Geological characteristics and genesis of the Dashiwan-cobalt manganese deposit in Huixian County, West Qinling mountains
-
摘要:
甘肃徽县大石湾钴锰矿床位于西秦岭造山带云台-迷坝成矿带东段, 矿体赋存于上志留统卓乌阔组第4段灰岩夹硅质岩建造、灰岩-硅质岩建造2套含矿建造中。为进一步指导该地区的找矿工作, 通过开展大石湾钴锰矿区建造构造专项填图, 结合探槽揭露和老硐编录, 分析建造构造与成矿之间的关系, 对地质特征、成矿规律进行了总结, 认为矿床成因类型为沉积-改造型钴锰矿。研究结果表明, 卓乌阔组第4段硅质岩与灰岩接触带(硅钙面)为主要赋矿空间, 其次为灰岩-硅质岩建造中层间断裂带。主要控矿构造方向为近EW向; 矿床的成矿具有多期次的特点, 与多期次的构造运动相对应; 加里东晚期是该矿床最主要的初始富集成矿期, 印支期是该矿床一个重要的构造期, 该期近EW向的挤压逆冲推覆构造对原始沉积层进行叠加改造; 燕山期NE向、NNE向压扭性断裂对早期含矿地质体截切错动, 并为后期钴锰再次淋滤富集提供了有利空间, 为成矿期后构造单元, 控制钴锰最终成矿的赋存状态。
Abstract:The Dashiwan cobalt-manganese deposit in Huixian County is located in the eastern section of the Yuntai-Miba mineralization belt in the West Qinling orogenic belt. The ore body occurs in two sets of ore bearing formations: the limestone intercalated siliceous rock formation and the limestone siliceous rock formation in the fourth segment of the Upper Silurian zhuowukuo Formation. In order to further guide the exploration work in the region, a special mapping of the construction structure of the Dashiwan cobalt-manganese mining area was carried out, combined with trench exploration and old cave logging. The relationship between the construction structure and mineralization was analyzed, and the geological characteristics and mineralization laws were summarized. It is believed that the genetic type of the deposit is a sedimentary reformed cobalt-manganese deposit. The research results indicate that the contact zone between siliceous rocks and limestone in the fourth segment of the zhuowukuo Formation (siliceous calcium surface) is the main ore-forming space, followed by the interlayer fault zone in the limestone siliceous rock formation. The main direction of the ore control structure is in the near EW direction. The mineralization of ore deposits has the characteristic of multiple stages, which corresponds to multiple stages of tectonic movements; The late Caledonian period was the main initial enrichment stage of this deposit, while the Indosinian period was an important tectonic period. During this period, the nearly EW trending compression thrust nappe structure superimposed and transformed the original sedimentary layers; The NE and NNE trending compressional and torsional faults during the Yanshanian period cut and dislocated the early ore-bearing geological bodies, providing favorable space for the subsequent leaching and enrichment of cobalt and manganese, and controlling the occurrence state of cobalt and manganese mineralization in the post mineralization tectonic units.
-
甘肃金家坪-虞关钴-铁-锰-金-磷成矿区所处的西秦岭造山带, 是中国大陆中央造山系的重要组成部分, 环绕岛链古隆起形成深水—半深水滞留断陷局限盆地, 发育与热水沉积有关的志留纪“黑色岩系”, 形成一系列与“黑色岩系”相关的铁锰多金属矿床(张新虎等, 2013), 如金家坪、石门沟、大石碑、包家沟等铁锰矿床(图 1), 探明锰矿石资源量218.21×104 t, 钴金属资源量1724 t, 具有很大的找矿潜力①。前人曾对该成矿带西段的成县金家坪、石门沟锰矿床开展了一定的勘查工作, 研究程度薄弱, 只有勘查单位根据勘查实践从矿床地质特征、围岩蚀变、控矿因素、找矿标志、锰的赋存状态等方面进行了描述性研究, 并对矿床成因进行了初步探讨(段得洪等, 2002;陈秉祥, 2007;施小彬, 2020),专注于伴生钴的找矿研究极少。钴矿作为中国重要的战略性矿产(刘彬等, 2014), 主要伴生于以沉积型铜-钴矿(赵俊兴等, 2019)为主的其他矿产中, 过去的研究多集中在主要成矿元素方面。2019年,笔者在该成矿带东段徽县大石湾一带开展了钴矿调查评价, 首次发现了徽县大石湾钴锰矿床, 为南秦岭“黑色岩系”钴锰找矿研究打开了窗口。本文在对锰矿床特征(侯宗林等, 1992)及中国锰矿成矿规律、资源潜力特征系统研究(付勇等, 2014;丛源等, 2018)的基础上, 运用叶天竺教授提出的“三位一体”找矿预测理论方法(叶天竺等, 2014;2017)进行了矿床地质、成矿类型等方面的研究。前人认为,该成矿带钴锰矿体主要受印支期—燕山期断裂构造的控制, 矿体形态呈“鸡窝状”、“囊状”, 深部延伸不足50 m, 为淋滤沉积形成①, 对原始沉积层并未形成系统的认识。本文在详细矿床地质调查的基础上, 通过对大石湾钴锰矿床含矿建造、主成矿结构面“硅钙面”、矿石组构、岩石地球化学特征等方面的分析, 结合国内外著名钴锰矿床特征(吴自成等, 2016;周琦等, 2016;付胜云等, 2017;瞿永泽等, 2018;卢安康等, 2021), 探讨矿床成因和成矿机制。
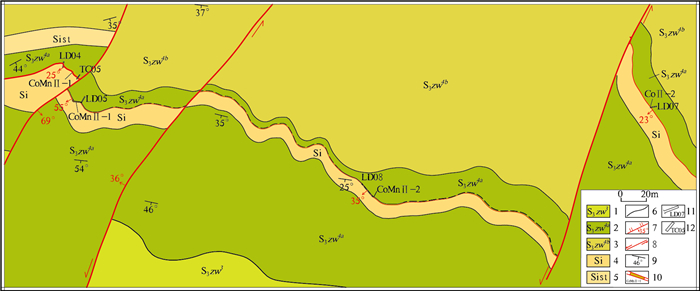
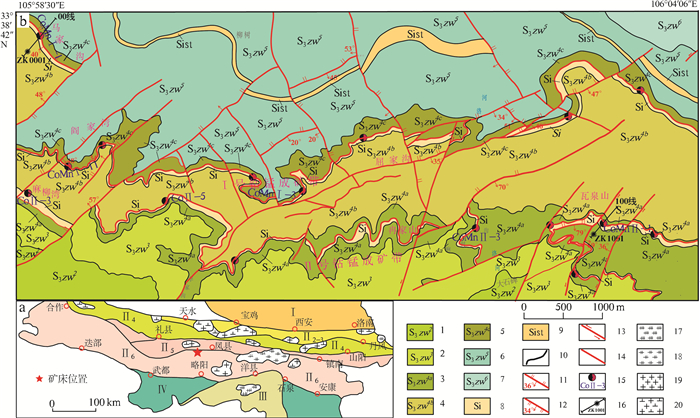
![]() 图 1 大石湾钴锰矿构造位置、矿区地质简图1—上志留统卓乌阔组2段灰岩夹板岩;2—上志留统卓乌阔组3段黄铁矿化炭质板岩;3—上志留统卓乌阔组4段灰岩夹硅质岩;4—上志留统卓乌阔组4段板岩夹灰岩;5—上志留统卓乌阔组4段灰岩-硅质岩;6—上志留统卓乌阔组5段板岩夹灰岩、硅质板岩;7—上志留统卓乌阔组6段灰岩夹板岩、硅质板岩;8—硅质岩;9—硅质板岩;10—地质界线;11—正断层;12—逆断层;13—平移断层;14—性质不明断层;15—钴锰矿点;16—勘探线及见矿钻孔位置;17—晋宁期中酸性侵入岩;18—加里东期中酸性侵入岩;19—海西期中酸性侵入岩;20—印支期、燕山期中酸性侵入岩;Ⅰ—华北板块;Ⅱ2-3—北秦岭岩浆弧;Ⅱ4—中秦岭陆缘盆地;Ⅱ5—泽库前陆盆地;Ⅱ6—西倾山-南秦岭陆缘裂谷带;Ⅲ—扬子板块;Ⅳ—巴颜喀拉褶皱系Figure 1. The structural location and geological map of Dashiwan cobalt-manganese mine
图 1 大石湾钴锰矿构造位置、矿区地质简图1—上志留统卓乌阔组2段灰岩夹板岩;2—上志留统卓乌阔组3段黄铁矿化炭质板岩;3—上志留统卓乌阔组4段灰岩夹硅质岩;4—上志留统卓乌阔组4段板岩夹灰岩;5—上志留统卓乌阔组4段灰岩-硅质岩;6—上志留统卓乌阔组5段板岩夹灰岩、硅质板岩;7—上志留统卓乌阔组6段灰岩夹板岩、硅质板岩;8—硅质岩;9—硅质板岩;10—地质界线;11—正断层;12—逆断层;13—平移断层;14—性质不明断层;15—钴锰矿点;16—勘探线及见矿钻孔位置;17—晋宁期中酸性侵入岩;18—加里东期中酸性侵入岩;19—海西期中酸性侵入岩;20—印支期、燕山期中酸性侵入岩;Ⅰ—华北板块;Ⅱ2-3—北秦岭岩浆弧;Ⅱ4—中秦岭陆缘盆地;Ⅱ5—泽库前陆盆地;Ⅱ6—西倾山-南秦岭陆缘裂谷带;Ⅲ—扬子板块;Ⅳ—巴颜喀拉褶皱系Figure 1. The structural location and geological map of Dashiwan cobalt-manganese mine1. 区域地质背景
大石湾钴锰矿床所在的金家坪-虞关铁-锰-金-磷成矿区位于西秦岭造山带的南部(图 1-a), 处于西倾山-南秦岭陆缘裂谷带和中秦岭陆缘盆地的结合部位(张新虎等, 2008)。其陆缘裂解盆地形成于志留纪末, 海相沉积成矿作用强烈, 基本构造格架定型于三叠纪以来的印支造山运动, 地质构造复杂(霍福臣等, 1995)。区域出露地层从老到新依次有志留系舟曲组和卓乌阔组、泥盆系古道岭组和星红铺组、泥盆系—石炭系铁岭组、白垩系周家湾组, 其中泥盆系—石炭系分布在大河店-广金坝区域断裂以北, 区域上受鸡峰山逆冲推覆构造的影响形成一系列近EW向展布的构造岩片, 主要岩性组合为微晶灰岩、泥晶灰岩、生物碎屑灰岩、含燧石条带泥晶灰岩夹钙质板岩、含铁石英砂岩、炭质页岩等, 主体为一套碳酸盐台地环境海相陆源碎屑沉积建造。上志留统卓乌阔组分布在大河店-广金坝区域断裂以南、成县宋坪-白水江断裂以北, 岩性为微晶灰岩、含燧石条带结晶灰岩夹炭质板岩、硅质板岩、硅质岩, 为一套深水相沉积建造②。研究区西南部侵入岩发育, 印支期迷坝二长花岗岩-花岗闪长岩-石英二长闪长岩等主要侵入体显EW向展布(孙卫东, 2000), 研究区可见同期闪长玢岩脉穿插钴锰矿层。大河店-广金坝区域断裂带(组)控制着区域矿床(点)的分布, NE向断裂及其与NW向断裂的交会部位及褶皱构造转折端虚脱部位往往是赋矿的有利空间③。矿床有成县金家坪钴锰矿(中型)、徽县大石湾钴锰矿、迭部黑拉铁矿(中型)、成县陈家庄铁锰矿(中型)。
2. 矿床地质特征
2.1 矿区地质
通过对矿区进行1:25 000岩性构造专项填图, 将上志留统卓乌阔组从上到下分为5个岩性段、7个建造类型(图 1-b), 总体呈近EW向展布, 详见表 1。
表 1 志留系卓乌阔组建造类型划分Table 1. Classification of construction types of the Silurian Zhuowukuo Formation建造类型 代号 岩性组合 含矿性 硅质灰岩夹板岩建造 S3zw6 深灰色中厚层-块状硅质灰岩、灰黑色中薄层硅质灰岩夹灰黑色炭质板岩、硅质板岩、浅灰绿色粉砂质板岩、灰色薄层状含硅质条带灰岩 板岩夹灰岩建造 S3zw5 灰青灰色板岩, 灰色钙质板岩, 灰色粉砂质板岩, 灰黑色含黄铁矿碎裂炭质板岩夹黑色硅质板岩、灰黑色薄层硅质灰岩、灰黑色中薄层细晶灰岩 灰岩夹硅质岩建造 S3zw4a 灰黑色细晶灰岩, 灰黑色板状微-粉晶灰岩夹浅灰色厚层-块状硅质岩、锰质岩、泥质岩 层状钴
锰矿体灰岩夹板岩建造 S3zw4b 灰黑色结晶灰岩夹灰黑色燧石条带灰岩夹灰绿色板岩、炭质板岩、炭质板岩, 偶见黑色硅质板岩 囊状钴
锰矿体灰岩-硅质岩建造 S3zw4c 下部为灰黑色含燧石条带微晶灰岩;上部为角砾状硅质岩、泥质岩、锰质岩, 顶部为灰黑色块状硅质灰岩 层状钴
锰矿体炭质板岩建造 S3zw3 黑色炭质板岩, 黑色黄铁矿化炭质板岩夹灰黑色硅质板岩 灰岩夹板岩建造 S3zw2 灰黑色结晶灰岩、灰黑色含硅质条带结晶灰岩夹板岩、黑色炭质板岩 类比参考姚敬劬等(1998)对中国含锰岩系的划分, 研究区卓乌阔组4段具有钙硅泥岩系成锰的特征, 当该套组合被碎屑岩所替代时, 锰矿层变劣质甚至尖灭。
地层变形较强, 揉皱、褶皱、节理、塑性变形等均较发育。早期NE向张性断裂可能为主成矿构造, 硅质岩与灰岩接触面为钴锰成矿最主要的成矿结构面, 经印支造山该结构面形成近EW向层间断裂构造, 并为钴锰再次富集成矿提供了有利的含矿空间, EW向断裂规模较大, 走向延伸可达15 km, 上盘硅质岩角砾岩化、褐铁矿化, 最宽处可达50 m, 被NE向、NW向断裂切割;该组断裂控制着钴锰矿化的分布、规模及产状变化情况, 断层产状具有波状变化, 控制的矿体形态随之膨大缩小、尖灭再现。NE向、NNE向压扭性断裂对早期含矿地质体截切错动, 并为后期钴锰再次淋滤富集提供了有利空间, 为成矿期后构造单元, 控制钴锰最终成矿的赋存状态。近矿围岩蚀变主要有钠长石化、碳化、泥化、硅化、褐铁矿化、碳酸盐化等。
2.2 矿床地质
2.2.1 矿化带特征
根据已知、新发现矿(化)点及土壤地球化学异常分布, 结合钴锰矿含矿建造的展布特征, 在研究区划分了马家沟-阎家湾-屈家沟Ⅰ号钴锰成矿带(北带)和麻柳湾-冉家山-瓦泉山Ⅱ号钴锰成矿带(南带)2个钴锰成矿带。
Ⅰ号钴锰成矿带呈NWW向弧形状展布, 倾向SW, 长约15 km, 宽50~350 m;矿带含矿建造为卓乌阔组第4段硅质岩-灰岩建造(S3zw4c), 矿体产于硅质岩下部薄层硅质灰岩中。目前在该成矿带内共圈出27条矿(化)体, 其中钴锰矿体10条、钴矿体13条、钴矿化体4条, 主要位于马家沟、阎家湾、屈家沟一带, 矿体受近EW向层间断裂和NE向压扭性断裂控制, 多呈层状、似层状产出;矿体厚0.54~20.21 m, 长90~620 m, Co品位为0.024%~0.24%,Mn品位为5.91%~27.54%。
Ⅱ号钴锰成矿带呈NWW向展布, 倾向SW, 长约9 km, 宽50~150 m, 矿化带含矿建造为卓乌阔组第4段灰岩夹硅质岩建造(S3zw4a), 矿体产于薄层硅质岩与硅质灰岩岩性接触面附近, 目前在该成矿带内共圈出10条矿体, 其中钴锰矿体5条、钴矿体5条, 主要位于瓦泉山、响洞沟、麻柳湾一带。矿体受层间断裂构造控制, 多呈层状、似层状产出, 矿体厚0.94~9.74 m, 长200~1023 m, Co品位0.02%~0.166%,Mn品位7.15%~22.93%, 部分矿体Cu、Ni亦达到边界品位。
2.2.2 矿体特征
通过老硐编录、探槽揭露及深部钻探验证, 共圈定矿(化)体37条, 钴锰矿体15条、钴矿体19条, 钴矿化体3条, 矿体特征见表 2。按矿体空间的集中分布特征, Ⅰ矿化带可分为马家沟、阎家湾、屈家沟3个矿段, Ⅱ矿化带可分为麻柳湾、响洞沟、瓦泉山3个矿段。
表 2 大石湾钴锰矿(化)体特征Table 2. Characteristics of cobalt-manganese ore (mineralized) body in Dashiwan矿体编号 工程编号 厚度/m 长度/m 单工程平均品位 矿体平均品位 产状/° 含矿建造构造 Co/% Mn/% Co/% Mn/% CoMnⅠ-1 LD01 5 620 0.076 17.63 0.094 16.75 217∠38 S3zw4c硅钙面 LD16 1.69 0.103 27.54 220∠30 LD02 3.49 0.103 11.25 210∠35 LD03 1.28 0.13 14.02 209∠33 ZK0001 1.06 0.085 24.8 CoMnⅠ-2 TC11 1.64 200 0.078 10.64 0.078 10.64 250∠66 S3zw4cEW向层间断裂 CoMnⅠ-3 LD12 1.93 350 0.065 15.16 0.074 9.74 161∠38 S3zw4c硅钙面 LD13 2.73 0.08 5.91 175∠45 CoMnⅠ-4 LD12 0.83 110 0.22 23.45 0.22 23.45 238∠41 CoMnⅠ-5 TC07 0.98 200 0.021 7.61 0.021 7.61 340∠70 CoMnⅠ-6 LD10 1.03 370 0.24 24.78 0.24 24.78 160∠20 S3zw4cNE向逆断层 LD11 1.13 0.024 0.84 0.024 0.84 220∠20 CoMnⅠ-7 LD11 1.79 90 0.134 15.67 0.134 15.67 220∠45 S3zw4cEW向层间断裂 CoMnⅠ-8 LD11 0.54 200 0.19 20.9 0.19 20.9 340∠40 NE向逆断层 CoMnⅠ-9 LD15 2.86 200 0.12 23.07 0.12 23.07 61∠70 S3zw4c硅质灰岩层间 CoMnⅠ-10 LD15 1.88 200 0.067 15.72 0.067 15.72 270∠20 NW向逆断层 CoMnⅠ-11 TC19 9.74 850 0.155 10.64 0.137 7.15 155∠75 S3zw4c硅钙面 TC20 4.56 0.124 1.61 65∠36 TC22 6.66 0.150 9.73 165∠45 LD20 2.31 0.144 2.33 LD21 2.73 0.053 1.72 175∠50 CoⅠ-1 TC01 0.71 200 0.019 0.019 170∠40 S3zw4a硅质岩层间断层 CoⅠ-2 LD09 0.59 130 0.033 0.033 50∠45 NW向逆断层 CoⅠ-3 LD09 4.3 90 0.075 0.075 S3zw4c硅质灰
岩层间断层CoⅠ-4 LD09 1.61 200 0.051 0.051 285∠40 CoⅠ-5 TC10 20.21 570 0.033 202∠25 TC17 0.88 0.032 2.64 0.037 225∠45 TC21 3.10 0.067 1.52 265∠55 CoⅠ-7 TC09 1.81 200 0.059 7.48 0.059 7.48 220∠55 CoⅠ-8 TC17 1.27 200 0.13 3.41 0.13 3.41 170∠75 NE向逆断层 CoⅠ-9 TC15 1.09 140 0.021 1.15 0.021 1.15 160∠40 CoⅠ-10 TC15 1.09 140 0.029 1.28 0.029 1.28 160∠40 CoⅠ-11 TC15 1.89 140 0.036 1.14 0.036 1.14 160∠40 CoⅠ-12 TC11 1.46 200 0.055 5.7 0.055 5.7 270∠41 S3zw4cEW向层间断裂 CoⅠ-13 TC12 5.16 200 0.051 7.75 0.051 7.75 150∠56 S3zw4c硅钙面 CoⅠ-14 TC12 2.15 200 0.024 2.38 0.024 2.38 150∠56 S3zw4c硅质灰岩
层间断层CoⅠ-15 TC13 1.09 200 0.023 1.25 0.023 1.25 170∠60 CoⅠ-16 TC13 1.45 200 0.017 0.72 0.017 0.72 170∠60 CoⅠ-17 TC15 1.09 140 0.018 1.15 0.018 1.15 160∠40 NE向逆断层 CoⅠ-18 TC15 2.18 140 0.016 0.65 0.016 0.65 160∠40 CoMnⅡ-1 LD04 1.19 1023 0.096 19.48 0.079 22.93 255∠25 S3zw4a硅钙面 LD05 2.03 0.078 29.6 235∠56 TC05 4.31 0.084 28.47 235∠45 LD22 1.23 0.055 8.38 CP02 1.18 0.073 9.86 145∠43 ZK1001 2.26 0.086 22.5 CoMnⅡ-2 LD08 1.51 250 0.166 20.44 0.166 20.44 225∠28 S3zw4a硅钙面 CoMnⅡ-3 LD17 3.15 470 0.105 13.85 0.164 13.6 345∠15 S3zw4a硅钙面 LD18 2.44 0.241 13.28 255∠20 CoMnⅡ-4 CP01 3.68 200 0.112 10.56 0.112 10.56 315∠75 NE向逆断层 CoⅡ-2 LD07 1.58 200 0.035 0.035 238∠23 S3zw4a硅钙面 CoⅡ-1 LD06 0.94 200 0.065 0.065 217~220 S3zw4a硅钙面 ∠5~48 CoⅡ-3 LD21 1.30 300 0.02 2.80 0.02 2.80 175∠50 S3zw4a硅质灰岩层间断层 CoⅡ-4 2.22 200 0.046 8.48 0.046 8.48 165∠70 CoⅡ-5 LD19 1.64 200 0.027 1.64 0.027 156∠28 S3zw4a硅钙面 根据矿体赋存位置及展布规律,可将研究区钴锰矿体分为以下3类。
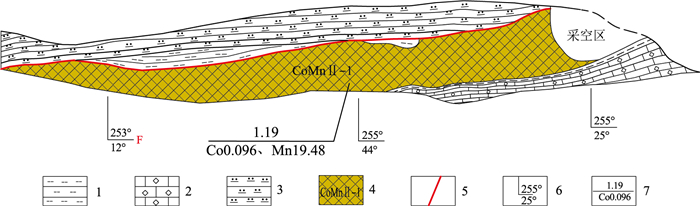
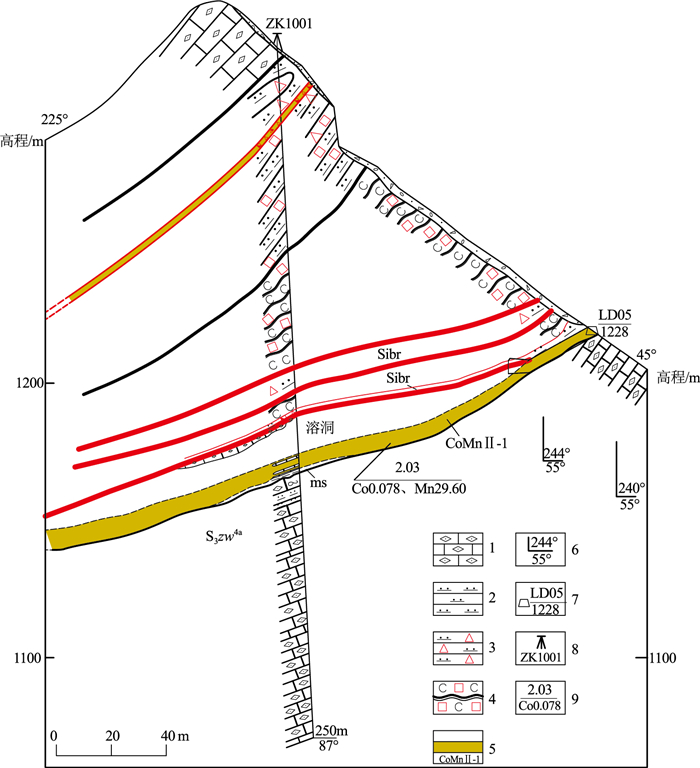
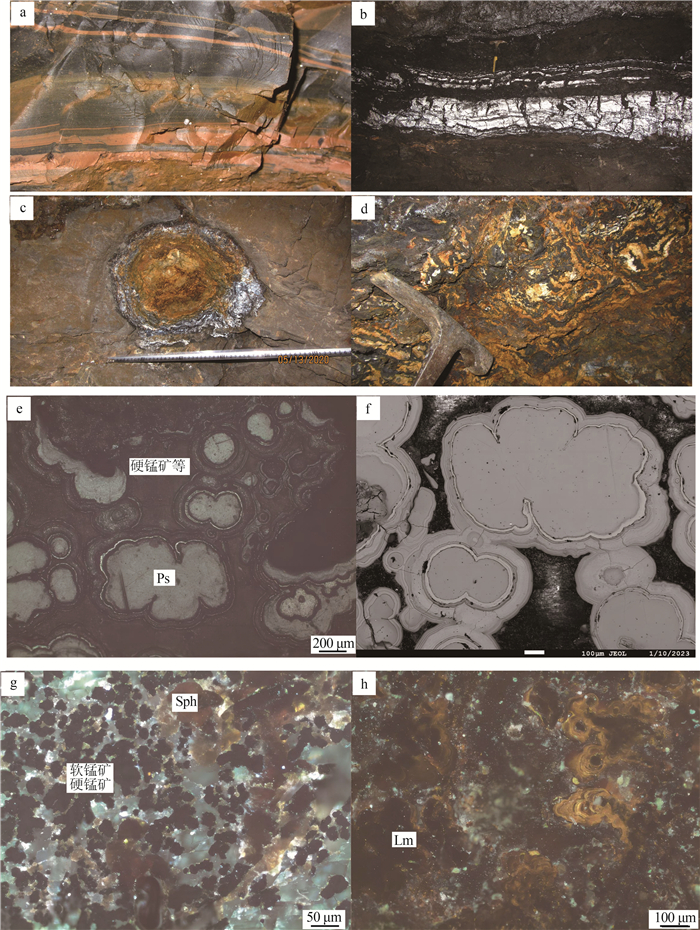
(1) 受“硅钙面”控制的沉积-改造型钴锰矿。该类矿体代表性的有阎家湾矿段CoMnⅠ-11、瓦泉山矿段CoMnⅡ-1, 矿体赋存于硅质岩与微晶灰岩接触面(图 2), 自下而上为含燧石条带微晶灰岩→泥质岩→含泥硅锰质岩与钠长岩互层(矿体)→泥质岩→硅质角砾岩(硅质岩)(图 3), 其接触面波状起伏, 矿体随之膨大收缩、尖灭再现, 并发生层间滑动;矿体形态呈层状、似层状, 矿体产状210°~245°∠30°~35°, 该类矿体走向延伸稳定, 已控制CoMnⅡ-1可达1023 m, 钻孔ZK1001控制斜深120 m(图 4)。
(2) 受灰岩层间断裂构造控制的钴锰矿。代表性的有阎家湾矿段CoMnⅠ-1、CoⅠ-5, 矿体赋存于灰黑色含燧石条带微晶灰岩层间断裂中, 接触面波状起伏, 形态呈似层状、脉状及不规则状, 在断层下盘常形成岩溶盆、岩溶凹槽, 矿体厚度亦随岩溶地貌的变化而膨大或缩小(张洪瑞等, 2012), 一般为1.28~5 m, 在岩溶盆中可达20.21 m, 矿体上部常被地下河沉积的砂砾石(具水平层理)掩盖(图 5)。
(3) 受NE向、NW向断裂构造控制的钴锰矿。代表性的有阎家湾矿段CoMnⅠ-6、瓦泉山矿段CoMnⅡ-4, 该类矿体出现于以上2类矿体的旁侧, 严格受不同方向断裂构造的控制, 靠近原始沉积层位则厚大, 远离则尖灭, 矿体延伸小于100 m, 普遍褐铁矿化较强烈, 形态呈囊状、透镜状、脉状及不规则状。
2.2.3 矿石特征
通过对主要矿石类型的光、薄片鉴定及基本化学分析, 大石湾钴锰矿以钴锰为主, 不存在单独钴矿物, 伴生铜、镍。矿石类型以含泥硅锰质岩为主, 其次为铁锰矿化角砾岩, 为氧化型矿石。矿石矿物主要为黑色纹层状、粉末状、土状软锰矿(图 6-a), 其次为葡萄状、鲕状硬锰矿(图 6-b), 少量褐锰矿、褐铁矿、赤铁矿。脉石矿物主要为方解石、钠长石、石英, 其次有高岭土、有机碳及少量岩屑等。
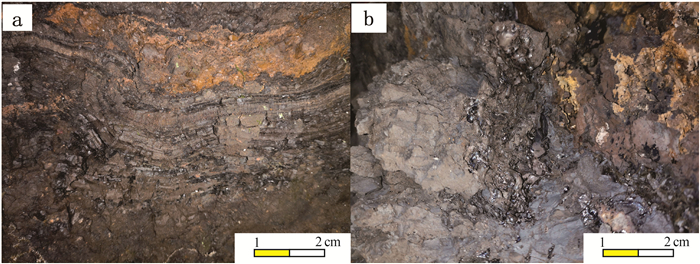
通过野外观察, 结合光、薄片鉴定结果, 矿石组构可分为原生和后生2种(叶杰等, 2002), 原生组构有条带状、似层状(图版Ⅰ-a)、条纹状构造(图版Ⅰ-b)、结核状构造(图版Ⅰ-c)及豆状构造, 鲕状(图版Ⅰ-e)、纹层状结构(图版Ⅰ-f)、隐晶质(图版Ⅰ-g)、胶状结构;后生组构有多孔状、蜂窝状(图版Ⅰ-d)、脉状构造, 土状、粉状结构(图版Ⅰ-h)。赋存于硅钙面及层间构造的矿石可见残留原生组构, 以条纹状构造为主;赋存于成矿期后不同方向断裂构造中的矿石以后生组构常见, 可见蜂窝状、土状、热液条带状构造为主。
对该矿床西邻成县金家坪钴锰矿床ⅠMn-4、ⅡMn-5所采矿石进行物相分析, 结果显示,锰主要集中在氧化锰矿物中(软锰矿、硬锰矿、水锰矿、褐锰矿), 占锰总含量的96%以上, 其中软锰矿和硬锰矿中锰占84%以上, 而菱酸锰矿中锰所占比例不超过4%, 几乎不含硅酸盐类锰。
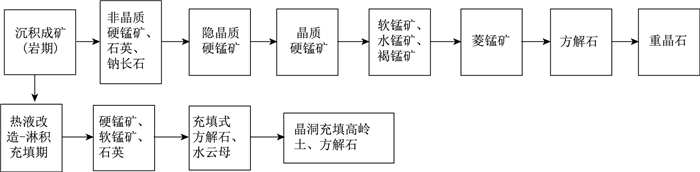
从锰矿物相的一般成因分析, 硬锰矿、软锰矿在原生及次生条件下均可以形成, 而鲕状硬锰矿、水锰矿和褐锰矿为原始沉积形成, 二者叠加作用成矿。根据本区锰矿体的产出状态、矿石的矿物成分和组构特征分析, 主要矿物的形成可分为沉积成矿(岩)和成矿(岩)后构造热液改造及表生裂隙淋积充填3个时期, 各时期的主要矿物生成顺序见图 7。
钴与锰矿密切共生, 均已达工业品位, 使矿区的锰矿体多数为钴锰矿体。钴主要以钴氧化物形式存在, 平均占有率98.83%, 其次有少量钴硫化物, 平均占有率1.17%, 不含钴难溶脉石(表 3)。
表 3 西邻金家坪锰矿床矿石中伴生钴物相分析结果Table 3. Analysis results of accompanying cobalt phases in the ore of the Jinjiaping manganese deposit in the west硫化物中 氧化物中 难溶脉石中 钴含量/% 所占比例/% 钴含量/% 所占比例/% 钴含量/% 所占比例/% 0.001 1.17 0.10 98.83 0.00 0.00 3. 岩石地球化学特征
3.1 主要金属元素富集特征
在研究区及周边采集卓乌阔岩组各类岩石样品750件, 岩石全分析样品13件, 由甘肃省地矿局一勘院试验测试中心测试, 分析结果分别见表 4、表 5。从岩石的元素富集特征分析, 硅质岩中Au、Sb等元素呈强富集型, V、Ba等元素呈弱富集型;硅质板岩中Au、Cu、Sb、Zn等元素呈强富集型, Co、Ni、Ba等元素呈弱富集型;炭质板岩中Au、Ba、Sb、Zn等元素呈强富集型, Cu、Ni等元素呈弱富集型。
表 4 卓乌阔组各类岩石中元素含量Table 4. Table of element content in various rocks of Zhuowukuo Formation岩石名称 数字特征 As Au Ba Co Cu Mn Ni Sb V Zn 志留系中均值 28.43 2.81 705.2 11.73 33.37 917.8 26.7 2.33 103.33 67.5 板岩 平均值 31.7 5.2 1920 10.1 38.5 664 29.2 3.7 228.4 109.5 标准偏差 25.9 3.3 1005 6.5 25.8 1134 21.5 3.89 118.2 72.1 浓集系数 1.12 1.85 2.72 0.86 1.15 0.72 1.09 1.59 2.21 1.62 硅质板岩 平均值 20.8 4.3 864 14.5 54.4 590 38.1 4.39 64.33 256.7 标准偏差 19.9 3.6 370 7.9 35.1 668 18.9 4.36 66.53 223.4 浓集系数 0.73 1.53 1.23 1.24 1.63 0.64 1.43 1.88 0.62 3.80 炭质板岩 平均值 29 4.4 1411 11.1 48.1 178 34.8 5.78 14.07 316.1 标准偏差 38.3 2.6 1033 6.2 50.2 168 22.2 6.44 10.51 256.8 浓集系数 1.02 1.57 2.00 0.95 1.44 0.19 1.30 2.48 0.14 4.68 结晶灰岩 平均值 8.2 5 576 3.9 32.1 532 12.7 0.77 128.6 34.7 标准偏差 5.9 5 553 2.1 58.2 770 3.6 0.7 65 20.3 浓集系数 0.29 1.78 0.82 0.33 0.96 0.58 0.48 0.33 1.24 0.51 细晶灰岩 平均值 5.3 1.8 623 3.3 20.1 374 13.3 1.62 94.2 39.8 标准偏差 3.8 1 645 2.3 17.5 343 8.2 1.34 44.9 28.1 浓集系数 0.19 0.64 0.88 0.28 0.60 0.41 0.50 0.70 0.91 0.59 硅质灰岩 平均值 13.4 1.9 552 4.9 22.2 286 18.3 3.34 98.1 45.7 标准偏差 10.7 1.6 547 4.4 19.2 225 11.4 2.89 50.4 30.8 浓集系数 0.47 0.68 0.78 0.42 0.67 0.31 0.69 1.43 0.95 0.68 含硅质条带灰岩 平均值 9 2.2 534 3 42.1 306 14.8 4.39 137.4 39.5 标准偏差 13.2 1 318 1.7 35.5 280 9.4 5.35 76.9 34.9 浓集系数 0.32 0.78 0.76 0.26 1.26 0.33 0.55 1.88 1.33 0.59 硅质岩 平均值 13.4 6.1 726 5.4 29.2 76 10.6 4.51 132 27.9 标准偏差 10.4 0.7 740 1.2 12.8 18 4.7 4.96 105.7 5.5 浓集系数 0.47 2.17 1.03 0.46 0.88 0.08 0.40 1.94 1.28 0.41 注: Au元素含量单位为10-9, 其他元素含量单位为10-6;浓集系数=平均值/志留系中均值 表 5 Ⅰ矿带钴锰矿石及围岩主量元素分析结果Table 5. Major content of cobalt-manganese ores and surrounding rocks in zone Ⅰ样品编号 PM02
YQ5-1D0137
YQ-1PM04
YQ8-1LD13
YQ1LD13
YQ2TC17
YQ1LD18
XT01TC20
XT1-1TC33
YQ2-1TC33
YQ4-1LD23
YQ2-1TC22
YQ-1岩矿石名称 硅质岩 硅质岩 硅质岩 钠长岩 锰矿化角砾岩 含泥硅锰质岩 钠长岩 粘土岩 含泥硅锰质岩 含泥硅锰质岩 粘土岩 含泥硅锰质岩 Al2O3 3.03 1.52 0.22 32.6 3.86 11.52 31.72 10.56 27.56 29.43 19.38 17.96 CaO 6.39 0.32 0.14 2.89 1.14 1.85 0.14 0.15 0.92 1.02 0.94 1.98 Fe2O3 0.14 0.66 1.86 1.7 63.28 7.07 1.09 14.83 2.42 1.44 3.76 17.78 MgO 0.26 0.18 0.072 0.29 0.41 0.2 0.27 0.65 0.18 0.19 0.24 0.47 MnO 0.07 0.019 0.015 2.38 4.04 6.22 0.177 0.033 2.14 4.28 0.23 14.94 P2O5 0.095 0.078 0.074 0.4 1.88 0.56 0.03 0.189 0.052 0.1 0.26 3.66 TiO2 0.18 0.049 0.018 0.045 0.04 0.054 0.088 0.853 0.091 0.066 0.54 0.066 SiO2 81.23 88.02 93.88 23.6 4.8 61.38 5.3 62.29 51.91 47.38 64.38 24.78 Na2O 0.2 0.05 0.09 0.06 0.2 0.078 0.14 0.08 0.28 0.26 0.4 0.43 K2O 0.66 0.09 0.3 0.12 0.31 0.2 0.12 1.75 0.39 0.45 3.38 0.44 FeO 0.68 1.28 1.29 0 0 0 0.28 1.79 0 0 0.26 0 H2O- 0.2 0.4 0.2 0.4 0.4 0.2 烧失量 6.78 0.94 1.3 35.74 19.92 10.4 57.6 5.01 13.3 14.85 5.66 16.48 注: 主量元素含量单位为% 从表 4可知, 研究区Co、Mn主成矿元素并不在任何一种岩石类型中富集, 且均小于元素平均值。Co元素在碳酸盐岩中平均值为3×10-6~4.9×10-6, 远小于志留系中Co元素平均值, 在板岩中平均值为10.1×10-6~14.5×10-6, 且在硅质板岩中呈弱富集。Mn元素在碳酸盐岩及板岩中平均值为286×10-6~664×10-6, 远小于志留系中Mn元素平均值, 在硅质岩中仅为76×10-6。前人认为,研究区钴锰成矿是淋滤卓乌阔组内元素富集层而形成囊状、鸡窝状矿体, 显然与本次调查所显示的元素地球化学特征不相符。事实是, 在沉积成岩阶段, Co、Mn等成矿元素仅富集于含泥硅锰质岩中, 并未在其他岩性层中富集。
3.2 主量元素特征
泥硅质锰质岩矿石中主要化学成分SiO2含量在24.78%~61.38%之间, Al2O3含量在11.52%~29.43%之间, 可以推断, 矿石中脉石矿物主要为石英或铝硅酸盐类矿物。次要化学成分为铁及钙镁质矿物(FeO、Fe2O3、CaO、MgO)等, 矿石中SiO2含量变化较大, 泥硅质锰质岩含量较高, 可能与海水硅质成分化学沉积有关, 钴锰矿化角砾岩中SiO2含量较低, 可能与后期改造再次富集相关。
3.3 稀土元素特征
在Ⅰ矿带矿体及围岩中采集稀土元素分析样品12件, 钠长岩采集于矿体夹层, 由甘肃省地矿局一勘院试验测试中心测试, 质谱仪型号为ICAP-Q型。稀土元素含量及特征参数见表 6, 稀土元素球粒陨石标准化型式见图 8。
表 6 Ⅰ矿带钴锰矿石及围岩稀土元素含量Table 6. Rare earth element content of cobalt-manganese ores and surrounding rocks in zone Ⅰ样品号 PM02
XT5-1D0137
XT-1PM04
XT8-1LD13
XT1LD13
XT2TC17
XT1LD18
XT01TC20
XT1-1TC33
XT2-1TC33
XT4-1LD23
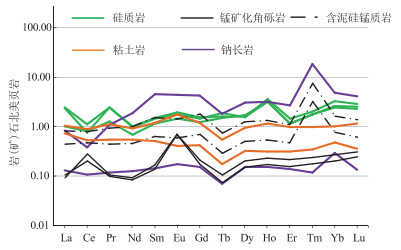
XT2-1样品名 硅质岩 硅质岩 硅质岩 钠长岩 含泥硅锰质岩 含泥硅锰质岩 钠长岩 粘土岩 锰矿化角砾岩 锰矿化角砾岩 粘土岩 La 78.6 32.8 76.4 26.5 26 14.4 4.2 23.3 3.4 3 33.2 Ce 83 59.6 56 28 58.8 34.6 7.9 39.3 14.8 20.8 64.6 Pr 19 10 19.5 8.6 7.4 3.5 0.94 4.4 0.79 0.84 9 Nd 33.5 23 32 61.8 33.2 15 4.1 18 2.8 3.1 30.6 Sm 8.7 6.6 8.3 25.7 8.6 3.6 0.83 2.9 0.79 0.97 6.9 Eu 2.4 1.8 2.2 5.5 1.8 0.75 0.22 0.51 0.88 0.86 2.2 Gd 8 6.4 7.6 21.8 9.2 3.6 0.8 2.2 0.9 1.1 6.3 Tb 3 2.8 3.5 3.4 1.4 0.54 0.13 0.33 0.14 0.2 1 Dy 9.2 9.8 9 17.8 7.3 2.9 0.91 1.9 0.87 1.2 5.6 Ho 3.3 3.4 3.8 3.3 1.4 0.56 0.16 0.33 0.18 0.24 1.2 Er 4 4 5 9.2 3.8 1.6 0.48 1.1 0.54 0.75 3.4 Tm 0.87 0.87 1 9.2 3.8 1.6 0.06 0.17 0.09 0.12 0.49 Yb 8 7.7 10.1 15.2 5.1 2.4 0.92 1.5 0.63 0.84 3.2 Lu 1.2 1.1 1.4 2 0.66 0.3 0.06 0.18 0.12 0.15 0.56 Y 44.3 40.5 52.3 58.6 27.8 15.5 4.4 9.6 2.5 2.7 20.4 ΣREE 262.77 169.87 235.8 238 168.46 85.35 21.74 96.07 26.93 34.17 168.25 LREE 225.2 133.8 194.4 156.1 135.8 71.85 18.22 88.35 23.46 29.57 146.5 HREE 37.57 36.07 41.4 81.9 32.66 13.5 3.52 7.72 3.47 4.6 21.75 LREE/HREE 5.99 3.71 4.7 1.91 4.16 5.32 5.17 11.44 6.76 6.43 6.74 (La/Yb)N 0.983 0.447 0.819 0.199 0.591 0.72 0.981 1.991 0.425 0.3 0.889 δEu 1.26 1.22 1.22 1.02 0.89 0.91 1.17 0.88 4.55 3.63 1.47 δCe 0.47 0.71 0.32 0.4 1.02 1.06 0.86 0.84 1.97 2.85 0.81 注: 稀土元素含量单位为10-6 ![]() 图 8 Ⅰ矿带钴锰矿石及围岩稀土元素北美页岩标准化配分模式图(北美页岩标准化数据据陈德潜等,1990)Figure 8. North American shale standardization patterns of rare earth elements cobalt-manganese ores and surrounding rocks in zone Ⅰ
图 8 Ⅰ矿带钴锰矿石及围岩稀土元素北美页岩标准化配分模式图(北美页岩标准化数据据陈德潜等,1990)Figure 8. North American shale standardization patterns of rare earth elements cobalt-manganese ores and surrounding rocks in zone Ⅰ分析结果显示, 粘土岩、硅质岩稀土元素总量(ΣREE)介于96.07×10-6~262.77×10-6之间, 反映典型深海沉积环境特征;泥硅质锰质岩及与之紧密共生的钠长岩稀土元素总量介于21.74×10-6~210.36×10-6之间, 相对偏低, 表现出与海水不一致的特点, 反映沉积阶段海水中早期形成大量锰质结核。轻重稀土元素比值(ΣLREE/ΣHREE)介于3.71~11.44之间, (La/Yb)N值大多小于1, 表明海水中重稀土元素较轻稀土元素富集的特点。钠长岩、硅质岩、粘土岩中δCe值介于0.32~0.92之间, 为负Ce异常, 表明在海水处于氧化环境下形成了化学沉积的海相沉积物;但有4件矿石样品δCe皆大于1, 表现为正Ce异常, 与现代海洋中锰结核的稀土元素特征相似, 矿石中正Ce异常的出现表明在沉积初期阶段已经形成锰质结核(傅群和, 2001;林枢等, 2017), Ce(OH)4与Co、Mn共同沉淀所致。
稀土元素北美页岩标准化图解(图 8)中的分配曲线向左倾斜, 表明重稀土元素富集而轻稀土元素亏损, 为重稀土元素富集型。硅质岩、钠长岩、粘土岩和含泥硅锰质岩4个样品的配分曲线基本类似, 反映出它们为同源产物;但锰矿化角砾岩2件样品表现出强烈的正Ce异常, 可能与地表氧化淋滤相关。
4. 讨论
4.1 矿床成因
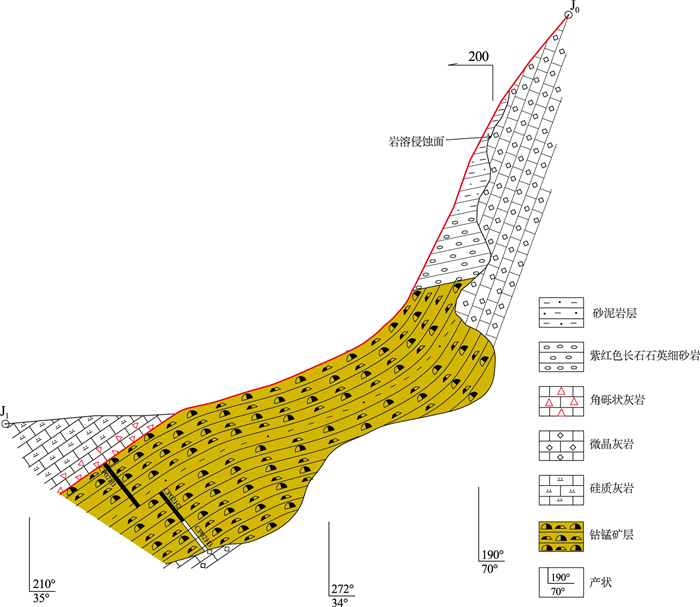
大石湾钴锰矿的形成与南秦岭陆缘裂解息息相关(张复新等, 2020), 在加里东期陆缘裂解过程中, 在志留纪晚期沉积了一套深海相的碳酸盐岩建造。根据卓乌阔组的各岩性段的建造类型分析, 存在多个沉积旋回, 其中卓乌阔组4段微晶灰岩夹硅质岩建造构成钴锰矿的容矿地层, 在研究区延伸可达7 km。已发现的主要钴锰矿体均赋存于该套建造硅质岩与微晶灰岩岩性界面(硅钙面), 自下而上为含燧石条带微晶灰岩→泥质岩→含泥硅锰质岩与钠长岩互层→泥质岩→硅质角砾岩(硅质岩), 构成含矿“泥硅锰”岩套。赋存于硅钙面的钴锰矿体具有典型的纹层状构造、条带状构造、豆状构造, 鲕状结构等沉积组构, 虽经印支造山期强烈的构造改造, 但原始沉积纹层仍随处可见。
另外, 硅质岩、钠长岩、粘土岩和含泥硅锰质岩的稀土元素配分曲线基本类似, 表明研究区含矿“泥硅锰”岩套属于同一构造环境, 沉积成岩与成矿相继发生, 在沉积成岩阶段形成的锰质岩主要由鲕状或胶状晶质硬锰矿、水锰矿、褐锰矿、交代(隐)晶质硬锰矿的软锰矿及微细粒他形粒状方解石、石英、钠长石组成, 钴共生于各类氧化锰中。经后期改造再次富集形成如今的矿体赋存状态。
综上所述, 根据《矿产地质勘查规范——铁、锰、铬》(DZ/T0200—2020)对中国锰矿床的划分标准(郝雨等,2020),参考张洪瑞等(2020)对钴矿床成因类型的研究,将徽县大石湾钴锰矿床成因类型划归海相沉积型黑色页岩系氧化型锰矿亚类。
4.2 矿床形成机制
综合前文矿体特征、矿石特征、岩石化学特征、岩(矿)石地球化学特征等研究, 按成矿作用及控矿因素特征, 该矿床可划分为3个成矿阶段。
(1) 沉积阶段: 据徐林刚等(2020)最近研究成果, 海相沉积型锰矿的成矿过程受古海洋沉积环境影响, 在晚志留世(加里东晚期)西倾山-南秦岭陆缘裂解环境下, 本区接受了半深水—深水陆架斜坡碳酸盐岩、含炭细碎屑岩、硅质岩沉积建造。远距离搬运的成矿物质在海底洼地形成化学(碳酸盐岩)、胶体状(硅质岩)沉淀物和褐锰矿、水锰矿、鲕状硬锰矿、软锰矿等沉淀形成的锰质岩, 结壳或结核中的铁锰氢氧化物(主要为水羟锰矿)强烈吸附海水中的Co2+离子, 造成钴富集(Manheim, 1986)。随着沉积层的加厚, 在重力或构造应力作用下成矿物质失水-结晶-固化, 形成矿体或矿胚层。
(2) 构造-热液叠加改造阶段: 印支期强烈的陆内碰撞造山作用, 在区域发生了强烈的地壳挤压收缩和强烈的逆冲推覆构造, 使研究区志留系全面褶皱回返发生强烈的构造变形, 尤其是在“硅钙面”附近发生一系列逆冲推覆, 使原始沉积矿层发生褶皱变形、矿石角砾岩化、透镜化;伴随构造热液的运移、充填交代原生矿石, 矿石组构发生强烈改变。印支运动以后该区结束了海相沉积历史, 进入陆内演化阶段。
(3) 表生氧化富集阶段: 自燕山期以来, 矿区抬升进入陆地造山演化, 已褶皱造山处于陆相环境的卓乌阔组碳酸盐岩、硅质细碎屑岩建造中, 包括张性顺层断裂在内的不同方向、不同类型、不同时代的断裂十分发育, 为钴锰矿床的再次富集提供了良好的成矿空间。从金家坪锰矿床3种锰矿物相在垂深方向上的变化分析, 矿体由地表至地下100 m, 有软锰矿中锰增加, 其他矿物相中锰减少的趋势, 软锰矿中锰所占的比例由73.45%增加到92.27%, 水锰矿和褐锰矿中锰由20.78%降低到4.54%, 菱锰矿中锰由5.77%降至3.19%。充分说明在炎热潮湿的氧化条件下, 充足的大气降水和地下潜水不断汲取含矿建造中的锰质成分, 在不同方向的断裂构造中以软锰矿再次沉淀。经这种长期循环的淋积作用, 最终形成沉积-改造型钴锰矿床。
5. 结论
(1) 大石湾钴锰矿含矿建造为卓乌阔组4段下部灰岩夹硅质岩建造(S3zw4a)和上部灰岩-硅质岩建造(S3zw4c), 硅质岩与灰岩接触面为钴锰成矿最主要的成矿结构面, 原始沉积的钴锰矿层均赋存于该含矿建造的硅钙面中, 构成含矿“泥硅锰”岩套。
(2) Co、Mn主成矿元素在任何一种岩石类型中均小于西秦岭地区志留系元素平均值, 含泥硅锰质岩中钠长岩夹层及硅质岩中稀土元素总量介于169.87×10-6~262.77×10-6之间, 反映典型深海沉积环境特征, 矿石正Ce异常与围岩负Ce异常的出现,表明在沉积成岩初期阶段大量形成锰质结核, 在沉积成岩阶段富含SiO2的胶体状含锰沉淀物形成原始锰质岩。
(3) 大石湾钴锰矿的形成与南秦岭陆缘裂解密切相关, 成矿作用与沉积成岩同时发生, 在印支期—燕山期经构造、淋积改造形成。
-
图 1 大石湾钴锰矿构造位置、矿区地质简图
1—上志留统卓乌阔组2段灰岩夹板岩;2—上志留统卓乌阔组3段黄铁矿化炭质板岩;3—上志留统卓乌阔组4段灰岩夹硅质岩;4—上志留统卓乌阔组4段板岩夹灰岩;5—上志留统卓乌阔组4段灰岩-硅质岩;6—上志留统卓乌阔组5段板岩夹灰岩、硅质板岩;7—上志留统卓乌阔组6段灰岩夹板岩、硅质板岩;8—硅质岩;9—硅质板岩;10—地质界线;11—正断层;12—逆断层;13—平移断层;14—性质不明断层;15—钴锰矿点;16—勘探线及见矿钻孔位置;17—晋宁期中酸性侵入岩;18—加里东期中酸性侵入岩;19—海西期中酸性侵入岩;20—印支期、燕山期中酸性侵入岩;Ⅰ—华北板块;Ⅱ2-3—北秦岭岩浆弧;Ⅱ4—中秦岭陆缘盆地;Ⅱ5—泽库前陆盆地;Ⅱ6—西倾山-南秦岭陆缘裂谷带;Ⅲ—扬子板块;Ⅳ—巴颜喀拉褶皱系
Figure 1. The structural location and geological map of Dashiwan cobalt-manganese mine
图 8 Ⅰ矿带钴锰矿石及围岩稀土元素北美页岩标准化配分模式图(北美页岩标准化数据据陈德潜等,1990)
Figure 8. North American shale standardization patterns of rare earth elements cobalt-manganese ores and surrounding rocks in zone Ⅰ
表 1 志留系卓乌阔组建造类型划分
Table 1 Classification of construction types of the Silurian Zhuowukuo Formation
建造类型 代号 岩性组合 含矿性 硅质灰岩夹板岩建造 S3zw6 深灰色中厚层-块状硅质灰岩、灰黑色中薄层硅质灰岩夹灰黑色炭质板岩、硅质板岩、浅灰绿色粉砂质板岩、灰色薄层状含硅质条带灰岩 板岩夹灰岩建造 S3zw5 灰青灰色板岩, 灰色钙质板岩, 灰色粉砂质板岩, 灰黑色含黄铁矿碎裂炭质板岩夹黑色硅质板岩、灰黑色薄层硅质灰岩、灰黑色中薄层细晶灰岩 灰岩夹硅质岩建造 S3zw4a 灰黑色细晶灰岩, 灰黑色板状微-粉晶灰岩夹浅灰色厚层-块状硅质岩、锰质岩、泥质岩 层状钴
锰矿体灰岩夹板岩建造 S3zw4b 灰黑色结晶灰岩夹灰黑色燧石条带灰岩夹灰绿色板岩、炭质板岩、炭质板岩, 偶见黑色硅质板岩 囊状钴
锰矿体灰岩-硅质岩建造 S3zw4c 下部为灰黑色含燧石条带微晶灰岩;上部为角砾状硅质岩、泥质岩、锰质岩, 顶部为灰黑色块状硅质灰岩 层状钴
锰矿体炭质板岩建造 S3zw3 黑色炭质板岩, 黑色黄铁矿化炭质板岩夹灰黑色硅质板岩 灰岩夹板岩建造 S3zw2 灰黑色结晶灰岩、灰黑色含硅质条带结晶灰岩夹板岩、黑色炭质板岩 表 2 大石湾钴锰矿(化)体特征
Table 2 Characteristics of cobalt-manganese ore (mineralized) body in Dashiwan
矿体编号 工程编号 厚度/m 长度/m 单工程平均品位 矿体平均品位 产状/° 含矿建造构造 Co/% Mn/% Co/% Mn/% CoMnⅠ-1 LD01 5 620 0.076 17.63 0.094 16.75 217∠38 S3zw4c硅钙面 LD16 1.69 0.103 27.54 220∠30 LD02 3.49 0.103 11.25 210∠35 LD03 1.28 0.13 14.02 209∠33 ZK0001 1.06 0.085 24.8 CoMnⅠ-2 TC11 1.64 200 0.078 10.64 0.078 10.64 250∠66 S3zw4cEW向层间断裂 CoMnⅠ-3 LD12 1.93 350 0.065 15.16 0.074 9.74 161∠38 S3zw4c硅钙面 LD13 2.73 0.08 5.91 175∠45 CoMnⅠ-4 LD12 0.83 110 0.22 23.45 0.22 23.45 238∠41 CoMnⅠ-5 TC07 0.98 200 0.021 7.61 0.021 7.61 340∠70 CoMnⅠ-6 LD10 1.03 370 0.24 24.78 0.24 24.78 160∠20 S3zw4cNE向逆断层 LD11 1.13 0.024 0.84 0.024 0.84 220∠20 CoMnⅠ-7 LD11 1.79 90 0.134 15.67 0.134 15.67 220∠45 S3zw4cEW向层间断裂 CoMnⅠ-8 LD11 0.54 200 0.19 20.9 0.19 20.9 340∠40 NE向逆断层 CoMnⅠ-9 LD15 2.86 200 0.12 23.07 0.12 23.07 61∠70 S3zw4c硅质灰岩层间 CoMnⅠ-10 LD15 1.88 200 0.067 15.72 0.067 15.72 270∠20 NW向逆断层 CoMnⅠ-11 TC19 9.74 850 0.155 10.64 0.137 7.15 155∠75 S3zw4c硅钙面 TC20 4.56 0.124 1.61 65∠36 TC22 6.66 0.150 9.73 165∠45 LD20 2.31 0.144 2.33 LD21 2.73 0.053 1.72 175∠50 CoⅠ-1 TC01 0.71 200 0.019 0.019 170∠40 S3zw4a硅质岩层间断层 CoⅠ-2 LD09 0.59 130 0.033 0.033 50∠45 NW向逆断层 CoⅠ-3 LD09 4.3 90 0.075 0.075 S3zw4c硅质灰
岩层间断层CoⅠ-4 LD09 1.61 200 0.051 0.051 285∠40 CoⅠ-5 TC10 20.21 570 0.033 202∠25 TC17 0.88 0.032 2.64 0.037 225∠45 TC21 3.10 0.067 1.52 265∠55 CoⅠ-7 TC09 1.81 200 0.059 7.48 0.059 7.48 220∠55 CoⅠ-8 TC17 1.27 200 0.13 3.41 0.13 3.41 170∠75 NE向逆断层 CoⅠ-9 TC15 1.09 140 0.021 1.15 0.021 1.15 160∠40 CoⅠ-10 TC15 1.09 140 0.029 1.28 0.029 1.28 160∠40 CoⅠ-11 TC15 1.89 140 0.036 1.14 0.036 1.14 160∠40 CoⅠ-12 TC11 1.46 200 0.055 5.7 0.055 5.7 270∠41 S3zw4cEW向层间断裂 CoⅠ-13 TC12 5.16 200 0.051 7.75 0.051 7.75 150∠56 S3zw4c硅钙面 CoⅠ-14 TC12 2.15 200 0.024 2.38 0.024 2.38 150∠56 S3zw4c硅质灰岩
层间断层CoⅠ-15 TC13 1.09 200 0.023 1.25 0.023 1.25 170∠60 CoⅠ-16 TC13 1.45 200 0.017 0.72 0.017 0.72 170∠60 CoⅠ-17 TC15 1.09 140 0.018 1.15 0.018 1.15 160∠40 NE向逆断层 CoⅠ-18 TC15 2.18 140 0.016 0.65 0.016 0.65 160∠40 CoMnⅡ-1 LD04 1.19 1023 0.096 19.48 0.079 22.93 255∠25 S3zw4a硅钙面 LD05 2.03 0.078 29.6 235∠56 TC05 4.31 0.084 28.47 235∠45 LD22 1.23 0.055 8.38 CP02 1.18 0.073 9.86 145∠43 ZK1001 2.26 0.086 22.5 CoMnⅡ-2 LD08 1.51 250 0.166 20.44 0.166 20.44 225∠28 S3zw4a硅钙面 CoMnⅡ-3 LD17 3.15 470 0.105 13.85 0.164 13.6 345∠15 S3zw4a硅钙面 LD18 2.44 0.241 13.28 255∠20 CoMnⅡ-4 CP01 3.68 200 0.112 10.56 0.112 10.56 315∠75 NE向逆断层 CoⅡ-2 LD07 1.58 200 0.035 0.035 238∠23 S3zw4a硅钙面 CoⅡ-1 LD06 0.94 200 0.065 0.065 217~220 S3zw4a硅钙面 ∠5~48 CoⅡ-3 LD21 1.30 300 0.02 2.80 0.02 2.80 175∠50 S3zw4a硅质灰岩层间断层 CoⅡ-4 2.22 200 0.046 8.48 0.046 8.48 165∠70 CoⅡ-5 LD19 1.64 200 0.027 1.64 0.027 156∠28 S3zw4a硅钙面 表 3 西邻金家坪锰矿床矿石中伴生钴物相分析结果
Table 3 Analysis results of accompanying cobalt phases in the ore of the Jinjiaping manganese deposit in the west
硫化物中 氧化物中 难溶脉石中 钴含量/% 所占比例/% 钴含量/% 所占比例/% 钴含量/% 所占比例/% 0.001 1.17 0.10 98.83 0.00 0.00 表 4 卓乌阔组各类岩石中元素含量
Table 4 Table of element content in various rocks of Zhuowukuo Formation
岩石名称 数字特征 As Au Ba Co Cu Mn Ni Sb V Zn 志留系中均值 28.43 2.81 705.2 11.73 33.37 917.8 26.7 2.33 103.33 67.5 板岩 平均值 31.7 5.2 1920 10.1 38.5 664 29.2 3.7 228.4 109.5 标准偏差 25.9 3.3 1005 6.5 25.8 1134 21.5 3.89 118.2 72.1 浓集系数 1.12 1.85 2.72 0.86 1.15 0.72 1.09 1.59 2.21 1.62 硅质板岩 平均值 20.8 4.3 864 14.5 54.4 590 38.1 4.39 64.33 256.7 标准偏差 19.9 3.6 370 7.9 35.1 668 18.9 4.36 66.53 223.4 浓集系数 0.73 1.53 1.23 1.24 1.63 0.64 1.43 1.88 0.62 3.80 炭质板岩 平均值 29 4.4 1411 11.1 48.1 178 34.8 5.78 14.07 316.1 标准偏差 38.3 2.6 1033 6.2 50.2 168 22.2 6.44 10.51 256.8 浓集系数 1.02 1.57 2.00 0.95 1.44 0.19 1.30 2.48 0.14 4.68 结晶灰岩 平均值 8.2 5 576 3.9 32.1 532 12.7 0.77 128.6 34.7 标准偏差 5.9 5 553 2.1 58.2 770 3.6 0.7 65 20.3 浓集系数 0.29 1.78 0.82 0.33 0.96 0.58 0.48 0.33 1.24 0.51 细晶灰岩 平均值 5.3 1.8 623 3.3 20.1 374 13.3 1.62 94.2 39.8 标准偏差 3.8 1 645 2.3 17.5 343 8.2 1.34 44.9 28.1 浓集系数 0.19 0.64 0.88 0.28 0.60 0.41 0.50 0.70 0.91 0.59 硅质灰岩 平均值 13.4 1.9 552 4.9 22.2 286 18.3 3.34 98.1 45.7 标准偏差 10.7 1.6 547 4.4 19.2 225 11.4 2.89 50.4 30.8 浓集系数 0.47 0.68 0.78 0.42 0.67 0.31 0.69 1.43 0.95 0.68 含硅质条带灰岩 平均值 9 2.2 534 3 42.1 306 14.8 4.39 137.4 39.5 标准偏差 13.2 1 318 1.7 35.5 280 9.4 5.35 76.9 34.9 浓集系数 0.32 0.78 0.76 0.26 1.26 0.33 0.55 1.88 1.33 0.59 硅质岩 平均值 13.4 6.1 726 5.4 29.2 76 10.6 4.51 132 27.9 标准偏差 10.4 0.7 740 1.2 12.8 18 4.7 4.96 105.7 5.5 浓集系数 0.47 2.17 1.03 0.46 0.88 0.08 0.40 1.94 1.28 0.41 注: Au元素含量单位为10-9, 其他元素含量单位为10-6;浓集系数=平均值/志留系中均值 表 5 Ⅰ矿带钴锰矿石及围岩主量元素分析结果
Table 5 Major content of cobalt-manganese ores and surrounding rocks in zone Ⅰ
样品编号 PM02
YQ5-1D0137
YQ-1PM04
YQ8-1LD13
YQ1LD13
YQ2TC17
YQ1LD18
XT01TC20
XT1-1TC33
YQ2-1TC33
YQ4-1LD23
YQ2-1TC22
YQ-1岩矿石名称 硅质岩 硅质岩 硅质岩 钠长岩 锰矿化角砾岩 含泥硅锰质岩 钠长岩 粘土岩 含泥硅锰质岩 含泥硅锰质岩 粘土岩 含泥硅锰质岩 Al2O3 3.03 1.52 0.22 32.6 3.86 11.52 31.72 10.56 27.56 29.43 19.38 17.96 CaO 6.39 0.32 0.14 2.89 1.14 1.85 0.14 0.15 0.92 1.02 0.94 1.98 Fe2O3 0.14 0.66 1.86 1.7 63.28 7.07 1.09 14.83 2.42 1.44 3.76 17.78 MgO 0.26 0.18 0.072 0.29 0.41 0.2 0.27 0.65 0.18 0.19 0.24 0.47 MnO 0.07 0.019 0.015 2.38 4.04 6.22 0.177 0.033 2.14 4.28 0.23 14.94 P2O5 0.095 0.078 0.074 0.4 1.88 0.56 0.03 0.189 0.052 0.1 0.26 3.66 TiO2 0.18 0.049 0.018 0.045 0.04 0.054 0.088 0.853 0.091 0.066 0.54 0.066 SiO2 81.23 88.02 93.88 23.6 4.8 61.38 5.3 62.29 51.91 47.38 64.38 24.78 Na2O 0.2 0.05 0.09 0.06 0.2 0.078 0.14 0.08 0.28 0.26 0.4 0.43 K2O 0.66 0.09 0.3 0.12 0.31 0.2 0.12 1.75 0.39 0.45 3.38 0.44 FeO 0.68 1.28 1.29 0 0 0 0.28 1.79 0 0 0.26 0 H2O- 0.2 0.4 0.2 0.4 0.4 0.2 烧失量 6.78 0.94 1.3 35.74 19.92 10.4 57.6 5.01 13.3 14.85 5.66 16.48 注: 主量元素含量单位为% 表 6 Ⅰ矿带钴锰矿石及围岩稀土元素含量
Table 6 Rare earth element content of cobalt-manganese ores and surrounding rocks in zone Ⅰ
样品号 PM02
XT5-1D0137
XT-1PM04
XT8-1LD13
XT1LD13
XT2TC17
XT1LD18
XT01TC20
XT1-1TC33
XT2-1TC33
XT4-1LD23
XT2-1样品名 硅质岩 硅质岩 硅质岩 钠长岩 含泥硅锰质岩 含泥硅锰质岩 钠长岩 粘土岩 锰矿化角砾岩 锰矿化角砾岩 粘土岩 La 78.6 32.8 76.4 26.5 26 14.4 4.2 23.3 3.4 3 33.2 Ce 83 59.6 56 28 58.8 34.6 7.9 39.3 14.8 20.8 64.6 Pr 19 10 19.5 8.6 7.4 3.5 0.94 4.4 0.79 0.84 9 Nd 33.5 23 32 61.8 33.2 15 4.1 18 2.8 3.1 30.6 Sm 8.7 6.6 8.3 25.7 8.6 3.6 0.83 2.9 0.79 0.97 6.9 Eu 2.4 1.8 2.2 5.5 1.8 0.75 0.22 0.51 0.88 0.86 2.2 Gd 8 6.4 7.6 21.8 9.2 3.6 0.8 2.2 0.9 1.1 6.3 Tb 3 2.8 3.5 3.4 1.4 0.54 0.13 0.33 0.14 0.2 1 Dy 9.2 9.8 9 17.8 7.3 2.9 0.91 1.9 0.87 1.2 5.6 Ho 3.3 3.4 3.8 3.3 1.4 0.56 0.16 0.33 0.18 0.24 1.2 Er 4 4 5 9.2 3.8 1.6 0.48 1.1 0.54 0.75 3.4 Tm 0.87 0.87 1 9.2 3.8 1.6 0.06 0.17 0.09 0.12 0.49 Yb 8 7.7 10.1 15.2 5.1 2.4 0.92 1.5 0.63 0.84 3.2 Lu 1.2 1.1 1.4 2 0.66 0.3 0.06 0.18 0.12 0.15 0.56 Y 44.3 40.5 52.3 58.6 27.8 15.5 4.4 9.6 2.5 2.7 20.4 ΣREE 262.77 169.87 235.8 238 168.46 85.35 21.74 96.07 26.93 34.17 168.25 LREE 225.2 133.8 194.4 156.1 135.8 71.85 18.22 88.35 23.46 29.57 146.5 HREE 37.57 36.07 41.4 81.9 32.66 13.5 3.52 7.72 3.47 4.6 21.75 LREE/HREE 5.99 3.71 4.7 1.91 4.16 5.32 5.17 11.44 6.76 6.43 6.74 (La/Yb)N 0.983 0.447 0.819 0.199 0.591 0.72 0.981 1.991 0.425 0.3 0.889 δEu 1.26 1.22 1.22 1.02 0.89 0.91 1.17 0.88 4.55 3.63 1.47 δCe 0.47 0.71 0.32 0.4 1.02 1.06 0.86 0.84 1.97 2.85 0.81 注: 稀土元素含量单位为10-6 -
Manheim F T. Marine cobalt resources[J]. Science, 1986, 232(4750): 600-608. doi: 10.1126/science.232.4750.600
陈德潜, 陈刚. 实用稀土元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1990. 陈秉祥. 甘肃省成县金家坪锰矿地质特征及找矿前景[J]. 甘肃地质, 2007, 16(3): 26-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSDZ200703005.htm 丛源, 董庆吉, 肖克炎, 等. 中国锰矿资源特征及潜力预测[J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25(3): 118-136. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.2018.03.010 段得洪, 罗学红. 甘肃张家川县闫家店金钴多金属矿地质特征及找矿潜力分析[J]. 矿床地质, 2002, 1: 339-344. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD201603005.htm 付胜云, 周超, 安江华. 湖南沉积型锰矿床的成矿模式[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(4): 145-152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201704018.htm 付勇, 徐志刚, 裴浩翔, 等. 中国锰矿成矿规律初探[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(12): 2192-2207. doi: 10.19762/j.cnki.dizhixuebao.2014.12.004 傅群和. "桃江式"锰矿床地质特征及其地球化学特征[J]. 湖南地质, 2001, 20(1): 15-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5603.2001.01.004 郝雨, 孟庆青, 邢福林, 等. 矿产地质勘查规范——铁、锰、铬(DZ/T0200—2020). 北京: 地质出版社, 2020. 侯宗林, 薛友智, 黄金水, 等. 扬子地台周边锰矿[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1992. 霍福臣, 李永军. 西秦岭造山带的建造与地质演化[M]. 西安: 西北大学出版社, 1995. 林枢, 吴湘滨, 杨东升, 等. 贵州松桃白石溪锰矿地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 南方金属, 2015, 2: 39-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NFGT201502010.htm 刘彬, 王银宏, 王臣, 等. 中国钴资源产业形势与对策建议[J]. 资源与产业, 2014, 16(3): 113-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZIYU201403026.htm 卢安康, 周琦, 覃永军, 等. 广西下雷锰矿床气液喷溢沉积构造的发现及地质意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6): 124-139. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202106015.htm 瞿永泽, 徐林刚, 毛景文, 等. 贵州铜仁地区南华系大塘坡组黑色页岩型菱锰矿碳、氧同位素特征及锰矿成矿作用[J]. 矿床地质, 2018, 37(1): 50-66. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201801004.htm 施小彬. 武都地区张家坪钴矿地质特征及意义[J]. 甘肃科技, 2020, 36(21): 23-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSKJ202021010.htm 孙卫东. 南秦岭花岗岩锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 地球化学, 2000, 29(3): 209-216. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200003000.htm 吴自成, 何志威. 贵州省松桃县道坨锰矿地质特征及成因分析[J]. 中国锰业, 2016, 3: 16-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMM201603004.htm 徐林刚. 沉积型锰矿床的形成及其与古海洋环境的协同演化[J]. 矿床地质, 2020, 39(6): 959-973. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202006001.htm 姚敬劬, 苏长国, 彭三国, 等. 湘中湘南古构造成锰盆地及锰矿找矿[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1998: 136-164. 叶杰, 刘建明, 张安立, 等. 沉积喷流型矿化的岩石学证据: 以大兴安岭南段黄岗和大井矿床为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2002, 18(4): 585-592. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200204017.htm 叶天竺, 吕志成, 庞振山, 等. 勘查区找矿预测理论与方法[总论][M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2014. 叶天竺, 韦昌山, 王玉往, 等. 勘查区找矿预测理论与方法(各论)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2017: 72-83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX202205009.htm 张复新, 王立社, 侯俊富. 秦岭造山带黑色岩系与金属矿床类型及成矿系列[J]. 中国地质, 2009, 36(3): 694-704. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200903018.htm 张洪瑞, 侯增谦, 杨志明, 等. 钴矿床类型划分初探及其对特提斯钴矿带的指示意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2020, 39(3): 501-510. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202003007.htm 张洪瑞, 杨天南, 宋玉财, 等. 古溶洞控矿构造在青藏高原中部的发现及意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2012, 31(3): 449-458. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201203005.htm 张新虎, 刘建宏, 梁民宏, 等. 甘肃省区域成矿及找矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2013. 张新虎, 刘建宏, 赵彦庆. 甘肃省成矿区(带)研究[J]. 甘肃地质, 2008, 2: 5-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSDZ200802003.htm 赵俊兴, 李光明, 秦克章, 等. 富含钴矿床研究进展与问题分析[J]. 科学通报, 2019, 64(24): 2484-2500. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201924005.htm 周琦, 杜远生, 袁良军, 等. 黔湘渝毗邻区南华纪武陵裂谷盆地结构及其对锰矿的控制作用[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(2): 177-188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201602001.htm ① 甘肃省地质矿产勘查开发局第一地质矿产勘查院. 甘肃省成县南康一带铁、锰及多金属矿普查报告[R]. 2008: 1-93. ② 陕西省地质调查院. 1: 250 000略阳县幅区域地质调查成果报告[R]. 2007: 218-300. ③ 甘肃省地质调查院. 甘肃省迷坝—南康一带铜铁多金属矿远景调查成果报告[R]. 2013: 1-305. -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 王帅,任宇,郭红,曹文庚,李祥志,肖舜禹. 河南黄河改道区浅层地下水化学特征与主控污染源解析. 环境科学. 2024(02): 792-801 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 吕永高,蔡五田,杨骊,边超,李敬杰,王明国. 某铬渣堆污染地下水六价铬污染特征与迁移转化规律研究. 水文地质工程地质. 2024(03): 180-190 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 邓国仕,岑鑫雨,唐业旗,钟金先. 乌蒙山以礼河流域岩溶地下水富集特征及供水意义研究. 中国岩溶. 2023(04): 685-698 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: