Age and geochemical characteristics of Late Cretaceous leucogranites pluton and dykes in Xieqiong area, Tibet: constraints on the post-collisional setting of Bangong Co-Nujiang belt
-
摘要:
藏东左贡地块的晚白垩世侵入岩鲜有报道。对谢穷地区侵入于新元古界酉西岩群中的花岗岩体和岩脉进行了岩石学、地球化学及锆石U-Pb测年研究,揭示其岩石成因及形成环境。岩体岩石类型为含电气石白云母二长花岗岩,岩脉岩石类型为细粒花岗质岩脉,二者的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄分别为88.5±0.7Ma和85.8±2.3Ma,均侵位于晚白垩世。岩体与岩脉含白云母,无角闪石,均具有高硅(SiO2=74.17%~78.88%)、富碱(K2O+Na2O=5.92%~9.00%)和富铝(Al2O3=12.61%~15.13%)的特点,铝饱和指数(A/CNK=1.11~1.40)和里特曼指数(δ<3.3),指示二者均属于过铝质钙碱性系列; 均富集Rb、U、K、P和Pb,亏损Nb、Ti和Ba,具强烈的负Eu异常(δEu=0.18~0.56),表明为一套强过铝质亚碱性S型花岗岩,具有电气石型淡色花岗岩的特征。其可能为地壳缩短增厚挤压环境向地壳伸展环境转换过程中,构造减压导致的上地壳变质泥岩中含水矿物(白云母)脱水部分熔融的产物,为班公湖-怒江缝合带在东部的后碰撞演化过程提供了新的制约。
Abstract:The Late Cretaceous intrusive rocks in the Zuogong Block,eastern Tibet are rarely reported. This article reports on the granitic pluton and dykes invaded in the Neoproterozoic Youxi Group in the Xieqiong area,through petrology,geochemistry and zircon U-Pb chronology,to reveal its petrogenesis and formation environment. The granitic pluton type is tourmaline-bearing muscovite monzonitic granite,and the dike rock type is fine-grained granitic dike. The LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb ages of the two are 88.5±0.7 Ma and 85.8±2.3 Ma,respectively,both invaded in the Late Cretaceous. They contains minor muscovite,no hornblende.The granitic pluton and dike are characterized by high SiO2(SiO2=74.17%~78.88%),rich alkali(K2O+Na2O=5.92%~9.00%)and rich Al(Al2O3=12.61%~15.13%),A/CNK =1.11~1.40,Ritman index δ < 3.3,indicating that they belongs to the peraluminous calc-alkaline series; all are enriched in Rb,U,K,P and Pb elements and depleted in Nb,Ti and Ba elements; and strong negative Eu anomalies(δEu=0.18~0.56),which are indicative of peraluminous sub-alkaline S-type granite,and characteristics of a tourmaline-type leucogranite. It may be the product of dehydration and partial melting of water-bearing minerals(muscovite)in the upper crustal metamorphic mudstone caused by the transition from shortening and thickening extrusion environment to crustal extension environment. This result provides new constraints for the post-collision evolution process of the Bangong Co -Nujiang suture zone in the east.
-
Keywords:
- Tibet /
- Late Cretaceous /
- Bangong Co-Nujiang /
- leucogranite /
- geological survey engineering /
- geochemistry
-
班公湖-怒江缝合带位于南羌塘地块与拉萨地块之间,是中特提斯存在的标志,东西横跨青藏高原,长达2000 km。虽然前人对该带做过大量研究,有关班公湖-怒江缝合带的关键地质问题仍存在较大争议,比如闭合后该带的活动性及方式,尤其是其所代表洋盆的演化过程,包括洋盆的性质、打开时限、俯冲极性和消亡过程等问题(Zhang et al., 2017;Hao et al., 2018;Guo et al., 2019)。通常认为洋盆形成于晚三叠世—早侏罗世,于中侏罗世俯冲消减,晚侏罗世—早白垩世晚期闭合。其中,闭合时限存在2种观点:一是晚侏罗世—早白垩世早期(王建平等,2002;Zhang et al., 2004;Kapp et al., 2007),二是早白垩世晚期(朱弟成等,2006;Fan et al., 2014;2015b)。至晚白垩世,班公湖-怒江特提斯洋已处于碰撞及碰撞后阶段。
前人有关中特提斯洋碰撞后演化过程的研究集中于中西段(张硕等,2014;李发桥等,2018),对东段的演化过程尚不明确。已有研究认为,班公湖地区出露的日松岩体和甲维酸性岩脉,其U-Pb年龄前者为82.0 Ma,后者为90.7 Ma和82.9 Ma,两者都具有埃达克岩特征,为后碰撞初期中特提斯洋闭合后板内热隆伸展、壳幔相互作用的产物(张硕等,2014);双湖县玛日埃错地区出露的花岗斑岩形成于晚白垩世晚期(78 Ma),为伸展背景下新生地壳部分熔融的产物(李发桥等,2018)。东部的左贡地块与南羌塘地块构造单元一致,却缺少同时期岩浆活动的有关报道。因此,本文以南羌塘-左贡地块中侵入于新元古界酉西岩群的谢穷晚白垩世花岗岩体和岩脉为研究对象,进行了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩地球化学分析,对其岩石成因和构造背景进行制约,为该地区中特提斯洋的构造演化提供更多信息。
1. 区域地质背景
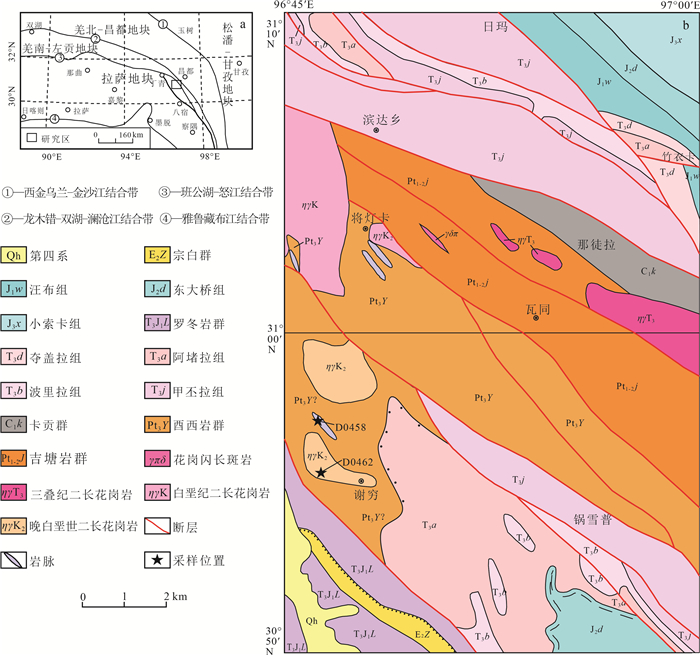
南羌塘—左贡地块位于青藏高原中部,北以龙木错-双湖-澜沧江板块缝合带为界,南以班公湖-怒江板块缝合带与拉萨地块相隔。研究区位于羌南-左贡地块东部类乌齐一带(图 1-a)。由于该区处于东西向构造向南北向构造转弯处,北西—南东向的褶皱和脆性、韧性断层十分发育(潘桂棠,1997)。其中,罗冬岩群曾经被认为属于班公湖-怒江缝合带的蛇绿混杂岩,为丁青蛇绿混杂岩的东段(Dewey et al., 1988;Yin et al., 2000;潘桂棠等,2004),主要由侏罗纪—白垩纪蛇绿混杂岩、洋岛、复理石沉积、弧岩浆岩等组成(Pan et al., 2012)。
![]() 图 1 研究区大地构造位置(a,据王保弟等,2011修改) 及地质简图(b)Figure 1. Tectonic position(a) and sketch geological map(b)of the study area
图 1 研究区大地构造位置(a,据王保弟等,2011修改) 及地质简图(b)Figure 1. Tectonic position(a) and sketch geological map(b)of the study area研究区出露古—中元古界吉塘岩群(Pt1-2J),新元古界酉西群(Pt3Y),石炭系卡贡群(C1k),上三叠统甲丕拉组(T3j)、波里拉组(T3b)、阿堵拉组(T3a)、夺盖拉组(T3d),中侏罗统东大桥组(J2d),古近系宗白群(E2Z)等。前人认为,研究区的晚三叠世岩层为一套碎屑岩-碳酸盐岩建造(李才等,2009)。本次在酉西岩群以南、宗白群以北原阿堵拉组中新识别出一套绿片岩相变质岩,包括强片理化的二云母片岩、白云母石英片岩、石英片岩、变玄武岩、绿泥石片岩、斜长角闪岩、辉长岩、堆晶辉长岩等基性岩块,另外还可见大理岩、变质石英砂岩、黑云斜长片麻岩、变砂砾岩(有序)等外来岩块,可能为酉西岩群的一部分。本次研究的岩体和岩脉就产出于该套变质岩中。
2. 岩体和岩脉的地质学特征
花岗岩体以岩滴状产出,呈长条状,整体NW—SE向展布,东西向长度约2 km。岩脉呈细长条状夹持于两岩体间,北西—南东向展布,含有电气石等矿物。
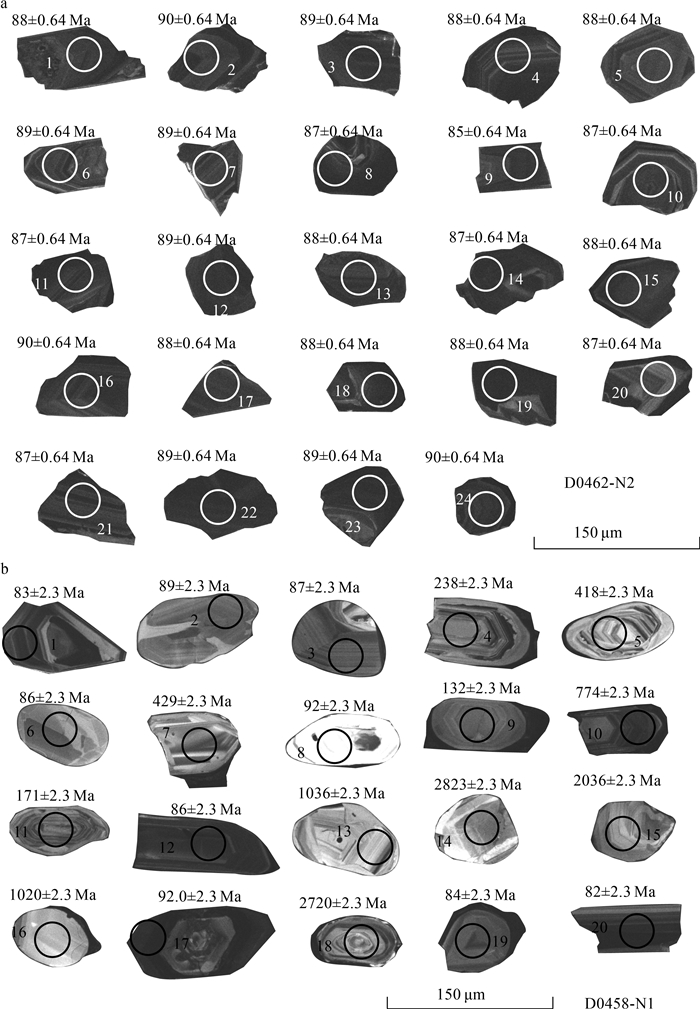
岩体岩性为含电气石白云母二长花岗岩(图版Ⅰ-a、b、d、f),浅灰白色,中粒花岗结构,块状构造。主要矿物为斜长石(40%~45%)、钾长石(30%)、石英(20%~25%)、白云母(5%)、电气石(1%~5%)和不透明矿物(1%~2%)。细粒花岗质岩脉(图版Ⅰ-c、e),岩石呈浅灰白色,细粒花岗结构,块状构造。主要矿物为斜长石(55%~60%)、石英(20%~25%)、钾长石(15%~20%)、白云母(5%)及不透明矿物(1%~2%)。副矿物可见电气石(图版Ⅰ-f)。
3. 分析方法
全岩主量和微量元素、LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素定年皆在武汉上谱分析科技有限责任公司完成。主量元素采用日本理学PrimusⅡ X射线荧光光谱仪(XRF)分析完成,测试精度为5%;微量元素分析利用Agilent 7700e ICP-MS分析完成。测试精度小于1%。锆石分选由河北省廊坊区域地质调查研究院地质实验室完成,锆石制靶和阴极发光(CL)照相由北京锆年领航科技有限公司完成。通过电磁和重液法分选,最后在双目镜下挑出锆石。将挑好的靶样进行透、反射光照相并采集阴极发光图像。根据CL图像判断锆石成因,结合透、反射照片,选择无包裹体、无裂隙的锆石微区圈定激光剥蚀区域。锆石U-Pb同位素定年采用LA-ICP-MS分析完成。详细的仪器参数和分析流程见参考文献(Zong et al., 2017)。GeolasPro激光剥蚀系统由COMPexPro 102 ArF 193 nm准分子激光器和MicroLas光学系统组成,ICP-MS型号为Agilent 7700e。激光剥蚀斑束直径和频率分别为32 μm和5 Hz,采用锆石标准91500和玻璃标准物质NIST610为外标进行同位素分馏校正。测试数据采用ICPMSDataCal软件进行处理(Liu et al., 2008;2010),年龄加权平均值计算及相关图解采用Isoplot/Exver3软件完成(Ludwig,2003)。
4. 测试结果
4.1 锆石U-Pb年龄
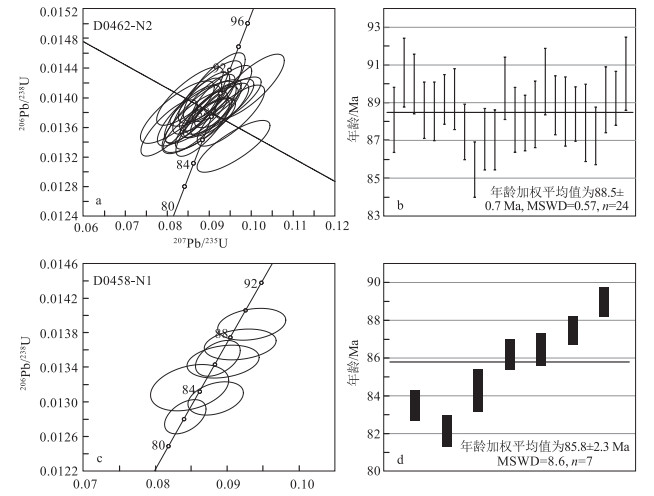
对含电气石白云母二长花岗岩(D0462-N2)和细粒花岗质岩脉(D0458-N1)进行了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年测试,数据见表 1。单点分析年龄误差和年龄加权平均值误差均为1σ。含电气石白云母二长花岗岩(D0462-N2)的锆石呈自形—半自形晶,绝大多数晶形完整,以纺锤状为主,少数为长柱状或短柱状。锆石长轴直径为70~120 μm,长宽比为1∶1~2∶1。阴极发光(CL)图像显示,锆石具有清晰的振荡环带(图 2-a),暗示其为岩浆成因(吴元保等,2004)。锆石的U含量为2608.98×10-6~7941.06×10-6,Th含量为17.40×10-6~101.25×10-6,Th/U值均小于0.01。样品D0462-N2共分析了24个测点,24个测点均位于U-Pb谐和线上,206Pb/238U年龄介于85~90 Ma之间,其年龄加权平均值为88.3±0.9 Ma(MSWD=0.45,n=24)(图 3-a、b),表明含电气石白云母二长花岗岩形成于晚白垩世。
表 1 谢穷岩体和岩脉LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb分析结果Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb analysis data for pluton and dyke from Xieqiong测点号 含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Pb Th U 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ D0462-N2-01 100.66 101.2 7273 0.01 0.0492 0.0027 0.0952 0.0053 0.0138 0.0003 92.3 4.9 88.1 1.7 D0462-N2-02 79.69 42.3 5354 0.01 0.0508 0.0030 0.0997 0.0054 0.0142 0.0003 96.5 5.0 90.6 1.8 D0462-N2-03 90.22 53.3 6335 0.01 0.0471 0.0025 0.0930 0.0047 0.0141 0.0002 90.3 4.4 90.0 1.6 D0462-N2-04 79.34 42.8 5654 0.01 0.0478 0.0025 0.0925 0.0046 0.0138 0.0002 89.8 4.2 88.6 1.5 D0462-N2-05 63.79 26.7 4546 0.01 0.0472 0.0026 0.0907 0.0046 0.0138 0.0002 88.2 4.2 88.5 1.6 D0462-N2-06 52.61 28.8 3718 0.01 0.0449 0.0028 0.0892 0.0056 0.0139 0.0002 86.7 5.2 89.2 1.3 D0462-N2-07 94.48 55.4 6530 0.01 0.0455 0.0023 0.0895 0.0044 0.0139 0.0003 87.1 4.1 89.2 1.6 D0462-N2-08 80.99 40.2 5660 0.01 0.0460 0.0024 0.0887 0.0045 0.0137 0.0002 86.3 4.2 87.4 1.5 D0462-N2-09 52.79 46.9 3777 0.01 0.0512 0.0033 0.0958 0.0057 0.0133 0.0002 92.9 5.3 85.5 1.5 D0462-N2-10 111.57 36.3 7941 0.00 0.0463 0.0025 0.0884 0.0042 0.0136 0.0003 86.0 3.9 87.1 1.6 D0462-N2-11 73.95 34.0 5224 0.01 0.0421 0.0026 0.0804 0.0044 0.0136 0.0003 78.5 4.2 87.0 1.6 D0462-N2-12 85.80 49.6 5805 0.01 0.0430 0.0028 0.0854 0.0052 0.0140 0.0003 83.2 4.9 89.8 1.7 D0462-N2-13 59.19 36.7 3980 0.01 0.0441 0.0029 0.0852 0.0050 0.0138 0.0003 83.0 4.7 88.1 1.7 D0462-N2-14 67.64 30.5 4574 0.01 0.0456 0.0030 0.0870 0.0049 0.0137 0.0002 84.7 4.6 87.9 1.5 D0462-N2-15 53.63 37.3 3592 0.01 0.0422 0.0030 0.0824 0.0058 0.0138 0.0003 80.4 5.4 88.4 1.8 D0462-N2-16 83.70 39.2 5466 0.01 0.0457 0.0026 0.0902 0.0050 0.0141 0.0003 87.7 4.6 90.1 1.8 D0462-N2-17 63.08 27.9 3801 0.01 0.0477 0.0030 0.0925 0.0054 0.0139 0.0002 89.8 5.0 88.9 1.6 D0462-N2-18 71.89 33.3 4795 0.01 0.0447 0.0025 0.0862 0.0045 0.0138 0.0003 83.9 4.2 88.5 1.8 D0462-N2-19 109.26 37.0 7164 0.01 0.0464 0.0024 0.0900 0.0046 0.0138 0.0002 87.5 4.3 88.4 1.4 D0462-N2-20 39.72 17.4 2609 0.01 0.0453 0.0030 0.0876 0.0058 0.0137 0.0003 85.3 5.4 87.9 2.1 D0462-N2-21 58.51 30.4 3761 0.01 0.0463 0.0031 0.0877 0.0057 0.0136 0.0002 85.3 5.3 87.2 1.5 D0462-N2-22 86.61 37.6 5477 0.01 0.0459 0.0026 0.0881 0.0045 0.0139 0.0003 85.7 4.2 89.2 1.7 D0462-N2-23 80.93 33.6 5062 0.01 0.0483 0.0028 0.0945 0.0052 0.0139 0.0002 91.6 4.9 89.2 1.4 D0462-N2-24 104.66 44.1 6591 0.01 0.0464 0.0026 0.0912 0.0049 0.0141 0.0003 88.6 4.5 90.5 1.9 D0458-N1-01 20.14 55.8 2013 0.03 0.0492 0.0014 0.0885 0.0025 0.0130 0.0001 86.1 2.4 83.5 0.8 D0458-N1-02 10.26 26.1 938 0.03 0.0487 0.0017 0.0935 0.0031 0.0139 0.0001 90.7 2.9 89.0 0.8 D0458-N1-03 13.82 79.1 1157 0.07 0.0485 0.0017 0.0919 0.0033 0.0137 0.0001 89.2 3.1 87.5 0.7 D0458-N1-04 220 1801 915 1.97 0.0520 0.0010 0.2705 0.0053 0.0376 0.0003 243 4.2 238 1.6 D0458-N1-05 54.3 160 417 0.38 0.0561 0.0012 0.5211 0.0121 0.0670 0.0008 426 8.1 418 4.7 D0458-N1-06 9.74 37.7 898 0.04 0.0480 0.0018 0.0895 0.0033 0.0135 0.0001 87.0 3.1 86.2 0.8 D0458-N1-07 119 390 618 0.63 0.0576 0.0012 0.5487 0.0108 0.0689 0.0005 444 7.1 429 3.1 D0458-N1-08 20.8 124 155 0.80 0.0530 0.0024 0.2830 0.0125 0.0389 0.0004 253 9.9 246 2.7 D0458-N1-09 17.5 68.4 698 0.10 0.0561 0.0020 0.1678 0.0128 0.0207 0.0011 157 11.1 132 7.1 D0458-N1-10 252 399 1113 0.36 0.0674 0.0013 1.1893 0.0259 0.1276 0.0015 796 12.0 774 8.7 D0458-N1-11 34.8 246 696 0.35 0.0505 0.0015 0.1881 0.0058 0.0269 0.0003 175 5.0 171 1.7 D0458-N1-12 126 2165 3564 0.61 0.0475 0.0011 0.0888 0.0021 0.0135 0.0001 86.3 1.9 86.5 0.9 D0458-N1-13 123 153 309 0.50 0.0741 0.0013 1.7895 0.0317 0.1744 0.0011 1042 11.6 1036 6.2 D0458-N1-14 481 187 283 0.66 0.2254 0.0031 17.1706 0.2306 0.5494 0.0042 2944 13.0 2823 17.6 D0458-N1-15 298 198 239 0.83 0.1239 0.0019 6.3827 0.0931 0.3715 0.0025 2030 12.9 2036 11.7 D0458-N1-16 60.8 83.2 130 0.64 0.0736 0.0016 1.7506 0.0401 0.1715 0.0017 1027 14.8 1020 9.4 D0458-N1-17 214 399 9733 0.04 0.0590 0.0011 0.1184 0.0027 0.0144 0.0002 114 2.5 92.0 1.0 D0458-N1-18 527 214 287 0.75 0.2893 0.0042 21.1059 0.3219 0.5255 0.0052 3143 14.9 2723 21.8 D0458-N1-19 12.24 53.9 875 0.06 0.0466 0.0020 0.0848 0.0036 0.0132 0.0002 82.7 3.4 84.3 1.1 D0458-N1-20 28.6 166 2449 0.07 0.0475 0.0011 0.0842 0.0019 0.0128 0.0001 82.1 1.8 82.2 0.8 细粒花岗质岩脉(D0458-N1)的锆石呈自形—半自形晶,大部分为纺锤状,少数为长柱状或短柱状,绝大多数晶形完整。锆石长轴直径为60~140 μm,长宽比为1∶1~2.5∶1。CL像显示,锆石具有清晰的振荡环带(图 2-b),U含量为155×10-6~9733×10-6,Th含量为26.1×10-6~2165×10-6,Th/U值为0.03~1.97,表明其为岩浆成因(吴元保等,2004)。样品D0458-N1共有20个测点。第一组13个测点获得较老的206Pb/238U年龄132~2823 Ma,该年龄范围广、差异大,可能为变质锆石或捕获围岩锆石的年龄。第二组7个测点获得的206Pb/238U年龄较一致(83~92 Ma),其年龄加权平均值为85.8±2.3 Ma(MSWD=8.6,n=7)(图 3-c、d),能够代表岩脉的侵位年龄。
4.2 全岩地球化学特征
4.2.1 主量元素
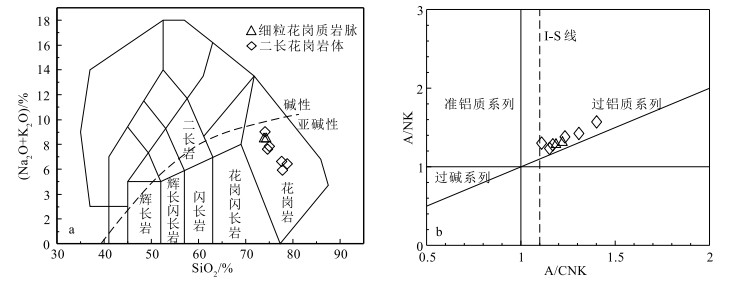
选取6件含电气石白云母二长花岗岩样品、2件细粒花岗质岩脉样品进行全岩地球化学测试。主量元素数据见表 2。含电气石白云母二长花岗岩样品SiO2含量为74.17%~78.88%,平均76.40%;Al2O3含量为12.61%~14.54%,平均13.91%;岩石全碱(Na2O+K2O)含量为5.92%~9.00%,平均7.24%;Na2O为3.58%~5.86%,K2O为0.76%~5.37%,CaO为0.47%~0.92%,MgO为0.15%~0.28%,Mg#值为32.3~73.1。在TAS图解(图 4-a)中,样品点均落入亚碱性花岗岩范围。里特曼指数δ为1.01~2.60(<3.3,计算公式为δ=[(K2O+Na2O)2]/ [(SiO2)-43]),表明岩体属于钙碱性系列。铝饱和指数(A/CNK)介于1.11~1.40之间,在A/CNK-A/NK图解(图 4-b)中落入过铝质系列区域。综上所述,含电气白云母二长花岗岩属强过铝质钙碱性花岗岩。
表 2 谢穷岩体和岩脉元素分析结果Table 2. Whole-rock element data of the pluton and dike from Xieqiong样品号 D0462-
H1D0462-
H2D0462-
H3D0462-
H4D0462-
H5D0462-
H6D0458-
H1D0458-
H2样品号 D0462-
H1D0462-
H2D0462-
H3D0462-
H4D0462-
H5D0462-
H6D0458-
H1D0458-
H2岩体 岩脉 岩体 岩脉 SiO2 77.71 75.09 77.87 78.88 74.17 74.70 74.20 73.81 Y 7.69 5.96 11.7 9.55 4.03 1.92 5.44 7.03 TiO2 0.03 0.04 0.03 0.03 0.01 0.06 0.04 0.08 Zr 39.3 28.8 30.2 20.2 10.9 30.8 24.8 30.9 Al2O3 13.39 14.49 13.35 12.61 14.54 15.13 14.58 14.54 Nb 19.4 22.0 18.4 5.64 16.7 31.4 25.3 26.5 TFe2O3 0.13 0.73 0.29 0.39 0.64 0.41 0.60 0.89 Sn 4.12 11.0 8.80 11.0 9.64 22.3 17.5 23.0 TFeO 0.12 0.65 0.26 0.35 0.58 0.37 0.54 0.80 Cs 2.29 8.97 5.00 4.46 11.9 21.0 20.8 23.3 FeO 0.10 0.56 0.22 0.30 0.49 0.31 0.46 0.68 Ba 15.6 25.4 33.8 56.5 5.54 31.8 114 119 Fe2O3 0.02 0.10 0.04 0.05 0.09 0.06 0.08 0.12 La 1.41 1.74 2.70 5.25 1.08 1.21 4.73 5.07 MnO 0.01 0.03 0.03 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.05 Ce 3.75 3.55 6.28 10.8 2.09 2.32 10.2 11.2 MgO 0.16 0.15 0.19 0.28 0.15 0.19 0.16 0.18 Pr 0.50 0.36 0.82 1.08 0.19 0.22 1.12 1.22 CaO 0.54 0.69 0.57 0.92 0.47 0.53 0.55 0.50 Nd 1.88 1.26 2.96 3.57 0.58 0.75 3.94 4.49 Na2O 5.86 3.58 3.70 4.88 3.63 4.25 3.72 3.19 Sm 0.91 0.55 1.41 1.13 0.27 0.28 1.24 1.52 K2O 0.76 4.27 2.22 1.55 5.37 3.36 4.79 5.32 Eu 0.061 0.11 0.11 0.17 0.031 0.039 0.22 0.24 P2O5 0.22 0.17 0.28 0.08 0.15 0.12 0.21 0.21 Gd 1.16 0.62 1.62 1.28 0.35 0.25 1.36 1.73 烧失量 1.25 0.98 1.62 0.65 0.57 1.10 0.77 0.82 Tb 0.27 0.18 0.39 0.28 0.12 0.059 0.25 0.35 总计 100.05 100.20 100.15 100.27 99.72 99.87 99.63 99.59 Dy 1.52 1.04 2.30 1.72 0.68 0.32 1.24 1.60 A/CNK 1.17 1.23 1.40 1.11 1.15 1.31 1.19 1.22 Ho 0.22 0.16 0.35 0.28 0.10 0.050 0.17 0.22 A/NK 1.28 1.38 1.57 1.30 1.23 1.42 1.29 1.32 Er 0.53 0.43 0.83 0.67 0.29 0.15 0.37 0.47 Na2O+K2O 6.62 7.84 5.92 6.43 9.00 7.61 8.50 8.51 Tm 0.076 0.068 0.12 0.087 0.045 0.028 0.048 0.060 K2O/Na2O 0.13 1.19 0.60 0.32 1.48 0.79 1.29 1.67 Yb 0.50 0.43 0.75 0.52 0.32 0.18 0.30 0.38 δ 1.26 1.92 1.01 1.15 2.60 1.83 2.32 2.35 Lu 0.071 0.064 0.096 0.072 0.038 0.029 0.036 0.049 Mg# 73.1 32.3 60.0 62.8 35.1 51.9 38.4 31.7 Hf 1.66 1.19 1.19 0.80 0.53 1.41 0.94 1.22 TZr 648.4 665.2 642.9 650.8 667.3 681.8 662.00 677.56 Ta 1.91 1.57 1.93 0.75 2.44 2.06 6.50 3.93 Li 8.05 26.7 13.4 11.4 39.9 57.4 8.34 19.2 Tl 0.33 1.36 0.77 0.43 2.11 2.00 1.87 2.18 Be 4.78 4.68 5.78 5.92 4.14 14.2 32.1 12.7 Pb 8.23 45.2 19.8 13.3 49.3 37.2 69.1 63.9 Sc 2.82 2.43 3.49 1.49 2.21 5.45 1.67 2.33 Th 0.72 0.79 1.41 3.04 0.43 0.57 2.59 2.49 V 3.19 1.52 2.05 3.52 0.92 1.93 3.05 3.16 U 1.66 19.9 4.37 1.11 1.33 11.1 8.77 8.54 Cr 0.98 1.08 0.91 0.95 0.86 1.07 1.20 1.19 LREE 8.52 7.57 14.27 21.95 4.25 4.82 21.47 23.78 Co 0.24 0.28 0.40 0.81 0.14 0.21 0.34 0.35 HREE 4.33 3.00 6.47 4.90 1.94 1.05 3.77 4.85 Ni 1.44 1.10 1.54 1.35 1.29 1.24 1.15 1.06 ΣREE 12.85 10.56 20.74 26.85 6.19 5.87 25.23 28.63 Cu 0.88 0.35 1.16 0.57 0.28 0.90 1.38 0.79 LREE/
HREE1.96 2.53 2.21 4.48 2.19 4.58 5.70 4.90 Zn 4.48 41.9 7.96 11.1 29.8 29.1 30.4 65.0 Ga 16.9 21.2 18.7 14.2 18.7 25.9 17.4 19.4 (La/Sm)N 0.97 1.97 1.20 2.91 2.49 2.70 2.39 2.08 Rb 46.9 267 136 85.5 374 360 327 375 (La/Yb)N 1.93 2.73 2.45 6.91 2.32 4.64 10.75 9.08 Sr 64.0 25.3 45.6 87.3 8.51 11.9 25.2 30.1 δEu 0.18 0.56 0.21 0.42 0.31 0.44 0.51 0.45 注:TZr为锆石饱和温度(℃)(Watson et al., 1983),主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 细粒花岗质岩脉样品SiO2含量为73.81%~74.42%,平均74.12%;Al2O3含量为14.54%~14.58%,平均14.56%;岩石全碱(Na2O+K2O)含量为8.50%~ 8.51%,Na2O含量为3.19%~3.72%,K2O含量为4.79%~5.32%,CaO含量为0.50%~0.55%,MgO含量为0.16%~0.18%,Mg#值为31.72~38.34。在TAS图解(图 4-a)中,样品点均落入花岗岩区域,属于亚碱性系列。里特曼指数δ=2.32~2.35(<3.3),为钙碱性。铝饱和指数(A/CNK)介于1.19~1.22之间,在A/CNK-A/NK图解(图 4-b)中,呈过铝质特征。综上所述,细粒花岗质岩脉属强过铝质钙碱性花岗岩。
4.2.2 微量和稀土元素
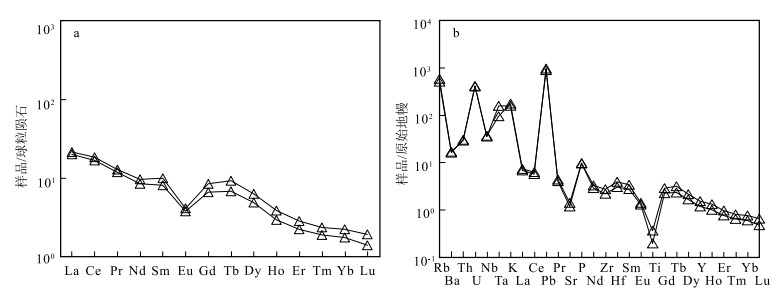
稀土和微量元素数据见表 2。岩体稀土元素总量(ΣREE)偏低,在5.87×10-6~26.85×10-6之间,轻、重稀土元素比值(LREE/HREE)为1.96~4.58,轻稀土元素相对富集。
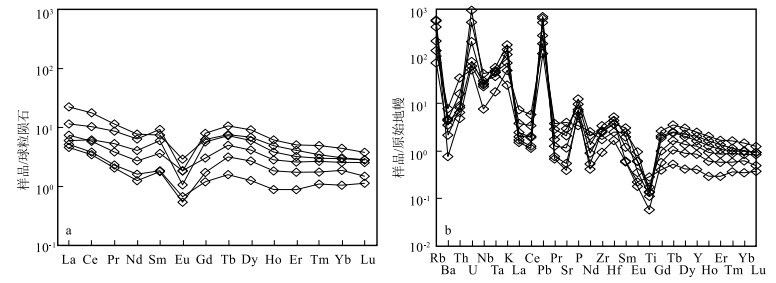
岩体的负Eu异常(图 5-a),表明岩浆源区有斜长石残留或是岩浆结晶分异过程中有大量斜长石分离结晶。在原始地幔标准化蛛网图(图 5-b)中,样品总体上富集Rb、U、K、P等大离子亲石元素(LILE),相对亏损Nb、Ta、Ti等高场强元素(HFSE)。
![]() 图 5 含电气石白云母二长花岗岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)和原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b, 标准化值据Sun et al.,1989)Figure 5. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element patterns(b) of the tourmaline-bearing muscovite monzogranite pluton
图 5 含电气石白云母二长花岗岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)和原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b, 标准化值据Sun et al.,1989)Figure 5. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element patterns(b) of the tourmaline-bearing muscovite monzogranite pluton岩脉稀土元素总量在25.23×10-6~28.63×10-6之间,轻、重稀土元素比值(LREE/HREE)为4.9~5.7,轻稀土元素相对富集((La/Yb)N=9.08~10.75)。在球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(图 6-a)上显示为右倾曲线,重稀土元素亏损明显,具有明显的负Eu异常(δEu=0.45~0.51)。从原始地幔标准化蛛网图(图 6-b)中可以看出,样品总体上富集Rb、U、K、Pb和P,相对亏损Ba、Nb、Ce和Ti。
5. 讨论
5.1 岩石成因类型与形成温压条件
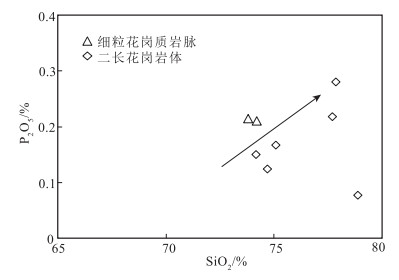
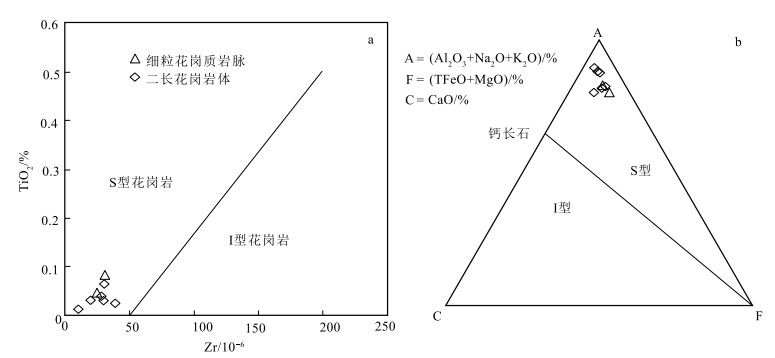
岩体和岩脉的样品具有高SiO2、Al2O3、K2O,低TiO2、Na2O、MnO和CaO的特征,均以强过铝质为主(A/CNK>1.1,图 4-b),稀土元素呈明显的四分组效应;强过铝质反映在造岩矿物上表现为出现较多高Al的原生矿物,如白云母、电气石等(刘经纬等,2017)(图版Ⅰ-d、e、f),具有陆壳重熔型花岗岩的特点。标准矿物计算中,所有样品均含刚玉分子(含量为1.43%~4.55%),表明属于铝和硅过饱和类型,显示出S型花岗岩的特征。在A型和I型花岗岩中,P2O5随着SiO2的增高而降低,并导致强分异型的A型和I型花岗岩的P2O5含量极低,而在S型花岗岩中却呈现P2O5含量随着SiO2的增加而呈增加或基本不变的趋势(Chappell,1999;李献华等,2007)。P2O5含量随着SiO2含量的增加而增加(图 7)。在ACF和Zr-TiO2判别图解(图 8)中,岩体和岩脉均落入S型花岗岩区,因此判定岩体和岩脉均为过铝质S型花岗岩。
![]() 图 8 岩体和脉体Zr-TiO2(a)图解和ACF图解(b, 底图据Fan et al., 2015a)Figure 8. Plots of the pluton and dike Zr-TiO2(a) and ACF(b)
图 8 岩体和脉体Zr-TiO2(a)图解和ACF图解(b, 底图据Fan et al., 2015a)Figure 8. Plots of the pluton and dike Zr-TiO2(a) and ACF(b)同时,样品与淡色花岗岩在岩石组合和地球化学特征方面具有高度的相似性。淡色花岗岩的典型矿物组合为石英+斜长石+钾长石+白云母±黑云母±电气石±石榴子石。常见副矿物包括磷灰石、锆石、独居石等,暗色矿物很少。典型的地球化学特征是主量元素含量稳定,SiO2≥72%、Al2O3≥14%、Na2O和K2O含量高,贫MgO、TFeO、TiO2等;微量元素总体高Rb,低Th、Sr和Ba,高Rb/Sr及低Sr/Y值等;稀土元素总量较一般花岗岩低,轻稀土元素轻度至中度富集,一般具负Eu异常。淡色花岗岩根据矿物组合的不同划分为3类:二云母或黑云母型、电气石型和石榴子石型。其中,电气石型淡色花岗岩是由变泥质岩在较低温度(≥640℃,350 Pa)下经白云母脱水熔融形成(Douce et al., 1998)。综合对比本文样品和电气石型淡色花岗岩在矿物组合(含电气石、白云母,不含黑云母)和形成机制(地壳加厚条件下变泥质岩在较低温度(岩体平均为676℃,岩脉平均为657℃)经白云母脱水熔融产生)两方面,笔者认为岩体岩脉与电气石型淡色花岗岩有较好的匹配性。
通过计算锆石饱和温度(Watson et al., 1983;2005),得到本文岩体全岩锆石饱和温度为594~681℃(平均为676℃), 岩脉全岩锆石饱和温度为648~665℃(平均为656℃)。
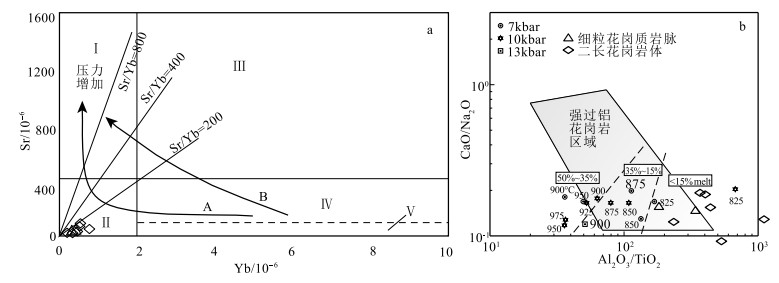
张旗等(2006)根据花岗岩中Sr=400×10-6、Yb=2×10-6为界,将其分为5种类型。压力的增加有2条途径:A为钠质系列,从低Sr高Yb型→低Sr低Yb型→高Sr低Yb型,压力逐渐增加;B为钾质系列(正长岩、钾玄岩),从低Sr高Yb型→高Sr高Yb型→高Sr低Yb型。本文样品的Sr(8.51×10-6~87.3×10-6)和Yb(0.30×10-6~4.66×10-6)含量较低,除个别样品的Yb含量大于2×10-6外,基本符合低Sr低Yb型,表明可能形成于中等压力条件,至少大于0.8 GPa,相应的形成深度为30 km(图 9-a)。在CaO/Na2O-Al2O3/TiO2图解(图 9-b)上,样品分布于高Al2O3/TiO2值范围,并具有中-低的CaO/Na2O值,表明可能在1 GPa左右的压力条件下产生了小于15%的熔体。
![]() 图 9 花岗岩Yb-Sr (a,据张旗等,2006修改)和Al2O3/TiO2-CaO/Na2O(b)图解Ⅰ—高Sr低Yb型;Ⅱ—低Sr高Yb型;Ⅲ—高Sr低Yb型;Ⅳ—低Sr高Yb型;Ⅴ—非常低Sr高Yb型Figure 9. The relationship between granite types and pressures(a) and Al2O3/TiO2-CaO/Na2O (b)diagram
图 9 花岗岩Yb-Sr (a,据张旗等,2006修改)和Al2O3/TiO2-CaO/Na2O(b)图解Ⅰ—高Sr低Yb型;Ⅱ—低Sr高Yb型;Ⅲ—高Sr低Yb型;Ⅳ—低Sr高Yb型;Ⅴ—非常低Sr高Yb型Figure 9. The relationship between granite types and pressures(a) and Al2O3/TiO2-CaO/Na2O (b)diagram5.2 岩浆源区
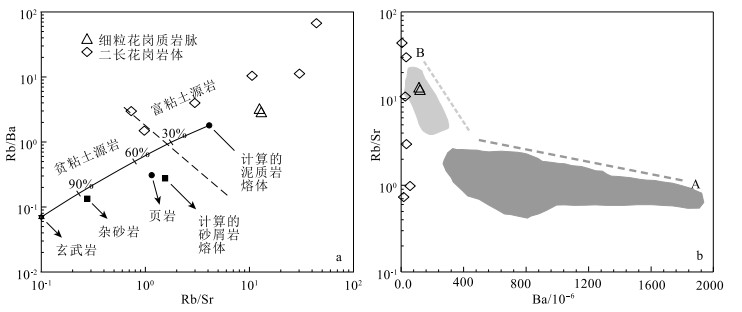
岩体和岩脉矿物特征和地球化学特征表明,二者都属于壳源强过铝质S型花岗岩。一般认为,以泥质岩和杂砂岩为源岩的副片麻岩是S型花岗岩的源岩。实验结果表明,在脱水熔融实验中,花岗岩熔体中的CaO/Na2O值与温度压力无关,主要受源岩成分控制(Jung et al., 2007)。由于泥质岩贫斜长石,如果斜长石完全消失,Na2O会逐渐富集到熔体中,而CaO会较多地集中在残余相(角闪石、单斜辉石)中。因此,以泥质为源岩的熔体CaO/Na2O值偏低(<0.3),而且,泥质岩为源岩的熔体Rb/Ba>0.25,Rb/Sr>2.6(Miller,1985;Harris et al., 1992)。本文岩体和岩脉的CaO/Na2O值除1个样品外,均小于0.3。根据岩体较高的Rb/Sr(0.73~43.95)和Rb/Ba(1.51~67.54)值推测,其源岩可能为泥质岩。此外,富集于长石和云母中的Sr、Rb、Ba含量及其比值也可以作为反映源区性质的标志(Zeng et al., 2005;2011;郭素淑等,2007)。在Rb/Ba-Rb/Sr判别图解(图 10-a)中,样品数据投点落入富粘土源岩的区域,与上述推测一致。综上,岩体与岩脉的源区为泥质岩区。
![]() 图 10 岩体与脉体Rb/Sr-Rb/Ba(a)图解和Ba-Rb/Sr关系图(b, 据王中刚,1989修改)A—水致白云母部分熔融;B—白云母脱水部分熔融Figure 10. Rb/Sr vs.Rb/Ba(a) and Ba vs.Rb/Sr(b)diagrams of the pluton and dike
图 10 岩体与脉体Rb/Sr-Rb/Ba(a)图解和Ba-Rb/Sr关系图(b, 据王中刚,1989修改)A—水致白云母部分熔融;B—白云母脱水部分熔融Figure 10. Rb/Sr vs.Rb/Ba(a) and Ba vs.Rb/Sr(b)diagrams of the pluton and dike曾令森等(2017)通过系统的研究将早中新世各类淡色花岗岩分为4类,即A类(水致白云母部分熔融)、B类(白云母脱水部分熔融)、C类(堆晶淡色花岗岩)和F类(高度分异淡色花岗岩)。本文岩体和岩脉的SiO2(73.81%~78.88%)、Al2O3含量(12.61%~15.13%)变化范围较小,FeO(0.12~1.10)、MgO(0.15~0.46)、MnO(0.01~0.05)和TiO2(0.01~0.14)含量都较低。A/CNK值大于1.0,高达1.35。除个别样品外,多数样品的Na2O/K2O值小于1.0,CaO小于0.9%。稀土元素地球化学特征表现为轻、重稀土元素分馏明显,轻稀土元素富集,亏损重稀土元素,(La/Yb)N=1.47~10.75;明显的负Eu异常(Eu/Eu*=0.06~0.43)。在Ba-Rb/Sr图解(图 10-b)上,Rb/Sr值与Ba呈负相关关系。综上可见,变泥质岩具有白云母脱水部分熔融(B类)的特征。
二长花岗岩体和岩脉源自白云母脱水部分熔融,在该过程中温度和压力是主控因素。岩体和岩脉的锆石饱和温度平均值分别为676℃和657℃,这一温度低于白云母脱水熔融的温度(720~770℃)(Patiño et al., 1998)。在缺少深部热源证据和剪切摩擦生热、地壳中放射性同位素衰变无法产生大规模岩浆作用的情况下(Nabelek et al., 2004),减压成为部分熔融的必要条件。
发育于喜马拉雅带藏南拆离系(STDS)的淡色花岗岩,为典型的S型花岗岩,其岩石成因受到STDS的控制,为大喜马拉雅结晶杂岩(GHC)变泥质岩无水条件下白云母脱水熔融的产物(王晓先等,2016)。将本文样品与之类比,在岩石地球化学特征相吻合的条件下,本文样品与该淡色花岗岩有相似的成因。综上所述,岩体和岩脉可能为构造减压导致的上地壳变泥质岩中含水矿物(白云母)脱水熔融的产物。
5.3 构造意义
班公湖-怒江特提斯洋的发展演化时间线为:晚三叠世—早侏罗世裂解扩展形成成熟洋盆,中侏罗世洋壳俯冲消减,直到晚侏罗世—早白垩世闭合。雍永源等(2000)提出,班公湖-怒江特提斯的消亡呈现东西向的穿时性,即班公湖-怒江缝合带东部在侏罗纪已经闭合,至晚白垩世进入碰撞后阶段,与该带东段丁青蛇绿岩及其沉积盖层(王建平等,2002)与古地磁(曹勇等,2020)证据所得出的结果一致。而夹持于羌塘地块与冈底斯地块之间的班公湖-怒江缝合带同样是研究特提斯地质演化和青藏高原隆升机制及其造山带地壳演化历史的重要窗口(邹光富,1996)。研究表明,研究区由缝合带形成的深大断裂在新特提斯洋俯冲过程中仍可能活化,刘俊等(2019)对类乌齐-左贡成矿带内的拉荣钨钼矿进行了详细研究,获得辉钼矿Re-Os等时线年龄为90±2.1 Ma,表明该矿床的成矿时代为晚白垩世,成矿带内深大断裂、褶皱构造十分发育。其中还大量发育岩浆岩,明显受到印支期-喜马拉雅期板块俯冲消减和碰撞活动的制约(刘英超等,2013)。
前人研究表明,南羌塘地区存在晚白垩世的岩浆活动。比如双湖地区的花岗斑岩形成于晚白垩世晚期(78.3±0.4 Ma),可能起源于伸展背景下的新生地壳的部分熔融(李发桥等,2018);在缝合带西部班公湖地区发现的日松花岗闪长岩体和甲维花岗闪长岩脉、花岗闪长玢岩脉锆石U-Pb年龄分别为82 Ma、90.7 Ma和82.9 Ma,形成于后碰撞初期,为中特提斯洋闭合后板内热隆伸展、壳幔相互作用的产物,也是班公湖地区由板块构造体制转向板内构造体制的标志(张硕等,2014);与以上研究同期产生的岩浆作用同样在缝合带南部的拉萨地块也有报道,刘函等(2015)在拉萨地块日土地区发现晚白垩世(82~84 Ma)的岩浆作用,研究表明,该期岩浆作用整体为后碰撞背景,其中琼贡二长花岗岩与拆沉作用导致的软流圈地幔上涌引发的玄武质岩浆底侵作用有关;班戈地区晚白垩世二长花岗岩(80 Ma)的发现表明,班公湖-怒江洋在晚白垩世进入了后碰撞阶段(高顺宝等,2011),同一地区的雪如岩体中的似斑状二长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄为76 Ma,为后碰撞伸展环境下中地壳部分熔融的产物,表明班公湖-怒江缝合带已进入后碰撞伸展阶段(鲁洪涛等,2020);Wang et al. (2014)在尼玛东南部地区发现的90 Ma富镁安山岩,与拉萨和羌塘闭合后的岩石圈拆沉有关。由此可见,南羌塘地体和拉萨地体碰撞后的伸展作用在班公湖-怒江缝合带及其两侧拉萨地块和南羌塘地块普遍存在。Hu et al.(2019)在类乌齐地区发现晚白垩世(92~89 Ma)具有高Sr/Y值特征的I型花岗岩,其可能是下地壳增厚部分熔融的产物及中部地区发现的晚白垩世(75~79 Ma)形成于后碰撞环境的火山岩(Li et al., 2013),可能与俯冲下地壳的深熔作用或幔源基性岩浆的底侵作用有关。由此表明,南羌塘地体地壳在晚白垩世已经显著增厚,构造活动强烈。
藏东地区晚白垩世的岩浆活动表明,早白垩世末该地区的地球动力学背景发生了突变。综合区域地质资料表明(Wilson et al., 2011;Tian et al., 2014;Leng et al., 2018),晚白垩世藏东地区具有相同的地球动力学背景,约76 Ma侵位于东羌塘地体的如多正长岩和邦达A型花岗岩即形成于伸展背景下。此外,该正长岩中的继承锆石年龄(87.8~83.8 Ma)表明藏东地区岩浆活动发生得较早,同样向伸展环境的转变也较早(Wang et al., 2019)。本文中88~85 Ma的花岗岩和岩脉则表明藏东左贡地块同样经历了该期伸展作用,可能标志着地壳缩短增厚挤压环境向地壳伸展减薄环境的转换。
6. 结论
(1) 藏东类乌齐谢穷地区酉西岩群中含电气石白云母二长花岗岩体和细粒花岗质岩脉LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年结果分别为88.3±0.9 Ma和85.8±2.3 Ma,表明岩浆活动集中在晚白垩世。
(2) 二长花岗岩体和岩脉的地球化学特征相似,具有富碱、强过铝质与钙碱性的特征;岩体和岩脉稀土元素配分曲线表现出强烈的负Eu异常,岩体与岩脉的形成温度近似值为654℃。
(3) 岩体和岩脉是地壳缩短增厚挤压环境向地壳伸展减薄环境转换条件下的产物,为地壳变泥质岩中含水矿物(白云母)脱水熔融的S型花岗岩。
致谢: 野外工作得到中国地质调查局成都地质调查中心张士贞、李俊、苟正彬工程师的帮助,在此一并致以衷心的感谢,并感谢审稿专家的意见和建议。 -
图 1 研究区大地构造位置(a,据王保弟等,2011修改) 及地质简图(b)
Figure 1. Tectonic position(a) and sketch geological map(b)of the study area
图 4 岩体和脉体TAS图解(a,据Middlemost et al., 1972)和A/CNK-A/NK图解(b, 据Shand et al., 1927)
Figure 4. TAS(a) and A/CNK-A/NK(b) diagrams of pluton and dike
图 5 含电气石白云母二长花岗岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)和原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b, 标准化值据Sun et al.,1989)
Figure 5. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element patterns(b) of the tourmaline-bearing muscovite monzogranite pluton
图 8 岩体和脉体Zr-TiO2(a)图解和ACF图解(b, 底图据Fan et al., 2015a)
Figure 8. Plots of the pluton and dike Zr-TiO2(a) and ACF(b)
图 9 花岗岩Yb-Sr (a,据张旗等,2006修改)和Al2O3/TiO2-CaO/Na2O(b)图解
Ⅰ—高Sr低Yb型;Ⅱ—低Sr高Yb型;Ⅲ—高Sr低Yb型;Ⅳ—低Sr高Yb型;Ⅴ—非常低Sr高Yb型
Figure 9. The relationship between granite types and pressures(a) and Al2O3/TiO2-CaO/Na2O (b)diagram
图 10 岩体与脉体Rb/Sr-Rb/Ba(a)图解和Ba-Rb/Sr关系图(b, 据王中刚,1989修改)
A—水致白云母部分熔融;B—白云母脱水部分熔融
Figure 10. Rb/Sr vs.Rb/Ba(a) and Ba vs.Rb/Sr(b)diagrams of the pluton and dike
表 1 谢穷岩体和岩脉LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb分析结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb analysis data for pluton and dyke from Xieqiong
测点号 含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Pb Th U 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ D0462-N2-01 100.66 101.2 7273 0.01 0.0492 0.0027 0.0952 0.0053 0.0138 0.0003 92.3 4.9 88.1 1.7 D0462-N2-02 79.69 42.3 5354 0.01 0.0508 0.0030 0.0997 0.0054 0.0142 0.0003 96.5 5.0 90.6 1.8 D0462-N2-03 90.22 53.3 6335 0.01 0.0471 0.0025 0.0930 0.0047 0.0141 0.0002 90.3 4.4 90.0 1.6 D0462-N2-04 79.34 42.8 5654 0.01 0.0478 0.0025 0.0925 0.0046 0.0138 0.0002 89.8 4.2 88.6 1.5 D0462-N2-05 63.79 26.7 4546 0.01 0.0472 0.0026 0.0907 0.0046 0.0138 0.0002 88.2 4.2 88.5 1.6 D0462-N2-06 52.61 28.8 3718 0.01 0.0449 0.0028 0.0892 0.0056 0.0139 0.0002 86.7 5.2 89.2 1.3 D0462-N2-07 94.48 55.4 6530 0.01 0.0455 0.0023 0.0895 0.0044 0.0139 0.0003 87.1 4.1 89.2 1.6 D0462-N2-08 80.99 40.2 5660 0.01 0.0460 0.0024 0.0887 0.0045 0.0137 0.0002 86.3 4.2 87.4 1.5 D0462-N2-09 52.79 46.9 3777 0.01 0.0512 0.0033 0.0958 0.0057 0.0133 0.0002 92.9 5.3 85.5 1.5 D0462-N2-10 111.57 36.3 7941 0.00 0.0463 0.0025 0.0884 0.0042 0.0136 0.0003 86.0 3.9 87.1 1.6 D0462-N2-11 73.95 34.0 5224 0.01 0.0421 0.0026 0.0804 0.0044 0.0136 0.0003 78.5 4.2 87.0 1.6 D0462-N2-12 85.80 49.6 5805 0.01 0.0430 0.0028 0.0854 0.0052 0.0140 0.0003 83.2 4.9 89.8 1.7 D0462-N2-13 59.19 36.7 3980 0.01 0.0441 0.0029 0.0852 0.0050 0.0138 0.0003 83.0 4.7 88.1 1.7 D0462-N2-14 67.64 30.5 4574 0.01 0.0456 0.0030 0.0870 0.0049 0.0137 0.0002 84.7 4.6 87.9 1.5 D0462-N2-15 53.63 37.3 3592 0.01 0.0422 0.0030 0.0824 0.0058 0.0138 0.0003 80.4 5.4 88.4 1.8 D0462-N2-16 83.70 39.2 5466 0.01 0.0457 0.0026 0.0902 0.0050 0.0141 0.0003 87.7 4.6 90.1 1.8 D0462-N2-17 63.08 27.9 3801 0.01 0.0477 0.0030 0.0925 0.0054 0.0139 0.0002 89.8 5.0 88.9 1.6 D0462-N2-18 71.89 33.3 4795 0.01 0.0447 0.0025 0.0862 0.0045 0.0138 0.0003 83.9 4.2 88.5 1.8 D0462-N2-19 109.26 37.0 7164 0.01 0.0464 0.0024 0.0900 0.0046 0.0138 0.0002 87.5 4.3 88.4 1.4 D0462-N2-20 39.72 17.4 2609 0.01 0.0453 0.0030 0.0876 0.0058 0.0137 0.0003 85.3 5.4 87.9 2.1 D0462-N2-21 58.51 30.4 3761 0.01 0.0463 0.0031 0.0877 0.0057 0.0136 0.0002 85.3 5.3 87.2 1.5 D0462-N2-22 86.61 37.6 5477 0.01 0.0459 0.0026 0.0881 0.0045 0.0139 0.0003 85.7 4.2 89.2 1.7 D0462-N2-23 80.93 33.6 5062 0.01 0.0483 0.0028 0.0945 0.0052 0.0139 0.0002 91.6 4.9 89.2 1.4 D0462-N2-24 104.66 44.1 6591 0.01 0.0464 0.0026 0.0912 0.0049 0.0141 0.0003 88.6 4.5 90.5 1.9 D0458-N1-01 20.14 55.8 2013 0.03 0.0492 0.0014 0.0885 0.0025 0.0130 0.0001 86.1 2.4 83.5 0.8 D0458-N1-02 10.26 26.1 938 0.03 0.0487 0.0017 0.0935 0.0031 0.0139 0.0001 90.7 2.9 89.0 0.8 D0458-N1-03 13.82 79.1 1157 0.07 0.0485 0.0017 0.0919 0.0033 0.0137 0.0001 89.2 3.1 87.5 0.7 D0458-N1-04 220 1801 915 1.97 0.0520 0.0010 0.2705 0.0053 0.0376 0.0003 243 4.2 238 1.6 D0458-N1-05 54.3 160 417 0.38 0.0561 0.0012 0.5211 0.0121 0.0670 0.0008 426 8.1 418 4.7 D0458-N1-06 9.74 37.7 898 0.04 0.0480 0.0018 0.0895 0.0033 0.0135 0.0001 87.0 3.1 86.2 0.8 D0458-N1-07 119 390 618 0.63 0.0576 0.0012 0.5487 0.0108 0.0689 0.0005 444 7.1 429 3.1 D0458-N1-08 20.8 124 155 0.80 0.0530 0.0024 0.2830 0.0125 0.0389 0.0004 253 9.9 246 2.7 D0458-N1-09 17.5 68.4 698 0.10 0.0561 0.0020 0.1678 0.0128 0.0207 0.0011 157 11.1 132 7.1 D0458-N1-10 252 399 1113 0.36 0.0674 0.0013 1.1893 0.0259 0.1276 0.0015 796 12.0 774 8.7 D0458-N1-11 34.8 246 696 0.35 0.0505 0.0015 0.1881 0.0058 0.0269 0.0003 175 5.0 171 1.7 D0458-N1-12 126 2165 3564 0.61 0.0475 0.0011 0.0888 0.0021 0.0135 0.0001 86.3 1.9 86.5 0.9 D0458-N1-13 123 153 309 0.50 0.0741 0.0013 1.7895 0.0317 0.1744 0.0011 1042 11.6 1036 6.2 D0458-N1-14 481 187 283 0.66 0.2254 0.0031 17.1706 0.2306 0.5494 0.0042 2944 13.0 2823 17.6 D0458-N1-15 298 198 239 0.83 0.1239 0.0019 6.3827 0.0931 0.3715 0.0025 2030 12.9 2036 11.7 D0458-N1-16 60.8 83.2 130 0.64 0.0736 0.0016 1.7506 0.0401 0.1715 0.0017 1027 14.8 1020 9.4 D0458-N1-17 214 399 9733 0.04 0.0590 0.0011 0.1184 0.0027 0.0144 0.0002 114 2.5 92.0 1.0 D0458-N1-18 527 214 287 0.75 0.2893 0.0042 21.1059 0.3219 0.5255 0.0052 3143 14.9 2723 21.8 D0458-N1-19 12.24 53.9 875 0.06 0.0466 0.0020 0.0848 0.0036 0.0132 0.0002 82.7 3.4 84.3 1.1 D0458-N1-20 28.6 166 2449 0.07 0.0475 0.0011 0.0842 0.0019 0.0128 0.0001 82.1 1.8 82.2 0.8 表 2 谢穷岩体和岩脉元素分析结果
Table 2 Whole-rock element data of the pluton and dike from Xieqiong
样品号 D0462-
H1D0462-
H2D0462-
H3D0462-
H4D0462-
H5D0462-
H6D0458-
H1D0458-
H2样品号 D0462-
H1D0462-
H2D0462-
H3D0462-
H4D0462-
H5D0462-
H6D0458-
H1D0458-
H2岩体 岩脉 岩体 岩脉 SiO2 77.71 75.09 77.87 78.88 74.17 74.70 74.20 73.81 Y 7.69 5.96 11.7 9.55 4.03 1.92 5.44 7.03 TiO2 0.03 0.04 0.03 0.03 0.01 0.06 0.04 0.08 Zr 39.3 28.8 30.2 20.2 10.9 30.8 24.8 30.9 Al2O3 13.39 14.49 13.35 12.61 14.54 15.13 14.58 14.54 Nb 19.4 22.0 18.4 5.64 16.7 31.4 25.3 26.5 TFe2O3 0.13 0.73 0.29 0.39 0.64 0.41 0.60 0.89 Sn 4.12 11.0 8.80 11.0 9.64 22.3 17.5 23.0 TFeO 0.12 0.65 0.26 0.35 0.58 0.37 0.54 0.80 Cs 2.29 8.97 5.00 4.46 11.9 21.0 20.8 23.3 FeO 0.10 0.56 0.22 0.30 0.49 0.31 0.46 0.68 Ba 15.6 25.4 33.8 56.5 5.54 31.8 114 119 Fe2O3 0.02 0.10 0.04 0.05 0.09 0.06 0.08 0.12 La 1.41 1.74 2.70 5.25 1.08 1.21 4.73 5.07 MnO 0.01 0.03 0.03 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.05 Ce 3.75 3.55 6.28 10.8 2.09 2.32 10.2 11.2 MgO 0.16 0.15 0.19 0.28 0.15 0.19 0.16 0.18 Pr 0.50 0.36 0.82 1.08 0.19 0.22 1.12 1.22 CaO 0.54 0.69 0.57 0.92 0.47 0.53 0.55 0.50 Nd 1.88 1.26 2.96 3.57 0.58 0.75 3.94 4.49 Na2O 5.86 3.58 3.70 4.88 3.63 4.25 3.72 3.19 Sm 0.91 0.55 1.41 1.13 0.27 0.28 1.24 1.52 K2O 0.76 4.27 2.22 1.55 5.37 3.36 4.79 5.32 Eu 0.061 0.11 0.11 0.17 0.031 0.039 0.22 0.24 P2O5 0.22 0.17 0.28 0.08 0.15 0.12 0.21 0.21 Gd 1.16 0.62 1.62 1.28 0.35 0.25 1.36 1.73 烧失量 1.25 0.98 1.62 0.65 0.57 1.10 0.77 0.82 Tb 0.27 0.18 0.39 0.28 0.12 0.059 0.25 0.35 总计 100.05 100.20 100.15 100.27 99.72 99.87 99.63 99.59 Dy 1.52 1.04 2.30 1.72 0.68 0.32 1.24 1.60 A/CNK 1.17 1.23 1.40 1.11 1.15 1.31 1.19 1.22 Ho 0.22 0.16 0.35 0.28 0.10 0.050 0.17 0.22 A/NK 1.28 1.38 1.57 1.30 1.23 1.42 1.29 1.32 Er 0.53 0.43 0.83 0.67 0.29 0.15 0.37 0.47 Na2O+K2O 6.62 7.84 5.92 6.43 9.00 7.61 8.50 8.51 Tm 0.076 0.068 0.12 0.087 0.045 0.028 0.048 0.060 K2O/Na2O 0.13 1.19 0.60 0.32 1.48 0.79 1.29 1.67 Yb 0.50 0.43 0.75 0.52 0.32 0.18 0.30 0.38 δ 1.26 1.92 1.01 1.15 2.60 1.83 2.32 2.35 Lu 0.071 0.064 0.096 0.072 0.038 0.029 0.036 0.049 Mg# 73.1 32.3 60.0 62.8 35.1 51.9 38.4 31.7 Hf 1.66 1.19 1.19 0.80 0.53 1.41 0.94 1.22 TZr 648.4 665.2 642.9 650.8 667.3 681.8 662.00 677.56 Ta 1.91 1.57 1.93 0.75 2.44 2.06 6.50 3.93 Li 8.05 26.7 13.4 11.4 39.9 57.4 8.34 19.2 Tl 0.33 1.36 0.77 0.43 2.11 2.00 1.87 2.18 Be 4.78 4.68 5.78 5.92 4.14 14.2 32.1 12.7 Pb 8.23 45.2 19.8 13.3 49.3 37.2 69.1 63.9 Sc 2.82 2.43 3.49 1.49 2.21 5.45 1.67 2.33 Th 0.72 0.79 1.41 3.04 0.43 0.57 2.59 2.49 V 3.19 1.52 2.05 3.52 0.92 1.93 3.05 3.16 U 1.66 19.9 4.37 1.11 1.33 11.1 8.77 8.54 Cr 0.98 1.08 0.91 0.95 0.86 1.07 1.20 1.19 LREE 8.52 7.57 14.27 21.95 4.25 4.82 21.47 23.78 Co 0.24 0.28 0.40 0.81 0.14 0.21 0.34 0.35 HREE 4.33 3.00 6.47 4.90 1.94 1.05 3.77 4.85 Ni 1.44 1.10 1.54 1.35 1.29 1.24 1.15 1.06 ΣREE 12.85 10.56 20.74 26.85 6.19 5.87 25.23 28.63 Cu 0.88 0.35 1.16 0.57 0.28 0.90 1.38 0.79 LREE/
HREE1.96 2.53 2.21 4.48 2.19 4.58 5.70 4.90 Zn 4.48 41.9 7.96 11.1 29.8 29.1 30.4 65.0 Ga 16.9 21.2 18.7 14.2 18.7 25.9 17.4 19.4 (La/Sm)N 0.97 1.97 1.20 2.91 2.49 2.70 2.39 2.08 Rb 46.9 267 136 85.5 374 360 327 375 (La/Yb)N 1.93 2.73 2.45 6.91 2.32 4.64 10.75 9.08 Sr 64.0 25.3 45.6 87.3 8.51 11.9 25.2 30.1 δEu 0.18 0.56 0.21 0.42 0.31 0.44 0.51 0.45 注:TZr为锆石饱和温度(℃)(Watson et al., 1983),主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 -
Chappell B W. Aluminium saturation in I and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46: 535-551. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00086-3
Dewey J F, Sun Y. The Tectonic Evolution of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Royal Society of London Philosophical Transactions, 1988, 327(1594): 379-413.
Douce A E P, Harris N. Experimental constraints on Himalayan Anatexis[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1998, 39(4): 689-710. doi: 10.1093/petroj/39.4.689
Fan J J, Li C, Xie C M, et al. Petrology, geochemistry, and geochro-nology of the Zhonggang ocean island, northern Tibet: Implications for the evolution of the Banggongco-Nujiang oceanic arm of the Neo-Tethys[J]. International Geology Review, 2014, 56(12): 1504-1520. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2014.947639
Fan J J, Li C, Liu Y M. Age and nature of the late Early Cretaceous Zhaga Formation, northern Tibet: constraints on when the Bangong-Nujiang Neo-Tethys Ocean closed[J]. International Geology Review, 2015a, 57(3): 342-353. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2015.1006695
Fan J J, Li C, Xie C M. Petrology and U-Pb zircon geochronology of bimodal volcanic rocks from the Maierze Group, northern Tibet: Constraints on the timing of closure of the Banggong-Nujiang Ocean[J]. Lithos, 2015b, 227: 148-160. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.03.021
Guo R H, Li S Z, Yu S Y, et al. Collisional processes between the Qiangtang Block and the Lhasa Block: Insights from structural analysis of the Bangong-Nujiang Suture Zone, central Tibet[J]. Geological Journal, 2019, 54(2): 946-960. doi: 10.1002/gj.3420
Hao L L, Wang Q, Zhang C F, et al. Oceanic plateau subduction during closure of the Bangong-Nujiang Tethyan Ocean: Insights from central Tibetan volcanic rocks[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2018, 131(5/6): 864-880.
Harris N B W, Inger S. Trace element modelling of pelite derived granites[J]. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 1992, 110: 46-56. doi: 10.1007/BF00310881
Hu P Y, Zhai Q G, Wang J, et al. Crustal Thickening of the South Qiangtang Terrane, Tibetan Plateau: Constraint from Late Cretaceous High-Sr/Y Granitic Rocks[J]. The Journal of Geology, 2019, 127(4): 457-473. doi: 10.1086/703527
Jung S, Pfander F J A. Source composition and melting temperatures of orogenic granitoids: Constraints from CaO/Na2O, Al2O3/TiO2 and accessory mineral saturation thermometry[J]. Eur. J. Mineral, 2007, 19: 859-870. doi: 10.1127/0935-1221/2007/0019-1774
Kapp P, Decelles P G, Gehrels G E, et al. Geological records of the Lhasa Qiangtang and Indo-Asian collisions in the Nima area of central Tibet[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2007, 119(7/8): 917-933.
Leng C B, Cooke D R, Hou Z Q, et al. Quantifying exhumation at the Giant Pulang Porphyry Cu-Au deposit using U-Pb-He dating[J]. Economic Geology, 2018, 113(5): 1077-1092. doi: 10.5382/econgeo.2018.4582
Li Y L, He J, Wang C S, et al. Late Cretaceous K-rich magmatism in central Tibet: Evidence for early elevation of the Tibetan plateau?[J]Lithos, 2013, 160-161: 1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.11.019
Liu Y S, Hu Z C, GaoS, et al. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 257(1/2): 34-43.
Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons of mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51(1/2): 537-571.
Ludwig K R. ISOPLOT 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley Geochronology Center, California, Berkeley, 2003.
Middlemost E A. A simple classification of volcanic rocks[J]. Bulletin Volcannlogique, 1972, 36(2): 382-397. doi: 10.1007/BF02596878
Miller C F. Are strongly peraluminous magmas derived from pelitic sedimentary sources?[J]. Journal of Geololy, 1985, 93: 673-689. doi: 10.1086/628995
Nabelek P I, Liu M. Petrologic and thermal constraints on the ori-gin of leucogranites in collisional orogens[J]. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh: Earth Sciences, 2004, 95: 73-85.
Pan G T, Wang L Q, Li R S, et al. Tectonic evolution of the Qinghai Tibet plateau[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 53: 3-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.12.018
Patiño D A E, Nigel H. Experimental Constraints on Himalayan Anatexis[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1998, 39(4): 689-710. doi: 10.1093/petroj/39.4.689
Shand S J. On the relations between silica, alumina, and the bases in eruptive rocks, considered as a means of classification[J]. Geological Magazine, 1927, 64(10): 446-449. doi: 10.1017/S0016756800103760
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics in ocean basalt: Implicationfor mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society of London Special Publications, 1989, 42: 313-345.
Tian Y T, Kohn B P, Hu S B, et al. Postorogenic rigid behavior of the eastern Songpan-Ganze terrane: Insights from low-temperature thermochronology and implications for intracontinental deformation in central Asia[J]. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 2014, 15, 453-474. doi: 10.1002/2013GC004951
Wang Q, Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, et al. Origin of the ca. 90Ma magnesia-rich volcanic rocks in SE Nyima, central Tibet: Products of lithospheric delamination beneath the Lhasa-Qiangtang collision zone[J]. Lithos, 2014, 198/199: 24-37. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.03.019
Wang X S, Williams-Jones A E, Bi X W, et al. Late Cretaceous Transtension in the Eastern Tibetan Plateau: Evidence FromPostcollisional A-Type Granite and Syenite in the Changdu Area, China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2019, 124(7): 6409-6427. doi: 10.1029/2018JB017072
Watson E B, Harrison T M. Zircon saturation revisited temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983, 64: 295-304. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(83)90211-X
Watson E B, Harrison T M. Zircon thermometer reveals minimum melting conditions on earliest Earth[J]. Science, 2005, 308(5723): 841-844. doi: 10.1126/science.1110873
Wilson C J L, Fowler A P. Denudational response to surface uplift in east Tibet: Evidence from apatite fission-track thermochronology[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2011, 123(9/10): 1966-1987.
Yin A, Harrison M T. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan Tibet an orogen[J]. Annual Review of Earth & Planetary Science, 2000, 28(1): 211-280.
Zeng L S, Asimow P, Saleeby J B. Coupling of anatectic reactions and dissolution of accessory phases and the Sr and Nd isotope systematics of anatectic melts from a metasedimentary source[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2005, 69(14): 3671-3682. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2005.02.035
Zeng L S, Gao L E, Xie K J, et al. Mid-Eocene high Sr/Y granites in the Northern Himalayan Gneiss Domes: Melting thickened lower continental crust[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 303(3/4): 251-266.
Zong K Q, Klemd R, Yuan Y, et al. The assembly of Rodinia: The correlation of early Neoproterozoic(ca. 900 Ma)high-grade metamorphism and continental arc formation in the southern Beishan Orogen, southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt(CAOB)[J]. Precambrian Research, 2017, 290: 32-48. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2016.12.010
Zhang K J. Secular geochemical variations of the Lower Cretaceous siliciclastic rocks from central Tibet(China)indicate a tectonic transition from continental collision to back-arc rifting[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 229: 73-89. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2004.10.030
Zhang Y X, Li Z W, Yang W G, et al. Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous episodic development of the Bangong Meso-Tethyan subduction: Evidence from elemental and Sr-Nd isotopic geochemistry of arc magmatic rocks, Gaize region, central Tibet, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 135: 212-242. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.12.043
曹勇, 孙知明, 李海兵. 班公湖-怒江缝合带东段晚白垩世红层古地磁研究及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(10): 3243-3255. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202010018.htm 高顺宝, 郑有业, 王进寿, 等. 西藏班戈地区侵入岩年代学和地球化学: 对班公湖-怒江洋盆演化时限的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(7): 1973-1982. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201107007.htm 郭素淑, 李曙光. 淡色花岗岩的岩石学和地球化学特征及其成因[J]. 地学前缘, 2007, 14(6): 290-298. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.06.036 李才, 谢尧武, 董永胜. 北澜沧江带的性质——是冈瓦纳板块与扬子板块的界线吗?[J]. 地质通报, 2009, 28(12): 1711-1719. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.12.004 李发桥, 刘治博, 唐菊兴, 等. 西藏玛日埃错地区花岗斑岩岩石成因及其对班公湖-怒江缝合带中段演化的制约[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(4): 1051-1069. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201804009.htm 李献华, 李武显, 李正祥. 再论南岭燕山早期花岗岩的成因类型与构造意[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 529: 981-991. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2007.09.001 刘函, 王保弟, 陈莉, 等. 拉萨地块西北日土花岗岩基锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及构造意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2015, 39(6): 1141-1155. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201506015.htm 刘经纬, 陈斌, 陈军胜, 等. 赣东北朱溪钨铜矿区高分异花岗岩的成因及与钨矿的关系[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 3310: 3162-3182. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201710013.htm 刘俊, 祝向平, 李文昌. 藏东拉荣斑岩钨钼矿床辉钼矿Re-Os定年及地质意义[J]. 地质学报2019, 93(7): 1708-1719. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.07.011 刘英超, 侯增谦, 于玉帅, 等. 西藏昌都地区拉拢拉类MVT铅锌矿床矿化特征与成因研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(4): 1407-1426. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201304024.htm 鲁洪涛, 黄维平, 刘振宇, 等. 西藏班戈地区后碰撞花岗岩岩石成因及其对班公湖-怒江缝合带演化的约束[J]. 吉林地质, 2020, 39(1): 12-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2427.2020.01.003 潘桂棠. 东特提斯地质构造形成演化[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1997. 潘桂棠, 朱弟成, 王立全, 等. 班公湖-怒江缝合带作为冈瓦纳大陆北界的地质地球物理证据[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(4): 371-382. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.04.004 王保弟, 王立全, 强巴扎西, 等. 早三叠世北澜沧江结合带碰撞作用: 类乌齐花岗质片麻岩年代学、地球化学及Hf同位素证[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 279: 2752-2762. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201109024.htm 王晓先, 张进江, 闫淑玉, 等. 藏南错那淡色花岗岩LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄、岩石地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2016, 35(1): 91-103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.01.008 王中刚. 稀土元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989. 王建平, 刘彦明, 李秋生, 等. 西藏班公湖-丁青蛇绿岩带东段侏罗纪盖层沉积的地层划分[J]. 地质通报, 2002, 21(7): 405-410. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.07.007 吴元保, 郑永飞. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(16): 1589-1604. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002 雍永源, 贾宝江. 板块剪式汇聚加地体拼贴-中特提斯消亡的新模式[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2000, 20(1): 85-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD200001006.htm 曾令森, 高利娥. 喜马拉雅碰撞造山带新生代地壳深熔作用与淡色花岗岩[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(5): 1420-1444. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201705004.htm 张旗, 王焰, 李承东, 等. 花岗岩的Sr-Yb分类及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(9): 2249-2269. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200609000.htm 张硕, 史洪峰, 郝海健, 等. 青藏高原班公湖地区晚白垩世埃达克岩年代学、地球化学及构造意义[J]. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 2014, 39(5): 509-524. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201405002.htm 朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 等. 中部中生代OIB型玄武岩的识别年代学、地球化学及其构造环境[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(9): 1312-1328. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200609008.htm 邹光富. 班公湖-怒江断裂带东段的构造特征[J]. 西藏地质, 1996, 2: 77-84. https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGKD200309002099.htm -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 王帅,任宇,郭红,曹文庚,李祥志,肖舜禹. 河南黄河改道区浅层地下水化学特征与主控污染源解析. 环境科学. 2024(02): 792-801 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 吕永高,蔡五田,杨骊,边超,李敬杰,王明国. 某铬渣堆污染地下水六价铬污染特征与迁移转化规律研究. 水文地质工程地质. 2024(03): 180-190 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 邓国仕,岑鑫雨,唐业旗,钟金先. 乌蒙山以礼河流域岩溶地下水富集特征及供水意义研究. 中国岩溶. 2023(04): 685-698 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: