Prediction of urban land subsidence by SBAS-InSAR and improved BP neural network
-
摘要:
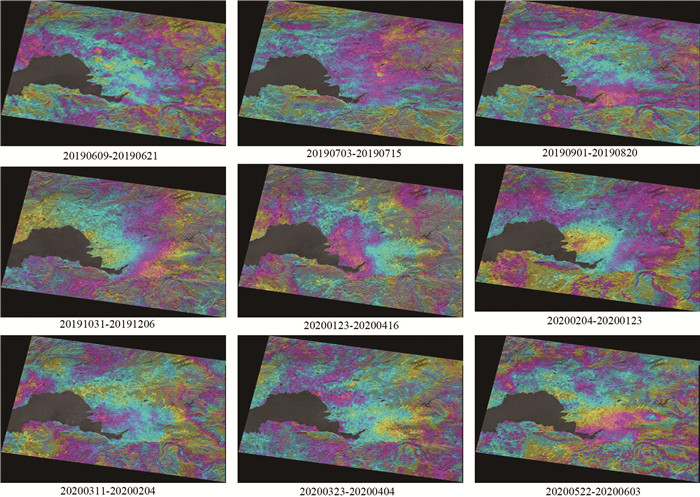
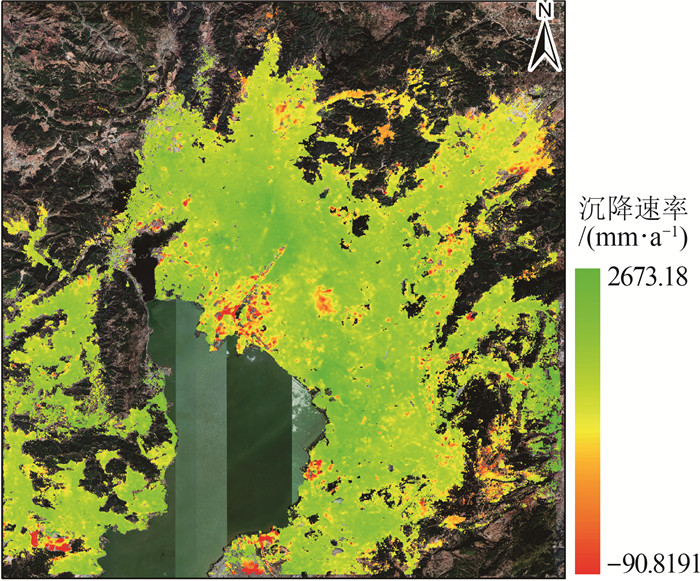
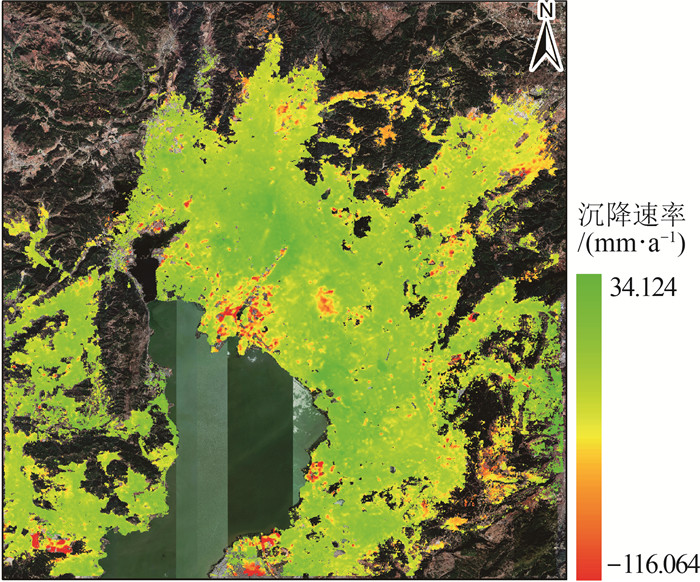
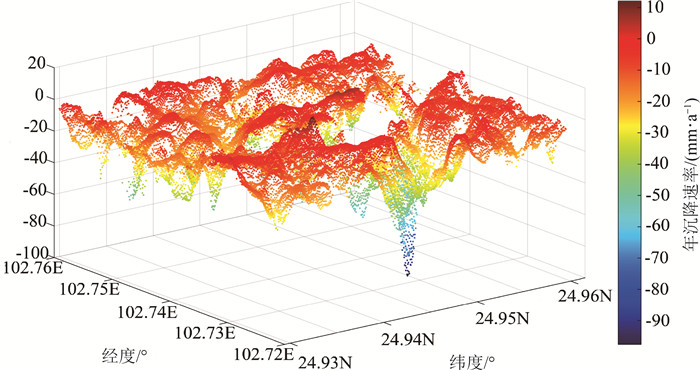
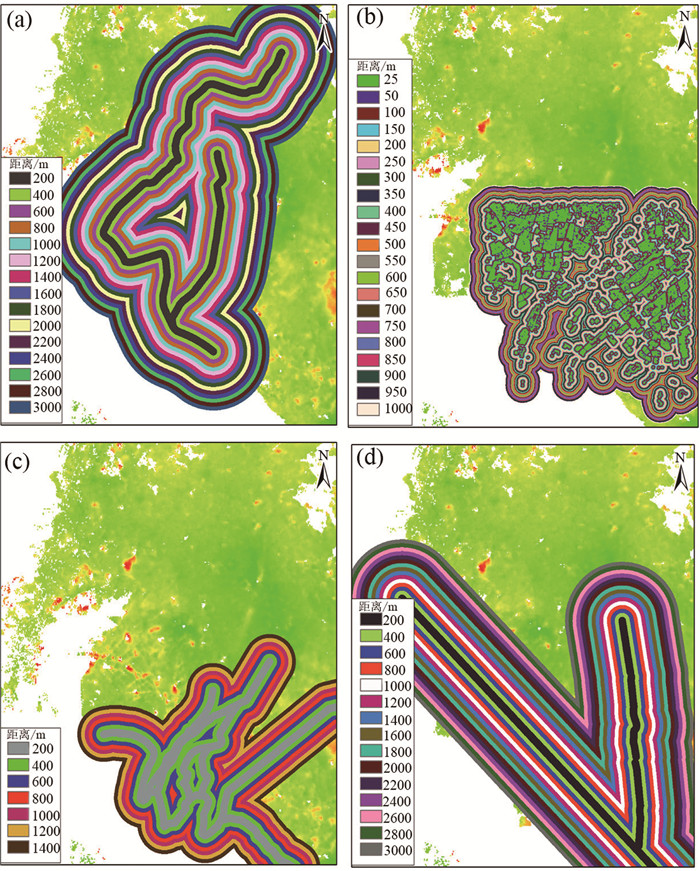
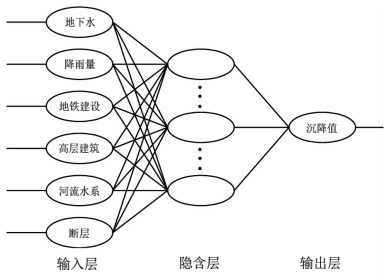
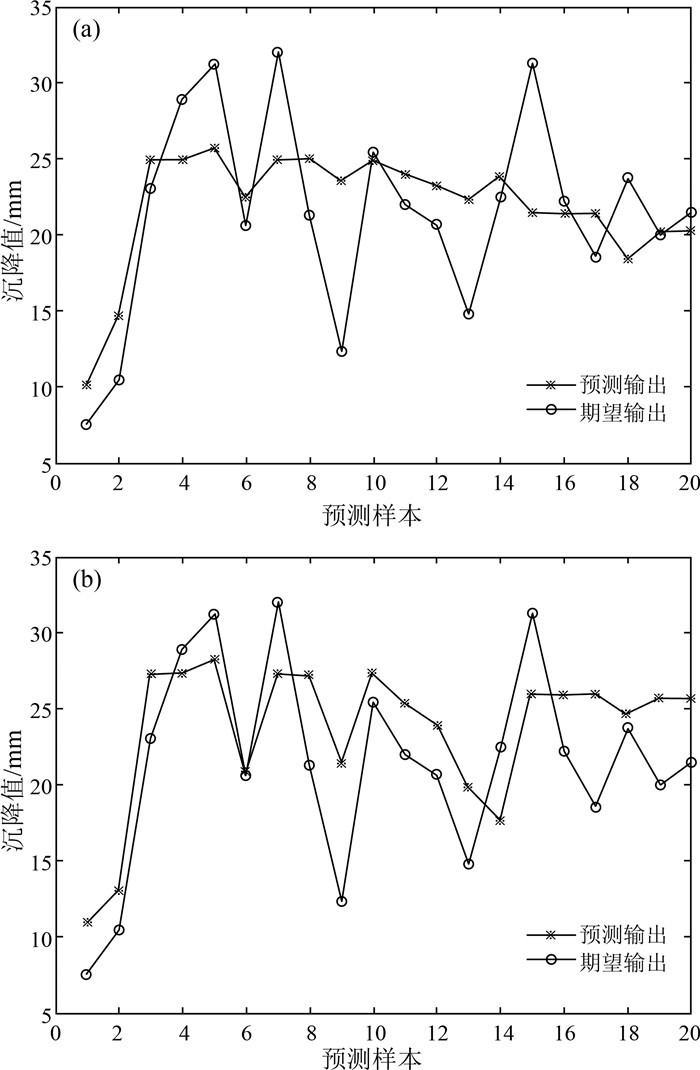
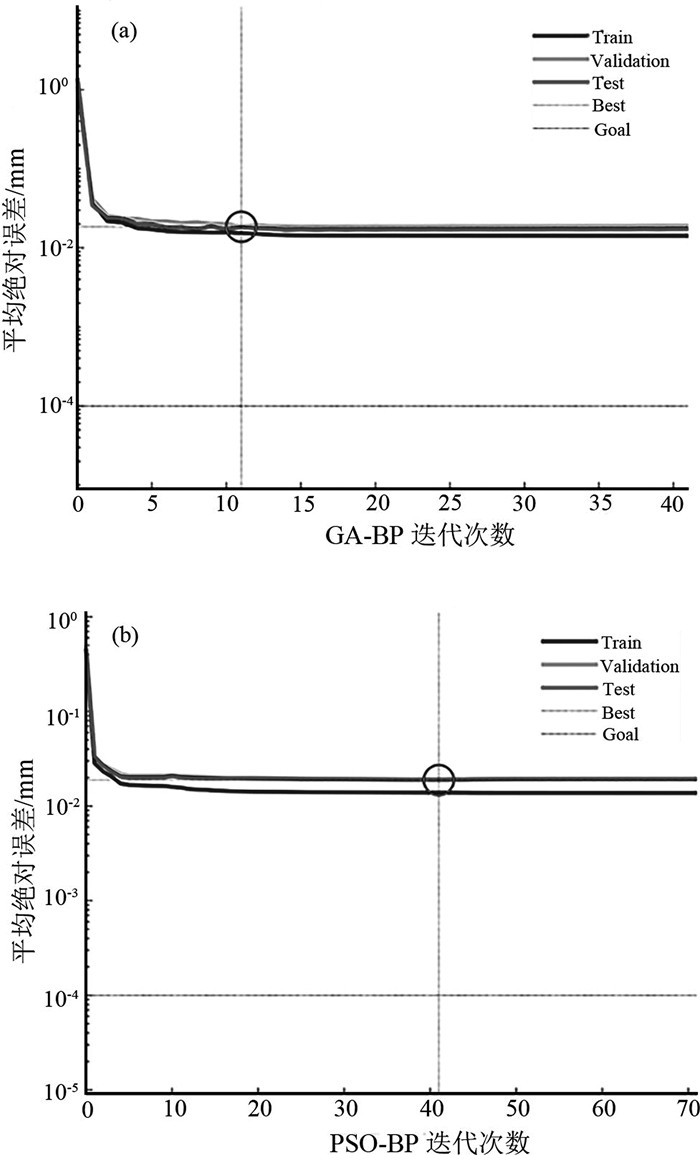
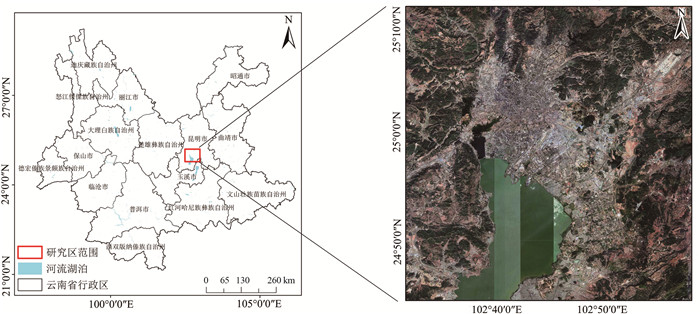
针对现有城市地面沉降预测方法过度依赖沉降数据、模型单一等问题,以云南省昆明市主城区为研究对象,从多时序多因子角度提出一种改进BP神经网络在城市地面沉降中的预测方法。首先,利用SBAS-InSAR技术获取主城区地面沉降监测值,然后通过SPSSAU软件中的灰色关联分析和因子分析选取主城区地面沉降的影响因子,并将其与获取的沉降监测值从多因子多时序角度构建GA-BP和PSO-BP预测模型,最后,得出最优的预测模型并进行预测性能验证。实验结果表明:利用SBAS-InSAR能有效监测城市地面沉降;GA-BP算法相比PSO-BP算法在城市地面沉降预测中性能更好、精度更高;该方法可对长时间、大范围城市地面沉降预测和对某一沉降点多期沉降趋势进行预测。该方法可作为城市地面沉降预测的有效手段,为政府部门决策提供了一种高效快速的方法。
-
关键词:
- SBAS-InSAR /
- 地面沉降 /
- 影响因子 /
- BP算法
Abstract:In response to the issues of excessive reliance on subsidence data and a lack of model diversity in existing urban ground subsidence prediction methods, this study focuses on the main urban area of Kunming City, Yunnan Province. A novel approach for predicting urban ground settlement is proposed, incorporating a multi-temporal sequence and multifactor perspective into the improved BP neural network. Firstly, SBAS-InSAR technology is utilized to acquire monitoring values of ground settlement in the main urban area. Subsequently, gray correlation analysis and factor analysis in SPSSAU software are employed to identify the influencing factors of ground settlement in this specific area. Based on the obtained settlement monitoring values and the identified influencing factors, GA-BP and PSO-BP prediction models are constructed from a multifactor multi-temporal sequence viewpoint. The optimal prediction model is determined and its performance is evaluated through comprehensive validation. Experimental results demonstrate that SBAS-InSAR effectively monitors urban ground settlement, while the GA-BP algorithm outperforms the PSO-BP algorithm in terms of prediction accuracy and overall performance. This method allows for long-term and large-scale predictions of urban ground settlement, as well as forecasting the settlement trends of specific points over multiple periods. Consequently, it serves as an effective tool for urban ground settlement prediction, providing governmental departments with an efficient and fast decision-making approach.
-
Keywords:
- SBAS-InSAR /
- subsidence monitoring /
- influence factor /
- BP algorithm
-
致谢: 非常感谢审稿专家提出的宝贵意见和建议,这对于改进和完善研究成果具有重要意义;向欧洲空间局(European Space Agency)致以诚挚的感谢,感谢他们提供哨兵1号的数据,为本次研究提供了重要支持。
-
表 1 Sentinenl-1A数据参数
Table 1 Sentinenl-1A data parameters
名称 参数 名称 参数 成像模式 IW 极化方式 VV 波段 C 距离分辨率/m 5 波长 5.63 方位分辨率/m 20 入射角/° 37.7 重访周期/d 12 方位角/° 90 表 2 GA/PSO-BP模型训练参数
Table 2 Training parameters of GA/PSO-BP model
参数名称 设置值 参数名称 设置值 动量因子 0.9 种群规模 10 学习速率 0.001 GA交叉概率 0.4 训练目标 0.001 GA变异概率 0.2 训练次数 20000 PSO学习因子 c1=c2=2.0 进化代数 55 PSO最大速度 0.2 表 3 预测值与实测值
Table 3 Predicted and measured values
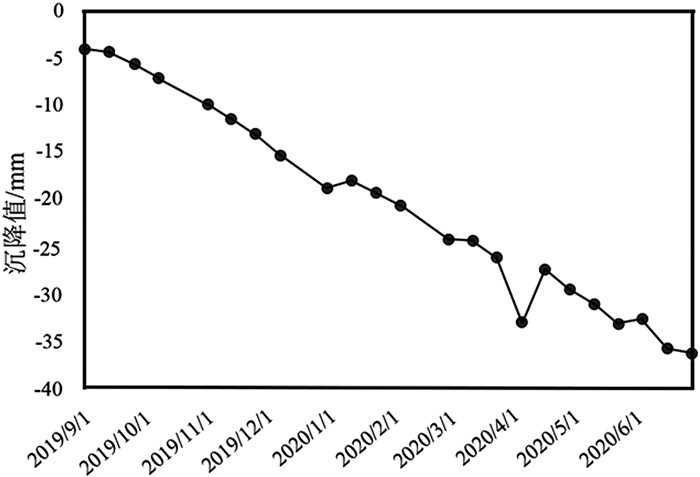
期数 实测值/mm GA-BP预测值/mm 202005 -33 -28.97 202006 -36.15 -29.79 -
Du W, Ji W, Xu L, et al. Deformation time series and Driving-Force Analysis of Glaciers in the Eastern Tienshan Mountains Using the SBAS InSAR Method[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(8): 2836. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17082836
Goldstein R. Atmospheric limitations to repeat-track radar interferometry[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1995, 22(18): 2517-2520. doi: 10.1029/95GL02475
Guo L, Gong H, Ke Y, et al. Mechanism of land subsidence mutation in Beijing plain under the background of urban expansion[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(16): 3086. doi: 10.3390/rs13163086
Li J C. Settlement Prediction of Buildings Based on BP Neural Network[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 602/605: 3232-3234. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.602-605.3232
Pradhan B, Abokharima M H, Jebur M N, et al. Land subsidence susceptibility mapping at Kinta Valley(Malaysia) using the evidential belief function model in GIS[J]. Natural Hazards, 2014, 73(2): 1019-1042. doi: 10.1007/s11069-014-1128-1
Wang C, Zhang H, Shan X, et al. Applying SAR Interferometry for ground deformation detection in China[J]. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 2004, 70(10): 1157-1165.
Zhang Y, Liu Y L, Jin M, et al. Monitoring land subsidence in Wuhan city(China) using the SBAS-InSAR Method with Radarsat-2 Imagery Data[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(3): 743. doi: 10.3390/s19030743
Zhang Z, Lou Y, Zhang W, et al. On the assessment GPS-Based WRFDA for InSAR Atmospheric Correction: A case study in Pearl River Delta region of China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(16): 3280. doi: 10.3390/rs13163280
Zhou D, Zuo X, Zhao Z. Constructing a large-scale urban land subsidence prediction method based on neural network algorithm from the perspective of multiple factors[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(8): 1803. doi: 10.3390/rs14081803
邓传军, 欧阳斌, 陈艳红. 一种基于PSO-BP神经网络的建筑物沉降预测模型[J]. 测绘科学, 2018, 43(6): 27-31, 38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHKD201806005.htm 杜东, 刘宏伟, 周佳慧, 等. 北京市通州区地面沉降特征与影响因素研究[J]. 地质学报, 2022, 96(2): 712-725. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202202024.htm 顾波, 刘炫. 试析灰色理论模型在地面沉降预测中的应用[C]//浙江省测绘与地理信息学会. 2016年度浙江省测绘与地理信息学会优秀论文集. 浙江省测绘与地理信息学会, 2016: 5. 郭海朋, 李文鹏, 王丽亚, 等. 华北平原地下水位驱动下的地面沉降现状与研究展望[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2021, 48(3): 162-171. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202103021.htm 贾林刚. 基于BP神经网络的地表沉降预测模型[J]. 煤矿开采, 2008, (1): 15-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MKKC200801007.htm 何永红, 靳鹏伟, 舒敏. 基于多尺度相关性分析的InSAR对流层延迟误差改正算法[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2020, 22(9): 1878-1886. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXX202009013.htm 李涛, 潘云, 娄华君, 等. 人工神经网络在天津市区地面沉降预测中的应用[J]. 地质通报, 2005, 24(7): 677-681. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200507135&flag=1 李红霞, 赵新华, 迟海燕, 等. 基于改进BP神经网络模型的地面沉降预测及分析[J]. 天津大学学报, 2009, 42(1): 60-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJDX200901012.htm 麻源源. 基于星载InSAR的地面沉降及山体滑坡监测[D]. 昆明理工大学硕士学位论文, 2019. 孟庆凯, 汪宝存, 苗放. 基于短基线集方法(SBAS-INSAR) 技术的山区城市地面沉降监测研究——以攀枝花为例[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2016, 16(13): 12-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201613003.htm 王霞迎, 张菊清, 张勤, 等. 升降轨InSAR与GPS数据集成反演西安形变场[J]. 测绘学报, 2016, 45(7): 810-817. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHXB201607009.htm 王聪, 王彦兵, 周朝栋. 通州区城市扩张对地面沉降的影响[J]. 首都师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 39(4): 68-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDSX201804013.htm 王博. 基于升降轨InSAR数据的地表二维形变场获取方法研究[D]. 河南大学硕士学位论文, 2020. 熊鹏, 左小清, 李勇发, 等. 双极化Sentinel-1数据在昆明市沉降监测中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2020, 35(4): 1317-1322. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ202004013.htm 张良均, 曹晶, 蒋世忠. 神经网络实用教程[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2008. 张金芝, 黄海军, 毕海波, 等. SBAS时序分析技术监测现代黄河三角洲地面沉降[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2016, 41(2): 242-248. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCH201602016.htm 张玲霞, 赵晓光, 曹庆东. GM-AR模型在城市地面沉降预测中的应用[C]//《建筑科技与管理》组委会. 2017年8月建筑科技与管理学术交流会论文集. 《建筑科技与管理》组委会: 北京恒盛博雅国际文化交流中心, 2017: 2. 张勤, 黄观文, 杨成生. 地质灾害监测预警中的精密空间对地观测技术[J]. 测绘学报, 2017, 46(10): 1300-1307. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHXB201710014.htm 种亚辉, 董少春, 胡欢. 基于时序InSAR技术的常州市地面沉降监测与分析[J]. 高校地质学报, 2019, 25(1): 131-143. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201901014.htm 周定义. 基于星载InSAR和神经网络的城市地面沉降监测及预测[D]. 昆明理工大学硕士学位论文, 2023. 周艳萍. 基于BP神经网络的太原市地面沉降预测及分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2011, 30(5): 115-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201105020.htm



 下载:
下载: