矿床Rb-Sr等时线年龄及其地质意义[J].矿床地质,2013,2:259-272. 毛景文,谢桂青,李晓峰,等.华南地区中生代大规模成矿作用与岩石圈多阶段伸展[J].地学前缘,2004,11(1):45-55. 毛景文,谢桂青,郭春丽,等.南岭地区大规模钨锡多金属成矿作用:成矿时限及地球动力学背景[J].岩石学报,2007,23(10):2329-2338. 毛景文,谢桂青,郭春丽,等.华南地区中生代主要金属矿床时空分布规律和成矿环境[J].高校地质学报,2008,14:510-526. 舒良树,周新民,邓平,等.南岭构造带的基本地质特征[J].地质论评,2006,52(2):251-265. 董树文,张岳桥,龙长兴,等.中国侏罗纪构造变革与燕山运动新诠释[J].地质学报,2007,81(11):1449-1461. 杨宗永,何斌.华南侏罗纪构造体制转换:碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学证据[J].大地构造与成矿学,2013,4:580-591. Zhang Z M, Liou J G, Coleman R G. The Mesozoic and Cenozoic tectonism in eastern China[C]//Ben-Avraham Z. The evolution of the Pacific Ocean:Oxford Monographs on Geology and Geophysics No. 8:New York, Oxford University Press, 1989:124-139. Zhang Z M, Liou J G, Coleman R G. The Mesozoic and Cenozoic tectonism in eastern China[C]//Ben-Avraham Z. The evolution of the Pacific Ocean:Oxford Monographs on Geology and Geophysics No. 8:New York, Oxford University Press, 1989:124-139.
张旗.中国东部中生代岩浆活动与太平洋板块向西俯冲有关吗?[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志,2013,1:113-128. Xu Z. Mesozoic volcanism and volcanogenic iron-ore deposits in eastern China[J]. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 1990,237:46. Xu Z. Mesozoic volcanism and volcanogenic iron-ore deposits in eastern China[J]. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 1990,237:46.
孙卫东,凌明星,汪方跃,等.太平洋板块俯冲与中国东部中生代地质事件[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报,2008,3:218-225. 肖庆辉,刘勇,冯艳芳,等.中国东部中生代岩石圈演化与太平洋板块俯冲消减关系的讨论[J].中国地质,2010,4:1092-1101. 郭锋.俯冲陆壳和洋壳对华北克拉通中生代岩石圈地幔改造的氧同位素记录[J].岩石矿物学杂志,2013,5:593-603. 张宏,王明新,柳小明.LA-ICP-MS测年对辽西-冀北地区髫髻山组火山岩上限年龄的限定[J].科学通报,2008,15:1815-1824. 陈义贤,陈文寄,等.辽西及邻区中生代火山岩-年代学地球化学和构造背景[M].北京:地震出版社,1997:1-279. Sylvester P J. Post-collision strongly peraluminous granites[J]. Lithos, 1998,45:29-44. Sylvester P J. Post-collision strongly peraluminous granites[J]. Lithos, 1998,45:29-44.



 下载:
下载: