Chronology and geochemical characteristics of the Lapeiquan Formation rhyolite in the Altun Kaladawan area, Xinjiang, and implications for tectonic evolution of the northern margin of Altun
-
摘要:
由于新疆阿尔金拉配泉组研究程度较低,其沉积时代及构造成因仍存在疑问。以拉配泉组流纹岩为研究对象,开展年代学、地球化学等方面的研究。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年结果显示,拉配泉组二段流纹岩年龄为497±2.0 Ma、三段流纹岩年龄为483.4±1.9 Ma。岩石地球化学研究显示,样品具有富硅(70.07%~78.55%)、低镁(0.32%~0.58%)、低Mg#(24~30)等特征。稀土元素分析结果显示,样品呈现富集轻稀土元素,相对亏损重稀土元素的特征,(La/Yb)N=10.23~12.73,负Eu异常明显(δEu=0.10~0.19);微量元素分析结果显示,样品明显富集La、Nd、Zr、Ce、Sm、U、Th、Hf等,相对亏损Sr、Nb、Ti等。结合前人研究成果,厘定拉配泉组沉积时代为晚寒武世—早奥陶世。二段流纹岩具有A型花岗岩特征,可能主要来源于地壳物质的部分熔融,构造环境为北阿尔金洋回转引起的弧后伸展环境。
Abstract:Due to the low level studies on the Altun Lapeiquan Formation in Xinjiang, its depositional age and tectonic genesis are still in doubt.Chronological and geochemical studies were carried out on the rhyolites of the Lapeiquan Formation.The results of zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating show that the ages of the second and third member rhyolites of the Lapaiquan Formation are 497±2.0 Ma and 483.4±1.9 Ma, respectively.The petrogeochemical studies show that the samples are Si-rich(70.07%~78.55%), Mg-poor(0.32%~0.58%), and Mg#-low(24~30).The rare earth elements exhibit the characteristics of enrichment of light rare earth elements and relatively deficient in heavy rare earth elements((La/Yb)N=10.23~12.73), and the negative Eu is abnormally obvious(δEu=0.10~0.19);the analysis of trace elements shows that the samples are obviously enriched in La, Nd, Zr, Ce, Sm, U, Th, Hf, etc., and relatively deficient in Sr, Nb, Ti, etc.Combined with the previous researches, the depositional age of the Lapeiquan Formation is determined to be Late Cambrian-Early Ordovician.The second member of rhyolite has the characteristics of A-type granite, and it most likely came from partial melting of crustal materials, and the tectonic environment is a post-arc extensional environment caused by the reversal of the North Altun Ocean.
-
Keywords:
- Lapeiquan Formation /
- rhyolite /
- U-Pb dating /
- geochemistry /
- Altun
-
近年来发现的新疆喀腊大湾矿集区,已成为阿尔金地区最重要的矿集区(倪康等,2017),发现有喀腊大湾大型铁矿、喀腊达坂大型铅锌矿、达坂西中小型铜矿、大平沟金矿等。拉配泉组是该矿集区主要的赋矿地层,也是研究阿尔金北缘地区构造演化进程的重要地质单元(倪康等,2017)。随着喀腊大湾地区矿产资源的开发,学者们陆续对该地区基础地质、矿床成因开展了研究工作(陈宣华等,2009;陈柏林等,2010;2016;倪康等,2017;Ye et al., 2018;武彬等,2019;王坤等,2023)。陈柏林等(2016)通过卓阿布拉克组中酸性火山岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb测年,获得年龄值477~485 Ma;倪康等(2017)对拉配泉组三段流纹岩开展了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年,获得年龄值为488 Ma。从前人研究结果分析,目前仅对拉配泉组三段的流纹岩进行了精确定年,缺少对其他地层流纹岩的精细定年和详细研究,制约了对拉配泉组流纹岩成因及形成构造环境,以及该地区构造演化与成矿研究的认识。因此,本文通过对拉配泉组二、三段中流纹岩进行锆石U-Pb精确定年及岩石地球化学研究,在准确厘定拉配泉组沉积时代的基础上,探讨流纹岩的成因及形成构造背景。该研究为阿尔金地区大地构造演化过程提供了新的制约,也对喀腊大湾地区矿产勘查具有重要指导意义。
1. 区域地质背景
阿尔金喀腊大湾地区位于青藏高原北缘(倪康等,2017;张传林等,2022),北接塔里木盆地南缘,南邻柴达木盆地(图 1-a)。阿尔金北缘地区可划分为太古宙混杂岩带、俯冲碰撞杂岩带、米兰河-金雁山地块(刘良等,2002;Liu et al., 2008)。研究区出露地层有太古宇米兰岩群达格拉格布拉克组(Ardg)、下古生界拉配泉组(

![]() 图 1 区域构造单元划分(a)和新疆喀腊大湾地质简图(b)(据陈宣华等,2009)1—中新统上干柴沟组; 2—中新统下油砂山组; 3—渐新统下干柴沟组; 4—上石炭统因格布拉克组; 5—拉配泉组三段; 6—拉配泉组二段; 7—拉配泉组一段; 8—金燕山组;9—太古宇达格拉格布拉克组; 10—志留纪二长花岗岩;11—志留纪花岗岩;12—志留纪辉长岩;13—奥陶纪闪长岩;14—奥陶纪花岗岩;15—寒武纪闪长岩;16—寒武纪花岗闪长岩;17—寒武纪花岗岩;18—采样位置;19—铁矿床;20—铅锌矿床;21—银铅矿床;22—地质界线;23—逆冲断层;24—板块缝合带;25—走滑断层Figure 1. Division of regional tectonic units(a) and schematic geologic map of Kaladawan area in Xinjiang(b)
图 1 区域构造单元划分(a)和新疆喀腊大湾地质简图(b)(据陈宣华等,2009)1—中新统上干柴沟组; 2—中新统下油砂山组; 3—渐新统下干柴沟组; 4—上石炭统因格布拉克组; 5—拉配泉组三段; 6—拉配泉组二段; 7—拉配泉组一段; 8—金燕山组;9—太古宇达格拉格布拉克组; 10—志留纪二长花岗岩;11—志留纪花岗岩;12—志留纪辉长岩;13—奥陶纪闪长岩;14—奥陶纪花岗岩;15—寒武纪闪长岩;16—寒武纪花岗闪长岩;17—寒武纪花岗岩;18—采样位置;19—铁矿床;20—铅锌矿床;21—银铅矿床;22—地质界线;23—逆冲断层;24—板块缝合带;25—走滑断层Figure 1. Division of regional tectonic units(a) and schematic geologic map of Kaladawan area in Xinjiang(b)喀腊大湾地区位于北东向阿尔金走滑断裂与东西向阿尔金北缘断裂之间,属阿尔金山构造带中部(倪康等,2017)。自太古宙以来,该区域经历了多期次的碰撞造山作用(倪康等,2017)。前人研究表明,在震旦纪晚期—早古生代早期,红柳沟-拉配泉裂谷带扩张成洋,晚寒武世发生板块俯冲作用,中晚奥陶世发生碰撞作用(崔军文等,1999;戚学祥等,2005;张建新等,2007;杨经绥等,2008;陈柏林等,2016;李猛等,2021)。晚中生代以来,受欧亚板块与印度板块碰撞造山的远程影响,阿尔金断裂带发生了较大规模的左行走滑(崔军文等,1999;陈正乐等,2002;Liu et al., 2006;陈柏林等,2010)。研究区断裂主要有阿尔金北缘断裂、白尖山断裂和喀腊达坂断裂(陈宣华等,2009;武彬等,2019),阿尔金北缘断裂呈近东西向,倾向北,分为主断裂及次级断裂,控制着区内晚寒武世火山岩、早奥陶世和早志留世侵入岩及石炭系的分布(武彬等,2019)。
研究区侵入岩发育,主要为加里东钙碱性侵入岩及部分高钾钙碱性侵入岩(武彬等,2019)。钙碱性侵入岩从基性至酸性均有出露(图 1),其中以基性岩为主(Ye et al., 2018),岩性包括辉长辉绿岩、辉长岩、辉绿岩,多呈近东西向不连续分布的岩株或岩脉产出,其展布方向大体受构造线方向控制,表现为顺地层侵入。高钾钙碱性侵入岩以中—酸性侵入岩为主,中—酸性岩广泛分布,多呈岩枝、岩基侵位于拉配泉组(陈宣华等,2009;Ye et al., 2018)。
2. 地层特征及样品采集
拉配泉组分布于阿尔金北缘地区俯冲碰撞杂岩带中部,阿尔金北缘断裂以南、喀腊达坂断裂以北区域,呈近东西向条带状展布,横贯研究区,向东延至阿尔金断裂带(武彬等,2019)。拉配泉组北与太古宇米兰岩群为断层接触,南与古近系渐新统下干柴沟组呈角度不整合接触(倪康等,2017)。依据岩性组合特征,将该组自下而上划分为3个岩性段(新疆维吾尔自治区地质矿产勘查开发局第一地质大队,2008)(图 1)。
拉配泉组一段(

拉配泉组二段(

拉配泉组三段(

地层中的流纹岩和凝灰岩是准确限定其时代最有效的定年载体(高林志等,2015;田辉等,2015)。本次对喀腊大湾北选取拉配泉组二段的1件流纹岩样品开展了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年,对8件新鲜流纹岩样品进行了主量、微量与稀土元素分析;由于喀腊达坂西矿区拉配泉组三段流纹岩已经发生矿化蚀变现象,故只选取1件流纹岩样品开展LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年。流纹岩呈层状、似层状,节理发育(图 2-a、c)。其两侧岩性为大理岩、玄武岩、变质含砾中粗粒岩屑砂岩等。流纹岩颜色呈灰白色—浅肉红色,斑状结构,块状构造,斑晶主要由钾长石、石英组成,含量20%~30%,粒径大小0.5~1.5 mm,镜下可见流动构造,具有定向排列特征,基质多呈隐晶质及细小的长英质矿物组成(倪康等,2017)(图 2-b、d)。
3. 测试方法
锆石U-Pb测年在中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心同位素实验室完成,实验所采用仪器为美国Thermo Fisher公司生产的电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(Neptune)和氟化氩准分子激光器(New Wave 193 nm FX)。实验过程中采用激光剥蚀系统产生的相应光束能量密度为10 J/cm2,束斑直径为32 μm,共剥蚀40 s,频率为5 Hz。以锆石91500为测试过程中的外标,校正仪器质量偏差与元素分馏;实验中以标准锆石GJ-1为盲样检验U-Pb定年数据质量;锆石中的Pb元素含量标定采用NIST SRM 610为外标,Si为内标;微量元素含量标定以Zr为内标(Liu et al., 2010a; Hu et al., 2011)。原始的测试数据用ICPMSDataCal软件(Liu et al., 2010b; 高林志等,2015)和Isoplot程序进行处理(Ludwig,2003)。
全岩主量元素分析在中国地质调查局南京地质调查中心实验室完成,主量元素用X射线荧光光谱法(XRF)分析,仪器为AFS-2202a型X射线荧光光谱仪,分析误差优于1%;在中国科学院地球化学研究所矿床地球化学国家重点实验室完成微量元素测试分析,实验仪器为ELAN-DRC-e ICP-MS,仪器灵敏度调整为1 ng/mL115In,约30000 cps。以多元素标准溶液为外标,以国际标样AMH-1(安山岩)OU-6(板岩)为标准参考物质。测试元素的相对误差优于±5%,具体步骤和全流程实验空白值据Qi et al.(2000)。
4. 测试结果
4.1 锆石U-Pb年龄
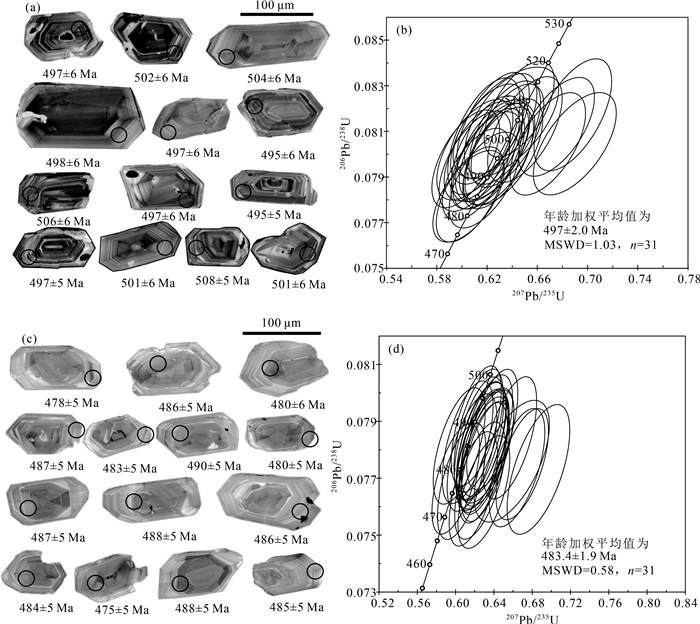
分析测试结果详见表 1,代表性锆石测试点位相应的206Pb/238U谐和年龄及阴极发光(CL)图像见图 3。
表 1 拉配泉组二段、三段流纹岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb测试结果Table 1. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb dating result of the second and third members of rhyolite of the Lapeiquan Formation编号 含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Pb U Th 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 2-1 80 925 771 0.8339 0.0801 0.0009 0.6158 0.0122 0.0557 0.0010 442 40 497 6 2-2 243 2620 3006 1.1472 0.0809 0.0009 0.6341 0.0116 0.0568 0.0009 484 36 502 6 2-3 92 1058 897 0.8472 0.0800 0.0009 0.6296 0.0116 0.0571 0.0010 495 37 496 6 2-4 128 1443 1418 0.9823 0.0808 0.0009 0.6363 0.0118 0.0571 0.0009 496 37 501 6 2-5 149 1663 1869 1.1239 0.0802 0.0009 0.6202 0.0116 0.0561 0.0009 455 37 498 6 2-6 53 623 443 0.7105 0.0814 0.0010 0.6350 0.0171 0.0566 0.0012 476 48 504 6 2-7 122 1320 1750 1.3258 0.0813 0.0009 0.6249 0.0118 0.0558 0.0010 443 38 504 6 2-8 93 1122 721 0.6422 0.0813 0.0009 0.6309 0.0118 0.0563 0.0010 463 38 504 6 2-9 55 670 432 0.6452 0.0801 0.0010 0.6334 0.0126 0.0574 0.0010 505 40 497 6 2-10 87 1054 806 0.7645 0.0797 0.0009 0.6195 0.0115 0.0564 0.0010 466 38 495 5 2-11 78 907 844 0.9299 0.0802 0.0009 0.6245 0.0121 0.0565 0.0010 472 39 497 6 2-12 99 1154 1013 0.8776 0.0808 0.0010 0.6177 0.0118 0.0555 0.0009 430 38 501 6 2-13 524 6685 3836 0.5738 0.0820 0.0009 0.6457 0.0114 0.0571 0.0009 496 36 508 5 2-14 102 1174 1053 0.8970 0.0811 0.0009 0.6502 0.0121 0.0582 0.0010 536 37 503 6 2-15 131 1470 1511 1.0278 0.0812 0.0009 0.6754 0.0123 0.0603 0.0010 615 36 503 5 2-16 55 663 452 0.6816 0.0809 0.0009 0.6205 0.0120 0.0556 0.0010 438 40 501 6 2-17 179 1996 2128 1.0662 0.0805 0.0009 0.6685 0.0123 0.0603 0.0010 613 36 499 6 2-18 107 1226 1223 0.9975 0.0817 0.0010 0.6883 0.0126 0.0611 0.0010 642 37 506 6 2-19 124 1415 1540 1.0882 0.0798 0.0009 0.6031 0.0110 0.0548 0.0009 405 37 495 5 2-20 142 1695 1593 0.9402 0.0782 0.0009 0.6063 0.0109 0.0562 0.0009 461 37 486 5 2-21 81 978 719 0.7354 0.0797 0.0009 0.6105 0.0117 0.0556 0.0010 435 39 494 6 2-22 50 603 391 0.6479 0.0802 0.0009 0.6104 0.0124 0.0552 0.0010 420 42 497 6 2-23 76 924 780 0.8441 0.0782 0.0008 0.6054 0.0116 0.0562 0.0010 460 40 485 5 2-24 142 1622 1721 1.0609 0.0798 0.0009 0.6289 0.0115 0.0571 0.0010 497 37 495 6 2-25 141 2072 3997 1.9291 0.0666 0.0007 0.5835 0.0105 0.0636 0.0011 727 37 415 4 2-26 64 779 494 0.6346 0.0798 0.0008 0.7140 0.0149 0.0649 0.0013 770 41 495 5 2-27 84 1050 552 0.5257 0.0798 0.0009 0.6214 0.0117 0.0565 0.0010 471 38 495 6 2-28 187 2098 2777 1.3238 0.0791 0.0008 0.6113 0.0109 0.0560 0.0009 454 37 491 5 2-29 127 1486 1399 0.9414 0.0801 0.0009 0.6255 0.0113 0.0566 0.0009 477 37 497 5 2-30 101 1136 1298 1.1429 0.0805 0.0009 0.6899 0.0135 0.0622 0.0011 681 36 499 6 2-31 127 1480 1573 1.0625 0.0789 0.0009 0.6184 0.0114 0.0568 0.0010 486 37 489 5 3-1 42 541 313 0.5783 0.0769 0.0008 0.6256 0.0108 0.0590 0.0009 567 34 478 5 3-2 61 552 338 0.6127 0.0905 0.0011 1.7886 0.0377 0.1433 0.0023 2267 28 559 7 3-3 56 698 444 0.6366 0.0776 0.0009 0.6587 0.0160 0.0616 0.0012 659 42 482 5 3-4 54 669 420 0.6277 0.0783 0.0009 0.6266 0.0105 0.0580 0.0009 531 32 486 5 3-5 62 763 520 0.6823 0.0778 0.0008 0.6297 0.0105 0.0587 0.0009 556 32 483 5 3-6 44 545 339 0.6215 0.0773 0.0009 0.6865 0.0133 0.0644 0.0010 755 34 480 6 3-7 49 603 359 0.5956 0.0784 0.0009 0.6569 0.0113 0.0608 0.0009 631 32 487 5 3-8 49 623 341 0.5477 0.0769 0.0008 0.6063 0.0103 0.0572 0.0009 499 33 478 5 3-9 42 543 282 0.5192 0.0766 0.0008 0.6186 0.0103 0.0585 0.0009 550 33 476 5 3-10 35 434 243 0.5603 0.0783 0.0009 0.6126 0.0108 0.0568 0.0009 483 35 486 5 3-11 59 707 457 0.6468 0.0785 0.0009 0.7416 0.0200 0.0685 0.0015 884 45 487 6 3-12 58 701 404 0.5764 0.0791 0.0008 0.7493 0.0121 0.0687 0.0011 891 32 490 5 3-13 41 509 275 0.5398 0.0788 0.0009 0.6216 0.0107 0.0572 0.0009 499 34 489 5 3-14 44 541 319 0.5883 0.0783 0.0008 0.6272 0.0106 0.0581 0.0009 533 35 486 5 3-15 59 743 451 0.6075 0.0779 0.0008 0.6172 0.0106 0.0575 0.0009 509 33 484 5 3-16 55 683 417 0.6095 0.0784 0.0009 0.6246 0.0105 0.0578 0.0009 521 34 487 5 3-17 62 774 497 0.6424 0.0774 0.0008 0.6642 0.0119 0.0623 0.0010 683 33 480 5 3-18 37 467 223 0.4783 0.0780 0.0009 0.6285 0.0112 0.0584 0.0010 546 36 484 5 3-19 47 596 322 0.5402 0.0779 0.0009 0.6289 0.0105 0.0585 0.0009 550 34 484 5 3-20 39 487 252 0.5185 0.0785 0.0009 0.6325 0.0111 0.0584 0.0009 546 35 487 5 3-21 55 686 406 0.5914 0.0776 0.0009 0.6311 0.0104 0.0590 0.0009 567 34 482 5 3-22 38 487 236 0.4847 0.0781 0.0008 0.6337 0.0111 0.0589 0.0010 562 36 485 5 3-23 67 833 550 0.6595 0.0775 0.0009 0.6287 0.0104 0.0588 0.0009 560 33 481 5 3-24 52 657 356 0.5421 0.0780 0.0009 0.6278 0.0112 0.0584 0.0009 544 34 484 5 3-25 51 655 379 0.5788 0.0765 0.0008 0.6296 0.0111 0.0597 0.0010 592 35 475 5 3-26 57 719 392 0.5451 0.0787 0.0009 0.6240 0.0105 0.0575 0.0009 512 33 488 5 3-27 49 621 404 0.6506 0.0770 0.0008 0.6002 0.0102 0.0565 0.0009 474 34 478 5 3-28 36 461 243 0.5263 0.0787 0.0009 0.6383 0.0109 0.0588 0.0009 560 34 488 5 3-29 32 421 177 0.4208 0.0781 0.0008 0.6038 0.0111 0.0560 0.0010 454 38 485 5 3-30 58 737 473 0.6415 0.0775 0.0008 0.6697 0.0112 0.0627 0.0009 697 32 481 5 3-31 40 514 247 0.4809 0.0782 0.0008 0.6328 0.0115 0.0587 0.0010 557 35 485 5 拉配泉组二段流纹岩(样品D1101)的锆石在单偏光镜下呈无色粉色,晶形较好,自形程度高,形态上呈柱状或长柱状,长50~150 μm,长宽比为1.2~2。在CL图像上可以清晰地看到锆石的振荡环带,显示典型的岩浆成因锆石特征(图 3-a)。对其中具有代表性的31粒锆石进行LA-ICP-MS U-Pb测年。Th、U含量变化总体较大,分别为391×10-6~3997×10-6和603×10-6~6885×10-6,Th/U值变化较大(表 1),介于0.13~3.78之间。31个测点除一个点具明显低的年龄值外(可能为试验误差),其余测点都位于谐和线上,其206Pb/238U年龄介于485±5~508±5 Ma之间,年龄加权平均值为497±2.0 Ma(MSWD=1.03)(图 3-b)。
拉配泉组三段流纹岩(样品DWTW01)的锆石在单偏光镜下呈无色、浅粉色,晶形较好,自形程度普遍较高,形态上呈柱状或长柱状,长60~130 μm,长宽比为1~2。在CL图像上可以清晰地看到锆石的振荡环带,显示典型的岩浆成因锆石特征(图 3-c)。31粒代表性锆石的Th、U含量变化较大,分别为177×10-6~550×10-6和421×10-6~833×10-6,Th/U值介于0.42~0.68之间,大部分在0.57左右(表 1)。31个测点除一个点明显高于其他点外,其余测点都位于谐和线上,206Pb/238U年龄介于475±5~490±5 Ma之间,年龄加权平均值为483.4±1.9 Ma(MSWD = 0.58)(图 3-d)。
4.2 全岩地球化学特征
拉配泉组二段流纹岩样品全岩地球化学分析结果见表 2。样品SiO2含量介于70.07%~78.55%之间,均值为73.90%;TiO2含量介于0.15%~0.19%之间,均值为0.17%,属低TiO2流纹岩;MgO含量介于0.32%~0.58%之间,均值为0.46%;CaO含量介于0.75%~2.60%之间,均值为1.63%;Na2O含量介于2.27%~5.97%之间,均值为4.39%;K2O含量介于1.57%~4.72%之间,均值为2.85%;Al2O3含量介于10.25%~14.38%之间,均值为12.71%。样品分异指数DI值高,在84.18~92.92之间,均大于80,平均为88.39,可能反映了岩石较高的分异程度或源岩为偏硅质的特征(邱家骧等,1991)。
表 2 拉配泉组二段流纹岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果Table 2. Major, trace and rare earth element analytical data of the rhyolite in the second member of the Lapeiquan Formation元素 D1101H1 D1101H2 D1101H3 D1101H4 D1101H5 D1101H6 D1101H7 D1101H8 SiO2 75.83 72.25 74.17 78.55 74.70 71.16 70.07 74.44 Al2O3 11.75 14.17 12.26 10.25 12.38 13.86 14.38 12.59 CaO 0.98 1.46 1.87 0.75 1.10 2.60 2.54 1.70 MgO 0.36 0.46 0.43 0.32 0.58 0.51 0.53 0.48 K2O 4.05 1.91 4.22 4.72 2.79 1.85 1.57 1.69 Na2O 3.45 5.86 2.97 2.27 4.25 5.29 5.97 5.06 TiO2 0.16 0.17 0.16 0.15 0.17 0.18 0.17 0.19 P2O5 0.021 0.019 0.024 0.020 0.021 0.022 0.024 0.022 MnO 0.037 0.050 0.053 0.034 0.053 0.069 0.064 0.053 烧失量 0.66 0.65 0.93 0.54 0.74 0.89 1.18 0.85 TFe2O3 2.10 2.47 2.54 1.94 2.72 3.25 3.07 2.58 BaO 0.15 0.07 0.18 0.19 0.12 0.07 0.06 0.06 总量 99.55 99.54 99.81 99.73 99.62 99.75 99.63 99.72 K2O/Na2O 0.85 3.07 0.70 0.48 1.52 2.86 3.80 2.99 FeO/MgO 5.25 4.83 5.32 5.46 4.22 5.74 5.21 4.84 A/NK 1.17 1.21 1.30 1.16 1.24 1.30 1.25 1.24 A/CNK 0.99 0.99 0.95 1.00 1.03 0.90 0.89 0.95 分异指数DI 91.68 88.80 87.23 92.92 89.28 84.18 84.91 88.12 Mg# 25.35 26.95 25.11 24.62 29.69 23.71 25.48 26.93 Li 1.58 1.55 1.92 1.22 1.89 1.27 1.62 1.48 Be 2.73 3.70 1.83 2.38 2.76 4.21 4.06 2.71 Sc 4.57 5.3 4.88 3.97 4.97 4.91 5.32 5.15 V 1.64 2.94 2.54 1.53 2.66 2.99 2.72 2.36 Cr 2.03 5 4.4 6.23 6.73 4.83 6.16 5.25 Co 164 126 174 181 152 124 99.5 134 Ni 7.59 5.68 7.26 10.6 11.3 6.51 5.35 5.29 Cu 1.14 1.14 1.95 1.28 1.93 1.35 1.61 1.07 Zn 60.7 80.5 61.9 61.2 85.6 76.2 79.3 59.4 Ga 14.9 19.4 21.3 12.2 17.2 25.3 22.3 18.7 Ge 1.14 1.37 1.66 0.886 1.24 2.06 1.68 1.59 As 0.99 1.14 1.39 1.14 1.12 1.60 1.53 1.33 Rb 92.9 46.4 96.1 89.2 67.5 47.1 44.5 44.1 Sr 92 182 181 74.4 124 286 249 172 Y 47.10 53.89 61.01 41.95 58.38 62.87 60.68 57.83 Zr 304 332 306 279 343 325 321 349 Nb 19.62 20.99 19.85 18.86 22.90 22.21 21.53 23.28 Sb 0.66 0.60 0.92 0.57 0.55 1.39 1.14 0.83 Ba 1470 679 1720 1830 1100 683 484 554 Nb/Ta 11.43 12.36 11.71 11.62 12.57 13.02 13.44 13.04 Rb/Nb 4.74 2.21 4.84 4.73 2.95 2.12 2.07 1.89 Rb/Sr 1.01 0.25 0.53 1.20 0.54 0.16 0.18 0.26 Sr/Y 1.95 3.38 2.97 1.77 2.12 4.55 4.10 2.97 La 62.1 71.4 62.5 57.3 72.2 66 62.3 70.5 Ce 107 113 111 103 122 120 111 124 Pr 12.5 13.5 12.5 11.2 14.3 13.4 12.3 14 Nd 45.3 49.3 46.7 42.1 52.5 50.2 45.2 51.4 Sm 8.29 9.28 9.31 8.08 9.56 9.56 8.52 9.99 Eu 0.96 1.22 1.74 0.79 1.14 1.44 1.32 1.14 Gd 8.18 8.66 9.23 8.26 9.29 9.52 8.75 9.37 Tb 1.28 1.44 1.48 1.16 1.52 1.56 1.42 1.54 Dy 7.7 8.82 9.29 7.26 9.37 9.94 9.39 9.18 Ho 1.53 1.79 1.85 1.4 1.98 2.11 1.94 1.96 Er 4.88 5.64 5.88 4.38 6 6.53 6.04 6 Tm 0.71 0.81 0.78 0.66 0.90 0.91 0.84 0.90 Yb 4.88 5.76 5.9 4.64 6.27 6.39 6.09 6.32 Lu 0.73 0.85 0.84 0.66 0.93 0.88 0.91 0.90 Hf 7.88 8.62 8.16 7.48 8.7 8.48 8.75 9.03 Ta 1.72 1.70 1.70 1.62 1.82 1.71 1.60 1.79 W 958 737 1080 1130 936 835 611 843 Pb 6.81 5.62 8.47 6.04 5.57 8.62 6.96 5.72 Th 23.5 24.8 23.3 21.4 26 24.8 23.9 26.7 U 5.87 7.25 8.19 4.82 7.01 7.83 7.6 6.92 LREE 283.25 311.59 304.77 264.42 330.08 323.48 301.32 328.87 HREE 29.88 33.76 35.25 28.42 36.27 37.84 35.38 36.17 ∑REE 313.14 345.36 340.02 292.84 366.34 361.31 336.70 365.04 LREE/HREE 9.48 9.23 8.65 9.30 9.10 8.55 8.52 9.09 (La/Yb)N 12.73 12.40 10.59 12.35 11.52 10.33 10.23 11.16 δEu 0.12 0.14 0.19 0.10 0.12 0.15 0.15 0.12 TZr/℃ 847 847 842 845 862 833 828 862 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量、稀土元素含量单位为10-6;A/NK= Al2O3 /(Na2O+ K2O); A/CNK= Al2O3 /(GaO+ Na2O+ K2O); DI=Qz+Qr+Ab+Ne+Lc+Kp;Mg#=100*(MgO/40.3044)/(MgO/40.3044+ TFeO/71.844);δEu=2Eu/(Sm+Gd); TZr/℃计算据Watson et al.(1983)温度计算公式 在TAS图解(图 4-a)上,样品点落入流纹岩区域。流纹岩总体具有较高的(Na2O+K2O)含量,介于6.75%~7.77%之间,均值为7.24%,除D1101H1、D1101H3、D1101H4样品的Na2O/K2O < 1外(可能存在局部钾长石含量较高),其余5个样品的Na2O/K2O>1.5,为钠质型(邱家骧等,1991)。在SiO2-K2O图解(图 4-b)上,样品主要为钙碱性系列,少量为高钾钙碱性系列。在AR-SiO2图(图 5-b)中,样品点位于钙碱性和碱性界线附近。A/CNK值介于0.89~1.03之间,A/NK值介于1.16~1.30之间,均值为1.42,在A/CNK-A/NK图解(图 5-a)中,样品点大部分位于准铝质范围,少量位于准铝质—过铝质过渡带。
![]() 图 4 拉配泉组流纹岩TAS(a)和SiO2-K2O图解(b)(底图据Le,1984)Figure 4. TAS(a) and K2O-SiO2(b)diagrams of rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation
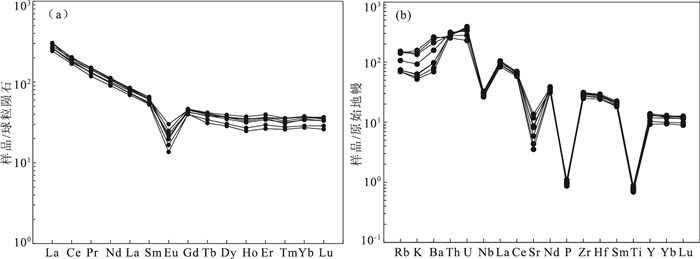
图 4 拉配泉组流纹岩TAS(a)和SiO2-K2O图解(b)(底图据Le,1984)Figure 4. TAS(a) and K2O-SiO2(b)diagrams of rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation稀土元素总量(∑REE)介于292.84×10-6~366.34×10-6之间,平均值为340.09×10-6。轻、重稀土元素含量比值LREE/HREE介于8.52~9.48之间,平均值为8.99;(La/Yb)N值为10.23~12.73,平均值为11.41。稀土元素标准化配分曲线总体呈右倾形式(图 6-a),轻、重稀土元素分馏明显。δEu=0.10~0.19,平均值为0.14,反映了较强烈的负Eu异常。在微量元素蛛网图(图 6-b)中,8个样品具有相似的配分模式,表现为大离子亲石元素(LILE)相对高场强元素(HFSE)明显富集,La、Nd、Ce、Sm、U、Th等相对富集,Nb、Ti等相对亏损。
![]() 图 6 拉配泉组流纹岩稀土元素配分图(a)和微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化值据Sun et al., 1989)Figure 6. REE patterns(a) and trace element spider diagrams(b)of the rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation
图 6 拉配泉组流纹岩稀土元素配分图(a)和微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化值据Sun et al., 1989)Figure 6. REE patterns(a) and trace element spider diagrams(b)of the rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation5. 讨论
5.1 火山岩形成的时代
已有研究表明,阿尔金北缘地区拉配泉组是喀腊大湾矿集区的主要赋矿地层(武彬等,2019),然而,对于其沉积时代及地层划分的认识还存在不足。20世纪80年代,1:20万索尔库里幅区域地质调查报告将其归为蓟县系塔昔达坂群(新疆维吾尔自治区地质局区域地质调查大队, 1981);2008年,1:5万区域地质调查报告将其划分为3段,归为奥陶系(新疆维吾尔自治区地质矿产勘查第一地质大队,2008)。近年来,不断有学者对该地区开展研究工作,陈柏林等(2006)运用SHRIMP锆石U-Pb方法对研究区沉积岩系中的中酸性火山岩进行了测年,获得477~485 Ma的年龄;倪康等(2017)对区内拉配泉组三段流纹岩开展了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年,获得488 Ma的年龄。本文研究表明,拉配泉组二段形成年龄为497±2.0 Ma,为晚寒武世,三段流纹岩年龄为483.4±1.9 Ma,与前人年龄数据相近,为早奥陶世。这一结果表明,拉配泉组属于晚寒武世—早奥陶世。
5.2 岩石成因
拉配泉组二段流纹岩地球化学特征显示,其具有高的SiO2含量(70.07%~78.55%)、低的TiO2(0.15%~0.19%)、Fe2O3(1.94%~3.25%)、Al2O3(10.25%~14.38%)和MgO(0.32%~0.58%)含量,大离子亲石元素LILE,如Rb、Ba等和轻稀土元素(LREE)明显富集,高场强元素Nb、Ta、Ti、Hf等相对亏损。以上特征表明,流纹岩具有壳源成因(Zen,1986;Xu et al., 2009;李成志等,2020)。
流纹岩具有较平坦的稀土元素配分模式,明显的Sr、Eu、Ti和P负异常和较高的Zr、Y、Ce含量,这些特征与A型花岗岩一致(Whalen et al., 1987;King et al., 1997;邱检生等,2000)。(Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)-(Na2O+K2O)/GaO和10000×Ga/Al-Zr图解(图 7)显示,拉配泉组流纹岩样品均位于A型花岗岩区域,具有A型花岗岩特征。A型花岗岩与高分异花岗岩根据元素含量特征可进行区分(胡培远等,2016),S型花岗岩一般为强过铝质,明显不同于本文流纹岩铝质含量特征,高分异的I型花岗岩具全铁含量小于1%的特征及较高的Rb含量(大于270×10-6),均明显不同于本文结果(王强等,2000;胡培远等,2016)。花岗岩的形成温度可通过Zr饱和温度(TZr)计算,由于锆石是花岗岩中较早结晶的矿物,Zr饱和温度可近似代表岩石结晶温度(胡培远等,2016)。根据Watson et al.(1983)温度计算公式,得到流纹岩样品锆石饱和温度为828~862℃,平均温度为845℃,符合A型花岗岩形成于较高温度的特征,高于S型花岗岩锆石饱和温度(平均764℃)和I型花岗岩锆石饱和温度(平均781℃)(King et al., 1997)。
![]() 图 7 拉配泉组流纹岩Zr+Nb+Ce+Y-(Na2O+K2O)/CaO(a)和10000 Ga/Al-Zr(b)图解(据Whalen et al., 1987)Figure 7. Zr+Nb+Ce+Y-(Na2O+K2O)/GaO(a) and 10000×Ga /Al-Zr(b)diagrams of the rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation
图 7 拉配泉组流纹岩Zr+Nb+Ce+Y-(Na2O+K2O)/CaO(a)和10000 Ga/Al-Zr(b)图解(据Whalen et al., 1987)Figure 7. Zr+Nb+Ce+Y-(Na2O+K2O)/GaO(a) and 10000×Ga /Al-Zr(b)diagrams of the rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation结合前人研究成果,本次研究通过地球化学分析认为,拉配泉组二段主要来源于地壳物质的部分熔融,主要依据为:①岩石微量元素比值显示, Y/Nb值为2.22~3.07,大于地幔成因的岩石(< 1.2),与壳源成因岩石(>1.2)相符(Eby,1992);②Zr-Zr/Sm图解(图 8-a)总体呈正相关,显示其成岩过程以部分熔融为主;③样品Mg#值为24~30(平均26),明显低于地幔部分熔融形成的岩石(朱弟成等,2006;李成志等,2020)(Mg#=68),与地壳物质熔融相符;④在C/MF-A/MF图解(图 8-b)中,样品点全部位于变质杂砂岩部分熔融区域。区域上,与陈柏林等(2016)研究认为陆壳物质对喀腊大湾地区中酸性火山岩影响作用较强的结果相符。Eu(δEu=0.10~0.19)、Sr和Ti负异常说明,岩浆源区可能存在斜长石残留(Rapp et al., 1991;Martin,1999;李梦瞳等,2020)。拉配泉组二段流纹岩成因可能主要是地壳物质的部分熔融,同时源区可能存在斜长石的残留。
5.3 构造环境
已有研究表明,在新元古代早期阿尔金地区与西北地区其他微地块一起成为Rodinia超大陆的一部分(倪康等,2017)。恰什坎萨伊沟南口双峰式火山岩年龄(750 Ma)表明,阿尔金北缘此时已经开始进入裂解阶段(Schiano et al., 2010),说明阿尔金北缘在新元古代已经开始裂解而形成初始洋盆,代表北阿尔金洋的形成。在贝壳滩—红柳泉地区发现高压低温变质带榴辉岩,于中寒武世(512±3 Ma)进入榴辉岩相峰期变质阶段,反映俯冲至少在中寒武世已经开始(杨经绥等,2008)。在520~495 Ma期间,北阿尔金洋板块回转引起了弧后伸展,导致软流圈上涌、岩浆岩发育(Ye et al.,2018)。490~460 Ma为大洋板块再次俯冲碰撞期(陈柏林等,2016;Ye et al.,2018)。本文拉配泉组二段流纹岩年龄为497±2 Ma,与上述大洋板块回转代表的时限相符,其形成构造环境可能为弧后伸展阶段,拉配泉组三段流纹岩483.4±1.9 Ma,与大洋板块再次俯冲时限相符(陈柏林等,2016;Ye et al.,2018)。
A型火成岩形成的构造背景具有独特的构造指示意义,前人根据构造背景把A型花岗岩定义为非造山花岗岩和碰撞后花岗岩(王强等,2000;李成志等,2020),其中A1型来源于地幔,代表非造山的大陆裂谷,A2型由地壳或岛弧派生,主要形成于碰撞后的拉张环境或板片俯冲引起的岩石圈伸展环境(蒋少涌等,2008)。在Y-Nb-Ce(图 9-a)和Y/Nb-Ce/Nb(图 9-b)图解中,拉配泉组火山岩样品点均落入A2型花岗岩区域。
![]() 图 9 拉配泉组流纹岩A1、A2类型判别图(据Eby,1992)a—Y-Nb-Ce图解;b—Y/Nb-Ce/Nb图解Figure 9. Diagrams for division of type A1 and type A2 of the rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation
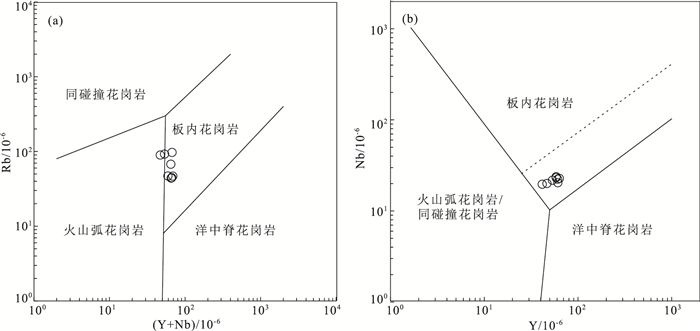
图 9 拉配泉组流纹岩A1、A2类型判别图(据Eby,1992)a—Y-Nb-Ce图解;b—Y/Nb-Ce/Nb图解Figure 9. Diagrams for division of type A1 and type A2 of the rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation不同的构造环境背景下形成的岩浆岩岩石类型不同,通过岩浆岩地球化学组分特征可以判断其形成的构造背景(董昕,2008;李成志等,2020)。拉配泉地区流纹岩在Y-Nb和(Y+Nb)-Rb构造环境判别图(图 10)中,除个别样品点落入火山弧花岗岩和板内花岗岩分界线附近外,其余样品点落在板内花岗岩区域,说明拉配泉组二段火山岩形成于伸展构造环境。结合区域构造背景及岩石地球化学特征,笔者认为,拉配泉组二段火山岩形成于北阿尔金洋俯冲回转引起的弧后伸展环境。
![]() 图 10 拉配泉组流纹岩(Y+Nb)-Rb(a)与Y-Nb(b)图解(据Pearce et al., 1984)Figure 10. (Y+Nb)-Rb(a) and Y-Nb(b)diagrams of the rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation
图 10 拉配泉组流纹岩(Y+Nb)-Rb(a)与Y-Nb(b)图解(据Pearce et al., 1984)Figure 10. (Y+Nb)-Rb(a) and Y-Nb(b)diagrams of the rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation6. 结论
(1) 通过对阿尔金喀腊大湾地区拉配泉组流纹岩进行LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年,准确限定拉配泉组二段流纹岩年龄为497±2.0 Ma,三段流纹岩年龄为483.4±1.9 Ma,拉配泉组二段至三段的形成时代为晚寒武世—早奥陶世。
(2) 拉配泉组二段流纹岩具有富硅、贫铁、低镁,富大离子亲石元素和轻稀土元素,相对亏损高场强元素的特征,结合微量元素分析结果,拉配组二段流纹岩的成因可能主要是地壳物质的部分熔融,同时源区可能存在斜长石的残留。
(3) 岩石地球化学特征显示,拉配泉组二段流纹岩具有A型火成岩特征,进一步划属于A2类。结合研究区前人构造地质背景研究成果,推测拉配泉组二段流纹岩构造环境为北阿尔金洋回转引起的弧后伸展环境。
致谢: 感谢中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心张健高级工程师,中国科学院地球化学研究所漆亮老师在实验分析测试中给予的帮助。感谢审稿专家对本文提出的宝贵意见。 -
图 1 区域构造单元划分(a)和新疆喀腊大湾地质简图(b)(据陈宣华等,2009)
1—中新统上干柴沟组; 2—中新统下油砂山组; 3—渐新统下干柴沟组; 4—上石炭统因格布拉克组; 5—拉配泉组三段; 6—拉配泉组二段; 7—拉配泉组一段; 8—金燕山组;9—太古宇达格拉格布拉克组; 10—志留纪二长花岗岩;11—志留纪花岗岩;12—志留纪辉长岩;13—奥陶纪闪长岩;14—奥陶纪花岗岩;15—寒武纪闪长岩;16—寒武纪花岗闪长岩;17—寒武纪花岗岩;18—采样位置;19—铁矿床;20—铅锌矿床;21—银铅矿床;22—地质界线;23—逆冲断层;24—板块缝合带;25—走滑断层
Figure 1. Division of regional tectonic units(a) and schematic geologic map of Kaladawan area in Xinjiang(b)
图 4 拉配泉组流纹岩TAS(a)和SiO2-K2O图解(b)(底图据Le,1984)
Figure 4. TAS(a) and K2O-SiO2(b)diagrams of rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation
图 6 拉配泉组流纹岩稀土元素配分图(a)和微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化值据Sun et al., 1989)
Figure 6. REE patterns(a) and trace element spider diagrams(b)of the rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation
图 7 拉配泉组流纹岩Zr+Nb+Ce+Y-(Na2O+K2O)/CaO(a)和10000 Ga/Al-Zr(b)图解(据Whalen et al., 1987)
Figure 7. Zr+Nb+Ce+Y-(Na2O+K2O)/GaO(a) and 10000×Ga /Al-Zr(b)diagrams of the rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation
图 8 拉配泉组流纹岩Zr-Zr/Sm(a,据Schiano et al., 2010)和C/MF-A/MF(b,据Altherr et al., 2000)图解
A/MF—摩尔Al2O3/(MgO+TFeO); C/MF—摩尔CaO/(MgO+TFeO)
Figure 8. Zr-Zr/Sm(b) and C/MF-A/MF diagrams of rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation
图 9 拉配泉组流纹岩A1、A2类型判别图(据Eby,1992)
a—Y-Nb-Ce图解;b—Y/Nb-Ce/Nb图解
Figure 9. Diagrams for division of type A1 and type A2 of the rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation
图 10 拉配泉组流纹岩(Y+Nb)-Rb(a)与Y-Nb(b)图解(据Pearce et al., 1984)
Figure 10. (Y+Nb)-Rb(a) and Y-Nb(b)diagrams of the rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation
表 1 拉配泉组二段、三段流纹岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb测试结果
Table 1 Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb dating result of the second and third members of rhyolite of the Lapeiquan Formation
编号 含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Pb U Th 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 2-1 80 925 771 0.8339 0.0801 0.0009 0.6158 0.0122 0.0557 0.0010 442 40 497 6 2-2 243 2620 3006 1.1472 0.0809 0.0009 0.6341 0.0116 0.0568 0.0009 484 36 502 6 2-3 92 1058 897 0.8472 0.0800 0.0009 0.6296 0.0116 0.0571 0.0010 495 37 496 6 2-4 128 1443 1418 0.9823 0.0808 0.0009 0.6363 0.0118 0.0571 0.0009 496 37 501 6 2-5 149 1663 1869 1.1239 0.0802 0.0009 0.6202 0.0116 0.0561 0.0009 455 37 498 6 2-6 53 623 443 0.7105 0.0814 0.0010 0.6350 0.0171 0.0566 0.0012 476 48 504 6 2-7 122 1320 1750 1.3258 0.0813 0.0009 0.6249 0.0118 0.0558 0.0010 443 38 504 6 2-8 93 1122 721 0.6422 0.0813 0.0009 0.6309 0.0118 0.0563 0.0010 463 38 504 6 2-9 55 670 432 0.6452 0.0801 0.0010 0.6334 0.0126 0.0574 0.0010 505 40 497 6 2-10 87 1054 806 0.7645 0.0797 0.0009 0.6195 0.0115 0.0564 0.0010 466 38 495 5 2-11 78 907 844 0.9299 0.0802 0.0009 0.6245 0.0121 0.0565 0.0010 472 39 497 6 2-12 99 1154 1013 0.8776 0.0808 0.0010 0.6177 0.0118 0.0555 0.0009 430 38 501 6 2-13 524 6685 3836 0.5738 0.0820 0.0009 0.6457 0.0114 0.0571 0.0009 496 36 508 5 2-14 102 1174 1053 0.8970 0.0811 0.0009 0.6502 0.0121 0.0582 0.0010 536 37 503 6 2-15 131 1470 1511 1.0278 0.0812 0.0009 0.6754 0.0123 0.0603 0.0010 615 36 503 5 2-16 55 663 452 0.6816 0.0809 0.0009 0.6205 0.0120 0.0556 0.0010 438 40 501 6 2-17 179 1996 2128 1.0662 0.0805 0.0009 0.6685 0.0123 0.0603 0.0010 613 36 499 6 2-18 107 1226 1223 0.9975 0.0817 0.0010 0.6883 0.0126 0.0611 0.0010 642 37 506 6 2-19 124 1415 1540 1.0882 0.0798 0.0009 0.6031 0.0110 0.0548 0.0009 405 37 495 5 2-20 142 1695 1593 0.9402 0.0782 0.0009 0.6063 0.0109 0.0562 0.0009 461 37 486 5 2-21 81 978 719 0.7354 0.0797 0.0009 0.6105 0.0117 0.0556 0.0010 435 39 494 6 2-22 50 603 391 0.6479 0.0802 0.0009 0.6104 0.0124 0.0552 0.0010 420 42 497 6 2-23 76 924 780 0.8441 0.0782 0.0008 0.6054 0.0116 0.0562 0.0010 460 40 485 5 2-24 142 1622 1721 1.0609 0.0798 0.0009 0.6289 0.0115 0.0571 0.0010 497 37 495 6 2-25 141 2072 3997 1.9291 0.0666 0.0007 0.5835 0.0105 0.0636 0.0011 727 37 415 4 2-26 64 779 494 0.6346 0.0798 0.0008 0.7140 0.0149 0.0649 0.0013 770 41 495 5 2-27 84 1050 552 0.5257 0.0798 0.0009 0.6214 0.0117 0.0565 0.0010 471 38 495 6 2-28 187 2098 2777 1.3238 0.0791 0.0008 0.6113 0.0109 0.0560 0.0009 454 37 491 5 2-29 127 1486 1399 0.9414 0.0801 0.0009 0.6255 0.0113 0.0566 0.0009 477 37 497 5 2-30 101 1136 1298 1.1429 0.0805 0.0009 0.6899 0.0135 0.0622 0.0011 681 36 499 6 2-31 127 1480 1573 1.0625 0.0789 0.0009 0.6184 0.0114 0.0568 0.0010 486 37 489 5 3-1 42 541 313 0.5783 0.0769 0.0008 0.6256 0.0108 0.0590 0.0009 567 34 478 5 3-2 61 552 338 0.6127 0.0905 0.0011 1.7886 0.0377 0.1433 0.0023 2267 28 559 7 3-3 56 698 444 0.6366 0.0776 0.0009 0.6587 0.0160 0.0616 0.0012 659 42 482 5 3-4 54 669 420 0.6277 0.0783 0.0009 0.6266 0.0105 0.0580 0.0009 531 32 486 5 3-5 62 763 520 0.6823 0.0778 0.0008 0.6297 0.0105 0.0587 0.0009 556 32 483 5 3-6 44 545 339 0.6215 0.0773 0.0009 0.6865 0.0133 0.0644 0.0010 755 34 480 6 3-7 49 603 359 0.5956 0.0784 0.0009 0.6569 0.0113 0.0608 0.0009 631 32 487 5 3-8 49 623 341 0.5477 0.0769 0.0008 0.6063 0.0103 0.0572 0.0009 499 33 478 5 3-9 42 543 282 0.5192 0.0766 0.0008 0.6186 0.0103 0.0585 0.0009 550 33 476 5 3-10 35 434 243 0.5603 0.0783 0.0009 0.6126 0.0108 0.0568 0.0009 483 35 486 5 3-11 59 707 457 0.6468 0.0785 0.0009 0.7416 0.0200 0.0685 0.0015 884 45 487 6 3-12 58 701 404 0.5764 0.0791 0.0008 0.7493 0.0121 0.0687 0.0011 891 32 490 5 3-13 41 509 275 0.5398 0.0788 0.0009 0.6216 0.0107 0.0572 0.0009 499 34 489 5 3-14 44 541 319 0.5883 0.0783 0.0008 0.6272 0.0106 0.0581 0.0009 533 35 486 5 3-15 59 743 451 0.6075 0.0779 0.0008 0.6172 0.0106 0.0575 0.0009 509 33 484 5 3-16 55 683 417 0.6095 0.0784 0.0009 0.6246 0.0105 0.0578 0.0009 521 34 487 5 3-17 62 774 497 0.6424 0.0774 0.0008 0.6642 0.0119 0.0623 0.0010 683 33 480 5 3-18 37 467 223 0.4783 0.0780 0.0009 0.6285 0.0112 0.0584 0.0010 546 36 484 5 3-19 47 596 322 0.5402 0.0779 0.0009 0.6289 0.0105 0.0585 0.0009 550 34 484 5 3-20 39 487 252 0.5185 0.0785 0.0009 0.6325 0.0111 0.0584 0.0009 546 35 487 5 3-21 55 686 406 0.5914 0.0776 0.0009 0.6311 0.0104 0.0590 0.0009 567 34 482 5 3-22 38 487 236 0.4847 0.0781 0.0008 0.6337 0.0111 0.0589 0.0010 562 36 485 5 3-23 67 833 550 0.6595 0.0775 0.0009 0.6287 0.0104 0.0588 0.0009 560 33 481 5 3-24 52 657 356 0.5421 0.0780 0.0009 0.6278 0.0112 0.0584 0.0009 544 34 484 5 3-25 51 655 379 0.5788 0.0765 0.0008 0.6296 0.0111 0.0597 0.0010 592 35 475 5 3-26 57 719 392 0.5451 0.0787 0.0009 0.6240 0.0105 0.0575 0.0009 512 33 488 5 3-27 49 621 404 0.6506 0.0770 0.0008 0.6002 0.0102 0.0565 0.0009 474 34 478 5 3-28 36 461 243 0.5263 0.0787 0.0009 0.6383 0.0109 0.0588 0.0009 560 34 488 5 3-29 32 421 177 0.4208 0.0781 0.0008 0.6038 0.0111 0.0560 0.0010 454 38 485 5 3-30 58 737 473 0.6415 0.0775 0.0008 0.6697 0.0112 0.0627 0.0009 697 32 481 5 3-31 40 514 247 0.4809 0.0782 0.0008 0.6328 0.0115 0.0587 0.0010 557 35 485 5 表 2 拉配泉组二段流纹岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 2 Major, trace and rare earth element analytical data of the rhyolite in the second member of the Lapeiquan Formation
元素 D1101H1 D1101H2 D1101H3 D1101H4 D1101H5 D1101H6 D1101H7 D1101H8 SiO2 75.83 72.25 74.17 78.55 74.70 71.16 70.07 74.44 Al2O3 11.75 14.17 12.26 10.25 12.38 13.86 14.38 12.59 CaO 0.98 1.46 1.87 0.75 1.10 2.60 2.54 1.70 MgO 0.36 0.46 0.43 0.32 0.58 0.51 0.53 0.48 K2O 4.05 1.91 4.22 4.72 2.79 1.85 1.57 1.69 Na2O 3.45 5.86 2.97 2.27 4.25 5.29 5.97 5.06 TiO2 0.16 0.17 0.16 0.15 0.17 0.18 0.17 0.19 P2O5 0.021 0.019 0.024 0.020 0.021 0.022 0.024 0.022 MnO 0.037 0.050 0.053 0.034 0.053 0.069 0.064 0.053 烧失量 0.66 0.65 0.93 0.54 0.74 0.89 1.18 0.85 TFe2O3 2.10 2.47 2.54 1.94 2.72 3.25 3.07 2.58 BaO 0.15 0.07 0.18 0.19 0.12 0.07 0.06 0.06 总量 99.55 99.54 99.81 99.73 99.62 99.75 99.63 99.72 K2O/Na2O 0.85 3.07 0.70 0.48 1.52 2.86 3.80 2.99 FeO/MgO 5.25 4.83 5.32 5.46 4.22 5.74 5.21 4.84 A/NK 1.17 1.21 1.30 1.16 1.24 1.30 1.25 1.24 A/CNK 0.99 0.99 0.95 1.00 1.03 0.90 0.89 0.95 分异指数DI 91.68 88.80 87.23 92.92 89.28 84.18 84.91 88.12 Mg# 25.35 26.95 25.11 24.62 29.69 23.71 25.48 26.93 Li 1.58 1.55 1.92 1.22 1.89 1.27 1.62 1.48 Be 2.73 3.70 1.83 2.38 2.76 4.21 4.06 2.71 Sc 4.57 5.3 4.88 3.97 4.97 4.91 5.32 5.15 V 1.64 2.94 2.54 1.53 2.66 2.99 2.72 2.36 Cr 2.03 5 4.4 6.23 6.73 4.83 6.16 5.25 Co 164 126 174 181 152 124 99.5 134 Ni 7.59 5.68 7.26 10.6 11.3 6.51 5.35 5.29 Cu 1.14 1.14 1.95 1.28 1.93 1.35 1.61 1.07 Zn 60.7 80.5 61.9 61.2 85.6 76.2 79.3 59.4 Ga 14.9 19.4 21.3 12.2 17.2 25.3 22.3 18.7 Ge 1.14 1.37 1.66 0.886 1.24 2.06 1.68 1.59 As 0.99 1.14 1.39 1.14 1.12 1.60 1.53 1.33 Rb 92.9 46.4 96.1 89.2 67.5 47.1 44.5 44.1 Sr 92 182 181 74.4 124 286 249 172 Y 47.10 53.89 61.01 41.95 58.38 62.87 60.68 57.83 Zr 304 332 306 279 343 325 321 349 Nb 19.62 20.99 19.85 18.86 22.90 22.21 21.53 23.28 Sb 0.66 0.60 0.92 0.57 0.55 1.39 1.14 0.83 Ba 1470 679 1720 1830 1100 683 484 554 Nb/Ta 11.43 12.36 11.71 11.62 12.57 13.02 13.44 13.04 Rb/Nb 4.74 2.21 4.84 4.73 2.95 2.12 2.07 1.89 Rb/Sr 1.01 0.25 0.53 1.20 0.54 0.16 0.18 0.26 Sr/Y 1.95 3.38 2.97 1.77 2.12 4.55 4.10 2.97 La 62.1 71.4 62.5 57.3 72.2 66 62.3 70.5 Ce 107 113 111 103 122 120 111 124 Pr 12.5 13.5 12.5 11.2 14.3 13.4 12.3 14 Nd 45.3 49.3 46.7 42.1 52.5 50.2 45.2 51.4 Sm 8.29 9.28 9.31 8.08 9.56 9.56 8.52 9.99 Eu 0.96 1.22 1.74 0.79 1.14 1.44 1.32 1.14 Gd 8.18 8.66 9.23 8.26 9.29 9.52 8.75 9.37 Tb 1.28 1.44 1.48 1.16 1.52 1.56 1.42 1.54 Dy 7.7 8.82 9.29 7.26 9.37 9.94 9.39 9.18 Ho 1.53 1.79 1.85 1.4 1.98 2.11 1.94 1.96 Er 4.88 5.64 5.88 4.38 6 6.53 6.04 6 Tm 0.71 0.81 0.78 0.66 0.90 0.91 0.84 0.90 Yb 4.88 5.76 5.9 4.64 6.27 6.39 6.09 6.32 Lu 0.73 0.85 0.84 0.66 0.93 0.88 0.91 0.90 Hf 7.88 8.62 8.16 7.48 8.7 8.48 8.75 9.03 Ta 1.72 1.70 1.70 1.62 1.82 1.71 1.60 1.79 W 958 737 1080 1130 936 835 611 843 Pb 6.81 5.62 8.47 6.04 5.57 8.62 6.96 5.72 Th 23.5 24.8 23.3 21.4 26 24.8 23.9 26.7 U 5.87 7.25 8.19 4.82 7.01 7.83 7.6 6.92 LREE 283.25 311.59 304.77 264.42 330.08 323.48 301.32 328.87 HREE 29.88 33.76 35.25 28.42 36.27 37.84 35.38 36.17 ∑REE 313.14 345.36 340.02 292.84 366.34 361.31 336.70 365.04 LREE/HREE 9.48 9.23 8.65 9.30 9.10 8.55 8.52 9.09 (La/Yb)N 12.73 12.40 10.59 12.35 11.52 10.33 10.23 11.16 δEu 0.12 0.14 0.19 0.10 0.12 0.15 0.15 0.12 TZr/℃ 847 847 842 845 862 833 828 862 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量、稀土元素含量单位为10-6;A/NK= Al2O3 /(Na2O+ K2O); A/CNK= Al2O3 /(GaO+ Na2O+ K2O); DI=Qz+Qr+Ab+Ne+Lc+Kp;Mg#=100*(MgO/40.3044)/(MgO/40.3044+ TFeO/71.844);δEu=2Eu/(Sm+Gd); TZr/℃计算据Watson et al.(1983)温度计算公式 -
Altherr R, Holl A, Hegner E, et al. High-potassium, calc-alkaline I-type plutonism in the European Variscides: Northern Vosges(France)and Northern Schwarzwald(Germany)[J]. Lithos, 2000, 50(1/2/3): 51-73.
Eby G N. Chemical Subdivision of the A-type granitoids: Petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992, 20(7): 641. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:CSOTAT>2.3.CO;2
Hu Z C, Liu Y S, Chen L, et al. Contrasting matrix induced elemental fractionation in NIST SRM and rock glasses during laser ablation ICP-MS analysis at high spatial resolution[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2011, 26(2): 425-430. doi: 10.1039/C0JA00145G
King P L, White A J R, Chappell B W, et al. Characterization and Origin of aluminous A-type granites from the Lachlan Fold Belt, Southeastern Australia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1997, 38(3): 371-391. doi: 10.1093/petroj/38.3.371
Le M R W. A proposal by the IUGS subcommission on the systematics of igneous rocks for a chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkali silica(TAS)diagram[J]. Australian. J. Earth Sci., 1984, 31: 243-255. doi: 10.1080/08120098408729295
Liu L, Wang C, Chen D L, et al. Petrology and geochronology of HP-UHP rocks from the south Altyn Tagh, northwestern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 35: 232-244. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.10.007
Liu Y J, Neubauer F, Genser J, et al. Geochronology of the initiation and displacement of the Altyn strike-slip fault, western China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2006, 29(2/3): 243-252.
Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced meltperidotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements inzircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010a, 51(1/2): 537-571.
Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Zong K Q, et al. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotopeand trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010b, 55(15): 1535-1546. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4
Ludwig K R. User's manual for isoplot 3.0: A geochemical toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J]. Berkely Geochronology Center Special Publication, 2003, 4: 1-70.
Martin H. Adakitic magmas: Modern analogues of Archaean granitoids[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46(3): 411-429. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00076-0
Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4): 956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
Qi L, Hu J, Gregoire D C. Determination of trace elements in granites by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Talanta, 2000, 51(3): 507-513. doi: 10.1016/S0039-9140(99)00318-5
Rapp R P, Watson E B, Miller C F. Partial melting of amphibolite/eclogite and the origin of Archean trondhjemites and tonalites[J]. Precambrian Research, 1991, 51(1/4): 1-25.
Schiano P, Monzier M, Eissen J P, et al. Simple mixing as the major control of the evolution of volcanic suites in the Ecuadorian Andes[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2010, 160(2): 297-312. doi: 10.1007/s00410-009-0478-2
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 1989, 42(1): 13-345.
Watson E B, Harrison T M. Zircon saturation revisited: Temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983, 64(2): 295-304. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(83)90211-X
Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell B W. A type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95(4): 407-419. doi: 10.1007/BF00402202
Xu W L, Ji W Q, Pei F P, et al. Triassic volcanism in eastern Heilongjiang and Jilin Provinces, NE China: Chronology, geochemistry, and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 34(3): 392-402. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.07.001
Ye X T, Zhang C L, Wang A G, et al. Early Paleozoic slab rollback in the North Altun, Northwest China: New evidence from mafic intrusions and high-Mg andesites[J]. Lithos phere, 2018, 10: 687-707.
Zen E A. Aluminum enrichment in silicate melts by fractional crystallization: Some mineralogic and petrographic constraints[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1986, 27(5): 1095-1117. doi: 10.1093/petrology/27.5.1095
陈柏林, 崔玲玲, 白彦飞, 等. 阿尔金断裂走滑位移的新认识——来自阿尔金山东段地质找矿进展的启示[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(11): 3387-3396. 陈柏林, 李松彬, 蒋荣宝, 等. 阿尔金喀腊大湾地区中酸性火山岩SHRIMP年龄及其构造环境[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(4): 708-727. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.04.008 陈宣华, 尹安, Gehrels G E, 等. 阿尔金山东段地质热年代学与构造演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2009, 16(3): 207-219. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.03.017 陈正乐, 万景林, 王小凤, 等. 阿尔金断裂8Ma左右的快速走滑及其地质意义[J]. 地球学报, 2002, 23(4): 295-300. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2002.04.002 崔军文, 唐哲民, 邓晋福, 等. 阿尔金断裂系[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1999: 1-249. 董昕. 西藏冈底斯带西南部中新生代花岗岩年代学与地球化学[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2008. 高林志, 尹崇玉, 张恒, 等. 云南晋宁地区柳坝塘组凝灰岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其对晋宁运动的制约[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(9): 1595-1604. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/cn/article/id/20150901 胡培远, 李才, 吴彦旺, 等. 青藏高原古特提斯洋早石炭世弧后拉张: 来自A型花岗岩的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(4): 1219-1231. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201604020.htm 蒋少涌, 赵葵东, 姜耀辉, 等. 十杭带湘南-桂北段中生代A型花岗岩带成岩成矿特征及成因讨论[J]. 高校地质学报, 2008, 14(4): 496-509. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200804006.htm 李猛, 查显锋, 胡朝斌, 等. 东昆仑西段阿确墩地区白沙河岩组锆石U-Pb年龄——对前寒武纪基底演化的约束[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(1): 42-58. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/cn/article/id/20210105 李梦瞳, 唐军, 王志伟, 等. 内蒙中部苏左旗早石炭世火山岩年代学与地球化学研究: 对中亚造山带东部石炭纪构造演化和地壳属性的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(3): 801-819. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202003010.htm 李成志, 杨文光, 朱利东, 等. 西藏墨竹工卡地区早侏罗世花岗岩地球化学、岩石成因及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(5): 1556-1572. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202005007.htm 刘良, 孙勇, 校培喜, 等. 阿尔金发现超高压(>3.8GPa)石榴二辉橄榄岩[J]. 科学通报, 2002, 47(9): 657-662. 倪康, 武彬, 叶现韬. 新疆阿尔金北缘拉配泉组流纹岩的锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 华东地质, 2017, 38(3): 168-174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HSDZ201703003.htm 戚学祥, 李海兵, 吴才来, 等. 北阿尔金恰什坎萨依花岗闪长岩的SHRIMP U-Pb锆石定年及其地质意义[J]. 科学通报, 2005, 50(6): 571-576. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB20050600B.htm 邱家骧, 林景仟. 岩石化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1991: 30-240. 邱检生, 王德滋, 蟹泽聪史, 等. 福建沿海铝质A型花岗岩的地球化学及岩石成因[J]. 地球化学, 2000, 29(4): 313-321. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200004000.htm 新疆维吾尔自治区地质矿产勘查开发局第一地质大队, 黄金地质研究所. 若羌县阿克达坂东一带区域地质调查报告(1: 5万)[R]. 2008. 田辉, 张健, 李怀坤, 等. 蓟县系中元古代高于庄组凝灰岩锆石LA-MC-ICPMS U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 地球学报, 2015, 36(5): 647-658. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201505014.htm 王坤, 蔡志超, 王玺, 等. 东昆仑西段原特提斯洋洋盆闭合时间——来自新疆木孜塔格地区同碰撞花岗岩的证据[J]. 地质通报, 2023, 42(9): 1556-1570. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2023.09.011 王强, 赵振华, 熊小林. 桐柏-大别造山带燕山晚期A型花岗岩的厘定[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2000, 19(4): 297-306. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200004001.htm 武彬, 王爱国, 张传林, 等. 新疆若羌喀腊大湾铁矿床辉钼矿Re-Os定年及成因[J]. 地质通报, 2019, 38(8): 1362-1368. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/cn/article/id/20190812 新疆维吾尔自治区地质局区域地质调查大队. 索尔库里幅区域地质报告(1: 20万)[R]. 1981. 杨经绥, 史仁灯, 吴才来, 等. 北阿尔金地区米兰红柳沟蛇绿岩的岩石学特征和SHRIMP定年[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(7): 1567-1584. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200807014.htm 张传林, 马华东, 李怀坤, 等. 塔里木北缘库鲁克塔格地区古元古界——祝贺芮行健先生90华诞[J]. 华东地质, 2022, 43(2): 133-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HSDZ202202001.htm 张建新, 孟繁聪, 于胜尧, 等. 北阿尔金HP/LT蓝片岩和榴辉岩的Ar-Ar年代学及其区域构造意义[J]. 中国地质, 2007, 34(4): 558-564. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200704003.htm 朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 等. 冈底斯中北部晚侏罗世—早白垩世地球动力学环境: 火山岩约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(3): 534-546. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200603002.htm




 下载:
下载: