Characteristics of Early Cretaceous prototype basin of Liupanshan Group in Liupanshan Basin
-
摘要:
六盘山盆地是近南北向狭长的中新生代断陷沉积盆地, 位于秦岭、祁连加里东褶皱带与鄂尔多斯盆地西缘断褶带之间, 华北古板块南部边缘, 为河西走廊东延部分。通过六盘山盆地六盘山群底部砾岩砾石特征、古水流等分析, 探讨下白垩统沉积时期的物源特征。从露头观察结果看, 三桥组沉积的粗粒砂砾岩具有分选性和磨圆度差的特点, 反映结构成熟度低及离物源近的特点。早白垩世初期, 六盘山盆地受晚侏罗世挤压构造的影响, 盆地周缘山体为剥蚀区, 西南缘沉积了一套以粗碎屑为主的冲积扇, 向盆地内部过渡为辫状河; 早白垩世晚期, 受伸展构造的影响, 盆地边界向外扩展, 坳陷一并向西部扩展, 随着气候的干旱-湿润交替出现, 发育冲积扇、河流、三角洲及浅湖、咸化湖沉积。
Abstract:Liupanshan Basin is a Mesozoic-Cesozoic rift sedimentary basin which is located in the southern North China Plate and the east extension part of Hexi Corridor and lies along Qinling-Qilian Caledonian fold belt. In this paper, the authors analyzed con-glomerate gravel characteristics and palaeocurrent of Liupanshan Basinand explored provenance characteristics of Lower Cretaceous strata. Outcrop observations show that separation and grinding roundness of conglomerate and sandstone of Sanqiao Group are poor, reflecting middle-low structure maturity and nearby source. At the beginning of the Early Cretaceous, basin boundary was affected by strong compressive tectonic background of Late Jurassic, a series of highland internal basins and peripheral mountains suffered from weathering denudation, and the southwestern margin was mainly characterized by coarse clastic sedimentary piedmont pluvial fan ac-cumulation and deposited piedmont pluvial fan of predominantly coarse fragments, which was gradually transitional to braided river towards the interior of the basin. In late Early Cretaceous, the basin boundary was expanded towards the west. Accompanied by alternate drought-humid climate, there developed alluvial fan, braided river, delta, shallow lake and saline lake facies.
-
Keywords:
- prototype basin /
- Early Cretaceous /
- basin boundary /
- Liupanshan Basin
-
随着中国石油勘探开发程度的加大、技术的提高,低渗透油气资源在中国油气资源中所占比例逐渐加大。低渗透储层具有岩性细、物性差、渗流阻力大、非均质强、可动流体饱和度较高、储层微裂缝发育、油藏受岩性控制、润湿性为弱亲水-中性、储层分布较稳定等特点[1-2]。根据中国的地质背景和油气勘探开发实践,一般将渗透率介于0.1×10-3~50×10-3μm2之间的储层统称为低渗透储层[3-6]。鄂尔多斯盆地中生界延长组储层绝大部分属于低渗透储层,是近几年鄂尔多斯盆地油气勘探的主要对象。
储层微观孔隙结构直接影响岩石的储集特性和渗流特性,是研究岩石孔隙度和渗透率的基础,对低渗透储层研究具有重要意义[7-11]。本文以典型的鄂尔多斯盆地志靖—安塞地区延长组长9油层组低渗透储层为例,采用物性分析、铸体技术、扫描电镜技术、高压压汞技术、恒速压汞技术等,对低渗透砂岩储层微观孔隙结构特征进行分析,为下一步勘探和开发提供依据。
1. 沉积背景
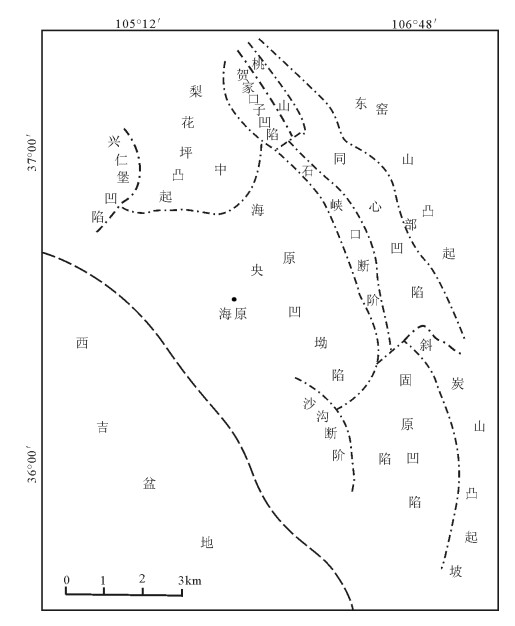
志靖—安塞地区地处鄂尔多斯盆地伊陕斜坡中西部,北起靖边,南至永宁,西自吴起,东至安塞,面积约1×104km2(图 1)。随着湖盆的下沉,研究区演化至延长组长9期主要发育曲流河三角洲沉积体系[12],整体位于水下环境,储集砂体主要为三角洲前缘砂体。长91期砂体继承了长92砂体发展的趋势,但是由于长9期湖盆持续下沉的影响,长91期分流间湾面积有所增加,泥质含量增加,砂体厚度减薄。砂体属于典型的曲流河三角洲前缘沉积的细粒沉积。这些达到一定厚度的砂体作为低渗透储层的骨架为油气储集提供了基础。
2. 岩石学特征
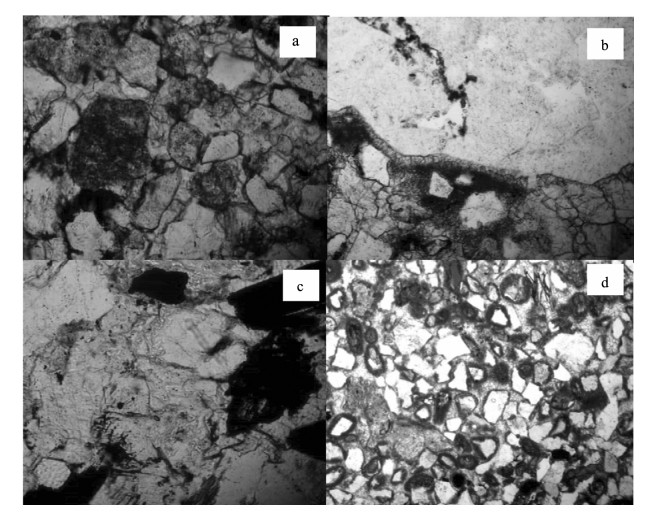
研究区长9砂岩主要发育灰绿色、灰白色岩屑长石砂岩(图 2),粒度以细砂、中砂为主。分选以中等、中等偏差为主,磨圆主要为次棱角状,颗粒接触类型以线、点-线、线-凹凸接触为主,支撑方式多为颗粒支撑,胶结类型以薄膜式、孔隙式、加大式胶结为主。
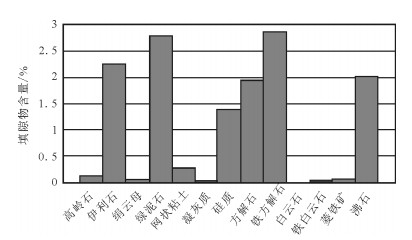
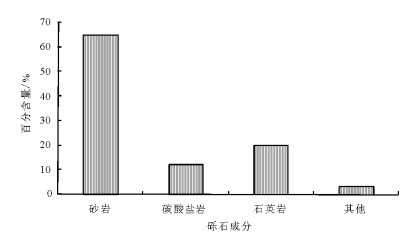
研究区长9储层填隙物种类较多,以粘土矿物和碳酸盐胶结物为主,主要有绿泥石、伊利石、浊沸石、铁方解石和硅质。填隙物总量可达14.12%,其中绿泥石占2.79%,硅质占1.39%,浊沸石占2.02%,伊利石占2.27%,铁方解石占2.85%,方解石占1.94%,高岭石占0.13%(图 3)。
3. 物性特征
通过对志靖—安塞地区长9储层近2000块岩心物性分析结果统计,志靖—安塞地区长91储层孔隙度在6%~12%之间,平均孔隙度为9.25%;长92孔隙度在6%~12%之间,平均孔隙度为8.74%。长91渗透率在0.1×10-3~0.3×10-3μm2和1×10-3~10×10-3μm2两个区间范围,平均渗透率为2.86×10-3μm2;长92渗透率为0.1×10-3~0.3×10-3μm2,平均渗透率为0.6×10-3μm2。总体志靖—安塞地区长9储层具有低孔、低渗特点,且长91物性好于长92。
4. 孔隙与喉道特征
孔隙和喉道是砂岩储集空间的2个基本因素。孔隙大小主要影响储层的孔隙度,喉道大小与连通状况直接影响储层有效性和渗透性[13],因而有必要研究储层的孔喉特征,即碎屑岩孔隙结构。
4.1 孔隙类型
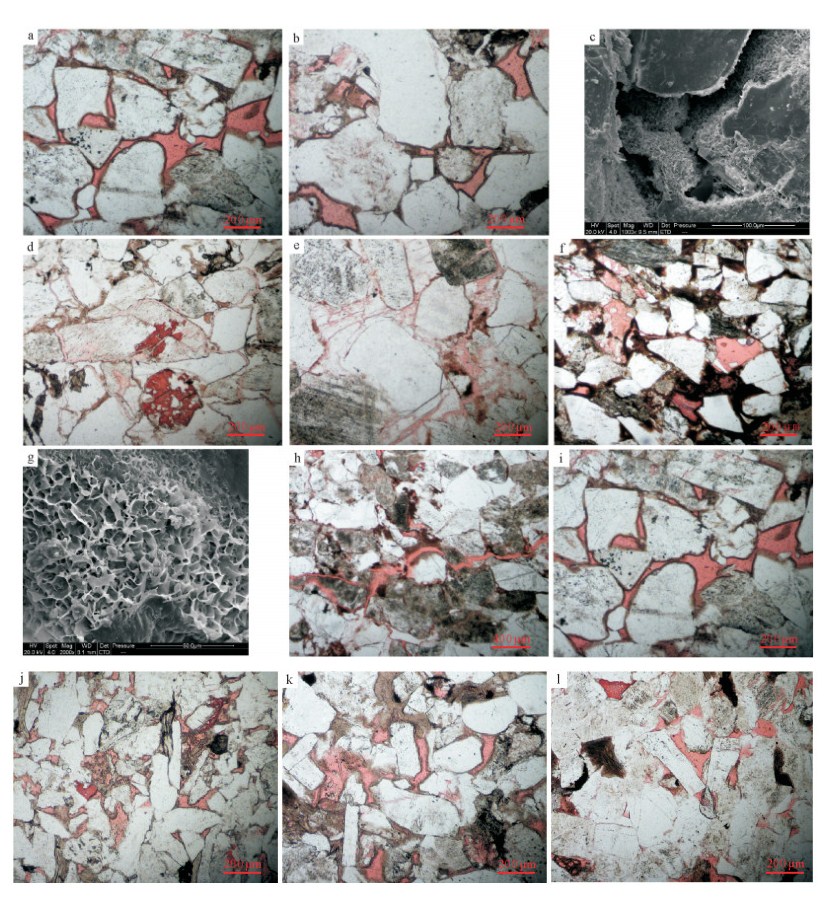
通过常规薄片、铸体薄片和扫描电镜观察,志靖—安塞地区长9储层发育多种孔隙类型,包括粒间孔、粒内孔、晶间孔、微裂缝等。其中粒间孔以残余粒间孔为主(图版Ⅰ-a~c),为成岩过程中原生粒间孔隙被部分压实和部分充填后剩余的孔隙,形态有三角形、多边形、不规则形等。这类孔隙在研究区长9储层中发育程度较高,可达2.05%,孔径较大,一般为10~50μm,但分布均一性较差,且连通性受成岩作用的影响较大,非均质性较强。
![]() a.X80井(1846.2m,单偏10×,粒间孔);b.X126井(2323.26m,单偏10×,粒间孔);c.X106井(2280.3m,扫描电镜1000×,粒间孔);d.A28井(2116.8m,单偏10×,长石粒内溶孔);e.X77井(2121m,单偏10×,沸石溶孔);f.G89井(2009.26m,单偏10×,铸模孔);g.A27井(2151.3m,扫描电镜2000×,晶间孔);h.X77井(2121m,单偏4×,微裂隙发育);i.X80井(1846.2m,单偏10×,缩颈型喉道);j.X283井(2252.3m,单偏10×,缩颈型喉道);k.X126井(2319m,单偏10×,片状、弯片状喉道);l.D43井(1587.3m,单偏10×,片状、弯片状喉道)
a.X80井(1846.2m,单偏10×,粒间孔);b.X126井(2323.26m,单偏10×,粒间孔);c.X106井(2280.3m,扫描电镜1000×,粒间孔);d.A28井(2116.8m,单偏10×,长石粒内溶孔);e.X77井(2121m,单偏10×,沸石溶孔);f.G89井(2009.26m,单偏10×,铸模孔);g.A27井(2151.3m,扫描电镜2000×,晶间孔);h.X77井(2121m,单偏4×,微裂隙发育);i.X80井(1846.2m,单偏10×,缩颈型喉道);j.X283井(2252.3m,单偏10×,缩颈型喉道);k.X126井(2319m,单偏10×,片状、弯片状喉道);l.D43井(1587.3m,单偏10×,片状、弯片状喉道)粒内孔是颗粒内部形成的孔隙,研究区长9储层以溶蚀粒内孔为主,主要溶蚀成分为长石、岩屑及浊沸石。其中长石相对粒内溶蚀较发育(图版Ⅰ-d),长石溶孔在研究区作为另一储集空间,其形成常受解理及交代矿物的限制,沿解理及裂隙进行溶蚀,形状呈网状或不规则的粒内溶孔。岩屑溶孔、沸石溶孔(图版Ⅰ-e)在本区分布局限,孔径较小,对储层砂岩的孔隙性能贡献较小。部分颗粒发生全部溶蚀后仍然保持原颗粒的形态形成铸模孔(图版Ⅰ-f)。
晶间孔主要是分布于自生矿物颗粒之间的孔隙空间,研究区长9储层砂岩中主要有自生绿泥石晶间孔隙、自生伊利石、伊/蒙混层晶间微孔隙(图版Ⅰ-g),孔隙直径较小,一般为1.0~5.0μm,连通性较差。
研究区长9储层主要发育2种微裂隙,一种是成岩作用过程中受外力影响产生的岩石破裂缝(图版Ⅰ-h),缝宽0.01~0.10mm,另一种为云母等发育的层理缝。微裂缝具很好的连通性,改善储集层的渗透性,但发育具很强的不均一性。由于其渗透性极佳,导致低渗透砂岩储层物性非均质性增强。
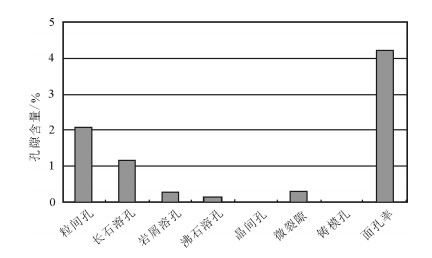
研究区长9储层孔隙类型以粒间孔(2.05%)、长石溶孔(1.16%)为主,其次为微裂隙(0.31%)和岩屑溶孔(0.27%),晶间孔和铸模孔含量较少。粒间孔、长石溶孔是本区最主要的储集空间(图 4)。面孔率中等,平均面孔率4.18%,平均孔径为43.28μm。
4.2 喉道类型及特征
喉道的几何形态特征受控于碎屑颗粒的磨圆度、分选程度、含量与大小、胶结物类型与含量、成岩作用的强度等因素。根据铸体薄片和扫描电镜分析,研究区储层喉道类型以缩颈型喉道为主,其次为片状或弯片状喉道(图版Ⅰ-i~l),孔隙之间连通性中等-较差,局部孔隙之间无喉道连通。
5. 微观孔隙结构特征
5.1 常规高压压汞研究
储层微观孔隙结构是岩石所具有的孔隙和喉道的几何形状、大小、分布及其相互连通关系[14]。在对研究区砂岩孔隙喉道进行镜下定性分析后,通过常规高压压汞技术得到储集层砂岩压汞数据,确定有关孔喉大小、分选情况和连通性的定量参数,绘制毛细管压力曲线,对孔隙结构特征进行分析和分类。反映孔隙结构特征的毛管压力参数主要有门槛压力(Pcd)、中值压力(PC50)、喉道分选系数(Sp)、变异系数(C)、歪度系数(Sk)、最大连通孔喉半径(Rd)、中值喉道半径(R50)等[15]。
对各参数统计发现(表 1),研究区长9储层平均渗透率较高,最大与最小渗透率值差异大,孔喉大小分布不均一,分选较差,粗歪度,连通性一般。最大进汞饱和度较高,但退汞效率很低。这也说明研究区储层砂岩发育多种孔喉组合。
表 1 志靖—安塞地区长9储层孔隙结构参数对比Table 1. Correlation of pore structure parameters of Chang 9 reservoir in Zhijing-Ansai area参数 物性 喉道大小 孔喉分布 孔喉连通性 层位 孔隙度
/%渗透率
/10-3μm2排驱压力
/MPa中值压力
/MPa中值半径
/μm均值
系数分选
系数变异
系数歪度
系数最大进汞
饱和度退汞
效率/%样品
块数长91 最大值 15.14 69.17 2.9 81.78 4.32 13.03 4.5 0.53 3.23 94.81 43.87 31 6.3 0.10 0.007 0.17 0.008 6.6 1.1 0.09 0.94 58.35 8.69 平均值 10.8 5.59 0.9 15.72 0.48 10.74 2.37 0.23 1.08 81.74 25.47 长92 最大值 14.4 35.69 1.81 43.92 1.98 12.82 3.63 0.36 1.98 93.27 45.75 31 最小值 5.47 0.1 0.004 0.37 0.02 7.52 1.17 0.12 0.78 65.88 8.97 平均值 10.59 2.26 0.72 8.3 0.28 10.92 2.41 0.23 0.93 81.38 26.76 表 2 志靖—安塞地区长9储层不同毛细管压力曲线特征分类Table 2. Characteristics of different capillary pressure curves of Chang9 reservoir in Zhijing-Ansai area毛管压力曲线类型 Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ 物性参数 孔隙度/% 变化范围 12.14~15.14 10.14~12.59 5.47~12.35 5.41~10.11 平均值 14.17 11.39 9.59 7.28 渗透率/10-3μm2 变化范围 12.59~69.17 0.50~3.49 0.10~0.50 0.04~0.1 平均值 34.50 1.50 0.26 0.08 孔隙结构参数 门槛压力/MPa 变化范围 0.007~1.17 0.007~0.72 0.004~1.81 0.72~4.51 平均值 0.30 0.33 1.01 2.06 中值半径/μm 变化范围 0.12~4.32 0.009~2.16 0.009~1.98 0.006~0.08 平均值 1.76 0.56 0.17 0.03 最大进汞
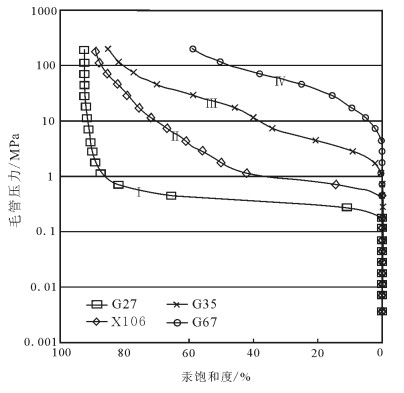
饱和度/%变化范围 84.78~92.84 78.50~93.24 63.69~94.81 58.75~88.94 平均值 90.58 88.37 83.87 78.77 分选系数 变化范围 1.10~3.04 1.70~4.09 1.72~4.5 1.97~4.94 平均值 2.22 2.48 2.69 2.99 歪度系数 变化范围 1.42~3.23 0.89~2.14 0.78~2.03 1.34~1.82 平均值 1.94 1.54 1.61 1.56 这些压汞定量参数在毛细管压力曲线中表现出不同的形态特征,根据不同的毛细管压力曲线特征,将62块样品归类研究,大致分为以下4种典型曲线形态(图 5)。其中不同形态的毛细管压力曲线对应一定范围的物性参数和孔隙结构参数(表 3),据此将孔隙结构类型分为4类。
表 3 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组孔隙、喉道分级标准Table 3. Pore and throat grading standards of Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin孔隙分级 平均孔隙/m 喉道分级 平均喉径/pm 大孔隙 > 100 粗喉道 > 3 中孔隙 100〜50 中细喉道 3〜1 小孔隙 50〜10 细喉道 1〜0.5 细孔隙 10〜0.5 微细喉道 0.5〜0.2 微孔隙 < 0.5 微喉道 < 0.2 Ⅰ类:门槛压力低,为0.007~1.17MPa,平均为0.30MPa;孔隙度很大,为12.14%~15.14%,平均值为14.17%;渗透率高,为12.59×10-3~69.17×10-3μm2,平均值为34.50×10-3μm2;中值半径为0.12~4.32μm,平均值为1.76μm。在毛细管压力曲线图上,这种类型的曲线相对在图的左下方,表明以粗喉道为主。同时,曲线具明显较宽的水平范围,代表了孔隙大小分选性好,有效孔隙度高的储层类型特征(图 5)。
Ⅱ类:门槛压力较Ⅰ类有所增高,为0.007~0.72MPa,平均值为0.33MPa;孔隙度降低,为10.14%~12.59%。平均值为11.39%;渗透率也相应变低,范围为0.50×10-3~3.49×10-3μm2,平均值为1.50×10-3μm2;中值半径为0.009~2.16μm,平均值为0.56μm。在毛细管压力曲线图上,曲线位于左下方偏上,表明喉道大小中等。曲线的水平范围短一些,代表了孔隙大小分选性较好,有效孔隙度较高的储层类型特征(图 5)。
Ⅲ类:门槛压力增高,为0.004~1.81MPa,平均值为1.01MPa;孔隙度为5.47%~12.35%,平均值为9.59%;渗透率为0.1×10-3~0.5×10-3μm2,平均为0.26×10-3μm2;中值半径为0.009~1.98μm,平均值为0.17μm。在毛细管压力曲线图上,曲线位于图的中部偏右上,表明喉道较细。曲线水平范围不明显,向陡斜状过度,说明分选中等,有效孔隙度较低的储层类型特征(图 5)。
Ⅳ类:门槛压力增高的更快,为0.72~4.51MPa,平均值为2.06MPa;孔隙度低,为5.41%~10.11%,平均7.28%;渗透率为0.04~0.1×10-3×10-3μm2,平均值为0.08×10-3μm2;中值半径为0.006~0.08μm,平均值为0.03μm。在毛细管压力曲线图上,曲线向图的右上方靠拢,并且曲线倾斜,无水平,表明该孔隙以微细或细喉道为主,孔隙分选差,反映了岩性较致密,有效孔隙度低的储层特征(图 5)。
4种孔隙结构组合类型共存于砂岩储层中,使得研究区储层微观非均质性加强。
5.2 恒速压汞研究
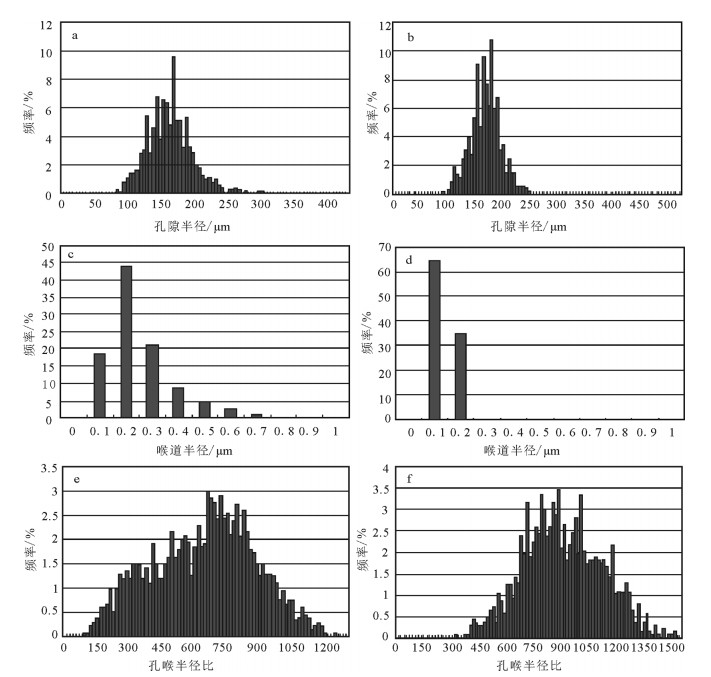
常规压汞只是给出了某一级别的喉道所控制的孔隙体积,并没有直接测量喉道数量。而恒速压汞实验不仅能够分别给出喉道和孔隙各自的发育情况,而且能够给出孔喉比的大小及其分布特征,可以克服这一不足[16]。此次研究又选取研究区目的层2块样品进行恒速压汞实验,1号样品孔隙度为7.66%,渗透率为0.51×10-3μm2,2号样品孔隙度为6.72%,渗透率为0.1×10-3μm2,接近低渗储层物性下限。
(1)如图 6-a、b所示,研究区2块样品的有效孔隙道半径分布特征为:1号样品平均孔隙半径为167.2μm,平均孔隙半径为161.9μm。2块样品孔隙半径大小及分布差异不大,主要分布在100~250μm之间,峰值在150~200μm之间。参照对比鄂尔多斯盆地延长组孔隙、喉道分级标准(表 3),以大孔喉为主,说明研究区砂岩储层微观非均质性受孔隙大小和分布影响不大。
(2)如图 6-c、d所示,研究区2块样品的有效喉道半径分布特征为:1号样品平均喉道半径为0.3μm,2号样品平均喉道半径为0.2μm。喉道半径差异较大,1号样品喉道半径主要分布在0.1×10-3~0.7×10-3μm2之间,并且大喉道数量递减,而2号喉道半径主要分布在0.1×10-3~0.2×10-3μm2之间,几乎没有半径大于0.3×10-3μm2的喉道存在。说明研究区砂岩储层喉道较细,以微细喉道为主。
(3)如图 6-e、f所示,研究区2块样品的有效孔喉半径比分布特征为:1号样品有效孔喉半径比主要分布在150~1200之间,峰值为600~900;2号样品有效孔喉半径比主要分布在300~1500之间,峰值为700~1000。岩样的孔喉半径比分布特征反映了岩样及储集层微观渗流能力的高低[17]。孔喉半径比增大,说明岩样喉道半径越小、孔隙半径越大,大部分孔隙被小喉道所控制,油越难从孔隙中流出;相反,孔喉半径比越小,说明喉道半径越大,流体越容易渗流或者被驱替。
从实验结果可以看出,样品孔喉结构具有大孔隙、细喉道,且分布不均一的特点,这也是导致其物性渗透率超低的主要原因。说明喉道的发育特征为控制储层渗透率的主要因素,而储层孔隙结构的多样性及不均一性是导致储层非均质性的主要原因。
6. 结论
对鄂尔多斯盆地志靖—安塞地区延长组长9段低渗透储层样品进行分析研究,得出以下结论。
(1)研究区长9储层物性表现为典型的低渗透储层特征。发育多种孔隙类型,包括粒间孔、粒内孔、晶间孔、微裂缝等。粒间孔、长石溶孔是本区最主要的储集空间。孔隙之间连通性中等-较差,局部孔隙之间无喉道连通。
(2)研究区储层砂岩发育多种孔喉组合。发育4类孔隙结构类型,分别为大-中孔粗喉型、中-小孔中喉型、中-小孔细喉型和小孔-微细喉型。最大连通喉道半径普遍较小,喉道分布范围宽且极不均匀,导致储层渗透性低、渗透率参数变化大,储层非均质性强。
(3)从恒速压汞实验结果可以看出,样品孔喉结构整体具有大孔隙、细喉道,且分布不均一的特点。微细喉道的发育是造成制物性渗透率超低的主要原因。储层孔隙结构的多样性及不均一性是导致储层非均质性的主要原因。
致谢: 西北大学地质学系李智超博士,赵敏、黄晓东硕士等参加了野外地质考察工作,陈萌、闻金华硕士协助完成岩石薄片鉴定,在此表示感谢。 -
-
章贵松, 张军, 任军峰, 等.六盘山弧形冲断体系构造新认识[J].新疆石油地质, 2006, 27(5):542-544. 王勇, 施炜.六盘山盆地白垩纪构造变形分析及其盆地形成演化[J].煤炭技术, 2007, 26(11):101-103. 白云来, 王新民, 刘化清, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地西部边界的确定及其地球动力学背景[J].地质学报, 2006, 80(6):792-813. 金学强, 曹炜华.宁夏六盘山地区白垩纪地层环境演化研究[J].宁夏工程技术, 2006, 5(1):1-3. 屈红军, 李文厚, 何希鹏, 等.六盘山盆地下白垩统沉积层序与含油气系统[J].西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 33(1):70-74. 戴霜, 朱强, 胡鸿飞.六盘山群磁性地层年代[J].地层学杂志, 2009, 33(2):188-192. 辛补社, 杨华, 付金华, 等.甘肃靖远宝积山地区上三叠统南营儿群底部凝灰岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其地层学意义[J].地质论评, 2013, 59(2):267-273. 付国斌, 李兴亮.六盘山盆地中新生代沉积地层[J].新疆石油学院学报, 2002, 14(2):24-27. 崔红庄, 王金铎, 尹克敏, 等.六盘山盆地早白垩世沉积演化特征分析[J].西安科技大学学报, 2013, 33(4):411-416 林小云, 胡望水, 谢锐杰.六盘山盆地与酒西盆地成藏条件对比[J].天然气工业, 2006, 26(4):21-23. 种俊丰, 魏巍.六盘山盆地海参1井油源对比与勘探意义[J].中国西部油气地质, 2006, 2(3):294-301. 李昌鸿.六盘山盆地西南缘构造与油气勘探潜力分析[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 36(3):243-248. 郇玉龙, 崔红庄, 尚应军.六盘山盆地构造样式与油气分布[J].海洋地质前沿, 2011, 27(5):31-46. 宁夏回族自治区地质矿产局.宁夏回族自治区区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 1990:180-186. 郇玉龙, 崔红庄, 尚应军, 等.六盘山盆地构造样式与油气分布[J].海洋地质前沿, 2011, 27(5):31-34, 46. 杨福忠.六盘山盆地含油气远景预测[J].石油勘探与开发, 1995, 22(1):5-8. 李昌鸿.六盘山盆地西南缘构造与油气勘探潜力分析[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 36(3):243-248. 刘运黎, 汤玉平.青藏高原东北缘六盘山盆地烃源岩的地球化学特征[J].地质通报, 2007, 26(4):483-491.



 下载:
下载: