Characteristics of microscopic pore structure in the low permeability sandstone reservoir:A case study of Chang 9 of Yanchang Formation in Zhijing-Ansai area of Ordos Basin
-
摘要:
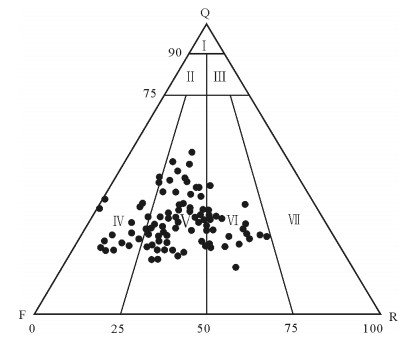
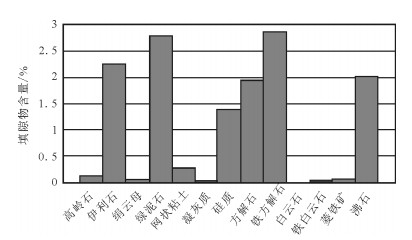
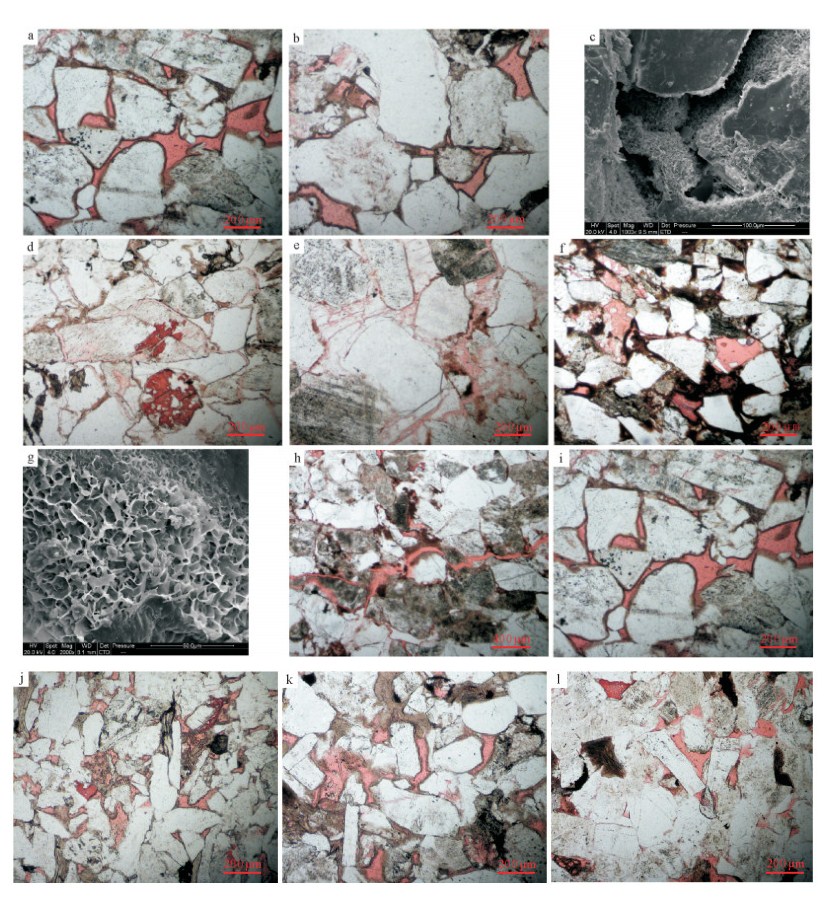
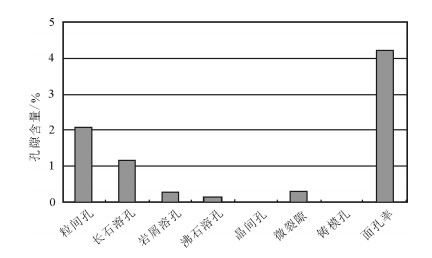
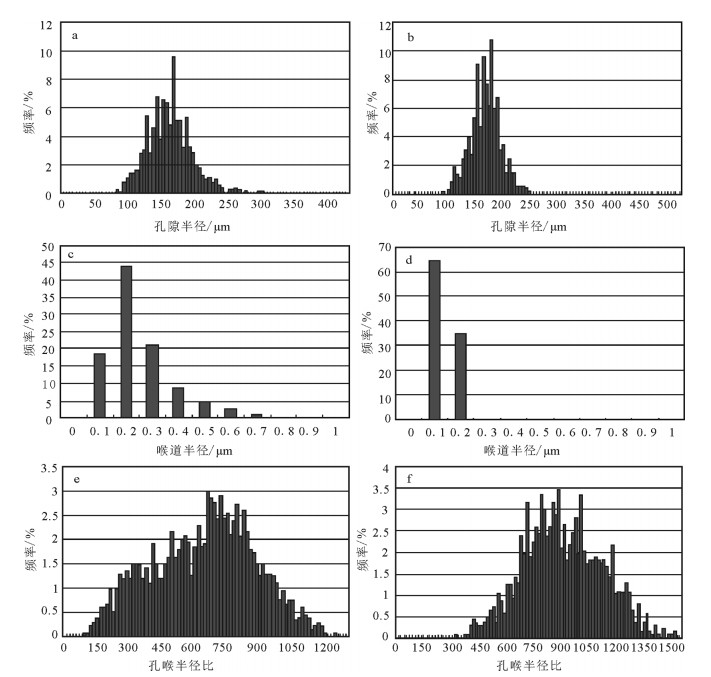
通过物性分析、铸体薄片、扫描电镜技术、常规高压压汞技术、恒速压汞技术等, 对选自鄂尔多斯盆地志靖-安塞地区长9段低渗透砂岩储层样品进行测试分析, 获取储层孔隙、喉道的形态、类型、连通程度等信息, 确定孔喉大小、分选情况和连通性的定量参数。研究表明, 研究层位孔隙类型主要为残余粒间孔、溶孔、微孔。将孔隙组合特征分为4种类型, 储层孔隙结构具多样性。样品孔喉结构整体上具有大孔隙、细喉道的特点, 微细喉道的发育是造成物性渗透率超低的主要原因。储层孔隙结构的多样性及不均一性是导致储层非均质性的主要原因。
Abstract:In this paper, the authors investigated characteristics of microscopic pore structure in low permeability sandstone reservoir for providing the basis for further exploration and development. By means of physical property analysis, SEM, casting slice, high pressure Hg injection, and rate-controlled Hg penetration, the authors selected low permeability sandstone samples from Chang 9 of Yanchang Formation in Zhijing-Ansai area of Ordos Basin and made analysis. The information of reservoir pores, types and the morphology of throat and its degree of connectivity was obtained, and the quantity factors about the size of pore and throat, sorting and connectivity were determined. The results show that the pores mainly consist of residual intergranular pores, solution pores and micro-pores. The pore combination is divided into four types which reflect the diversity of pore structure. Pore structure of the samples is characterized by large pore and fine throat. The development of fine throat is the main reason responsible for ultra-low permeability.The diversity and heterogeneity of the reservoir pore structure is the main cause of the reservoir heterogeneity.
-
致谢: 感谢西安石油大学地球科学与工程学院郭艳琴副教授在论文修改过程中悉心指导,感谢评审专家对本文所提出的宝贵修改意见。
-
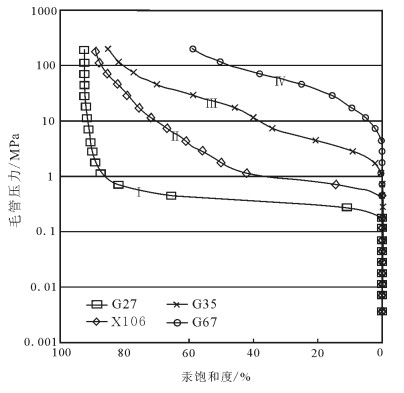
表 1 志靖—安塞地区长9储层孔隙结构参数对比
Table 1 Correlation of pore structure parameters of Chang 9 reservoir in Zhijing-Ansai area
参数 物性 喉道大小 孔喉分布 孔喉连通性 层位 孔隙度
/%渗透率
/10-3μm2排驱压力
/MPa中值压力
/MPa中值半径
/μm均值
系数分选
系数变异
系数歪度
系数最大进汞
饱和度退汞
效率/%样品
块数长91 最大值 15.14 69.17 2.9 81.78 4.32 13.03 4.5 0.53 3.23 94.81 43.87 31 6.3 0.10 0.007 0.17 0.008 6.6 1.1 0.09 0.94 58.35 8.69 平均值 10.8 5.59 0.9 15.72 0.48 10.74 2.37 0.23 1.08 81.74 25.47 长92 最大值 14.4 35.69 1.81 43.92 1.98 12.82 3.63 0.36 1.98 93.27 45.75 31 最小值 5.47 0.1 0.004 0.37 0.02 7.52 1.17 0.12 0.78 65.88 8.97 平均值 10.59 2.26 0.72 8.3 0.28 10.92 2.41 0.23 0.93 81.38 26.76 表 2 志靖—安塞地区长9储层不同毛细管压力曲线特征分类
Table 2 Characteristics of different capillary pressure curves of Chang9 reservoir in Zhijing-Ansai area
毛管压力曲线类型 Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ 物性参数 孔隙度/% 变化范围 12.14~15.14 10.14~12.59 5.47~12.35 5.41~10.11 平均值 14.17 11.39 9.59 7.28 渗透率/10-3μm2 变化范围 12.59~69.17 0.50~3.49 0.10~0.50 0.04~0.1 平均值 34.50 1.50 0.26 0.08 孔隙结构参数 门槛压力/MPa 变化范围 0.007~1.17 0.007~0.72 0.004~1.81 0.72~4.51 平均值 0.30 0.33 1.01 2.06 中值半径/μm 变化范围 0.12~4.32 0.009~2.16 0.009~1.98 0.006~0.08 平均值 1.76 0.56 0.17 0.03 最大进汞
饱和度/%变化范围 84.78~92.84 78.50~93.24 63.69~94.81 58.75~88.94 平均值 90.58 88.37 83.87 78.77 分选系数 变化范围 1.10~3.04 1.70~4.09 1.72~4.5 1.97~4.94 平均值 2.22 2.48 2.69 2.99 歪度系数 变化范围 1.42~3.23 0.89~2.14 0.78~2.03 1.34~1.82 平均值 1.94 1.54 1.61 1.56 表 3 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组孔隙、喉道分级标准
Table 3 Pore and throat grading standards of Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin
孔隙分级 平均孔隙/m 喉道分级 平均喉径/pm 大孔隙 > 100 粗喉道 > 3 中孔隙 100〜50 中细喉道 3〜1 小孔隙 50〜10 细喉道 1〜0.5 细孔隙 10〜0.5 微细喉道 0.5〜0.2 微孔隙 < 0.5 微喉道 < 0.2 -
王道富, 付金华, 雷启鸿, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地低渗透油气田勘探开发技术与展望[J].岩性油气藏, 2007, 19(3):126-130. 蒋凌志, 顾家裕, 郭彬程.中国含油气盆地碎屑岩低渗透储层的特征及形成机理[J].沉积学报, 2004, 22(1):13-18. 罗蛰潭, 王允诚.油气储集层的孔隙结构[M].北京:科学出版社, 1986. 李道品, 罗迪强, 刘雨芬.低渗透油田概念及我国储量分布状况[J].低渗透油气田, 1996, 1(1):1-7. SY/T6285中华人民共和国石油天然气行业标准[S]. 1997. 王允诚.油气储层地质学[M].北京:地质出版社, 2008. 王瑞飞, 陈明强, 孙卫.特低渗透砂岩储层微观孔隙结构分类评价[J].地球学报, 2008, 29(2):213-220. 高永利, 孙卫, 张昕.鄂尔多斯盆地延长组特低渗透储层微观地质成因[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2013, 43(1):13-19. 王瑞飞, 陈明强, 孙卫.鄂尔多斯盆地延长组超低渗透砂岩储层微观孔隙结构特征研究[J].地质论评, 2008, 54(2):270-277. 杨县超, 张林, 李江, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地苏里格气田储层微观孔隙结构特征[J].地质科技情报, 2009, 28(3):73-76. 冉新权, 吴胜和, 付晶, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区延长组低渗透储层孔隙结构分类研究[J].地学前缘(自然科学版), 2013, 20(2):77-85. 李文厚, 庞军刚, 曹红霞, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地晚三叠世延长期沉积体系及岩相古地理演化[J].西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 39(3):501-506. 胡江柰, 张哨楠, 李德敏.鄂尔多斯盆地北部下石盒子组-山西组成岩作用与储层的关系[J].成都理工学院学报, 2001, 28(4):169-173 陈欢庆, 曹晨, 梁淑贤, 等.储层孔隙结构研究进展[J].天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(2):227-237. 吴元燕, 吴胜和, 蔡正旗, 等.油矿地质学[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2005. 于俊波, 郭殿军, 王新强.基于恒速压汞技术的低渗透储层物性特征[J].大庆石油学院学报, 2006, 30(2):22-25. 朱永贤, 孙卫, 于锋.应用常规压汞和恒速压汞实验方法研究储层微观孔隙结构——以三塘湖油田牛圈湖区头屯河组为例[J].天然气地球科学, 2008, 19(4):553-556.



 下载:
下载: