Reservoir characteristics of thick sandstone and micro-anisotropy of delta front micro-facies:A case study of Chang 6 reservoir in Wucangbu area
-
摘要:
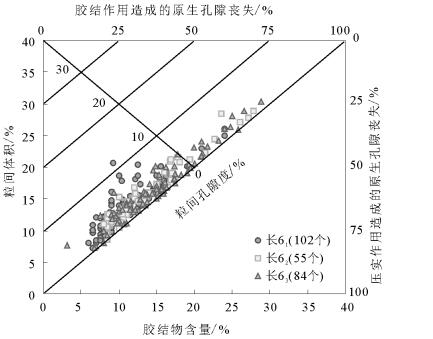
依据薄片、压汞、扫描电镜、物性分析及油水驱替实验资料, 对吴仓堡地区三角洲前缘亚相长6厚层砂岩储层的岩石学特征、孔渗特征、孔隙结构特征、成岩作用、微观渗流特征等进行深入研究, 分析影响储层储集性能的主控因素。结果表明, 受东北物源控制的长6厚层砂岩储层具有成分成熟度中等、结构成熟度较好的特点, 储集空间主要为残余粒间孔和粒间溶孔、粒内溶孔, 为典型中低孔、特低渗储集层; 储层储集性能主要受沉积微相和成岩作用控制。对储层发育影响最大的成岩期位于中成岩A期, 中等压实-粘土膜胶结残余粒间孔发育成岩相和弱压实-残余粒间孔+溶蚀孔隙发育成岩相是最有利储层发育的成岩相带。根据微观渗流特征, 可划分出4种驱油类型, 微观孔隙结构比宏观物性更能反映储层的本质特征。
Abstract:Based on data obtained from cast slice, mercury injection test, SEM, physical properties, and oil/water micro-displacement experiment, the authors made a thorough study of the petrological characteristics, porosity and permeability characteristics, pore structure characteristics, diagenesis and micro-anisotropy of Chang 6 reservoir in Wucangbu area, and analyzed the main influ-encing factors. The results show that the sedimentary environment of the Chang 6 thick sandstones reservoir is a delta front derived from the provenance in the northeast. In addition, the reservoir is characterized by medium compositional maturity and high textual maturity. The reservoir space includes residual intergranular pores, intergranular emposieu and intragranular emposieu. The sedimentary micro-facies and diagenesis constitute the main factors controlling the reservoir properties. The diagenetic period affecting reservoir development is stage A of middle diagenesis. The middle compaction, clay film cementation, residual intergranular pore diagenesis facies with weaker compaction and the secondary dissolution pore diagenesis facies are favorable diagenetic facies belts for reservoir development. Four oil displacement types are distinguished by studying reservoir microscopic heterogeneity, and the microscopic pore structures can more really reflect the reservoir's essential characteristics than the macroscopically physical properties.
-
随着地球科学家对地球系统研究的不断深入,人们发现新元古代时地球系统发生了一系列的剧烈变化。在地球地质历史的这一时期,地球从较稳定的古-中元古代(17~7.5亿年)[1],进入剧烈变动的中-晚新元古代时期(7.5~5.4亿年)。中-晚新元古代地球上出现多期极冷事件[2-7],条带状铁矿也在消失十多亿年后,在新元古代中期又重新出现[1, 8],大洋与大气圈的氧含量快速增加[9-11]。地球系统这一系列的剧变很可能发生在Rodinia超大陆裂解的背景下。因此,重建这一时期的古地理古板块位置对于理解这些剧变至关重要。然而,由于这一时期(7.5~5.4亿年)全球不同块体古地磁数据的缺乏和可靠性问题,其古地理重建一直存在较大的争议[12-20]。
影响这一时期古地磁数据可靠性的因素,除了考虑剩磁的获得时间外,近年来越来越多的学者注意到非偶极子场及磁倾角偏低对古地磁数据的影响[21-26],特别是红层中存在普遍的磁倾角偏低现象[27-28]。
最近,Jing等[29]报道了湖北宜昌三峡地区莲沱组红层可靠的古地磁极,并根据Lan等[30]最新的SIMS锆石U-Pb定年研究,确定这一古地磁极年龄应为720Ma。虽然这一古地磁极通过了Van der Voo[31]的6项Q检验,确保其剩磁获得的原生性,但这一结果是否受到后期压实作用的影响并产生磁倾角偏低,以及影响程度的大小等问题,都需要进一步研究。在长阳地区,由于古城冰碛岩覆盖在莲沱组之上,因此准确确定莲沱组的磁倾角,对确定华南这一时期的古纬度及“雪球地球”的研究都具有重要意义。另外,目前华南地块莲沱组古地磁极与南沱组古地磁极相似的问题,一直没有得到可信的解释,本文通过磁倾角偏低的研究,对这一问题进行探讨。
1. 区域地质概况及采样
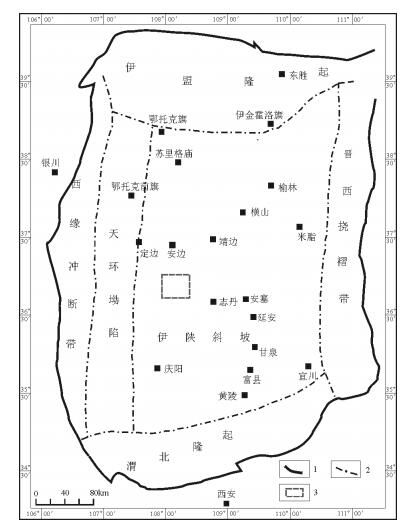
采样区位于华南新元古代地层典型剖面区,湖北三峡地区(图 1)。研究区出露的新元古代沉积地层包括莲沱组、南沱组、陡山沱组、灯影组等。莲沱组一般不整合覆盖于黄陵花岗岩之上,主要为厚层的紫红色砂岩和砾岩,可分为2个大的沉积旋回(图 2),每个旋回底部为砾石或粗粒石英砂岩,向上逐渐变为粉砂岩、泥质砂岩,含多层凝灰岩或凝灰质碎屑岩。在区域上,西北部地层厚度较大,向西南变薄。本区南沱组与莲沱组平行不整合接触或低角度不整合接触,南沱组主要为暗绿色冰碛砾岩,部分为红色冰碛岩[32]。
![]() 图 2 本次研究获取的采点(下划线标注TLS编号)在地层上的分布(TL编号为Jing等[29]采点)Figure 2. Stratigraphic column of the Liantuo Formation and detailed sampling layer positions of three sub-sections at Yichang
图 2 本次研究获取的采点(下划线标注TLS编号)在地层上的分布(TL编号为Jing等[29]采点)Figure 2. Stratigraphic column of the Liantuo Formation and detailed sampling layer positions of three sub-sections at Yichang在三峡地区南部的长阳地区,莲沱组之上覆盖古城组冰碛岩和大塘坡组页岩,而不是直接与南沱组接触[33]。古城组冰碛岩应与扬子西南部广泛发育的长安组冰碛岩一致[33],属于Sturtian冰期的产物。古城组沉积时间应始于715Ma左右[33]。
三峡地区从埃迪卡拉纪开始长期沉积碳酸盐岩,早寒武世有一次沉积间断,直到志留纪宜昌地区大规模抬升,沉积间断接受剥蚀,随后沉陷到早三叠世再次抬升[34-35]。本地区经历了3次主要的构造运动:加里东期、印支期和燕山期构造运动。同时中扬子地区存在与这3次构造运动相关的3期油气生成和排烃过程[36]。区域内构造变形较弱。
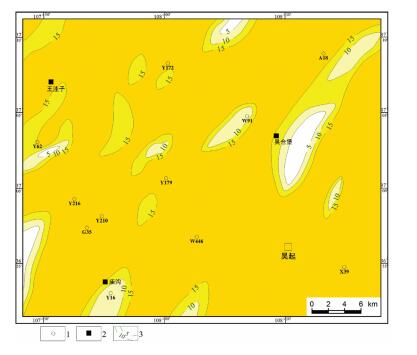
本次在宜昌花鸡坡、头顶石及田家院子3个剖面共采集了17块手标本样品(TLS1-17),对莲沱组是否存在磁倾角偏低现象进行检验(图 2)。样品在野外用罗盘测量层面的走向和倾角,并标记在层面上。
2. 实验方法
在室内用台式钻机垂直手标本层面钻取2根以上岩心,并加工出1~2块高2.2cm、直径2.5cm的标准岩心样品。每根岩心选取1~2块,共31块标准样品进行系统热退磁实验。同时对应选择了30块样品进行Hodych等[23]磁倾角偏低校正实验。所有实验工作均在中国地质科学院地质力学研究所国土资源部古地磁与古构造重建重点实验室完成。使用美国ASC Scientific Inc.公司生产的IM-10-30脉冲充磁仪对样品进行充磁,样品系统热退磁由TD-48大型热退磁仪完成,样品剩磁测量在ARGICO-JR6A旋转磁力仪上完成。另外,对部分样品利用KLY-3 Kappabridges进行了氮气环境下磁化率随温度变化实验(K-T),获取连续加热-冷却曲线分析样品磁化率的变化。
3. 实验结果
3.1 逐步热退磁结果
宜昌三峡地区花鸡坡、头顶石及田家院子剖面莲沱组样品的岩石磁学实验结果显示,岩石的特征剩磁载磁矿物为赤铁矿[29]。因此,系统热退磁温度区间在低温段以50~100℃为间隔,高温段温度区间以20℃为间隔,热退磁温度达到680℃(图 3)。样品使用主向量分析法[37]进行剩磁组分分析。
逐步热退磁结果显示,样品中共可以分离出3个剩磁方向(图 3):低温分量一般在小于等于300℃的情况下分离出来, 共有15块样品分离出此分量,其在地理坐标系下的统计方向(Dg=5.9°,Ig=60.1°,kg=81.3, ɑ95=4.3°)与采样点现代地磁场方向接近,应为现代地磁场的热粘滞剩磁;中温分量的温度区间一般在300~600~640℃之间,共有6块样品分离出此分量,其平均方向在地理坐标系下为Dg=34.5°,Ig=78.1°,kg=244.2,ɑ95=4.3°,在地层坐标系下为Ds=78.9°,Is=78.4°,ks=243.5,ɑ95=4.3°。另外,从11块样品中分离出了与宜昌剖面得到的特征分量相似的高温分量(600~680℃),其平均方向在地理坐标系下为Dg=67.0°,Ig=71.6°,kg=124.7,ɑ95=3.9°,在地层坐标系下为Ds=95.3°,Is=67.8°,ks=196.0,ɑ95=3.1°。
3.2 等温剩磁各向异性实验结果
对12个样品,在与其层面呈45°方向,从低到高逐步增加等温直流磁场,获得平行于层面IRMx和垂直于层面IRMz的等温剩磁,直流磁场大小由20、40、60、100、225、315、415、510、510、710、810、950、1200mT依次递增。在每步施加直流场后使用JR6旋转磁力仪对样品进行剩磁测试。然后用TD48大型热退磁炉对所有样品进行系统热退磁,相关数据结果列于表 1中。
表 1 宜昌地区剖面莲沱组样品等温热剩磁各向异性及磁倾角偏低值Table 1. Anisotropy of isothermal remnant magnetization for Liantuo Formation red beds in Yichang areaID Iobs IRMz/IRMx
(610~1200mT)IF1 ΔI1(=IF1-Iobs) IRMz/IRMx
(600°C以上)IF2 ΔI2(=IF2-Iobs) 15 64.4 0.7796 69.518 5.118 0.8542 67.7425 3.3425 15-2c 71.5 0.8414 74.277 2.777 0.8513 74.1009 2.6009 15-5b 65 0.899 67.256 2.256 0.8757 67.7876 2.7876 17-1 72.1 0.831 74.976 2.876 0.8118 75.3075 3.2075 3-1 73 0.87 75.105 2.105 0.8859 74.8452 1.8452 4-2b 66.3 0.6147 74.899 8.599 0.901 68.4206 2.1206 5-2b 64.2 0.8472 67.728 3.528 0.9117 66.2153 2.0153 5-4b 66 0.7989 70.420 4.420 0.872 68.7818 2.7818 7-1 61.9 0.8579 65.389 3.489 0.8731 65.0054 3.1054 8-3 70 0.8737 72.359 2.359 0.856 72.6951 2.6951 8-4 66.8 0.8701 69.548 2.748 0.8977 68.9555 2.1555 平均值 67.8 0.8258 71.377 3.577 0.8719 70.4146 2.6146 注:ID为样品号,Iobs为热退磁实验所得样品磁倾角,IRMz/IRMx(610~1200mT)为610~1200mT之间垂直层面方向和平行层面方向等温剩磁大小的比值,IRMz/IRMx(600°C以上)为600 °C以上垂直层面方向和平行层面方向等温剩磁大小的比值,IF为校正后磁倾角,ΔI为校正值 考虑到实验过程中样品的等温剩磁方向可能受天然剩磁的影响,以及载磁矿物主要为赤铁矿,所以施加外部直流场在200~1200mT之间及系统热退磁温度在600~680℃之间的IRMz/IRMx拟合线反映了赤铁矿的剩磁各向异性特征。
由于垂直于层面的IRMz值大部分在500mT之后略小于平行于层面的IRMx值(图 4-a、d),所以从磁场强度方面考虑,选取在500mT之后的610~1200mT区间的IRMz/IRMx拟合线的斜率作为磁倾角偏低校正因子,其大小为0.8258,对应的沉积压实为18%。另外,从热退磁的方面考虑,选取600~680℃区间的IRMz/IRMx热退磁结果拟合线的斜率作为磁倾角偏低校正因子,其大小为0.8719,对应的沉积压实为13%。利用公式IRMz/ IRMx=tan (Iobs)/tan (IF)进行校正后得到莲沱组磁倾角分别为71.4°和70.4°,两者的磁倾角值差别不大。
![]() 图 4 45°方向加场后平行于层面方向(IRMx)和垂直于层面方向(IRMz)等温剩磁获得曲线图(a, d),IRMz/IRMx关系图(b, e)和IRMz/IRMx的热退磁结果(c, f)Figure 4. Plots of IRMx (parallel to bedding) and IRMz (perpendicular to bedding) acquisitions produced by applying magnetic field at 45° to bedding as function of increasing field (a, d), plots of IRMZ/IRMX(b, e), the thermal demagnetization results of IRMZ/IRMX(c, f)
图 4 45°方向加场后平行于层面方向(IRMx)和垂直于层面方向(IRMz)等温剩磁获得曲线图(a, d),IRMz/IRMx关系图(b, e)和IRMz/IRMx的热退磁结果(c, f)Figure 4. Plots of IRMx (parallel to bedding) and IRMz (perpendicular to bedding) acquisitions produced by applying magnetic field at 45° to bedding as function of increasing field (a, d), plots of IRMZ/IRMX(b, e), the thermal demagnetization results of IRMZ/IRMX(c, f)3.3 岩石磁学实验结果
为了排除样品在加热过程中可能存在的磁性矿物的变化,对几个代表性样品进行了磁化率随温度变化实验(K-T,图 5)。结果表明,部分样品在加热和冷却过程中样品磁化率明显不同(图 5,TLS11),可能是因为样品在加热过程中生成了一部分磁铁矿。但580~680℃之间的加热曲线与冷却曲线一致,表明加热过程中磁性矿物的变化并未影响到样品中赤铁矿的剩磁变化(图 5,TLS11),因此,不影响磁倾角偏低实验的结果。另一部分样品的K-T曲线显示,在加热与冷却过程中,样品的磁化率没有明显的差异,因此样品中不存在明显的磁性矿物的改变(图 5,TLS4)。
由于加热过程并未影响到高温分量载磁性矿物赤铁矿,再考虑到赤铁矿较大的矫顽力,因此,选用600~680℃区间的IRMz/IRMx值作为磁倾角偏低校正因子,利用公式IRMz/IRMx=tan (Iobs)/tan(IF)计算得到校正后的莲沱组磁倾角大小为70.4°,与热退磁实验所得莲沱组磁倾角67.8°比较,莲沱组的磁倾角偏低大小为2.6°。
4. 磁倾角偏低对莲沱组古纬度及古地磁极的影响
利用本研究得到的莲沱组磁倾角偏低校正因子,对Jing等[29]所得高温分量进行磁倾角偏低校正,利用校正后的高温分量求得的三峡地区莲沱组沉积古纬度为47.7°±5.1°,比校正前的43.7°±4.8°向高纬度地区运动了3.9°±6°。
校正后古地磁极(LT-corr)为14.7°N, 153.9°E, dp/dm=4.9/6.0,与未校正的莲沱组古地磁极(LT:12.7°N,157.4°E,dp/dm=4.5/5.8)相比更偏西北。虽然校正前后,莲沱组古地磁极在统计分析上不能显著区分,但校正后的莲沱组古地磁极与现有华南南沱组古地磁极(Nantuo)[38]明显不同(图 6)。
5. 讨论
由于Evans等[39]得到的莲沱组古地磁极与南沱组古地磁极重合,使得一些学者认为莲沱组古地磁结果可能比以前认为的更年轻[40],或是南沱期重磁化的结果。然而,Jing等[29]对宜昌莲沱组的古地磁研究表明,莲沱组中下部到顶部至少存在5个正负极性时,因此现有的莲沱组古地磁结果应该不是重磁化的结果。另外,Jing等[29]通过总结前人在三峡地区对莲沱组大量的定年结果[41-45],认为现有华南莲沱组古地磁极年龄应在720Ma左右,比之前认为的750Ma年轻,但仍老于635Ma的南沱组古地磁结果。
Jing等[29]得到的莲沱组古地磁极与南沱组古地磁极相差不大。Yang等[46]认为,莲沱组采样区可能发生过局部构造旋转作用;Zhang等[38]则认为,没有证据表明莲沱组采样区发生过局部旋转。
排除以上各方面的影响因素,笔者认为,造成莲沱组与南沱组古地磁极相似的原因应该与莲沱组岩石受压实作用影响、发生微弱的磁倾角偏低现象有关。由于目前未对南沱组取得高温分量的古地磁样品进行磁倾角偏低实验,两者真实的差别还不能确定,需要进一步研究。
经磁倾角偏低校正后的华南板块在720Ma时应位于中纬度地区(图 6)。这一时期扬子地块多处发育冰碛岩沉积,从该时期华南板块上发育的冰碛岩分布看[40],当时整个地球应处于较寒冷的气候阶段。但由于这一时期华南板块位于中纬度地区,对于地球这一时期是否处于“雪球地球”的环境,仅从莲沱组的古地磁结果不能做出明确的判定。
为此,笔者重建了华南板块及与华南关系较紧密的澳大利亚-东南极板块720Ma的古地理位置(图 6)。图 6中,将莲沱组古地磁极通过欧拉极(34.4°N、100°E,98.6°)旋转到地理北极。MDS、YF及EF分别为澳大利亚755Ma,640Ma和635Ma古地磁极[22, 47-48],位于同一大圆弧上(虚线),利用内插法求出其720Ma的古地磁极位置,通过欧拉极(-0.4°N、53.7°E,44.1°)旋转使其与莲沱组古地磁极重合。通过这一古地理重建,可以清楚地看到,这一时期有大量冰川从中纬度地区一直延续到赤道地区。这一证据直接证明,当时地球处于“雪球地球”的环境。
6. 结论
对华南三峡地区莲沱组的等温剩磁各向异性研究表明,通过磁倾角偏低校正后的莲沱组古地磁极与南沱组古地磁极存在明显差别,这表明造成莲沱组与南沱组古地磁极相似的一个重要原因是地层压实引起的磁倾角偏低。利用720Ma古地磁数据对华南和澳大利亚进行古地理重建,并对比这一时期冰碛岩的分布,结果表明,当时地球确实处于“雪球地球”的环境中。
致谢: 长庆油田分公司勘探开发研究与低渗透油气田勘探开发国家工程实验室提供了大量基础资料和分析化验数据,在此表示感谢。 -
表 1 吴仓堡长6段不同孔隙类型对面孔率的贡献值
Table 1 The contribution of pore types to surface porosity in Chang 6 reservoir of Wucangbu area
残余粒间孔隙/% 溶蚀粒间孔隙/% 溶蚀粒内孔隙/% 自生矿物晶间微孔隙/% 微裂隙
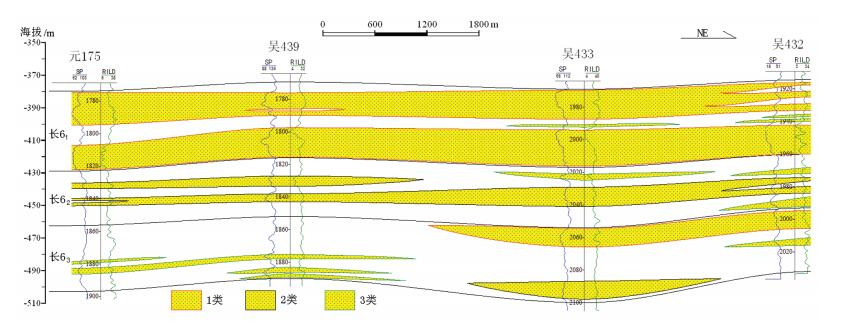
/%长石溶孔 岩屑溶孔 沸石溶孔 杂基溶孔 铸模孔 71.68 1.8 16.3 5.9 1.4 0.64 0.33 1.26 0.66 表 2 吴仓堡地区长6储层物性与孔喉特征分类
Table 2 Statistics of physical properties and pore-throat characteristics of Chang 6 reservoir in Wucangbu area
级別 物性特征 孔隙类型 孔隙喉道参数 孔隙度/% 渗透率/10-3pm2 门槛压力/MPa 喉道中值半径/μm 分选系数/Sp Ⅰ类
(好)> 12 > 1.0 混合孔隙型
(残余粒间孔+溶蚀孔)< 0.5 > 0.2 < 2.5 Ⅱ类
(中等)9 〜 12 0.3 〜 1.0 残余孔隙型
(残余粒间孔为主)0.5 〜 1.5 0.2 〜 0.05 2.5 〜 3 Ⅲ类
(差)< 9 < 0.3 致密孔隙型
(少量残余粒间孔、晶间微孔)> 0.5 < 0.05 > 3.0 表 3 吴仓堡地区长6段不同沉积微相砂体物性统计
Table 3 Porosity and permeability statistics for different sedimentary microfacies sandbodies of Chang 6 reservoir in Wucangbu area
沉积微相类型 孔隙度/% 渗透率/10-3pm2 样品数/个 分布范围 平均值 分布范围 平均值 水下分流河道 9.6〜15.6 12.3 0.18〜3.46 1.32 213 河口坝 7.1〜13.2 11.5 0.15〜2.78 0.85 89 远砂坝 5.9〜12.4 10.2 0.12〜0.91 0.39 73 分流间湾 2.7〜11.1 8.5 0.04〜0.34 0.12 25 -
王昌勇, 郑荣才, 王海红, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地史家湾地区长6油层组物源区分析[J].沉积学报, 2008, 25(4):933-938. 朱静.胡尖山-吴起地区延长组长6油层组沉积相研究[D].西北大学硕士学位论文, 2008:89, 93. 杨晓萍, 裘亦楠.鄂尔多斯盆地上三叠统延长组浊沸石的形成机理、分布规律与油气关系[J].沉积学报, 2002, 20(4):628-632. 付金华, 罗安湘, 喻建, 等.西峰油田成藏地质特征及勘探方向[J].石油学报, 2004, 25(2):25-29. 魏钦廉, 郑荣才, 肖玲, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地吴旗地区长6储层特征及影响因素分析[J].岩性油气藏, 2007, 9(4):40-50. 黄思静, 谢连文, 张萌, 等.中国三叠系陆相砂岩中自生绿泥石的形成机制及其与储层孔隙保存的关系[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 31(3):273-281. 肖玲, 田景春, 魏钦廉, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地吴旗地区长6储层孔隙结构特征[J].新疆地质, 2007, 25(1):101-102. 黄龙, 田景春, 肖玲, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地富县地区长6砂岩储层特征及评价[J].岩性油气藏, 2008, 20(1):83-85. 郑荣才, 耿威, 周刚, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地白豹地区长6砂岩成岩作用与成岩相研究[J].岩性油气藏, 2007, 19(2):1-8. 郑浚茂, 庞明.碎屑储集岩的成岩作用[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1989:58-59. Housknecht D W.Assessing the relative importance of compaction processes and cementation to reduction of porosity in sand stones[J]. AAPG Bulletin,1987,71:633-642 Housknecht D W.Assessing the relative importance of compaction processes and cementation to reduction of porosity in sand stones[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1987, 71:633-642
李斌, 孟自芳, 李相博, 等.靖安油田上三叠统长6储层成岩作用研究[J].沉积学报, 2005, 23(4):574-583. 窦伟坦, 田景春, 王峰, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地长6油层组储集砂岩成岩作用及其对储层性质的影响[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 36(2):156-157. Hurst A, Nadeau H P. Clay micro-porosity in reservoir sand-stones:an application of quantitative electron microscopy in petrophysical evaluation[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1995,79(4):563-573. Hurst A, Nadeau H P. Clay micro-porosity in reservoir sand-stones:an application of quantitative electron microscopy in petrophysical evaluation[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1995, 79(4):563-573.
姚泾利, 王琪, 张瑞, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地华庆地区延长组长6砂岩绿泥石膜的形成机理及其环境指示意义[J].沉积学报, 2011, 29(1):75-76. 何自新, 贺静.鄂尔多斯盆地中生界储层图册[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2004:59-60. 朱平, 黄思静, 李德敏, 等.粘土矿物绿泥石对碎屑储集岩孔隙的保护[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 31(2):153-156. 贾振岐, 孙念, 吴景春, 等.特低渗透岩心相对渗透率实验研究[J].特种油气藏, 2009, 16(1):82-83. 高辉.特低渗透砂岩储层微观孔隙结构与渗流机理研究[D].西北大学硕士学位论文, 2009:102-105. 邦德.残余油饱和度确定方法[M].王平等译.北京:石油工业出版社, 1982. 闫健, 张宁生, 刘晓娟, 等.低渗气藏单相气体渗流特征分析[J].西安石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 25(1):41-44. 杨仁锋, 姜瑞忠, 孙君书, 等.低渗透油藏非线性微观渗流机理[J].油气地质与采收率, 2011, 18(2):90-97. 黄延章.低渗透油层渗流机理[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 1995.




 下载:
下载: