Geological origin of Jinggu earthquake swarm in 2014 in southwest Yunnan: A response to propagation process of the Chafang-Puwen fault zone
-
摘要:
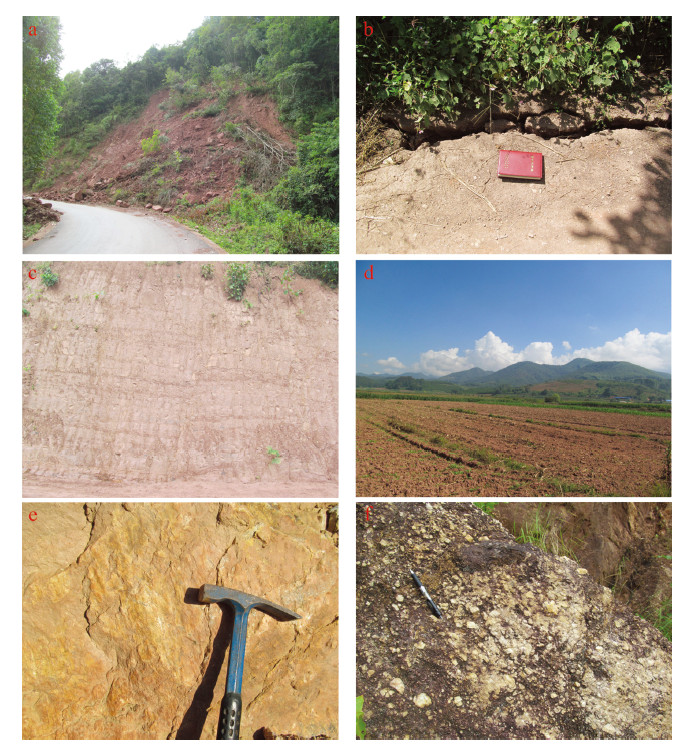
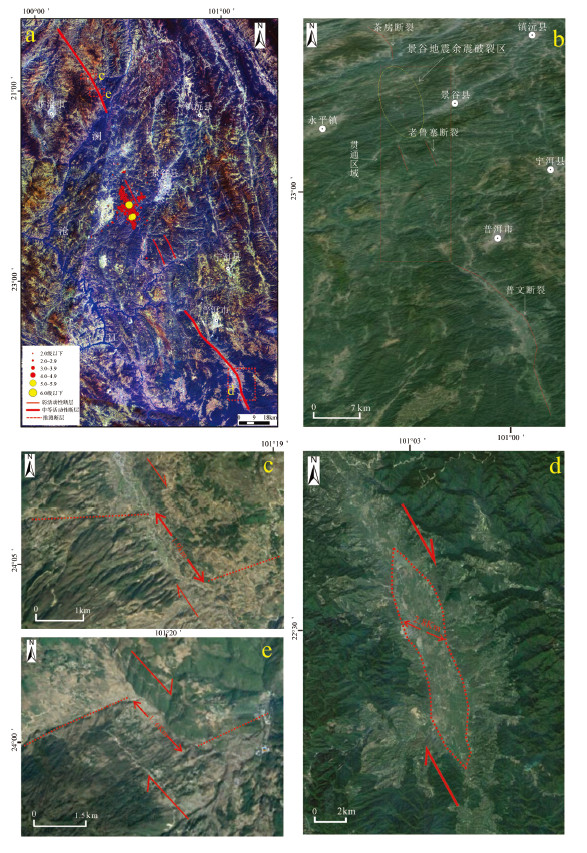
2014年10-12月期间, 云南景谷接连发生了Ms6.6、Ms5.8、Ms5.9三次中-强地震。为确定地震的地质构造成因, 在地表调查的基础上, 综合该区的地质构造情况、烈度与余震分布、震源机制解等资料, 确定此次震群活动的宏观震中位于永平盆地东南侧山地, 发震断层为地质与地貌表现不显著的NW向右旋走滑断层。此次震群活动及余震迁移过程指示, 由于断层斜接部位岩桥的临时阻碍, Ms6.6地震破裂在向南东扩展过程中发生短暂停滞, 突破障碍后进一步引发了Ms5.8和Ms5.9地震, 这符合震源破裂沿NW向发震断裂分段破裂的行为。区域活动断裂的遥感解译结果发现, 发震断层位置恰好处于NW向右旋走滑的茶房断裂与普文断裂之间, 区域上属于该断裂带的不连贯部位, 指示此次中-强震群活动应该是茶房-普文断裂带贯通过程的构造活动表现。结合思茅地块的历史地震资料发现, 思茅地块地震活动多以小于等于6.8级为主, 发震构造多为NW向断裂。指示在现今构造应力场作用下, 该区NW向断裂的活动性相对NE向断裂更加显著, 属于该区主要控震构造, 应在今后的地震地质工作中给予更多关注。
Abstract:Yongping Town in Jinggu of Yunnan Province experienced three times of strong earthquakes from October to December in 2014, which were Ms6.6, Ms5.8, Ms5.9 respectively. In order to determine the cause of this earthquake swarm in the geological structure area, the authors, based on the investigation at the surface in combination with the geological structure, intensity and the aftershock distribution and focal mechanism solution, have reached the conclusion that the macro epicenter of the earthquake swarm activity was located in the mountain area on the southeast side of Yongping basin. The seismogenic fault was the NW-trending dextral strike slip fault which had no obvious geological and geomorphological features. The southeastward migration phenomenon of the aftershocks indicates, due to the temporary block of the oblique connecting position of the rock bridge fault, there was a brief stagnation when Ms6.6 earthquake rupture propagation was spread southeastward. Nevertheless, on December 6th, after breaking through barriers, the earthquake rupture further triggered the Ms5.8 and Ms5.9 earthquakes. This shows that the earthquake swarm activity accorded with the behavior of focal rupture along the NW seismogenic fault segment rupture. The remote sensing interpretation of regional active faults indicates that the seismogenic fault lay just between Chafang NW-trending right strike-slip faults and Puwen NW-trending right strike-slip faults. The area belongs to the incoherent area of Chafang-Puwen fault zone. The authors point out that the strong earthquake swarm activities should be tectonic activities during the coalescence of Chafang-Puwen fault in the upper crust. Combined with the historical seismic data of the Simao block, it is held that the grades of all the seismic activities were less than or equal to 6.8, and the seismogenic structures were mostly NW-trending faults. These phenomena indicate that, in the present tectonic stress field, the NW-trending fault activity is more obvious relative to the NE-trending fault and belongs to the main earth-quake controlling structure, which deserves much attention in furture seismic geological work.
-
致谢: 特别感谢司机黄争鸣在野外调查过程中的翻译工作,以及首都师范大学黄小巾硕士、中国地质大学(北京)田婷婷硕士在文章撰写与图件绘制过程中给予的相关帮助,在此表示衷心的感谢。
-
图 2 景谷Ms6.6地震烈度分布及思茅地块主要活动断裂和地震分布
F1—把边江断裂;F2—无量山断裂东支(磨黑断裂);F3—无量山断裂中支(普洱断裂);F4-1—无量山断裂西支(普文断裂);F4-2—茶房断裂;F5-1—益智-思茅港断裂;F5-2—博尚断裂;F6—麻栗河断裂;F7—平村-大文断裂;F8—南汀河断裂;F9—澜沧-景洪断裂
Figure 2. Seismic intensity distribution of Jinggu Ms6.6 earthquake and main active faults and earthquake events on the southern margin of the Simao block
表 1 不同地震台网记录的地震参数
Table 1 Seismic parameters recorded by different seismic networks
日期 时间 纬度/° 经度/° 深度4m 震级 数据来源 2014-10-7 21:49:39.5 23.4N 100.5E 5 6.6 CENC 2014-10-7 21:49:39.0 23.38N 100.47 E 8.5 Mw6.1 NEIC 2014-12-6 02:43:44.0 23.3N 100.5E 9 5.8 CENC 2014-12-6 02:43:46.4 23.32N 100.47E 11 Mw5.5 NEIC 2014-12-6 18:20:00.0 23.3N 100.5E 10 5.9 CENC 2014-12-6 18:20:02.0 23.38N 100.52E 10 Mw5.5 NEIC CENC 为中国地震台网中心http://www.csndmc.ac.cn/" newweb/index.jsp;NEIC 为美国国家地震信息中心http://earthquake.usgs.gov/contactus/golden/neic.php 表 2 2014年云南景谷地震的震源机制解
Table 2 Focal mechanism solutions of the 2014 Jinggu earthquake
编号 震级
/Ms节面I 节面Ⅱ P轴
方向资料
来源走向 倾角 滑动角 走向 倾角 滑动角 1 6.6 151° 90° -178° 61° 88° 0° 16° USGS 2 6.6 150° 61° 177° 241° 87° 29° 8° CENC 3 5.8 165° 87° -168° 74° 78° -3° 30° USGS 4 5.8 162° 68° 175° 255° 85° 22° 27° 滇西试验场 5 5.9 161° 81° -174° 70° 84° -9° 25° USGS 注:USGS为美国地质调查局http://www.usgs.gov;CENC为中国地震台网中心http://www.csndmc.ac.cn/newweb/ index.jsp -
虢顺民, 汪洋, 计风桔.云南思茅-普洱地区中强震群发生的构造机制[J].地震研究, 1999, 22(2):105-115. 樊耀新.思普地区地震活动和地质构造的相关性研究[J].地震研究, 1998, 21(1):65-70. 皇甫岗.云南地震活动性研究[D].合肥:中国科学技术大学博士学位论文, 2009. Tapponnier P, Peltzer G, Le Dain A Y, et al. Propagating extrusion tectonics in Asia:New insights from simple experiments with plasticine[J]. Geology, 1982, 10:611-616. Tapponnier P, Peltzer G, Le Dain A Y, et al. Propagating extrusion tectonics in Asia:New insights from simple experiments with plasticine[J]. Geology, 1982, 10:611-616.
毛玉平, 韩新民, 谷一山, 等.云南地区强震(M≥6)研究[M].昆明:云南科技出版社, 2003:1-15. Molnar P, Tapponnier P. Cenozoic tectonics of Asia:effects of a continental collision[J]. Science, 1975, 280:419-426. Molnar P, Tapponnier P. Cenozoic tectonics of Asia:effects of a continental collision[J]. Science, 1975, 280:419-426.
Tapponnier P, Molnar P. Slip-line field theory and large scale continental tectonic[J]. Nature, 1976, 264(25):319-324. Tapponnier P, Molnar P. Slip-line field theory and large scale continental tectonic[J]. Nature, 1976, 264(25):319-324.
Eengland P C, McKenzie D P. A thin viscous sheet model for continental deformation[J]. Geophys. J. R. Astron. Soc., 1982, 70:295-321. Eengland P C, McKenzie D P. A thin viscous sheet model for continental deformation[J]. Geophys. J. R. Astron. Soc., 1982, 70:295-321.
Dewey J F, Stephen C, Walter C P. Tectonic evolution of the India/Eurasia Collision zone[J]. Eclogae. Geol. Helv., 1989, 82(3):717-734. Dewey J F, Stephen C, Walter C P. Tectonic evolution of the India/Eurasia Collision zone[J]. Eclogae. Geol. Helv., 1989, 82(3):717-734.
马宗晋, 张家声, 汪一鹏.青藏高原三维变形运动学的时段划分和新构造分区[J].地质学报, 1998, 56(3):211-227. 邓起东, 张裕明, 许桂林.中国构造应力场特征及其与板块运动的关系[J].地震地质, 1979, 1(1):11-22. 张培震, 王琪, 马宗晋.青藏高原现今构造变形特征与GPS速度场[J].地学前缘, 2002, 9(2):442-450. 季建清, 钟大赉, 张连生.滇西南新生代走滑断裂运动学、年代及对青藏高原东南部块体运动的意义[J].地质科学, 2000, 35(3):336-349. 谢富仁, 苏刚, 崔效锋, 等.滇西南地区现代构造应力场分析[J].地震学报, 2001, 23(1):17-23. 钱晓东, 秦嘉政, 刘丽芳.云南地区现代构造应力场研究[J].地震地质, 2011, 33(1):91-106. 皇甫岗, 秦嘉政, 李忠华, 等.云南地震类型分区研究[J].地震学报, 2007, 29(2):142-150. 谢英情, 李岩峰, 张建国, 等. 2007年宁洱6.4级地震发震构造分析[J].地震研究, 2007, 30(4):350-358. 徐锡伟, 闻学泽, 郑荣章, 等.川滇地区活动块体最新构造变动样式及其动力来源[J].中国科学(D辑), 2003, 33(4):151-162. 张海峰, 仝亚博, 王恒, 等.印支地块思茅地区早白垩世古地磁结果及其构造意义[J].地质学报, 2012, 86(6):923-939. 仝亚博, 杨振宇, 王恒, 等.中国西南思茅地体中部白垩纪古地磁结果及陆内地壳变形特征[J].地球物理学报, 2014, 57(1):1-20. 吴中海, 龙长兴, 范桃园, 等.青藏高原东南缘弧形旋钮活动构造体系及其动力学特征与机制[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(1):1-31. 吴中海, 赵根模, 龙长兴, 等.青藏高原东南缘现今大震活动特征及其趋势:活动构造体系角度的初步分析结果[J].地质学报, 2014, 88(8):1401-1416. 吴中海, 赵希涛, 范桃园, 等.泛亚铁路滇西大理至瑞丽沿线主要活动断裂与地震地质特征[J].地质通报, 2012, 31(2/3):191-217. 刘凤山, 吴中海, 张岳桥, 等.青藏高原东缘新构造与活动构造研究新进展及展望[J].地质通报, 2014, 33(4):403-418. 范桃园, 孙玉军, 吴中海.青藏高原东缘旋转变形机制的数值模拟分析[J].地质通报, 2014, 33(4):497-502. 云南省地质矿产局.云南省区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 1990:613-630. 李克昌, 赵维城, 侯学英, 等.从思茅、普洱地震探讨断块内部地震地质特征[J].地震研究, 1980, 3(1):38-44. 王多义吴征朱永明.景谷盆地遥感地质解译及原盆地恢复[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 30(6):597-602. 刘丽芳, 苏有锦, 付虹, 等.云南省Ms≥6.0地震序列的基本特征[J].内陆地震, 2002, 16(1):62-68. 吴中海, 周春景, 冯卉, 等.青海玉树地区活动断裂与地震[J].地质通报, 2014, 33(4):419-469. 黄小龙, 吴中海, 蒋瑶, 等. 2013年3月3日云南大理洱源MS5.5级地震烈度分布及发震构造[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(1):135-145. 黄小龙, 吴中海, 赵小艳, 等. 2014年5月云南盈江Ms5.6, Ms6.1地震发震构造分析[J].地球学报, 2015, 36(6):761-770. 周春景, 吴中海, 尼玛次仁, 等.青海玉树Ms7.1级地震同震地表破裂构造[J].地质通报, 2014, 33(4):551-566. 蒋瑶, 吴中海, 刘艳辉, 等.青海玉树活动断裂带的多期古地震滑坡及其年龄[J].地质通报, 2014, 33(4):503-516. 郑文俊, 郭华, 袁道阳, 等.遥感影像信息在活动断裂研究中的应用[J].高原地震, 2002, 14:15-21. 邹谨敞, 邵顺妹.活动断裂的遥感影像研究[J].环境遥感, 1995, 3:183-187. 古斌, 松田时彦.活断层研究[M].北京.地震出版社, 1983. 杨春景, 李有利.活动构造与地貌学[M].北京:北京大学出版社, 2011. 黄小巾, 吴中海, 李家存.滇西北裂陷带的构造地貌特征与第四纪构造活动性[J].地质通报, 2014, 33(4):578-593. 马丹, 吴中海, 李家存, 等.川西理塘断裂带的空间展布与第四纪左旋走滑活动的遥感影像标志[J].地质学报, 2014, 88(8):1417-1435. 李跃华, 吴中海, 叶培盛, 等.玉树断裂带左旋走滑活动标志及其几何学与运动学特征[J].地质通报, 2013, 32(9):1410-1422. Lacassin R, Replumaz A, Leloup P H. Hairpin river loops and slipsense inversion on southeast Asian strike-slip faults[J]. Geology, 1998, 26(8):703-706. Lacassin R, Replumaz A, Leloup P H. Hairpin river loops and slipsense inversion on southeast Asian strike-slip faults[J]. Geology, 1998, 26(8):703-706.
Schoenbohm L M, Burchfiel B C, Chen L, et al. Miocene to pres-ent activity along the Red River fault, China, in the contest of con-tinental extrusion, upper-crustal rotation, and lower-crustal flow[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2006, 118(5/6):672-688. Schoenbohm L M, Burchfiel B C, Chen L, et al. Miocene to pres-ent activity along the Red River fault, China, in the contest of con-tinental extrusion, upper-crustal rotation, and lower-crustal flow[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2006, 118(5/6):672-688.
Replumaz A, Lacassin R, Tapponnier P, et al. Large river offsets and Plio-Quaternary dextral strike-slip rate on the Red River fault(Yunnan, China)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Researth, 2001, 106(B1):819-836. Replumaz A, Lacassin R, Tapponnier P, et al. Large river offsets and Plio-Quaternary dextral strike-slip rate on the Red River fault(Yunnan, China)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Researth, 2001, 106(B1):819-836.
张宗祜.川滇南北构造带中段晚新生代地质研究[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 1994:19-160. 王铠元, 孙克祥, 段彦学.云南新构造运动的几个问题[J].水文地质工程地质, 1982, (3):25-27. 皇甫岗, 苏有锦, 石绍先. 20世纪云南地区地震活动研究[J].地震研究, 2000, 23(1):1-9. 苏有锦. 2003年7月21日、10月16日云南大姚6.2级和6.1级地震预测预报回顾与讨论[J].国际地震动态, 2004, (1):18-21. 付正新, 非明伦, 施伟华等.大姚6.1级地震烈度与震害分析[J].地震研究, 2005, 28(2):197-201. 非明伦, 周光全, 施伟华, 等.大姚6.2级地震的烈度与震害分析[J].地震研究, 2004, 27(增刊):70-74. 包丰, 倪四道, 汪贞杰, 等. 2003年云南大姚两次强震破裂区重叠程度的研究[J].地震学报, 2011, 33(3):279-292. 华卫, 刘杰, 郑斯华, 等. 2003年云南大姚6.2、6.1级地震序列特征分析及地震触发研究[J].中国地震, 2006, 22(1):10-23. 毛玉平, 万登堡. 2000年云南姚安6.5级地震[M].昆明:云南科技出版社, 2001:189-237. 张建国, 刘丽芳, 李西, 等.姚安、大姚中强震区地震构造初析[J].地震地质, 2009, 31(3):536-543. 虢顺民, 徐锡伟, 向宏发, 等.龙陵-澜沧新生断裂带地震破裂分段与地震预测研究[J].地震地质, 2002, 24(2):133-144. 虢顺民, 向宏发, 徐锡伟, 等.滇西南龙陵-澜沧第四纪新生断裂带特征和形成机制研究[J].地震地质, 2000, 22(3):277-284. 虢顺民, 向宏发, 周瑞琦, 等.滇西南龙陵-澜沧断裂带——大陆地壳上一条新生的破裂带[J].科学通报, 1999, 44(19):2118-2121. 向宏发, 张晚霞, 虢顺民, 等.新生地震破裂带的识别类型划分及其地震地质意义[J].中国地震, 1999, 15(3):257-267. 徐杰.新生地震构造带的研究——地震地质研究新开拓的一项工作[J].华南地震, 2011, 31(4):23-28. 徐杰, 王若柏, 王春华, 等.我国华北和西南地区两条新生地震构造带的初步研究[J].西北地震学报, 1998, 20(2):1-7.




 下载:
下载: