Reservoir characteristics of thick sandstone and micro-anisotropy of delta front micro-facies:A case study of Chang 6 reservoir in Wucangbu area
-
摘要:
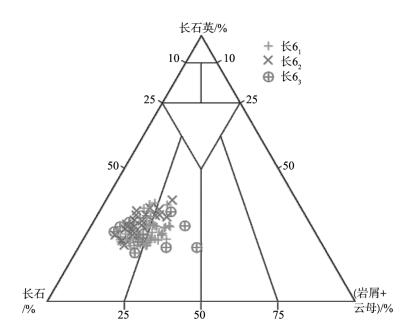
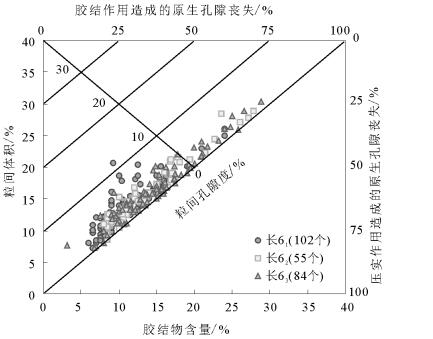
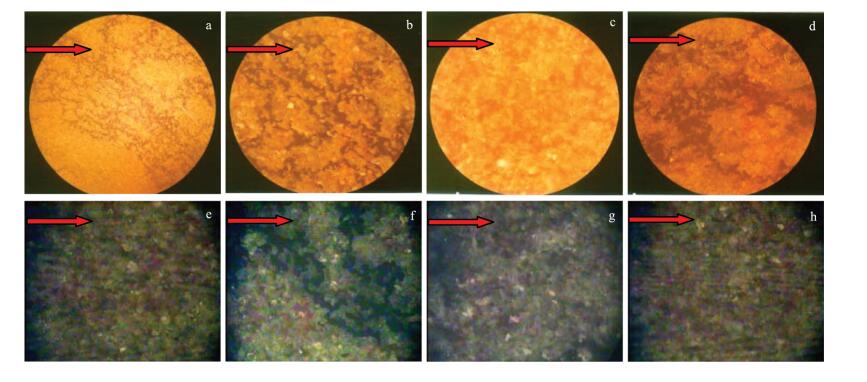
依据薄片、压汞、扫描电镜、物性分析及油水驱替实验资料, 对吴仓堡地区三角洲前缘亚相长6厚层砂岩储层的岩石学特征、孔渗特征、孔隙结构特征、成岩作用、微观渗流特征等进行深入研究, 分析影响储层储集性能的主控因素。结果表明, 受东北物源控制的长6厚层砂岩储层具有成分成熟度中等、结构成熟度较好的特点, 储集空间主要为残余粒间孔和粒间溶孔、粒内溶孔, 为典型中低孔、特低渗储集层; 储层储集性能主要受沉积微相和成岩作用控制。对储层发育影响最大的成岩期位于中成岩A期, 中等压实-粘土膜胶结残余粒间孔发育成岩相和弱压实-残余粒间孔+溶蚀孔隙发育成岩相是最有利储层发育的成岩相带。根据微观渗流特征, 可划分出4种驱油类型, 微观孔隙结构比宏观物性更能反映储层的本质特征。
Abstract:Based on data obtained from cast slice, mercury injection test, SEM, physical properties, and oil/water micro-displacement experiment, the authors made a thorough study of the petrological characteristics, porosity and permeability characteristics, pore structure characteristics, diagenesis and micro-anisotropy of Chang 6 reservoir in Wucangbu area, and analyzed the main influ-encing factors. The results show that the sedimentary environment of the Chang 6 thick sandstones reservoir is a delta front derived from the provenance in the northeast. In addition, the reservoir is characterized by medium compositional maturity and high textual maturity. The reservoir space includes residual intergranular pores, intergranular emposieu and intragranular emposieu. The sedimentary micro-facies and diagenesis constitute the main factors controlling the reservoir properties. The diagenetic period affecting reservoir development is stage A of middle diagenesis. The middle compaction, clay film cementation, residual intergranular pore diagenesis facies with weaker compaction and the secondary dissolution pore diagenesis facies are favorable diagenetic facies belts for reservoir development. Four oil displacement types are distinguished by studying reservoir microscopic heterogeneity, and the microscopic pore structures can more really reflect the reservoir's essential characteristics than the macroscopically physical properties.
-
致谢: 长庆油田分公司勘探开发研究与低渗透油气田勘探开发国家工程实验室提供了大量基础资料和分析化验数据,在此表示感谢。
-
表 1 吴仓堡长6段不同孔隙类型对面孔率的贡献值
Table 1 The contribution of pore types to surface porosity in Chang 6 reservoir of Wucangbu area
残余粒间孔隙/% 溶蚀粒间孔隙/% 溶蚀粒内孔隙/% 自生矿物晶间微孔隙/% 微裂隙
/%长石溶孔 岩屑溶孔 沸石溶孔 杂基溶孔 铸模孔 71.68 1.8 16.3 5.9 1.4 0.64 0.33 1.26 0.66 表 2 吴仓堡地区长6储层物性与孔喉特征分类
Table 2 Statistics of physical properties and pore-throat characteristics of Chang 6 reservoir in Wucangbu area
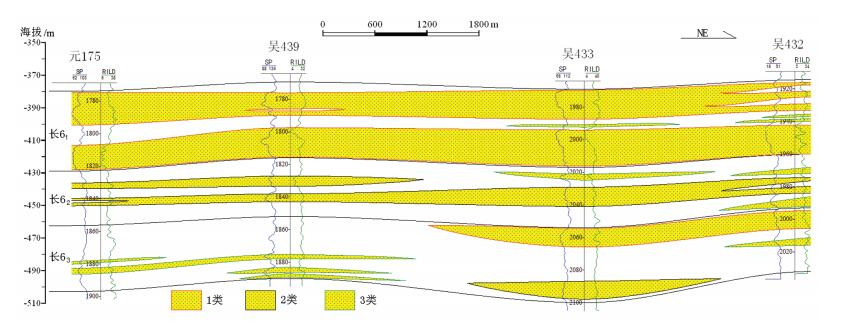
级別 物性特征 孔隙类型 孔隙喉道参数 孔隙度/% 渗透率/10-3pm2 门槛压力/MPa 喉道中值半径/μm 分选系数/Sp Ⅰ类
(好)> 12 > 1.0 混合孔隙型
(残余粒间孔+溶蚀孔)< 0.5 > 0.2 < 2.5 Ⅱ类
(中等)9 〜 12 0.3 〜 1.0 残余孔隙型
(残余粒间孔为主)0.5 〜 1.5 0.2 〜 0.05 2.5 〜 3 Ⅲ类
(差)< 9 < 0.3 致密孔隙型
(少量残余粒间孔、晶间微孔)> 0.5 < 0.05 > 3.0 表 3 吴仓堡地区长6段不同沉积微相砂体物性统计
Table 3 Porosity and permeability statistics for different sedimentary microfacies sandbodies of Chang 6 reservoir in Wucangbu area
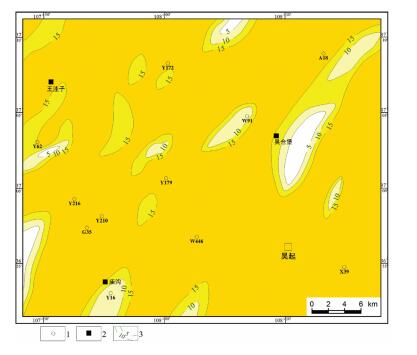
沉积微相类型 孔隙度/% 渗透率/10-3pm2 样品数/个 分布范围 平均值 分布范围 平均值 水下分流河道 9.6〜15.6 12.3 0.18〜3.46 1.32 213 河口坝 7.1〜13.2 11.5 0.15〜2.78 0.85 89 远砂坝 5.9〜12.4 10.2 0.12〜0.91 0.39 73 分流间湾 2.7〜11.1 8.5 0.04〜0.34 0.12 25 -
王昌勇, 郑荣才, 王海红, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地史家湾地区长6油层组物源区分析[J].沉积学报, 2008, 25(4):933-938. 朱静.胡尖山-吴起地区延长组长6油层组沉积相研究[D].西北大学硕士学位论文, 2008:89, 93. 杨晓萍, 裘亦楠.鄂尔多斯盆地上三叠统延长组浊沸石的形成机理、分布规律与油气关系[J].沉积学报, 2002, 20(4):628-632. 付金华, 罗安湘, 喻建, 等.西峰油田成藏地质特征及勘探方向[J].石油学报, 2004, 25(2):25-29. 魏钦廉, 郑荣才, 肖玲, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地吴旗地区长6储层特征及影响因素分析[J].岩性油气藏, 2007, 9(4):40-50. 黄思静, 谢连文, 张萌, 等.中国三叠系陆相砂岩中自生绿泥石的形成机制及其与储层孔隙保存的关系[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 31(3):273-281. 肖玲, 田景春, 魏钦廉, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地吴旗地区长6储层孔隙结构特征[J].新疆地质, 2007, 25(1):101-102. 黄龙, 田景春, 肖玲, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地富县地区长6砂岩储层特征及评价[J].岩性油气藏, 2008, 20(1):83-85. 郑荣才, 耿威, 周刚, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地白豹地区长6砂岩成岩作用与成岩相研究[J].岩性油气藏, 2007, 19(2):1-8. 郑浚茂, 庞明.碎屑储集岩的成岩作用[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1989:58-59. Housknecht D W.Assessing the relative importance of compaction processes and cementation to reduction of porosity in sand stones[J]. AAPG Bulletin,1987,71:633-642 Housknecht D W.Assessing the relative importance of compaction processes and cementation to reduction of porosity in sand stones[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1987, 71:633-642
李斌, 孟自芳, 李相博, 等.靖安油田上三叠统长6储层成岩作用研究[J].沉积学报, 2005, 23(4):574-583. 窦伟坦, 田景春, 王峰, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地长6油层组储集砂岩成岩作用及其对储层性质的影响[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 36(2):156-157. Hurst A, Nadeau H P. Clay micro-porosity in reservoir sand-stones:an application of quantitative electron microscopy in petrophysical evaluation[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1995,79(4):563-573. Hurst A, Nadeau H P. Clay micro-porosity in reservoir sand-stones:an application of quantitative electron microscopy in petrophysical evaluation[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1995, 79(4):563-573.
姚泾利, 王琪, 张瑞, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地华庆地区延长组长6砂岩绿泥石膜的形成机理及其环境指示意义[J].沉积学报, 2011, 29(1):75-76. 何自新, 贺静.鄂尔多斯盆地中生界储层图册[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2004:59-60. 朱平, 黄思静, 李德敏, 等.粘土矿物绿泥石对碎屑储集岩孔隙的保护[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 31(2):153-156. 贾振岐, 孙念, 吴景春, 等.特低渗透岩心相对渗透率实验研究[J].特种油气藏, 2009, 16(1):82-83. 高辉.特低渗透砂岩储层微观孔隙结构与渗流机理研究[D].西北大学硕士学位论文, 2009:102-105. 邦德.残余油饱和度确定方法[M].王平等译.北京:石油工业出版社, 1982. 闫健, 张宁生, 刘晓娟, 等.低渗气藏单相气体渗流特征分析[J].西安石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 25(1):41-44. 杨仁锋, 姜瑞忠, 孙君书, 等.低渗透油藏非线性微观渗流机理[J].油气地质与采收率, 2011, 18(2):90-97. 黄延章.低渗透油层渗流机理[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 1995.



 下载:
下载: