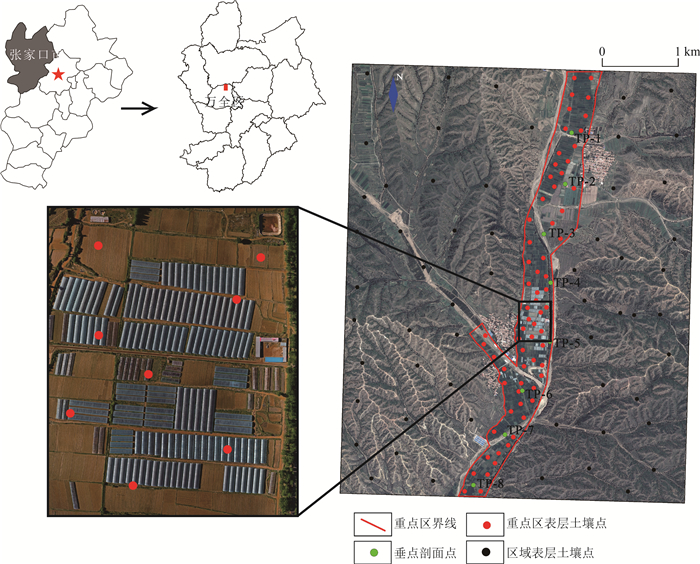
Ecological stoichiometry and spatial variation characteristics of soil nutrients in a cultivation area of Zhangjiakou City, Hebei Province
-
摘要:
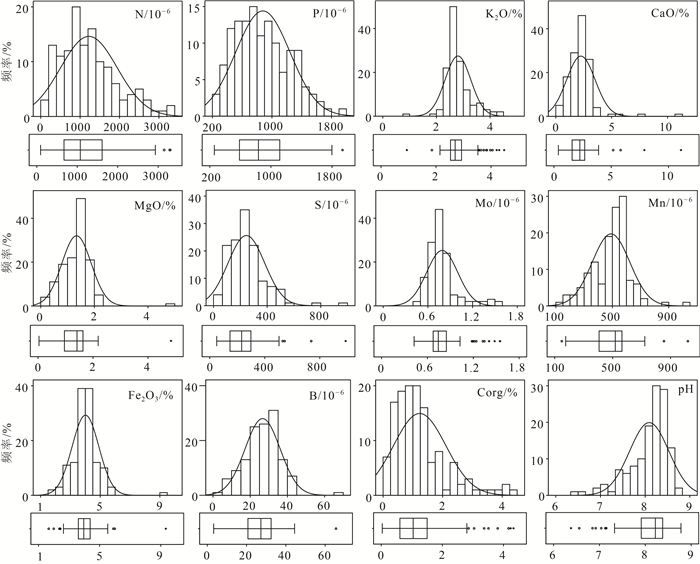
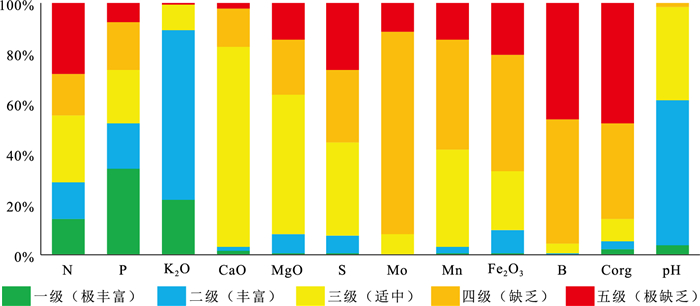
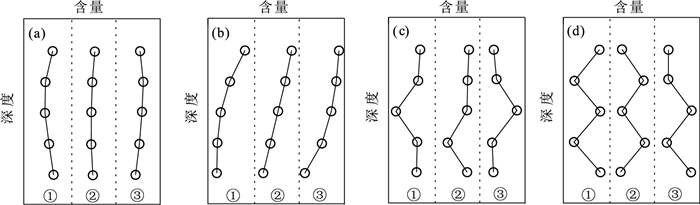
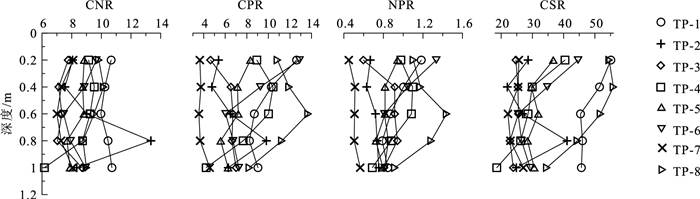
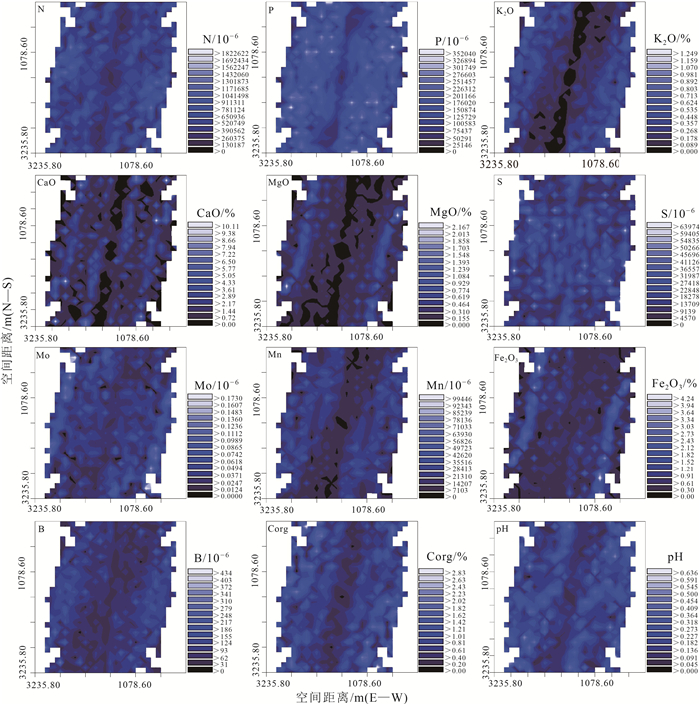
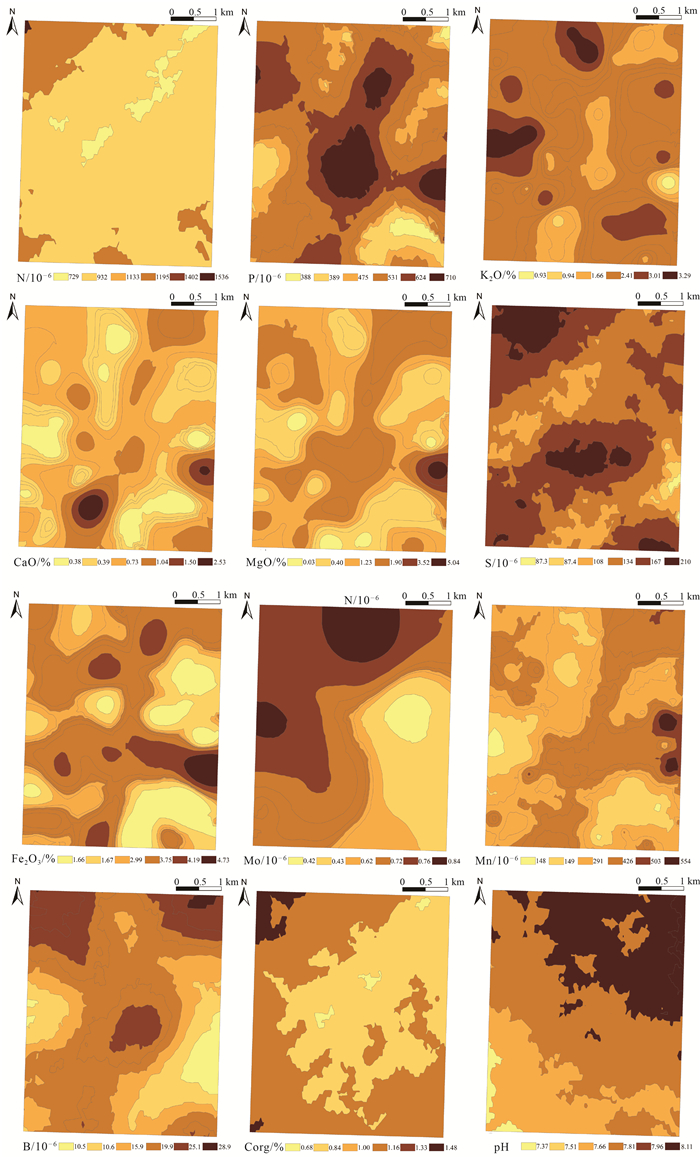
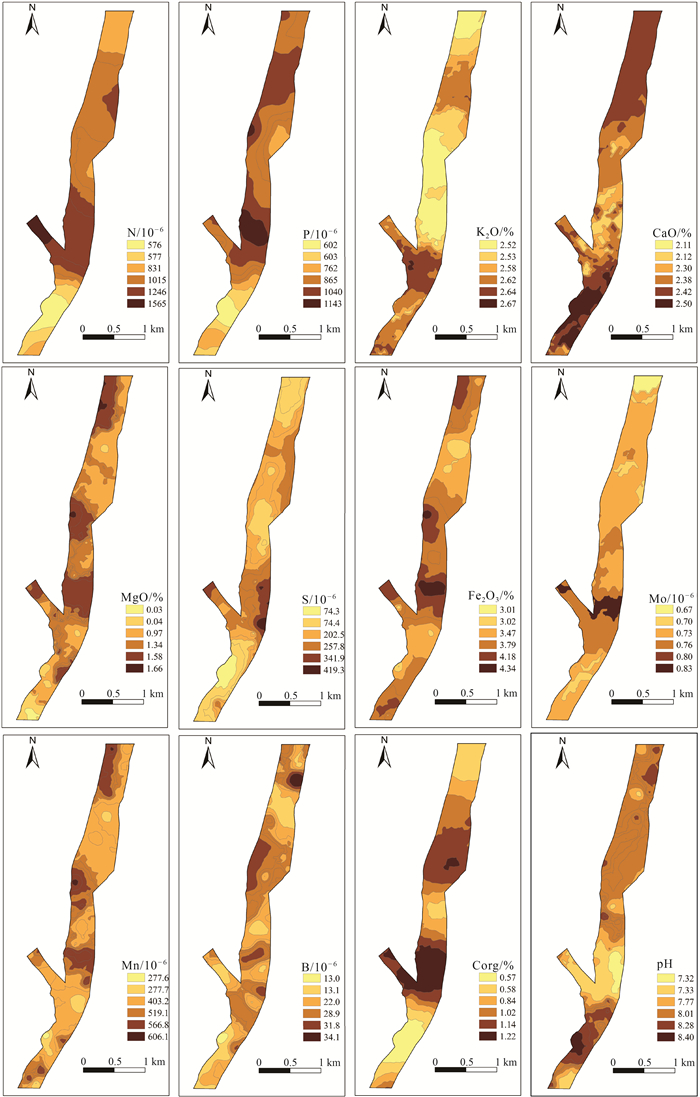
应用地统计学、生态化学计量学和GIS技术,对河北省张家口市万全区某种植区的表层土壤N、P、K2O、CaO、MgO、S、Mo、Mn、Fe2O3、B、Corg、pH等参数含量特征、趋势分布、空间变异性及生源要素的分布特征进行研究。结果表明,研究区Corg属于较强分异型,变异系数为71.54%,其余元素均属于弱或均匀分异型。N、P、K2O和pH整体呈现极丰富和丰富等级,S、Mo、Mn、Fe2O3、B和Corg则处于缺乏和极缺乏等级。通过不同趋势阶数中误差的比较叠加块金系数分析,初步确定研究区可分为3种预测类型,即无趋势预测、一阶趋势预测和二阶趋势预测。K2O、CaO、MgO、S、Mn和Corg主要受结构型影响,N、P、Mo、Fe2O3、B和pH主要受结构型和随机性混合影响,其中S和Mo的变异函数表面具有较弱的方向性。生态化学计量学表明,生源要素平均含量K2O>Corg>N>P>S,土壤CNR和NPR主要受控于土壤Corg和N,垂向上表现为以表聚型和平稳型分布为主,以突变型和锯齿型分布为辅。最后通过普通克里格插值清晰可见区域范围内N、P、K2O、CaO、MgO、Mn均表现为由东北部至西南部流域范围内明显异常区,主要受控于河流迁移搬运作用,重点区中N和P属于梯型,K2O、CaO和pH属于内凹型,S和Mo属于外凸型,MgO、Fe2O3、Mn、B和Corg属于跳跃型。
Abstract:By applying geostatistics, ecological chemometrics and GIS techniques, the characteristics of the content, trend distribution, spatial variability and distribution of biogenic elements of N, P, K2O, CaO, MgO, S, Mo, Mn, Fe2O3, B, Corg, pH and other parameters in the surface soil of a planting area in Wanquan District, Zhangjiakou City, Hebei Province were studied.The results showed that Corg belonged to the strongly differentiated variation type with a coefficient of variation of 71.54%, while the rest of the elements belonged to the weak or uniform differentiation type.N, P, K2O and pH were in the very abundant and abundant classes, while S, Mo, Mn, Fe2O3, B and Corg were in the deficient and extremely deficient classes.By comparing the errors in different trend orders superimposed on the block gold coefficient analysis, it was tentatively determined that the study area could be classified into three prediction types, namely, no trend prediction, first-order trend prediction and second-order trend prediction, with K2O, CaO, MgO, S, Mn and Corg mainly influenced by the structural type, and N, P, Mo, Fe2O3, B and pH mainly influenced by a mixture of structural and stochastic properties, among which S and Mo variance functions surface with weak directionality.Ecological chemometrics showed that the average content of biogenic elements K2O > Corg > N > P > S.Soil CNR and NPR were mainly controlled by soil Corg and N, and the vertical direction showed a predominantly epistatic and smooth distribution, supplemented by mutational and sawtooth distribution.Finally, ordinary kriging interpolation clearly shows that N, P, K2O, CaO, MgO, and Mn all show obvious anomalous areas in the watershed range from northeast to southwest, mainly controlled by river migration and transport, with N and P in the key area being of the trapezoidal type, K2O, CaO, and pH of the inner concave type, S and Mo of the outer convex type, and MgO, Fe2O3, Mn, B, and Corg belong to the jump type.
-
浅覆盖区覆盖层的地质调查和研究与深部隐伏基岩的物性、构造特征研究密不可分。一方面,深部基岩面构造特征制约了上覆盖层的沉积演化,沉积层中的同沉积构造变形可进一步细化区域构造演化史,另一方面,沉积物也可以通过侵蚀、搬运、负载等方式对基岩的构造特征进行改造,二者是一对耦合关系。常规的地表地质调查很难获得隐伏基岩及断裂的特征信息,故本次研究采用地质钻探与重力异常相结合的方法进行重力异常钻孔约束反演,重力位场数据横向分辨能力较高,地质钻孔数据可提供岩石物性特征并进行深度约束,因此,可有效减少重力异常数据地质解释的多解性,构建较准确的基岩地质模型。研究区郯庐断裂带泗洪地区距离曾发生8.5级地震的郯城仅130余千米,由于该区域被第四纪—新近纪沉积物广为覆盖,前人对其深部构造特征的研究较薄弱,故本次研究结合区域第四纪—新近纪覆盖层沉积结构,探讨断裂的空间展布特征,具有一定科学意义。
1. 区域地质及基岩物性特征
1.1 区域地质背景
郯庐断裂带是贯穿中国东部大陆边缘的一条NNE向走滑剪切断裂带。研究表明,这条断裂在晚新生代仍然活动,是一条重要的地震活动带,其分段特征明显,从南到北可分为苏皖段、山东段及东北段3段[1-2], 其中苏皖段途经地区人口稠密、经济发达,受到国内外学者的广泛关注。中生代以来,郯庐断裂带经历了华南-华北板块碰撞、太平洋板块俯冲,以及白垩纪、古近纪强烈的地幔热作用等一系列重大地质事件,构造演化复杂[3-5]。第四纪以来,郯庐断裂带依然活动频繁,发生过多次中强级以上地震,如1668年莒县-郯城8.5级地震,1888年渤海湾7.5级地震,1969年渤海7.4级地震,1975年海城7.3级地震等,其中1668年莒县-郯城8.5级地震是中国东部有记录的最强烈的地震。郯庐断裂带泗洪地区位于郯城以南约130 km,归属郯庐断裂带苏皖段的中北部,位于华北板块、苏鲁造山带及扬子板块的结合部位(图 1-a),该地区被第四纪—新近纪沉积物大面积覆盖(图 1-b),基岩及断裂以隐伏断裂为主,仅在重岗山、朱山附近有基岩出露。前人认为,郯庐断裂带在泗洪地区主要由山左口-泗洪断裂(F1)、新沂-新店断裂(F2)、墨河-凌城断裂(F3)、王集-朱山断裂(F4)和桥北镇-宿迁断裂(F5)5条分支断裂延伸组成,宽20~30 km,其中F2、F3和F4分别由山东段的安丘-莒县断裂、沂水-汤头断裂和鄌郚-葛沟断裂延续而来[1, 4, 6-7]。该区域性断裂带西靠华北板块,东临苏鲁造山带,同时受到邻近扬子板块挤压、东侧太平洋板块俯冲及远端喜马拉雅抬升的共同作用,构造演化极其复杂,前人将郯庐断裂带的构造演化总结为4个阶段,分别为早中生代左旋转换走滑,晚侏罗世—早白垩世早期左行平移,早白垩世—古近纪大规模伸展正断及新近纪以来挤压逆冲兼具右行走滑[8-18]。不同区段内部受物性结构及动力学背景差异影响,构造演化特征存在偏差。根据采取的研究手段精度及研究时间尺度的不同,对郯庐断裂带构造演化仍存在争议,如万天丰等[19]将其演化总结为:1次左行走滑(250~208 Ma);2次正断层(135~52 Ma与23.3~0.73 Ma);3次挤压逆冲断层(208~135 Ma、52~23.3 Ma、0.73 Ma以来)。而张岳桥等[20]将郯庐断裂带中生代的运动学演化概括为“两大运动时期、五个发展阶段”。Li等[21]的研究显示,郯庐断裂带泗洪地区缺失古近纪地层,指示泗洪地区在晚白垩世末期—古近纪经历挤压抬升,同时泗洪县南部的反射地震剖面显示其下伏断裂为第四纪正断层,说明郯庐断裂带部分地区在第四纪仍处于伸展状态。
1.2 基岩地层及物性特征
泗洪地区仅沿郯庐断裂带零星分布的孤丘可见基岩露头,为中—新元古代地层组成的丘陵岗地,其余大部分地区被第四纪松散层覆盖,其沉积厚度差异较大、地层发育不全。
基岩地层单元以郯庐断裂带为界,划分为3个大区,西侧属华北地层区,在朱山附近出露新元古代八公山群兰陵组(Pt3l)及九顶山组上段(Pt3jd2),分别为石英岩及微晶灰岩;断裂带内为晚白垩世红色砂岩、砂砾岩,在重岗山地区出露,岩石普遍风化较强,砂砾岩中砾石主要为片麻岩巨砾、漂砾,且沿重岗山东、西两侧分别可见其逆冲于新近系、第四系之上,断层走向近正北;东侧为苏鲁造山带锦屏岩群,地表未见露头,钻孔揭露显示基底为花岗片麻岩。据2016—2018年研究区完成的29个地质钻孔岩心特征,研究区普遍缺失古近系。基岩及覆盖层时代特征及填图单位分布如表 1所示。
表 1 基岩填图单位Table 1. The mapping units of the bedrock中新生代盖层 华北板块 苏鲁造山带 时代 古近纪(缺失) 白垩纪 新元古代 新元古代—中元古代 中元古代—古元古代 地层及代号 三垛组(E2-3s) 戴南组(E2d) 阜宁组(E1f) 泰州组(E1t) 王氏组(K2w) 青山群(K1qs) 淮河群 八公山群 云台岩群(Pt2-3Y) 锦屏岩群 九顶山组(Pt3jd) 张渠组(Pt3zh) 魏集组(Pt3wj) 兰陵组(Pt3l) 石英岩片麻岩组(Pt1-2Jqg) 磷灰岩片麻岩组(Pt1-2Jpg) 岩石物性资料来源于中国地质调查局南京地质调查中心的实测物性成果资料。在重岗山、柳山、朱山、大庄村基岩出露点用取样机进行取心,通过对取心样品和钻孔内基岩样品进行物性测量,得到样品密度参数。本次物性测量共采集密度标本191块,野外采集中新生代、新元古代露头143块,采集钻孔标本48块,经加工为圆柱体后对标本的密度进行测定(表 2)。
表 2 泗洪地区部分岩石密度参数Table 2. The densities of the bedrock in the Sihong area年代 岩性 标本数/块 密度/(103 kg·m-3) 最小值 最大值 平均值 标准差 白垩纪 粉砂岩 13 2.033 2.346 2.191 0.131 白垩纪 砂岩 43 2.243 2.535 2.330 0.048 白垩纪 火山岩 23 2.254 2.368 2.330 0.028 元古宙 花岗片麻岩 19 2.426 2.669 2.585 0.065 元古宙 片麻岩 24 2.545 2.806 2.658 0.062 元古宙 灰岩 32 2.616 2.857 2.800 0.050 元古宙 石英岩 34 2.598 2.676 2.643 0.014 元古宙 斜长角闪岩 3 2.456 2.616 2.552 0.069 从岩石密度统计表(表 2)可以看出,元古宙地层密度高于中新生代盖层密度,元古宙地层中灰岩密度最高,均值为2.800×103 kg/m3,其次为片麻岩和石英岩,密度均值分别为2.658×103 kg/m3、2.643×103 kg/m3,斜长角山岩密度均值为2.552×103 kg/m3,花岗片麻岩密度均值为2.585×103 kg/m3。结果显示,中新生代地层密度值在2.191×103~2.330×103 kg/m3之间。
2. 数据及处理
郯庐断裂带泗洪地区及其邻区重力异常数据来源于中国地质调查局南京地质调查中心,数据网格化间隔为1500 m,参与处理与反演的重力异常均为布格重力异常。
本次重力异常所选区域略大于研究区,泗洪地区及其邻区布格重力异常特征如图 2所示,从NWW至SEE体现了较明显的分区特征:郯庐断裂带在异常图中显示出明显的NNE向线性梯度带、串珠状异常特征,异常规模较大,宽约30 km且纵贯整个区域中部,断裂带内部以中等正异常为主。以此条中等正异常串珠状条带为界,西侧为低重力起伏区,东侧为高重力起伏区,东南角则为高重力平缓区,分别对应华北板块、苏鲁造山带及扬子板块的基底特征。
区域布格异常显示该区的主导构造应力方向与构造单元分布情况,郯庐断裂带泗洪地区布格异常指示构造特征方向为NNE向,内部主要包括华北地块、郯庐断裂带及苏鲁造山带。郯庐断裂带在泗洪地区各分支断裂的展布形态在布格异常图中不明显,仅重岗山西侧、朱山东侧发育的梯级带较好地指示了F2和F4断裂的发育特征。
由于重力异常数据是不同深度的异常场源在某一观测面的叠加,因此区域异常场和局部异常场的分离是异常反演和解释的关键性问题之一[22]。随着近年场源分离技术方法及相关反演理论的发展,重力异常数据解释也越来越多地被应用于覆盖区隐伏基岩的调查与研究中[23-25],常用的分离区域异常场方法有多项式曲面拟合法[26]、最小曲率法[27]、有限元分析[28]、小波多尺度分解[29-32]等,本次选用小波多尺度分解与对数功率谱相结合方法进行重力异常的位场分离及深度估算。
小波分析可将位场信号分解到不同的尺度空间,并且通过伸缩、平移聚焦到信号的任一细节进行分析[29]。根据小波多尺度分解方法原理[30-32],选取db11小波基[33-34],采用Mallat重构算法[35],重力异常场Δf(x, y)的一阶分解为:
Δf(x,y)=A1Δf(x,y)+Dh1Δf(x,y)+Dv1Δf(x,y)+Dd1Δf(x,y) (1) 其中,A1Δf(x, y)代表分解中的低频部分,Dh1Δf(x,y),Dv1Δf(x,y),Dd1Δf(x,y)为第一阶分解中的EW(水平)、SN(垂直)和NE-SW(对角线)方向上的高频细节部分,可用来进行断裂识别,在这里将公式(1)简写为:
Δf(x,y)=A1Δf(x,y)+D1Δf(x,y) (2) 再对A1Δf(x, y)进行分解得到:
A1Δf(x,y)=A2Δf(x,y)+D2Δf(x,y) (3) 以此类推,可将Δf(x, y)分解为:
Δf(x,y)=AnΔf(x,y)+D1Δf(x,y)+D2Δf(x,y)+D3Δf(x,y)+⋯+DnΔf(x,y) (4) 其中,AnΔf(x, y)为第n阶小波变换的逼近部分,DnΔf(x, y)为第n阶小波变换高频细节部分。
通过对泗洪地区布格异常进行2阶小波分解,得到1、2阶小波细节异常(D1G和D2G)及2阶小波逼近异常(A2G)(图 3-a~c)。随后运用对数功率谱法[36]对研究区的各阶重力异常细节进行场源深度估算(图 3-d、e),得到D1G和D2G反映的平均场源深度约为1 km和2 km。
根据对重力小波细节异常场源深度的估算,D1G和D2G可以反映泗洪地区地壳顶部不同密度体引起的重力异常,如隐伏基岩不同年代地层的分布和呈线性特征的断裂等,其中D1G的不均一性较明显,且场源深度较浅,可以作为基岩面顶部物性分布及起伏特征的反映,而D2G的线性特征更突出,场源深度更深,更适合研究基岩断裂的平面展布特征;A2G则较好地反映了区域构造分区特征,其特征显示出华北板块与苏鲁造山带的物性差异。结合泗洪地区钻孔揭露的基岩面平均深度(约200 m),本次选取D1G进行隐伏基岩埋深和密度特征反演,同时对一、二阶小波细节异常的水平、垂直和对角线方向上的高频细节特征(据公式4)进行分析,推测区内基岩断裂的展布特征。
由于研究区构造线走向主要为NNE—近SN向,郯庐断裂带也以此走向为主,故本区的断裂划分以D1G和D2G在SN向上的分量特征作为主要依据,结合对角线方向与东西向的细节特征,勾画研究区断裂展布特征。结果显示,郯庐断裂带在泗洪地区的5条分支断裂在SN向特征分量上(图 4-b、e)呈明显的近SN向连续的重力梯级带,同时在近NW—SE向上(图 4-a、d)也有许多串珠状异常呈线性排布,指示一系列走滑剪切断裂发育。该走滑断裂系在研究区中部与SN向和NNE向的断裂相互交切,形成了较复杂的断裂体系,且近EW向与NW向断裂多切割NNE—NE向的郯庐断裂带各分支断裂。据此推断,本区存在多期次的构造叠加,郯庐断裂NNE向构造体系被较新的NW向构造运动改造,形成现今的断裂体系。
3. 结果与讨论
3.1 基岩面埋深及密度分布
根据线性回归近似反演理论[37-38],如果密度界面起伏平缓,可以认为重力变化与密度界面的起伏近似呈线性关系,即:
h=a+b⋅Δg (5) 式中,h为界面深度,Δg为界面起伏引起的重力异常,a,b为2个系数,它们与重力异常起算点处界面深度和界面上下层物质层的密度差有关。
如果已有n个已知基岩面深度,设其深度为hi(i=1, 2, ..., n),根据最小二乘原理,为了确定a,b,应使得各点深度hi与计算出的深度hi偏差的平方和最小,即:
ϕ(a,b)=n∑i=1(h−ˉhi)=min (6) 令\partial \varphi /\partial a、\partial \varphi /\partial b分别等于零,可得:
\sum {{{\rm{h}}_{\rm{i}}}} - {\rm{na}} - \sum {\rm{b}} \Delta {g_i} = 0 (7) \sum {{h_i}} \Delta {g_i} - \sum a \Delta {g_i} - \sum b \Delta g_i^2 = 0 (8) 两式联立,解之得:
a = \frac{{\sum \Delta {g_i}^2\sum {{h_i}} - \sum \Delta {g_i}\sum \Delta {g_i}{h_i}}}{{n\sum \Delta {g_i}^2 - {{\left( {\sum \Delta {g_i}} \right)}^2}}} (9) b = \frac{{n\sum {\Delta {g_i}} {h_i} - \sum {{h_i}} \sum \Delta {g_i}{\rm{ }}}}{{n\sum {\Delta {g_i}^2} - {{\left( {\sum \Delta {g_i}} \right)}^2}}} (10) a,b求出后,则可根据公式(5)计算出各测点下方密度界面的深度。
本次研究应用前期完成的26个地质钻孔的基岩面埋深数据及朱山基岩露头高程数据作为已知数据,钻孔位置见图 1-b,其对应的重力一阶小波细节异常值如表 3所示。
表 3 用于线性回归反演的地质钻孔信息Table 3. The geological boreholes for linear regression inversion序号 钻孔编号及基岩出露点 钻孔高程/m 基岩面高程/m Δg值/(10-6 m·s-2) 1 SHJ01 18.88 -41.4 0.082 2 SHJ03 18.47 -234.11 -0.097 3 SHJ05 18.12 -232.78 -0.061 4 SHJ07 22.47 -146.31 -0.034 5 SHJ08 19.59 -195.38 -0.062 6 SHJ09 18.71 -206.85 0.037 7 SHJ10 18.69 -220 0.086 8 SHJ11 18.13 -223.4 -0.086 9 SHJ14 16.37 -154 -0.207 10 SHJ15 16.71 -113.6 -0.188 11 SHJ17 16.09 -83.65 0.005 12 SHJ18 18.82 -171.8 0.026 13 SHJ19 46.04 -162.36 0.013 14 SHJ20 22.77 -158.72 -0.021 15 SHJ21 16.47 -77.86 0.087 16 SHJ22 15.46 -117 0.009 17 SHJ23 13.02 -194.1 -0.065 18 SHJ24 20.42 -254.77 -0.209 19 SHJ25 20.86 -165.05 -0.087 20 SHJ26 18.39 -125.67 0.057 21 SHJ28 15.32 -184.8 0.051 22 SHJ31 16.73 -103.49 -0.096 23 SHJ34 15.03 -106.3 -0.036 24 SHJ35 19.63 -155.18 0.088 25 SHJ37 16.38 -139.25 0.017 26 SHJ38 26.07 -108 -0.072 27 朱山 / 157.2 0.458 从钻孔基岩面高程数据(图 5-a)与对应重力小波一阶细节异常数据(图 5-b)的分布特征图中,可以看出二者具有一定的线性相关性。进一步依据相关系数的计算公式:
{R_{j, z}} = \frac{{{\rm{cov}}\left( {j, z} \right)}}{{{S_j} \times {S_z}}} (11) 计算得出二者的相关系数为0.684,属于中度相关(图 5-c),可以进行线性回归分析[39],其中cov(j, z)为基岩面高程数据与重力异常数据的协方差,Sj和Sz分别为基岩面高程数据和重力异常数据的标准差。
据公式(6)~(10)得到基岩面高程与重力一阶小波细节异常线性方程为:
h = 433.49 \times \Delta g - 140.24 (12) 根据线性回归方程(公式(12))对重力一阶小波细节异常未知基岩面高程数据点进行计算,得到研究区基岩面高程分布特征(图 6-a):研究区的基岩波动起伏较明显,起伏范围为-220~20 m,西北角及中部偏西位置为2个较明显的隆起,走向NNE向,与朱山、重岗山位置较吻合,2处基岩出露岩性分别为新元古代白云质灰岩及晚白垩世泥质粉砂岩,西侧由F1~F5组成的郯庐断裂带内基岩面埋深起伏较大,形态上呈明显的坳隆相间分布,构造上为地堑地垒交替出现样式,朱山东侧和重岗山附近均发育NNE向展布的地堑,朱山附近、上塘—黑塔东一线及重岗山东侧为3处地垒构造。据基岩起伏特征及小波断裂分析结果可勾画出区内基岩断裂的发育情况。
本次采用频率域视密度填图方法[40]对基底密度分布特征进行反演,用于反演的重力异常为重力一阶小波细节异常,选取本次线性回归反演得到的基岩面深度为密度层上界面深度,下界面深度选为对数功率谱标定的D1G平均深度1 km,平均密度设为2.3×103 kg/m3,经6次迭代得到近基岩面深度视密度分布特征(图 6-b)。郯庐断裂带泗洪地区地堑构造内为明显的低密度特征,密度值在2.14×103~2.26×103 kg/m3之间,与晚白垩世粉砂岩、砂岩的密度特征吻合;西北角朱山地垒为明显的高密度特征,密度值在2.42×103~2.6×103 kg/m3之间,与新元古代石英岩物性特征相似;而上塘-黑塔地垒与重岗山东地垒体现出的高密度体可能与断裂带内深部岩体侵入或古老变质结晶基底残留有关;东部苏鲁造山带内则总体为高密度分布,局部凹陷内表现为低密度特征,对比低密度区钻孔岩心特征,其基岩岩性为晚白垩世粉砂岩,结合区内断裂分布解释结果,说明苏鲁造山带内的晚白垩世地层为局部断陷沉积。
3.2 讨论
本文依据钻孔数据,对目标重力异常场界面起伏特征进行了反演,得到泗洪地区隐伏基岩面起伏特征与Jiang等[41]总结的区域构造地质特征较吻合,同时结合重力异常小波断裂分析、视密度填图等方法对断裂展布和岩性特征分布进行了解释,得到郯庐断裂带泗洪地区较精细的隐伏基岩地质模型。该模型具有一定的可信度,但受限于重力异常数据处理与解释过程中的多解性及反演方法基本假定的不精确性,该模型仍存在一些不足。首先,受位场分离方法精度限制,提取的小波一阶细节异常可近似反演隐伏基岩异常特征,精度不足;其次,线性回归反演理论假设重力变化与密度界面的起伏近似呈线性关系,忽略了重力异常变化一般与密度正相关这一因素,故在基岩岩石密度较高地区,界面深度反演结果偏深(或矮),而在基岩密度较低区,深度偏浅(或高)。
4. 结论
(1) 已知钻孔约束下的重力异常反演方法可以在较少人为干预下,较高效地构建浅覆盖区隐伏基岩的地质模型,能够在覆盖区的地质填图中起到深部基岩构造的辅助解释作用,但其精度受制于位场分离方法与线性回归算法的粗糙性,仍有待进一步提升。
(2) 郯庐断裂带泗洪地区基岩地质模型显示:①泗洪地区郯庐断裂带的5条分支断裂在研究区中部呈NNE向平行排列,且发现区内多条NW向左行走滑断裂发育,并切割郯庐断裂带,说明该区域受到新的构造应力叠加;②郯庐断裂带在泗洪地区的隐伏基岩面呈“凹-隆-凹-隆”起伏特征; ③基岩视密度填图结果显示, 泗洪地区郯庐断裂带内的基岩物性特征存在较大的不均一性,高密度体物性特征与苏鲁造山带锦屏岩群相似,但断裂带内岩浆活动频繁,也不排除其为岩浆侵入成因。
-
表 1 132件样品中土壤营养元素描述性统计
Table 1 Descriptive statistics of soil nutrient elements in the 132 samples
指标 最小值 最大值 中位数 平均值 标准差 变异系数(Cv)/% 偏度 峰度 黄淮海平原(孙厚云等,2022) 全国土壤背景(孙厚云等,2022) N/10-6 93 3296 1075 1223 721 58.95 0.80 0.24 381 707 P/10-6 259 1937 836 878 366 41.69 0.47 -0.36 517 570 K2O/% 0.94 4.48 2.70 2.80 0.48 17.14 0.83 3.14 2.34 2.36 CaO/% 0.39 11.09 2.26 2.24 1.28 57.14 3.31 19.5 4.10 2.74 MgO/% 0.04 4.83 1.42 1.34 0.55 41.04 1.57 11.64 1.88 1.43 S/10-6 51 988 232 245 137 55.92 1.79 6.48 142 245 Mo/10-6 0.43 1.55 0.74 0.79 0.21 26.58 1.75 3.59 0.52 0.7 Mn/10-6 149 1020 518 491 134 27.29 -0.04 1.64 705 569 Fe2O3/% 1.67 9.33 3.96 4.01 0.90 22.44 1.43 8.64 3.71 2.8 B/10-6 3.26 65.51 27.29 26.67 9.40 35.25 0.18 1.40 52 43 Corg/% 0.03 4.33 1.05 1.23 0.88 71.54 1.51 2.42 0.26 0.6 pH 6.38 8.78 8.22 8.09 0.44 5.44 -1.41 2.20 8.61 8 CNR 1.58 112.59 9.30 10.41 9.26 88.95 10.39 115.26 6.82 8.49 CPR 0.34 62.26 11.08 15.76 13.40 85.03 1.89 2.92 5.03 10.53 NPR 0.05 4.55 1.18 1.49 0.94 63.09 1.68 2.45 0.74 1.24 CSR 6.60 107.30 45.84 48.69 19.03 39.08 0.59 0.57 18.31 24.49 表 2 研究区土壤营养元素及pH值相关性分析
Table 2 Correlation analysis of soil nutrients and pH in the study area
指标 N P K2O CaO MgO S Mo Mn Fe2O3 B Corg pH N 1 P 0.375** 1 K2O -0.170 -0.570** 1 CaO -0.025 0.386** -0.711** 1 MgO 0.153 0.660** -0.808** 0.663** 1 S 0.837** 0.531** -0.303** 0.145 0.281** 1 Mo 0.025 0.046 0.330** -0.111 -0.027 0.068 1 Mn 0.255** 0.654** -0.683** 0.476** 0.724** 0.349** -0.054 1 Fe2O3 0.150 0.506** -0.554** 0.415** 0.763** 0.202* 0.279** 0.646** 1 B 0.414** 0.463** -0.545** 0.366** 0.429** 0.500** -0.080 0.510** 0.260** 1 Corg 0.863** 0.115 -0.036 -0.114 0.003 0.709** -0.020 0.111 0.034 0.291** 1 pH -0.318** 0.077 -0.233** 0.370** 0.202* -0.275** -0.245** 0.271** -0.040 0.171 -0.341** 1 注:*表示在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关(双尾),**表示在0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关(双尾),n=132 表 3 研究区土壤营养元素分级统计
Table 3 Classification statistics of soil nutrients in the study area
指标 一级 二级 三级 四级 五级 分级标准 数量 分级标准 数量 分级标准 数量 分级标准 数量 分级标准 数量 N/10-6 >2000 19 1500~2000 19 1000~1500 35 750~1000 22 ≤750 37 P/10-6 >1000 45 800~1000 24 600~800 28 400~600 25 ≤400 10 K2O/% >3.01 29 2.41~3.01 89 1.81~2.41 13 1.21~1.81 0 ≤1.21 1 CaO/% >7.32 2 4.23~7.32 2 1.30~4.23 105 0.50~1.30 20 ≤0.50 3 MgO/% >2.45 1 1.87~2.45 10 1.23~1.87 73 0.75~1.23 29 ≤0.75 19 S/10-6 >757 1 430~757 9 245~430 49 156~245 38 ≤156 35 Mo/10-6 >5.0 0 2.3~5.0 0 1.1~2.3 11 0.6~1.1 106 ≤0.6 15 Mn/10-6 >967 1 711~967 3 540~711 51 342~540 58 ≤342 19 Fe2O3/% >6.23 1 5.04~6.23 12 4.24~5.04 31 3.46~4.24 61 ≤3.46 27 B/10-6 >82.3 0 58.6~82.3 1 41~58.6 5 25.9~41 65 ≤25.9 61 Corg/% >4.0 3 3.0~4.0 4 2.0~3.0 12 1.0~2.0 50 ≤1.0 63 pH >8.6 5 8.1~8.6 76 6.8~8.1 49 5.3~6.8 2 ≤5.3 0 表 4 土壤元素含量变异函数理论模型及其相关参数
Table 4 Soil elements content and variogram model parameters
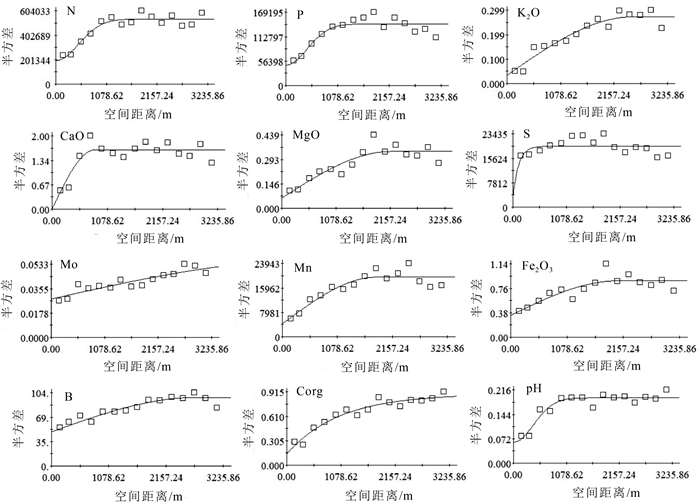
元素指标 变程/m 块金值(C0) 基台值(C0+C) 块金系数C0/(C0+C) 决定系数R2 残差RSS 拟合模型 N 1191.65 194000 537600 0.361 0.889 2.04×1010 Gaussian P 1091.19 47300 142500 0.332 0.808 2.79×109 Gaussian K2O 2522 0.0336 0.2722 0.123 0.913 7.927×10-3 Spherical CaO 833 0.001 1.623 0.001 0.763 0.601 Spherical MgO 2157 0.0609 0.3408 0.179 0.802 0.0261 Spherical S 348 3000 19570 0.153 0.146 7.12×107 Exponential Mo 5222 0.02808 0.05626 0.499 0.808 1.563×10-4 Spherical Mn 1848 4240 19540 0.217 0.835 5.72×107 Spherical Fe2O3 2047 0.342 0.88 0.389 0.715 0.151 Spherical B 2704 48.7 97.5 0.499 0.87 445 Spherical Corg 3153 0.14 0.89 0.157 0.933 0.0372 Exponential pH 1001.13 0.0621 0.1932 0.321 0.884 2.74×10-3 Gaussian -
An Y L, Huang Y, Yin Z Q, et al. Spatial distribution patterns and sources for potential toxic elements in soil in the Daxing District, Beijing, China[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2022, 15(8) : 1-21.
Bekele A, Hudnall W H. Spatial variability of soil chemical properties of a prairie-forest transition in Louisiana[J]. Plant and Soil, 2006, 280: 7-21. doi: 10.1007/s11104-005-4983-4
Burgess T M, Webster R. Optimal interpolation and isarithmic mapping of soil properties: Ⅱ. BlockKriging[J]. Journal of Soil Science, 1980, 31: 333-341. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2389.1980.tb02085.x
Cambardella C A, Moorman T B, Novak J M, et al. Field-scale variability of soil properties in Central IOWA soils[J]. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., 1994, 58: 1501-1511. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1994.03615995005800050033x
Cleveland C C, Liptzin D. C: N: P stoichiometry in soil: is there a "Redfield ratio" for the microbial biomass[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2007, 85(3) : 235-252. doi: 10.1007/s10533-007-9132-0
Cole C V. Mechanisms of phosphate adsorption by calciumcarbonate[J]. Soil. Sci. Soc. Amer. Proc., 1953, 17: 352-35. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1953.03615995001700040013x
Dayani M, Mohammadi J. Geostatistical assessment of Pb, Zn and Cd contamination in near-surface; soils of the urban-mining transitional region of Isfahan, Iran[J]. Pedosphere, 2010, 20(5) : 568-577. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0160(10)60046-X
Deluigne J, Bisdom E, Sleeman J, et al. Olivines, their pseudomorphs and secondary products[J]. Pedologie, 1979, 29(3) : 247-300.
Elser J J, Acquisti C, Kumar S. Stoichiogenomics: theevolutionary ecology of macromolecular elemental composition [J]. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 2011, 26(1) : 38-44.
Elser J J, Fagan W F, Kerkhoff A J, et al. Biological stoichiometry of plant production: metabolism, scaling and ecological response to global change[J]. New Phytologist, 2010, 186(3) : 593-608. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03214.x
Facchinelli A, Sacchi E, Mallen L. Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify heavymetal sources in soils[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2001, 114(3) : 313-324. doi: 10.1016/S0269-7491(00)00243-8
Huang B, Sun W, Zhao Y, et al. Temporal and spatial variability of soil organic matter and total nitrogen in an agricultural ecosystem as affected by farming practices[J]. Geoderma, 2007, 139(3/4) : 336-345.
Jordan T E, Cornwell J C, Boynton W R, et al. Changes in phosphorus biogcochemistry along an estuarine salinity gradient: The iron conveyer belt[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2008, 53(1) : 172-184. doi: 10.4319/lo.2008.53.1.0172
LiuR, Wang M, Chen W P, et al. Spatial pattern of heavy metals accumulation risk in urban soils of Beijing and its influencing factors[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 210: 174-181. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.11.044
Negrin V L, Spetter C V, Asteasuain R O, et al, Influence of flooding and vegetation oncarbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus dynamics in the pore water of a Spartina alterniflora salt marsh[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2011, 23(2) : 212-221. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60395-6
Oliver M A, Webster R. Kriging: a method of interpolation for geographical informationsystems[J]. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst., 1990, 4: 313-332. doi: 10.1080/02693799008941549
Sah R N, Mikkelsen D S. Effects of anaerobic decomposition of organic matter on sorption and transformations of phosphate in drained soils: Ⅰ[J]. Effects on Phosphate Sorption Soil Science, 1986, 142(5) : 267-274.
Sardans J, Rivasubach A, Penuelas J. The C: N: P stoichiometry of organisms and ecosystems in a changing world: A review and perspectives[J]. Perspectives in Plant Ecology Evolution & Systematics, 2012, 14(1) : 33-47.
Zhang Z M, Zhou Y C, Huang X F, et al. Applicability of GIS-based spatial interpolation and simulation for estimating the soil organic carbon storage in karst regions[J]. Global Ecology and Conservation, 2020, 21: e00849. doi: 10.1016/j.gecco.2019.e00849
安永龙, 杜子图, 黄勇. 基于地统计学和GIS技术的北京市大兴区礼贤镇土壤养分空间变异性研究[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(6) : 1311-1321. doi: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2018.06.19 安永龙, 万利勤, 李霞, 等. 承德市土壤重金属空间结构与分布特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2020, 47(6) : 119-131. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202006015.htm 常妮. 汉诺坝碱性玄武岩巨量地幔岩石堆积机制研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 硕士学位论文, 2020. 陈绪钰, 王东辉, 倪化勇, 等. 长江经济带上游地区丘陵城市工程建设适宜性评价——以泸州市规划中心城区为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2020, 50(1) : 194-207. doi: 10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.20180303 董正武, 玉米提· 哈力克, 李生宇, 等. 古尔班通古特沙漠西南缘柽柳沙包的土壤化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(20) : 7389-7400. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB202020030.htm 付海曼, 贾黎明. 土壤对氮、磷吸附/解吸附特性研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2009, 25(21) : 198-203. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNTB200921045.htm 贾恒义. 黄土高原主要土壤成壤过程与矿物元素再分配[J]. 水土保持研究, 1995, (4) : 56-60, 68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBY504.013.htm 姜华, 唐晓华, 杨利亚, 等. 基于土地资源的市县级多要素国土空间开发适宜性评价研究——以湖北省宜昌市为例[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6) : 1776-1792. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202006015.htm 李启权, 岳天祥, 范泽孟, 等. 中国表层土壤有机质空间分布模拟分析方法研究[J]. 自然资源学报, 2010, 25(8) : 1385-1399. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZX201008015.htm 林燕, 白秀佳, 叶泽宇, 等. 基于ArcGIS的南通市农业生产适宜性评价[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(6) : 968-977. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20210612&flag=1 刘雪松, 刘金巍, 魏建朋, 等. 赣江梅江河河流作用对土壤元素分配的影响[J]. 人民长江, 2019, 50(10) : 69-72, 76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RIVE201910012.htm 刘永生, 杨楠, 王轶, 等. 保定—沧州地区基于空间自相关分析的土壤区域监测点网络密度研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2012, 39(5) : 126-131. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201205024.htm 刘源, 李晓晶, 段玉玺, 等. 库布齐沙漠东部植被恢复对土壤生态化学计量的影响[J]. 干旱区研究, 2022, 39(3) : 924-932. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHQJ202203025.htm 卢建男, 刘凯军, 王瑞雄, 等. 中国荒漠植物-土壤系统生态化学计量学研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2) : 173-182. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSS202202020.htm 罗艳, 贡璐, 朱美玲, 等. 塔里木河上游荒漠区4种灌木植物叶片与土壤生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(24) : 8326-8335. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201724019.htm 骆珊, 张德明, 卢定彪, 等. 乌蒙山区毕节市耕地土壤微量元素丰缺评价及其影响因素[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(9) : 1570-1583. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20210916&flag=1 秦王念, 颜雄, 李文昭, 等. 基于CNKI数据库的生态化学计量文献计量分析[J]. 现代农业科技, 2021, (24) : 228-230. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ANHE202124085.htm 曲林雨. 汉诺坝玄武岩结构和化学特征多样性的联系[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 硕士学位论文, 2020. 石建省, 马荣, 马震. 区域地球多圈层交互带调查探索研究[J]. 地球学报, 2019, 40(6) : 767-780. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201906001.htm 孙厚云, 卫晓锋, 贾凤超, 等. 冀北承德地区土壤生源要素生态化学计量与空间分异特征[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(5) : 1750-1765. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB202205008.htm 孙厚云, 卫晓锋, 张晓敏, 等. 河北承德中部伊逊河红旗地区土壤生源要素空间分布格局及其影响因素[J]. 矿产勘查, 2021, 12(4) : 1008-1018. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS202104030.htm 田静, 盛茂银, 汪攀, 等. 西南喀斯特土地利用变化对植物凋落物-土壤C、N、P化学计量特征和土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(9) : 4278-4286. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201909050.htm 汪璇, 王成秋, 唐将, 等. 基于地统计学和GIS的三峡库区土壤微量营养元素空间变异性研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2009, 40(2) : 359-365. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB200902037.htm 王学求, 周建, 徐善法, 等. 全国地球化学基准网建立与土壤地球化学基准值特征[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(5) : 1469-1480. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201605001.htm 卫晓锋, 孙厚云, 张竞, 等. 承德特色林果资源的生态地球化学过程及其品质提升意义[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2020, 47(6) : 99-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202006013.htm 魏卓群, 白军红, 张玲, 等. 黄河口潮间带芦苇湿地土壤生源要素的时空动态变化特征[J]. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(1) : 43-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BSDZ202101008.htm 吴美玲, 田晋文. 基于GIS和地统计学的黔西北农业园区土壤养分空间变异特征研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(17) : 48-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNTB201917009.htm 吴云霞, 蔡奎, 吕凤军, 等. 冀西北农牧交错带表层土壤营养元素特征研究——以河北省康保县为例[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2019, 33(1) : 84-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH201901013.htm 奚小环. 自然资源时期: 大数据与地球系统科学——再论全面发展时期的勘查地球化学[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(3) : 449-460. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201903001.htm 夏汉平, 高子勤. 磷酸盐在白浆土中的吸附与解吸特性[J]. 土壤通报, 1992, 23: 283-287. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB199302004.htm 熊杏, 熊清华, 郭熙, 等. 南方典型丘陵区耕地土壤全氮、有机碳和碳氮比空间变异特征及其影响因素[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(9) : 1656-1668. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWYF202009009.htm 杨社锋, 方维萱, 胡瑞忠, 等. 老挝南部波罗芬高原玄武岩砖红壤风化壳微量元素地球化学特征[J]. 矿产与地质, 2005, (6) : 723-727. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD200506029.htm 杨之江, 陈效民, 景峰, 等. 基于GIS和地统计学的稻田土壤养分与重金属空间变异[J]. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(6) : 1893-1901. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB201806021.htm 赵明松, 张甘霖, 王德彩, 等. 徐淮黄泛平原土壤有机质空间变异特征及主控因素分析[J]. 土壤学报, 2013, 50(1) : 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB201301001.htm 中国环境监测总站. 中国土壤元素背景[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990: 1-501. 中华人民共和国国资源部. DZ/T 0295—2016, 土地质量地球化学评价规范[S]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2016. 中华人民共和国国土资源部. DZ/T 0258—2014, 多目标区域地球化学调查规范(1∶250000) [S]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2014. 朱礼学. 土壤pH值及CaCO3在多目标地球化学调查中的研究意义[J]. 四川地质学报, 2001, (4) : 226-228. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCDB200104005.htm 朱秋莲, 邢肖毅, 张宏, 等. 黄土丘陵沟壑区不同植被区土壤生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(15) : 4674-4682. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201315019.htm -
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 孙旭鹏,李超楠. 瞬变电磁法在煤矿老窑采空区积水探测中的应用. 煤炭技术. 2024(03): 208-212 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 胡斌. 瞬变电磁法在煤矿超前地质勘查中的应用. 能源与环保. 2024(06): 70-75 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. WEI Laonao,LIU Yunhe,ZHANG Bo. UAV-based transient electromagnetic 3D forward modeling and inversion and analysis of exploration capability. Global Geology. 2024(03): 154-166 .  必应学术
必应学术
4. 都兵,张旭晴,孙涛,陈峰,王琳炜. 基于时序InSAR的吉林省松原市宁江区地下水活动研究. 世界地质. 2024(03): 424-433 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 翟皓,李桐林,康鑫泽,吴宇豪. 半航空瞬变电磁数据处理与解释在贺斯格乌拉露天煤矿水灾害勘探中的应用. 世界地质. 2024(03): 434-443 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 秦莉旻. 物探技术在地下水资源污染防治中的应用研究. 环境科学与管理. 2023(03): 72-76 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 范莹琳,潘树仁,杜松,李萌,赵岳,张玉峰,丁晏,宋思彤,车巧慧,王锋利. 基于半航空瞬变电磁法识别复杂地形废弃煤矿富水空间的应用研究. 煤炭科学技术. 2023(12): 79-89 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 林康利. 基于航空物探的铁路地质选线研究. 工程地球物理学报. 2022(05): 603-609 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: