Geochemical characteristics, zircon U-Pb age and metallogenic tectonic background of the Mesozoic acidic volcanic rocks from Xianqiao area in North Dabie Mountain
-
摘要:
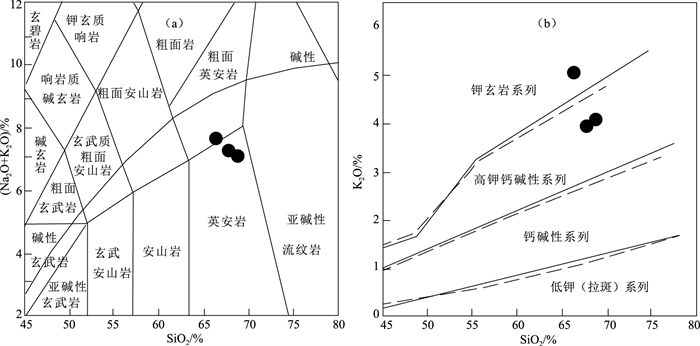
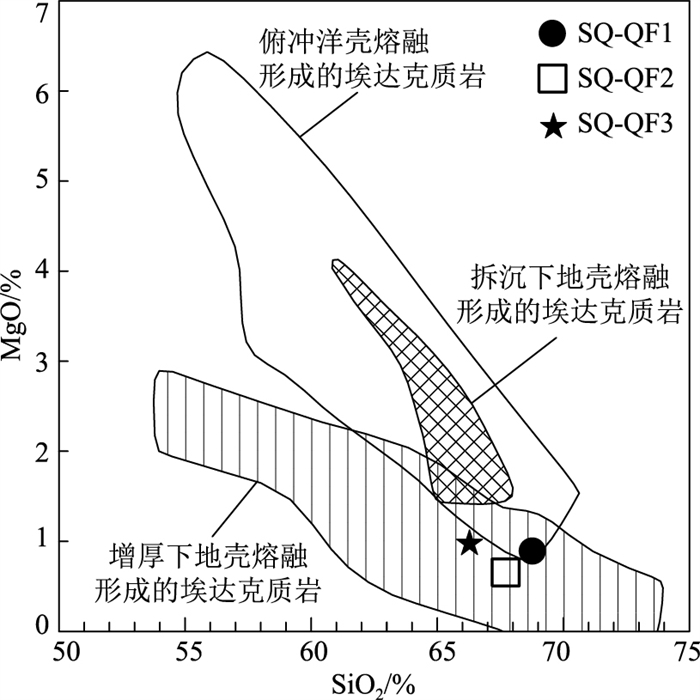
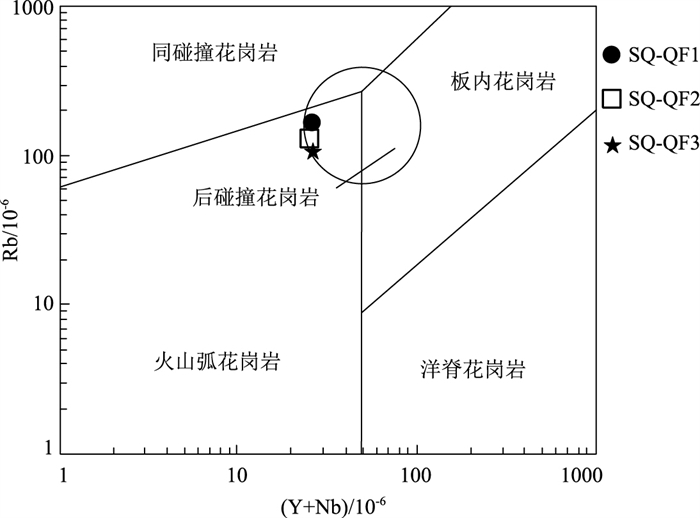
东秦岭-北大别山构造-岩浆演化是热点研究问题,关于该带火山岩喷发时限存在较大的争议,其岩石成因和成岩构造环境尚不清楚。对北大别山西段仙桥膨润土矿床英安岩进行锆石U-Pb同位素测年和岩石地球化学研究,结果表明,仙桥酸性火山岩具有高钾(3.96%~5.01%)、富碱(K2O+Na2O介于7.97%~8.96%之间)、弱过铝质(A/CNK为1.0~1.15)等特点,属高钾钙碱性-钾玄岩系列火山岩。岩石轻稀土元素富集,重稀土元素亏损明显,负Eu异常不明显,Nb、Ta亏损明显,且具有高Nb/Ta、(La/Yb)N、Sr/Y值,表现为典型的埃达克质岩石地球化学特征。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素定年测得,仙桥成矿岩石英安岩喷发年龄为133±1 Ma,与邻区双桥膨润土、皇城山银矿床陈棚组火山岩的年龄一致。研究认为,仙桥火山岩具有埃达克岩的特征,由增厚下地壳物质部分熔融形成,产生于中生代后碰撞构造环境,在133 Ma左右,北大别山仙桥地区还未发生大规模的拆沉减薄的岩浆活动。
Abstract:The structural-magmatic evolution of East Qinling-North Dabie Mountains is a popular issue.The eruption time of the volcanic rocks in the belt still has a greater dispute for a long time, which is still unclear during rock formation and diagenetic tectonic environment.Based on the studies of geochemistry, zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of dacite in Xianqiao bentonite deposit in the western segment of North Dabie Mountains, it is shown that acidic volcanic rocks from Xianqiao area display high contents of K2O(3.96%~5.01%), are enriched in K2O+Na2O(7.97%~8.96%)and weak peraluminous, with A/CNK values of 1.0~1.15.The volcanic rocks should belong to high-K calc-alkaline to shoshonite series.The rocks are enriched LREE and depleted HREE, with weak negative Eu anomaly, strongly depleted in the high field strength elements Nb and Ta and high Nb / Ta ratio, and has high(La/Yb)N(25.68~28.25)and Sr/Y(34.92~41.42)ratios, which has obvious geochemical characteristics of adakite.Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating result shows that the Xianqiao ore-forming rocks(dacite)was erupted at 133±1 Ma, consistent with the age of volcanic rocks of Chenpeng Formation in Shuangqiao bentonite deposit and Huangchengshan silver deposit.This research reveals that the Mesozoic acidic volcanic rocks from Xianqiao area with the characteristics of adakitic rocks were formed by partial melting of the thickened lower crust, which were formed at post-collisional tectonic setting in Mesozoic.The large-scale magma activity resulting from lower crust delamination and thinning of the lithosphere has not yet occurred in the Xianqiao area of North Dabie Mountains at about 133 Ma.
-
Keywords:
- acid volcanic rocks /
- zircon U-Pb age /
- petrogenesis /
- North Dabie Mountain
-
受复杂地形地貌、地质构造、强震和强降雨等因素影响,中国地质灾害极发育[1],特别是在青藏高原地区,发育一系列大型—巨型滑坡,危害极严重。青藏高原东部断裂广泛发育,断裂带规模大且活动性强,强震频发,受历史强震影响,区内地震诱发滑坡-堵江-溃坝等次生地质灾害危险性高[2-5]。强烈地震时,在高山峡谷地区,地震诱发的地质灾害危害程度和影响范围往往比地震直接造成的危害更大、分布范围更广[6-9]。据统计,诱发区域性地震滑坡的最小震级约为Ms 4级,最小地震烈度约为Ⅵ度[10-12]。研究表明,当强震Ms≥7.0级时,地震引发的滑坡危害程度尤为显著[13-14],2008年四川汶川Ms 8.0级地震触发的地质灾害达15000多处,灾害导致两万余人死亡,在所有隐患点中滑坡占比高达40%[7]。目前,关于地震滑坡危险性评价的研究成果较丰富,但由于中国地质灾害的发育条件和分布规律较复杂,空间数据质量和各类危险性评价模型方法具有一定的局限性,难以采用统一的模型方法开展危险性评估,尤其是活动断裂带等地震高发区域的潜在地震滑坡预测研究尚需加强[15-16]。
鲜水河断裂带位于青藏高原东部,断裂带北起甘孜东谷附近,向南经炉霍、道孚至石棉县,总体走向北北西,呈略向北东凸出的弧形,是古生代形成的一条大型左旋走滑断裂[17-22]。鲜水河断裂由9条分支断裂组成,沿线历史地震频发、地震滑坡危害严重[17-18, 23-24]。如1786年由磨西Ms 73╱4级地震触发的摩岗岭滑坡造成大渡河阻断,溃坝后的泥石流等到达下游石棉县城境内,造成数万人死亡[25]。据前人研究,鲜水河断裂带未来具有发生Ms 6~7级强震的可能性[24],该区正在规划建设川藏铁路等工程,铁路建设面临地震滑坡的风险较高,进行鲜水河断裂带地震滑坡预测评价研究具有重要意义[24]。
目前,评价地震滑坡危险性的方法主要有数理统计模型和确定力学模型2种方法。数理统计模型评价侧重对现有滑坡与其影响因子间的分析统计,确定力学模型中的Newmark模型方法适用发震构造清楚或地震动参数记录较完整的情况,注重震后地震滑坡影响要素分析和危险性评价[26]。已有研究基于Newmark模型对汶川地震、尼泊尔地震等诱发的地震滑坡进行危险性评价,获得了较精确的结果[27-29]。因此,本文以鲜水河断裂带全线两侧约20 km范围为研究区,通过遥感解译和野外地质调查在区内共发现399处历史地震滑坡,采用Newmark模型对鲜水河断裂带地震滑坡进行危险性分区评价。研究结果可为该区地质灾害防治和川藏铁路等重大工程建设提供参考和指导。
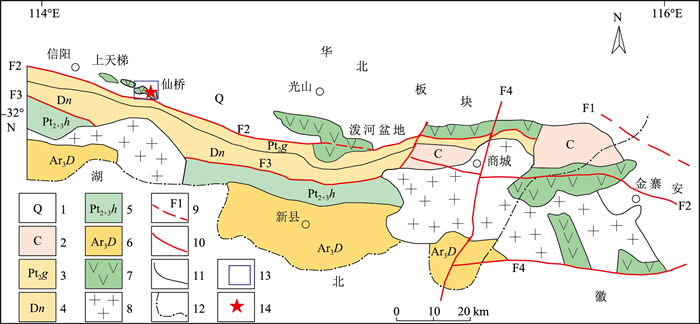
1. 地质背景
鲜水河断裂带平均海拔在3000 m以上,地形起伏度在1000 m/km2以上,坡度多处于20°~40°,为典型的高山峡谷地区。研究区气候垂直分带较明显,降雨量区域分布差异较大。鲜水河断裂带由炉霍断裂、道孚断裂、乾宁断裂、雅拉河断裂、中谷断裂、色拉哈-康定断裂、折多塘断裂、木格措南断裂和磨西断裂9条分支断裂组成(图 1),均为全新世活动断裂[17-18, 23-24, 30]。
自1725年至今,沿鲜水河断裂带发生8次Ms≥7级的强震,其中1973年发生的炉霍Ms 7.9级地震是鲜水河断裂带内有记载的震级最大的一次地震,距今最近的一次强震是1981年发生的道孚Ms 6.9级地震[23, 31]。2014年康定地区附近发生了Ms 5.9及Ms 5.6级2次地震,但释放的能量远小于自1955年康定Ms 7.5级地震以来积累的能量,研究认为,未来一段时间内在色拉哈-康定段具有产生Ms 6~7级以上强震的风险[24, 32]。
2. 鲜水河断裂带历史地震滑坡发育分布特征
2.1 地震滑坡空间分布特征
地震滑坡是由地震作用或地震力触发的一种滑坡类型,指地震震动引起岩体或土体沿一个缓倾面剪切滑移一定距离,斜坡岩体或土体脱离滑源区,瞬间失稳的一种地质现象[33-35]。由地震引起的地质灾害有时远超过地震作用本身造成的危害,如磨西Ms 73╱4地震、炉霍Ms 7.9地震都造成巨大的破坏,诱发大量的地震滑坡。历史记录和调查研究认为,鲜水河断裂带的地震滑坡主要分布在地震烈度Ⅷ~Ⅹ度区,空间上主要位于断裂带两侧2 km范围内[36]。结合野外地质调查和鲜水河断裂带地震滑坡的发育规律,可将断裂带分为3段,东谷—八美段河谷较宽,地震滑坡以蠕滑下错为主,后壁较明显,堆积层较薄,滑体主要由第四纪堆积物组成;在八美—康定段,八美土石林构造破碎和风化强烈,地质灾害发育,折多山段为高山风化冻融地貌,灾害发育较少;康定—磨西段河谷变窄,受大渡河及大渡河断裂的影响,滑坡较发育,堆积体主要为碎块石和第四纪堆积物。
较典型的1973年四川省炉霍县的Ms 7.9级地震,震源深度17 km,震中烈度Ⅹ度。地震造成2175人死亡,2756人受伤,极震区内房屋倒塌严重,崩塌、滑坡等地震次生地质灾害对公路交通造成了严重影响。由炉霍地震触发的滑坡有160多处[8, 37],多数集中分布于朱倭—仁达之间(图 2),在断裂带两侧各2 km的范围内其分布与地表破裂带高度重合,主要分布于地震烈度Ⅷ~Ⅹ度区,滑坡破坏形式以崩塌和溜滑为主,发生坡度主要为30°~50°[38]。
![]() 图 2 1973年炉霍Ms 7.9级地震地质灾害分布图[38]Figure 2. Distribution map of geological hazards during the Luhuo Ms 7.9 earthquake in 1973
图 2 1973年炉霍Ms 7.9级地震地质灾害分布图[38]Figure 2. Distribution map of geological hazards during the Luhuo Ms 7.9 earthquake in 19732.2 地震滑坡主要类型
通过遥感解译、历史资料收集分析和1:5万地质灾害调查发现,在鲜水河断裂带两侧20 km范围内共有399处历史地震滑坡[38](图 3)。地震滑坡总体表现为高位远程、一滑到底、裂而未滑等特点。
(1) 高位远程滑坡
高位远程滑坡指滑体重心和剪出口位置高,滑坡剪出口与滑坡前缘的高差较大,滑源区岩体受山脊拉应力作用致使裂缝扩展,在中国青藏高原地区分布广泛,具有较大势能的滑坡,常伴有滑坡-堵江- 溃坝等链生地质灾害特征[39-40]。区内最典型的高位远程滑坡有八美镇幸福沟滑坡(图版Ⅰ-a)、摩岗岭滑坡等。幸福沟滑坡左侧以陡坎为界,右侧以冲沟为界,后缘以高陡基岩后壁为界,前缘以河流为界,滑动后已经挤压河道,该滑坡纵约130 m,宽约60 m,推测堆积体厚约10 m,体积约为7.8×104 m3。
(2) 一滑到底型滑坡
一滑到底型滑坡是在地震震动的作用下,原来处于接近平衡的斜坡松散堆积物重心失稳,堆积体从坡顶启动,直达最低处的坡脚或河谷地区[37],如泸定县河口村河庄子滑坡(图版Ⅰ-b)和四十七道班滑坡(图版Ⅰ-c)。河庄子滑坡平面形态呈舌型,后缘以基岩为界,左右侧以下错陡坎为界,中部和前缘存在平台,滑坡纵长约620 m,宽350 m,厚约10 m,体积约为1.53×106 m3,目前该滑坡稳定性较好。
(3) 裂而未滑型滑坡
裂而未滑型滑坡指在强烈的地震作用下,震区的山体发生大范围破裂,形成了大量拉裂缝,但整个山体松而未动、裂而未滑,处于临界稳定状态,在外力作用下极易发生滑动[41]。如道孚县东南足湾村滑坡为典型的裂而未滑型滑坡,该滑坡拉裂缝极发育,稳定性较差,在强降雨或地震作用下,极易发生滑动[36]。
2.3 典型地震滑坡发育特征
(1) 摩岗岭高位远程滑坡-堵江-溃坝灾害链
摩岗岭滑坡位于四川省泸定县大渡河右岸,鲜水河断裂带的分支断裂磨西断裂从滑体中部穿过,由1786年6月1日Ms 73╱4级地震诱发形成[25, 36]。该滑坡后缘呈典型圈椅状,地震的强大动力作用,使坡体后壁的岩体被抛射到大渡河左岸,堆积体体积约1.8×108m3(图 4)。滑坡造成大渡河堵塞,在堰塞坝堵断大渡河9天后发生溃决,形成的泥石流、洪水造成石棉县城境内数万人死亡[25, 36, 42]。
![]() 图 4 摩岗岭滑坡全貌图和工程地质剖面图a—摩岗岭滑坡全貌图(镜像SWW);b—摩岗岭工程地质剖面图[25]Figure 4. The overall picture and engineering geological profile of the Mogangling landslide
图 4 摩岗岭滑坡全貌图和工程地质剖面图a—摩岗岭滑坡全貌图(镜像SWW);b—摩岗岭工程地质剖面图[25]Figure 4. The overall picture and engineering geological profile of the Mogangling landslide(2) 炉霍55道班滑坡
55道班滑坡位于四川省炉霍县317国道附近,鲜水河断裂带分支断裂从坡体中部穿过,后壁高陡,为典型的地震滑坡[8, 39]。该滑坡平面形态呈舌型,滑坡体积约1000×104m3,滑坡规模为特大型,在平面上分为Ⅰ区、Ⅱ区和Ⅲ区3个区域(图 5)。目前滑坡北侧前缘变形破坏迹象明显,整体稳定性差,坡体中下部发育拉裂缝,引起地面隆起、挡墙开裂和317国道改线绕行[36]。
![]() 图 5 55道班滑坡典型地貌图和工程地质平面图a—55道班滑坡工程地质平面图[36];b—55道班滑坡发育全貌图(镜像NW); Qh—冰川冰水堆积物;Qp—残坡积物;T3y1—变质砂岩夹板岩;T3ln2—砂板岩互层;T3ln1—变质砂岩夹板岩、砾岩;T3r2—玄武岩、凝灰岩、板岩;T3r1—板岩夹薄层变质砂岩;T2z2—变质砂岩夹板岩;T2z1—变质砂岩、板岩、灰岩;T1b—板岩、灰岩、角砾岩Figure 5. Typical geomorphological map and engineering geological plan of the 55 Daoban landslide
图 5 55道班滑坡典型地貌图和工程地质平面图a—55道班滑坡工程地质平面图[36];b—55道班滑坡发育全貌图(镜像NW); Qh—冰川冰水堆积物;Qp—残坡积物;T3y1—变质砂岩夹板岩;T3ln2—砂板岩互层;T3ln1—变质砂岩夹板岩、砾岩;T3r2—玄武岩、凝灰岩、板岩;T3r1—板岩夹薄层变质砂岩;T2z2—变质砂岩夹板岩;T2z1—变质砂岩、板岩、灰岩;T1b—板岩、灰岩、角砾岩Figure 5. Typical geomorphological map and engineering geological plan of the 55 Daoban landslide3. 基于Newmark模型的地震滑坡危险性评价
地震滑坡危险性评价指将地震作为潜在不确定因素,分析潜在地震及其诱发滑坡的时空分布概率,具体的危险性描述要素包括潜在地震滑坡的位置、体积或面积、滑坡类型和运移速度,以及一定时期内的发生概率等[43-44]。地震滑坡危险性评价的研究逐渐从定性向半定量、定量化发展,主要有基于统计分析的综合评价法[43-44]、基于极限平衡理论的拟静力法[45-47]、基于边坡累积位移的Newmark模型方法[48-50]。其中,Newmark方法适用于发震构造清楚或地震动强度和参数记录较完整的情况,注重震后对地震滑坡影响要素分析和危险性反演评估[44]。因此,本文采用Newmark模型开展鲜水河断裂带地震滑坡危险性评价。
3.1 Newmark斜坡位移模型
Newmark斜坡位移模型是英国科学家Newmark于1965年基于无限斜坡的极限平衡理论提出的一种地震滑坡危险性评价方法[48]。该模型把滑体看作是一个刚体,对坡体的静态安全系数和临界加速度进行研究,当外力的作用低于临界加速度时,坡体不会发生位移;当外力的作用高于临界加速度时,会出现有限位移;在地震作用下,则会产生滑动的永久位移。通过二次积分外载荷加速度和临界加速度的差值,即可获得永久位移(公式(1))[48, 51-53]。
Dn=∫t∫t[a(t)−ac]dts (1) 本文采用概率地震条件下的地震动峰值加速度作为潜在地震参数,采用的地震滑坡危险性计算步骤主要有:①利用岩土体力学参数和斜坡坡度,计算斜坡静态安全系数(Fs);②利用斜坡静态安全系数(Fs)和坡度,计算获得斜坡临界加速度(ac);③利用斜坡临界加速度(ac)和地震动峰值地面加速度(PGA),计算概率地震扰动下的坡体累积位移(Dn);④根据斜坡位移和滑坡发生概率的统计规律,预测评价概率地震滑坡危险性[9, 50, 53];⑤最后,利用历史地震滑坡对地震滑坡危险性分区结果进行检验。鲜水河断裂带地震滑坡危险性评价流程图如图 6所示。
3.2 Newmark模型评价过程
(1) 静态安全系数(Fs)
根据基于滑块极限平衡理论的斜坡安全系数公式(公(2))[49, 53],利用岩土体物理力学参数和坡度,计算得到斜坡静态安全系数(Fs)。
Fs=c′γtsinα+tanφ′tanα−mγwtanφ′γtanα=c′γtsinα+(1−mγwγ)×tanφ′tanα (2) 式中:c'为粘聚力(kPa);φ'为有效内摩擦角(°);γ为岩体重度(kN/m3);γw为地下水重度(kN/m3);t为潜在滑体厚度(m);α为潜在滑面倾角(°);m为潜在滑体中饱和部分占总滑体厚度的比例。
(2) 斜坡临界加速度(ac)
斜坡临界加速度(ac)指在地震作用下,滑块的下滑力与抗滑力相等时对应的地震动加速度。通过比较无外力作用和地震作用下滑块的受力状态,建立滑块在地震作用下的极限平衡状态方程,利用安全系数(Fs)推导出ac的计算公式(公(3))[54]。
ac=(Fs−1)gsinα (3) 式中:g为重力加速度(m/s2);α为滑面倾角(°)。
(3) 地震诱发斜坡位移(Dn)
通过分析大量地震加速度记录和地震滑坡实例,获得地震诱发斜坡累积位移(Dn)与临界加速度(ac)和地震动峰值加速度(PGA)的相互关系式(公式(4))[55]。其中,斜坡累积位移(Dn)与地震动峰值地面加速度强度(PGA)成正比,与斜坡临界加速度(ac)成反比[56]。采用中国第五代地震动峰值地面加速度计算鲜水河断裂带区域50年超越概率10%地震诱发斜坡位移(Dn)。
lgDn=0.215+log[(1−acPGA)2.341(aiPGA)−1.438] (4) 式中:ac为斜坡临界加速度;PGA为地震动峰值加速度。
(4) 地震诱发滑坡危险性(P)
地震诱发斜坡位移并不一定会发生坡体滑动,只有当斜坡位移累积到一定程度时,坡体才会发生失稳,并沿滑动面下滑产生滑坡灾害。因此,根据地震斜坡位移和滑坡发生概率之间的相关关系(公式(5))[49],计算地震作用下的滑坡发生概率(P)。
P=0.335[1−exp(−0.048D1.565n)] (5) 式中:Dn为斜坡位移。
4. 鲜水河断裂带地震滑坡危险性评价结果
4.1 地震滑坡危险性计算
(1) 地形坡度
据地震滑坡危险性评估经验,地形坡度小于10°的斜坡通常较稳定,很少发生大规模的滑坡,因此,地形坡度小于10°的斜坡不参与计算[27-28]。研究区的地形坡度起伏较大,大渡河流域、鲜水河流域等地坡度较大(图 7-a)。
![]() 图 7 鲜水河断裂带地形坡度和工程地质岩组(岩组编号见表 1中ID)a—地形坡度分布图;b—工程地质岩组分布图Figure 7. Topographic slope and engineering geological rock group of Xianshuihe fault zone表 1 鲜水河断裂带工程地质岩组与物理力学参数Table 1. Physical and mechanical properties of engineering geological rock groups in the Xianshuihe fault zone
图 7 鲜水河断裂带地形坡度和工程地质岩组(岩组编号见表 1中ID)a—地形坡度分布图;b—工程地质岩组分布图Figure 7. Topographic slope and engineering geological rock group of Xianshuihe fault zone表 1 鲜水河断裂带工程地质岩组与物理力学参数Table 1. Physical and mechanical properties of engineering geological rock groups in the Xianshuihe fault zoneID 工程地质岩组名称 c'/kPa ϕ'/° γ/(kN·m-3) 1 坚硬的厚层状砂岩岩组 26 33 26 2 较坚硬—坚硬的中—厚层状砂岩夹砾岩、泥岩、板岩岩组 25 32 25 3 软硬相间的中—厚层状砂岩、泥岩夹灰岩、泥质灰岩及其互层岩组 25 32 24 4 软弱—较坚硬薄—中厚层状砂、泥岩及砾、泥岩互层岩组 20 27 23 5 软弱的薄层状泥、页岩岩组 24 31 21 6 坚硬的中—厚层状灰岩及白云岩岩组 23 31 25 7 较坚硬的薄—中厚层状灰岩、泥质灰岩岩组 23 30 24 8 软硬相间的中—厚层状灰岩、白云岩夹砂、泥岩、千枚岩、板岩岩组 22 29 23 9 较坚硬—坚硬薄—中厚层状板岩、千枚岩与变质砂岩互层岩组 21 28 22 10 较弱—较坚硬的薄—中厚层状千枚岩、片岩夹灰岩、砂岩、火山岩岩组 28 35 21 11 坚硬的块状玄武岩为主的岩组 27 34 29 12 坚硬块状花岗岩、安山岩、闪长岩岩组 19 26 28 13 软质散体结构岩组 15 25 18 注:ID与图 7-b中的工程地质岩组号码一致,c'为粘聚力,φ'为有效内摩擦角,γ为岩体重度 (2) 工程地质岩组划分
综合考虑地质构造、地层年代、岩土体类型、岩体风化破碎程度等因素,将鲜水河断裂带地层岩性划分为13个工程地质岩组。根据《工程地质手册》 (第五版)[56],结合区内地层岩性分布与典型岩体的力学强度测试结果,获得工程地质岩组的物理力学参数。
(3) 静态斜坡安全系数计算
采用公式(2)计算静态安全系数(Fs),通过多次迭代循环计算,调整模型参数,使斜坡在无外力作用下的斜坡静态安全系数(Fs)大于1。因地形坡度小于10°的斜坡通常十分稳定,本文相应区域的斜坡不进行静态安全系数的计算,以此确定模型参数为:c'、φ'和γ。其中,C'为粘聚力,φ'为有效内摩擦角,r为岩体重度,具体参数值见表 1,γw=10kN/m3,t=2.5m,m=0.3,α取值为地形坡度(图 7-a)。计算得到的鲜水河断裂带斜坡静态安全系数(Fs)见图 8-a,具有较低静态安全性的斜坡沿深切河谷分布,总体上呈现北北东向;具有静态安全性较高的斜坡主要分布在地形坡度较缓的地区,如塔公草原附近静态安全系数大于5。
(4) 鲜水河断裂带临界加速度计算
据公式(3)利用静态安全系数(Fs)和斜坡坡度计算得到鲜水河断裂带斜坡临界加速度(ac)(图 8-b),与静态安全系数相对应,坡度越高的地区其稳定性越差,即静态安全系数越低,诱发斜坡失稳所需的临界加速度越小。在坡度较陡的斜坡上,临界加速度小于0.15 g,在坡度较缓的河谷、盆地和塔公草原,临界加速度大于0.6 g,最大值可达到0.98 g。
(5) 地震动峰值加速度
地震动峰值加速度用于计算地震诱发斜坡位移,采用中国第五代地震动峰值地面加速度分区值来计算鲜水河断裂带区域地震诱发斜坡位移(Dn)。据图 9-a显示,随着距离鲜水河断裂带越远,地震动峰值加速度值减小,在康定附近达到最大值0.4 g。
(6) 鲜水河断裂带斜坡位移计算
给定斜坡一个地震动值,当临界加速度相同时,斜坡将产生相同的位移[27]。根据式(4)计算得到鲜水河断裂带斜坡位移(Dn)。结果显示,斜坡位移较大的区域主要分布在临界加速度较小和地震动峰值加速度较大的区域,即康定—磨西段、大渡河流域及坡度较大的地区,位移可达10 cm以上(图 9-b)。
4.2 危险性分区与结果检验
利用Newmark模型计算获得鲜水河断裂带地震滑坡危险性分区,根据地震滑坡发生概率,参考《地质灾害危险性评估规范》(DZ/T 0286—2015)和国内外地震滑坡危险性分区研究成果[49],进一步把鲜水河断裂带划分为地震滑坡低危险区、中等危险区、高危险区和极高危险区(图 10),并统计历史地震滑坡在各分区中的分布(表 2)。结合已有地震滑坡点验证,各分区特点如下。
表 2 地震滑坡危险性分级统计Table 2. Seismic landslide hazards classification statistics地震滑坡危险区 分级面积/km2 分级面积比例/% 已发现的地震滑坡 滑坡数量/个 滑坡数量比例/% 滑坡面积/km2 滑坡面积比例/% 极高危险区 1931 6.28 140 35.09 57.76 70.62 高危险区 3619 11.77 114 28.57 15.34 18.75 中等危险区 10249 33.33 108 27.07 8.36 10.21 低危险区 14951 48.62 37 9.27 0.34 0.42 (1) 地震滑坡低危险区约占研究区面积的48.62%,主要分布在地形坡度较缓的东谷附近河谷地区及塔公草原地区,约有9.27%已调查发现的滑坡分布在地震滑坡低危险区。
(2) 地震滑坡中等危险区约占研究区面积的33.33%,约有27.07%已调查发现的滑坡分布在地震滑坡中等危险区,主要分布在鲜水河断裂带北段鲜水河河谷两侧坡度较缓的斜坡(图 10-a)。
(3) 地震滑坡高危险区约占研究区面积的11.77%,约有28.57%已调查发现的滑坡分布在地震滑坡高危险区,地震滑坡高危险区主要分布在康定市及周边地区(图 10-b)。
(4) 地震滑坡极高危险区约占区域面积的6.28%,约有35.09%已调查发现的滑坡分布在地震滑坡极高危险区,地震滑坡极高危险区主要分布在坡度较陡的大渡河流域和康定—磨西段(图 10-c)。
本文采用地质灾害危险性评价常用的成功率(ROC)曲线方法,对鲜水河断裂带地震滑坡危险性评价结果进行检验。ROC曲线下的面积值(AUC)越接近1.0,说明模型的构建效果越好,即评价结果越好;相反,若AUC值越接近0.5,说明模型的准确性越低[57]。本次鲜水河断裂带滑坡危险性评价结果的ROC曲线下方面积值为0.743(图 11),表明基于Newmark模型的鲜水河断裂带地震滑坡危险性评价结果具有较好的精度。
5. 讨论
5.1 鲜水河断裂带地震滑坡趋势
分析表明,已调查发现的399处历史地震滑坡主要沿地震动峰值加速度较高的区域分布。基于Newmark模型计算获得地震滑坡危险性分区,结果显示,有63.66%的地震滑坡分布在极高危险和高危险区。地震滑坡的发生受地震震级、震源深度、地形地貌、工程地质条件等因素影响。鲜水河断裂带构造活动强烈、工程地质条件较差,根据野外地质调查和地震滑坡危险性评价结果,鲜水河断裂带东南段的地震滑坡危险性较高。
前人研究认为,色拉哈-康定具有产生Ms 6~7级以上地震的风险[24, 32]。以上地震滑坡危险性评价结果显示,若沿鲜水河断裂带发生Ms 7.0级及以上强震,则康定周边、大渡河流域及康定—磨西段有较高的地震滑坡危险性。
5.2 鲜水河断裂带地震滑坡预测方法
王涛等[41]利用地震地质灾害形成和演化规律,提出广义的地震滑坡危险性评估框架。历史地震滑坡重点关注研究区历史强震,利用Newmark模型对历史地震诱发滑坡位移进行评估;同震滑坡的评估则是利用基础地质调查、遥感解译、地震动等参数,开展区域同震滑坡危险性评估;震后降雨滑坡结合地质灾害易发性进行地质灾害危险性评估[58];潜在地震滑坡主要依靠概率地震危险性分析方法,综合考虑区域工程地质条件与发震环境的相互作用,利用Newmark模型进行潜在地震滑坡危险性评估[59]。
层次分析法、信息量模型、加权线性叠加、支持向量机、逻辑回归等统计分析方法,具有数据量过大、不适合面积较大区域,忽视了与灾害问题的对应关系和适用条件等不足[60]。Newmark模型适用于发震构造清楚或地震动强度和参数记录较完整的情况,注重震后对地震滑坡影响要素的分析和危险性反演评估[44],可以利用中国第五代地震动峰值加速度计算当前地震动加速度下的潜在地震滑坡危险性,也可以通过阿里亚斯烈度(Arias)计算某次历史地震或设置的潜在地震点下的地震滑坡危险性。本文在考虑区域地震地质背景的基础上,基于Newmark模型方法的定量化评价优势,采用该方法开展鲜水河断裂带地震滑坡危险性评价。通过对比鲜水河断裂带地震滑坡危险性评估结果与区内历史地震滑坡分布,发现历史地震滑坡分布密集的区域与危险性评估结果中的极高危险区和高危险区分布较一致。
5.3 对重大工程规划建设的影响
鲜水河断裂带地处四川省境内川西地区,活动性强,未来具有发生强震的可能性[24]。根据鲜水河断裂带地震滑坡危险性评估结果显示,地震滑坡极高和高危险区主要分布在坡度较陡的大渡河流域和康定—磨西段、康定市及周边地区,研究区约有63.66%的历史地震滑坡分布在地震滑坡极高和高危险区。研究区城镇、公路等沿鲜水河、大渡河密集分布,且沿岸又是地质灾害高发区,部分居民点和公路存在地质灾害风险,城镇规划区应远离地震滑坡高危险区、河谷岸坡等地区;重要入藏公路G318穿越鲜水河断裂带地震滑坡高危险区,受到地质灾害严重威胁,需加强潜在地震诱发地质灾害防控意识、防护排查等处置措施;并且该区正在规划建设川藏铁路等重大工程,铁路建设面临地震滑坡的风险极高,规划铁路线经泸定县、康定市地震滑坡危险性较高的地区,但该路段以隧道为主,因此,铁路等工程规划建设需加强二郎山隧道、宝灵山隧道、郭达山隧道、康定隧道等的进出口地震滑坡危害评判及防控。
6. 结论
(1) 地震滑坡极高危险性区、高危险区、中等危险区和低危险区分别占研究区总面积的6.28%、11.77%、33.33%和48.62%,危险性较高的地区主要分布在康定—磨西段、大渡河附近及坡度较陡的斜坡上。
(2) 通过对比地震滑坡危险性评价结果与历史地震滑坡分布,发现已调查的399处地震滑坡有254处地震滑坡分布在地震滑坡极高和高危险区,与评估揭示的极高—高危险区分布较吻合,成功率(ROC)曲线检验结果显示,地震滑坡危险性评价的准确率为74.3%,评价结果精确度较高。
(3) 地震滑坡危险性分区受活动断裂和地形地貌影响显著,距离断层越近、坡度越大的斜坡,地震滑坡危险性越高。
(4) 根据危险性分区结果,若鲜水河断裂带发生强震,在大渡河流域及康定-磨西段有较高的危险性。川藏铁路经泸定县、康定地震滑坡危险性较高的地区,在铁路建设需加强铁路隧道口附近的地震滑坡危害评判及防控。
-
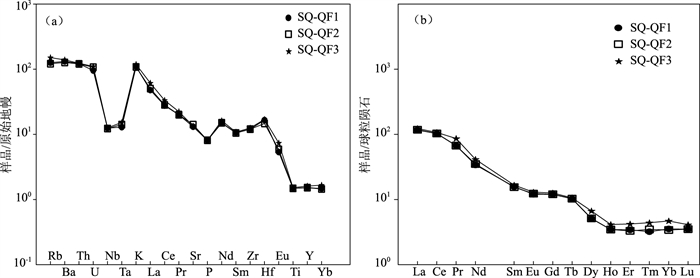
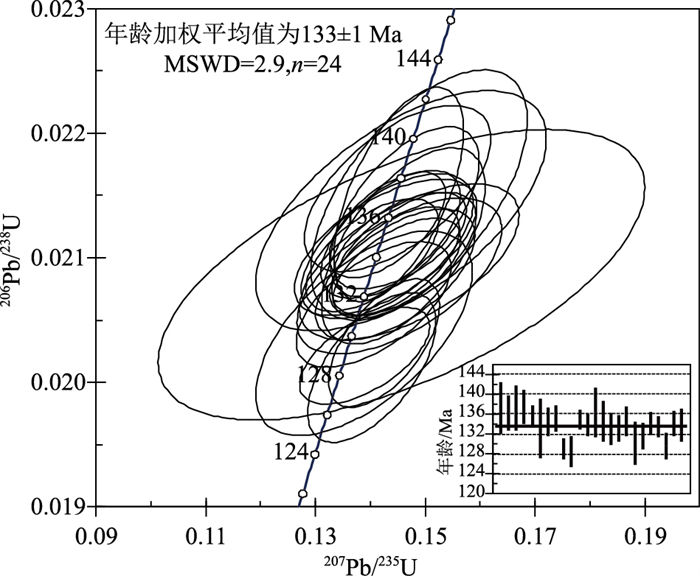
图 3 仙桥矿区英安岩微量元素蛛网图(a, 原始地幔标准化值据Sun et al.,1989)和稀土元素配分图(b, 球粒陨石标准化值据Boynton,1984)
Figure 3. Spider diagram of trace elements(a) and rare earth element patterns(b)in dacite from Xianqiao
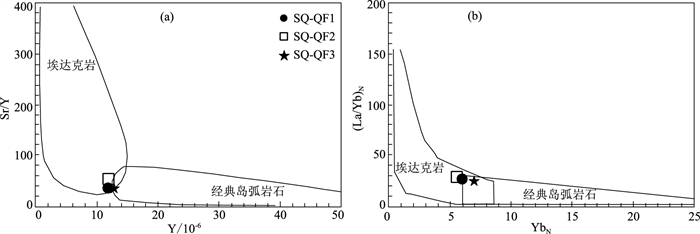
图 6 仙桥英安岩Y-Sr/Y图解(a,底图据Defant et al., 1990)和YbN-(La/Yb)N图解(b,底图据Martin,1999)
Figure 6. Y-Sr/Y(a) and YbN-(La/Yb)N(b)diagrams of dacite from Xianqiao
表 1 仙桥矿区英安岩主量、微量和稀土元素含量
Table 1 Major, trace and rare earth element contents of dacite in Xianqiao
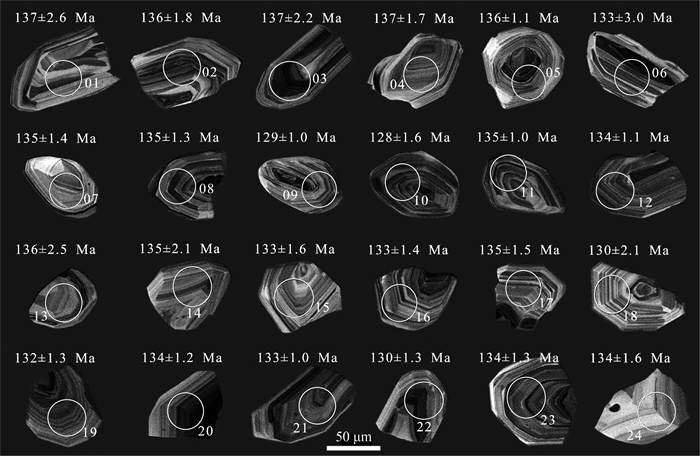
元素 SQ-QF1 SQ-QF2 SQ-QF3 元素 SQ-QF1 SQ-QF2 SQ-QF3 SiO2 68.72 67.70 66.28 Hf 9.24 7.77 9.53 TiO2 0.55 0.55 0.57 Ta 0.82 0.97 1.09 Al2O3 14.56 14.50 15.17 Th 15.1 14.8 15.5 Fe2O3 3.85 2.93 2.37 U 2.08 2.69 2.92 FeO 0.17 0.71 0.76 La 49.3 50.7 56 CaO 1.81 2.75 2.96 Ce 89.1 90.7 102 MgO 0.89 0.67 0.97 Pr 10.3 10.3 11.5 MnO 0.051 0.07 0.065 Nd 34.7 35.4 39.3 K2O 4.10 3.96 5.04 Sm 5.4 5.28 5.82 Na2O 2.96 3.26 2.60 Eu 1.27 1.33 1.48 P2O5 0.20 0.20 0.20 Gd 4.42 4.47 4.93 烧失量 1.60 1.81 2.70 Tb 0.52 0.53 0.58 H2O+ 1.53 0.95 1.99 Dy 2.37 2.38 2.71 总量 99.46 99.11 99.685 Ho 0.42 0.42 0.47 σ 1.94 2.11 2.51 Er 1.22 1.19 1.39 A/CNK 1.15 0.99 1.00 Tm 0.18 0.19 0.22 K2O+Na2O 7.06 7.22 7.64 Yb 1.24 1.21 1.47 Cr 61.4 62.5 90 Lu 0.19 0.19 0.21 Ni 29 24.8 28.1 Y 12 12 13 Ga 18.4 19.7 21.9 ∑REE 200.63 204.29 228.08 Rb 121 112 166 δEu 0.77 0.82 0.82 Sr 435 497 454 (La/Yb)N 26.80 28.25 25.68 Zr 193 193 211 (La/Sm)N 5.74 6.04 6.05 Nb 13.4 12.9 13.6 (Gd/Yb)N 2.88 2.98 2.71 Ba 1457 1356 1610 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 表 2 仙桥英安岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果
Table 2 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb isotopic analysis results from Xianqiao dacite
测点号 含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Pb U Th 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ 232Th/238U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ SQ.NY1.001 5 174 283 1.628 0.0215 0.0004 0.149 0.008 0.0502 0.0025 0.0075 0.0001 1.670 0.017 137 2.6 141 7.6 206 117.3 SQ.NY1.002 15 544 713 1.311 0.0214 0.0003 0.146 0.006 0.0496 0.0016 0.0073 0.0001 1.345 0.014 136 1.8 139 5.2 178 74.2 SQ.NY1.003 52 1968 2095 1.065 0.0215 0.0004 0.145 0.005 0.0490 0.0012 0.0072 0.0001 1.092 0.051 137 2.2 138 4.6 146 58.4 SQ.NY1.004 9 308 481 1.562 0.0216 0.0003 0.145 0.007 0.0488 0.0022 0.0073 0.0001 1.602 0.010 137 1.7 137 6.6 137 107.6 SQ.NY1.005 26 984 1013 1.030 0.0213 0.0002 0.143 0.004 0.0488 0.0011 0.0073 0.0001 1.056 0.012 136 1.1 136 4.1 139 53.4 SQ.NY1.006 9 351 373 1.062 0.0209 0.0005 0.146 0.018 0.0506 0.0061 0.0065 0.0003 1.089 0.014 133 3.0 138 17.2 224 280.4 SQ.NY1.007 7 249 328 1.316 0.0211 0.0002 0.143 0.007 0.0491 0.0022 0.0072 0.0001 1.350 0.013 135 1.4 136 6.4 153 106.9 SQ.NY1.008 14 477 715 1.500 0.0212 0.0002 0.144 0.005 0.0492 0.0016 0.0076 0.0001 1.538 0.015 135 1.3 136 4.9 157 75.1 SQ.NY1.009 16 615 808 1.314 0.0202 0.0002 0.139 0.005 0.0499 0.0015 0.0069 0.0001 1.348 0.007 129 1.0 132 4.6 188 69.4 SQ.NY1.010 19 815 663 0.814 0.0201 0.0002 0.140 0.005 0.0506 0.0015 0.0071 0.0001 0.835 0.005 128 1.6 133 4.5 221 70.3 SQ.NY1.011 15 557 723 1.296 0.0211 0.0002 0.146 0.005 0.0499 0.0014 0.0072 0.0001 1.330 0.013 135 1.0 138 4.6 192 63.4 SQ.NY1.012 18 721 667 0.926 0.0210 0.0002 0.144 0.005 0.0500 0.0014 0.0073 0.0001 0.950 0.005 134 1.1 137 4.6 193 63.6 SQ.NY1.013 6 254 223 0.877 0.0214 0.0004 0.146 0.011 0.0494 0.0038 0.0078 0.0003 0.900 0.007 136 2.5 138 10.2 167 179.9 SQ.NY1.014 10 413 285 0.689 0.0211 0.0003 0.146 0.006 0.0502 0.0019 0.0093 0.0002 0.707 0.005 135 2.1 138 5.8 205 90.1 SQ.NY1.015 5 198 203 1.027 0.0209 0.0003 0.145 0.008 0.0505 0.0026 0.0075 0.0001 1.054 0.005 133 1.6 138 7.2 220 117.0 SQ.NY1.016 11 343 728 2.121 0.0209 0.0002 0.145 0.006 0.0502 0.0019 0.0073 0.0001 2.175 0.013 133 1.4 137 5.6 206 88.7 SQ.NY1.017 7 243 325 1.340 0.0211 0.0002 0.143 0.006 0.0492 0.0020 0.0075 0.0001 1.375 0.013 135 1.5 136 6.1 157 96.0 SQ.NY1.018 9 274 612 2.230 0.0204 0.0003 0.139 0.008 0.0494 0.0028 0.0073 0.0001 2.288 0.016 130 2.1 132 7.7 166 131.7 SQ.NY1.019 17 701 636 0.908 0.0206 0.0002 0.141 0.006 0.0494 0.0018 0.0063 0.0001 0.932 0.005 132 1.3 134 5.5 168 86.3 SQ.NY1.020 20 826 564 0.682 0.0210 0.0002 0.140 0.005 0.0484 0.0014 0.0075 0.0001 0.700 0.003 134 1.2 133 4.7 120 70.2 SQ.NY1.021 17 719 513 0.714 0.0209 0.0002 0.145 0.005 0.0502 0.0014 0.0074 0.0001 0.732 0.004 133 1.0 137 4.5 205 64.5 SQ.NY1.022 42 1719 1796 1.045 0.0203 0.0002 0.143 0.004 0.0509 0.0010 0.0065 0.0001 1.072 0.017 130 1.3 135 3.9 235 45.6 SQ.NY1.023 16 583 788 1.351 0.0210 0.0002 0.146 0.005 0.0504 0.0016 0.0075 0.0001 1.386 0.007 134 1.3 138 5.1 213 73.3 SQ.NY1.024 4 177 143 0.810 0.0210 0.0003 0.147 0.008 0.0509 0.0027 0.0073 0.0002 0.831 0.004 134 1.6 139 7.8 235 122.7 -
Anderson T. Coerrction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chem. Geol., 2002, 192(1/2): 59-79. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035461073210_cc88.html
Boynton W V. Cosmochemistry of therarearth elements: metoritstudes[J]. Developments in Geocheemistry, 1984, 2(2): 63-114.
Defant M J, Drummond M S. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subduction lithosphhere[J]. Nature, 1990, 347: 662-665. doi: 10.1038/347662a0
Gao S, Luo T C, Zhang B R, et al. Chemical Composition of the Continental Crust as Revealed by Studies in East China[J]. Geochimical et Cosmochimica Acta, 1998, 62(11): 1959-1975. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00121-5
Gao Y, Yang Y C, Han S J, et al. Geochemistry of zircon and apatite from the Mo ore-forming granites in the Dabie Mo belt, East China: Implications for petrogenesis and mineralization[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 126: 103733. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103733
He Y S, Li S G, Hoefs J, et al. Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic compositions of Early Cretaceous granitoids from the Dabie orogen: Constraints on the recycled lower continental crust[J]. Lithos, 2013, 156/159: 204-217. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.10.011
Ludwig K R. Isoplot-A plotting and regression profram for radiogenic-isotoope data[J]. U. S Geological Survey Open-File Report, 1991, (39): 91-94.
Martin H. Adakitic magmas: modern analogues of Archean grantitiodse[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46: 411-429. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00076-0
Pearce J. Sources and Settings of Granitic Rocks[J]. Episodes, 1996, 19: 120-125. doi: 10.18814/epiiugs/1996/v19i4/005
Ren Z, Zhou T, Holling P, et al. Magmatism in the Shapinggou district of the Dabie orogen, China: Implications for the formation of porphyry Mo deposits in a collisional orogenic belt[J]. Lithos, 2018, 308/309: 346-363. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2018.03.013
Rudnick R L, Fountain D M. Nature and Composition of the Continenal: A Lower Crustal Perspective[J]. Peviews of Geohpysics, 1995, 33(3): 267-310. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035647858110_fa29.html
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 1989, 42: 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Xiong X L, Liu X C, Zhu Z M, et al. Adakitic rocks and destruction of the North China Craton: Evidence from experimental petrology and geochemistry[[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2011, 54(6): 858-870. doi: 10.1007/s11430-010-4167-9
邓晋福, 罗照华, 苏尚国, 等. 岩石成因、构造环境与成矿作用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2004: 1-380. 高山, 张本仁, 金振民. 秦岭-大别造山带下地壳拆沉作用[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 1999, 29(6): 532-541. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199906007.htm 何永胜. 大别造山带碰撞后花岗质岩浆作用地球化学对去山根过程及山根结构的制约[D]. 中国科学技术大学博士学位论文, 2010: 1-161. 黄丹峰, 罗照华, 卢欣祥. 大别山北缘金刚台火山岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及构造意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2010, 17(1): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201001002.htm 黄丹峰, 卢欣祥, 罗照华, 等. 大别山北缘商城岩体SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学及地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(11): 3829-3844. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201911021.htm 李厚民, 陈毓川, 叶会寿, 等. 东秦岭-大别地区中生代与岩浆活动有关钼(钨) 金银铅锌矿床成矿系列[J]. 地质学报, 2008, 82(11): 1468-1477. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.11.002 李积山, 张军杰, 刘伟, 等. 豫南史庄一带金伯利岩中石榴子石矿物学特征及其形成条件的约束[J]. 地质通报, 2022, 41(5): 824-835. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20220508&flag=1 李曙光, 何永胜, 王水炯, 等. 大别造山带的去山根过程与机制: 碰撞后岩浆岩的年代学和地球化学制约[J]. 科学通报, 2013, 58(28): 2316-2322. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201323014.htm 李鑫浩, 高昕宇, 张忠慧, 等. 北淮阳早白垩世金刚台组火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及地层对比[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2015, 39(4): 718-728. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201504014.htm 马昌前, 杨坤光, 明厚利, 等. 大别山中生代地壳从挤压转向伸展的时间: 花岗岩的证据[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2003, 22(9): 817-827. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200309000.htm 毛景文, 张作衡, 余金杰, 等. 华北及邻区中生代大规模成矿的地球动力学背景: 从金属矿床年龄精测得到启示[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2003, 33(4): 289-299. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200304000.htm 毛景文, 叶会寿, 王瑞廷, 等. 东秦岭中生代钼铅锌银多金属矿床模型及其找矿评价[J]. 地质通报, 2009, 28(1): 72-79. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090109&flag=1 陀健超. 大别山北部商城地区早白垩世岩浆活动及构造意义[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 硕士学位论文, 2021: 1-73. 王岳军, 范蔚茗, 郭锋, 等. 北大别晚中生代火山岩的地球化学特征及对北大别构造属性的启示[J]. 地学前缘, 2003, 10(4): 529-538. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200304026.htm 武广, 陈衍景, 孙丰月, 等. 大兴安岭北端晚侏罗世花岗岩类地球化学及其地质和找矿意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(4): 899-910. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200804029.htm 熊小林, 韩江伟, 吴金花. 变质玄武岩体系相平衡及矿物-熔体微量元素分配: 限定TTG/埃达克岩形成条件和大陆壳生长模型[J]. 地学前缘, 2007, 14(2): 151-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200702011.htm 续海金, 叶凯, 马昌前. 北大别早白垩纪花岗岩类的Sm-Nd和锆石Hf同位素及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(1): 87-103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200801008.htm 徐义刚, 李洪颜, 洪路兵, 等. 东亚大地幔楔与中国东部新生代板内玄武岩成因[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2018, 48: 825-843. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201807003.htm 严育通, 贾宝剑, 周红升, 等. 珍珠岩矿床地质背景研究进展[J]. 信阳师范学院学报(自然科学版), 2016, 29(4): 645-649. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYSK201604037.htm 杨梅珍, 曾键年, 任爱琴, 等. 大别山北缘西段双桥中生代火山岩地球化学及锆石U-Pb同位素年代学[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2012, 31(2): 133-144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201202003.htm 袁德志, 唐相伟, 史兴俊, 等. 大别山北部桃花岭岩体年代学、地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 信阳师范学院学报(自然科学版), 2022, 35(1): 97-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYSK202201016.htm 曾威, 周红英, 孙丰月, 等. 北秦岭官坡地区稀有金属伟晶岩锡石U-Pb年龄[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(2): 2179-2182. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20211220&flag=1 张国伟, 张本仁, 袁学城, 等. 秦岭造山带与大陆动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001. 张超, 马昌前. 大别山晚中生代巨量岩浆活动的启动: 花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素制约[J]. 矿物岩石, 2008, 28(4): 71-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS200804014.htm 张旗, 王焰, 李承东, 等. 花岗岩的Sr-Yb分类及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(9): 2249-2269. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200609000.htm 张旗, 焦守涛, 刘惠云. Sr和两个元素对花岗岩理论的重要意义[J]. 甘肃地质, 2021, 30(1): 1-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSDZ202101001.htm 赵子福, 郑永飞, 魏春生, 等. 大别山中生代中酸性岩浆岩锆石U-Pb定年、元素和氧同位素地球化学研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2004, 2(5): 162-185. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200405011.htm 朱江, 吴昌雄, 彭三国, 等. 大别山皇城山银矿区及外围陈棚组火山岩U-Pb年代学、地球化学和成矿构造背景[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(7): 2404-2418. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201807015.htm 朱江, 陕亮, 吴越, 等. 大别山北麓白石坡银矿区花岗斑岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学和Sr-Nd-Hf同位素组成及其地质意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(5): 317-329. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201905026.htm 朱江, 吴波, 王光洪, 等. 西大别山腹地晚中生代安山岩U-Pb年代学和地球化学特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 44(6): 824-833. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEFE202106019.htm 朱日祥, 徐义刚. 西太平洋板块俯冲与华北克拉通破坏[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2019, 49(9): 1346-1356. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201909003.htm -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 吴浩,徐祖阳,严维兵,郝宇杰,刘海永. 西藏中部聂尔错地区辉绿岩锆石U-Pb年龄与地球化学特征:对新特提斯洋板片断离的指示. 中国地质. 2023(06): 1804-1816 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: