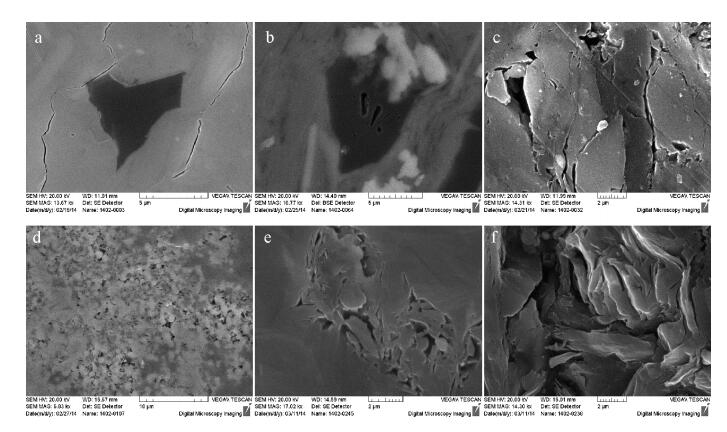
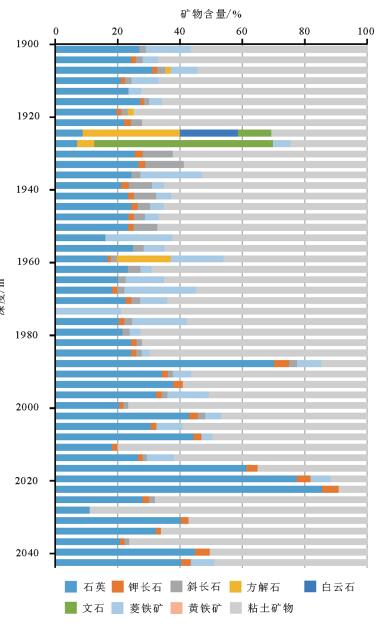
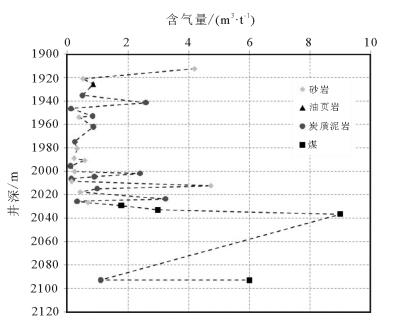
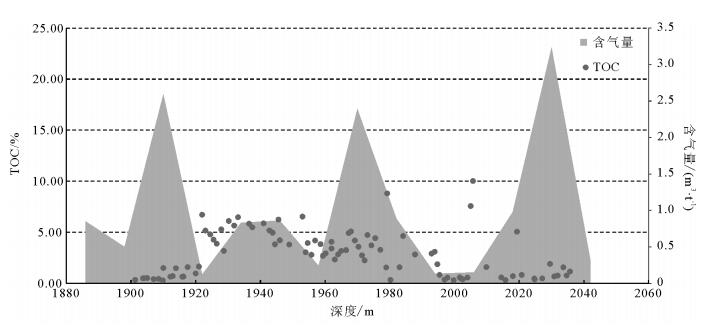
Organic geochemistry characteristics and reservoir conditions of Jurassic shale in Yuqia depression of northern Qaidam Basin:A case study of Chaiye-1 well
-
摘要:
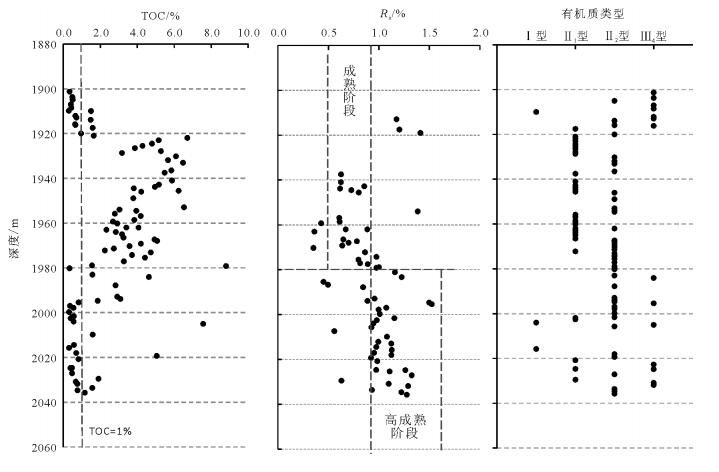
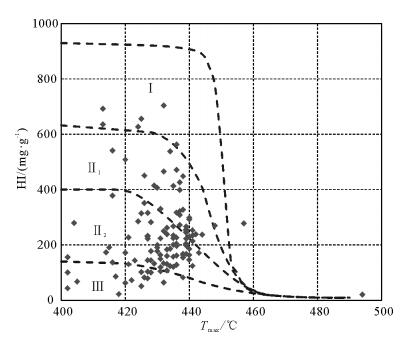
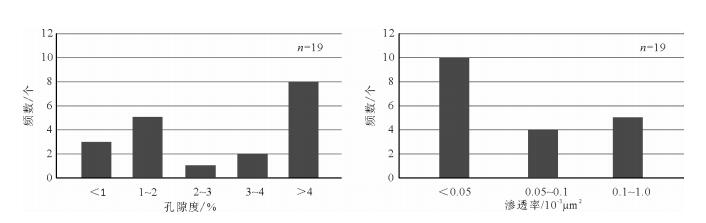
柴达木盆地北缘鱼卡凹陷发育的侏罗系泥页岩是中国北方陆相页岩气勘探的目的层系之一。为进一步明确鱼卡凹陷侏罗系泥页岩地化-储集条件, 系统采集了柴页1井泥页岩岩心样品, 开展了总有机碳、热解氢指数、镜质体反射率、孔隙度和渗透率、扫描电镜、矿物组成及等温吸附特征实验分析。结果表明, 柴页1井中侏罗统大煤沟组泥页岩有机质类型和成熟度利于有机质孔隙发育, 较高的总有机碳含量利于页岩气富集; 粘土矿物的存在虽然抑制了泥页岩微孔隙的发育, 但对其吸附能力有促进作用。鱼卡凹陷具有良好的页岩气生成和储集条件, 是页岩气勘探的有利地区
Abstract:Yuqia depression in northern Qaidam Basin, as a potential continental shale gas exploration target of Northwest China, is a sedimentary center of Jurassic lacustrine strata with thick dark mudstone and shale layers. Based on such means as the analysis of total organic carbon(TOC), hydrogen index(HI), vitrinite reflectance(Ro), porosity and permeability of shale, scanning electron microscope analysis(SEM), mineral composition and isothermal adsorption features of cores from the well Chaiye-1, the authors investigated natural gas reservoir forming conditions of Yuqia depression. The assessment results show that the organic types and maturity are favorable for the development of organic-matter pores and microfractures. The gas content of Dameigou Formation shale is high because of high TOC content. Clay mineral content has hindered the development of the cracks of the shale but accelerated its adsorption capacity. The shale of the Middle Jurassic Dameigou Formation is thus a significant target of the shale gas exploration in northern Qaidam Basin.
-
Keywords:
- Yuqia depression /
- shale gas /
- geochemistry /
- reservoir conditions
-
近年来,随着对鄂尔多斯西部靖边气田风化壳气藏勘探研究的不断深入,作为马五1+2气藏含气面积外扩的马五41气藏不断取得勘探新进展[1-3]。研究发现,岩石中有机组分的转化直接受碳酸盐岩风化壳储层成岩作用控制,决定了岩石中孔隙的形成、演化,以及储集类型和规模[4],其中,建设性埋藏成岩作用对岩石孔隙类型、成分改变具有重要作用。随着埋深的增加,岩石受到孔隙流体、地压应力、构造应力、水化效应等多重因素叠加的影响,有利于孔隙发育、保存,优化储层物性。成岩作用的研究不仅是重要的理论问题,而且具有实际意义[5],其对沉积盆地含油气性预测、潜在储层评价、成岩圈闭油藏的勘探等均具有重要意义[6]。因此,开展靖边气田高桥区块马五41段储层埋藏环境下建设性成岩作用的研究,对于下古生界勘探开发的持续发展和寻找更多的储量接替区块具有重要意义。
1. 研究区概况
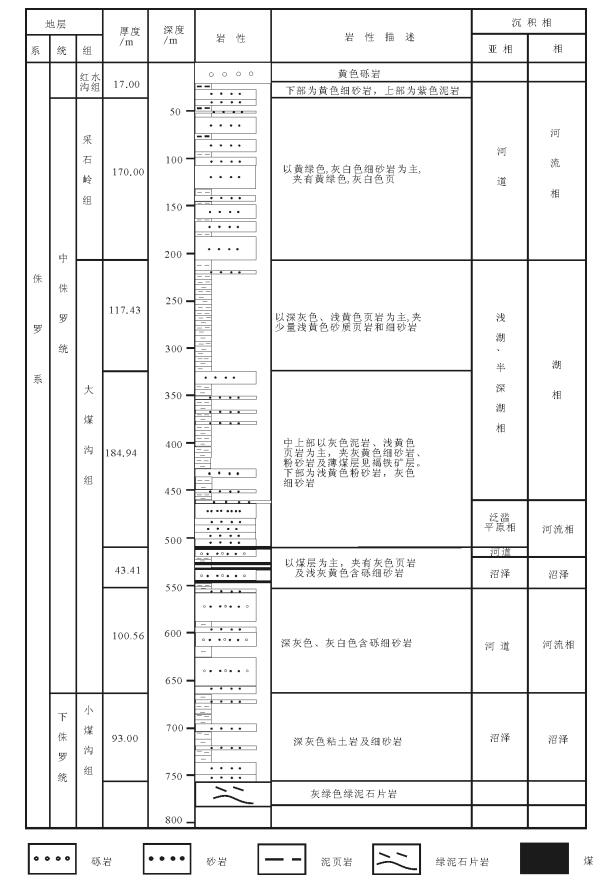
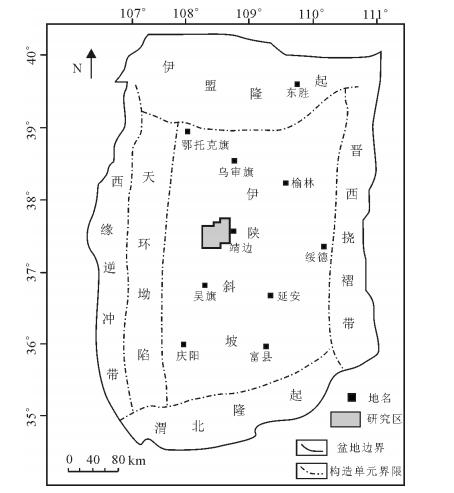
高桥区块位于鄂尔多斯盆地靖边气田西部,北起城川,南至五谷城,西起胡尖山,东至靖边,总面积约为6300km2(图 1)。奥陶系沉积后受加里东期运动的影响,地层被抬升到地表,经历了140Ma的风化、淋滤、剥蚀,形成了孔洞发育的风化壳岩溶储层[7]。研究区地层呈南北向展布,向西逐渐尖灭,马五41段主要位于岩溶斜坡-浅洼区及台地剥蚀区,气藏主要分布在台地剥蚀区,其次为浅洼区,马五41段主要为马五4亚段的主力产气层位[8]。马五41段地层沉积时主要为蒸发潮坪环境,沿剥蚀线自西向东发育云坪相及含膏云坪相,这类相带的大面积稳定分布,不仅为靖边气田孔洞型储层的成层发育提供了良好的物质条件,而且其在气田西侧的局部保存,为进一步向西扩边增加储量奠定了基础。
2. 样品采集及测试
白云岩样品均采自鄂尔多斯盆地靖边气田高桥区块的钻井岩心,对应层位为马家沟组马五41段,深度范围为3211.3~4300.05m。本次实测样品测试项目为C、O同位素,每份样品重量大于等于10g,采用MAT253气体同位素质谱仪,在北京核工业研究所进行测试,分析误差为0.01%,分析结果以PDB为标准。
3. 岩石学特征
钻井岩心、显微特征显示,研究区岩性有泥晶云岩、粉晶云岩、细-粗晶云岩、岩溶角砾白云岩、膏质云岩等,以泥晶白云岩和晶粒白云岩为主(图版Ⅰ-A~H)。其中,岩心观察发现泥晶白云岩呈暗灰色或深灰色,较致密,微观上具有典型的泥晶结构,含少量粘土矿物,孔隙度较小,储集性能差(图版Ⅰ-A)。含石膏假晶的泥晶云岩多为灰色、褐灰色,石膏假晶多呈不规则状,石膏极容易在浅部或深部溶蚀,形成溶蚀孔隙或垮塌孔隙,储集性能好(图版Ⅰ-E~F)。晶粒白云岩多呈灰色、灰白色,粉晶、细-粗晶结构,自形程度较高,孔缝充填的粗晶白云石,阴极发光下具环带结构,发光性强,多为橙黄色-橙红色,原岩为泥晶白云岩,发暗紫红色光,偏光镜下特征表明,其早期为亮晶白云石,后期发育暗色泥晶云岩环带。自生石英及充填在晶间孔中的石膏含量极少,晶间孔、晶间溶孔和膏模孔部分发育,储集性能较好(图版Ⅰ-B~D)。岩心及镜下薄片观察可以看出,研究区马五41段未见原生孔隙,次生孔隙发育,主要有晶间孔、晶间溶孔、膏核铸模孔及裂缝(图版Ⅰ-G~O)。其中,缝合线的出现(图版Ⅰ-N),表明研究区经历了埋藏成岩阶段。
4. 建设性埋藏成岩作用
4.1 埋藏白云石化作用
本区的白云岩大都是白云石化的结果[9]。大量研究表明,地层中的白云岩大部分形成于埋藏阶段[10]。埋藏白云石化与深部的孔隙有直接联系,其发生与分布对深部孔隙有直接影响。研究区埋藏白云石化作用广泛分布且具有明显的特征,孔缝中充填的自形、晶体粗大的白云石和铁白云石在阴极发光下具环带状结构,发橙黄色-橙红色光,说明其形成于埋藏还原环境(图版Ⅰ-K~L)。
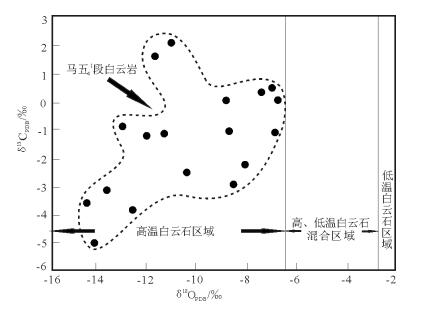
测得研究区白云岩样品的δ18OPDB值介于-14.5‰~-6.8‰之间,平均为-9.59‰;δ13OPDB值在-3.8‰~ 0.6‰范围内,平均为-1.38‰。其中,泥微晶白云岩的δ18O值为-7.1‰~-6.8‰,平均为-6.95‰;δ13C值为0.2‰~0.6‰,平均为0.4‰。晶粒白云岩的δ18O值为-14.5‰~-6.9‰,平均为-10.19‰;δ13C值为-3.8‰~0.3‰,平均为-1.81‰。岩溶充填物的δ18OPDB值介于-14.2‰~-8.69‰之间,平均为-11.41‰,δ13OPDB值在-5‰~-2.17‰范围内,平均为-1.21‰(表 1)。一般认为,海水C、O同位素的值制约了不同成因的白云岩C、O同位素值的变化[11],因此,将测得的样品C、O同位素值与奥陶纪海水C、O同位素值(δ18O=-6.6‰~-4.0‰,δ13C=-2.0‰~0.5‰)[12-14]进行对比,可以看出,研究区碳酸盐岩样品的O同位素值明显比奥陶纪海水O同位素值偏负(表 1),其原因可能是受表生期大气淡水林滤作用和埋藏期高温作用的影响[11, 15-16]。将本文样品的C、O同位素值与Allan等[11]提出的高、低温白云石进行比对(图 2)可知,晶粒白云岩样品的C、O值均在高温白云石区,即为埋藏白云岩区,说明研究区马五41段晶粒白云岩的白云石化作用是在埋藏(高温)环境中发生的。埋藏白云石化,即由深埋藏环境下粘土矿物转化和压溶作用释放含钙镁离子到孔隙溶液中,再加上随着埋藏加深,温度升高,使孔隙流体的镁钙比增加而引起的[17]。再者,研究区成岩流体是否受有机碳的影响可以用δ13C进行判定,若白云石化作用发生在油气生成时期,有机碳的加入能够使成岩流体中富集12C,最终导致δ13C值比奥陶纪海水值明显偏负[9],研究区马五41段白云岩的δ13C值比奥陶纪海水δ13C值偏负,说明研究区碳酸盐岩在成岩作用过程中受有机碳影响较大,表明白云石化发生在埋藏高温环境下。
表 1 高桥区块马五41段白云岩、岩溶充填物C、O同位素组成表Table 1. Carbon and oxygen isotope compositions of dolomite and void-fillings from ma541 in Gaoqiao area样号 深度/m 岩性 δ18O/‰ δ13C/‰ Z27 3211.3 铸模孔充填方解石 -8.8 0.2 S148 3349.7 孔洞充填方解石 -14.2 -5 S225 3461.1 充填白云石 -10.38 -2.64 S6-1 3584.8 充填方解石 -8.69 -2.89 S6-2 3586.4 充填方解石 -11.38 -0.13 S6-3 3592.4 充填方解石 -12.9 -0.82 S6-4 3576.9 结晶方解石 -11.76 1.75 S164 3284.3 溶缝充填方解石 -13.58 -3.11 S6-5 3585.2 溶缝结晶方解石 -10.95 2.17 S7 3333.4 含膏泥晶云岩 -7.1 0.6 S7 3360.3 含膏泥晶云岩 -6.8 0.2 S40 3286.1 泥粉晶白云岩 -7.4 0.3 S45 3299.3 细-粗晶白云岩 -8.7 -1 S51 3691.9 细-粗晶白云岩 -6.9 -1.2 S51 3705.3 细-粗晶白云岩 -8.2 -2.2 S358 3655.4 细-粗晶白云岩 -12 -1.3 S348 4032.4 细-粗晶白云岩 -12.6 -3.8 T14 3513.4 细-粗晶白云岩 -14.5 -3.6 ![]() 图 2 马五41段白云岩δ18O值与统计的高低温白云石[11]Figure 2. Theδ18O comparison diagram of dolomite from the Ma541 member with the statistics of the high and low temperature dolomites
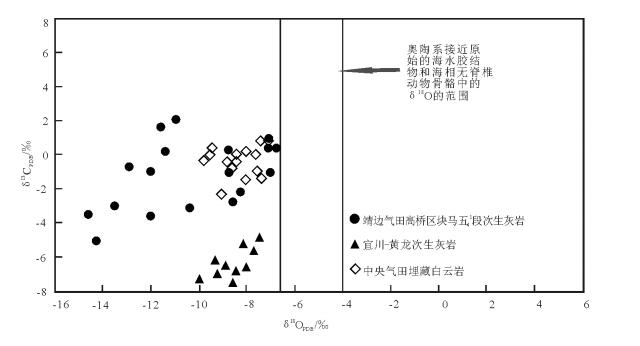
图 2 马五41段白云岩δ18O值与统计的高低温白云石[11]Figure 2. Theδ18O comparison diagram of dolomite from the Ma541 member with the statistics of the high and low temperature dolomites若白云石形成于埋藏高温环境的结论可靠,则生成的白云石经表生期大气淡水林滤去云化作用,其次生方解石的O同位素值会更偏负[18]。本文将研究区马五41段孔洞、缝中充填的次生方解石的O同位素与鄂尔多斯盆地中央气田马五段埋藏白云岩的C、O同位素值[19]及宜川—黄龙地区马五段风化壳中淡水改造的次生方解石O同位素值[20]进行比对(图 3)发现,研究区孔洞、缝中充填的次生方解石大部分比马五段埋藏白云岩及宜川—黄龙地区的淡水改造方解石的O同位素更加偏负,说明研究区白云石形成于埋藏高温环境,后期受大气淡水林滤使其更加偏负,证明了埋藏温度效应的存在。
由于Mg离子半径小于Ca离子半径,当白云石交代方解石时能使体积缩小13%,有利于白云石晶间孔的形成。白云石化作用后,白云石晶间孔内残留的灰质组分可以被深层的酸性流体溶解,其先前生成的白云石也易于被溶蚀,生成晶间溶孔,有利于提高岩石的孔隙度[21]。如果后期再经历与有机质成熟有关的埋藏溶解作用,亦能产生一些细小的晶间溶孔。因此,埋藏白云石化作用对研究区次生孔隙的形成是一个重要的建设性成岩作用类型。
4.2 埋藏溶解作用
从成岩环境的角度出发,笔者认为,埋藏溶解作用是在中-深埋藏环境下发生的一切溶解现象。前人认为,中-深埋藏环境下成岩流体不受大气淡水和海水的直接影响,且上覆压力在成岩作用过程中具有重要性,多以化学压实的出现为标志,其产物为一定数量的孔、洞、缝[16]。埋藏溶解作用被认为是建设性成岩作用之一。一般常温、常压条件下,白云岩溶解能力极其有限,随着埋藏深度的增加,温度、压力逐渐升高,相同性质的流体对白云岩的溶解能力大幅度上升,说明埋藏条件下相对的高温、高压条件有利于白云石溶解[22]。大多数碳酸盐岩原始孔隙小,孔隙度、渗透率低,而埋藏溶解能使次生孔隙发育,最终提高储层的孔隙度和渗透率,易于形成优质储层。
中-深埋藏环境下碳酸盐岩溶解作用的识别非常困难,其溶解所产生的孔隙多为非组构性溶蚀孔、洞、缝[16]。研究区马五41段储层中可见非组构性孔隙(图版Ⅰ-A, M-O),缝合线的存在表明,地层处于中-深埋藏条件。地下水-岩作用可极大地改变原始孔隙水性质。埋藏溶解直接控制孔隙的形成、分布和大小,埋藏期溶解作用对前期溶蚀孔隙进行了调整改造,具体表现为:埋藏白云石化作用后,白云石晶间孔内残留的灰质组分可以被酸性流体溶解,已经生成的白云石也可遭到溶解。研究区马五41段埋藏溶解形成溶蚀孔、洞和颗粒云岩中的细-粗晶方解石(白云石),可见晶粒边缘的溶蚀圆化现象。研究区埋藏溶解作用使裂缝与溶蚀孔洞相连通,此类组合的存在表明,研究区地层经历了埋藏溶解作用(图版Ⅰ-A)。
![]() A.泥晶云岩,×5,3655.5m,S358井;B.粉晶云岩,×5,3369.6m,S2井;C.细晶云岩,×5,3354.7m,S39井;D.细-粗晶云岩,×5,3853.6m,S352井;E.含膏泥晶云岩,×5,3369.2m,S7井;F.含膏泥晶云岩,×5,3370.6m,S148井;G.晶间孔,×5,3462m,S225井;H.晶间溶孔,3356.3m,×5,S39井;I.膏核铸模孔,×5,3211m,Z27井;J.阴极发光下铸模孔充填白云石,白云石发橙黄色,残余石膏不发光,×5,3211m,Z27井;K.孔缝充填粗晶白云石,×5,3461.1m,S225井;L.孔缝充填粗晶白云石,×5,3461.1m,S225井;M.早期构造缝被方解石充填,后期溶解形成溶蚀孔洞(0.3cm×1.2cm),3212.07m,T14井;N.成岩缝(缝合线),3853.8m,S352井;O.溶蚀缝,3852m,S352井
A.泥晶云岩,×5,3655.5m,S358井;B.粉晶云岩,×5,3369.6m,S2井;C.细晶云岩,×5,3354.7m,S39井;D.细-粗晶云岩,×5,3853.6m,S352井;E.含膏泥晶云岩,×5,3369.2m,S7井;F.含膏泥晶云岩,×5,3370.6m,S148井;G.晶间孔,×5,3462m,S225井;H.晶间溶孔,3356.3m,×5,S39井;I.膏核铸模孔,×5,3211m,Z27井;J.阴极发光下铸模孔充填白云石,白云石发橙黄色,残余石膏不发光,×5,3211m,Z27井;K.孔缝充填粗晶白云石,×5,3461.1m,S225井;L.孔缝充填粗晶白云石,×5,3461.1m,S225井;M.早期构造缝被方解石充填,后期溶解形成溶蚀孔洞(0.3cm×1.2cm),3212.07m,T14井;N.成岩缝(缝合线),3853.8m,S352井;O.溶蚀缝,3852m,S352井4.3 裂缝作用
裂缝有利于碳酸盐岩孔隙度的增加,虽然增加的量微乎其微,但是这些裂隙对增加孔隙的连通性有重要的意义,有利于油气的运移,提高岩石渗透率,最终改善岩石的储集和渗流性能。因此,裂缝对油气的物性具有十分重要的作用。国外的一些高产油气田也与裂缝相关,如卡拉布拉克-阿卡鲁奇油田、谢里油田、西伯利亚基底油田等裂隙性油田(表 2)。
表 2 世界不同地区油田的裂缝率[21]Table 2. Fracture percentage of the global oilfields油田名称 裂缝率平均值/% 卡拉布拉克-阿卡鲁奇油田 0.013 谢里油田 0.17 西伯利亚基底油田 0.3 研究区储层主要见构造缝(破裂缝)、成岩缝和溶蚀缝3种类型。镜下观察裂缝宽0.01~1mm,岩心观察到的裂缝宽度一般在1~5mm之间,最宽可达1~2cm。不同的成因必然产生不同形态特征的裂缝和裂隙,具体特征如下。
(1)构造缝
在埋藏环境(尤其达深埋)下,脆性的碳酸盐岩地质体时刻受到地压应力和构造应力的作用。应力的迅速增加(尤其在低围压条件下)和释放,必然导致脆性碳酸盐岩岩层的破裂,而岩体中所固有的流体通道(尽管有时十分狭窄),同样有助于在应力条件下破裂作用的产生。研究区内早期破裂作用形成的构造裂缝,大多数被方解石、白云石等充填,后又经历溶蚀,形成次生溶孔(图版Ⅰ-M)。
(2)成岩缝
研究区压溶缝、溶塌缝比较发育,主要是由于岩石脱水收缩或被化学压溶生成的。岩心观察发现缝合线比较多见(图版Ⅰ-N),另外还可见层间缝、溶蚀缝洞等。
(3)溶蚀缝
研究区溶蚀缝普遍发育(图版Ⅰ-O),主要是由于酸性地下水或含有机质的酸性压释水溶蚀岩石中的可溶性物质,或溶蚀先前的成岩裂缝、构造裂缝使其扩大,缝壁被溶蚀的凹凸不平,缝的宽窄也大小不一,外观上多呈弯曲或网状。普遍发育的溶蚀缝可与原本孤立的孔隙相连通。但溶蚀缝的发育程度受岩性、水介质等条件控制。
5. 地质控制因素分析
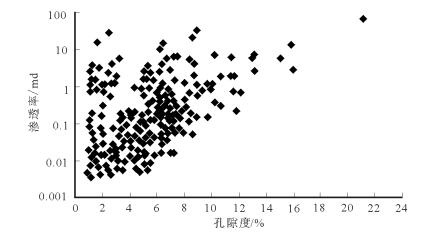
通过对研究区马五41储层段岩心孔隙度进行分析,发现468块样品的平均孔隙度为5.56%,分布在0.96%~21.2%之间,中值为5.5%;统计344块样品渗透率平均值为0.88×10-3μm2,分布在0.0043×10-3~ 14.3×10-3μm2之间,中值为0.13×10-3μm2。从马五41段孔隙度-渗透率相关图可以看出,靖边气田高桥区块马五41储层段的孔隙度-渗透率相关性较差(图 4),主要原因是原生孔隙基本丧失殆尽,但次生孔隙发育。进一步分析岩心孔-渗关系发现,由于裂缝作用造成实测孔隙度偏大,所以异常区大多数为正异常,主要分布在正常趋势的上方,即小孔隙、大渗透率,表明马五41储层具有裂隙-溶蚀孔双重孔隙结构特征,即当裂缝与原本存在的孔隙类型相配套时,则可形成良好的储集空间。
研究区马五41古地貌自剥蚀线向东依次为台地剥蚀区和岩溶斜坡-浅洼区。在古地貌的不同部位,淡水影响的深度、水动力条件及水的性质等均有差异[23],这种差异控制了埋藏白云石化作用、埋藏溶解作用及裂缝作用的进行。处于古构造高部位的岩溶台地,以地表水向下渗流为主,高地和邻近高地的平台渗流强度最强烈,同时该区处于含膏云坪相带,含丰富的易溶组分,因此,溶蚀型孔、洞、缝比较发育,虽多次被白云石和方解石充填,但充填晶粒为粉-细晶,形成的晶间孔及成岩缝提供了流体运移的通道,为后期的溶解作用创造了条件,最终形成溶蚀型孔-缝复合优质储层。斜坡-浅洼区主要为水平潜流,垂向溶蚀作用相对较弱,常常会形成顺层的溶缝、溶孔,对原岩为泥云岩的储层改造程度相对较弱。另外,由于石炭系—二叠系煤系地层上覆于马家沟组,孔隙水为酸性,对于埋藏溶解作用、白云石化作用及裂缝作用也有重要贡献。
6. 结论
(1)靖边气田高桥区块马五41段岩性以泥晶白云岩和晶粒白云岩为主,建设性埋藏成岩作用主要有埋藏白云石化作用、埋藏溶解作用和裂缝作用。
(2)靖边气田高桥区块马五41段晶粒白云岩O同位素明显偏负,低于奥陶纪海水的值,为埋藏白云石化作用形成,其C同位素值与奥陶纪海水C同位素值相比也偏负,在一定程度上受到有机碳的影响,表明地层经历埋藏高温环境,孔缝中充填的方解石的O同位素值更偏负,进一步显示出埋藏增温效应的影响;埋藏溶解作用促使非组构性的溶蚀孔、洞、缝的形成,且由于埋藏溶解作用,细-粗晶云岩晶粒边缘有溶蚀圆化的现象。研究区的裂缝主要有构造缝、成岩缝、溶蚀缝,这些裂缝后期被矿物充填或进一步溶蚀。
(3)埋藏白云石化作用促进了晶间孔的形成,溶解作用形成了溶蚀孔、洞、缝,而裂缝是在前二者基础上的叠置,作为渗滤通道,有效地连通了溶蚀孔洞;埋藏白云石化作用、埋藏溶解作用及裂缝作用三者相互叠加,使得研究区具有裂隙-溶蚀孔双重孔隙结构特征,提高了储层的储集性能。
致谢: 感谢青海油田公司勘探开发研究院的甘贵元和赵为永高级工程师在样品采集、测试过程中给予的帮助,感谢中国地质调查局油气资源调查中心包书景研究员在成文过程中给予的指导,对柴页1井钻探现场的各方工作人员一并表示感谢。 -
表 1 柴页1井等温吸附实验数据
Table 1 Data of isothermal adsorption in Chaiye-1 well
深度/m 吸附气量/(m3·t-1) Langmuir压力/MPa 1925.5 1.79 5.95 1937.5 1.25 2.70 1953.3 2.94 7.94 1954.6 0.68 3.06 1958.6 0.71 6.66 1962 2.07 7.56 1963 2.15 9.02 1965 0.93 2.32 1966.5 1.22 3.94 1967.3 1.07 3.70 1971.4 1.66 8.80 1975.5 1.61 9.02 1987.8 0.57 5.05 1997.82 1.08 9.16 2017.08 1.25 3.65 2018.05 0.84 7.03 2023.68 0.55 5.49 2092.9 1.43 8.83 2293.5 5.93 2.88 -
Chalmers G R L, Bustin R M, Lower Cretaceous gas shale of North-eastern British Columbia[J]. Bulletin of Canadian Petroleum Geology, 2008, 56(1):22-61. Chalmers G R L, Bustin R M, Lower Cretaceous gas shale of North-eastern British Columbia[J]. Bulletin of Canadian Petroleum Geology, 2008, 56(1):22-61.
李新景, 胡素云, 程克明.北美裂缝性页岩气勘探开发的启示[J].石油勘探与开发, 2007, 34(4):392-400. Nelson R A. Geologic Analysis of Naturally Fractured Reservoirs:Contributions in Petroleum Geology and Engineering[M]. Houston:Gulf Publishing Company, 1985:1-320. Nelson R A. Geologic Analysis of Naturally Fractured Reservoirs:Contributions in Petroleum Geology and Engineering[M]. Houston:Gulf Publishing Company, 1985:1-320.
Chalmers G R, Bustin R M, Power I M. Characterization of gas shale pore systems by porosimetry, pycnometry, surface area, and field emission scanning electron microscopy/transmission electron microscopy image analyses:Examples from the Barnett, Woodford, Haynesville, Marcellus, and Doig units[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(6):1099-1199. Chalmers G R, Bustin R M, Power I M. Characterization of gas shale pore systems by porosimetry, pycnometry, surface area, and field emission scanning electron microscopy/transmission electron microscopy image analyses:Examples from the Barnett, Woodford, Haynesville, Marcellus, and Doig units[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(6):1099-1199.
Ambrose R J, Hartman R C, Diaz-Campos M, et al. New porescale considerations for shale gas in place calculations[C]//SPE 131772,Unconventional Gas Conf., Fed. 23-25, Pittsburgh Pennsylvania, USA, 2010. Ambrose R J, Hartman R C, Diaz-Campos M, et al. New porescale considerations for shale gas in place calculations[C]//SPE 131772, Unconventional Gas Conf., Fed. 23-25, Pittsburgh Pennsylvania, USA, 2010.
王玉满, 董大忠, 杨桦, 等.川南下志留统龙马溪组页岩储集空间定量表征[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2014, 44(6):1348-1356. 王杰, 秦建中, 饶丹, 等.不同类型页岩富集烃气能力模拟实验及微观结构特征研究[J].天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(04):652-658. Loucks R G, Reed R M, Ruppel S C, et al.Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrixrelated mudrock pores[J].AAPG Bulletin,2012,96(6):1071-1098. Loucks R G, Reed R M, Ruppel S C, et al.Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrixrelated mudrock pores[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(6):1071-1098.
大忠, 邹才能, 李建忠, 等.页岩气资源潜力与勘探开发前景[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(2/3):324-336 张金川, 边瑞康, 荆铁亚, 等.页岩气理论研究的基础意义[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(2/3):318-323. 岳鹏升, 王平, 郁东良, 等.柴达木盆地北缘下中侏罗统沉积特征及其石油地质意义[J].海洋地质前沿, 2011, 27(11):38-44. 汪立群, 罗晓容.柴达木盆地北缘油气成藏与勘探实践[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2012:23-41. Jarvie D M, Hill R J, Ruble T E, et al. Unconventional shale gas system:the mississippian barnett shale of north-central Texas as onemodel for thermogenic shale gas assessment[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2007,91(4):475-499. Jarvie D M, Hill R J, Ruble T E, et al. Unconventional shale gas system:the mississippian barnett shale of north-central Texas as onemodel for thermogenic shale gas assessment[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2007, 91(4):475-499.
Bowker K A. Barnett shalegasproduction, FortWorth Basin:issue-sanddiscussion[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2007, 91(4):523-533. Bowker K A. Barnett shalegasproduction, FortWorth Basin:issue-sanddiscussion[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2007, 91(4):523-533.
Chalmsrs G R, Bustin R M. Lower Cretaceousgas shales of North-eastern British Columbia:geological controls on gas capacity and re-gional evaluation of apotential resource[C]//AAPG Annual Con-vention.San Antonio,Texas:AAPG,2008 Chalmsrs G R, Bustin R M. Lower Cretaceousgas shales of North-eastern British Columbia:geological controls on gas capacity and re-gional evaluation of apotential resource[C]//AAPG Annual Con-vention.San Antonio, Texas:AAPG, 2008
陈丽华, 缪昕, 于众.扫描电镜在地质上的应用[M].北京:科学出版社, 1986:45-61. 罗小平, 吴飘, 赵建红, 等.富有机质泥页岩有机质孔隙研究进展[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 42(1):50-59. Karen E H, Horst Z, Agnes G R, et al. Diagenesis, porosity evolution, and petroleum emplacement in tight gas reservoirs, Taranaki Basin, New Zealand[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2007, 77(12):1003-1025. Karen E H, Horst Z, Agnes G R, et al. Diagenesis, porosity evolution, and petroleum emplacement in tight gas reservoirs, Taranaki Basin, New Zealand[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2007, 77(12):1003-1025.
Srevor T M, Harris N B, Elliott W C, et al. Diagenesis of a tight gassand reservoir:Upper Cretaceous Mesaverde Group, Piceance Basin, Colorado[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 40(4):48-68. Srevor T M, Harris N B, Elliott W C, et al. Diagenesis of a tight gassand reservoir:Upper Cretaceous Mesaverde Group, Piceance Basin, Colorado[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 40(4):48-68.
Curtis J B. Fractured shale-gas system[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2002, 86(11):1921-1938. Curtis J B. Fractured shale-gas system[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2002, 86(11):1921-1938.
聂海宽, 张金川.页岩气储层类型和特征研究[J].石油实验地质, 2011, 33(3):219-235. 吴元燕, 吴胜和, 蔡正其.油矿地质学[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2005. Loucks R G, Reed R M, Ruppel S C,et al. Spectrumof pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrixrelated mudrockpores[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2012,96(6):1071-1098. Loucks R G, Reed R M, Ruppel S C, et al. Spectrumof pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrixrelated mudrockpores[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(6):1071-1098.
Loucks R G, Reed R M, Ruppel S C, et al. Morphology, genesis, and distribution of nanometerscalepores in siliceous mudstones of the Mississippian Barnett shale[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2009,79:848-861. Loucks R G, Reed R M, Ruppel S C, et al. Morphology, genesis, and distribution of nanometerscalepores in siliceous mudstones of the Mississippian Barnett shale[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2009, 79:848-861.
王道富, 王玉满, 董大忠, 等.川南下寒武统筇竹寺组页岩储集空间定量表征[J].天然气工业, 2013, 33(07):1-10. 陈尚斌, 夏筱红, 秦勇, 等.川南富集区龙马溪组页岩气储层孔隙结构分类[J].煤炭学报, 2013, 38(05):760-765. 黄振凯, 陈建平, 薛海涛, 等.松辽盆地白垩系青山口组泥页岩孔隙结构特征[J].石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(1):58-65. Bustin R M. Gas shale tapped for Big Play[J]. AAPG, 2005, 26(2):5-7. Bustin R M. Gas shale tapped for Big Play[J]. AAPG, 2005, 26(2):5-7.
张雪芬, 陆现彩, 张林晔, 等.页岩气的赋存形式研究及其石油地质意义[J].地球科学进展, 2010, 25(6):597-602. Curtis J B. Fractured shale-gas systems[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2002, 86(11):1921-1938. Curtis J B. Fractured shale-gas systems[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2002, 86(11):1921-1938.
Lu X C, Li F C, Watson A T. Adsorption measurements in Devonian shales[J]. Fuel, 1995, 74:599-603. Lu X C, Li F C, Watson A T. Adsorption measurements in Devonian shales[J]. Fuel, 1995, 74:599-603.
徐国盛, 张震, 罗小平, 等.湘中和湘东南坳陷上古生界泥页岩含气性及其影响因素[J].成都理工大学学报, 2013, 40(5):577-587. Curtis J B. Fractured Shale-gas Systems[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2002, 86(11):1921-1938. Curtis J B. Fractured Shale-gas Systems[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2002, 86(11):1921-1938.



 下载:
下载: