Age and geochemistry of volcanic rocks of Baishan Formation in Yagan tectonic zone, Northern Alxa and their constraints on regional tectonic evolution
-
摘要:
阿拉善北部雅干地区古生代火山岩发育,研究其形成时代和地质特征,对探讨中亚造山带中段南缘北山弧盆系的演化具有重要的意义。对雅干地区原划奥陶系火山岩进行了同位素年代学与地球化学研究,获得流纹岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为298.4±1.5Ma,时代为早二叠世初期,结合岩石组合特征和区域对比,将其重新厘定为上石炭统—下二叠统白山组。该套火山岩富SiO2、高K2O、低TiO2,属于钙碱性系列; 相对富集Rb、Pb、K等大离子亲石元素,明显亏损Ta、Nb、P、Ti等高场强元素; 呈现为轻稀土元素相对富集、重稀土元素相对亏损的的右倾特征,具有较明显的负Eu异常,显示出陆缘弧火山岩的地球化学特征。上述证据表明,雅干地区白山组火山岩形成于古亚洲洋向明水-旱山地块北缘俯冲的陆缘弧构造环境。
Abstract:Paleozoic volcanic rocks are developed in Yagan area,northern Alxa,which is of great significance to study their formation age and geological characteristics for the evolution of the North Mountain arc basin system in the southern margin of the Middle Central Asian orogenic belt. In this paper,the isotope chronology and geochemical characterization of the proto-Ordovician volcanic rocks of the Yagan region are studied. The results show that the LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age of the rhyolite is 298.4±1.5 Ma,which belongs to the early Early Permian. It is redetermined to the Upper Carbonifeous-Lower Permian Baishan Formation based on the characteristics of the lithological assemblage. This set of volcanic rocks belong to the calc-alkaline series,which have higher content of SiO2,higher content of K2O and lower content of TiO2. They are relatively enriched in large ion lithophile elements such as Rb,Pb,K,and are obviously depleted high field strength elements such as Ta,Nb,P and Ti. The sample apparent right-leaning distribution patterns of the REE with depletion in LREE and enrichment in HREE and negative Eu anomaly,and they have the geochemistry characteristics of continental arc. The new evidence shows that Baishan Formation in Yagan area formed in the subduction of Paleo-Asian Ocean towards the northern margin of Mingshui-Hanshan block,and it was resulted from magmatism of the active continental margin.
-
阿拉善北部雅干地区位于中亚造山带中段南缘北山弧盆系北部,该构造带由一系列微地块、洋壳残片、增生楔、岩浆弧等拼贴而成,是研究古亚洲洋构造演化的重要窗口(Windley et al., 2007;Kröner et al., 2008;Xiao et al., 2011;2013;Zheng et al., 2014;潘桂棠等, 2016)。阿拉善北部额济纳地区广泛分布的古生代岩浆岩作为区内古生代岩浆作用的产物,对研究北山弧盆系俯冲增生作用及古亚洲洋构造体系的演化过程具有重要的启示意义(Xiao et al., 2011)。但该地区包括这些岩浆岩在内的很多地质体的形成时代和构造背景仍不明确或存在很大争议,因而造成对区域构造格局认识不清,制约了对中亚造山带演化的认识(左国朝等, 2011;党犇等, 2011;Xiao et al., 2013;Zheng et al., 2014)。近几年,额济纳西部早古生代岩浆岩的研究取得了很大进展,例如李敏等(2020)研究了北山造山带公婆泉早古生代岩浆弧的分布规律,并系统划分出不同的构造演化阶段;闫涛等(2020)报道了红石山-百合山蛇绿构造混杂岩带南侧大红山地区的一套泥盆纪弧花岗岩,并论述了地质特征、岩石学、地球化学、年代学及其岩石成因和构造背景。以上成果使人们对北山弧盆系的演化有了新的认识。但是这些研究多集中在额济纳旗西部马鬃山—黑鹰山地区,关于额济纳东部雅干地区古生代构造岩浆演化的研究还很薄弱。雅干北部呼仍巴斯克地区1∶5万区域地质调查发现,由于普遍缺乏精确的火山岩同位素年龄资料,1∶20万区调划分的奥陶系中裹夹着石炭纪火山岩①,制约了该地区地层格架的建立,也阻碍了区域构造演化时间与作用过程的深入研究。前人系统研究了区内的奥陶纪火山岩,认为其形成于Zoolen洋向明水-旱山地块北缘俯冲的陆缘弧构造背景(陈智斌等, 2020),但是对于区内晚古生代火山岩的研究仍很薄弱,导致对晚古生代构造演化过程尚不明确。因此,对雅干地区晚古生代火山岩的研究,不仅有助于厘清该地区的地层格架,对于认识北山弧盆系构造格局和演化过程也具有重要意义。
笔者对雅干地区出露的火山岩开展了详细的野外地质调查,选取白山组火山岩开展岩石学、同位素测年及岩石地球化学研究,探讨其形成时代、成因和大地构造环境,为阿拉善北部北山弧盆系构造演化研究提供新证据。
1. 地质背景
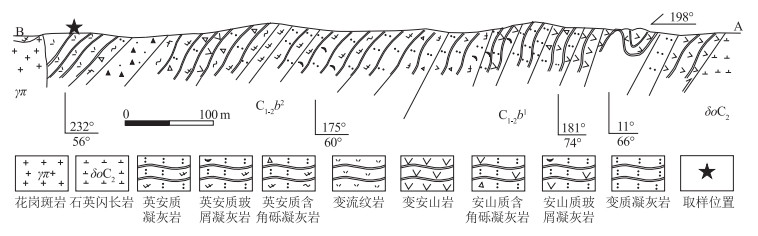
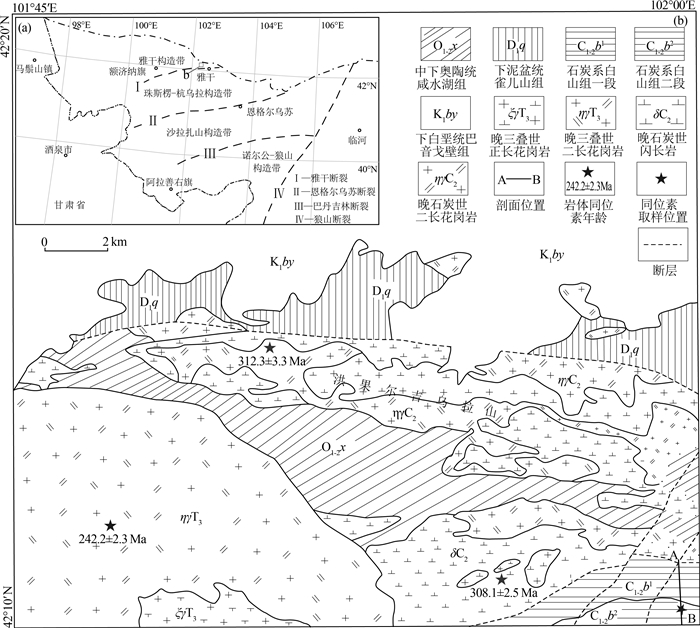
研究区位于内蒙古额济纳旗东北部中蒙边境洪果尔吉乌拉山南部,雅干断裂带北部,大地构造位置属于天山-北山造山系北山弧盆系园包山岩浆弧, 其南侧为明水-旱山地块(潘桂棠等,2016)(图 1-a)。园包山岩浆弧分布于甘肃红石山—内蒙古额济纳旗呼仍巴斯克地区, 沿中蒙边境呈近东西向展布,带内发育中奥陶统—下二叠统火山-沉积岩系(左国朝等,2003)。明水-旱山地块分布于甘肃方山口—碱泉子一线,区内发育一套以片麻岩为主的高级变质岩系,即北山岩群(左国朝等,1990;龚全胜等,2003)。在长期的地质演化历史中,经历了多期构造变形、叠加、改造和置换,形成了研究区现今复杂的地质景观。
区内出露的地层主要有中—下奥陶统咸水湖组、下泥盆统清河沟组、上石炭统—下二叠统白山组。咸水湖组一段为一套中性火山岩建造,咸水湖组二段主要为碎屑岩组合;清河沟组下部为碎屑岩夹少量碳酸盐,上部为碎屑岩夹火山岩。白山组是本次从原1∶20万区调划分的中奥陶世岩组中新厘定出的地层,主体为一套安山岩-流纹岩的火山岩、火山碎屑岩组合,与围岩晚石炭世闪长岩呈断层接触。白山组一段为基性—中性火山岩、火山碎屑岩,岩性以深灰色安山岩、暗紫色蚀变玄武安山岩(含角砾)及安山质凝灰熔岩为主,包含少量灰红色—灰紫色流纹质凝灰岩、英安岩、安山质角砾凝灰岩和安山质火山角砾岩;白山组二段以浅灰色—深灰色具流纹构造的英安岩,夹灰白色—深灰色流纹岩、流纹质火山碎屑岩和火山熔岩为主,局部可见少量火山碎屑岩。
侵入岩主要有晚石炭世二长花岗岩(锆石U-Pb年龄为312.3±3.3 Ma),分布于洪果尔吉乌拉山地区,侵入中—下奥陶统咸水湖组和下泥盆统清河沟组中;晚石炭世闪长岩(锆石U-Pb年龄308.1± 2.5 Ma),分布于洪果尔吉乌拉山南部,侵入中—下奥陶统咸水湖组和石炭系白山组,以及研究区西南部的乔伦恩格次晚三叠世二长花岗岩(锆石U-Pb年龄为242.2±2.3 Ma)侵入体中②(图 1-b)。
2. 样品采集和分析方法
2.1 样品采集
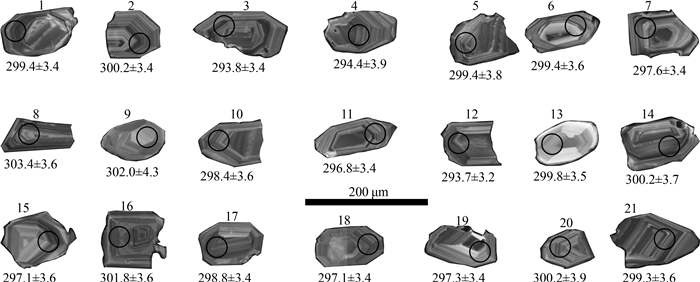
白山组实测剖面位于洪果尔吉乌拉山南部,岩性为一套中酸性火山岩组合,一段主要为中基性—中性火山岩、火山碎屑岩,岩性以深灰色安山岩、暗紫色蚀变玄武安山岩(含角砾)安山质凝灰熔岩为主;二段以浅灰色—深灰色具流纹构造的英安岩,夹灰白色—深灰色流纹岩、火山碎屑岩火山熔岩为主(图 2)。本次锆石U-Pb测年样品TW4389采自剖面白山组二段流纹岩夹层中,取样坐标:北纬42°10′2″、东经101°58′42″(图 1-b)。流纹岩风化面呈浅灰色,新鲜面为浅灰黑色,斑状结构,流纹构造。基质主要由长英质和少量黑云母组成,长英质多呈粒径小于0.1 mm的微晶状,少数粒径达0.1~0.3 mm,分布较杂乱,部分长石呈半自形板状,具高岭土化、绢云母化等,可见聚片双晶;部分钾长石与石英呈文象状交生,构成显微文象结构;黑云母呈鳞片状,片径一般小于0.2 mm,均被绿泥石交代呈现假像,含量小于3%;可见较少的石英斑晶(图 3)。
2.2 分析方法
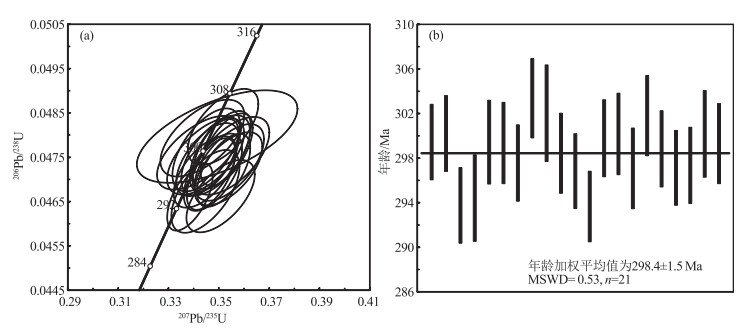
锆石U-Pb测年样品在河北省区域地质调查研究所实验室进行锆石单矿物分离,将样品破碎到60~80目,经过常规浮选和磁选方法分选后,在双目镜下挑选晶形较好的锆石颗粒,粘在双面胶上用无色透明环氧树脂固定,而后将锆石表面抛光至锆石内部暴露。阴极发光(CL)和背散射电子图像在北京锆年领航科技有限公司扫描电镜实验室完成。锆石U-Pb同位素年龄分析利用LA-ICP-MS方法在中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心实验室完成,测试仪器为UP193-FX ArF准分子激光器的激光剥蚀系统和Neptune质谱仪。利用激光器对锆石进行激光剥蚀,通过氦气将激光剥蚀物吹送到Neptune质谱仪。实验中用标样NIST610优化仪器,外标校正选用标准锆石GJ-1进行分析。采用Ludwig(2003)编写的Isoplot程序作图,单点误差为1σ,206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值的置信度为95%。
选取新鲜样品在中国地震局地壳应力研究所实验室完成主量和微量元素分析。主量元素采用碱熔法进行前处理,测试使用Panalytical Axios X荧光光谱仪完成。微量与稀土元素采用Thermo X-series Ⅱ型电感耦合等离子质谱仪(ICP-MS)测定,将200目以下的粉末样品放入高压密闭Teflon溶样罐中,经高纯硝酸和氢氟酸酸化,加盖装入溶样钢套,放入烘箱,170℃恒温条件下充分溶样后进行测定。在测试过程中,以Rh和Re为内标进行严格的质量监控和检验,保证数据的准确性。主量元素精度在1%以内,微量元素测试数据误差RSD≤5%。
3. 分析结果
3.1 锆石U-Pb年龄
选取样品TW4389中21颗晶形较好的锆石进行U-Pb同位素分析。锆石CL图像多呈无色透明,自形程度较好,短柱状—长柱状,粒径在50~110 μm之间,大部分具有清楚的韵律环带,总体上无退晶质化现象(图 4)。Th、U含量较高,呈现出较好的正相关性,Th/U值介于0.33~0.71之间(表 1)。以上特征表明,测年锆石具有岩浆锆石的特征(龚全胜等, 2003;Ludwig, 2003)。在U-Pb谐和图中,测试点均位于谐和线上或其附近,分布较集中。206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为298.4±1.5 Ma(MSWD= 0.53)(图 5),表明其结晶年龄为早二叠世初期。
表 1 白山组流纹岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素测试数据Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb isotopic analysis data of rhyolite from Baishan Formation测点 含量/10-6 同位素比值 年龄/Ma 谐和度/% Pb Th U 206Pb/
238U1σ 207Pb/
235U1σ 207Pb/
206Pb1σ 206Pb/
238U1σ 207Pb/
235U1σ 207Pb/
206Pb1σ 1 20 271 391 0.0475 0.0005 0.3482 0.0064 0.0531 0.0009 299.4 3.4 303 6 334 37 101 2 16 139 329 0.0477 0.0005 0.3531 0.0068 0.0537 0.0009 300.2 3.4 307 6 359 40 102 3 15 134 322 0.0466 0.0005 0.3507 0.0090 0.0546 0.0012 293.8 3.4 305 8 394 50 104 4 14 168 274 0.0467 0.0006 0.3447 0.0089 0.0535 0.0012 294.4 3.9 301 8 350 52 102 5 12 113 245 0.0475 0.0006 0.3487 0.0090 0.0532 0.0012 299.4 3.8 304 8 337 49 101 6 10 128 191 0.0475 0.0006 0.3548 0.0101 0.0541 0.0014 299.4 3.6 308 9 377 59 103 7 9 100 185 0.0472 0.0005 0.3538 0.0089 0.0543 0.0013 297.6 3.4 308 8 384 53 103 8 11 108 226 0.0482 0.0006 0.3517 0.0092 0.0529 0.0013 303.4 3.6 306 8 326 56 101 9 4 34 84 0.0480 0.0007 0.3493 0.0211 0.0528 0.0031 302.0 4.3 304 18 321 133 101 10 10 81 208 0.0474 0.0006 0.3541 0.0091 0.0542 0.0013 298.4 3.6 308 8 380 54 103 11 21 282 395 0.0471 0.0005 0.3469 0.0064 0.0534 0.0009 296.8 3.4 302 6 346 37 102 12 26 214 547 0.0466 0.0005 0.3385 0.0060 0.0527 0.0008 293.7 3.2 296 5 315 36 101 13 8 76 156 0.0476 0.0005 0.3421 0.0110 0.0521 0.0016 299.8 3.5 299 10 290 70 100 14 17 154 318 0.0477 0.0006 0.3512 0.0076 0.0534 0.0010 300.2 3.7 306 7 347 43 102 15 14 129 272 0.0472 0.0006 0.3477 0.0076 0.0535 0.0010 297.1 3.6 303 7 349 44 102 16 11 109 215 0.0479 0.0006 0.3435 0.0110 0.0520 0.0015 301.8 3.6 300 10 284 65 99 17 15 187 283 0.0474 0.0005 0.3455 0.0082 0.0528 0.0011 298.8 3.4 301 7 321 48 101 18 12 113 248 0.0472 0.0005 0.3445 0.0082 0.0530 0.0012 297.1 3.4 301 7 328 51 101 19 17 207 325 0.0472 0.0005 0.3519 0.0070 0.0541 0.0010 297.3 3.4 306 6 374 40 103 20 13 107 255 0.0477 0.0006 0.3450 0.0089 0.0525 0.0012 300.2 3.9 301 8 307 53 100 21 11 74 224 0.0475 0.0006 0.3447 0.0101 0.0526 0.0015 299.3 3.6 301 9 312 64 100 3.2 地球化学特征
3.2.1 主量元素
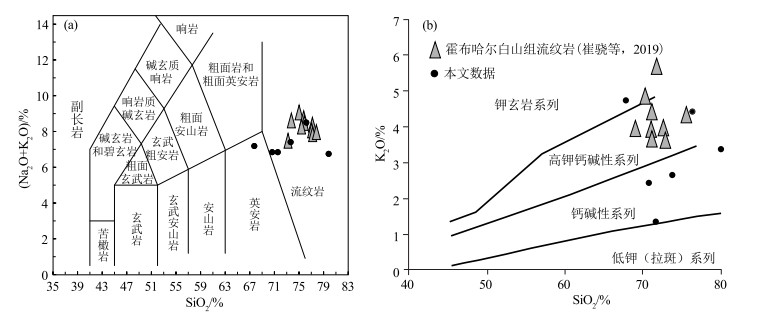
本次于洪果尔吉乌拉山南采集白山组二段火山岩地球化学样品6件,主量元素含量见表 2。样品SiO2含量介于67.74%~79.89%之间,平均为73.3%,属于酸性岩类;Al2O3含量为10.32%~14.35%;全碱(Na2O+K2O)含量为6.74%~8.48%,其中Na2O含量介于2.44%~5.47%之间,K2O含量介于1.36%~4.74%之间;MgO(0.12%~1.23%)、CaO(0.33%~2.23%)、TiO2(0.10%~0.40%)含量均较低;A/CNK指数在0.816~1.087之间,A/NK指数在1.105~1.569之间。里特曼指数σ(1.23~2.16)指示样品属于钙碱性系列。洪果尔吉乌拉山南白山组酸性火山岩在全岩TAS图解上绝大多数落入流纹岩区域,邻近本区南侧的雅干霍布哈尔地区白山组中酸性火山岩也多为流纹岩(图 6-a);在SiO2-K2O图解中,本区和霍布哈尔地区流纹岩(崔骁等,2019)投影点大多数落在钙碱性-高钾钙碱性系列(图 6-b)。
表 2 白山组火山岩主量、微量和稀土元素含量Table 2. Contents of major, trace element and REE of volcanic rocks from Baishan Formation编号 GS118 GS120 GS124 GS135-1 GS136-2 GS142 编号 GS118 GS120 GS124 GS135-1 GS136-2 GS142 SiO2 73.67 67.74 70.68 71.56 79.89 76.24 Pb 3 6.99 7.67 11.14 6.28 7.1 TiO2 0.37 0.31 0.4 0.3 0.29 0.1 Th 10.65 11.18 8.28 16.51 8.76 17.64 Al2O3 13 14.35 12.57 13.75 10.32 12.66 U 3.75 3.43 2.51 5.29 2.63 4.79 Fe2O3 2.88 4.42 2.7 2.3 1.15 1.29 La 37.9 18.82 18.67 24.14 23.98 47.04 MnO 0.09 0.11 0.07 0.07 0.05 0.02 Ce 96.34 42.34 42.16 52.04 54.74 93.72 MgO 0.32 0.65 0.92 1.23 0.28 0.12 Pr 12.02 5.08 5.19 5.96 7.19 12.16 CaO 1.04 2.23 3.05 2.27 0.61 0.33 Nd 50.5 21.06 22.54 23.24 31.14 49.54 Na2O 4.72 2.44 4.39 5.47 3.36 4.05 Sm 10.46 4.74 5.25 4.43 7.19 9.8 K2O 2.66 4.74 2.44 1.36 3.38 4.43 Eu 1.74 0.91 1.25 0.84 1.35 0.74 P2O5 0.07 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.05 0.02 Gd 10.43 5.28 5.86 4.72 8.04 10.21 烧失量 1.02 2.78 2.58 1.47 0.51 0.61 Tb 1.33 0.73 0.85 0.68 1.16 1.47 Na2O/K2O 1.77 0.51 1.8 4.02 0.99 0.91 Dy 8.93 5.11 5.89 4.12 8.34 8.64 σ 1.77 2.04 1.66 1.62 1.23 2.16 Ho 1.87 1.07 1.22 0.82 1.75 1.67 AR 3.22 1.83 2.55 2.49 4.19 4.31 Er 6.08 3.35 3.79 2.63 5.51 5.42 A/NK 1.221 1.569 1.274 1.313 1.123 1.105 Tm 0.94 0.49 0.55 0.39 0.81 0.77 A/CNK 1.037 1.087 0.816 0.942 1.002 1.05 Yb 6.82 3.52 3.87 2.68 5.55 5.29 Rb 57.9 139.06 56.22 28.32 91.46 88.72 Lu 0.99 0.5 0.56 0.41 0.77 0.79 Sr 146.68 145.64 160.32 356 83.68 69.36 Y 48.88 28.18 32.22 22.06 48.64 43.98 Zr 484.2 175.9 203.6 156.68 233.4 301 ΣREE 246.38 113 117.66 127.1 157.52 247.26 Nb 11.47 5.46 6.02 6.05 6.74 8.82 LREE 208.97 92.95 95.07 110.65 125.6 213 Cd 0.77 0.33 0.37 0.27 0.35 0.52 HREE 37.41 20.05 22.58 16.45 31.92 34.26 Cs 1.21 2.23 0.81 1.44 2.65 3.7 LREE/
HREE5.59 4.64 4.21 6.73 3.93 6.22 Ba 670.8 727.8 594 371.6 699.2 618.4 Hf 12.74 5.24 5.88 4.96 6.6 9.73 LaN/YbN 3.98 3.84 3.46 6.47 3.1 6.38 Ta 0.79 0.45 0.46 0.55 0.48 0.66 δEu 0.5 0.55 0.69 0.56 0.54 0.22 W 1.11 1.47 1.13 0.57 0.54 0.57 δCe 1.1 1.04 1.03 1.03 1.01 0.94 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 ![]() 图 6 白山组火山岩TAS图解(a, 底图据Le Bas et al., 2004)和SiO2-K2O图解(b, 底图据Peccerillo, 1976)Figure 6. TAS(a) and SiO2-K2O (b) diagrams of the volcanic rocks from Baishan Formation
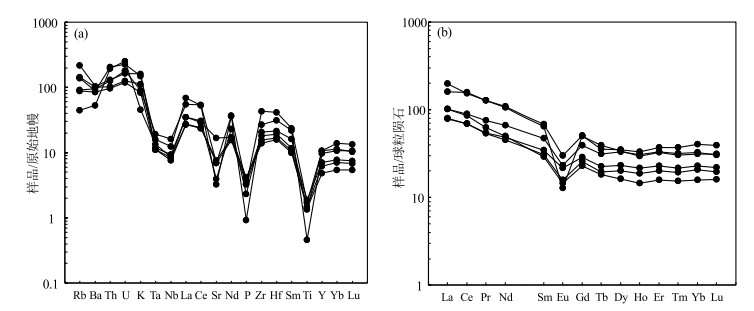
图 6 白山组火山岩TAS图解(a, 底图据Le Bas et al., 2004)和SiO2-K2O图解(b, 底图据Peccerillo, 1976)Figure 6. TAS(a) and SiO2-K2O (b) diagrams of the volcanic rocks from Baishan Formation3.2.2 微量和稀土元素
火山岩微量和稀土元素含量见表 2。从原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图解(图 7-a)可见,白山组流纹岩相对富集Rb、Pb、K等大离子亲石元素,明显亏损Ta、Nb、P、Ti等高场强元素,显示弧火山岩的特点,微量元素配分型式也与弧火山岩相似。样品稀土元素总量(∑REE)介于113.00×10-6~247.26×10-6之间,平均值为168.15×10-6;LREE/HREE值为3.93~6.73,平均值为5.22;(La/Yb)N值为3.10~6.47,平均值为4.54;δEu值为0.22~0.69,平均值为0.51。球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图解(图 7-b)显示,各样品配分曲线大致平行,具有轻稀土元素富集、重稀土元素亏损的的右倾特征,且均显示负Eu异常。
4. 讨论
4.1 成岩时代
本次在雅干地区洪果尔吉乌拉山南白山组二段上部流纹岩中获得锆石U-Pb年龄298.4±1.5 Ma(MSWD=0.53),表明该地区白山组火山岩成岩时代为晚石炭世—早二叠世。1∶20万区调将这套火山岩划归到中奥陶世岩组,本次依据年龄证据和区域地层对比,将其划归到上石炭统—下二叠统白山组。
区域上,《内蒙古自治区岩石地层》(1996)显示,白山组是与早石炭世绿条山组复理石建造密切伴生的一套形成于岛弧环境的火山岩。前人对白山组火山岩的同位素年代学研究主要集中于巴丹吉林沙漠以西的北山地区:卢进才等(2013)获得北山红石山地区晚古生代长英质火山岩的锆石U-Pb年龄分别为296.8±3.5 Ma、314.9±3.3 Ma和299.4±5.9 Ma;牛亚卓等(2013)测得北山黑鹰山地区白山组火山岩的年龄分别为308.6±1.0 Ma和299.1±2.4 Ma;贾元琴等(2016)获得风雷山白山组流纹岩的锆石U-Pb年龄为318.5±1.2 Ma,时代为晚石炭世;任云伟等(2019)于内蒙古哈珠地区白山组安山岩、英安岩、流纹岩中分别获得325.6±1.4 Ma、313.5±3.4 Ma和314.7±1.7 Ma的锆石U-Pb年龄。以上研究表明,白山组火山岩成岩年龄主要为晚石炭世—早二叠世。而在巴丹吉林沙漠以东阿拉善北部的雅干构造带内未见白山组火山岩的同位素年龄。本次在雅干地区洪果尔吉乌拉山南白山组二段上部流纹岩获得298.4±1.5 Ma的锆石U-Pb年龄,与北山地区白山组的年龄基本一致,属于同一时代岩浆活动的产物,成岩时代均为晚石炭世—早二叠世,表明该地区晚石炭世—早二叠世火山活动强烈。该研究为北山弧盆系构造演化提供了年代学依据。
4.2 岩石成因与构造环境
白山组火山岩主要分布在北山地区额济纳旗西部的哈珠、黑鹰山、交叉沟等地,向东延伸到雅干地区,整体呈北西—近东西向带状展布,构成所谓的白山岩浆弧(也称明水岩浆弧)(潘桂棠等, 2009;辛后田等, 2020)。本次研究认为,雅干地区洪果尔吉乌拉山南白山组以中基性—中酸性火山岩为主,主要由安山岩、英安岩、流纹岩和同成分的火山碎屑岩组成。白山组流纹岩样品具有富SiO2、高K2O、低TiO2的特征,属于钙碱性系列;相对富集Rb、Pb、K等大离子亲石元素,明显亏损Ta、Nb、P、Ti等高场强元素,具有钙碱性弧火山岩的特征,而钙碱性系列岩石被认为是洋壳俯冲消减作用的产物(Wyllie, 1981)。有学者认为,白山组火山岩是形成于裂谷环境的双峰式火山岩(牛亚卓等, 2013),但随着近几年北山地区1∶5万区调工作的陆续开展,有研究成果显示,白山组火山岩以安山岩和流纹岩为主,玄武岩仅有极少量存在,不具有双峰式火山岩的特征,总体上为一套钙碱性弧火山岩组合(贾元琴等, 2016;任云伟等, 2019)。
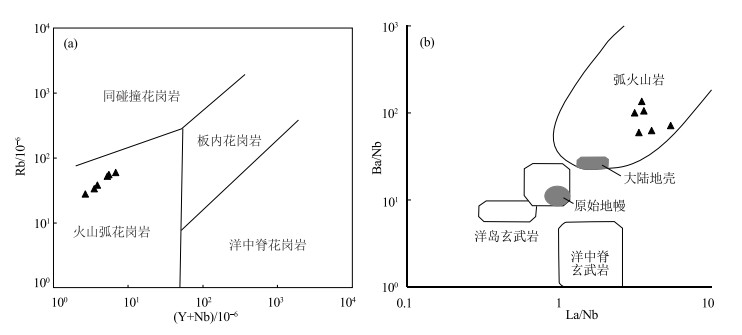
在火山岩Rb-(Y+Nb)图解和La/Nb-Ba/Nb图解(图 8)中,洪果尔吉乌拉山南白山组流纹岩样品投点均落于弧火山岩区域,其岩石组合、地球化学特征显示,研究区火山岩应为活动陆缘弧岩浆活动的产物。区域上,最新研究成果显示,白山组火山岩具有陆缘弧岩浆岩的特征,例如风雷山地区白山组流纹岩(贾元琴等, 2016)、哈珠地区白山组火山岩(任云伟等, 2019)、霍布哈尔地区白山组流纹岩(崔骁等, 2019),其地球化学特征与本次获得的流纹岩地球化学特征类似;与白山组同期的侵入岩,例如北山地区交叉沟晚石炭世石英闪长岩、独龙包晚石炭世花岗闪长岩、哈珠地区晚石炭世—早二叠世花岗闪长岩和二长花岗岩,也具有陆缘弧岩浆岩的特征,被认为是洋壳向明水-旱山地块北缘俯冲形成的(龚全胜等, 2003;赵志雄等, 2015;2018;辛后田等, 2020;李敏等, 2020)。
![]() 图 8 白山组火山岩构造环境判别图解a—(Y+Nb)-Rb图解(底图据Pearce et al., 1984);b—La/Nb-Ba/Nb图解(底图据Pearce, 1982)Figure 8. Tectonic discriminant diagrams for the volcanic rocks of Baishan Formation
图 8 白山组火山岩构造环境判别图解a—(Y+Nb)-Rb图解(底图据Pearce et al., 1984);b—La/Nb-Ba/Nb图解(底图据Pearce, 1982)Figure 8. Tectonic discriminant diagrams for the volcanic rocks of Baishan Formation在呼任巴斯克1∶5万区域地质调查工作及后续研究中,陈智斌等(2020)获得研究区咸水湖组流纹岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄为462±3 Ma,地球化学特征显示为一套具有陆缘弧特征的钙碱性系列火山岩,揭示了呼任巴斯克北侧蒙古境内的古亚洲洋(Zoolen洋)在中—晚奥陶世向南侧的明水-旱山地块北缘俯冲。呼仍巴斯克地区的陆缘岩浆弧环境显示其具有较厚的陆壳基底,最新的区调工作和研究在紧邻呼任巴斯克南部的雅干地区厘定出北山岩群③,获得了该地区存在微陆块的确切证据,认为其应为明水-旱山地块的东延部分,证实该区存在较厚的陆壳基底。
研究区白山组火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄为298.4±1.5 Ma,为一套早二叠世陆缘弧火山岩,表明古亚洲洋向明水-旱山地块下俯冲不晚于中奥陶世晚期,在晚石炭世—早二叠世仍在俯冲。
5. 结论
(1) 内蒙古阿拉善北部雅干地区洪果尔吉乌拉山南部原划奥陶系流纹岩的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb谐和年龄为298.4±1.5 Ma(MSWD=0.53),时代为早二叠世初期,结合岩石组合特征和区域对比,将其重新厘定为上石炭统—下二叠统白山组。
(2) 白山组流纹岩富SiO2、高K2O、低TiO2,属于钙碱性系列;相对富集Rb、Pb、K等大离子亲石元素,显著亏损P和Ta、Nb、Ti等高场强元素,样品显示负Eu异常,具轻稀土元素相对富集、重稀土元素亏损的右倾特征,显示陆缘弧火山岩的地球化学特征。
(3) 雅干地区洪果尔吉乌拉山南部白山组形成于晚石炭世—早二叠世古亚洲洋向明水-旱山地块下俯冲的陆缘弧环境。
注释
① 甘肃省地质局地质力学区域测试队.1∶20万黑鹰山幅区域地质图及调查报告[R].1981.
② 原中国人民武装警察部队黄金第二支队.内蒙古自治区额济纳旗呼仍巴斯克、查布汗其啥尔乌拉、敦德乌苏、勃温陶来幅1∶5万区域地质矿产调查报告[R].2019.
③ 原中国人民武装警察部队黄金第二支队.内蒙古自治区额济纳旗生格嘎顺、霍布哈尔幅1∶5万区域地质矿产调查报告[R].2019.
致谢: 感谢中国地质大学(武汉)张克信教授在野外调查期间的指导和帮助,感谢内蒙古农业大学李钢柱教授在成文过程中的悉心指导和有益讨论,感谢审稿专家提出的建设性建议。 -
图 1 洪果尔吉乌拉山地区大地构造位置(a,据潘桂棠等, 2016;陈智斌等, 2020修改)和地质简图(b)
Figure 1. The tectonic location (a) and geological sketch(b) of the Hongol Giula Mountain area
图 6 白山组火山岩TAS图解(a, 底图据Le Bas et al., 2004)和SiO2-K2O图解(b, 底图据Peccerillo, 1976)
Figure 6. TAS(a) and SiO2-K2O (b) diagrams of the volcanic rocks from Baishan Formation
图 8 白山组火山岩构造环境判别图解
a—(Y+Nb)-Rb图解(底图据Pearce et al., 1984);b—La/Nb-Ba/Nb图解(底图据Pearce, 1982)
Figure 8. Tectonic discriminant diagrams for the volcanic rocks of Baishan Formation
表 1 白山组流纹岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素测试数据
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb isotopic analysis data of rhyolite from Baishan Formation
测点 含量/10-6 同位素比值 年龄/Ma 谐和度/% Pb Th U 206Pb/
238U1σ 207Pb/
235U1σ 207Pb/
206Pb1σ 206Pb/
238U1σ 207Pb/
235U1σ 207Pb/
206Pb1σ 1 20 271 391 0.0475 0.0005 0.3482 0.0064 0.0531 0.0009 299.4 3.4 303 6 334 37 101 2 16 139 329 0.0477 0.0005 0.3531 0.0068 0.0537 0.0009 300.2 3.4 307 6 359 40 102 3 15 134 322 0.0466 0.0005 0.3507 0.0090 0.0546 0.0012 293.8 3.4 305 8 394 50 104 4 14 168 274 0.0467 0.0006 0.3447 0.0089 0.0535 0.0012 294.4 3.9 301 8 350 52 102 5 12 113 245 0.0475 0.0006 0.3487 0.0090 0.0532 0.0012 299.4 3.8 304 8 337 49 101 6 10 128 191 0.0475 0.0006 0.3548 0.0101 0.0541 0.0014 299.4 3.6 308 9 377 59 103 7 9 100 185 0.0472 0.0005 0.3538 0.0089 0.0543 0.0013 297.6 3.4 308 8 384 53 103 8 11 108 226 0.0482 0.0006 0.3517 0.0092 0.0529 0.0013 303.4 3.6 306 8 326 56 101 9 4 34 84 0.0480 0.0007 0.3493 0.0211 0.0528 0.0031 302.0 4.3 304 18 321 133 101 10 10 81 208 0.0474 0.0006 0.3541 0.0091 0.0542 0.0013 298.4 3.6 308 8 380 54 103 11 21 282 395 0.0471 0.0005 0.3469 0.0064 0.0534 0.0009 296.8 3.4 302 6 346 37 102 12 26 214 547 0.0466 0.0005 0.3385 0.0060 0.0527 0.0008 293.7 3.2 296 5 315 36 101 13 8 76 156 0.0476 0.0005 0.3421 0.0110 0.0521 0.0016 299.8 3.5 299 10 290 70 100 14 17 154 318 0.0477 0.0006 0.3512 0.0076 0.0534 0.0010 300.2 3.7 306 7 347 43 102 15 14 129 272 0.0472 0.0006 0.3477 0.0076 0.0535 0.0010 297.1 3.6 303 7 349 44 102 16 11 109 215 0.0479 0.0006 0.3435 0.0110 0.0520 0.0015 301.8 3.6 300 10 284 65 99 17 15 187 283 0.0474 0.0005 0.3455 0.0082 0.0528 0.0011 298.8 3.4 301 7 321 48 101 18 12 113 248 0.0472 0.0005 0.3445 0.0082 0.0530 0.0012 297.1 3.4 301 7 328 51 101 19 17 207 325 0.0472 0.0005 0.3519 0.0070 0.0541 0.0010 297.3 3.4 306 6 374 40 103 20 13 107 255 0.0477 0.0006 0.3450 0.0089 0.0525 0.0012 300.2 3.9 301 8 307 53 100 21 11 74 224 0.0475 0.0006 0.3447 0.0101 0.0526 0.0015 299.3 3.6 301 9 312 64 100 表 2 白山组火山岩主量、微量和稀土元素含量
Table 2 Contents of major, trace element and REE of volcanic rocks from Baishan Formation
编号 GS118 GS120 GS124 GS135-1 GS136-2 GS142 编号 GS118 GS120 GS124 GS135-1 GS136-2 GS142 SiO2 73.67 67.74 70.68 71.56 79.89 76.24 Pb 3 6.99 7.67 11.14 6.28 7.1 TiO2 0.37 0.31 0.4 0.3 0.29 0.1 Th 10.65 11.18 8.28 16.51 8.76 17.64 Al2O3 13 14.35 12.57 13.75 10.32 12.66 U 3.75 3.43 2.51 5.29 2.63 4.79 Fe2O3 2.88 4.42 2.7 2.3 1.15 1.29 La 37.9 18.82 18.67 24.14 23.98 47.04 MnO 0.09 0.11 0.07 0.07 0.05 0.02 Ce 96.34 42.34 42.16 52.04 54.74 93.72 MgO 0.32 0.65 0.92 1.23 0.28 0.12 Pr 12.02 5.08 5.19 5.96 7.19 12.16 CaO 1.04 2.23 3.05 2.27 0.61 0.33 Nd 50.5 21.06 22.54 23.24 31.14 49.54 Na2O 4.72 2.44 4.39 5.47 3.36 4.05 Sm 10.46 4.74 5.25 4.43 7.19 9.8 K2O 2.66 4.74 2.44 1.36 3.38 4.43 Eu 1.74 0.91 1.25 0.84 1.35 0.74 P2O5 0.07 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.05 0.02 Gd 10.43 5.28 5.86 4.72 8.04 10.21 烧失量 1.02 2.78 2.58 1.47 0.51 0.61 Tb 1.33 0.73 0.85 0.68 1.16 1.47 Na2O/K2O 1.77 0.51 1.8 4.02 0.99 0.91 Dy 8.93 5.11 5.89 4.12 8.34 8.64 σ 1.77 2.04 1.66 1.62 1.23 2.16 Ho 1.87 1.07 1.22 0.82 1.75 1.67 AR 3.22 1.83 2.55 2.49 4.19 4.31 Er 6.08 3.35 3.79 2.63 5.51 5.42 A/NK 1.221 1.569 1.274 1.313 1.123 1.105 Tm 0.94 0.49 0.55 0.39 0.81 0.77 A/CNK 1.037 1.087 0.816 0.942 1.002 1.05 Yb 6.82 3.52 3.87 2.68 5.55 5.29 Rb 57.9 139.06 56.22 28.32 91.46 88.72 Lu 0.99 0.5 0.56 0.41 0.77 0.79 Sr 146.68 145.64 160.32 356 83.68 69.36 Y 48.88 28.18 32.22 22.06 48.64 43.98 Zr 484.2 175.9 203.6 156.68 233.4 301 ΣREE 246.38 113 117.66 127.1 157.52 247.26 Nb 11.47 5.46 6.02 6.05 6.74 8.82 LREE 208.97 92.95 95.07 110.65 125.6 213 Cd 0.77 0.33 0.37 0.27 0.35 0.52 HREE 37.41 20.05 22.58 16.45 31.92 34.26 Cs 1.21 2.23 0.81 1.44 2.65 3.7 LREE/
HREE5.59 4.64 4.21 6.73 3.93 6.22 Ba 670.8 727.8 594 371.6 699.2 618.4 Hf 12.74 5.24 5.88 4.96 6.6 9.73 LaN/YbN 3.98 3.84 3.46 6.47 3.1 6.38 Ta 0.79 0.45 0.46 0.55 0.48 0.66 δEu 0.5 0.55 0.69 0.56 0.54 0.22 W 1.11 1.47 1.13 0.57 0.54 0.57 δCe 1.1 1.04 1.03 1.03 1.01 0.94 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 -
Kröner A, Hegner E, Lehmann B, et al. Palaeozoic Arc Magmatism in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt of Kazakhstan: SHRIMP Zircon Ages and Whole-Rock Nd Isotopic Systematics. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences[J]. 2008, 32(2/3/4): 118-130.
Le Bas M J, Le Maitre R W, Streckeisen A, et al. A Chemical Classification of Volcanic Rocks Based on the Total Alkali-Silica Diagram[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1986, 27(3): 745-750. doi: 10.1093/petrology/27.3.745
Ludwig K R. ISOPLOT 3.0: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, 2003, 4: 1-71.
Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. Trace Element Discrimination Diagrams for the Tectonic Interpretation of Granitic Rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25: 956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
Pearce J. Trace element characteristics of lavas from destructive plate boundaries[C]//Andesites and Related Rocks. John Willey & Sons, 1982: 525-548.
Peccerillo A, Taylor S R. Geochemistry of Eocene Calc-Alkaline Volcanic Rocks from the kastamonu Area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1): 63-81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Windley B F, Alexeiev D, Xiao W J, et al. Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic belt[J]. Geol. Soc. Lond., 2007, 164: 31-47. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492006-022
Wyllie P J. Plate tectonics and magma genesis[J]. Geologische Rundschau, 1981, 70(1): 128-153. doi: 10.1007/BF01764318
Xiao W J, Mao Q G, Windley B F, et al. Paleozoic Multiple Accretionary and Collisional Processes of the Beishan Orogenic Collage[J]. American Journal of Science, 2011, 310(10): 1553-1594.
Xiao W J, Windley B F, Allen M B, et al. Paleozoic Multiple Accretionary and Collisional Tectonics of the Chinese Tianshan Orogenic Collage[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23(4): 1316-1341. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.01.012
Zheng R G, Wu T R, Zhang W, et al. Late Paleozoic Subduction System in the Northern Margin of the Alxa Block, Altaids: Geochronological and Geochemical Evidences from Ophiolites[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 25(2): 842-858. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.05.011
陈智斌, 于洋, 薄海军. 内蒙古额济纳地区奥陶纪火山岩地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(2): 503-518. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202002012.htm 崔骁, 王根厚, 王振义, 等. 塔里木板块东北缘霍布哈尔白山组流纹岩地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 46(3): 268-279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2019.03.02 党犇, 赵虹, 林广春, 等. 阿拉善北部地区石炭纪火山岩岩石成因及构造意义[J]. 地球科学, 2013, 38(5): 963-974. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201305007.htm 龚全胜, 刘明强, 梁明宏, 等. 北山造山带大地构造相及构造演化[J]. 西北地质, 2003, 36(1): 11-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2003.01.002 贾元琴, 赵志雄, 许海, 等. 北山风雷山地区白山组流纹岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及构造环境[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43: 91-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201601006.htm 李敏, 辛后田, 田健, 等. 北山造山带公婆泉岩浆弧的组成, 时代及其大地构造意义[J]. 地球科学, 2020, (7): 2393-2412. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202007014.htm 李文国. 内蒙古自治区岩石地层[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1996. 卢进才, 牛亚卓, 魏仙样, 等. 北山红石山地区晚古生代火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(8): 2685-2694. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201308006.htm 牛亚卓, 魏建设, 史冀忠, 等. 甘肃北山地区北部上石炭统火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其构造意义[J]. 地质通报, 2013, 32(11): 1720-1727. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2013.11.004 潘桂棠, 陆松年, 肖庆辉, 等. 中国大地构造阶段划分和演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(6): 1-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201606006.htm 潘桂棠, 肖庆辉, 陆松年, 等. 中国大地构造单元划分[J]. 中国地质, 2009, 36(1): 1-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200901004.htm 任云伟, 任邦方, 牛文超, 等. 内蒙古哈珠地区石炭纪白山组火山岩: 北山北部晚古生代活动陆缘岩浆作用的产物[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(1): 312-327. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201901024.htm 吴元保, 郑永飞. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(16): 1589-1604. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200416001.htm 辛后田, 牛文超, 田健, 等. 内蒙古北山造山带时空结构与古亚洲洋演化[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(9): 1297-1316. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200901&flag=1 闫涛, 辛后田, 卫彦升, 等. 对内蒙古北山造山带洋-陆转换认识的新思考——来自大红山南泥盆纪弧花岗岩的证据[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(9): 1341-1366. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200904&flag=1 赵志雄, 贾元琴, 许海, 等. 北山交叉沟石英闪长岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄及构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(7): 1210-1218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201507005.htm 赵志雄, 熊煜, 贾元琴, 等. 北山独龙包地区晚石炭世陆缘弧岩浆作用——花岗闪长岩锆石U-Pb年龄及地球化学证据[J]. 地质论评, 2018, 64(3): 597-609. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201803007.htm 左国朝, 何国琦. 北山板块构造及成矿规律[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 1990. 左国朝, 李绍雄. 塔里木盆地东北缘早古生代构造格局及演化[J]. 中国地质, 2011, 38(4): 945-960. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201104013.htm 左国朝, 刘义科, 刘春燕. 甘新蒙北山地区构造格局及演化[J]. 甘肃地质, 2003, (1): 1-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSDZ200301000.htm



 下载:
下载: