Research progress and prospects of the giant Yigong long run-out landslide, Tibetan Plateau, China
-
摘要:
高位远程滑坡指剪出口高、滑动距离长、体积大和速度快的滑坡,具有强动能、强烈碎屑化-流体化、铲刮效应等特征,滑坡及其诱发的灾害链对人类生命财产安全、路桥基础设施、水利水电工程等危害巨大。在遥感解译和野外调查的基础上,总结了2000年西藏易贡高位远程滑坡的研究进展,分析了滑坡启滑机制、体积、运动速度、堰塞湖体积、溃坝机制等,进一步揭示了内外动力耦合作用是西藏易贡高位远程滑坡的主要影响因素,以及该滑坡具有溯源侵蚀复发型的周期性启滑机制。基于GIS与高精度DEM进一步核算了易贡高位远程滑坡的体积,认为滑源区崩滑体体积约9225×104 m3,滑坡堆积体体积约为2.81×108~3.06×108 m3,其中堆积体体积与国内外研究的认识基本一致。易贡滑坡崩滑源区还发育2个潜在失稳区,潜在崩滑体方量约1.86×108 m3,一旦失稳可能再次形成滑坡-堵江-溃坝灾害链,危害巨大,故提出了进一步加强易贡高位远程滑坡潜在崩滑体稳定性研究、灾害链流域性影响范围预测和监测预警等建议,对于指导该区正在规划建设的铁路、水利水电等重大工程建设和城镇防灾减灾具有重要意义。
Abstract:Long run-out landslide is a landslide with high shear outlet, long sliding distance, large volume and high speed, which is characterized by strong kinetic energy, strong fragmentation-fluidization and entrainment effect.The landslide itself and its induced hazard chain are great harm to human life and property safety, road and bridge infrastructure and water conservancy and hydropower projects.Based on remote sensing interpretation and field investigation, this paper summarizes the research progress of the giant Yigong long run-out landslide in Xizang in 2000.It also delves into the initiation mechanism, landslide volume, movement speed, dammed lake volume and dam failure mechanism of Yigong landslide.Furthermore, it reveals that internal and external dynamic coupling is the main influencing factor of the Yigong landslide and considers that the landslide has periodic sliding mechanism of retrogressive erosion recurrence type.In additon, this paper calculates the landslide volume based on GIS and high-precision DEM and reveals that the landslide volume in the landslide source zone is about 9225×104 m3.The landslide accumulation volume is about 2.81×108~3.06×108 m3, which is close to the domestic and international research.There are two potential instability rockmass in the landslide source zone of Yigong landslide, with a total volume of about 1.86×108 m3.Once the two potential instability rockmass are unstable, the hazard chain of landslide-river blockage-dam break might be formed again and cause great harm.This study concludes by proposing research directions to further research the stability of the potential landslide of the Yigong landslide, predict the basin influence range of the hazard chain, establish the monitoring and early warning system.These suggestions have important guiding significance for the construction of major projects such as railway and hydropower projects being planned and constructed in this area, as well as for urban hazard prevention and mitigation.
-
Keywords:
- Yigong /
- long run-out landslide /
- initiation mechanism /
- landslide volume /
- hazard chain
-
高位远程滑坡指滑体剪出口高(相对高差大于100 m),滑动距离长(常用等值摩擦系数H/L,即滑坡体重心位置的垂直位移H和水平位移L之比表示,H/L一般小于0.6)、体积大(具有铲刮侵蚀效应,体积大于106 m3)和速度快(最大速度可达上百米每秒)的滑坡(Clague et al., 1987; 程谦恭等, 2007; 张明等, 2010; 殷跃平等, 2017; 高杨等, 2020)。高位远程滑坡在世界各地均有发育,常具有高位隐蔽性、规模大、强动能、铲刮侵蚀放大效应和强碎屑化-流体化等特征,往往造成严重的危害,如2017年四川茂县新磨滑坡,约450×104 m3的高位岩体失稳崩滑,历时2 min,运动水平距离约2800 m,滑坡高差1200 m,形成体积约1637×104 m3的堆积体,其强动能的滑坡碎屑流导致新磨村被掩埋,90余人失踪(殷跃平等, 2017; Fan et al., 2017; 何思明等, 2017; 许强等, 2017);2019年贵州水城滑坡,约70×104 m3岩体从斜坡中上部失稳剪出,运动水平距离约1250 m,滑坡高差约465 m,形成约191×104 m3的堆积体,导致21幢房屋毁坏,50余人遇难(郑光等, 2020; 高浩源等, 2020; 李华等, 2020; Zhuang et al., 2020);1974年秘鲁Mayunmarca滑坡,历时约3 min,运动距离约8.25 km,运动平均速度约36 m/s,滑坡高差约1870 m,滑坡体积约10×108 m3,摧毁了Mayunmarca村,造成450余人死亡(Kojan et al., 1978)。
青藏高原是中国乃至世界上地质构造最复杂与地质灾害最发育的地区之一,高位远程滑坡等地质灾害是该地区的典型地质灾害,引起了世界学者的关注。最典型的是发生于2000年的西藏易贡高位远程滑坡,该滑坡历时6 min,运动距离约10 km,高差约3330 m,形成长约2.5 km,宽约2.5 km,平均厚60 m的天然堰塞坝体,总堆积方量约3.0×108 m3(殷跃平, 2000; Xu et al., 2012),形成的灾害链到达了下游印度境内。关于易贡滑坡的启滑机制、滑动速度和体积等研究还存在一些争议(Evans et al., 2011; Delaney et al., 2015; Guo et al., 2020),本文在野外调查的基础上,系统分析总结了易贡高位远程滑坡的启滑机制、滑坡体积、滑坡速度、堰塞湖体积、溃坝机制、复发周期等方面的研究进展,提出了关于易贡滑坡滑源区潜在崩滑体稳定性、灾害链影响范围预测、监测预警等方面的研究展望,对于指导该地区铁路、水利水电等重大工程的规划建设和城镇防灾减灾具有重要意义。
1. 地质背景
1.1 地形地貌与地质构造
西藏易贡高位远程滑坡位于西藏东南部波密县易贡乡扎木弄沟,属于易贡藏布的中下游,区内海拔平均4000 m以上,V形深切河谷发育,峡谷区域斜坡坡度40°~60°,属于典型极高山峡谷地貌,同时也发育冰斗、角峰、冰碛垄等冰川地貌。该区降水量集中在5—10月份,占全年的约78%,年平均气温约11.4℃,冬季气温至零下,昼夜和季节存在较大温差。
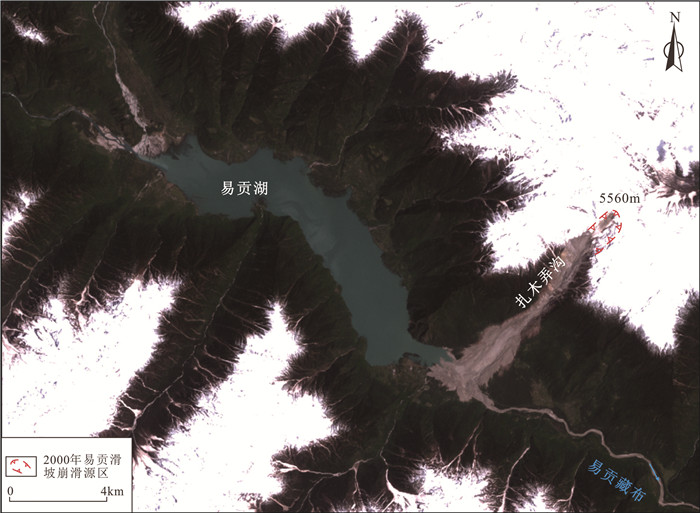
扎木弄沟位于易贡-鲁朗断裂和察隅-嘉黎断裂成近正交的位置,构造运动强烈,历史上多发大地震,区内震级最大可达Ms8.6级(1950年察隅Ms8.6级地震)。沟内滑源区为喜马拉雅早期花岗岩体,滑源区以下地层主要由大理岩、砂岩、板岩等组成,沟内还广泛发育第四系松散堆积物(Zhou et al., 2016)。
1.2 2000年易贡滑坡概况
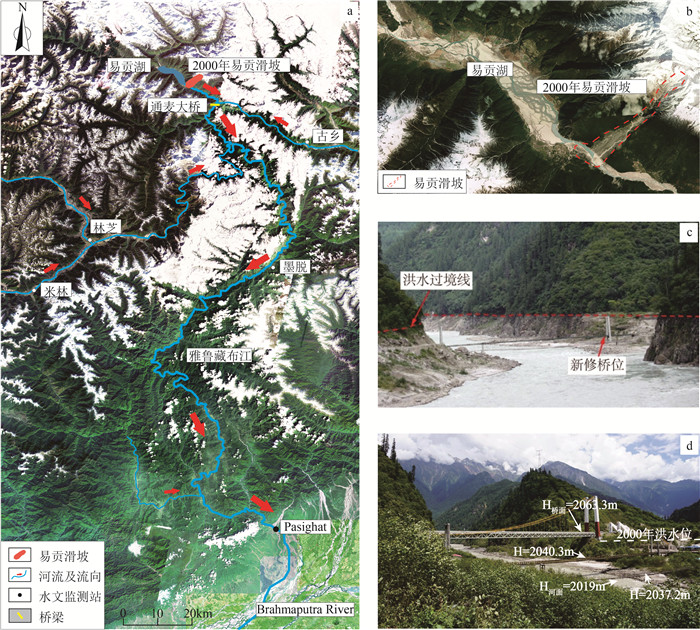
2000年4月9日,西藏波密地区发生易贡高位远程滑坡,殷跃平(2000)首次研究报道了该滑坡,认为扎木弄沟后缘约上亿方的滑坡体从海拔约5520 m处发生崩塌,滑坡高差约3330 m,滑坡历时约6 min,崩滑岩体快速下落冲击了沟内厚层松散堆积物,并裹挟碎屑块石等形成了高速碎屑流,沿途不断铲刮狭窄段沟谷,运移约10 km后堆积于易贡湖出水口处,堵塞易贡藏布,形成长宽约2.5 km,平均厚60 m,最厚处可达100 m的堰塞坝(图 1),滑坡堆积体方量约3×108 m3(殷跃平, 2000; 任金卫等, 2001)。2020年6月10日,易贡堰塞湖湖水冲毁人工导流明渠,发生溃决,位于17 km外的通麦大桥处水位上升41.77 m,水位高出桥面约32 m,洪水不仅冲毁了桥梁和沿岸的道路及通讯设施,而且诱发崩塌、滑坡等次生灾害,甚至波及到下游印度境内,给下游造成上亿元的经济损失(Delaney et al., 2015; 夏式伟, 2018)。
![]() 图 1 2000年易贡滑坡遥感影像图(据Guo et al., 2020改编)Figure 1. Remote sensing image of Yigong landslide area in 2000
图 1 2000年易贡滑坡遥感影像图(据Guo et al., 2020改编)Figure 1. Remote sensing image of Yigong landslide area in 20002. 易贡滑坡工程地质特征研究进展
2.1 空间分布特征
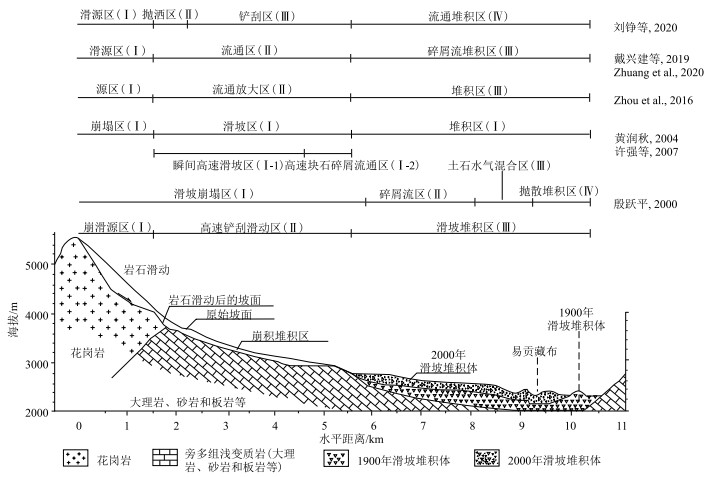
殷跃平(2000)根据野外调查分析,将易贡高位远程滑坡划分为4个区域:滑坡崩塌区、碎屑流区、土石水气混合流区和抛散堆积区;黄润秋(2004)和许强等(2007)根据易贡滑坡发生过程中不同部位物质运动及堆积特征,将其划分为崩塌区、滑坡区和堆积区3个大区,其中滑坡区分为瞬间高速滑坡区和高速块石碎屑流流通区,堆积区划分为块石堆积带、碎屑、砂及粉尘堆积带、铲削-碎屑叠加堆积带和气浪波及影响带;戴兴建等(2019)和Zhuang et al. (2020)根据滑坡前后的遥感影像和现场调查情况,划分为滑源区、流通区和碎屑流堆积区;刘铮等(2020)划分为滑源区、抛洒区、铲刮区和流通堆积区。根据已有分析研究,结合野外调查,认为3个分区可以描述易贡高位远程滑坡的基本运动学特征。在突出运动特征和动力行为的基础上,建议分别命名为崩滑源区(Ⅰ)、高速铲刮滑动区(Ⅱ)和滑坡堆积区(Ⅲ)(图 2)。
![]() 图 2 2000年易贡滑坡空间分区图(据殷跃平, 2000修改)Figure 2. Spatial zoning map of Yigong landslide in 2000
图 2 2000年易贡滑坡空间分区图(据殷跃平, 2000修改)Figure 2. Spatial zoning map of Yigong landslide in 2000(1) 崩滑源区(Ⅰ)
该区域位于扎木弄沟后缘,海拔范围为4400~5300 m,投影水平长约1390 m,该区常年覆盖冰雪,受地震、构造、气候等因素影响,干湿循环和冻融风化作用强烈,基岩裸露,岩体节理裂隙发育且结构破碎,据调查统计,崩滑体受到3组节理控制,产状分别为203°∠34°、94°∠57°、211°∠86°,小倾角的节理控制着滑动面的形成,大倾角的节理则促使后缘拉张裂缝的形成(李俊等, 2018)。易贡滑坡滑源区崩滑体总体上呈楔形,下部窄上部宽,2000年崩滑后留下深V形悬谷,受岩体结构、密集微震和气候变化影响,目前该区域仍然存在2个巨型潜在崩滑体。
(2) 高速铲刮滑动区(Ⅱ)
该区域位于扎木弄沟中上部,海拔范围为2900~ 4400 m,斜坡斜度为16°~27°,沟谷较窄呈狭长形,沟谷两侧崩坡积物和第四系松散堆积物发育,滑坡发生后沟谷两侧基岩出露,有擦痕存在,说明源区陡峭的斜坡让崩滑体获得的高位重力势能在狭窄沟谷段快速转化为强烈的动能,因此,滑体不仅在此区域达到最快速度,而且由于速度差异及碰撞效应产生了解体,且不断铲刮沿途堆积物形成了碎屑流。
(3) 滑坡堆积区(Ⅲ)
该区域位于扎木弄沟中下部,与易贡藏布相接,海拔范围为2200~2900 m,平均坡度5°~7°,地形由狭窄较陡过渡为平缓开阔,碎屑流在此处减速堆积形成具有一定分选的堆积扇,并堵塞河流形成了平均厚60 m的堰塞体。该区在2000年易贡滑坡之前已经存在1900年崩滑形成的堆积扇,而此次崩滑的堆积体即覆盖于1900年的残余堆积体之上。
2.2 滑坡体积
2.2.1 滑坡源区崩滑体体积
关于易贡滑坡滑源区崩滑体的体积,存在不同认识。殷跃平(2000)认为约有上亿方的滑坡体饱水失稳;薛果夫等(2000)认为有1000×104 m3的岩体从扎木弄沟滑源区崩落;刘伟(2002)通过野外地质调查分析,认为崩塌发生前滑源区呈角峰状,岩体边坡达50°~70°,滑动后裸露V形悬谷,推算滑源楔形体体积约为3000×104 m3。Shang et al.(2003)、Yin et al.(2012)、Zhou et al.(2016)和Zhuang et al.(2020)认为,滑源区约10000×104 m3的楔形饱水岩体失稳;王治华(2006)结合2000年4月9日滑坡前后图像对比分析,确定了滑前块体的位置及上宽下窄的不规则多边形结构,得出滑源投影面积约0.691 km2,通过DEM分析和影像比对,认为滑动后滑源区域的高程降幅在0~318 m之间,滑走部分的体积为9118×104 m3。Evans et al.(2011)认为,9118×104 m3的规模不合理,通过计算得到初始崩滑体积约为7500×104 m3,碎裂膨胀之后的体积约为9000×104 m3;Xu et al.(2012)调查分析失稳岩体体积为9000×104 m3;Delaney et al.(2015)通过DEM数据分析和LANDSAT-7影像比对,认为9100×104 m3左右的初始崩滑体体积较合理,且滑体碎裂膨胀后的体积为初始的1.2倍左右(表 1)。
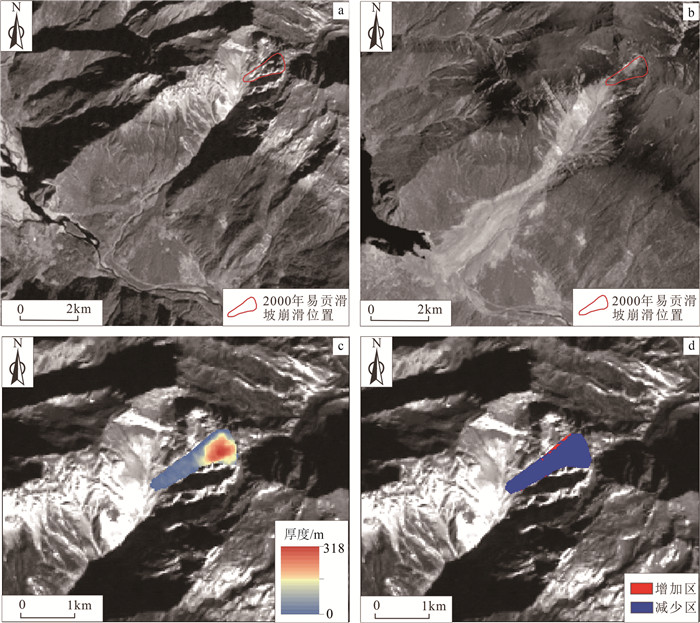
表 1 2000年易贡滑坡初始崩滑体体积历史研究统计结果Table 1. The statistics table of historical studies of the initial landslide volume of Yigong landslide in 2000序号 崩塌区体积/m3 研究方法 文献来源 1 上亿 野外调查、估算 殷跃平, 2000 2 1000×104 野外调查、估算 薛果夫等, 2000 3 3000×104 野外调查、估算 刘伟, 2002; 黄润秋, 2004 4 4000×104 遥感解译 Zhang et al., 2013 5 7500×104 DEM数据分析、遥感解译、滑体等高线重建 Evans et al., 2011 6 9000×104 DEM数据分析、遥感解译、根据铲刮等参数推测 Delaney et al., 2015 7 9118×104 DEM数据分析、遥感解译比对 王治华, 2006 8 10000×104 野外调查、估算 Shang et al., 2003; Yin et al., 2012; Zhou et al., 2016; Zhuang et al., 2020 9 9225×104 DEM数据作差分析、遥感解译 本文 根据2000年1月5日和5月4日的Landsat影像和现场调查,圈定了滑源区位置,投影面积约703210 m2(图 3)。2000年易贡滑坡前的DEM数据滑源区缺失,现有的数据为滑坡后DEM插值填补空白。因此,根据现场调查和遥感解译,恢复了滑源区滑动前后的地形数据(采用AW3D30作为原始数据开展地形修复)。将滑动前的地形与滑动后的地形进行GIS空间分析,得到源区滑体特征,高程降幅为0~318 m,平均厚98.8 m,体积约9225×104 m3。
![]() 图 3 2000年易贡滑坡崩滑源区对比图(a、b底图为Landsat5、7影像, 据USGS: http://glovis.usgs.gov/;c基于GIS空间分析的DEM作差结果,DEM据https://earthdata.nasa.gov/)a—2000年1月5日影像;b—2000年5月4日影像;c—2000年滑坡前后DEM作差分析结果;d—2000年滑坡前后DEM挖填分析结果Figure 3. Comparison of slide source zone of Yigong landslide before and after sliding in 2000
图 3 2000年易贡滑坡崩滑源区对比图(a、b底图为Landsat5、7影像, 据USGS: http://glovis.usgs.gov/;c基于GIS空间分析的DEM作差结果,DEM据https://earthdata.nasa.gov/)a—2000年1月5日影像;b—2000年5月4日影像;c—2000年滑坡前后DEM作差分析结果;d—2000年滑坡前后DEM挖填分析结果Figure 3. Comparison of slide source zone of Yigong landslide before and after sliding in 20002.2.2 滑坡堆积区体积
滑坡堆积体穿过并堰塞了易贡藏布,形成的堆积区海拔范围为2200~2900 m,包括滑坡减速堆积的区域及越过河流对岸的部分区域,面积约5.2 km2。殷跃平(2000)、刘宁(2000)、周刚炎等(2000)和刘国权等(2001a)调查分析得出,易贡滑坡的堆积体规模为2.8×108~3.0×108 m3。黄润秋(2004)认为堆积体规模为2.8×108 m3。Zhou et al.(2001)、柴贺军等(2001)、Wang et al.(2002)、Shang et al.(2003)、Xu et al.(2012)和Zhuang et al.(2020)估算堆积体规模约为3×108 m3。任金卫等(2001)根据便携式GPS实地测量数据和滑坡前后遥感影像的比对,分析堆积体方量超过3.8×108 m3。Evans et al.(2011)通过DEM分析认为,易贡滑坡铲刮量为1.5×107 m3,堆积方量为1.05×108 m3。Wang et al.(2008)通过对比滑源区、运移区、堆积区等,认为堆积体体积为3×108 m3不合理,这是因为之前没有区分2000年之前的新老堆积体,且主要流动区和泥水、强气流溅射区也没有分开,经过区分后认为堆积方量为9.11×107 m3更合理;Delaney et al.(2015)则认为,9.11×107 m3的堆积体方量不合理,因为没有考虑滑源区滑体滑动过程中的碎裂膨胀效应和铲刮夹带作用,通过SRTM-3 DEM数据和LANDSAT-7影像,计算得出易贡滑坡的堆积方量为1.15×108 m3。Ekström et al.(2013)认为,易贡滑坡的堆积总质量为4.4×1011 kg,按照平均密度为2630 kg/m3计算,堆积体积约为1.67×108 m3。Liu et al.(2018)基于1971年和2003年的数字地形资料重建基底滑动面,计算得到的最终体积约为1.29×108 m3(表 2)。
表 2 易贡滑坡堆积体体积历史研究统计结果Table 2. The statistics table of historical studies for Yigong landslide accumulation volume序号 体积/m3 研究方法 文献来源 1 9.11×107 遥感解译、DEM数据分析 Wang, 2008 2 2.80×108~3.00×108 野外调查 殷跃平, 2000;刘宁, 2000;周刚炎等, 2000;刘国权等, 2001b 3 3.00×108 野外调查、遥感解译等 Zhou et al., 2001; 柴贺军等, 2001; Wang et al., 2002; Shang et al., 2003; Xu et al., 2012; Zhuang et al., 2020 4 >3.80×108 GPS实地测量、遥感解译 任金卫等, 2001 5 1.05×108 遥感解译、DEM数据分析 Evans et al., 2011 6 1.15×108 遥感解译、DEM数据分析、GPS野外测绘 Delaney et al., 2015 7 1.67×108 质量密度分析 Ekströmet al., 2013 8 1.29×108 数字地形数据分析 Liu et al., 2018 9 2.81×108~3.06×108 对比分析、遥感解译 本文 殷跃平(2000)根据遥感解译和现场调查,认为堆积体厚度平均为60 m,最厚处可达100 m,面积5 km2;Zhou et al.(2016)认为,沉积区的尾部厚4~10 m,中部厚35~65 m,前部厚50~80 m。本文通过遥感影像解译,测量滑坡堆积区面积约5.2 km2,若按照殷跃平(2000)现场调查得到的滑坡堆积体平均厚度60 m计算,则堆积体方量约为3.06×108 m3;若按照沉积区尾部平均厚度7 m,面积约0.5 km2,中部平均厚度50 m,面积约1.5 km2,尾部平均厚度65 m,面积约3.2 km2计算,则堆积体方量约为2.81×108 m3。
因此,通过文献梳理和滑坡前后影像解译、DEM计算分析,笔者认为,易贡高位远程滑坡初始崩滑体体积约为9225×104 m3,滑坡堆积体方量为2.81×108~3.06×108 m3。
3. 易贡滑坡启滑机制与运动速度研究进展
3.1 易贡高位远程滑坡运动速度
国际地科联滑坡小组划分的滑坡速度,其中极迅速级别的下限速度为5 m/s(IUGS, 1995),易贡高位远程滑坡的速度已经远超该值。地形地貌是滑坡速度的重要影响因素之一,扎木弄沟的极大高差赋予了崩滑体巨大的势能,在崩塌过程中,由于崩滑源区坡度较大,转换动能较高,之后由于铲刮作用、摩擦作用、变缓的地形等使能量逐渐耗尽,运动方式随之转变为减速堆积。通过野外调查分析、地震波曲线计算、数值模拟等方法,众多学者对易贡滑坡的速度进行了研究(表 3)。统计得出易贡滑坡崩塌过程中的速度最大可至90 m/s,其碎屑流状态时的速度为16~28.5 m/s,滑坡过程中最大速度通常位于高速铲刮滑动区的上部,最大速度为44~138 m/s,滑坡全过程的平均速度范围为15.6~40 m/s。其中,根据地震波曲线计算的滑坡速度,是基于岩体或碎屑流冲击震动的波峰进行分析计算,因此合理划分运动阶段波峰,找到准确的碰撞点尤为重要。数值模拟计算得到的结果受模型精确度和模拟方法的影响,模拟结果差异较大,但是基本符合滑坡动力学的规律,较准确的速度特征分布需要结合野外调查、室内试验、高精度地形数值计算程序等方法进一步研究。
表 3 易贡滑坡速度研究结果统计结果Table 3. Speed statistics of Yigong landslide序号 速度/(m·s-1) 研究方法 参考文献 1 Vmax=50 野外调查 朱平一等, 2000 2 V1=48, V2=16 根据地震波曲线计算 任金卫等, 2001 3 V3=37~39;Vmax=65 数值模拟(离散元法) 柴贺军等, 2001 4 V3=37~39 野外调查 刘伟, 2002 5 V3>14 野外调查 Shang et al., 2003 6 Vmax>44 野外调查 黄润秋, 2004 7 Vmax=44 野外调查 许强等, 2007 8 Vmax=117 数值计算 周鑫等, 2010 9 V3=15.6;Vmax=129.9 数值模拟(DAN软件) Delaney et al., 2015 10 Vmax=53 数值模拟(PFC软件) 陈锣增, 2016 11 Vmax=110.4 数值模拟 Liu et al., 2018 12 V1=90;V2=28.5;V3=30.12;Vmax=121 根据地震波曲线计算 李俊等, 2018 13 V3=35;Vmax=90 数值模拟(DAN软件) 戴兴建等, 2019; Zhuang et al., 2020 14 V3=40;Vmax=100 数值模拟(SPH方法) Dai et al., 2021 15 Vmax=138 数值模拟 Zhou et al., 2020 注: V1—崩塌下落的平均速度;V2—碎屑流的平均速度;V3—滑坡全过程平均速度;Vmax—滑坡过程中最大速度;SPH—Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics,光滑粒子流体动力学 3.2 破坏启滑机制分析
关于易贡滑坡的破坏启滑机制,研究者的观点主要体现在:气候变化导致崩滑、地震诱发崩滑、活动断裂控制崩滑、内外动力耦合作用导致崩滑等方面。
(1) 气候变化引起崩滑
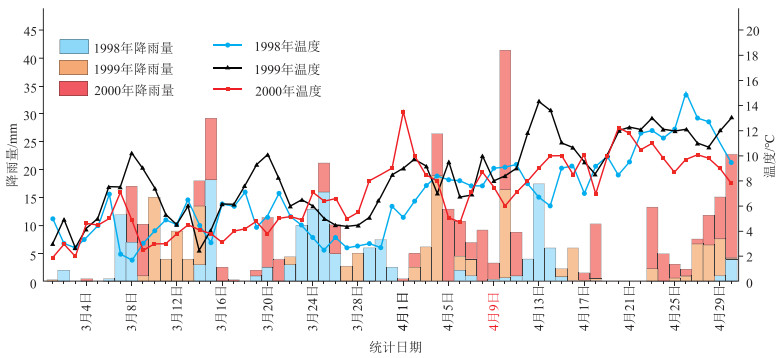
青藏高原是地球的“第三极”,是全球气候变化响应的启动区、敏感区和关键区,1970—2000年以来的气温资料和模型预测显示,青藏高原将持续升温(姚檀栋等, 1994;2000;王绍令等, 1996; 李潮流等, 2006; Hao et al., 2013; 李菲等, 2021)。升温导致雪线上升和冰雪融化等,会增大崩塌、滑坡、泥石流等地质灾害的发生概率,促进地质灾害链的延拓和转换(Mcguire, 2010; 崔鹏等, 2014)。2000年易贡滑坡的发生和气候变化具有相关性,郭广猛(2005)综合遥感影像、气象和MODIS数据,对冰雪解冻范围、气温和地温进行了分析,认为在易贡滑坡发生前1个月气温已经升至0℃以上,灾前两周,崩滑体中心由于岩体破碎容易吸热,导致崩滑体位置温度高于周围2~8℃,表现为一个高温中心,3月28日地温至5℃时,崩滑体周围开始解冻。Zhou et al.(2016)通过1998年、1999年和2000年3月1日—5月4日易贡地区气温对比(图 4),认为3年的气温变化没有显著的区别,但是2000年4月1日的显著增温可能对滑坡有一定的影响。气温转暖导致的冰雪融水和滑坡前的连续降雨(2000年4月1日—9日地区连续降水50 mm,比同期平均值高50%~90%),入渗到崩滑源区楔形体的节理裂隙内,导致结构面软化和孔隙水压力上升,最终诱发了楔形体失稳崩滑(万海斌, 2000; 周昭强等, 2000)。
![]() 图 4 1998年、1999年和2000年3月1日至4月30日易贡地区降雨与温度统计图(据Zhou et al.,2016修改)Figure 4. Statistics of rainfall and temperature in Yigong area from March 1 to April 30 in 1998, 1999 and 2000
图 4 1998年、1999年和2000年3月1日至4月30日易贡地区降雨与温度统计图(据Zhou et al.,2016修改)Figure 4. Statistics of rainfall and temperature in Yigong area from March 1 to April 30 in 1998, 1999 and 2000(2) 地震诱发崩滑
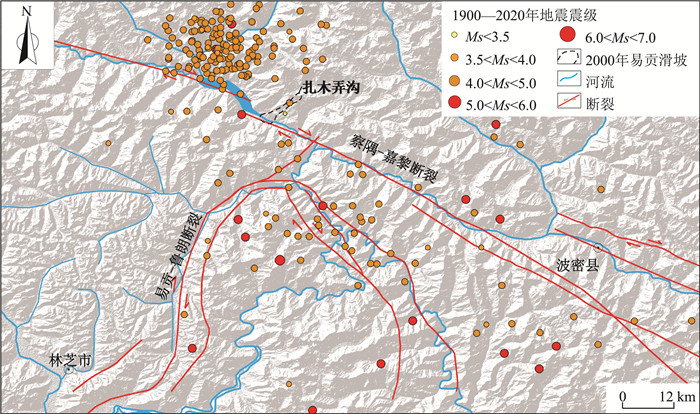
地震是诱发地质灾害的重要因素之一,如2008年Ms 8.0级汶川地震触发了15000多处滑坡、崩塌和泥石流,且震后导致的地质灾害隐患点高达10000余处(殷跃平, 2008),2014年Ms 6.5级鲁甸地震触发约10559处滑坡(吴玮莹等, 2018)。易贡高位远程滑坡位于喜马拉雅东构造结地区,该区位于印度洋板块俯冲亚欧板块的前缘,地震活动频繁,且近直立和陡立的边坡发育,“V”形高山峡谷地貌不仅放大地震波,而且扩大了灾害效应。据统计,1900—2020年该区域地震超过200余次,其中以Ms 3.0~5.0级中小地震为主,大多分布在扎木弄沟的西北侧35 km内(图 5),影响到易贡地区的地震可达100余次,其中以中小地震为主(邵翠茹, 2009; 李俊等, 2018)。频繁的中小级地震不仅会增加岩体的脆弱性,而且会成为岩体失稳的触发因素。李俊等(2018)通过分析历年地震、气温资料及滑坡前2个月的降水情况,认为经历长期作用的滑源区花岗岩体处在极限平衡状态,且具有一定的损伤,受4月9日8点0分9秒距离易贡滑坡13 km处的林芝地区Ms 4.8级地震的影响,随后8点0分11.95秒发生易贡特大高位远程滑坡。基于地震加速度和易贡滑坡的时空耦合分析,认为地震是易贡滑坡的诱发因素。
(3) 活动断裂控制崩滑
扎木弄沟区域断裂发育(图 5),大区域上主要受察隅-嘉黎断裂带的影响,其断裂的蠕滑和粘滑作用控制着区域的地形地貌、岩体结构和斜坡应力场,导致一定范围内的灾害极其发育(张永双等, 2016),如川西鲜水河断裂带对地质灾害有明显的控制作用,约67.5%的地质灾害发育于距断裂带1.5 km范围内,滑坡的滑动方向多垂直于断裂走向(郭长宝等, 2015);而扎木弄沟则受到达嫩-泽普断裂和达德-阿尼扎次级断裂的影响较大,断裂附近岩体结构破碎,易在外力的驱动下产生失稳崩滑。鲁修元等(2000)综合分析了气候、地形地貌和地质构造对易贡滑坡的影响,认为地质构造是滑坡形成和滑动的主要因素之一。刘国权等(2000)也认为,地质构造是易贡滑坡发生的主要因素之一,且扎木弄沟在阿扎-易贡断裂和申错九子拉-朗呷马断裂的影响下形成下凹地形,构造运动导致形成了密集的节理裂隙发育带。该带在风化等作用下产生大量崩坡积物,一旦达到极限平衡状态时便会诱发大型滑坡。
(4) 内外动力耦合作用导致崩滑
地震、地壳抬升、断层活动等内动力作用和风化、剥蚀、搬运、沉积等外动力作用相互耦合下,会导致岩土体应力释放或结构松弛,内外动力作用均直接或间接影响滑坡的形成过程(王思敬, 2002; 李晓等, 2008)。关于易贡滑坡的内外动力作用,吕杰堂等(2003a)认为,扎木弄沟地区因为线性构造的切割作用、冻融风化作用等,导致岩体结构极破碎;活动断裂和地震加剧了岩体结构的弱化和滑坡物质的积累。滑源处大量堆积的冰雪,增加了坡体自重,受季节性气候影响,大量冰雪融水和降水入渗破碎岩体,增大了孔隙水压力,降低了结构面强度,因此地质、构造、气象等内外动力因素共同作用导致了易贡滑坡的发生。Zhou et al.(2016)认为,易贡滑坡是长期演变和短期效应耦合作用的结果,在长期作用中,冰雪对岩体产生加卸载,与季节性、日冻融循环等共同作用,导致岩体力学性质逐渐降低,节理裂隙联合贯通;而易贡滑坡发生前的气温升高加速了冰雪融化,加之连续的暴雨短期效应,导致滑源区岩体裂隙孔压上升,岩体力学强度急剧下降,从而触发滑坡。Wen et al.(2004)统计了国内自1900年以来的70次大型滑坡,认为其成因机制非常复杂,构造条件、地质情况、岩性、地形地貌等是导致大型滑坡发生的主要原因,而诱发大型滑坡的因素通常是降雨、地震、坡顶荷载、融雪等。
综上,易贡高位远程滑坡的破坏启滑,受到内外动力作用的共同控制,是在岩体长期蠕变过程中,由气候季节性变化、强降雨、强地震等短期影响而触发的。长期控制岩体蠕变的因素表现为:①地震作用,据统计,1900—2020年区内可影响到扎木弄沟的地震达100余次,以Ms 3.0~5.0级中小地震为主,多次地震让岩体损伤不断积累;②断裂蠕滑作用,察隅-嘉黎断裂带中部走滑速率1.3 mm/a,挤压速率2.9 mm/a,处于蠕滑的状态(唐方头等, 2010),其控制着区域的地形地貌、岩体结构和斜坡应力等;③冻融与加卸载循环作用,扎木弄沟后缘海拔超过5000 m,多年经历降雪-融雪的循环,即经历冻融循环和加卸载作用,导致后缘基岩的节理裂隙不断扩展;④干湿循环作用,扎木弄沟的独特地理位置带来了丰富的降水,让区域干湿循环极为强烈,不断弱化岩体强度。以上因素在长时间内控制着区域的岩体蠕变。短期影响表现为,2000年4月1—9日,扎木弄沟地区降水累计50 mm以上,且自3月27日起区域升温,4月1日气温达到3年来的最高值(图 4),融雪和降雨效应均大于同期,该时间段内扎木弄沟崩滑源区岩体已经接近极限平衡状态,当气温升高产生的冰雪融水和连续的强降雨进入节理裂隙发育的岩体,岩体结构面强度降低,孔隙水压力升高,最后突破极限状态打破锁固段束缚产生失稳崩滑。
4. 易贡滑坡-堵江-溃坝灾害链研究进展
2000年易贡滑坡形成的堰塞坝,其底宽2200~2500 m,轴线长约1000 m,坝体平面面积约2.5 km2,库容最大可达288×108 m3(殷跃平, 2000),也有学者认为最大库容为201.5×108 m3(Delaney et al., 2015)。易贡藏布堵塞后采取了开渠引流的方案进行疏通,2000年5月3日开始施工,6月4日完工,渠道为梯形断面,底宽30 m,渠深20 m,长600~1000 m。6月8日渠道开始泄流,6月10日20时坝体开始溃决,6月11日19时基本恢复原状,泄流过程中瞬间最大流量出现在6月11日2时,坝体下游水位上涨至少48.2 m,下游通麦大桥处流量达12×104 m3/s,河水水位约41.77 m,高出桥面32 m,6月12日,易贡湖约30×108 m3的库水全部排出(鲁修元, 2000;Shang et al., 2003),溃决的洪水冲毁桥梁道路、诱发次生灾害等,对下游造成了巨大的危害。
4.1 易贡堰塞湖体积
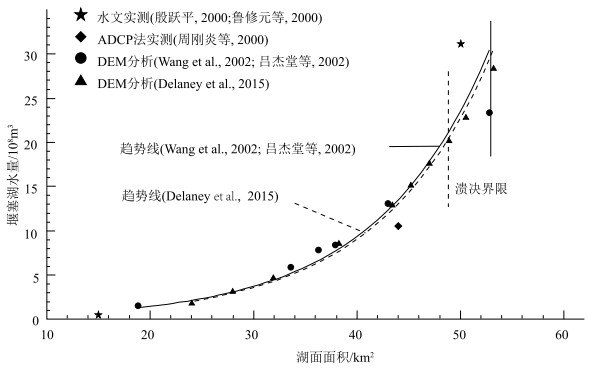
据研究,易贡滑坡-堵江形成的堰塞湖溃决下泄水量约为30×108 m3(鲁修元等, 2000; 万海斌, 2000; 周昭强等, 2000; Shang et al., 2003)。堵江发生后,堰塞湖的面积和体积不断扩大,扩大的程度与气候因素、上游流量等密切相关,本文主要统计了实测和数字高程模型数据(DEM)分析等方法求得的堰塞湖体积(表 4)。另外,还有学者使用数值模拟,经验公式等方法对易贡堰塞湖体积、溃决流量,以及对下游流量、河道冲刷等影响进行了分析(邢爱国等, 2010; Delaney et al., 2015; 夏式伟, 2018; Liu et al., 2018; Turzewski et al., 2019; Zhou et al., 2020; Zhuang et al., 2021)。通过对比(图 6),由DEM数据计算得出的堰塞湖的面积和体积变化趋势相似,但是与实测得出的结果有差距。关于溃决时的面积和水量判断也有差异,Wang et al.(2002)、吕杰堂等(2003b)和王治华(2005)通过分析,认为溃决时的水面高程、面积和体积分别为2244 m、52.855 km2和23.29×108 m3,Delaney et al.(2015)则认为其值分别为2265 m、48.926 km2和20.15×108 m3。综上,笔者认为易贡堰塞湖溃决前体积约为20×108~30×108 m3,未来可进一步综合野外测绘数据,结合高精度历史遥感影像,校正遥感影像解译的高程值,对易贡堰塞湖的体积进行精细计算。
表 4 2000年易贡滑坡堰塞湖方量统计结果Table 4. The statistical table of volume for Yigong landslide dammed lake in 2000时间 水面高程/m 湖水面积/km2 水量/108m3 研究方法 参考文献 堰塞之前 / 15.000 0.70 水文实测 殷跃平, 2000 5月24日 44.400 10.70 ADCP法实测 周刚炎等, 2000 6月8日 50.000 31.44 水文实测 鲁修元等, 2000 4月13日 / 19.900 / 遥感解译 王治华等, 2001 5月4日 33.700 5月9日 37.300 5月20日 43.600 4月13日 2214 18.909 1.55 遥感解译
DEM数据分析Wang et al., 2002; 王治华, 2005 5月4日 2225 33.659 5.84 5月9日 2228 36.320 7.76 5月12日 2229 37.979 8.41 5月20日 2234 43.121 13.05 6月10日 2244 52.855 23.29 6月17日 2209 9.280 0.43 / 2220 24.072 1.75 遥感解译
DEM数据分析Delaney et al., 2015 2225 28.010 3.13 2230 31.939 4.69 2240 38.241 8.51 2250 43.371 12.87 2255 45.251 15.11 2260 47.064 17.59 2265 48.926 20.15 2270 50.578 22.80 2280 53.272 28.29 注:ADCP(Acoustic Doppler Current Profilers)——声学多普勒流速剖面仪 4.2 易贡堰塞坝溃坝机制
鲁修元等(2000)认为,易贡滑坡堰塞坝泄流渠道附近以含碎块石砂壤土为主,其粉细砂含量较高,结构松散、抗冲刷能力差,经过泄流的淘蚀,极易发生溃决;刘国权等(2001b)从坝体的物质组成、渠道纵剖面形状、连日降雨猛涨的水位等方面对溃决机制进行了分析:首先渠道断面统计得出各部位的物质组成有差异(表 5),砂壤土含碎、块石,因为碎、块石粒径大小不一,流动堆积后容易呈松散架构状,且砂壤土颗粒较细,极易被流水冲刷带走,所以坝体整体的抗冲刷能力较差;其次引水渠道纵断面看进口低,中间高,渠尾低无坡降,不能顺利排水,导致进水口浸泡,宽扩大约350 m,而中部至渠尾,由于落差较大,导致水流流速变大,渠尾向上游下切,渠两岸向里崩塌,最后6月8—10日易贡湖上游连日降雨,入库水量大于下泄水量,因此水库水位涨速较快,形成了高水头差,造成坝体溃决。Shang et al.(2003)认为,降雨、融水等大量进入堰塞湖,渠道导流完成太晚,库水超出导流前预测的水量,导致水位上升较快出现了管涌和渗漏,再加上松散的坝体堆积,所以发生了溃坝和洪水。李俊等(2017)通过分析2000年的堰塞坝物质及物质颗分曲线,认为坝体的岩块不仅磨圆度较差、粒径大小不一,而且粘粒含量高,为典型的高粘粒含量的宽级配土体,这种坝体通常随着坝体水位的升高结构强度大幅降低,极易产生漫顶溃决。宽级配坝体的稳定性主要受坝体的物质组成与结构类型、引流渠断面形状、河湖水位高差等因素的影响,易出现渗流效应、浸泡垮塌等破坏,引流时应充分考虑这些影响因素,能够减少风险损失。
表 5 2000年易贡滑坡堰塞坝体物质组成(刘国权等, 2001b)Table 5. Material composition table of Yigong landslide dam body in 2000泄流渠尾部 泄流渠中部 引水进口处 渠道高程 低 高 低 物质组成 碎、块石含量30%~40%,灰白(褐)色砂壤土含碎石、块石、大块石,块径一般3~20 cm,大的1~5 m,个别大于10 m 碎、块石含量50%~60%,碎、块石砂壤土 碎、块石含量60%~70%,砂壤土含碎石、块石,碎石、块石成分以大理岩、石英岩、混合花岗岩为主 4.3 堰塞湖-溃坝灾害链特征
高山峡谷区复杂的地形使得该区洪水产生强烈的水动力作用,对河床的剪应力增大,尤其在陡峭的峡谷和河谷收缩变窄的区域,洪水能搬走数米大小的块石,对地形地貌的改造能力极强(Turzewski et al., 2019)。易贡高位远程滑坡具有典型的崩塌-滑坡-碎屑流-堵江-溃坝-洪水-次生灾害链等地质灾害链特征,其中溃坝-洪水灾害链影响范围深远,危害较大,不仅摧毁了下游的桥梁、道路和基础设施,而且诱发了许多次生灾害(图 7)。万海斌(2000)、朱博勤等(2001)通过多期遥感数据分析对比,认为溃坝的洪水导致下游新增了约25个不同规模的浅层滑坡和滑落,且原有的森林和草地部分被新河床滩地占据。刘伟(2002)和吕杰堂等(2003a)认为,易贡滑坡溃坝灾害链影响至下游沿江地区约450 km的范围,数百千米的河谷由于洪水冲蚀发生了不同程度的坡脚失稳现象,部分河谷由V形变为U形,岸坡更陡立,增加了崩塌的风险,另外部分河谷成为浅层牵引滑坡带,在影响区域带中形成的滑坡和崩塌至少有15处,其体积多在数百方至数方之间。王治华(2005)和Xu et al.(2012)通过遥感解译等方法,认为下游120 km的主河道两岸触发了约35处斜坡表层滑塌、浅层滑坡和坡面泥石流,其中最大一处坡面泥石流的面积达0.8 km2,使河道加宽了2~10倍以上,影响范围超过120 km。Delaney et al.(2015)研究认为,易贡滑坡溃坝-洪水灾害链,至少摧毁了6座桥梁,影响范围延伸至距离滑坡位置下游500 km处的印度东北部布拉马普特拉(Brahmaputra),同时位于462 km处的Pasighat监测站监测到水位上升了5.5 m(图 7-a)。溃坝-洪水灾害链影响范围远,不仅会诱发次生灾害,还严重危害沿途的工程设施,目前研究内容集中在次生灾害数量和洪水波及范围,手段多为遥感解译和监测站数据分析。
5. 易贡高位远程滑坡复发周期研究进展
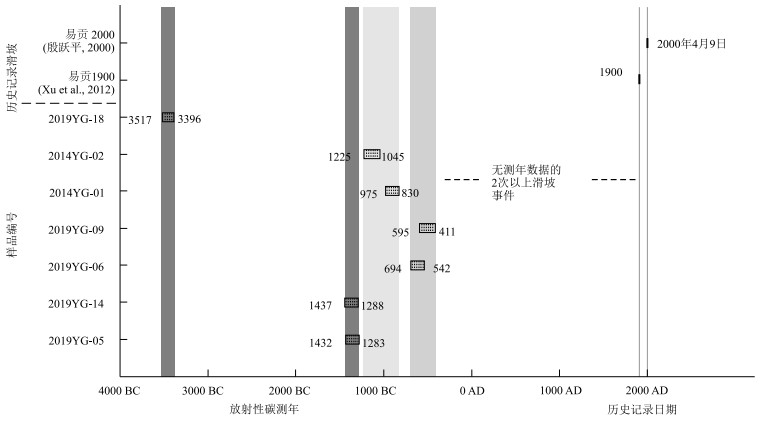
滑坡复发周期指在环境条件相对稳定的条件下,滑坡原址多次发生一定规模的滑坡,且每次滑坡出现的时间具有一定的周期性。复发周期和气候、地震、河流等引起的侵蚀、堆积速率具有一定的关系。Shang et al.(2003)假设100 a为易贡滑坡原址复发周期,以3×108 m3的物质和20.2 km2的扎木弄沟面积来计算物质生成率,其物质积累速率约为每平方米0.149 m3/a,当物质积累到极限状态,受到一定的影响便会触发,2000年易贡滑坡之后,在区域气候、构造等因素的影响下,扎木弄沟进入一个新的物质与能量的积累区间,当突破界限阈值,极有可能再次发生滑坡-堵江特大危害事件。Guo et al.(2020)通过对易贡滑坡堆积区开展了野外调查、地质剖面测量、地层精细厘定和14C测年等研究,首次揭示了易贡滑坡具有周期性高位远程滑坡-堰塞易贡藏布-溃坝灾害链的复发规律,且认为:①2000年易贡滑坡源区在过去5500 a间发生了至少8次以上的高位远程滑坡事件,分别为3500 BC、1300 BC、1000 BC、600 BC、1900年和2000年滑坡事件,以及600 BC至1900年间缺少测年数据的2次滑坡事件(图 8);②考虑到后期滑坡事件侵蚀堆积体及滑坡-堰塞事件记录的不完整性,易贡地区大型高位远程滑坡可能存在百年尺度的复发周期。以易贡滑坡为例,原址溯源周期型的滑坡在相对稳定的环境条件下,经历了气候、微震、断裂蠕滑等长期作用,物质会不断积累,岩体损伤持续加剧,在没有急剧突发事件影响的前提下,在一定时间内达到极限状态也会形成滑坡事件。
![]() 图 8 易贡地区不同期次滑坡地质年代分布特征(据Guo et al., 2020)Figure 8. Age ranges dating the different landslides at the Yigong location
图 8 易贡地区不同期次滑坡地质年代分布特征(据Guo et al., 2020)Figure 8. Age ranges dating the different landslides at the Yigong location6. 研究展望
6.1 易贡崩滑源区岩体稳定性与失稳趋势
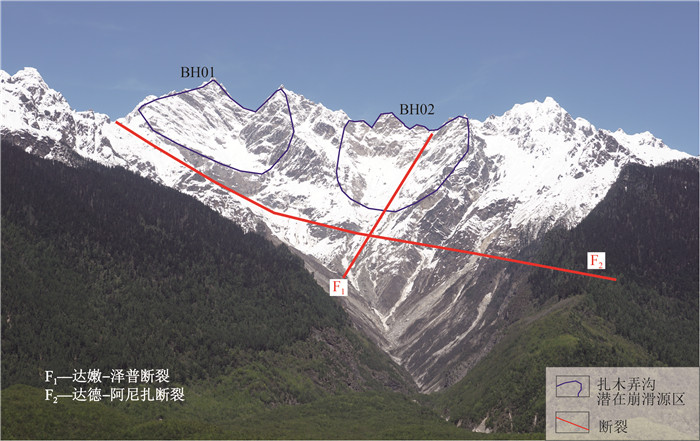
扎木弄沟后缘仍然存在较大的崩塌风险,吕杰堂(2003a)认为,扎木弄沟内还残留有1×107 m3的松散物质,且目前处于2000年易贡滑坡后的物质与能量积累的新周期;朱成明等(2015)通过遥感影像解译,认为扎木弄沟源头区目前存在的松散堆积物和潜在不稳定楔形岩体总体积达1.6×108 m3以上,在强降雨、冰雪融水、雪崩等因素影响下,极易产生崩塌滑坡;李俊等(2017)通过工程地质分析方法和野外实际调查,认为易贡扎木弄沟后缘仍存在2块巨型潜在崩滑体,其发生滑坡堵江的基础和激发条件依然存在,基于FLAC 2D软件反演潜在崩滑体的规模,结果为BH01方量0.94×108 m3,BH02方量0.92×108 m3(图 9),最后采用MacCormack-TVD有限差分数值方法,模拟了潜在崩滑体在地震烈度为Ⅷ度和极端气候工况下BH01和BH02少量崩滑、BH01和BH02局部崩滑、BH02全部崩滑、BH01和BH02全部崩滑4种情况下的失稳堵江风险,计算结果认为4种失稳情况均会造成堵江。刘铮等(2020)分析了易贡地区山体对地震波的响应特征,使用FLAC 3D软件研究了潜在崩滑体的稳定性,认为在静力作用下,潜在崩滑体稳定,安全系数为1.27,而在近场强震作用下,潜在崩滑体会失稳破坏。目前判断扎木弄沟危险性的关键是判别滑源区潜在崩滑体的稳定性与失稳趋势,因此需要开展易贡地区花岗岩体强度弱化机理研究,揭示高山高寒区岩体的破坏模式和弱化影响因素,在此基础上再定量化地对其稳定性和失稳趋势作出论证。
![]() 图 9 扎木弄沟潜在崩滑体发育特征(镜向NE, 照片由辛鹏研究员提供, 范围据李俊等, 2017修改)Figure 9. The location of potential collapse zone in Zhamunong gully
图 9 扎木弄沟潜在崩滑体发育特征(镜向NE, 照片由辛鹏研究员提供, 范围据李俊等, 2017修改)Figure 9. The location of potential collapse zone in Zhamunong gully6.2 易贡滑坡-堵江-溃坝灾害链影响范围研究
2000年易贡高位远程滑坡诱发的灾害链致灾性强、影响范围大,对路桥等基础设施和下游城镇居民造成了巨大的危害。目前,建设规划中的易贡藏布大桥等桥梁位于溃坝-洪水影响范围内,如果潜在崩滑体失稳堵江,诱发的流域灾害链会导致路桥被毁、铁路中断,将造成巨大损失,因此需要准确分析计算易贡湖库容、潜在崩滑体崩滑堵江后溃坝的洪水位、灾害链影响范围等要素。灾害链影响范围研究常用的方法主要有野外迹象识别、遥感影像解译、数值模拟、InSAR监测、监测站记录等,当下研究关注较多的是溃坝-洪水诱发的次生灾害规模数量,而溃坝洪水动力特征及诱发灾害机制、次生灾害区域性特征等研究较少,可以加强该类研究,有助于支撑铁路线路、桥梁设计等工程建设,制定防灾减灾措施,降低重大灾害风险。
表 6 扎木弄沟潜在崩滑体特征(李俊等, 2017)Table 6. Characteristics of potential collapse rockmass in Zhamunong gully崩塌体编号 宽度/m 平均崩滑面积/m2 体积/108 m3 BH01 935.30 100314.00 0.94 BH02 822.07 111879.50 0.92 6.3 极高山高位远程滑坡监测预警研究
极高山地区的高位远程滑坡如易贡高位远程滑坡,具有超视距隐蔽性、高位启动、过程时间短等特点,其通常位于V形河谷区陡峭坡体中上部,海拔可高达4000 m之上。滑源区通常被冰雪或植被覆盖,常因为人工难以进入排查而被忽略,因此对于高位滑坡的超视距隐蔽性,传统的人工排查方法已经不再适用。许强等(2019)提出了空-天-地一体化三查体系,能够有效进行高位隐蔽性重大地质灾害的早期识别,即先利用光学遥感和合成孔径雷达干涉测量技术(InSAR),从“深空”宏观视角对大面积区域进行灾害的识别普查,其次基于机载激光雷达(LiDAR)和无人机摄影技术,从“天空”次宏观视角对部分重大隐患区域或重大隐患单体进行详查,最后根据专业人员的实地调查和坡体监测手段,对具有重大隐患的滑坡、崩塌、泥石流等地质灾害进行地面调查。极高山高位远程滑坡,地形地貌、地质背景和成因机制复杂,亟需开展现代化技术协同的多手段调查、高危险性个体重点监测研究、多源因素耦合指标预警、重大地质灾害应急处置等研究(许强, 2020; 黄细超等, 2021; 杨成业等, 2022),对于防治极高山高位远程滑坡等重大地质灾害具有重要的科学意义。
7. 结论
(1) 基于遥感解译、高精度DEM数据和野外调查等方法,进一步核算认为2000年易贡高位远程滑坡滑源区崩滑体积约为9225×104 m3,堆积体方量为2.81×108~3.06×108 m3。
(2) 易贡高位远程滑坡的最大速度位于高速铲刮滑动区的上部,据统计,滑坡最大速度为44~138 m/s,滑坡全过程的平均速度为15.6~40 m/s,碎屑流状态时的速度为16~28.5 m/s,目前滑坡速度的分布特征认识存在差异,可基于高分辨率的地形数据、野外调查分析、地震波曲线、试验等深入分析论证。
(3) 易贡高位远程滑坡的破坏启滑,受到内外动力作用共同控制,是在岩体长期蠕变(频繁的中小地震、冻融循环、干湿循环、加卸载循环等作用)过程中,受到短期影响(强降雨、强震、冰雪融水等作用)而触发的,该分析对于高山高寒区的高位岩体稳定性研判和失稳趋势研究具有一定的指导意义。
(4) 易贡高位远程滑坡具有原址溯源周期性的特征,其复发周期可能为百年尺度,目前认为滑源区存在2块单个体积近千万方的潜在不稳定岩体,可能再次发生滑坡-堵江-溃坝-洪水灾害链,建议对该区的高位潜在失稳岩体开展InSAR形变监测、岩体损伤规律与潜在失稳规律研究、滑坡-堵江-溃坝灾害链效应研究,提升该滑坡和该区的防灾减灾能力和水平。
致谢: 中国地质科学院地质力学研究所辛鹏研究员提供了易贡滑坡滑源区照片(图 9),中国地质大学(北京)博士生张献兵、硕士生张怡颖、李彩虹在部分图件绘制中提供了帮助,在此一并表示感谢。 -
图 1 2000年易贡滑坡遥感影像图(据Guo et al., 2020改编)
Figure 1. Remote sensing image of Yigong landslide area in 2000
图 2 2000年易贡滑坡空间分区图(据殷跃平, 2000修改)
Figure 2. Spatial zoning map of Yigong landslide in 2000
图 3 2000年易贡滑坡崩滑源区对比图(a、b底图为Landsat5、7影像, 据USGS: http://glovis.usgs.gov/;c基于GIS空间分析的DEM作差结果,DEM据https://earthdata.nasa.gov/)
a—2000年1月5日影像;b—2000年5月4日影像;c—2000年滑坡前后DEM作差分析结果;d—2000年滑坡前后DEM挖填分析结果
Figure 3. Comparison of slide source zone of Yigong landslide before and after sliding in 2000
图 4 1998年、1999年和2000年3月1日至4月30日易贡地区降雨与温度统计图(据Zhou et al.,2016修改)
Figure 4. Statistics of rainfall and temperature in Yigong area from March 1 to April 30 in 1998, 1999 and 2000
图 8 易贡地区不同期次滑坡地质年代分布特征(据Guo et al., 2020)
Figure 8. Age ranges dating the different landslides at the Yigong location
图 9 扎木弄沟潜在崩滑体发育特征(镜向NE, 照片由辛鹏研究员提供, 范围据李俊等, 2017修改)
Figure 9. The location of potential collapse zone in Zhamunong gully
表 1 2000年易贡滑坡初始崩滑体体积历史研究统计结果
Table 1 The statistics table of historical studies of the initial landslide volume of Yigong landslide in 2000
序号 崩塌区体积/m3 研究方法 文献来源 1 上亿 野外调查、估算 殷跃平, 2000 2 1000×104 野外调查、估算 薛果夫等, 2000 3 3000×104 野外调查、估算 刘伟, 2002; 黄润秋, 2004 4 4000×104 遥感解译 Zhang et al., 2013 5 7500×104 DEM数据分析、遥感解译、滑体等高线重建 Evans et al., 2011 6 9000×104 DEM数据分析、遥感解译、根据铲刮等参数推测 Delaney et al., 2015 7 9118×104 DEM数据分析、遥感解译比对 王治华, 2006 8 10000×104 野外调查、估算 Shang et al., 2003; Yin et al., 2012; Zhou et al., 2016; Zhuang et al., 2020 9 9225×104 DEM数据作差分析、遥感解译 本文 表 2 易贡滑坡堆积体体积历史研究统计结果
Table 2 The statistics table of historical studies for Yigong landslide accumulation volume
序号 体积/m3 研究方法 文献来源 1 9.11×107 遥感解译、DEM数据分析 Wang, 2008 2 2.80×108~3.00×108 野外调查 殷跃平, 2000;刘宁, 2000;周刚炎等, 2000;刘国权等, 2001b 3 3.00×108 野外调查、遥感解译等 Zhou et al., 2001; 柴贺军等, 2001; Wang et al., 2002; Shang et al., 2003; Xu et al., 2012; Zhuang et al., 2020 4 >3.80×108 GPS实地测量、遥感解译 任金卫等, 2001 5 1.05×108 遥感解译、DEM数据分析 Evans et al., 2011 6 1.15×108 遥感解译、DEM数据分析、GPS野外测绘 Delaney et al., 2015 7 1.67×108 质量密度分析 Ekströmet al., 2013 8 1.29×108 数字地形数据分析 Liu et al., 2018 9 2.81×108~3.06×108 对比分析、遥感解译 本文 表 3 易贡滑坡速度研究结果统计结果
Table 3 Speed statistics of Yigong landslide
序号 速度/(m·s-1) 研究方法 参考文献 1 Vmax=50 野外调查 朱平一等, 2000 2 V1=48, V2=16 根据地震波曲线计算 任金卫等, 2001 3 V3=37~39;Vmax=65 数值模拟(离散元法) 柴贺军等, 2001 4 V3=37~39 野外调查 刘伟, 2002 5 V3>14 野外调查 Shang et al., 2003 6 Vmax>44 野外调查 黄润秋, 2004 7 Vmax=44 野外调查 许强等, 2007 8 Vmax=117 数值计算 周鑫等, 2010 9 V3=15.6;Vmax=129.9 数值模拟(DAN软件) Delaney et al., 2015 10 Vmax=53 数值模拟(PFC软件) 陈锣增, 2016 11 Vmax=110.4 数值模拟 Liu et al., 2018 12 V1=90;V2=28.5;V3=30.12;Vmax=121 根据地震波曲线计算 李俊等, 2018 13 V3=35;Vmax=90 数值模拟(DAN软件) 戴兴建等, 2019; Zhuang et al., 2020 14 V3=40;Vmax=100 数值模拟(SPH方法) Dai et al., 2021 15 Vmax=138 数值模拟 Zhou et al., 2020 注: V1—崩塌下落的平均速度;V2—碎屑流的平均速度;V3—滑坡全过程平均速度;Vmax—滑坡过程中最大速度;SPH—Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics,光滑粒子流体动力学 表 4 2000年易贡滑坡堰塞湖方量统计结果
Table 4 The statistical table of volume for Yigong landslide dammed lake in 2000
时间 水面高程/m 湖水面积/km2 水量/108m3 研究方法 参考文献 堰塞之前 / 15.000 0.70 水文实测 殷跃平, 2000 5月24日 44.400 10.70 ADCP法实测 周刚炎等, 2000 6月8日 50.000 31.44 水文实测 鲁修元等, 2000 4月13日 / 19.900 / 遥感解译 王治华等, 2001 5月4日 33.700 5月9日 37.300 5月20日 43.600 4月13日 2214 18.909 1.55 遥感解译
DEM数据分析Wang et al., 2002; 王治华, 2005 5月4日 2225 33.659 5.84 5月9日 2228 36.320 7.76 5月12日 2229 37.979 8.41 5月20日 2234 43.121 13.05 6月10日 2244 52.855 23.29 6月17日 2209 9.280 0.43 / 2220 24.072 1.75 遥感解译
DEM数据分析Delaney et al., 2015 2225 28.010 3.13 2230 31.939 4.69 2240 38.241 8.51 2250 43.371 12.87 2255 45.251 15.11 2260 47.064 17.59 2265 48.926 20.15 2270 50.578 22.80 2280 53.272 28.29 注:ADCP(Acoustic Doppler Current Profilers)——声学多普勒流速剖面仪 表 5 2000年易贡滑坡堰塞坝体物质组成(刘国权等, 2001b)
Table 5 Material composition table of Yigong landslide dam body in 2000
泄流渠尾部 泄流渠中部 引水进口处 渠道高程 低 高 低 物质组成 碎、块石含量30%~40%,灰白(褐)色砂壤土含碎石、块石、大块石,块径一般3~20 cm,大的1~5 m,个别大于10 m 碎、块石含量50%~60%,碎、块石砂壤土 碎、块石含量60%~70%,砂壤土含碎石、块石,碎石、块石成分以大理岩、石英岩、混合花岗岩为主 表 6 扎木弄沟潜在崩滑体特征(李俊等, 2017)
Table 6 Characteristics of potential collapse rockmass in Zhamunong gully
崩塌体编号 宽度/m 平均崩滑面积/m2 体积/108 m3 BH01 935.30 100314.00 0.94 BH02 822.07 111879.50 0.92 -
Clague J J, Evans S G. Canadian geographer/Le Géographe Canadian[J]. Rock Avalanches, 1987, 31(3): 278-282.
Dai Z L, Xu K, Wang F W, et al. Numerical investigation on the kinetic characteristics of theYigong debris flow in Tibet, China[J]. Water, 2021, 13(8): 1076. doi: 10.3390/w13081076
Delaney K B, Evans S G. The 2000 Yigong landslide(Tibetan Plateau), rockslide-dammed lake and outburst flood: Review, remote sensing analysis, and process modelling[J]. Geomorphology, 2015, 246: 377-393. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.06.020
Ekstrom G, Stark C P. Simple scaling of catastrophic landslide dynamics[J]. Science, 2013, 339(6126): 1416-1419. doi: 10.1126/science.1232887
Evans S G, Delaney K B. Characterization of the 2000 Yigong Zangbo River(Tibet) landslide dam and impoundment by remote sensing, natural and artificial rockslide dams[J]. Geomorphology, 2011, 133: 543-559.
Fan J R, Zhang X Y, Su F H, et al. Geometrical feature analysis and disaster assessment of theXinmo landslide based on remote sensing data[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2017, 14(9): 1677-1688. doi: 10.1007/s11629-017-4633-3
Guo C B, Montgomery D R, Zhang Y S, et al. Evidence for repeated failure of the giantYigong landslide on the edge of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Scientific reports, 2020, 10(1): 14317. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71330-1
Hao Z C, Ju Q, Jiang W J, et al. Characteristics and Scenarios Projection of Climate Change on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. The Scientific World Journal, 2013: 129793.
International Union of Geological Sciences Working Group on Landslides. A suggested method for describing the rate of movement of a landslide[J]. Bulletin of the International Association of Engineering Geology, 1995, 52(1): 75-78. doi: 10.1007/BF02602683
Kojan E, Hutchinson J N. Mayunmarca Rockslide and Debris Flow, Peru-ScienceDirect[J]. Developments in Geotechnical Engineering, 1978, 14: 315-353.
Liu W, He S M. Dynamic simulation of a mountain disaster chain: landslides, barrier lakes, and outburst floods[J]. Natural Hazards, 2018, 90(5): 1-19.
Mcguire B. Potential for a hazardous geospheric response to projected future climate changes[J]. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng., 2010, 368(1919): 2317-2345.
Shang Y J, Yang Z F, Li L H, et al. A super-large landslide in Tibet in 2000: background, occurrence, disaster, and origin[J]. Geomorphology, 2003, 54: 225-243. doi: 10.1016/S0169-555X(02)00358-6
Turzewski M D, Huntington K W, Leveque R J. The geomorphic impact of outburst floods: integrating observations and numerical simulations of the 2000 Yigong Flood, Eastern Himalaya[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 2019, 124(5): 1056-1079. doi: 10.1029/2018JF004778
Wang Z H, Lv J T. Satellite monitoring of the Yigong landslide in Tibet, China[J]. Proceedings of SPIE-The International Society for Optical Engineering, 2002, 4814: 34-38.
Wang Z H. A thunder at the beginning of the 21st century-The giantYigong Landslide[C]//The Tenth International Symposium on Landslides and Engineered Slopes, 2008: 1068-1075.
Wen B P, Wang S J, Wang E Z, et al. Characteristics of rapid giant landslides in China[J]. Landslides, 2004, 1(4): 247-261. doi: 10.1007/s10346-004-0022-4
Xu Q, Shang Y J, Asch T V, et al. Observations from the large, rapidYigong rock slide-debris avalanche, southeast Tibet[J]. NRC Research Press, 2012, 49(5): 589-606.
Yin Y P, Xing A G. Aerodynamic modeling of theYigong gigantic rock slide-debris avalanche, Tibet, China[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2012, 71(1): 149-160. doi: 10.1007/s10064-011-0348-9
Zhang M, Yin Y P. Dynamics, mobility-controlling factors and transport mechanisms of rapid long-runout rock avalanches in China[J]. Engineering Geology, 2013, 167(12): 37-58.
Zhou C H, Yue Z Q, Lee C F, et al. Satellite image analysis of a huge landslide at Yi Gong, Tibet, China[J]. Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology & Hydrogeology, 2001, 34(4): 325-332.
Zhou G G D, Roque P J C, Xie Y X, et al. Numerical study on the evolution process of a geohazards chain resulting from the Yigong landslide[J]. Landslides, 2020, 17: 2563-2576. doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01448-w
Zhou J W, Cui P, Hao M H. Comprehensive analyses of the initiation and entrainment processes of the 2000Yigong catastrophic landslide in Tibet, China[J]. Landslides, 2016, 13(1): 39-54. doi: 10.1007/s10346-014-0553-2
Zhuang Y, Yin Y P, Xing A G, et al. Combined numerical investigation of theYigong rock slide-debris avalanche and subsequent dam-break flood propagation in Tibet, China[J]. Landslides, 2020, 17(9): 2217-2229. doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01449-9
Zhuang Y, Xang A G, Leng Y Y, et al. Investigation of characteristics of long runout landslides based on the multi-source data collaboration: a case study of the Shuicheng basalt landslide in Guizhou, China[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2021, 54: 3783-3798. doi: 10.1007/s00603-021-02493-0
柴贺军, 王士天, 许强, 等. 西藏易贡滑坡物质运动全过程数值模拟研究[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护, 2001, 12(2): 1-3+82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2001.02.001 程谦恭, 张倬元, 黄润秋. 高速远程崩滑动力学的研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 山地学报, 2007, 25(1): 72-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA200701007.htm 陈锣增. 易贡高速远程滑坡运动颗粒流数值分析[D]. 西南交通大学硕士学位论文, 2016. 崔鹏, 陈容, 向灵芝, 等. 气候变暖背景下青藏高原山地灾害及其风险分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2014, 10(2): 103-109. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHBH201402004.htm 戴兴建, 殷跃平, 邢爱国. 易贡滑坡-碎屑流-堰塞坝溃坝链生灾害全过程模拟与动态特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2019, 30(5): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201905001.htm 高浩源, 高杨, 贺凯, 等. 贵州水城"7.23"高位远程滑坡冲击铲刮效应分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(4): 535-546. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202004009.htm 高杨, 李滨, 高浩源, 等. 高位远程滑坡冲击铲刮效应研究进展及问题[J]. 地质力学学报, 2020, 26(4): 510-519. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX202004008.htm 郭长宝, 杜宇本, 张永双, 等. 川西鲜水河断裂带地质灾害发育特征与典型滑坡形成机理[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(1): 121-134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.01.010 郭广猛. 对西藏易贡特大滑坡的新认识[J]. 地学前缘, 2005, 12(2): 276-276. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200502010.htm 何思明, 白秀强, 欧阳朝军, 等. 四川省茂县叠溪镇新磨村特大滑坡应急科学调查[J]. 山地学报, 2017, 35(4): 598-603. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA201704020.htm 黄润秋. 中国西部地区典型岩质滑坡机理研究[J]. 地球科学进展, 2004, 19(3): 443-450. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ200403015.htm 黄细超, 余天彬, 王猛, 等. 金沙江结合带高位远程滑坡灾害链式特征遥感动态分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2021, 32(5): 40-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH202105005.htm 李潮流, 康世昌. 青藏高原不同时段气候变化的研究综述[J]. 地理学报, 2006, 61(3): 327-335. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2006.03.012 李菲, 郜永祺, 万欣, 等. 全球变暖与地球"三极"气候变化[J]. 大气科学学报, 2021, 44(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJQX202101001.htm 李华, 史文兵, 朱要强, 等. 贵州省水城县"7·23"灾难性滑坡形成机制研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2020, 29(6): 188-198. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH202006020.htm 李俊, 陈宁生, 欧阳朝军, 等. 扎木弄沟滑坡型泥石流物源及堵河溃坝可能性分析[J]. 灾害学, 2017, 32(1): 80-84, 116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2017.01.014 李俊, 陈宁生, 刘美, 等. 2000年易贡乡扎木弄沟滑坡型泥石流主控因素分析[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2018, 16(6): 187-193. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NSBD201806026.htm 李晓, 李守定, 陈剑, 等. 地质灾害形成的内外动力耦合作用机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2008, 27(9): 1792-1792. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200809008.htm 鲁修元, 杨明刚, 赵丹, 等. 西藏易贡藏布扎木弄沟特大型滑坡成因及溃决分析[C]//第六届全国工程地质大会论文集, 2000: 263-264. 吕杰堂, 王治华, 周成虎. 西藏易贡滑坡堰塞湖的卫星遥感监测方法初探[J]. 地球学报, 2002, (4): 363-368. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200204014.htm 吕杰堂, 王治华, 周成虎. 西藏易贡大滑坡成因探讨[J]. 地球科学, 2003a, 47(1): 107-110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200301018.htm 吕杰堂, 王治华, 周成虎. 西藏易贡滑坡堰塞湖的卫星遥感监测方法初探[J]. 地球学报, 2003b, 24(4): 363-368. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200204014.htm 刘国权, 鲁修元. 西藏易贡藏布扎木弄沟特大型山体崩塌滑坡泥石流成因分析[J]. 西藏科技, 2000, 7(4): 15-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XZKJ200004003.htm 刘国权, 鲁修元, 李扬. 西藏扎木弄沟山体滑坡和泥石流成因分析[J]. 东北水利水电, 2001a, 19(6): 49-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBSL200106023.htm 刘国权, 鲁修元, 李扬. 西藏易贡崩塌滑坡泥石流堆积体溃决分析[J]. 东北水利水电, 2001b, 19(7): 26-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBSL200107013.htm 刘宁. 科学制定西藏易贡滑坡堵江减灾预案[J]. 中国水利, 2000, 51(7): 37-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLZG200007019.htm 刘伟. 西藏易贡巨型超高速远程滑坡地质灾害链特征研析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2002, 13(3): 11-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH200203001.htm 刘铮, 李滨, 贺凯, 等. 地震作用下西藏易贡滑坡动力响应特征分析[J]. 地质力学学报, 2020, 26(4): 471-480. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX202004004.htm 任金卫, 单新建, 沈军, 等. 西藏易贡崩塌-滑坡-泥石流的地质地貌与运动学特征[J]. 地质论评, 2001, 66(6): 642-647+4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200106018.htm 邵翠茹. 雅鲁藏布大峡谷地区地震活动性研究[D]. 中国地震局地球物理研究所硕士学位论文, 2009. 唐方头, 宋键, 曹忠权, 等. 最新GPS数据揭示的东构造结周边主要断裂带的运动特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 2010, 53(9): 2119-2128. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201009013.htm 万海斌. 西藏易贡巨型山体滑坡抢险减灾概况[J]. 中国减灾, 2000, 10(4): 28-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJI200004010.htm 王思敬. 地球内外动力耦合作用与重大地质灾害的成因初探[J]. 工程地质学报, 2002, 10(2): 115-117. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200202000.htm 王绍令, 赵秀锋, 郭东信, 等. 青藏高原冻土对气候变化的响应[J]. 冰川冻土, 1996, 18(S1): 157-165. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT1996S1018.htm 王治华, 吕杰堂. 从卫星图像上认识西藏易贡滑坡[J]. 遥感学报, 2001, 5(4): 312-316. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXB200104011.htm 王治华. 中国滑坡遥感[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2005, 18(1): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTYG200704003.htm 王治华. 大型个体滑坡遥感调查[J]. 地学前缘, 2006, 13(5): 516-523. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200605017.htm 吴玮莹, 许冲. 2014年鲁甸MW 6.2地震触发滑坡新编目[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(5): 1140-1148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201805014.htm 夏式伟. 易贡滑坡-碎屑流-堰塞坝溃决三维数值模拟研究[D]. 上海交通大学硕士学位论文, 2018. 邢爱国, 徐娜娜, 宋新远. 易贡滑坡堰塞湖溃坝洪水分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2010, 18(1): 78-83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201001014.htm 许强, 董思萌. 西藏易贡特大山体崩塌滑坡事件[C]//中国岩石力学与工程实例第一届学术会议论文集. 中国岩石力学与工程学会, 2007: 53-58. 许强, 李为乐, 董秀军, 等. 四川茂县叠溪镇新磨村滑坡特征与成因机制初步研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2017, 36(11): 2612-2628. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201711002.htm 许强, 董秀军, 李为乐. 基于天-空-地一体化的重大地质灾害隐患早期识别与监测预警[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2019, 44(7): 957-966. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCH201907002.htm 许强. 对滑坡监测预警相关问题的认识与思考[J]. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(2): 360-374. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202002017.htm 薛果夫, 刘宁, 蒋乃明, 等. 西藏易贡高速巨型滑坡堵江事件的调查与减灾措施分析[C]//第六次全国岩石力学与工程学术大会, 2000: 640-644. 杨成业, 张涛, 高贵, 等. SBAS-InSAR技术在西藏江达县金沙江流域典型巨型滑坡变形监测中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2022, 33(3): 94-105. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH202203011.htm 姚檀栋, 杨志红, 刘景寿. 冰芯记录所揭示的青藏高原升温[J]. 科学通报, 1994, 45(5): 438-441. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199405015.htm 姚檀栋, 刘晓东, 王宁练. 青藏高原地区的气候变化幅度问题[J]. 科学通报, 2000, 51(1): 98-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200001020.htm 殷跃平. 西藏波密易贡高速巨型滑坡特征及减灾研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2000, 44(4): 8-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200004002.htm 殷跃平. 汶川八级地震地质灾害研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2008, 16(4): 433-444. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200804000.htm 殷跃平, 王文沛, 张楠, 等. 强震区高位滑坡远程灾害特征研究——以四川茂县新磨滑坡为例[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(5): 827-841. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201705002.htm 张永双, 郭长宝, 姚鑫, 等. 青藏高原东缘活动断裂地质灾害效应研究[J]. 地球学报, 2016, 37(3): 277-286. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201603004.htm 张明, 殷跃平, 吴树仁, 等. 高速远程滑坡-碎屑流运动机理研究发展现状与展望[J]. 工程地质学报, 2010, 18(6): 805-817. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201006001.htm 郑光, 许强, 刘秀伟, 等. 2019年7月23日贵州水城县鸡场镇滑坡-碎屑流特征与成因机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(3): 541-556. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202003012.htm 周刚炎, 李云中, 李平. 西藏易贡巨型滑坡水文抢险监测[J]. 人民长江, 2000, 31(9): 30-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RIVE200009013.htm 周鑫, 邢爱国, 陈禄俊. 易贡高速远程滑坡近程凌空飞行数值分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2010, 44(6): 833-838. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHJT201006025.htm 周昭强, 李宏国. 西藏易贡巨型山体滑坡及防灾减灾措施[J]. 水利水电技术, 2000, 42(12): 47-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJWJ200012022.htm 朱博勤, 聂跃平. 易贡巨型高速滑坡卫星遥感动态监测[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2001, 10(3): 103-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH200103019.htm 朱成明, 张彩霞. 西藏扎木弄沟地质灾害治理初步探讨[J]. 人民长江, 2015, 46(18): 26-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RIVE201518008.htm 朱平一, 王成华, 唐邦兴. 西藏特大规模碎屑流堆积特征[J]. 山地学报, 2000, 18(5): 453-456. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA200005018.htm -
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 李朝辉,张柯宏. 藏东南某滑坡成因分析及稳定性评价. 铁道勘察. 2025(01): 13-19 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 石有权,叶文科,李雪松,张蕊,赵利奎. 复杂艰险山区铁路高陡边坡的研究与防治措施. 云南水力发电. 2025(02): 196-202 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 田旭文,王彦兵,朱姝,姚鑫,李显鑫. 藏东南输电走廊北线区域地质环境与主要地质安全问题. 地质力学学报. 2025(01): 91-108 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 邵杰,杨欣杰,陈喜庆,滕超,易锦俊,董美玲,张泽琛,曹军,朱宁,肖登,孙思远,吕菲. 西藏易贡湖流域地表水水化学特征及其控制因素. 干旱区研究. 2024(02): 250-260 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 杜鹏,陈宁生,伍康林,李志,张瀛玉龙. 基于随机森林模型的藏东南地区滑坡易发性评价及主控因素分析. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(02): 328-344 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(6)



 下载:
下载: