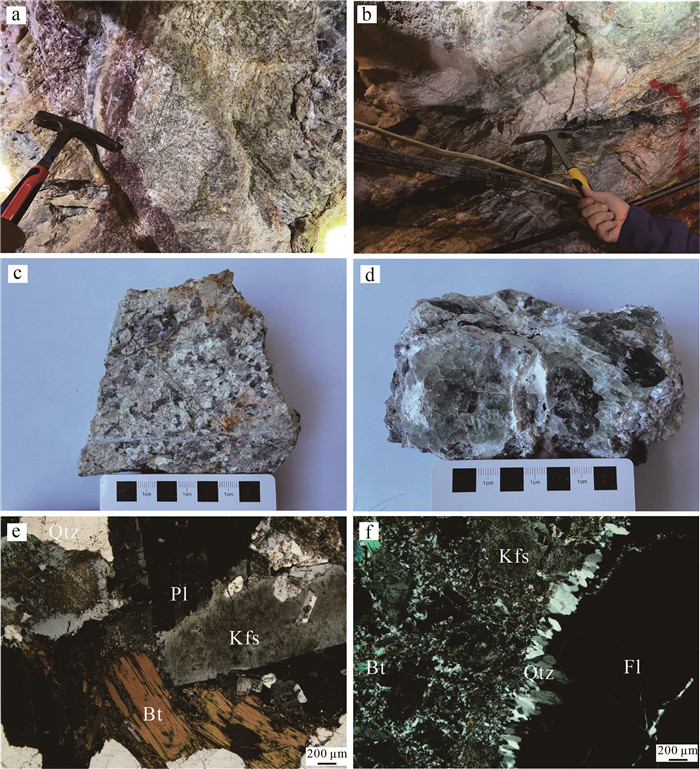
Geochemical characteristics of biotite granite in the Guangming fluorite deposit in eastern Hunan, China: Implications to fluorite mineralization
-
摘要:
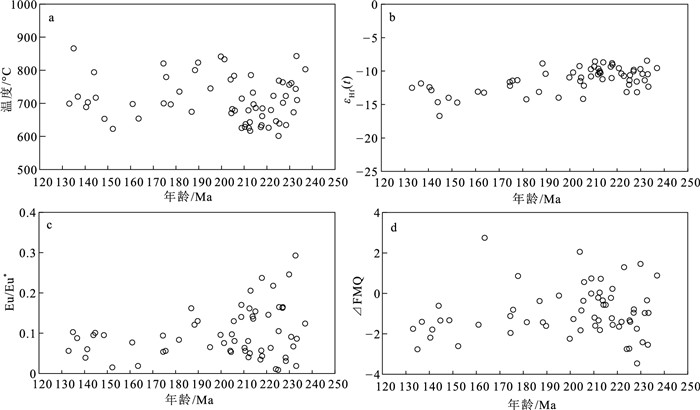
光明萤石矿产出于湘东锡田岩体北部,为探究矿区内黑云母花岗岩与萤石成矿的关联,对岩体和萤石矿体进行了系统的地球化学研究,并利用LA-(MC)-ICP-MS对黑云母花岗岩中锆石开展了U-Pb年代学、微量元素及Hf同位素地球化学研究。结果显示,黑云母花岗岩具有高硅(SiO2=72.62%~77.34%)、高碱(Na2O+K2O=6.03%~8.66%)、富铝(Al2O3=12.02%~13.83%)特征,A/CNK值介于1.07~1.14之间,为过铝质花岗岩。3个样品低U锆石的206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值在215~218 Ma之间,指示花岗岩侵位于印支期。矿区黑云母花岗岩印支期—燕山期锆石年龄为237~133 Ma,在230~210 Ma、190~170 Ma、150~130 Ma存在3个较集中的年龄峰期,暗示岩浆侵位后受到热事件影响,推测矿区岩浆活动具有多阶段性。黑云母花岗岩岩体有较强的负Eu异常,且富集大离子亲石元素Rb、Th、U,亏损Ba、Nb等元素;萤石具有中等程度的负Eu异常,Rb、Ba、Nb、Hf相对亏损,U、La、Nd、Zr、Y相对富集。按照燕山期成矿岩浆活动时间(133 Ma)估算,岩体εNd(t)=-11.2~-10.6,二阶段模式年龄为1793~1837 Ma;萤石εNd(t)=-11.3~-10.0,二阶段模式年龄为1741~1848 Ma,二者具有较一致的Nd同位素组成。岩体锆石Hf同位素测定值具有较大的变化范围,176Hf/177Hf=0.282234~0.282420,εHf(t)=-16.7~-8.5,TDM2=1756~2214 Ma,显示古—中元古代地壳模式年龄。综合研究发现,光明萤石矿多阶段岩浆活动起源于成熟地壳白云母的脱水熔融,经历了印支期—燕山期多期次的岩浆补给和较强的结晶分异。萤石矿石与矿区内燕山期花岗岩具有相似的稀土与微量元素特征,与黑云母花岗岩不同,暗示光明矿床萤石成矿与区内燕山期岩浆活动有关,成矿流体主要为岩浆热液,并有少量大气降水加入。
Abstract:Guangming fluorite deposit is located in the north of Xitian granite pluton in the eastern Hunan.Aiming to investigate the correlationship between the biotite granite and fluorite mineralization in the mining district, systematic geochemical studies of the rock mass and the orebody, as well as zircon LA-(MC) -ICP-MS U-Pb age, trace element and Hf isotopic characteristics of the biotite granite have been carried out.Biotite granite in the Guangming deposit is characterized by elevated SiO2, Al2O3 and total alkali contents, with A/CNK ratios of 1.07~1.14, showing peraluminous.Low-U zircons from three samples yield weighted average 206Pb/238U ages from 215 Ma to 218 Ma, indicative of Indosinian emplacement.The granite has zircon ages ranging from 237 Ma to 133 Ma, yielding three relatively concentrated age peaks at 230~210 Ma, 190~170 Ma and 150~130 Ma, indicating the influence of multi-stage magmatic activity.The biotite granite has strong Eu negative anomaly with weak positive Ce anomaly, being enriched in LILE(Rb, Th, U) and depleted in Ba, Nb, etc.The fluorite has moderate negative Eu anomaly with relatively depletion of Rb, Ba, Nb, Sm, Hf, Eu and enrichment of U, La, Nd, Zr, Y.The granite has εNd(t) values of -11.2 to -10.6 and the corresponding TDM2=1793~1837 Ma, while the fluorite has εNd(133 Ma) values of -11.3 to -10.0 and the corresponding TDM2=1741~1848 Ma.Hafnium isotope compositions showing a large variation, 176Hf/177Hf=0.282234~0.282420, εHf(133 Ma)=-16.70~-8.45, TDM2=1756~2214 Ma, indicating the crustal model age of Paleo-Mesoproterozoic.The comprehensive analysis suggests that the biotite granite in the Guangming deposit originated from the dehydration melting of muscovite in the mature crust, experienced multiple magmatic activities from Indosinian to Yanshanian.The biotite granite experienced strong differentiation and finally formed in an environment with low oxygen fugacity.The Yanshanian granite and the fluorite have similar characteristics of rare earth and trace elements, as well as the identical Nd isotopic compositions, different from Indosinian biotite granite, suggesting that fluorite mineralization in the Guangming deposit is related to the Yanshanian magmatism in the area.The ore-forming fluid is dominated by magmatic hydrothermal with minor addition of meteoric water.
-
Keywords:
- Yanshanian granitoid /
- fluorite /
- Xitian granite complex /
- eastern Hunan /
- South China
-
近年来发现的新疆喀腊大湾矿集区,已成为阿尔金地区最重要的矿集区(倪康等,2017),发现有喀腊大湾大型铁矿、喀腊达坂大型铅锌矿、达坂西中小型铜矿、大平沟金矿等。拉配泉组是该矿集区主要的赋矿地层,也是研究阿尔金北缘地区构造演化进程的重要地质单元(倪康等,2017)。随着喀腊大湾地区矿产资源的开发,学者们陆续对该地区基础地质、矿床成因开展了研究工作(陈宣华等,2009;陈柏林等,2010;2016;倪康等,2017;Ye et al., 2018;武彬等,2019;王坤等,2023)。陈柏林等(2016)通过卓阿布拉克组中酸性火山岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb测年,获得年龄值477~485 Ma;倪康等(2017)对拉配泉组三段流纹岩开展了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年,获得年龄值为488 Ma。从前人研究结果分析,目前仅对拉配泉组三段的流纹岩进行了精确定年,缺少对其他地层流纹岩的精细定年和详细研究,制约了对拉配泉组流纹岩成因及形成构造环境,以及该地区构造演化与成矿研究的认识。因此,本文通过对拉配泉组二、三段中流纹岩进行锆石U-Pb精确定年及岩石地球化学研究,在准确厘定拉配泉组沉积时代的基础上,探讨流纹岩的成因及形成构造背景。该研究为阿尔金地区大地构造演化过程提供了新的制约,也对喀腊大湾地区矿产勘查具有重要指导意义。
1. 区域地质背景
阿尔金喀腊大湾地区位于青藏高原北缘(倪康等,2017;张传林等,2022),北接塔里木盆地南缘,南邻柴达木盆地(图 1-a)。阿尔金北缘地区可划分为太古宙混杂岩带、俯冲碰撞杂岩带、米兰河-金雁山地块(刘良等,2002;Liu et al., 2008)。研究区出露地层有太古宇米兰岩群达格拉格布拉克组(Ardg)、下古生界拉配泉组(

![]() 图 1 区域构造单元划分(a)和新疆喀腊大湾地质简图(b)(据陈宣华等,2009)1—中新统上干柴沟组; 2—中新统下油砂山组; 3—渐新统下干柴沟组; 4—上石炭统因格布拉克组; 5—拉配泉组三段; 6—拉配泉组二段; 7—拉配泉组一段; 8—金燕山组;9—太古宇达格拉格布拉克组; 10—志留纪二长花岗岩;11—志留纪花岗岩;12—志留纪辉长岩;13—奥陶纪闪长岩;14—奥陶纪花岗岩;15—寒武纪闪长岩;16—寒武纪花岗闪长岩;17—寒武纪花岗岩;18—采样位置;19—铁矿床;20—铅锌矿床;21—银铅矿床;22—地质界线;23—逆冲断层;24—板块缝合带;25—走滑断层Figure 1. Division of regional tectonic units(a) and schematic geologic map of Kaladawan area in Xinjiang(b)
图 1 区域构造单元划分(a)和新疆喀腊大湾地质简图(b)(据陈宣华等,2009)1—中新统上干柴沟组; 2—中新统下油砂山组; 3—渐新统下干柴沟组; 4—上石炭统因格布拉克组; 5—拉配泉组三段; 6—拉配泉组二段; 7—拉配泉组一段; 8—金燕山组;9—太古宇达格拉格布拉克组; 10—志留纪二长花岗岩;11—志留纪花岗岩;12—志留纪辉长岩;13—奥陶纪闪长岩;14—奥陶纪花岗岩;15—寒武纪闪长岩;16—寒武纪花岗闪长岩;17—寒武纪花岗岩;18—采样位置;19—铁矿床;20—铅锌矿床;21—银铅矿床;22—地质界线;23—逆冲断层;24—板块缝合带;25—走滑断层Figure 1. Division of regional tectonic units(a) and schematic geologic map of Kaladawan area in Xinjiang(b)喀腊大湾地区位于北东向阿尔金走滑断裂与东西向阿尔金北缘断裂之间,属阿尔金山构造带中部(倪康等,2017)。自太古宙以来,该区域经历了多期次的碰撞造山作用(倪康等,2017)。前人研究表明,在震旦纪晚期—早古生代早期,红柳沟-拉配泉裂谷带扩张成洋,晚寒武世发生板块俯冲作用,中晚奥陶世发生碰撞作用(崔军文等,1999;戚学祥等,2005;张建新等,2007;杨经绥等,2008;陈柏林等,2016;李猛等,2021)。晚中生代以来,受欧亚板块与印度板块碰撞造山的远程影响,阿尔金断裂带发生了较大规模的左行走滑(崔军文等,1999;陈正乐等,2002;Liu et al., 2006;陈柏林等,2010)。研究区断裂主要有阿尔金北缘断裂、白尖山断裂和喀腊达坂断裂(陈宣华等,2009;武彬等,2019),阿尔金北缘断裂呈近东西向,倾向北,分为主断裂及次级断裂,控制着区内晚寒武世火山岩、早奥陶世和早志留世侵入岩及石炭系的分布(武彬等,2019)。
研究区侵入岩发育,主要为加里东钙碱性侵入岩及部分高钾钙碱性侵入岩(武彬等,2019)。钙碱性侵入岩从基性至酸性均有出露(图 1),其中以基性岩为主(Ye et al., 2018),岩性包括辉长辉绿岩、辉长岩、辉绿岩,多呈近东西向不连续分布的岩株或岩脉产出,其展布方向大体受构造线方向控制,表现为顺地层侵入。高钾钙碱性侵入岩以中—酸性侵入岩为主,中—酸性岩广泛分布,多呈岩枝、岩基侵位于拉配泉组(陈宣华等,2009;Ye et al., 2018)。
2. 地层特征及样品采集
拉配泉组分布于阿尔金北缘地区俯冲碰撞杂岩带中部,阿尔金北缘断裂以南、喀腊达坂断裂以北区域,呈近东西向条带状展布,横贯研究区,向东延至阿尔金断裂带(武彬等,2019)。拉配泉组北与太古宇米兰岩群为断层接触,南与古近系渐新统下干柴沟组呈角度不整合接触(倪康等,2017)。依据岩性组合特征,将该组自下而上划分为3个岩性段(新疆维吾尔自治区地质矿产勘查开发局第一地质大队,2008)(图 1)。
拉配泉组一段(

拉配泉组二段(

拉配泉组三段(

地层中的流纹岩和凝灰岩是准确限定其时代最有效的定年载体(高林志等,2015;田辉等,2015)。本次对喀腊大湾北选取拉配泉组二段的1件流纹岩样品开展了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年,对8件新鲜流纹岩样品进行了主量、微量与稀土元素分析;由于喀腊达坂西矿区拉配泉组三段流纹岩已经发生矿化蚀变现象,故只选取1件流纹岩样品开展LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年。流纹岩呈层状、似层状,节理发育(图 2-a、c)。其两侧岩性为大理岩、玄武岩、变质含砾中粗粒岩屑砂岩等。流纹岩颜色呈灰白色—浅肉红色,斑状结构,块状构造,斑晶主要由钾长石、石英组成,含量20%~30%,粒径大小0.5~1.5 mm,镜下可见流动构造,具有定向排列特征,基质多呈隐晶质及细小的长英质矿物组成(倪康等,2017)(图 2-b、d)。
3. 测试方法
锆石U-Pb测年在中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心同位素实验室完成,实验所采用仪器为美国Thermo Fisher公司生产的电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(Neptune)和氟化氩准分子激光器(New Wave 193 nm FX)。实验过程中采用激光剥蚀系统产生的相应光束能量密度为10 J/cm2,束斑直径为32 μm,共剥蚀40 s,频率为5 Hz。以锆石91500为测试过程中的外标,校正仪器质量偏差与元素分馏;实验中以标准锆石GJ-1为盲样检验U-Pb定年数据质量;锆石中的Pb元素含量标定采用NIST SRM 610为外标,Si为内标;微量元素含量标定以Zr为内标(Liu et al., 2010a; Hu et al., 2011)。原始的测试数据用ICPMSDataCal软件(Liu et al., 2010b; 高林志等,2015)和Isoplot程序进行处理(Ludwig,2003)。
全岩主量元素分析在中国地质调查局南京地质调查中心实验室完成,主量元素用X射线荧光光谱法(XRF)分析,仪器为AFS-2202a型X射线荧光光谱仪,分析误差优于1%;在中国科学院地球化学研究所矿床地球化学国家重点实验室完成微量元素测试分析,实验仪器为ELAN-DRC-e ICP-MS,仪器灵敏度调整为1 ng/mL115In,约30000 cps。以多元素标准溶液为外标,以国际标样AMH-1(安山岩)OU-6(板岩)为标准参考物质。测试元素的相对误差优于±5%,具体步骤和全流程实验空白值据Qi et al.(2000)。
4. 测试结果
4.1 锆石U-Pb年龄
分析测试结果详见表 1,代表性锆石测试点位相应的206Pb/238U谐和年龄及阴极发光(CL)图像见图 3。
表 1 拉配泉组二段、三段流纹岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb测试结果Table 1. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb dating result of the second and third members of rhyolite of the Lapeiquan Formation编号 含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Pb U Th 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 2-1 80 925 771 0.8339 0.0801 0.0009 0.6158 0.0122 0.0557 0.0010 442 40 497 6 2-2 243 2620 3006 1.1472 0.0809 0.0009 0.6341 0.0116 0.0568 0.0009 484 36 502 6 2-3 92 1058 897 0.8472 0.0800 0.0009 0.6296 0.0116 0.0571 0.0010 495 37 496 6 2-4 128 1443 1418 0.9823 0.0808 0.0009 0.6363 0.0118 0.0571 0.0009 496 37 501 6 2-5 149 1663 1869 1.1239 0.0802 0.0009 0.6202 0.0116 0.0561 0.0009 455 37 498 6 2-6 53 623 443 0.7105 0.0814 0.0010 0.6350 0.0171 0.0566 0.0012 476 48 504 6 2-7 122 1320 1750 1.3258 0.0813 0.0009 0.6249 0.0118 0.0558 0.0010 443 38 504 6 2-8 93 1122 721 0.6422 0.0813 0.0009 0.6309 0.0118 0.0563 0.0010 463 38 504 6 2-9 55 670 432 0.6452 0.0801 0.0010 0.6334 0.0126 0.0574 0.0010 505 40 497 6 2-10 87 1054 806 0.7645 0.0797 0.0009 0.6195 0.0115 0.0564 0.0010 466 38 495 5 2-11 78 907 844 0.9299 0.0802 0.0009 0.6245 0.0121 0.0565 0.0010 472 39 497 6 2-12 99 1154 1013 0.8776 0.0808 0.0010 0.6177 0.0118 0.0555 0.0009 430 38 501 6 2-13 524 6685 3836 0.5738 0.0820 0.0009 0.6457 0.0114 0.0571 0.0009 496 36 508 5 2-14 102 1174 1053 0.8970 0.0811 0.0009 0.6502 0.0121 0.0582 0.0010 536 37 503 6 2-15 131 1470 1511 1.0278 0.0812 0.0009 0.6754 0.0123 0.0603 0.0010 615 36 503 5 2-16 55 663 452 0.6816 0.0809 0.0009 0.6205 0.0120 0.0556 0.0010 438 40 501 6 2-17 179 1996 2128 1.0662 0.0805 0.0009 0.6685 0.0123 0.0603 0.0010 613 36 499 6 2-18 107 1226 1223 0.9975 0.0817 0.0010 0.6883 0.0126 0.0611 0.0010 642 37 506 6 2-19 124 1415 1540 1.0882 0.0798 0.0009 0.6031 0.0110 0.0548 0.0009 405 37 495 5 2-20 142 1695 1593 0.9402 0.0782 0.0009 0.6063 0.0109 0.0562 0.0009 461 37 486 5 2-21 81 978 719 0.7354 0.0797 0.0009 0.6105 0.0117 0.0556 0.0010 435 39 494 6 2-22 50 603 391 0.6479 0.0802 0.0009 0.6104 0.0124 0.0552 0.0010 420 42 497 6 2-23 76 924 780 0.8441 0.0782 0.0008 0.6054 0.0116 0.0562 0.0010 460 40 485 5 2-24 142 1622 1721 1.0609 0.0798 0.0009 0.6289 0.0115 0.0571 0.0010 497 37 495 6 2-25 141 2072 3997 1.9291 0.0666 0.0007 0.5835 0.0105 0.0636 0.0011 727 37 415 4 2-26 64 779 494 0.6346 0.0798 0.0008 0.7140 0.0149 0.0649 0.0013 770 41 495 5 2-27 84 1050 552 0.5257 0.0798 0.0009 0.6214 0.0117 0.0565 0.0010 471 38 495 6 2-28 187 2098 2777 1.3238 0.0791 0.0008 0.6113 0.0109 0.0560 0.0009 454 37 491 5 2-29 127 1486 1399 0.9414 0.0801 0.0009 0.6255 0.0113 0.0566 0.0009 477 37 497 5 2-30 101 1136 1298 1.1429 0.0805 0.0009 0.6899 0.0135 0.0622 0.0011 681 36 499 6 2-31 127 1480 1573 1.0625 0.0789 0.0009 0.6184 0.0114 0.0568 0.0010 486 37 489 5 3-1 42 541 313 0.5783 0.0769 0.0008 0.6256 0.0108 0.0590 0.0009 567 34 478 5 3-2 61 552 338 0.6127 0.0905 0.0011 1.7886 0.0377 0.1433 0.0023 2267 28 559 7 3-3 56 698 444 0.6366 0.0776 0.0009 0.6587 0.0160 0.0616 0.0012 659 42 482 5 3-4 54 669 420 0.6277 0.0783 0.0009 0.6266 0.0105 0.0580 0.0009 531 32 486 5 3-5 62 763 520 0.6823 0.0778 0.0008 0.6297 0.0105 0.0587 0.0009 556 32 483 5 3-6 44 545 339 0.6215 0.0773 0.0009 0.6865 0.0133 0.0644 0.0010 755 34 480 6 3-7 49 603 359 0.5956 0.0784 0.0009 0.6569 0.0113 0.0608 0.0009 631 32 487 5 3-8 49 623 341 0.5477 0.0769 0.0008 0.6063 0.0103 0.0572 0.0009 499 33 478 5 3-9 42 543 282 0.5192 0.0766 0.0008 0.6186 0.0103 0.0585 0.0009 550 33 476 5 3-10 35 434 243 0.5603 0.0783 0.0009 0.6126 0.0108 0.0568 0.0009 483 35 486 5 3-11 59 707 457 0.6468 0.0785 0.0009 0.7416 0.0200 0.0685 0.0015 884 45 487 6 3-12 58 701 404 0.5764 0.0791 0.0008 0.7493 0.0121 0.0687 0.0011 891 32 490 5 3-13 41 509 275 0.5398 0.0788 0.0009 0.6216 0.0107 0.0572 0.0009 499 34 489 5 3-14 44 541 319 0.5883 0.0783 0.0008 0.6272 0.0106 0.0581 0.0009 533 35 486 5 3-15 59 743 451 0.6075 0.0779 0.0008 0.6172 0.0106 0.0575 0.0009 509 33 484 5 3-16 55 683 417 0.6095 0.0784 0.0009 0.6246 0.0105 0.0578 0.0009 521 34 487 5 3-17 62 774 497 0.6424 0.0774 0.0008 0.6642 0.0119 0.0623 0.0010 683 33 480 5 3-18 37 467 223 0.4783 0.0780 0.0009 0.6285 0.0112 0.0584 0.0010 546 36 484 5 3-19 47 596 322 0.5402 0.0779 0.0009 0.6289 0.0105 0.0585 0.0009 550 34 484 5 3-20 39 487 252 0.5185 0.0785 0.0009 0.6325 0.0111 0.0584 0.0009 546 35 487 5 3-21 55 686 406 0.5914 0.0776 0.0009 0.6311 0.0104 0.0590 0.0009 567 34 482 5 3-22 38 487 236 0.4847 0.0781 0.0008 0.6337 0.0111 0.0589 0.0010 562 36 485 5 3-23 67 833 550 0.6595 0.0775 0.0009 0.6287 0.0104 0.0588 0.0009 560 33 481 5 3-24 52 657 356 0.5421 0.0780 0.0009 0.6278 0.0112 0.0584 0.0009 544 34 484 5 3-25 51 655 379 0.5788 0.0765 0.0008 0.6296 0.0111 0.0597 0.0010 592 35 475 5 3-26 57 719 392 0.5451 0.0787 0.0009 0.6240 0.0105 0.0575 0.0009 512 33 488 5 3-27 49 621 404 0.6506 0.0770 0.0008 0.6002 0.0102 0.0565 0.0009 474 34 478 5 3-28 36 461 243 0.5263 0.0787 0.0009 0.6383 0.0109 0.0588 0.0009 560 34 488 5 3-29 32 421 177 0.4208 0.0781 0.0008 0.6038 0.0111 0.0560 0.0010 454 38 485 5 3-30 58 737 473 0.6415 0.0775 0.0008 0.6697 0.0112 0.0627 0.0009 697 32 481 5 3-31 40 514 247 0.4809 0.0782 0.0008 0.6328 0.0115 0.0587 0.0010 557 35 485 5 拉配泉组二段流纹岩(样品D1101)的锆石在单偏光镜下呈无色粉色,晶形较好,自形程度高,形态上呈柱状或长柱状,长50~150 μm,长宽比为1.2~2。在CL图像上可以清晰地看到锆石的振荡环带,显示典型的岩浆成因锆石特征(图 3-a)。对其中具有代表性的31粒锆石进行LA-ICP-MS U-Pb测年。Th、U含量变化总体较大,分别为391×10-6~3997×10-6和603×10-6~6885×10-6,Th/U值变化较大(表 1),介于0.13~3.78之间。31个测点除一个点具明显低的年龄值外(可能为试验误差),其余测点都位于谐和线上,其206Pb/238U年龄介于485±5~508±5 Ma之间,年龄加权平均值为497±2.0 Ma(MSWD=1.03)(图 3-b)。
拉配泉组三段流纹岩(样品DWTW01)的锆石在单偏光镜下呈无色、浅粉色,晶形较好,自形程度普遍较高,形态上呈柱状或长柱状,长60~130 μm,长宽比为1~2。在CL图像上可以清晰地看到锆石的振荡环带,显示典型的岩浆成因锆石特征(图 3-c)。31粒代表性锆石的Th、U含量变化较大,分别为177×10-6~550×10-6和421×10-6~833×10-6,Th/U值介于0.42~0.68之间,大部分在0.57左右(表 1)。31个测点除一个点明显高于其他点外,其余测点都位于谐和线上,206Pb/238U年龄介于475±5~490±5 Ma之间,年龄加权平均值为483.4±1.9 Ma(MSWD = 0.58)(图 3-d)。
4.2 全岩地球化学特征
拉配泉组二段流纹岩样品全岩地球化学分析结果见表 2。样品SiO2含量介于70.07%~78.55%之间,均值为73.90%;TiO2含量介于0.15%~0.19%之间,均值为0.17%,属低TiO2流纹岩;MgO含量介于0.32%~0.58%之间,均值为0.46%;CaO含量介于0.75%~2.60%之间,均值为1.63%;Na2O含量介于2.27%~5.97%之间,均值为4.39%;K2O含量介于1.57%~4.72%之间,均值为2.85%;Al2O3含量介于10.25%~14.38%之间,均值为12.71%。样品分异指数DI值高,在84.18~92.92之间,均大于80,平均为88.39,可能反映了岩石较高的分异程度或源岩为偏硅质的特征(邱家骧等,1991)。
表 2 拉配泉组二段流纹岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果Table 2. Major, trace and rare earth element analytical data of the rhyolite in the second member of the Lapeiquan Formation元素 D1101H1 D1101H2 D1101H3 D1101H4 D1101H5 D1101H6 D1101H7 D1101H8 SiO2 75.83 72.25 74.17 78.55 74.70 71.16 70.07 74.44 Al2O3 11.75 14.17 12.26 10.25 12.38 13.86 14.38 12.59 CaO 0.98 1.46 1.87 0.75 1.10 2.60 2.54 1.70 MgO 0.36 0.46 0.43 0.32 0.58 0.51 0.53 0.48 K2O 4.05 1.91 4.22 4.72 2.79 1.85 1.57 1.69 Na2O 3.45 5.86 2.97 2.27 4.25 5.29 5.97 5.06 TiO2 0.16 0.17 0.16 0.15 0.17 0.18 0.17 0.19 P2O5 0.021 0.019 0.024 0.020 0.021 0.022 0.024 0.022 MnO 0.037 0.050 0.053 0.034 0.053 0.069 0.064 0.053 烧失量 0.66 0.65 0.93 0.54 0.74 0.89 1.18 0.85 TFe2O3 2.10 2.47 2.54 1.94 2.72 3.25 3.07 2.58 BaO 0.15 0.07 0.18 0.19 0.12 0.07 0.06 0.06 总量 99.55 99.54 99.81 99.73 99.62 99.75 99.63 99.72 K2O/Na2O 0.85 3.07 0.70 0.48 1.52 2.86 3.80 2.99 FeO/MgO 5.25 4.83 5.32 5.46 4.22 5.74 5.21 4.84 A/NK 1.17 1.21 1.30 1.16 1.24 1.30 1.25 1.24 A/CNK 0.99 0.99 0.95 1.00 1.03 0.90 0.89 0.95 分异指数DI 91.68 88.80 87.23 92.92 89.28 84.18 84.91 88.12 Mg# 25.35 26.95 25.11 24.62 29.69 23.71 25.48 26.93 Li 1.58 1.55 1.92 1.22 1.89 1.27 1.62 1.48 Be 2.73 3.70 1.83 2.38 2.76 4.21 4.06 2.71 Sc 4.57 5.3 4.88 3.97 4.97 4.91 5.32 5.15 V 1.64 2.94 2.54 1.53 2.66 2.99 2.72 2.36 Cr 2.03 5 4.4 6.23 6.73 4.83 6.16 5.25 Co 164 126 174 181 152 124 99.5 134 Ni 7.59 5.68 7.26 10.6 11.3 6.51 5.35 5.29 Cu 1.14 1.14 1.95 1.28 1.93 1.35 1.61 1.07 Zn 60.7 80.5 61.9 61.2 85.6 76.2 79.3 59.4 Ga 14.9 19.4 21.3 12.2 17.2 25.3 22.3 18.7 Ge 1.14 1.37 1.66 0.886 1.24 2.06 1.68 1.59 As 0.99 1.14 1.39 1.14 1.12 1.60 1.53 1.33 Rb 92.9 46.4 96.1 89.2 67.5 47.1 44.5 44.1 Sr 92 182 181 74.4 124 286 249 172 Y 47.10 53.89 61.01 41.95 58.38 62.87 60.68 57.83 Zr 304 332 306 279 343 325 321 349 Nb 19.62 20.99 19.85 18.86 22.90 22.21 21.53 23.28 Sb 0.66 0.60 0.92 0.57 0.55 1.39 1.14 0.83 Ba 1470 679 1720 1830 1100 683 484 554 Nb/Ta 11.43 12.36 11.71 11.62 12.57 13.02 13.44 13.04 Rb/Nb 4.74 2.21 4.84 4.73 2.95 2.12 2.07 1.89 Rb/Sr 1.01 0.25 0.53 1.20 0.54 0.16 0.18 0.26 Sr/Y 1.95 3.38 2.97 1.77 2.12 4.55 4.10 2.97 La 62.1 71.4 62.5 57.3 72.2 66 62.3 70.5 Ce 107 113 111 103 122 120 111 124 Pr 12.5 13.5 12.5 11.2 14.3 13.4 12.3 14 Nd 45.3 49.3 46.7 42.1 52.5 50.2 45.2 51.4 Sm 8.29 9.28 9.31 8.08 9.56 9.56 8.52 9.99 Eu 0.96 1.22 1.74 0.79 1.14 1.44 1.32 1.14 Gd 8.18 8.66 9.23 8.26 9.29 9.52 8.75 9.37 Tb 1.28 1.44 1.48 1.16 1.52 1.56 1.42 1.54 Dy 7.7 8.82 9.29 7.26 9.37 9.94 9.39 9.18 Ho 1.53 1.79 1.85 1.4 1.98 2.11 1.94 1.96 Er 4.88 5.64 5.88 4.38 6 6.53 6.04 6 Tm 0.71 0.81 0.78 0.66 0.90 0.91 0.84 0.90 Yb 4.88 5.76 5.9 4.64 6.27 6.39 6.09 6.32 Lu 0.73 0.85 0.84 0.66 0.93 0.88 0.91 0.90 Hf 7.88 8.62 8.16 7.48 8.7 8.48 8.75 9.03 Ta 1.72 1.70 1.70 1.62 1.82 1.71 1.60 1.79 W 958 737 1080 1130 936 835 611 843 Pb 6.81 5.62 8.47 6.04 5.57 8.62 6.96 5.72 Th 23.5 24.8 23.3 21.4 26 24.8 23.9 26.7 U 5.87 7.25 8.19 4.82 7.01 7.83 7.6 6.92 LREE 283.25 311.59 304.77 264.42 330.08 323.48 301.32 328.87 HREE 29.88 33.76 35.25 28.42 36.27 37.84 35.38 36.17 ∑REE 313.14 345.36 340.02 292.84 366.34 361.31 336.70 365.04 LREE/HREE 9.48 9.23 8.65 9.30 9.10 8.55 8.52 9.09 (La/Yb)N 12.73 12.40 10.59 12.35 11.52 10.33 10.23 11.16 δEu 0.12 0.14 0.19 0.10 0.12 0.15 0.15 0.12 TZr/℃ 847 847 842 845 862 833 828 862 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量、稀土元素含量单位为10-6;A/NK= Al2O3 /(Na2O+ K2O); A/CNK= Al2O3 /(GaO+ Na2O+ K2O); DI=Qz+Qr+Ab+Ne+Lc+Kp;Mg#=100*(MgO/40.3044)/(MgO/40.3044+ TFeO/71.844);δEu=2Eu/(Sm+Gd); TZr/℃计算据Watson et al.(1983)温度计算公式 在TAS图解(图 4-a)上,样品点落入流纹岩区域。流纹岩总体具有较高的(Na2O+K2O)含量,介于6.75%~7.77%之间,均值为7.24%,除D1101H1、D1101H3、D1101H4样品的Na2O/K2O < 1外(可能存在局部钾长石含量较高),其余5个样品的Na2O/K2O>1.5,为钠质型(邱家骧等,1991)。在SiO2-K2O图解(图 4-b)上,样品主要为钙碱性系列,少量为高钾钙碱性系列。在AR-SiO2图(图 5-b)中,样品点位于钙碱性和碱性界线附近。A/CNK值介于0.89~1.03之间,A/NK值介于1.16~1.30之间,均值为1.42,在A/CNK-A/NK图解(图 5-a)中,样品点大部分位于准铝质范围,少量位于准铝质—过铝质过渡带。
![]() 图 4 拉配泉组流纹岩TAS(a)和SiO2-K2O图解(b)(底图据Le,1984)Figure 4. TAS(a) and K2O-SiO2(b)diagrams of rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation
图 4 拉配泉组流纹岩TAS(a)和SiO2-K2O图解(b)(底图据Le,1984)Figure 4. TAS(a) and K2O-SiO2(b)diagrams of rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation稀土元素总量(∑REE)介于292.84×10-6~366.34×10-6之间,平均值为340.09×10-6。轻、重稀土元素含量比值LREE/HREE介于8.52~9.48之间,平均值为8.99;(La/Yb)N值为10.23~12.73,平均值为11.41。稀土元素标准化配分曲线总体呈右倾形式(图 6-a),轻、重稀土元素分馏明显。δEu=0.10~0.19,平均值为0.14,反映了较强烈的负Eu异常。在微量元素蛛网图(图 6-b)中,8个样品具有相似的配分模式,表现为大离子亲石元素(LILE)相对高场强元素(HFSE)明显富集,La、Nd、Ce、Sm、U、Th等相对富集,Nb、Ti等相对亏损。
![]() 图 6 拉配泉组流纹岩稀土元素配分图(a)和微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化值据Sun et al., 1989)Figure 6. REE patterns(a) and trace element spider diagrams(b)of the rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation
图 6 拉配泉组流纹岩稀土元素配分图(a)和微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化值据Sun et al., 1989)Figure 6. REE patterns(a) and trace element spider diagrams(b)of the rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation5. 讨论
5.1 火山岩形成的时代
已有研究表明,阿尔金北缘地区拉配泉组是喀腊大湾矿集区的主要赋矿地层(武彬等,2019),然而,对于其沉积时代及地层划分的认识还存在不足。20世纪80年代,1:20万索尔库里幅区域地质调查报告将其归为蓟县系塔昔达坂群(新疆维吾尔自治区地质局区域地质调查大队, 1981);2008年,1:5万区域地质调查报告将其划分为3段,归为奥陶系(新疆维吾尔自治区地质矿产勘查第一地质大队,2008)。近年来,不断有学者对该地区开展研究工作,陈柏林等(2006)运用SHRIMP锆石U-Pb方法对研究区沉积岩系中的中酸性火山岩进行了测年,获得477~485 Ma的年龄;倪康等(2017)对区内拉配泉组三段流纹岩开展了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年,获得488 Ma的年龄。本文研究表明,拉配泉组二段形成年龄为497±2.0 Ma,为晚寒武世,三段流纹岩年龄为483.4±1.9 Ma,与前人年龄数据相近,为早奥陶世。这一结果表明,拉配泉组属于晚寒武世—早奥陶世。
5.2 岩石成因
拉配泉组二段流纹岩地球化学特征显示,其具有高的SiO2含量(70.07%~78.55%)、低的TiO2(0.15%~0.19%)、Fe2O3(1.94%~3.25%)、Al2O3(10.25%~14.38%)和MgO(0.32%~0.58%)含量,大离子亲石元素LILE,如Rb、Ba等和轻稀土元素(LREE)明显富集,高场强元素Nb、Ta、Ti、Hf等相对亏损。以上特征表明,流纹岩具有壳源成因(Zen,1986;Xu et al., 2009;李成志等,2020)。
流纹岩具有较平坦的稀土元素配分模式,明显的Sr、Eu、Ti和P负异常和较高的Zr、Y、Ce含量,这些特征与A型花岗岩一致(Whalen et al., 1987;King et al., 1997;邱检生等,2000)。(Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)-(Na2O+K2O)/GaO和10000×Ga/Al-Zr图解(图 7)显示,拉配泉组流纹岩样品均位于A型花岗岩区域,具有A型花岗岩特征。A型花岗岩与高分异花岗岩根据元素含量特征可进行区分(胡培远等,2016),S型花岗岩一般为强过铝质,明显不同于本文流纹岩铝质含量特征,高分异的I型花岗岩具全铁含量小于1%的特征及较高的Rb含量(大于270×10-6),均明显不同于本文结果(王强等,2000;胡培远等,2016)。花岗岩的形成温度可通过Zr饱和温度(TZr)计算,由于锆石是花岗岩中较早结晶的矿物,Zr饱和温度可近似代表岩石结晶温度(胡培远等,2016)。根据Watson et al.(1983)温度计算公式,得到流纹岩样品锆石饱和温度为828~862℃,平均温度为845℃,符合A型花岗岩形成于较高温度的特征,高于S型花岗岩锆石饱和温度(平均764℃)和I型花岗岩锆石饱和温度(平均781℃)(King et al., 1997)。
![]() 图 7 拉配泉组流纹岩Zr+Nb+Ce+Y-(Na2O+K2O)/CaO(a)和10000 Ga/Al-Zr(b)图解(据Whalen et al., 1987)Figure 7. Zr+Nb+Ce+Y-(Na2O+K2O)/GaO(a) and 10000×Ga /Al-Zr(b)diagrams of the rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation
图 7 拉配泉组流纹岩Zr+Nb+Ce+Y-(Na2O+K2O)/CaO(a)和10000 Ga/Al-Zr(b)图解(据Whalen et al., 1987)Figure 7. Zr+Nb+Ce+Y-(Na2O+K2O)/GaO(a) and 10000×Ga /Al-Zr(b)diagrams of the rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation结合前人研究成果,本次研究通过地球化学分析认为,拉配泉组二段主要来源于地壳物质的部分熔融,主要依据为:①岩石微量元素比值显示, Y/Nb值为2.22~3.07,大于地幔成因的岩石(< 1.2),与壳源成因岩石(>1.2)相符(Eby,1992);②Zr-Zr/Sm图解(图 8-a)总体呈正相关,显示其成岩过程以部分熔融为主;③样品Mg#值为24~30(平均26),明显低于地幔部分熔融形成的岩石(朱弟成等,2006;李成志等,2020)(Mg#=68),与地壳物质熔融相符;④在C/MF-A/MF图解(图 8-b)中,样品点全部位于变质杂砂岩部分熔融区域。区域上,与陈柏林等(2016)研究认为陆壳物质对喀腊大湾地区中酸性火山岩影响作用较强的结果相符。Eu(δEu=0.10~0.19)、Sr和Ti负异常说明,岩浆源区可能存在斜长石残留(Rapp et al., 1991;Martin,1999;李梦瞳等,2020)。拉配泉组二段流纹岩成因可能主要是地壳物质的部分熔融,同时源区可能存在斜长石的残留。
5.3 构造环境
已有研究表明,在新元古代早期阿尔金地区与西北地区其他微地块一起成为Rodinia超大陆的一部分(倪康等,2017)。恰什坎萨伊沟南口双峰式火山岩年龄(750 Ma)表明,阿尔金北缘此时已经开始进入裂解阶段(Schiano et al., 2010),说明阿尔金北缘在新元古代已经开始裂解而形成初始洋盆,代表北阿尔金洋的形成。在贝壳滩—红柳泉地区发现高压低温变质带榴辉岩,于中寒武世(512±3 Ma)进入榴辉岩相峰期变质阶段,反映俯冲至少在中寒武世已经开始(杨经绥等,2008)。在520~495 Ma期间,北阿尔金洋板块回转引起了弧后伸展,导致软流圈上涌、岩浆岩发育(Ye et al.,2018)。490~460 Ma为大洋板块再次俯冲碰撞期(陈柏林等,2016;Ye et al.,2018)。本文拉配泉组二段流纹岩年龄为497±2 Ma,与上述大洋板块回转代表的时限相符,其形成构造环境可能为弧后伸展阶段,拉配泉组三段流纹岩483.4±1.9 Ma,与大洋板块再次俯冲时限相符(陈柏林等,2016;Ye et al.,2018)。
A型火成岩形成的构造背景具有独特的构造指示意义,前人根据构造背景把A型花岗岩定义为非造山花岗岩和碰撞后花岗岩(王强等,2000;李成志等,2020),其中A1型来源于地幔,代表非造山的大陆裂谷,A2型由地壳或岛弧派生,主要形成于碰撞后的拉张环境或板片俯冲引起的岩石圈伸展环境(蒋少涌等,2008)。在Y-Nb-Ce(图 9-a)和Y/Nb-Ce/Nb(图 9-b)图解中,拉配泉组火山岩样品点均落入A2型花岗岩区域。
![]() 图 9 拉配泉组流纹岩A1、A2类型判别图(据Eby,1992)a—Y-Nb-Ce图解;b—Y/Nb-Ce/Nb图解Figure 9. Diagrams for division of type A1 and type A2 of the rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation
图 9 拉配泉组流纹岩A1、A2类型判别图(据Eby,1992)a—Y-Nb-Ce图解;b—Y/Nb-Ce/Nb图解Figure 9. Diagrams for division of type A1 and type A2 of the rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation不同的构造环境背景下形成的岩浆岩岩石类型不同,通过岩浆岩地球化学组分特征可以判断其形成的构造背景(董昕,2008;李成志等,2020)。拉配泉地区流纹岩在Y-Nb和(Y+Nb)-Rb构造环境判别图(图 10)中,除个别样品点落入火山弧花岗岩和板内花岗岩分界线附近外,其余样品点落在板内花岗岩区域,说明拉配泉组二段火山岩形成于伸展构造环境。结合区域构造背景及岩石地球化学特征,笔者认为,拉配泉组二段火山岩形成于北阿尔金洋俯冲回转引起的弧后伸展环境。
![]() 图 10 拉配泉组流纹岩(Y+Nb)-Rb(a)与Y-Nb(b)图解(据Pearce et al., 1984)Figure 10. (Y+Nb)-Rb(a) and Y-Nb(b)diagrams of the rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation
图 10 拉配泉组流纹岩(Y+Nb)-Rb(a)与Y-Nb(b)图解(据Pearce et al., 1984)Figure 10. (Y+Nb)-Rb(a) and Y-Nb(b)diagrams of the rhyolite in the Lapeiquan Formation6. 结论
(1) 通过对阿尔金喀腊大湾地区拉配泉组流纹岩进行LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年,准确限定拉配泉组二段流纹岩年龄为497±2.0 Ma,三段流纹岩年龄为483.4±1.9 Ma,拉配泉组二段至三段的形成时代为晚寒武世—早奥陶世。
(2) 拉配泉组二段流纹岩具有富硅、贫铁、低镁,富大离子亲石元素和轻稀土元素,相对亏损高场强元素的特征,结合微量元素分析结果,拉配组二段流纹岩的成因可能主要是地壳物质的部分熔融,同时源区可能存在斜长石的残留。
(3) 岩石地球化学特征显示,拉配泉组二段流纹岩具有A型火成岩特征,进一步划属于A2类。结合研究区前人构造地质背景研究成果,推测拉配泉组二段流纹岩构造环境为北阿尔金洋回转引起的弧后伸展环境。
致谢: 野外工作中得到原湖南省地质矿产勘查开发局四一六队工作人员的大力支持,审稿专家提出了许多建设性意见,在此一并表示衷心的感谢。 -
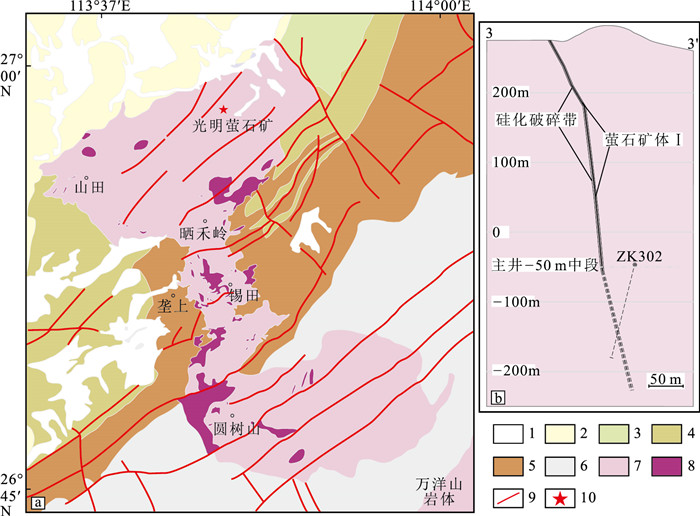
图 1 锡田岩体和光明萤石矿地质简图(a)(据苏红中等, 2015修改)与3线地质剖面(b)
1—第四系松散堆积层;2—白垩系;3—二叠系;4—石炭系;5—泥盆系;6—奥陶系;7—印支期花岗岩;8—燕山期花岗岩;9—断裂;10—矿床位置
Figure 1. Geological map of the Xitian granite and Guangming fluorite deposit(a) and geological profile of Line 3(b)
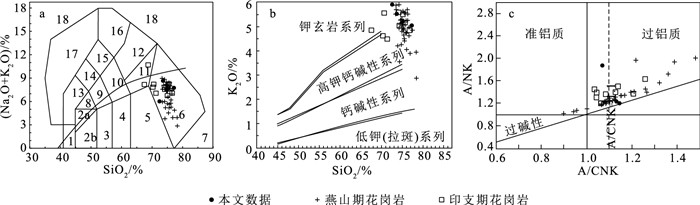
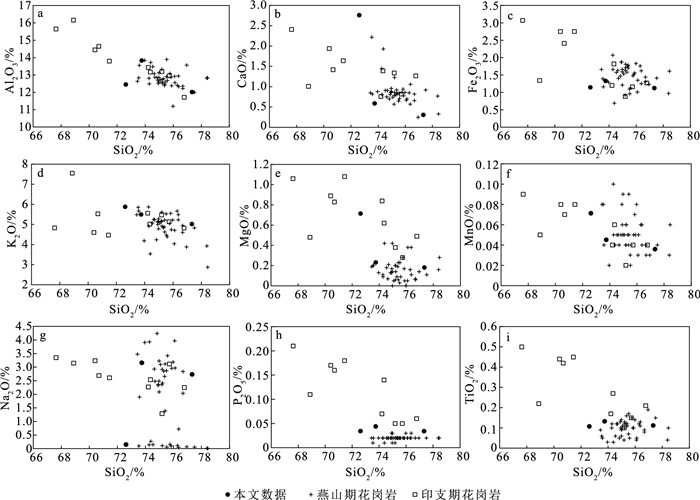
图 4 锡田岩体岩石类型和系列划分图解(燕山期花岗岩数据据Zhou et al., 2015; 印支期花岗岩数据据何苗等, 2018; 图 5、图 6、图 8中相关数据来源同此图)
a—SiO2-(Na2O+K2O)图解(底图据Wilson, 1989)(1—橄榄辉长岩;2a—碱性辉长岩;2b—亚碱性辉长岩;3—辉长闪长岩;4—闪长岩;5—花岗闪长岩;6—花岗岩;7—硅英岩;8—二长辉长岩;9—二长闪长岩;10—二长岩;11—石英二长岩;12—正长岩;13—副长石辉长岩;14—副长石二长闪长岩;15—副长石二长正长岩;16—副长石正长岩;17—副长石深成岩;18—霓方钠岩/磷霞岩/粗白榴岩);b—SiO2- K2O图解(底图据LeMaitre, 2002);c—A/CNK-A/NK图解
Figure 4. Classification and series diagrams of the Xitian granitoids
图 5 稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线图(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化配分曲线图(b) (球粒陨石、原始地幔数据据Sun et al., 1989)
Figure 5. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element patterns(b)
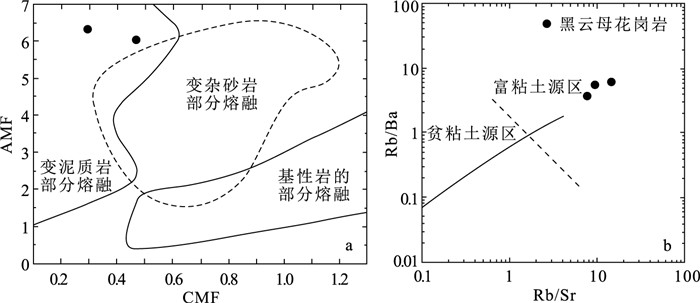
图 7 花岗岩CMF-AMF源区判别图解(a, 底图据Rainer et al., 2000)和花岗岩Rb/Sr-Rb/Ba源区判别图解(b, 底图据Paul, 1998)
(AMF=摩尔Al2O3/(MgO+TFeO); CMF=摩尔CaO/(MgO+TFeO))
Figure 7. CMF vs.AMF diagram(a) and Rb/Sr vs.Rb/Ba diagram(b)of the granite
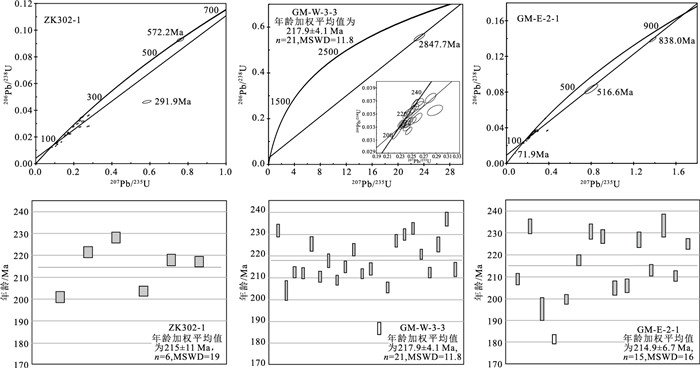
表 1 光明萤石矿区黑云母花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb分析结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb results of biotite granite in the Guangming fluorite deposit
测点号 含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Th U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238Pb 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ ZK302-1-01 719 10965 0.07 0.0525 0.0006 0.1690 0.0028 0.0233 0.0003 0.0085 0.0001 158.6 2.4 148.5 2.2 170.3 2.8 ZK302-1-02 1687 14600 0.12 0.0517 0.0007 0.0868 0.0013 0.0121 0.0001 0.0046 0.0001 84.5 1.3 77.7 0.9 92.3 1.4 ZK302-1-03 1524 10782 0.14 0.0522 0.0007 0.1078 0.0017 0.0149 0.0002 0.0050 0.0001 103.9 1.6 95.6 1.3 101.8 1.6 ZK302-1-04 1193 3146 0.38 0.0713 0.0012 0.2750 0.0045 0.0280 0.0003 0.0121 0.0002 246.7 3.6 177.7 2.0 242.8 4.4 ZK302-1-05 749 7827 0.10 0.0509 0.0005 0.2466 0.0033 0.0350 0.0004 0.0120 0.0002 223.8 2.7 221.8 2.4 242.0 3.5 ZK302-1-06 1402 11571 0.12 0.0529 0.0006 0.1522 0.0031 0.0209 0.0004 0.0066 0.0002 143.9 2.8 133.0 2.6 133.7 3.3 ZK302-1-07 1139 18840 0.06 0.0572 0.0008 0.1117 0.0019 0.0141 0.0002 0.0098 0.0004 107.5 1.7 90.4 1.3 196.4 7.1 ZK302-1-08 770 13986 0.06 0.0575 0.0009 0.1048 0.0022 0.0131 0.0002 0.0108 0.0004 101.2 2.0 84.1 1.2 217.2 7.9 ZK302-1-09 2811 8457 0.33 0.0610 0.0008 0.2322 0.0040 0.0274 0.0003 0.0049 0.0002 212.0 3.3 174.4 2.0 99.0 3.2 ZK302-1-10 1172 9037 0.13 0.0503 0.0006 0.2393 0.0034 0.0344 0.0004 0.0111 0.0002 217.8 2.8 218.0 2.6 224.0 3.2 ZK302-1-11 1015 13859 0.07 0.0569 0.0008 0.1139 0.0021 0.0145 0.0002 0.0084 0.0003 109.5 1.9 92.5 1.1 169.6 5.3 ZK302-1-12 760 4906 0.16 0.0498 0.0006 0.2364 0.0034 0.0343 0.0004 0.0122 0.0002 215.5 2.8 217.3 2.4 245.0 3.8 ZK302-1-13 147 456 0.32 0.0591 0.0008 0.7595 0.0121 0.0928 0.0009 0.0270 0.0004 573.7 7.0 572.2 5.5 538.5 7.9 ZK302-1-14 1498 8735 0.17 0.0518 0.0006 0.1976 0.0031 0.0276 0.0004 0.0059 0.0001 183.1 2.6 175.7 2.4 119.9 2.6 ZK302-1-15 587 9824 0.06 0.0554 0.0006 0.2765 0.0037 0.0361 0.0004 0.0313 0.0006 247.9 2.9 228.3 2.4 622.7 10.8 ZK302-1-16 951 9954 0.10 0.0524 0.0006 0.1554 0.0023 0.0214 0.0003 0.0100 0.0002 146.7 2.0 136.8 1.8 201.8 3.2 ZK302-1-17 626 2046 0.31 0.0521 0.0007 0.2320 0.0036 0.0322 0.0004 0.0112 0.0002 211.8 3.0 204.0 2.2 224.5 3.5 ZK302-1-18 562 10704 0.05 0.0598 0.0008 0.1344 0.0023 0.0162 0.0002 0.0154 0.0005 128.0 2.1 103.7 1.2 309.3 9.0 ZK302-1-19 717 11187 0.06 0.0496 0.0014 0.1499 0.0022 0.0220 0.0003 0.0083 0.0002 141.8 2.0 140.4 1.9 167.5 3.4 ZK302-1-20 519 9576 0.05 0.0585 0.0009 0.1802 0.0037 0.0221 0.0003 0.0193 0.0010 168.2 3.2 141.2 1.8 385.5 19.7 ZK302-1-21 2525 5587 0.45 0.0529 0.0007 0.2188 0.0037 0.0299 0.0004 0.0087 0.0001 200.9 3.1 189.7 2.5 175.7 2.3 ZK302-1-22 2149 10613 0.20 0.0531 0.0006 0.1145 0.0017 0.0156 0.0002 0.0052 0.0001 110.1 1.5 99.6 1.1 104.6 1.4 ZK302-1-23 2215 5998 0.37 0.0544 0.0007 0.1699 0.0031 0.0226 0.0003 0.0064 0.0001 159.3 2.7 143.9 2.2 129.0 2.9 ZK302-1-24 930 3578 0.26 0.0560 0.0009 0.2463 0.0050 0.0317 0.0004 0.0119 0.0002 223.6 4.1 201.3 2.5 239.1 4.2 ZK302-1-25 756 1247 0.61 0.0906 0.0017 0.5838 0.0150 0.0463 0.0007 0.0225 0.0006 466.9 9.6 291.9 4.5 450.5 11.8 GM-W-3-3-01 867 3101 0.28 0.0503 0.0006 0.2543 0.0036 0.0366 0.0004 0.0113 0.0002 230.1 2.9 231.7 2.7 227.4 3.3 GM-W-3-3-02 458 4245 0.11 0.0506 0.0006 0.2252 0.0054 0.0322 0.0007 0.0114 0.0002 206.2 4.5 204.3 4.4 229.0 3.9 GM-W-3-3-03 363 2586 0.14 0.0499 0.0006 0.2313 0.0035 0.0335 0.0004 0.0110 0.0002 211.2 2.9 212.6 2.4 220.5 3.2 GM-W-3-3-04 427 2221 0.19 0.0509 0.0007 0.2357 0.0041 0.0334 0.0004 0.0110 0.0002 214.9 3.3 212.1 2.4 221.4 3.2 GM-W-3-3-05 244 1296 0.19 0.0506 0.0008 0.2495 0.0050 0.0356 0.0005 0.0115 0.0002 226.2 4.0 225.5 3.2 230.6 3.9 GM-W-3-3-06 455 2890 0.16 0.0509 0.0007 0.2337 0.0038 0.0332 0.0004 0.0108 0.0002 213.3 3.1 210.6 2.3 217.3 3.4 GM-W-3-3-07 222 684 0.33 0.0545 0.0009 0.2587 0.0053 0.0344 0.0005 0.0118 0.0002 233.6 4.3 217.9 3.1 236.7 4.8 GM-W-3-3-08 280 1467 0.19 0.0530 0.0008 0.2409 0.0040 0.0329 0.0004 0.0109 0.0003 219.1 3.3 208.9 2.2 220.0 5.0 GM-W-3-3-09 760 2124 0.36 0.0534 0.0008 0.2502 0.0044 0.0339 0.0004 0.0093 0.0002 226.7 3.6 215.1 2.5 186.7 4.7 GM-W-3-3-10 515 498 1.03 0.0506 0.0011 0.2449 0.0055 0.0352 0.0004 0.0106 0.0003 222.4 4.5 222.9 2.7 213.0 6.2 GM-W-3-3-11 817 11192 0.07 0.0564 0.0007 0.1646 0.0022 0.0212 0.0002 0.0101 0.0003 154.7 1.9 134.9 1.4 203.3 6.7 GM-W-3-3-12 184 324 0.57 0.3018 0.0035 23.3042 0.5551 0.5554 0.0105 0.1313 0.0050 3239.7 23.3 2847.7 43.5 2493.3 90.0 GM-W-3-3-13 404 1644 0.25 0.0525 0.0008 0.2419 0.0042 0.0334 0.0004 0.0109 0.0004 220.0 3.4 211.9 2.2 218.5 9.0 GM-W-3-3-14 484 11618 0.04 0.0551 0.0007 0.1810 0.0043 0.0239 0.0005 0.0161 0.0007 168.9 3.7 152.2 3.3 323.3 14.8 GM-W-3-3-15 496 1244 0.40 0.0514 0.0009 0.2398 0.0050 0.0338 0.0004 0.0086 0.0004 218.3 4.1 214.1 2.8 173.5 7.9 GM-W-3-3-16 355 1228 0.29 0.0559 0.0010 0.2261 0.0047 0.0294 0.0004 0.0104 0.0005 207.0 3.9 186.9 2.8 210.1 9.1 GM-W-3-3-17 1178 2666 0.44 0.0548 0.0008 0.2443 0.0037 0.0324 0.0004 0.0083 0.0003 222.0 3.0 205.6 2.4 167.0 6.7 GM-W-3-3-18 345 775 0.44 0.0514 0.0009 0.2539 0.0050 0.0359 0.0004 0.0111 0.0004 229.7 4.0 227.1 2.8 222.4 7.3 GM-W-3-3-19 216 520 0.42 0.0524 0.0011 0.2624 0.0057 0.0363 0.0004 0.0118 0.0004 236.6 4.6 229.9 2.6 236.4 7.1 GM-W-3-3-20 404 497 0.81 0.0515 0.0011 0.2609 0.0057 0.0368 0.0004 0.0102 0.0003 235.4 4.6 232.7 2.6 205.2 5.1 GM-W-3-3-21 173 1225 0.14 0.0501 0.0008 0.2406 0.0040 0.0348 0.0004 0.0115 0.0003 218.9 3.3 220.8 2.3 231.2 5.7 GM-W-3-3-22 715 1836 0.39 0.0505 0.0007 0.2341 0.0039 0.0335 0.0004 0.0107 0.0002 213.5 3.2 212.5 2.3 215.1 3.9 GM-W-3-3-23 383 737 0.52 0.0585 0.0015 0.2886 0.0085 0.0356 0.0005 0.0120 0.0002 257.4 6.7 225.3 3.3 240.2 4.8 GM-W-3-3-24 253 665 0.38 0.0542 0.0010 0.2811 0.0060 0.0374 0.0005 0.0121 0.0002 251.5 4.8 236.9 3.1 242.2 4.6 GM-W-3-3-25 727 2314 0.31 0.0522 0.0007 0.2436 0.0045 0.0337 0.0005 0.0087 0.0001 221.3 3.7 213.8 3.1 175.8 2.9 GM-E-2-1-01 170 508 0.34 0.0659 0.0013 0.7998 0.0412 0.0834 0.0035 0.0289 0.0012 596.7 23.2 516.6 21.0 575.2 23.7 GM-E-2-1-02 736 950 0.78 0.0519 0.0008 0.2369 0.0042 0.0329 0.0004 0.0110 0.0002 215.9 3.5 208.9 2.5 221.1 3.1 GM-E-2-1-03 533 11878 0.04 0.0525 0.0005 0.3658 0.0056 0.0503 0.0007 0.0465 0.0006 316.5 4.2 316.5 4.2 917.9 11.6 GM-E-2-1-04 868 9886 0.09 0.0757 0.0008 0.3857 0.0061 0.0368 0.0005 0.0631 0.0015 331.2 4.4 233.0 3.2 1237.3 28.3 GM-E-2-1-05 1876 1984 0.95 0.0527 0.0009 0.2245 0.0071 0.0307 0.0008 0.0094 0.0002 205.7 5.9 195.2 5.1 188.9 3.1 GM-E-2-1-06 1191 3519 0.34 0.0554 0.0007 0.2188 0.0032 0.0286 0.0003 0.0073 0.0001 200.9 2.6 181.5 2.0 147.8 2.2 GM-E-2-1-07 1092 3617 0.30 0.0535 0.0007 0.2327 0.0035 0.0315 0.0003 0.0098 0.0002 212.5 2.9 199.8 2.1 198.0 3.2 GM-E-2-1-08 1715 12849 0.13 0.0559 0.0007 0.0864 0.0014 0.0112 0.0002 0.0044 0.0001 84.1 1.3 71.9 1.0 88.8 1.7 GM-E-2-1-09 679 2632 0.26 0.0505 0.0006 0.2398 0.0038 0.0343 0.0004 0.0110 0.0002 218.3 3.1 217.7 2.5 220.2 3.2 GM-E-2-1-10 291 755 0.39 0.0533 0.0009 0.2689 0.0060 0.0364 0.0006 0.0117 0.0002 241.8 4.8 230.8 3.5 235.3 4.7 GM-E-2-1-11 367 9215 0.04 0.0594 0.0007 0.2958 0.0045 0.0361 0.0005 0.0333 0.0009 263.1 3.5 228.5 3.0 661.5 17.9 GM-E-2-1-12 881 2315 0.38 0.0519 0.0007 0.2311 0.0040 0.0323 0.0005 0.0085 0.0002 211.1 3.3 204.7 3.1 171.0 3.1 GM-E-2-1-13 1303 5338 0.24 0.0557 0.0006 0.2494 0.0041 0.0325 0.0005 0.0134 0.0002 226.1 3.3 205.9 3.0 269.7 4.3 GM-E-2-1-14 683 11034 0.06 0.0505 0.0005 0.1791 0.0027 0.0257 0.0003 0.0147 0.0002 167.3 2.3 163.5 2.0 295.3 4.6 GM-E-2-1-15 470 10638 0.04 0.0503 0.0005 0.2458 0.0032 0.0354 0.0004 0.0131 0.0002 223.1 2.6 224.0 2.2 263.1 3.4 GM-E-2-1-16 163 225 0.72 0.0528 0.0016 0.2595 0.0083 0.0358 0.0005 0.0108 0.0002 234.2 6.7 226.9 3.4 216.8 3.7 GM-E-2-1-17 686 8464 0.08 0.0526 0.0007 0.1642 0.0029 0.0227 0.0004 0.0094 0.0002 154.4 2.6 144.7 2.4 188.8 3.4 GM-E-2-1-18 325 1198 0.27 0.0532 0.0009 0.2173 0.0036 0.0296 0.0003 0.0104 0.0002 199.7 3.0 188.3 2.0 209.5 3.3 GM-E-2-1-19 895 719 1.24 0.0541 0.0010 0.2519 0.0058 0.0336 0.0004 0.0102 0.0001 228.1 4.7 213.0 2.5 205.9 2.9 GM-E-2-1-20 395 1092 0.36 0.0537 0.0008 0.2783 0.0094 0.0368 0.0008 0.0121 0.0002 249.3 7.5 233.3 5.2 243.6 4.7 GM-E-2-1-21 172 1016 0.17 0.0506 0.0008 0.2321 0.0045 0.0332 0.0004 0.0116 0.0002 211.9 3.7 210.3 2.4 232.7 4.1 GM-E-2-1-22 1290 8723 0.15 0.0542 0.0006 0.2058 0.0038 0.0274 0.0004 0.0097 0.0001 190.0 3.2 174.6 2.8 194.4 3.0 GM-E-2-1-23 17 841 0.02 0.0720 0.0009 1.3805 0.0205 0.1388 0.0018 0.0468 0.0014 880.7 8.8 838.0 9.9 923.8 28.0 GM-E-2-1-24 1008 6387 0.16 0.0547 0.0007 0.1914 0.0032 0.0253 0.0003 0.0086 0.0001 177.8 2.7 160.9 2.2 173.0 2.7 GM-E-2-1-25 596 12662 0.05 0.0508 0.0006 0.2496 0.0032 0.0355 0.0004 0.0160 0.0002 226.2 2.6 225.1 2.5 320.3 4.7 表 2 光明矿区黑云母花岗岩锆石元素分析结果
Table 2 Contents of element in zircon grains for the biotite granite in the Guangming fluorite deposit
测试点 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Y Ti Zr/% Hf/% Zr/Hf Eu/Eu* ΔFMQ TTi/℃ ZK302-1-01 3.92 24.0 2.06 10.4 8.91 0.65 48.5 22.9 342 140 765 183 1816 345 4614 3.35 45.5 1.94 23.5 0.10 -1.32 653 ZK302-1-02 4.73 40.8 3.13 15.9 15.3 1.12 80.2 32.6 441 171 872 196 1841 343 5474 7.80 45.4 1.70 26.7 0.10 -1.39 720 ZK302-1-03 115 291 32.8 135 56.2 1.57 122 38.4 443 158 780 175 1642 306 5217 19.6 45.5 1.59 28.7 0.06 1.49 804 ZK302-1-04 3.94 60.2 3.66 21.1 17.4 25.3 51.7 16.3 185 64 298 63 564 105 2073 5.91 47.6 1.24 38.5 2.58 0.86 697 ZK302-1-05 2.06 23.1 1.92 12.3 10.3 0.46 48.1 19.1 260 105 547 123 1180 225 3375 4.76 47.1 1.72 27.4 0.06 -1.40 680 ZK302-1-06 3.02 26.0 1.82 10.1 10.4 0.45 58.3 25.3 361 146 767 174 1671 315 4769 6.07 45.5 1.77 25.7 0.06 -1.75 699 ZK302-1-07 13.8 76.1 8.77 46.3 33.3 1.13 129 54.3 759 300 1579 360 3510 651 9860 17.9 43.5 1.88 23.1 0.05 -1.24 795 ZK302-1-08 13.4 69.6 7.92 40.9 25.1 0.89 88.8 37.1 528 209 1142 282 2906 552 7007 18.9 44.5 2.04 21.8 0.06 -1.19 800 ZK302-1-09 7.54 62.4 8.87 45.3 36.8 1.89 102 35.9 445 164 837 194 1916 365 5310 23.2 45.6 2.00 22.8 0.09 -1.12 821 ZK302-1-10 1.33 23.6 1.34 8.37 10.2 0.33 52 21.1 286 112 572 128 1212 230 3560 5.09 46.3 1.60 28.9 0.04 -1.55 685 ZK302-1-11 20.8 101 13.73 71.8 44.0 1.48 114 43.0 580 225 1191 290 2963 559 7413 55.4 44.3 1.97 22.4 0.06 -1.46 918 ZK302-1-12 4.16 25.4 1.93 10.6 8.5 0.23 46.8 18.8 251 97 488 108 1009 190 3077 2.36 47.6 1.52 31.3 0.03 -0.22 628 ZK302-1-13 0.02 1.77 0.02 0.28 0.81 0.37 5.11 1.77 22.3 7.64 33.7 6.59 55.8 10.0 246 3.86 49.0 1.13 43.3 0.56 -3.21 664 ZK302-1-14 8.79 61.6 7.63 42.2 31.1 0.98 90.6 32.7 405 150 764 175 1711 327 4774 15.2 45.4 1.81 25.1 0.06 -0.80 779 ZK302-1-15 3.10 27.7 2.55 13.5 11.4 0.32 52.9 24.1 356 143 796 207 2190 425 4759 8.06 45.6 2.20 20.8 0.04 -1.75 722 ZK302-1-16 2.94 33.5 3.66 14.5 13.8 0.82 58.8 25.4 354 138 729 172 1709 324 4469 7.87 45.9 1.75 26.2 0.09 -1.40 720 ZK302-1-17 52.1 149 20.31 92.8 25.5 0.59 39.4 9.9 109 39 186 40 378 71.0 1189 14.1 47.4 1.23 38.4 0.06 2.06 772 ZK302-1-18 10.5 59.7 7.85 41.5 28.8 1.05 97.4 41.6 581 229 1231 303 3187 619 7682 23.1 44.7 2.19 20.4 0.06 -1.40 820 ZK302-1-19 1.66 18.6 1.49 7.99 8.66 0.27 49.5 24.3 372 153 841 210 2189 409 5043 5.33 45.4 2.03 22.4 0.04 -2.19 689 ZK302-1-20 3.37 23.8 2.62 14.0 10.5 0.44 46.1 21.8 323 132 737 190 2025 394 4388 6.42 45.3 2.18 20.8 0.06 -1.78 703 ZK302-1-21 2.61 38.9 1.87 10.9 12.1 1.11 55.1 20.9 271 103 512 114 1056 193 3216 23.8 43.6 1.32 32.9 0.13 -1.60 823 ZK302-1-22 10.8 67.0 6.51 31.9 24.2 3.32 83.7 31.2 391 142 684 151 1381 249 4518 15.6 44.3 1.36 32.6 0.22 -0.85 781 ZK302-1-23 3.8 61.6 4.05 25.5 28.4 1.64 96.9 32.8 393 137 651 140 1280 233 4295 17.8 45.3 1.20 37.6 0.10 -0.61 794 ZK302-1-24 2.74 39.7 3.30 21.6 21.0 1.00 76.9 24.5 289 103 485 103 930 172 3258 26.1 45.3 1.26 36.0 0.08 -1.26 833 ZK302-1-25 11.0 34.2 2.18 12.4 9.84 2.87 32.2 9.84 114 42 207 45.1 423 81.5 1359 137 42.9 1.00 42.8 0.49 -2.05 1039 GM-W-3-3-01 0.46 17.9 0.40 3.36 5.65 0.28 28.5 10.7 137 50 248 53.8 501 93.9 1597 4.37 47.9 1.28 45.9 0.13 -0.80 692 GM-W-3-3-02 0.70 12.6 0.66 4.11 4.88 0.20 26.0 10.6 150 61 324 75.4 741 143 1995 4.22 47.3 1.52 44.6 0.17 0.74 714 GM-W-3-3-03 0.00 6.82 0.01 0.54 2.17 0.10 17.1 7.26 107 44 239 55.0 540 108 1425 2.01 43.7 1.36 21.7 0.02 -1.50 606 GM-W-3-3-04 0.00 8.86 0.03 0.72 2.64 0.09 18.9 7.34 101 40 201 45.1 429 82.6 1249 2.28 44.1 1.32 25.4 0.02 -2.54 843 GM-W-3-3-05 0.00 7.14 0.01 0.38 1.29 0.20 10.3 3.97 55 23 120 28.0 276 55.8 714 2.75 48.4 1.26 43.4 0.07 -0.11 745 GM-W-3-3-06 0.15 9.43 0.12 1.02 3.20 0.15 21.5 8.74 123 50 266 60.7 591 116 1611 2.68 46.2 1.35 34.8 0.08 -1.42 735 GM-W-3-3-07 2.09 15.5 0.84 4.99 2.84 0.43 11.0 3.52 45 18 90 20.6 201 39.5 553 3.74 46.3 1.27 34.9 0.10 -2.24 841 GM-W-3-3-08 3.20 15.5 1.35 6.36 3.70 0.33 14.2 5.45 73 29 152 34.5 335 65.7 892 2.28 42.6 1.32 27.2 0.22 -1.43 995 GM-W-3-3-09 1.16 20.3 0.86 5.17 6.02 0.63 25.4 9.61 122 45 225 49.6 458 85.9 1392 5.16 47.0 1.23 36.6 0.06 -1.22 634 GM-W-3-3-10 0.28 36.0 0.64 9.08 14.4 2.09 59.6 17.5 197 68 302 58.7 505 91.4 2026 8.09 47.0 1.00 42.5 0.09 -2.41 761 GM-W-3-3-11 3.84 34.5 5.83 40.3 51.5 2.54 110 42.9 530 192 1003 241 2468 462 6016 35.5 43.9 2.09 17.7 0.03 -3.46 635 GM-W-3-3-12 0.08 12.1 0.11 1.38 2.15 0.41 10.3 3.49 43 17 90 20.3 202 43.2 567 11.0 46.7 1.02 38.1 0.10 -0.84 683 GM-W-3-3-13 5.40 21.0 1.83 8.40 5.74 0.31 24.7 8.76 115 44 220 47.4 449 86.2 1380 4.72 45.2 1.22 26.2 0.08 0.57 678 GM-W-3-3-14 0.55 9.53 0.38 1.69 4.93 0.07 42.2 23.2 366 151 861 226.2 2507 492 5082 2.18 44.0 2.22 21.5 0.02 2.75 654 GM-W-3-3-15 0.86 16.7 0.66 4.14 5.12 0.46 21.1 7.57 93 34 163 34.2 313 58.6 1002 5.96 44.8 1.18 21.8 0.01 -2.75 646 GM-W-3-3-16 0.50 16.0 0.53 3.92 5.23 0.56 21.1 7.29 90 33 167 36.4 339 65.7 1018 4.46 47.5 1.26 46.3 0.16 -0.96 764 GM-W-3-3-17 5.79 44.9 4.83 27.4 28.2 2.12 87.9 30.2 338 111 500 98.8 850 151 3286 15.9 43.4 1.18 27.0 0.10 -1.34 717 GM-W-3-3-18 0.01 11.9 0.12 1.86 3.83 0.45 18.2 5.77 74 28 142 30.8 290 56.7 878 6.3 47.9 1.18 38.9 0.12 -1.43 800 GM-W-3-3-19 5.55 48.9 2.80 15.2 7.58 0.98 19.6 5.43 64 23 112 24.0 224 44.5 705 11.9 47.3 1.11 46.4 0.21 0.72 785 GM-W-3-3-20 0.08 15.8 0.35 4.96 6.96 1.43 31.8 9.27 107 38 182 37.6 342 65.6 1167 10.3 47.4 1.00 42.1 0.09 -0.96 710 GM-W-3-3-21 0.01 5.53 0.01 0.26 0.87 0.12 7.21 2.99 44 19 105 25.0 254 51.1 606 2.29 47.5 1.35 35.9 0.06 -1.19 629 GM-W-3-3-22 0.12 20.2 0.23 3.53 6.97 0.80 32.8 11.2 142 53 264 56.5 520 99.1 1667 2.92 44.7 1.22 29.2 0.05 -1.95 700 GM-W-3-3-23 0.87 12.5 0.78 8.24 11.8 0.85 51.0 15.1 175 62 288 57.8 515 96.5 1916 13.6 47.3 1.02 34.6 0.25 -5.94 678 GM-W-3-3-24 15.9 50.9 5.35 24.2 7.22 0.46 17.9 5.33 65 24 116 24.5 225 43.5 727 19.5 44.8 1.09 29.4 0.08 -1.55 698 GM-W-3-3-25 3.70 31.9 3.74 20.2 22.7 1.77 63.6 22.9 255 79 354 72.8 618 109 2301 9.06 43.7 1.25 18.9 0.01 -2.73 602 GM-E-2-1-01 0.08 9.05 0.15 2.23 4.37 0.42 23.1 7.46 95 36 172 36.2 336 68.7 1070 5.59 46.9 1.04 36.8 0.07 -0.97 673 GM-E-2-1-02 0.30 34.37 0.58 8.04 12.1 1.40 52.0 15.2 174 60 273 53.9 469 85.8 1846 7.33 46.3 1.06 30.5 0.05 -1.82 670 GM-E-2-1-03 4.06 16.02 1.91 8.25 7.13 0.11 43.3 22.5 355 148 828 207 2121 400 4915 1.7 47.1 2.01 34.7 0.05 -1.81 617 GM-E-2-1-04 1.64 33.07 1.83 9.67 9.33 0.14 51.2 22.9 330 133 709 167 1618 307 4299 28.7 47.4 1.74 35.9 0.04 -1.33 626 GM-E-2-1-05 0.09 36.39 0.49 8.19 13.3 0.60 59.2 17.1 198 67 302 60.6 531 94.0 2026 10.5 47.8 1.11 38.0 0.16 -1.40 639 GM-E-2-1-06 1.12 21.54 1.66 8.61 13.2 0.72 51.8 22.3 292 103 512 110 998 186 3242 9.38 47.3 1.33 35.0 0.06 -1.60 637 GM-E-2-1-07 1.94 23.63 1.29 8.74 13.2 0.89 60.4 23.4 307 110 531 110 990 183 3463 28.3 47.7 1.33 37.7 0.24 0.23 661 GM-E-2-1-08 28.5 133.96 17.64 66.9 48.5 5.59 121 51.9 677 239 1230 281 2705 493 7927 101 47.3 1.57 35.8 0.14 0.00 626 GM-E-2-1-09 0.01 10.9 0.04 1.05 3.36 0.16 21.0 8.20 109 41 208 45.7 421 80.8 1300 2.56 46.6 1.28 37.7 0.15 -0.57 686 GM-E-2-1-10 0.13 6.50 0.27 3.97 8.05 0.53 39.0 12.6 153 55 260 53.0 463 89.9 1706 12.5 47.4 1.11 47.3 0.22 1.30 723 GM-E-2-1-11 0.22 5.66 0.19 1.41 4.37 0.12 33.3 18.6 287 115 660 179 1994 395 3910 2.58 43.6 2.48 20.9 0.10 -2.76 866 GM-E-2-1-12 1.11 17.7 0.56 3.31 5.36 0.40 28.5 11.3 154 58 289 63.5 576 108 1753 4.94 47.9 1.23 46.9 0.27 -0.50 750 GM-E-2-1-13 2.74 58.7 2.62 14.5 12.9 0.65 46.4 18.1 245 96 507 121 1181 230 3120 4.67 47.6 1.72 38.8 0.08 -0.21 679 GM-E-2-1-14 56.0 253 31.7 121 31.5 0.28 63.2 25.2 364 144 804 206 2175 423 4806 3.38 43.7 2.05 19.8 0.02 -2.61 623 GM-E-2-1-15 0.23 9.93 0.22 1.54 4.75 0.05 42.3 22.9 367 156 876 216 2191 420 5125 3.04 47.5 2.05 40.3 0.14 -0.56 697 GM-E-2-1-16 0.08 8.34 0.19 2.75 5.30 0.58 22.2 6.29 73 25 111 22.3 197 37.2 723 12.9 47.8 1.03 37.9 0.16 -0.38 675 GM-E-2-1-17 3.70 31.5 2.60 11.6 12.6 0.86 53.4 25.4 370 148 786 183 1757 329 4769 7.57 46.6 1.61 39.4 0.13 -0.36 783 GM-E-2-1-18 3.50 17.7 1.04 3.98 3.12 0.27 14.6 5.36 71 27 142 31.5 300 60.0 875 18.9 47.5 1.23 40.3 0.17 -0.79 702 GM-E-2-1-19 1.85 44.0 1.40 15.7 19.3 2.53 72.7 20.0 216 71 313 60.3 504 93.2 2191 16.2 47.3 1.02 42.8 0.25 1.46 756 GM-E-2-1-20 0.03 13.5 0.16 2.79 5.45 0.36 29.0 9.62 117 42 200 42.4 389 74.2 1297 6.94 47.4 1.13 47.2 0.29 -0.34 744 GM-E-2-1-21 0.01 6.64 0.03 0.32 1.19 0.07 8.47 3.45 48 20 103 23.4 226 45.7 611 2.38 47.4 1.32 35.0 0.15 -1.64 626 GM-E-2-1-22 0.87 20.2 1.00 5.73 8.66 0.37 49.9 22.3 315 121 622 138 1284 236 3841 6.15 46.8 1.53 38.3 0.16 0.05 643 GM-E-2-1-23 0.02 0.55 0.04 0.35 0.74 0.18 6.31 3.61 56 22 116 26.8 260 50.9 702 4.65 47.2 1.37 46.3 0.11 -1.33 769 GM-E-2-1-24 1.30 21.5 1.46 7.05 10.1 0.55 47.4 21.3 290 111 560 126 1170 217 3446 5.99 47.3 1.52 43.2 0.12 0.88 803 GM-E-2-1-25 0.06 7.90 0.03 0.74 4.32 0.04 44.1 24.9 392 157 897 241 2684 532 5278 1.59 46.5 2.31 37.1 0.14 -0.34 732 注:除Zr和Hf外,其他元素单位均为10-6 表 3 光明矿区黑云母花岗岩锆石Lu-Hf同位素分析结果
Table 3 Zircon Lu-Hf isotopic compositions of the biotite granite in the Guangming fluorite deposit
测试点 年龄/Ma 176Yb/177Hf 176Lu/177Hf 176Hf/177Hf ±1σ εHf(t) ±1σ TDM/Ma TDM2/Ma ZK302-1-01 77.7 0.109563 0.003218 0.282345 0.000007 -13.99 0.23 1360 1994 ZK302-1-02 95.6 0.112632 0.003343 0.282329 0.000006 -14.23 0.21 1390 2023 ZK302-1-03 148.5 0.108219 0.003287 0.282321 0.000006 -13.45 0.23 1399 2014 ZK302-1-04 177.7 0.052182 0.001538 0.282358 0.000009 -11.35 0.30 1281 1906 ZK302-1-05 221.8 0.075239 0.002341 0.282362 0.000006 -10.37 0.22 1303 1879 ZK302-1-06 133.0 0.100715 0.003117 0.282356 0.000006 -12.50 0.22 1340 1943 ZK302-1-07 90.4 0.158253 0.004829 0.282297 0.000007 -15.55 0.25 1499 2101 ZK302-1-08 84.1 0.111703 0.003640 0.282346 0.000009 -13.87 0.31 1376 1992 ZK302-1-09 174.4 0.111799 0.003516 0.282358 0.000006 -11.64 0.23 1353 1922 ZK302-1-10 218.0 0.070187 0.002153 0.282401 0.000009 -9.04 0.31 1240 1793 ZK302-1-11 92.5 0.109851 0.003486 0.282319 0.000006 -14.66 0.21 1410 2047 ZK302-1-12 217.3 0.070914 0.002128 0.282393 0.000009 -9.35 0.33 1251 1811 ZK302-1-13 572.2 0.008371 0.000251 0.282493 0.000009 2.34 0.32 1052 1353 ZK302-1-14 175.7 0.103485 0.003315 0.282362 0.000009 -11.44 0.32 1338 1910 ZK302-1-15 228.3 0.102071 0.003316 0.282329 0.000007 -11.57 0.24 1389 1959 ZK302-1-16 136.8 0.092679 0.002887 0.282372 0.000007 -11.84 0.24 1308 1905 ZK302-1-17 204.0 0.035416 0.001144 0.282400 0.000009 -9.26 0.32 1209 1795 ZK302-1-18 103.7 0.139388 0.004624 0.282284 0.000010 -15.74 0.34 1511 2123 ZK302-1-19 140.4 0.094020 0.002984 0.282354 0.000008 -12.41 0.27 1339 1944 ZK302-1-20 141.2 0.104102 0.003539 0.282342 0.000008 -12.85 0.28 1377 1971 ZK302-1-21 189.7 0.091367 0.002798 0.282381 0.000011 -10.41 0.38 1291 1857 ZK302-1-22 99.6 0.084885 0.002493 0.282363 0.000007 -12.88 0.25 1307 1941 ZK302-1-23 143.9 0.110712 0.003594 0.282290 0.000014 -14.65 0.49 1457 2086 ZK302-1-24 201.3 0.067915 0.002060 0.282378 0.000008 -10.19 0.27 1270 1852 ZK302-1-25 291.9 0.065459 0.002014 0.282389 0.000009 -7.89 0.33 1252 1778 GMW33-01 231.7 0.075950 0.002295 0.282328 0.000013 -11.38 0.45 1351 1950 GMW33-02 204.3 0.087788 0.002935 0.282343 0.000008 -11.49 0.27 1352 1935 GMW33-03 212.6 0.069982 0.002219 0.282377 0.000009 -10.01 0.31 1277 1849 GMW33-04 212.1 0.047604 0.001568 0.282386 0.000010 -9.63 0.35 1243 1825 GMW33-05 225.5 0.057594 0.001924 0.282351 0.000010 -10.62 0.34 1304 1897 GMW33-06 210.6 0.041625 0.001381 0.282416 0.000016 -8.55 0.57 1193 1756 GMW33-07 217.9 0.036130 0.001201 0.282404 0.000012 -8.82 0.42 1205 1779 GMW33-08 208.9 0.032407 0.001109 0.282383 0.000018 -9.72 0.62 1230 1828 GMW33-10 222.9 0.052691 0.001615 0.282348 0.000011 -10.73 0.38 1297 1902 GMW33-12 2847.7 0.026759 0.000941 0.281255 0.000035 9.00 1.23 2780 2739 GMW33-13 211.9 0.048844 0.001581 0.282362 0.000007 -10.48 0.26 1277 1878 GMW33-14 152.2 0.128569 0.003918 0.282285 0.000007 -14.71 0.25 1479 2096 GMW33-15 214.1 0.046583 0.001505 0.282411 0.000019 -8.68 0.69 1204 1767 GMW33-16 186.9 0.079904 0.002483 0.282305 0.000016 -13.12 0.56 1390 2023 GMW33-17 205.6 0.106696 0.003257 0.282268 0.000024 -14.16 0.86 1476 2103 GMW33-18 227.1 0.035354 0.001148 0.282370 0.000009 -9.80 0.33 1251 1847 GMW33-19 229.9 0.035796 0.001210 0.282372 0.000012 -9.69 0.42 1250 1843 GMW33-20 232.7 0.025720 0.000860 0.282404 0.000011 -8.45 0.38 1194 1767 GMW33-21 220.8 0.022977 0.000802 0.282379 0.000009 -9.56 0.30 1226 1827 GMW33-22 212.5 0.044409 0.001405 0.282368 0.000008 -10.23 0.27 1262 1862 GMW33-23 225.3 0.050889 0.001689 0.282329 0.000011 -11.37 0.39 1327 1944 GMW33-24 236.9 0.031680 0.001017 0.282371 0.000012 -9.55 0.42 1245 1839 GMW33-25 213.8 0.063082 0.002097 0.282342 0.000011 -11.21 0.39 1323 1925 GME-2-1-01 516.6 0.031990 0.001196 0.282315 0.000017 -5.53 0.60 1330 1804 GME-2-1-02 208.9 0.046352 0.001514 0.282354 0.000010 -10.80 0.34 1285 1895 GME-2-1-03 316.5 0.118779 0.004223 0.282271 0.000007 -12.05 0.23 1513 2056 GME-2-1-04 233.0 0.062348 0.002145 0.282352 0.000007 -10.46 0.26 1310 1893 GME-2-1-05 195.2 0.122612 0.004076 0.282282 0.000010 -13.98 0.37 1490 2083 GME-2-1-06 181.5 0.115470 0.003891 0.282283 0.000013 -14.21 0.45 1481 2087 GME-2-1-07 199.8 0.084925 0.002608 0.282360 0.000007 -10.94 0.24 1316 1897 GME-2-1-08 71.9 0.182906 0.006059 0.282102 0.000027 -22.85 0.94 1868 2539 GME-2-1-09 217.7 0.063458 0.002110 0.282345 0.000013 -11.04 0.47 1320 1917 GME-2-1-10 230.8 0.054088 0.001859 0.282354 0.000023 -10.42 0.81 1298 1888 GME-2-1-11 228.5 0.089284 0.003200 0.282283 0.000011 -13.15 0.40 1451 2057 GME-2-1-12 204.7 0.084999 0.002554 0.282356 0.000009 -10.96 0.33 1319 1903 GME-2-1-13 205.9 0.099748 0.003253 0.282324 0.000009 -12.18 0.33 1393 1979 GME-2-1-14 163.5 0.098653 0.003537 0.282319 0.000012 -13.22 0.44 1411 2012 GME-2-1-15 224.0 0.126375 0.004774 0.282293 0.000009 -13.14 0.32 1503 2053 GME-2-1-16 226.9 0.024166 0.000840 0.282362 0.000015 -10.03 0.54 1251 1861 GME-2-1-17 144.7 0.123112 0.004257 0.282234 0.000010 -16.70 0.34 1571 2214 GME-2-1-18 188.3 0.029116 0.000990 0.282420 0.000016 -8.86 0.58 1176 1759 GME-2-1-19 213.0 0.061467 0.002038 0.282369 0.000028 -10.28 0.98 1283 1866 GME-2-1-20 233.3 0.039615 0.001215 0.282295 0.000009 -12.34 0.32 1358 2010 GME-2-1-21 210.3 0.027236 0.000927 0.282393 0.000014 -9.33 0.48 1211 1805 GME-2-1-22 174.6 0.128474 0.003948 0.282343 0.000013 -12.20 0.46 1391 1956 GME-2-1-23 838.0 0.033263 0.001033 0.282038 0.000039 -8.28 1.39 1710 2224 GME-2-1-24 160.9 0.105005 0.003191 0.282324 0.000014 -13.07 0.49 1390 2000 GME-2-1-25 225.1 0.118336 0.003862 0.282320 0.000009 -12.02 0.32 1423 1984 表 4 光明矿区黑云母花岗岩和萤石主量、稀土及微量元素分析结果
Table 4 Results of major, rare earth and trace element compositions of biotite granite and fluorite in the Guangming deposit
样品号 ZK302-1 GM-E-2-1 GM-W-3-3 GM-C-2-1 GM-W-3-1 样品号 ZK302-1 GM-E-2-1 GM-W-3-3 GM-C-2-1 GM-W-3-1 样品类型 花岗岩 花岗岩 花岗岩 萤石 萤石 样品类型 花岗岩 花岗岩 花岗岩 萤石 萤石 Al2O3 13.83 12.02 12.46 / / Ga 17.1 14.4 18.7 0.67 0.75 CaO 0.59 0.31 2.76 / / As 4.18 6.25 3.83 0.70 1.58 Fe2O3 1.33 1.12 1.15 / / Se 1.25 1.00 1.30 0.47 0.53 K2O 5.50 5.02 5.88 / / Rb 382 359 612 0.72 0.57 MgO 0.23 0.18 0.71 / / Sr 49.7 37.9 42.2 68.2 74.0 MnO 0.05 0.04 0.07 / / Y 39.3 30.4 43.0 35.3 64.7 Na2O 3.16 2.73 0.15 / / Zr 103 88.5 89.6 1.11 0.80 P2O5 0.04 0.03 0.03 / / Nb 18.1 16.7 17.0 0.07 0.06 TiO2 0.13 0.11 0.11 / / Mo 0.46 0.34 0.45 0.55 0.21 SiO2 73.75 77.34 72.62 / / Sn 14.3 17.7 18.6 <LOD <LOD 烧失量 0.86 0.78 3.65 / / Cs 17.7 19.3 63.6 0.07 0.08 总计 99.47 99.69 99.60 / / Ba 105 65.9 101 3.67 2.96 K2O+Na2O 8.66 7.76 6.03 / / Hf 3.63 3.23 3.39 0.02 0.02 A/CNK 1.13 1.14 1.07 / / Ta 2.33 2.62 2.73 0.01 0.03 A/NK 1.24 1.21 1.88 / / Yb 3.76 2.87 4.00 1.71 3.22 Li 76.0 32.8 40.2 0.69 1.08 Pb 99.4 82.7 54.0 0.29 0.17 Be 4.59 6.97 7.26 0.23 0.44 Th 45.5 37.5 39.4 0.13 0.16 Sc 3.17 2.79 4.53 0.09 0.08 U 28.3 24.2 25.5 0.13 0.15 Ti 797 674 671 4.89 3.81 Nb/Ta 7.75 6.38 6.21 4.59 1.98 V 7.05 5.95 6.03 0.65 0.52 Zr/Hf 28.3 27.4 26.5 53.2 42.4 Cr 2.42 1.50 7.12 2.78 16.5 ΣREE 193 161 194 34.6 44.6 Mn 348 281 624 21.4 7.84 δEu 0.15 0.13 0.14 0.50 0.44 Co 1.16 0.95 0.94 0.14 0.25 δCe 1.04 1.13 1.01 0.96 0.97 Ni 2.15 1.05 3.42 2.18 8.42 (La/Nd)N 2.19 2.24 2.18 2.00 1.65 Cu 0.34 0.83 0.74 0.17 0.42 (La/Sm)N 3.10 3.27 3.08 2.18 1.55 Zn 33.8 30.6 34.8 < LOD < LOD (La/Yb)N 6.78 7.24 6.47 2.15 1.13 (Gd/Yb)N 1.37 1.39 1.31 0.84 0.72 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6; “/”表示无数据;<LOD表示低于检出限 表 5 光明矿区黑云母花岗岩和萤石Nd同位素分析结果
Table 5 Results of Nd isotope compositions in biotite granite and fluorite from the Guangming deposit
样品号 样品类型 含量/10-6 147Sm/144Nd (143Nd/144Nd)t ±1σ εNd(t) TDM2/Ma εNd(t) TDM2/Ma Sm Nd (133 Ma) (218 Ma) ZK302-1 花岗岩 7.66 33.4 0.1385 0.512016 0.000003 -11.15 1837 -10.5 1855 GM-E-2-1 花岗岩 5.94 26.7 0.1347 0.512024 0.000003 -10.93 1819 -10.3 1834 GM-W-3-3 花岗岩 7.83 34.0 0.1391 0.512045 0.000004 -10.60 1793 -10.0 1811 GM-C-2-1 萤石 1.58 5.29 0.1801 0.512113 0.000006 -9.97 1741 GM-W-3-1 萤石 2.20 6.32 0.2102 0.512071 0.000002 -11.29 1848 -
Bailey J C. Fluorine in granitic rocks and melts: a review[J]. Chemical Geology, 1977, 19(1/4): 1-42.
Bau M, Dulski P. Compartive study of yttrium and rare-earth element behaviors in fluorine-rich hydrothermal fluids[J]. Contribution to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1995, 119: 213-223. doi: 10.1007/BF00307282
Chamberlain K J, Wilson C J, Wooden J L, et al. New perspectives on the Bishop Tuff from zircon textures, ages and trace elements[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2014, 55(2): 395-426. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egt072
Coleman D S, Gray W, Glazner A F. Rethinking the emplacement and evolution of zoned plutons: geochronologic evidence for incremental assembly of the Tuolumne Intrusive Suite, California[J]. Geology, 2004, 32: 433-436.
Glazner A F, Bartley J M, Coleman D S, et al. Are plutons assembled over millions of years by amalgamation fromsmall magma chambers?[J] GSA Today, 2004, 14(4/5): 4-11.
Graupner T, Mühlbach C, Schwarz-Schampera U, et al. Mineralogy of high-field-strength elements(Y, Nb, REE) in the world-class Vergenoeg fluorite deposit, South Africa[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 64: 583-601. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.02.012
Huang Z L, Xu C, Andrew M, et al. REE geochemistry of fluorite from the Maoniuping REE Deposit, Sichuan Province, China: implications for the source of ore-forming fluids[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2007, 81: 622-636. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2007.tb00986.x
LeMaitre R W. Igneous rocks: A classification and glossary of terms[M]. Cambridge University Press, 2002: 1-256.
Li X H, Li W X, Li Z X. On the genetic classification and tectonic implications of the Early Yanshanian granitoids in the Nanling Range, South China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2007, 52(14): 1873-1885. doi: 10.1007/s11434-007-0259-0
Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Zong K Q, et al. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(15): 1535-1546. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4
Loucks R R, Fiorentini M L, Henríquez G J. New magmatic oxybarometer using trace elements in zircon[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2020, 61(3): egaa034. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egaa034
Lu H Z, Liu Y M, Wang C L, et al. Mineralization and fluid inclusion study of the Shizhuyuan W-Sn-Bi-Mo-F skarn deposit, Hunan province, China[J]. Economic Geology, 2003, 98: 955-974. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.98.5.955
McLennan S M, Taylor S R. Rare earth element mobility associated with uranium mieralization[J]. Nature, 1979, 282: 247-250. doi: 10.1038/282247a0
Möller P, Parekh P P, Schneider H J. The application of Tb/Ca-Tb/La abundance ratios to problems of fluorite genesis[J]. Mineral Deposita, 1976, (11): 111-116.
Münker C, Pfänder J A, Weyer S, et al. Evolution of planetary cores and the earth-moon system from Nb/Ta systematics[J]. Science, 2003, 301(5629): 84-87. doi: 10.1126/science.1084662
Paul J S. Post-collisional strongly peraluminous granites[J]. Lithos, 1998, 49: 29-44.
Petford N, Cruden A R, McCaffrey K J W, et al. Granite magma formation, transport and emplacement in the Earth's crust[J]. Nature, 2000, 408(6813): 669-673. doi: 10.1038/35047000
Rainer A, Albert H, Ernst H, et al. High-potassium, calc-alkaline Ⅰ-type plutonism in the European Variscides: northern Vosges(France) and northern Schwarzwald(Germany)[J]. Lithos, 2000, 50: 51-73. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(99)00052-3
Rudnick R L, Gao S. Composition of the continental crust[C]//Holland H D, Turekian K K. Treatise on Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2004, 3: 1-64.
Simonetti A, Bell K. Nd, Pd, and Sr isotope systematics of fluorite at the AmbaDongar carbonatite complex, India: evidence for hydrothermal and crustal fluid mixing[J]. Economic Geology, 1995, 90: 2018-2027. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.90.7.2018
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society Special Publication, 1989: 313-345.
Tang M, Wang X L, Shu X J, et al. Hafnium isotopic heterogeneity in zircons from granitic rocks: geochemical evaluation and modelling of 'zircon effect' in crustal anatexis[J]. Earth Planet Science Letter, 2014, 389: 188-199. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2013.12.036
USGS. Mineral commodity summaries 2019[M]. USGS, 2019.
Veksler I V, Dorfman A M, Kamenetsky M, et al. Partitioning of lanthanides and Y between immiscible silicate and fluoride melts, fluorite and cryolite and the origin of the lanthanide tetrad effect in igneous rocks[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2005, 69(11): 2847-2860. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2004.08.007
Watson E B, Wark D A, Thomas J B. Crystallization thermometers for zircon and rutile[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2006, 151: 413-433. doi: 10.1007/s00410-006-0068-5
Wilson M. Igneous petrogenesis: A global tectonic approach[M]. London: Unwin Hyman, 1989: 1-468.
Xie L, Wang R C, Groat L A, et al. A combined EMPA and LA-ICP-MS study of Li-bearing mica and Sn-Ti oxide minerals from the Qiguling topaz rhyolite(Qitianling District, China): the role of fluorine in origin of tin mineralization[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65: 779-792. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.08.013
Yan L L, He Z Y, Beier C, et al. Geochemical constraints on the link between volcanism and plutonism at the Yunshan caldera complex, SE China[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2018, 173: 4. doi: 10.1007/s00410-017-1430-5
Yan L L, He Z Y, Klemd R, et al. Tracking crystal-melt segregation and magma recharge using zircon trace element data[J]. Chemical Geology, 2020, 542: 119596. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.119596
Yuan S D, Peng J T, Hu R Z, et al. Characteristics of rare-earth elements(REE), strontium and neodymium isotopes in hydrothermal fluorites from the Bailashui tin deposit in the Furong ore field, southern Hunan Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 2008, 27: 342-350. doi: 10.1007/s11631-008-0342-5
Yuan S D, Mao J W, Cook N J, et al. A late cretaceous tin metallogenic event in nanling W-Sn metallogenic province: constraints from U-Pb, Ar-Ar geochronology at the Jiepailing Sn-Be-F deposit, Hunan, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65: 283-293. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.10.006
Zhou Y, Liang X Q, Wu S C, et al. Isotopic geochemistry, zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes of A-type granites from the Xitian W-Sn deposit, SE China: Constraints on petrogenesis and tectonic significance[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 105: 122-139. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.03.006
包志伟, 赵振华. 佛冈铝质A型花岗岩的地球化学及其形成环境初探[J]. 地质地球化学, 2003, 31: 52-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ200301008.htm 蔡杨, 马东升, 陆建军, 等. 湖南邓阜仙岩体和锡田岩体的地球化学及成矿差异性对比[J]. 矿物学报, 2011, 增刊: 4-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB2011S1003.htm 曹俊臣. 华南低温热液脉状萤石矿床稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 地球化学, 1995, 24(3): 225-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX503.002.htm 曹俊臣. 中国萤石矿床稀土元素地球化学及萤石的矿物物理特征[J]. 地质与勘探, 1997, 33(2): 18-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT199702003.htm 陈璟元, 杨进辉. 佛冈高分异Ⅰ型花岗岩的成因: 来自Nb-Ta-Zr-Hf等元素的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(3): 846-854. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201503017.htm 陈小明, 王汝成, 刘昌实, 等. 广东从化佛冈(主体) 黑云母花岗岩定年和成因[J]. 高校地质学报, 2002, 8(3): 293-307. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200203005.htm 方贵聪, 王登红, 陈毓川, 等. 南岭萤石矿床成矿规律及成因[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(1): 161-178. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202001013.htm 付建明, 伍式崇, 徐德明, 等. 湘东锡田钨锡多金属矿区成岩成矿时代的再厘定[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 2009, 3: 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKC200903001.htm 付建明, 程顺波, 卢友月, 等. 湖南锡田云英岩-石英脉型钨锡矿的形成时代及其赋矿花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年[J]. 地质与勘探, 2012, 48(3): 313-320. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201202014.htm 郭乐群, 唐晓珊, 彭和求. 湖南益阳早前寒武纪镁铁质-超镁铁质火山岩的Sm-Nd同位素年龄[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 2003, 2: 46-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKC200302007.htm 何苗, 刘庆, 孙金凤, 等. 湘东地区锡田印支期花岗岩的地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(7): 2065-2086. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201807016.htm 刘飚, 吴堑虹, 孔华, 等. 湖南锡田矿田花岗岩时空分布与钨锡成矿关系: 来自锆石U-Pb年代学与岩石地球化学的约束[J]. 地球科学, 2022, 47(1): 240-258. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202201020.htm 刘道荣, 严生贤, 陈荫, 等. 浙西北岩前高氟岩体地球化学特征及其与新类型萤石矿床成矿关系[J]. 地质与勘探, 2012, 48(5): 884-893. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201205005.htm 刘国庆, 伍式崇, 杜安道, 等. 湘东锡田钨锡矿区成岩成矿时代研究[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2008, 32(1): 63-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200801010.htm 彭建堂, 胡瑞忠, 漆亮, 等. 晴隆锑矿床中萤石的稀土元素特征及其指示意义[J]. 地质科学, 2002, 37(3): 277-287. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX200203003.htm 彭强, 江小均, 李超, 等. 云南个旧西凹蚀变花岗岩型铜-锡多金属矿床萤石地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2021, 40(6): 1182-1198. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202106003.htm 沈宏飞, 李立兴, 李厚民, 等. 湘南中生代钨锡大规模成矿控制因素: 锆石年龄和微量元素的启示[J]. 地质通报, 2022, 41(2/3): 461-485. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2022020324&flag=1 苏红中, 郭春丽, 伍式崇, 等. 锡田印支-燕山期复式花岗质岩浆-热液活动时限和物质来源[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(10): 1853-1872. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201510013.htm 孙祥, 杨子荣, 刘敬党, 等. 义县萤石矿床稀土元素地球化学特征及其指示意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2008, 27(5): 579-586. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200805005.htm 唐晓珊, 贾宝华, 黄建中. 湖南早前寒武纪变质结晶基底的Sm-Nd同位素年龄[J]. 资源调查与环境, 2004, 25(1): 55-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HSDZ200401009.htm 王吉平, 商朋强, 熊先孝, 等. 中国萤石矿床成矿规律[J]. 中国地质, 2015, 42(1): 18-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201501002.htm 吴福元, 刘小驰, 纪伟强, 等. 高分异花岗岩的识别与研究[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2017, 47(7): 745-765. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201707001.htm 谢玲琳, 谢文安. 从稳定同位素测年信息探讨湖南的结晶基底[J]. 湖南地质, 2000, 19(4): 219-225. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNDZ200004003.htm 徐夕生, 鲁为敏, 贺振宇. 佛冈花岗岩基及乌石闪长岩-角闪辉长岩体的形成年龄和起源[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2007, 37(1): 27-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200701002.htm 杨世文, 丰成友, 楼法生, 等. 赣南隆坪萤石矿床成矿时代及成因初探: 来自萤石Sm-Nd测年及黑云母电子探针的证据[J]. 高校地质学报, 2019, 25(3): 341-351. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201903003.htm 于津海, 周新民, 赵蕾, 等. 壳幔作用导致武平花岗岩形成——Sr-Nd-Hf-U-Pb同位素证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(3): 651-644. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200503008.htm 于津海, O'Reilly Y S, 王丽娟, 等. 华夏地块古老物质的发现和前寒武纪地壳的形成[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 52(1): 11-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200701001.htm 张鲲, 胡俊良, 徐德明. 湖南桃林铅锌矿区花岗岩地球化学特征及其与成矿的关系[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 2012, 28(4): 307-314. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKC201204003.htm 周云, 梁新权, 梁细荣, 等. 湖南锡田含W-Sn A型花岗岩年代学与地球化学特征[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2013, 37(3): 511-529. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201303017.htm -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 刘博华,吴芳,张绪教,崔加伟,董晓朋. 青藏高原东北缘红寺堡盆地晚更新世沉积物元素地球化学特征及其环境指示意义. 地质通报. 2024(01): 33-45 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 何中波,冀华丽,胡宝群,孙萧,钟军,杨喆,陈虹. 准噶尔盆地北部晚白垩世至新近纪沉积介质环境演化特征及其对铀成矿的制约. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版). 2024(03): 800-810 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张耀堂,王万能,赵见波,袁永盛,李锁明,张宏辉,郑洪福,李金旺. 地球化学揭示早—中侏罗世陆相地层气候环境变化特征——以滇中川街盆地老文村剖面为例. 地质论评. 2024(06): 2212-2224 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)




 下载:
下载: