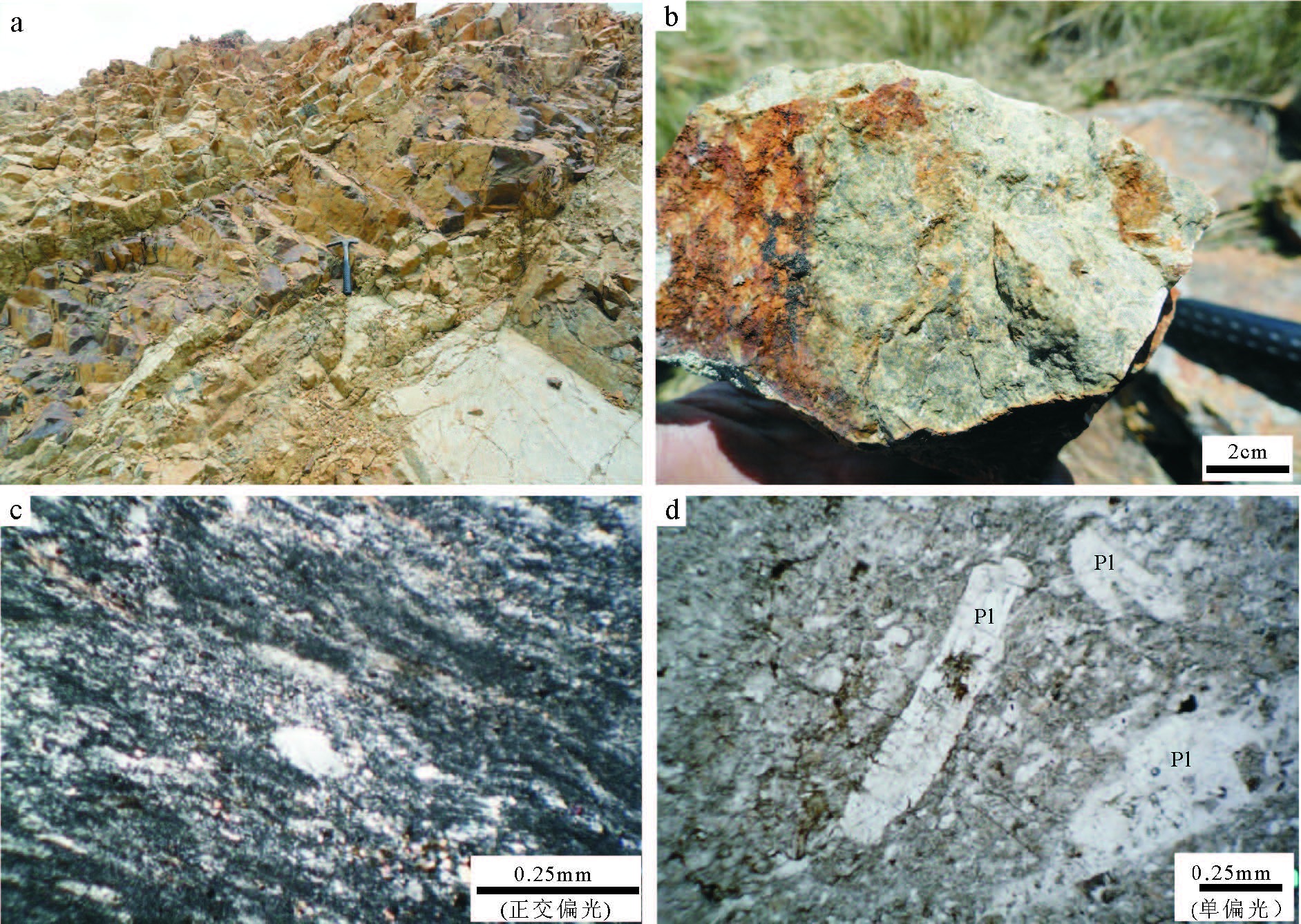
Geochronological and geochemical features of volcanic rocks of Dashizhai Formation in Ural Sutai of Xilin Hot, Inner Mongolia, and their geological significance
-
摘要:
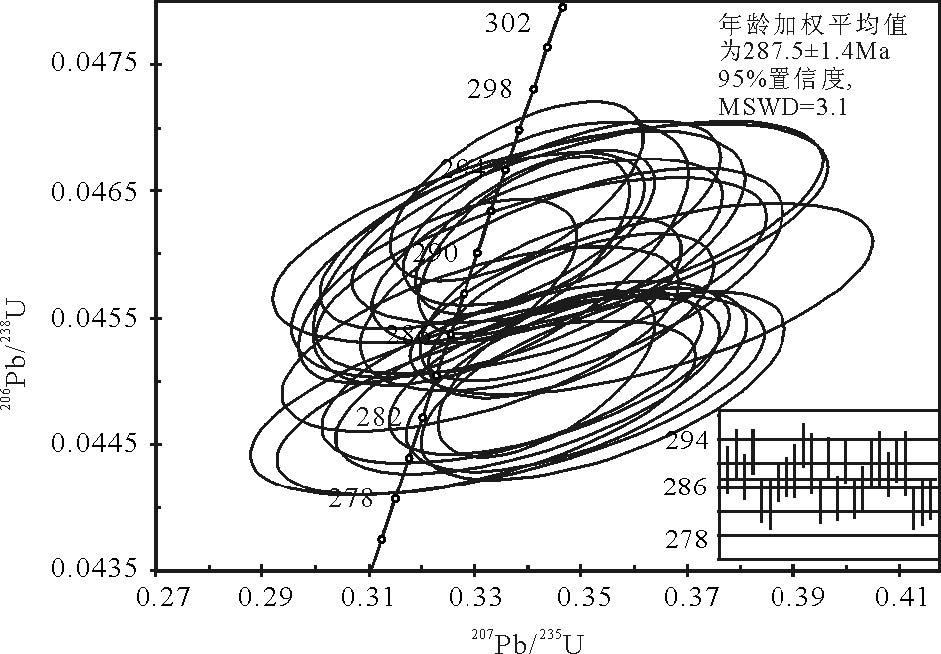
通过1:5万区域地质调查,对中亚造山带南缘内蒙古锡林浩特乌拉苏太地区发育的大石寨组酸性火山岩进行了野外地质、岩石学、锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学等研究。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素定年结果显示,该火山岩年龄为287.5±1.4Ma(MSWD=3.1),形成于早二叠世早期。岩石地球化学研究表明,大石寨组火山岩为一套中酸性火山岩,以高硅、富碱、高铝为特征,Ti、Mg、Fe、Ca等元素含量较低。微量元素总体含量较高,具有一致的配分曲线,Rb、Ba、Th、U、K、LREE等大离子亲石元素相对于Nb、Ta、HREE等高场强元素明显富集。稀土元素总量偏高,具有一致的右倾海鸥式配分型式。地球化学特征显示,该套火山岩具有岛弧火山岩的属性。结合大石寨组岩石学及地质学特征,大石寨组火山岩最可能形成于弧后扩张(或弧间)盆地,是早二叠世早期古亚洲洋闭合前洋壳俯冲消减作用的产物。
Abstract:Based on 1:50000 regional geological survey, the authors studied the volcanic rocks of Dashizhai Formation developed in southern Central Asia Orogenic Belt (CAOB) within Ural Sutai of Xilin Hot, Inner Mongolia in such aspects as filed occurrence, petrology, zircon U-Pb isotopic geochronology and geochemistry. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results show that the rocks were formed at about 287.5±1.4Ma (MSWD=3.1) in the early period of Early Permian. Petrological and geochemical data reveal that the rocks are a suite of mid-acid volcanic rocks characterized by rich Si, alkali and Al, poor Ti, Mg, Fe and Ca, and abundant trace elements and REEs with coincident distribution pattern exhibiting a right-inclined seagull-type distribution pattern. The LILE, such as Rb, Ba, Th, U, K, and LREE are richer than HFSE like Nb, Ta and HREE, suggesting that the volcanic rocks were formed in an island-arc setting geochemically. Together with their petrological and geological features, the rocks were most probably formed in a back-arc or intra-arc spreading basin triggered by oceanic crust subduction before closure of the Paleoasian Ocean in the early period of Early Permian.
-
致谢: 感谢项目组成员在野外和室内整理工作中的大力支持,论文撰写过程中,中国石化石油勘探开发研究院冯建赟博士提出了宝贵意见、给予了帮助,审稿专家对本文进行了认真的审查并提出了宝贵的修改意见,在此一并致以衷心的感谢。
-
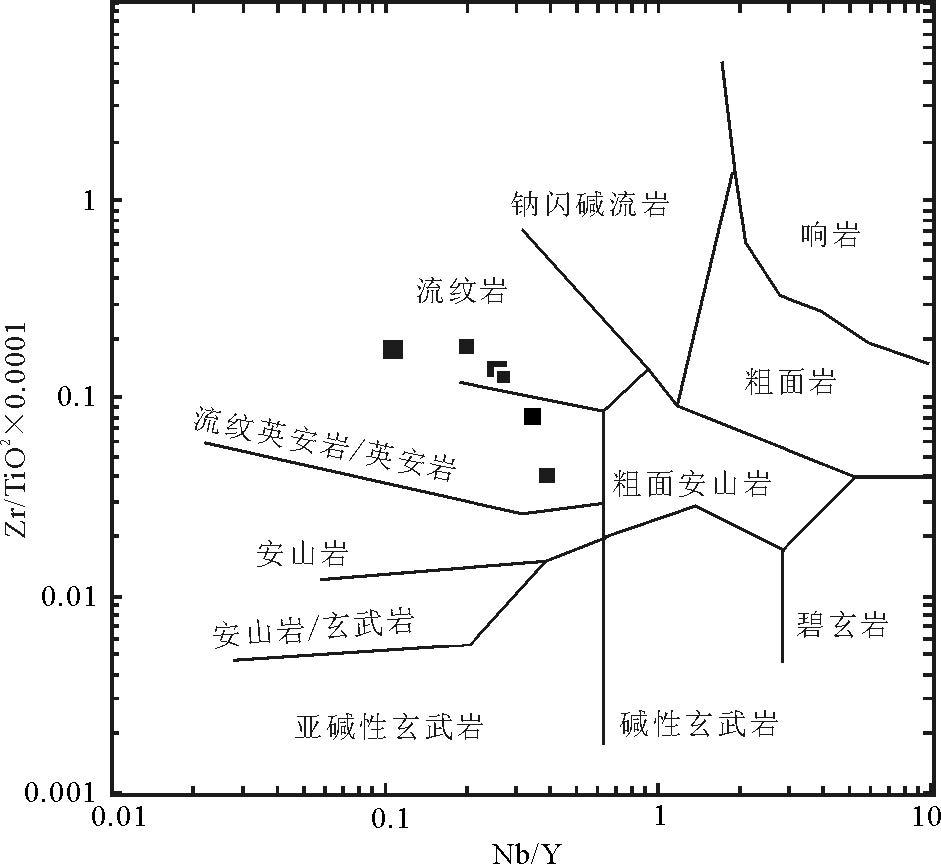
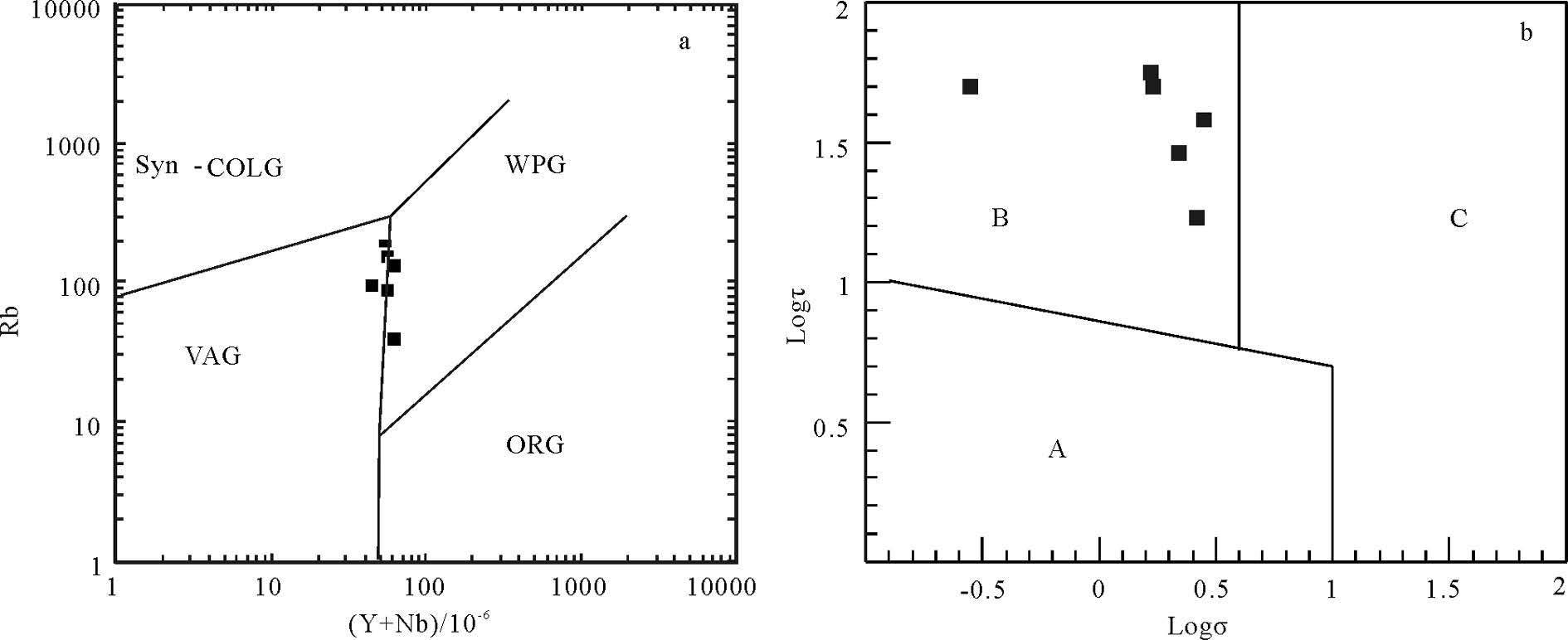
图 6 大石寨组火山岩Nb/Y-Zr/TiO2×0.0001 图解[23]
Figure 6. Nb/Y-Zr/TiO2×0.0001 diagram of volcanic rocks from Dashizhai Formation
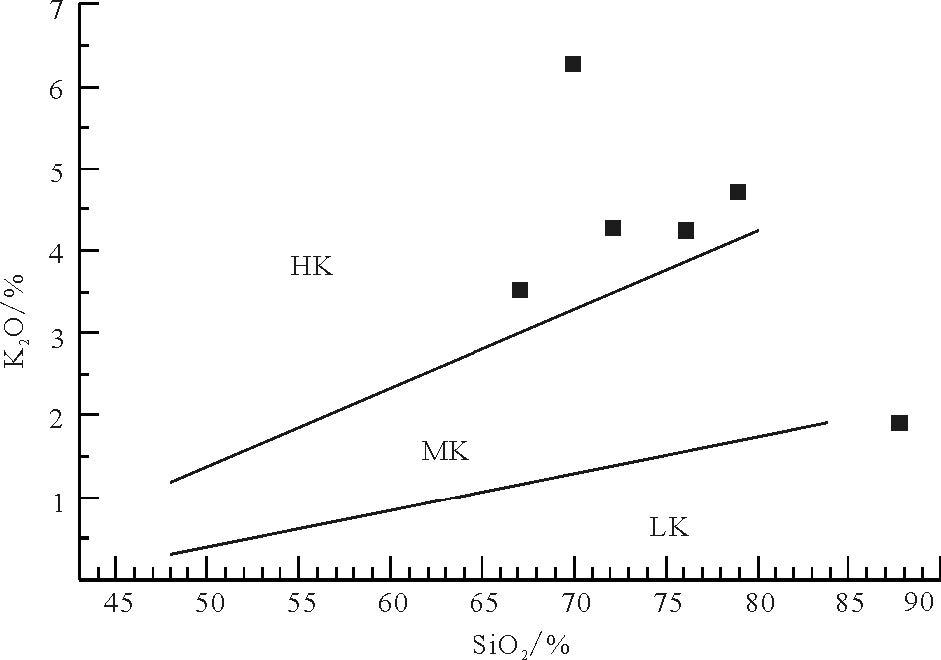
图 7 大石寨组火山岩SiO2-K2O 图解[24]
Hk—高钾岩系;MK—中钾岩系;LK—低钾岩系
Figure 7. SiO2-K2O diagram of volcanic rocks from Dashizhai Formation
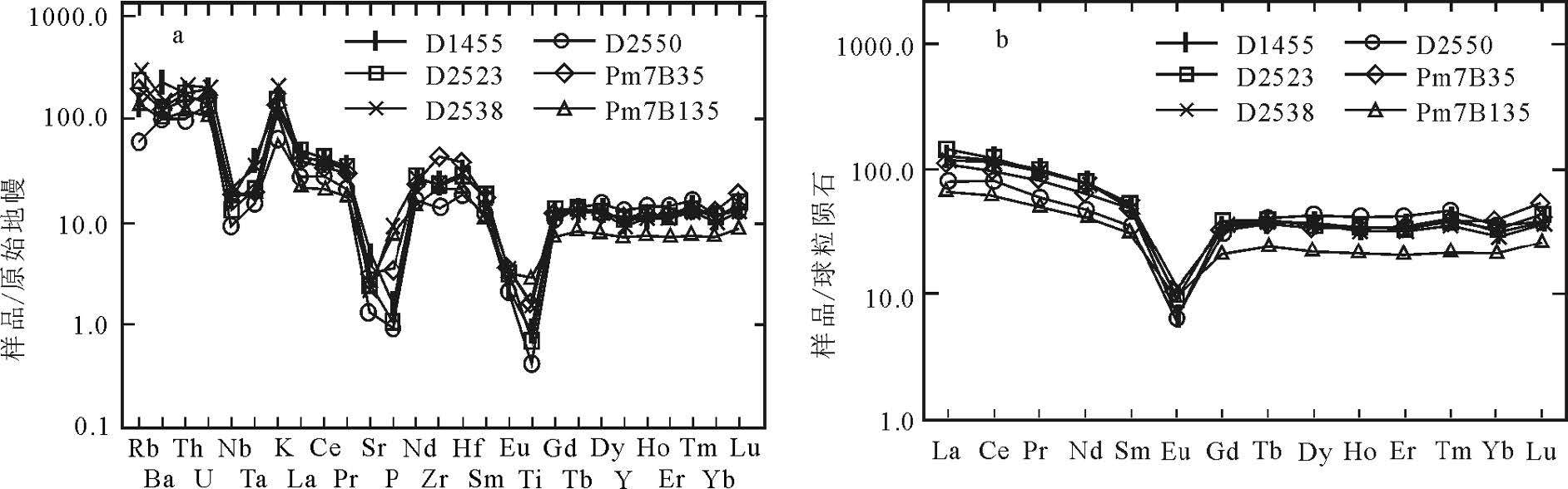
图 8 乌拉苏太地区大石寨组火山岩原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(a)和稀土元素配分图(b)(标准值据参考文献[30])
Figure 8. Primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagrams (a) and chondrite-normalized REE patterns (b) of volcanic rocks from Dashizhai Formation in Ural Sutai
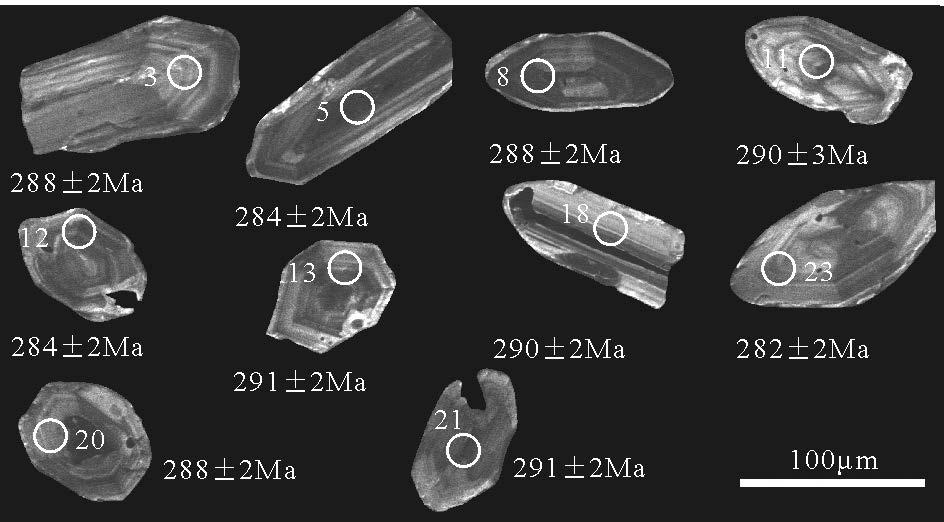
表 1 大石寨组英安岩LA-ICP-MS 锆石U-Th-Pb 年龄分析结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircons U-Th-Pb data from Dashizhai Formation
点 号 含量/10-6 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Pb U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ 232Th/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 1 8 156 0.0542 0.0035 0.342 0.022 0.0458 0.0003 0.0176 0.0003 0.482 0.001 379 111 299 15 289 2 2 10 218 0.0551 0.0041 0.351 0.027 0.0463 0.0003 0.0264 0.0007 0.230 0.001 415 111 306 16 292 2 3 8 175 0.0574 0.0035 0.361 0.023 0.0456 0.0003 0.0206 0.0005 0.331 0.001 508 108 313 15 288 2 4 18 361 0.0542 0.0026 0.346 0.018 0.0463 0.0003 0.0203 0.0002 0.482 0.001 380 77 302 11 292 2 5 20 393 0.0562 0.0031 0.349 0.021 0.0450 0.0003 0.0229 0.0006 0.470 0.001 462 78 304 11 284 2 6 8 160 0.0543 0.0039 0.336 0.024 0.0449 0.0003 0.0152 0.0004 0.494 0.001 384 129 294 17 283 2 7 20 418 0.0555 0.0024 0.348 0.015 0.0455 0.0003 0.0229 0.0006 0.276 0.001 431 69 303 10 287 2 8 18 380 0.0547 0.0021 0.344 0.014 0.0456 0.0003 0.0254 0.0007 0.268 0.001 400 62 300 9 288 2 9 10 201 0.0551 0.0041 0.348 0.029 0.0458 0.0004 0.0264 0.0010 0.361 0.001 418 91 303 14 289 2 10 15 273 0.0527 0.0029 0.338 0.020 0.0465 0.0003 0.0238 0.0003 0.596 0.001 316 63 296 9 293 2 11 9 179 0.0533 0.0043 0.338 0.029 0.0460 0.0004 0.0215 0.0005 0.421 0.001 342 111 296 15 290 3 12 14 294 0.0548 0.0025 0.340 0.016 0.0450 0.0003 0.0152 0.0002 0.477 0.001 405 95 297 13 284 2 13 18 370 0.0536 0.0018 0.341 0.012 0.0462 0.0003 0.0199 0.0002 0.423 0.001 355 60 298 8 291 2 14 11 235 0.0546 0.0027 0.340 0.017 0.0451 0.0003 0.0145 0.0002 0.589 0.001 397 103 297 14 284 2 15 13 244 0.0534 0.0026 0.339 0.017 0.0461 0.0003 0.0335 0.0005 0.349 0.001 346 53 297 7 290 2 16 13 260 0.0552 0.0022 0.343 0.014 0.0451 0.0003 0.0175 0.0002 0.530 0.001 422 77 300 11 284 2 17 22 436 0.0530 0.0030 0.331 0.022 0.0453 0.0003 0.0196 0.0006 0.538 0.001 327 90 290 13 286 2 18 9 196 0.0541 0.0034 0.344 0.022 0.0460 0.0003 0.0240 0.0006 0.299 0.001 377 86 300 12 290 2 19 7 146 0.0541 0.0047 0.344 0.031 0.0462 0.0004 0.0213 0.0004 0.317 0.002 375 138 300 19 291 2 20 11 222 0.0513 0.0031 0.323 0.021 0.0457 0.0003 0.0263 0.0005 0.377 0.002 252 74 284 9 288 2 21 13 271 0.0521 0.0029 0.331 0.019 0.0461 0.0003 0.0195 0.0003 0.432 0.001 291 84 291 11 291 2 22 8 192 0.0528 0.0049 0.335 0.032 0.0460 0.0004 0.0292 0.0005 0.063 0.001 319 96 293 13 290 3 23 12 266 0.0538 0.0025 0.332 0.016 0.0448 0.0003 0.0142 0.0002 0.401 0.001 362 106 291 14 282 2 24 11 243 0.0571 0.0035 0.354 0.022 0.0450 0.0003 0.0200 0.0003 0.319 0.001 496 85 308 12 284 2 25 22 477 0.0553 0.0014 0.343 0.009 0.0451 0.0003 0.0148 0.0001 0.382 0.002 424 52 300 7 284 2 表 2 乌拉苏太大石寨组火山岩地球化学分析结果
Table 2 Geochemical composition of volcanic rocks from Dashizhai Formation in Ural Sutai
样品编号 岩性 SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 FeO MnO MgO CaO Na2O K2O P2O5 H2O+ H2O- 灼失量 A/CNK Na2O+K2O D2538 英安岩 69.98 0.33 14.85 2.11 1.10 0.011 0.56 0.31 2.42 6.27 0.203 1.42 0.34 1.72 1.31 8.69 Pm7B135 67.12 0.63 15.22 2.82 1.59 0.027 1.55 0.51 4.43 3.52 0.169 2.07 0.74 2.27 1.27 7.95 D1455 流纹岩 76.06 0.19 12.70 0.69 0.69 0.007 0.30 0.25 3.26 4.25 0.034 1.02 0.27 1.33 1.22 7.51 D2523 78.95 0.15 11.38 0.51 0.29 0.002 0.06 0.11 3.03 4.71 0.024 0.45 0.21 0.65 1.11 7.73 D2550 87.75 0.09 6.16 0.81 0.34 0.006 0.24 0.13 1.63 1.91 0.020 0.63 0.21 0.83 1.24 3.54 Pm7B35 72.12 0.35 13.68 2.14 0.97 0.035 0.4 0.46 3.69 4.27 0.076 1.29 0.4 1.65 1.19 7.96 样品编号 Cs Rb Sr Ba Ga Nb Ta Zr Hf Th V Cr Co Ni Li Sc U D2538 5.00 186.80 46.60 1037.00 21.89 14.93 1.48 268.70 9.44 18.07 25.40 6.50 2.50 23.50 18.15 8.67 4.25 Pm7B135 4.53 90.9 56.1 738 20.2 13.6 0.82 250 6.96 10.5 58.9 36.3 7.83 25.4 17.7 11.6 2.33 D1455 2.85 85.40 101.70 1635.00 16.60 12.31 1.62 266.60 9.59 15.58 28.00 3.80 1.61 4.50 5.02 10.85 4.04 D2523 4.12 148.7 53.2 884.5 21.4 9.86 0.87 263.3 8.85 14.79 38.6 11.5 0.5 7.9 9.1 9.2 2.95 D2550 5.00 38.20 27.30 699.00 6.56 6.39 0.62 153.40 5.68 8.04 15.60 2.00 0.35 2.40 9.22 6.75 2.87 Pm7B35 4.58 127 65.6 875 20.2 13.9 0.82 478 11.9 13.3 34.7 16.9 1.89 5.62 26.8 13.4 3.46 样品编号 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Y ΣREE δEu D2538 28.73 68.58 9.19 36.06 7.83 0.58 7.22 1.41 9.30 1.85 5.37 0.94 4.91 0.95 42.74 225.66 0.24 Pm7B135 15.9 38.8 5.17 20.3 5.01 0.56 4.45 0.92 5.9 1.26 3.61 0.58 3.7 0.66 33.5 140.32 0.36 D1455 30.72 70.77 9.14 35.62 7.66 0.39 7.29 1.46 9.85 2.00 5.93 1.05 5.46 1.02 46.82 235.18 0.16 D2523 35.36 75.97 9.44 37.38 8.17 0.52 7.88 1.48 9.19 1.99 5.45 0.98 5.62 1.15 48.85 249.42 0.20 D2550 19.13 49.68 5.66 21.99 5.34 0.35 6.20 1.49 11.09 2.34 6.90 1.19 5.84 0.96 58.76 196.92 0.19 Pm7B35 27.1 61 8.07 32 7.74 0.6 7.18 1.43 8.99 1.94 5.71 0.96 6.42 1.38 51.8 222.32 0.25 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素为10-6 表 3 大石寨组火山岩前人测年数据
Table 3 Summary of the published isotope dating data from Dashizhai Formation
测试方法 采样位置 岩性及年龄 资料来源 K-Ar 赤峰 中基性火山岩242~264.7Ma [7] Rb-Sr 林西 玄武岩和中酸性火山岩270Ma [8] Rb-Sr 苏尼特左旗 安山岩281Ma [14] 同位素稀释法单颗粒锆石U-Pb 满都拉 玄武岩285±11Ma、斜长岩280.4±1.1Ma [15] SHRIMP锆石U-Pb 锡林浩特 双峰式火山岩玄武安山岩281±3Ma、流纹岩279±3Ma [9] SHRIMP锆石U-Pb 大石寨 玄武岩439±3Ma [10] SHRIMP 锆石U-Pb 西乌旗 流纹岩279±4.3Ma, [25] LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 科右前旗 英安岩314±1Ma [26] LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 锡林浩特毛登牧场 细碧-角斑岩系角斑岩287.4±1.7Ma [27] LA-ICP-MS 锆石U-Pb 西乌旗猴头庙 流纹岩274.1±2.8Ma [28] -
Xiao W J,Windley B F,Huang B C,et al.End-Permian to Mid-Triassic termination of the accretionary processes of the southern Altaids:implications for the geodynamics evolution,Phanerozoic continental growth, and metallogeny of Central Asia[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences,2009,98(6):1189-1217. Xiao W J,Windley B F,Huang B C,et al.End-Permian to Mid-Triassic termination of the accretionary processes of the southern Altaids:implications for the geodynamics evolution,Phanerozoic continental growth, and metallogeny of Central Asia[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences,2009,98(6):1189-1217.
Xiao W J,Windley B F,Hao J,et al.Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture,Inner Mongolia, China:Termination of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Tectonics,2003,22:1069-1089. Xiao W J,Windley B F,Hao J,et al.Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture,Inner Mongolia, China:Termination of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Tectonics,2003,22:1069-1089.
Tang K D.Tectonic development of Paleozoic fold-belts at the northern margin of the Sino-Korean Craton[J]. Tectonics,1990,9:249-260. Tang K D.Tectonic development of Paleozoic fold-belts at the northern margin of the Sino-Korean Craton[J]. Tectonics,1990,9:249-260.
徐备,陈斌.内蒙古北部华北板块与西伯利亚板块之间中古生代造山带的结构与演化[J]. 中国科学(D辑),1997, 27(3):227-232. 李双林,欧阳自远.兴蒙造山带及邻区的构造格局与构造演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,1998,18(3):45-54. 王荃.内蒙古中部中朝与西伯利亚古板块间缝合线的确定[J]. 地质学报,1986,1:31-43. 汪润洁.大兴安岭南段下二叠统大石寨组K-Ar法同位素年龄的讨论[J].岩石学报,1987,2:80-91. Zhu Y F,Sun S H,Gu L B,et al.Permian volcanism in the Mongolian orgenic zone,northeast China:geochemistry, magma sources and petrogenesis[J]. Geological Magazine,2001,138:101-115. Zhu Y F,Sun S H,Gu L B,et al.Permian volcanism in the Mongolian orgenic zone,northeast China:geochemistry, magma sources and petrogenesis[J]. Geological Magazine,2001,138:101-115.
Zhang X H,Zhang H F,Tang Y J,et al.Geochemistry of Permian bimodal volcanic rocks from central Inner Mongolia,North China:Implication for tectonic setting and Phanerozoic continental growth in Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Chemical Geology,2008,249:262-281. Zhang X H,Zhang H F,Tang Y J,et al.Geochemistry of Permian bimodal volcanic rocks from central Inner Mongolia,North China:Implication for tectonic setting and Phanerozoic continental growth in Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Chemical Geology,2008,249:262-281.
郭锋,范蔚茗,李超文,等.早古生代古亚洲洋俯冲作用:来自内蒙古大石寨玄武岩的年代学与地球化学证据[J].中国科学(D辑), 2009,39(5):569-579. 吕志成,段国正,郝立波,等.大兴安岭中段二叠系大石寨组细碧岩的岩石学地球化学特征及其成因探讨[J].岩石学报,2002,18(2):212-222. 吕志成,郝立波,段国正,等.大兴安岭南段早二叠世两类火山岩岩石地球化学特征及其构造意义[J].地球化学,2002,31(4):338-346. 邵济安. 中朝板块北缘中段地壳演化[M]. 北京:北京大学出版社,1991:135-136. 高德臻,将干清.内蒙古苏尼特左旗二叠系的重新厘定及大地构造演化分析[J].中国区域地质, 1998, 17(4):403-411. 陶继雄,白立兵,宝音乌力吉, 等.内蒙古满都拉地区二叠纪俯冲造山过程的岩石记录[J].地质调查与研究,2003, 26(4):241-249. 耿明山.内蒙古中部下二叠统火山岩特征及构造环境意义[J].地质与勘探,1998,34(1):13-19. Yuan H L,Gao S L Xiao M,et al.Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2004,28(3):353-370. Yuan H L,Gao S L Xiao M,et al.Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2004,28(3):353-370.
Ludwig K R.Isoplot/Ex version 3.0 A-Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M].Berkeley Geochronology Centre Special Publication,2003,4:1-70. Ludwig K R.Isoplot/Ex version 3.0 A-Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M].Berkeley Geochronology Centre Special Publication,2003,4:1-70.
Anderson T.Correction of common Pb in U-Pb analyses that donot report 204Pb[J].Chemical Geology,2002, 192(1/2):59-79. Anderson T.Correction of common Pb in U-Pb analyses that donot report 204Pb[J].Chemical Geology,2002, 192(1/2):59-79.
Ludwig K R.Isoplot/Ex,Version 249.A Geochronological Toolkit it for Microsoft Excel[M].Berkeley:Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, 1999:47. Ludwig K R.Isoplot/Ex,Version 249.A Geochronological Toolkit it for Microsoft Excel[M].Berkeley:Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, 1999:47.
简平,程裕淇,刘敦一.变质锆石成因的岩相学研究——高级变质岩U-Pb年龄解释的依据[J].地学前缘,2001,8(3):183-191. 吴元保,郑永飞.锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J].科学通报,2004,49(16):1589-1604. Winchester J A,Floyd P A. Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements[J].Chemical Geology,1977,20:325-343. Winchester J A,Floyd P A. Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements[J].Chemical Geology,1977,20:325-343.
Rickwood P C.Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J].Lithos,1989,22:247-263. Rickwood P C.Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements[J].Lithos,1989,22:247-263.
陈彦,张志诚,李可,等.内蒙古西乌旗地区二叠纪双峰式火山岩的年代学、地球化学特征和地质意义[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版),2014,50(5):843-858. 曾维顺,周建波,张兴洲,等.内蒙古科右前旗大石寨组火山岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄及其形成背景[J].地质通报,2011,30(2/3):270-277. 程天赦,杨文静,王登红.内蒙古锡林浩特毛登牧场大石寨组细碧-角斑岩系地球化学特征、锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J].现代地质,2013,27(3):525-536. 刘建峰.内蒙古林西-东乌旗地区晚古生代岩浆作用及其对区域构造演化的制约[D]. 吉林大学博士学位论文.2009. Sun S S,McDonough W F.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geology,1989, 42:313-345. Sun S S,McDonough W F.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geology,1989, 42:313-345.
杨现力.扎兰屯浅变质岩系地质特征及碎屑锆石年代学研究[D]. 吉林大学硕士学位论文.2007. 施光海,苗来成,张福勤,等.内蒙古锡林浩特A型花岗岩的时代及区域构造意义[J]. 科学通报,2004,49(4):384-389. 尚庆华.北方造山带内蒙古中、东部地区二叠纪放射虫的发现及意义[J].科学通报,2004,49(24):2574-2579. 张拴宏,赵越,刘建民,等.华北地块北缘晚古生代-早中生代岩浆活动期次、特征及构造背景[J].岩石矿物学杂志,2010,29(6):824-842. Pearce J A,Harris N B W,Tindle A G.Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology,1984,25:956-983. Pearce J A,Harris N B W,Tindle A G.Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology,1984,25:956-983.
Rittmann A. Stable mineral assemblages of igneous rocks[M].Heideberg:Springer,1973.1-262. Rittmann A. Stable mineral assemblages of igneous rocks[M].Heideberg:Springer,1973.1-262.
李锦轶,高立明,孙桂华,等.内蒙古东部双井子中三叠世同碰撞壳源花岗岩的确定及其对西伯利亚与中朝古板块碰撞时限的约束[J]. 岩石学报,2007,23(3):565-582. 董策,周建波.内蒙古东北部中二叠统哲斯组砂岩地球化学特征分析及物源区示踪[J].岩石矿物学杂志,2012, 31(5):663-673. 江小燕,刘永江,周冰,等.大兴安岭南段兴-蒙草原区二叠纪砂岩物源分析[J]. 地质通报, 2011, 30(7):1087-1098. 王玉净,樊志勇.内蒙古西拉木伦河北部蛇绿岩带中二叠纪放射虫的发现及其地质意义[J].古生物学报,1997, 36(1):58-69. 叶栩松,廖群安,葛梦春.内蒙古锡林浩特-林西地区三叠纪过铝质花岗岩的成因及构造意义[J].地质科技情报, 2011,30(3):57-64. Chen B,Jahn B M,Wilde S,et al.Two contrasting Paleozoic magmatic belts in northern Inner Mongolia,China:Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J].Tectonophysics,2000,328:157-182. Chen B,Jahn B M,Wilde S,et al.Two contrasting Paleozoic magmatic belts in northern Inner Mongolia,China:Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J].Tectonophysics,2000,328:157-182.
陈斌,赵国春, Wilde S.内蒙古苏尼特左旗南两类花岗岩同位素年代学及其构造意义[J].地质论评,2011, 47(4):361-367. 范中林,柯于富,陈文,等.内蒙古锡林浩特I型花岗岩的时代及构造意义[J]. 资源调查与环境, 2012,33(3):191-197.



 下载:
下载: