Analysis of the physiographic stages of the development and evolution process of karst geomorphology in Guilin, China
-
摘要:
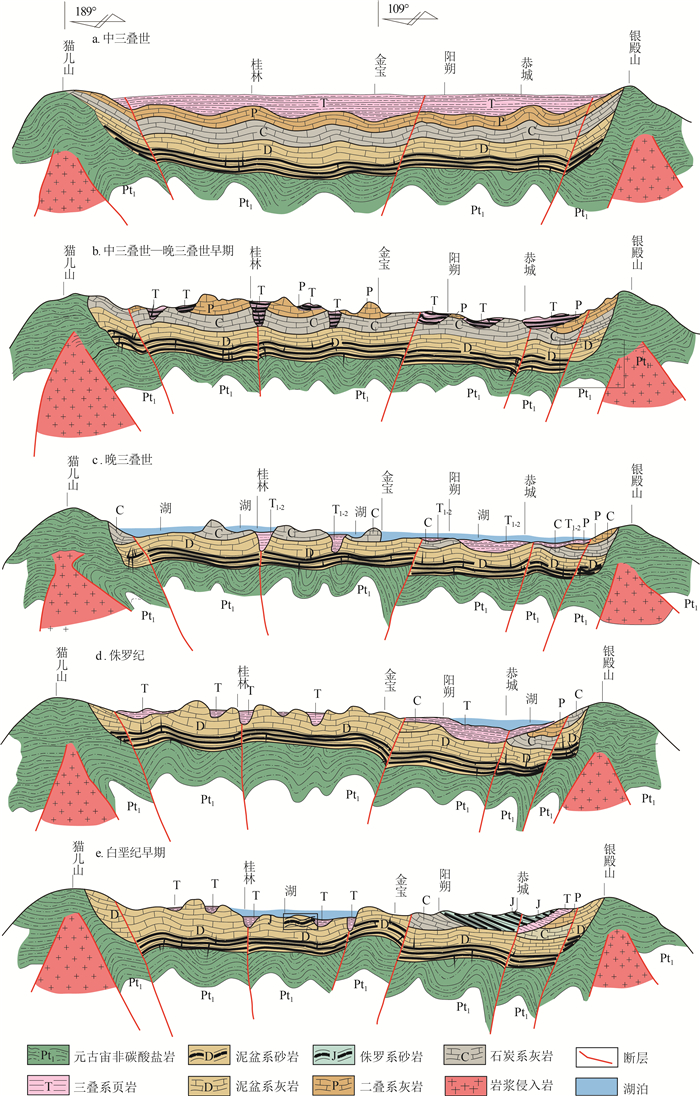
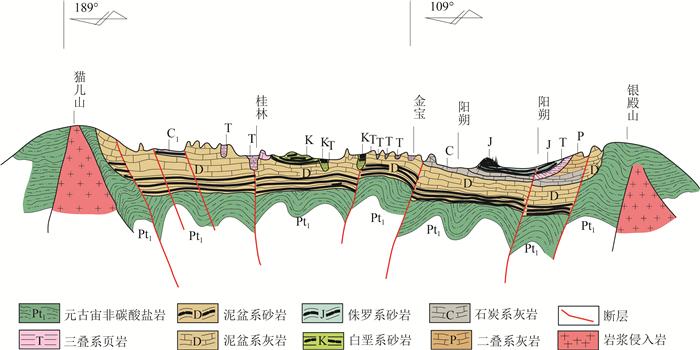
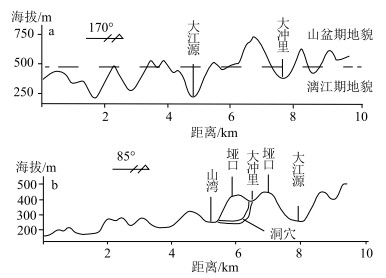
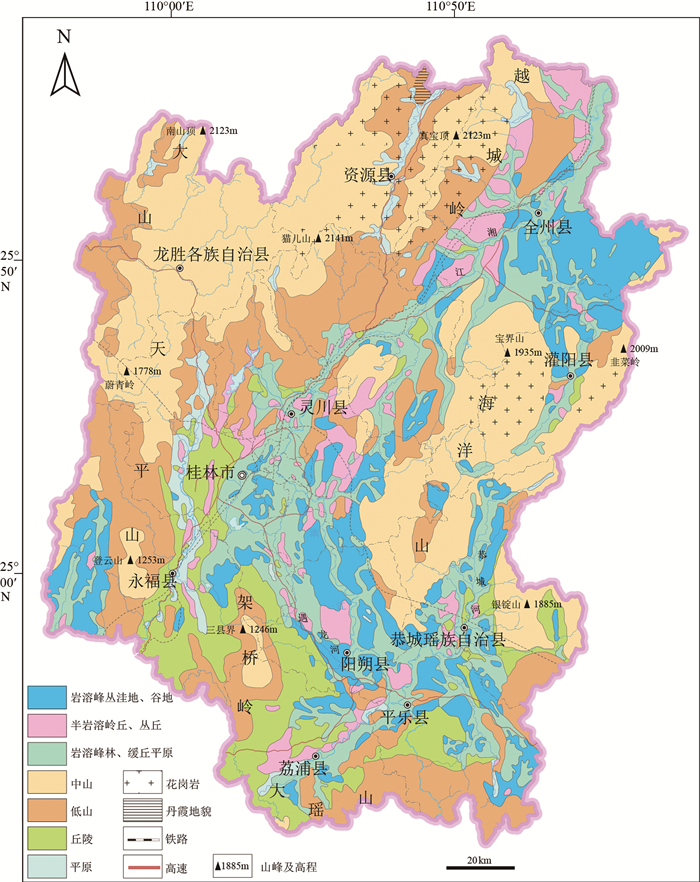
从地文期角度,分析桂林岩溶地貌的发育演化过程,为研究岩溶地貌发育演化规律及探讨岩溶地貌保护利用和可持续发展提供科学依据。通过调查区内地层、地貌的空间展布特征,塑造地貌营力(水系)变化,结合区内构造发展史及岩相古地理环境变化等要素,对桂林地貌发育演化过程的地文时期进行解析。研究表明,①中三叠世—白垩纪晚期,由地壳升降运动引起海进海退,为研究区现代岩溶地貌发育奠定了物质基础和地势基本构架;②古新世—上新世,区内发育的内陆断陷、凹陷盆地,为现代岩溶地貌发育水动力奠定了地形条件;③渐新世末期,广西南部断块构造异常显著,区内向南流的水系溯源侵蚀能力加强,使阳朔与桂林水系贯通(漓江的形成),在水文效应下塑造了桂林现代岩溶地貌景观。因此,根据区内地质演化史、外部营力变化(水系)、地貌特征等要素,桂林岩溶地貌发育演化分为猫儿山期、山盆期和漓江期3个地文期。
Abstract:This paper analyzes the development and evolution process of karst geomorphology in Guilin from the perspective of physiognomy.In order to provide scientific basis for studying the development and evolution law of karst geomorphology and exploring the protection, utilization and sustainable development of karst geomorphology.Through examining the spatial distribution characteristics of strata and landforms within the area, as well as the changes to geomorphic forces(hydrological systems), and integrating factors such as the area's tectonic development history and the changes in lithofacies paleogeographic environments, we can analyze the stages of Guilin's geomorphological development and evolution.The research indicates that: ①From the Middle Triassic to the Late Cretaceous, the rise and fall of the Earth's crust caused marine transgressions and regressions, which established the material foundation and fundamental framework for the development of the modern karst landforms in the study area.②From the Paleocene to the Pliocene, the development of inland basins due to faulting and subsidence provided the topographical conditions necessary for the development of hydrodynamic forces in modern karst landforms.③In the end of the Oligocene, the fault block structure in southern Guangxi became significantly pronounced, strengthening the ability of the region's southward flowing water systems to erode and trace their paths upstream, thereby connecting the water systems of Yangshuo and Guilin(leading to the formation of the Lijiang River).This resulted in the shaping of Guilin's modern karst landform landscape under the influence of these hydrological effects.Therefore, based on the geological evolution history, changes in external forces(hydrological systems), and geomorphological characteristics of the area, the development and evolution of Guilin's karst geomorphology can be categorized into three geologic periods: the Maoershan period, the Mountain Basin period, and the Lijiang period.
-
致谢: 感谢桂东北岩溶系统基础地质调查项目组的其余同事,在项目执行期间给予极大的帮助,为论文撰写提供了翔实素材;感谢中国地质科学院岩溶地质研究所岩溶区域地质地貌与洞穴团队和贵州省山地资源研究所洞穴与旅游中心团队在项目执行及论文撰写期间的帮助;感谢审稿专家对论文修改提出的宝贵意见与建议。
-
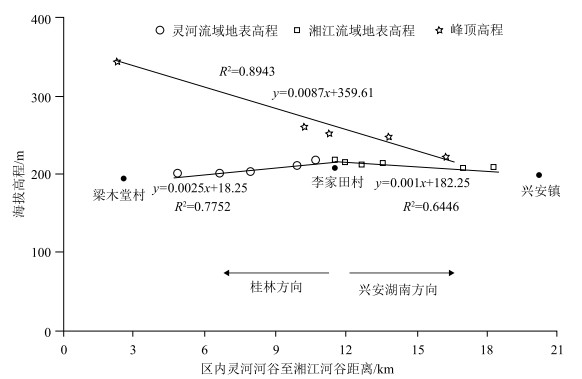
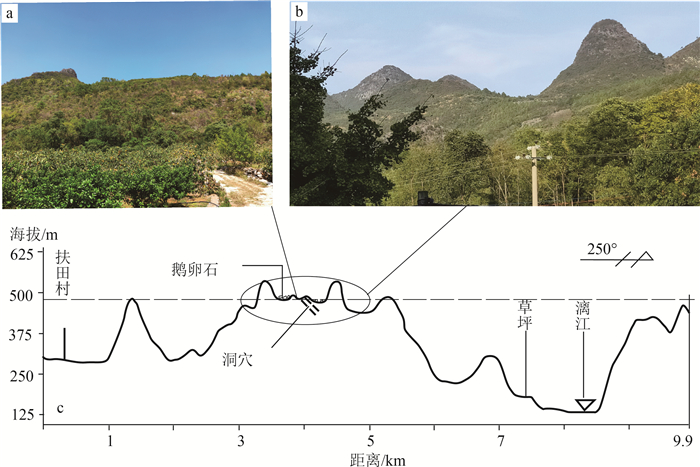
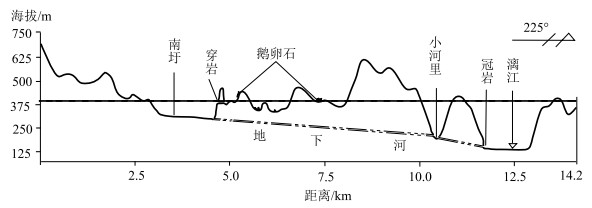
图 3 桂林湘桂走廊地貌高程拟合图(据罗书文等,2021)
Figure 3. Geomorphic elevation fitting map of Xiang-Gui Corridor in Guilin
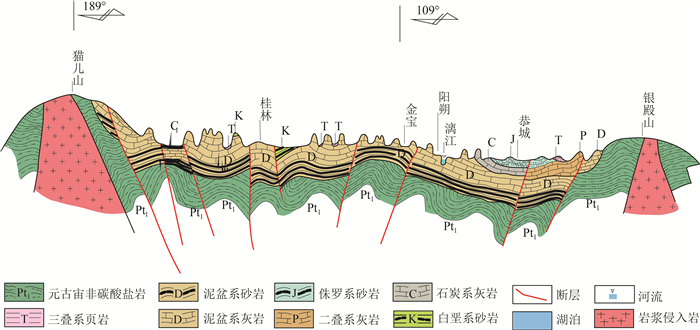
表 1 研究区出露地层及构造运动
Table 1 Outcrops and tectonic movements in the study area

表 2 三叠纪地层残积状况(刘金荣,1997a)
Table 2 Statistical table of residual state in Triassic strata
残积所处地貌位置 岩溶平原及谷地内 坡脚处 山坡上 峰丛洼地内 溶隙及洞穴内 山顶 数量/处 26 9 6 7 2 0 相对高度/m 0~30 0~25 20~310 20~290 13.8~70 所占比例/% 52 18 12 14 4 0 表 3 漓江阶地划分(据缪钟灵,1998修改)
Table 3 The terraces of Lijiang River
-
Keith A. Some stages of Appalachian erosion[J]. Bull. Geol. Soc. Amer., 1896, 7(6): 519-525.
Perrineau A, Woerd J V D, Gaudemer Y, et al. Incision rate of the Yellow River in Northeastern Tibet constrained by 10Be and 26Al cosmogenic isotope dating of fluvial terraces: Implications for catchment evolution and plateau building[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2011, 353(1): 189-219. doi: 10.1144/SP353.10
Richards K, Clifford N J. The nature of explanation in geomorphology[C]//Gregory K J, Goudie A. The SAGE Handbook of Geomorphology. Los Angeles; London: SAGE, 2011.
Yamashita S, Naruse H, Nakajo T. Reconstruction of sediment-transport pathways on a modern microtidal coast by a new grain-size trend analysis method[J]. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci., 2018, 5: 7. doi: 10.1186/s40645-018-0166-9
陈治平, 刘金荣. 桂林盆地岩溶发育史的探讨[J]. 地理学报, 1980, (4): 338-347. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1980.04.006 邓自强, 林玉石, 张美良, 等. 桂林岩溶洼地和洞穴发生、发展的构造控制剖析[J]. 中国岩溶, 1987, (2): 48-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR198702011.htm 邓自强, 林玉石, 张美良, 等. 桂林地质构造与岩溶地貌发育的时序关系[J]. 中国岩溶, 1986, (4): 57-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR198604007.htm 邓自强, 林玉石, 张美良, 等. 略论古岩溶不整合——以广西阳朔白沙堡晚白垩世岩溶为例[J]. 广西地质, 1994, (2): 61-70 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDZ402.005.htm 邓自强, 林玉石, 刘功余, 等. 岩溶发育过程中的改造与建造作用分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 1993, (1): 26-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR199301003.htm 邓自强, 林玉石, 刘功余, 等. 桂林岩溶与地质构造[M]. 重庆: 重庆出版社, 1988. 甘大昌. 桂林岩溶盆地第四纪粘土砾石层沉积与漓江袭夺[J]. 广西地质, 1992, (2): 83-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDZ199202013.htm 广西地方志编纂委员会编. 广西地质志[M]. 南宁: 广西人民出版社, 1985. 蒋忠诚. 论中国岩溶峰丛洼地的形成(英文)[J]. 中国岩溶, 1996, (Z1): 89-96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR1996Z1011.htm 李长安, 邵磊, 袁胜元, 等. 地文期-构造节律-气候旋回耦合与三峡地质灾害关系的探讨[J]. 地质科技情报, 2012, 31(5): 65-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201205010.htm 李兴中. 贵州高原喀斯特区地文期辨析[J]. 贵州地质, 2001, 18(3): 182-186. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZDZ200103008.htm 李吉均, 康建成. 中国第四纪冰期、地文期和黄土记录[J]. 第四纪研究, 1989, (3): 269-278. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1989.03.011 林玉石, 邓自强, 刘功余, 等. 岩溶交代改造断裂构造岩——以桂林岩溶区为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 1984, (1): 3-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR198401000.htm 刘功余, 林玉石, 邓自强, 等. 碳酸盐岩构造岩的类型及其特征——以桂林岩溶区为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 1987, (3): 5-14, 89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR198703000.htm 刘功余, 张美良, 邓自强, 等. 桂林晚白垩世红色岩溶建造中溶积钙质泥岩的成因及地质意义初探[J]. 中国岩溶, 1992, (2): 72-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR199202011.htm 刘金荣. 桂林三叠世古地理古气候及热带岩溶发育程度探讨[J]. 广西地质, 1997, (3): 31-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDZ703.005.htm 刘金荣. 广西热带岩溶地貌发育历史及序次探讨[J]. 中国岩溶, 1997, (4): 52-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR704.006.htm 刘金荣, 黄国彬, 黄学灵, 等. 广西区域热带岩溶地貌不同类型的演化浅议[J]. 中国岩溶, 2001, (4): 2-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR200104000.htm 刘金荣, 梁耀成. 在桂林机床厂又有第三纪地层发现[J]. 中国岩溶, 2005, (3): 249-254. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR200503014.htm 刘强, 汤民强, 贺惠忠, 等. 广东阳西沙扒海域埋藏古河道沉积特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2022, 52(6): 1791-1799. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202206004.htm 罗书文, 张远海, 陈伟海, 等. 基于流域水文地貌系统的清江流域地貌研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2010, 38(3): 1646-1649. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHNY201003193.htm 罗书文, 杨桃, 潘晓东, 等. 贵州落脚河峡谷景观特征及形成机制[J]. 重庆师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 36(4): 112-121. 罗书文, 贺卫, 杨桃, 等. 湘桂走廊地貌发育特征的地学意义及形成机制研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(5): 750-759. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202105002.htm 缪钟灵. 漓江发育演化及与相邻流域关系[J]. 中国岩溶, 1998, (4): 3-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR804.011.htm 邱维理. 中国地文期研究史[J]. 中国科技史料, 1999, (2): 3-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKS902.000.htm 卫彦升, 冯志强, 闫涛, 等. 华北板块中部中生代构造演化——以山西为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2022, 52(4): 1127-1152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202204008.htm 吴忱, 张秀清, 王然, 等. 华北山地夷平面研究[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2017, 33(1): 124-126, 封3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLGT201701022.htm 杨明德, 梁虹. 喀斯特流域水文地貌系统[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1998. 杨怀仁. 贵州中部之地形发育[J]. 地理学报, 1944, 11: 6-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLXB194400000.htm 袁宝印, 王振海. 青藏高原隆起与黄河地文期[J]. 第四纪研究, 1995, (4): 353-359. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ504.010.htm 袁宝印, 郭正堂, 乔彦松, 等. 地文期及其在新生代黄土和古地理研究中的意义[J]. 地质通报, 2008, (3): 300-307. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20080302&flag=1 袁道先. 论峰林地形[J]. 广西地质, 1984, (0): 79-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDZ198400011.htm 张维淹. 广西早、中三叠世层序地层[J]. 广西地质, 1995, (8:3). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDZ503.000.htm 张美良, 刘功余, 邓自强, 等. 广西晚白垩世古岩溶与成矿研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2010. 中国地科院地研所, 武汉地院. 中国古地理图集[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1985. 朱德浩. 桂林地区峰丛洼地的形态量计及其演化[J]. 中国岩溶, 1982, (2): 50-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR198202006.htm 朱学稳. 峰林喀斯特的性质及其发育和演化的新思考(1)[J]. 中国岩溶, 1991a, (1): 54-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR199103000.htm 朱学稳. 峰林喀斯特的性质及其发育和演化的新思考(2)[J]. 中国岩溶, 1991b, (2): 50-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR199103000.htm 朱学稳. 峰林喀斯特的性质及其发育和演化的新思考(3)[J]. 中国岩溶, 1991c, (3): 4-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR199103000.htm



 下载:
下载: