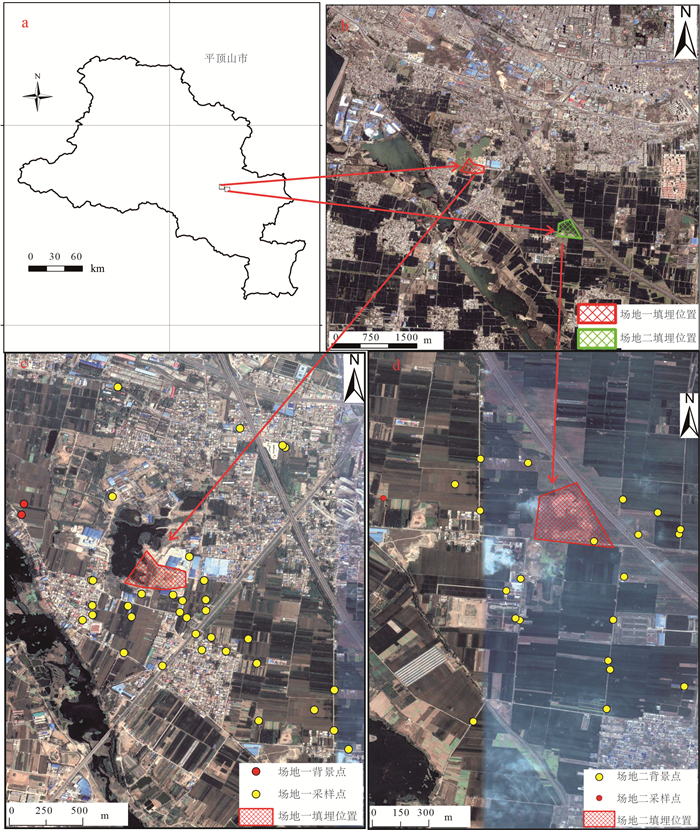
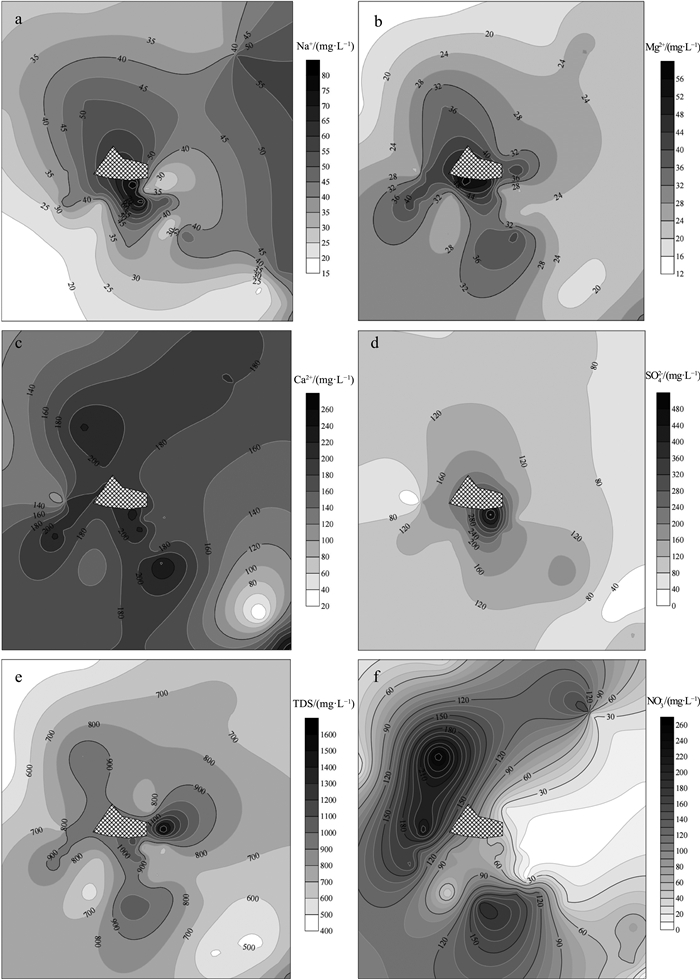
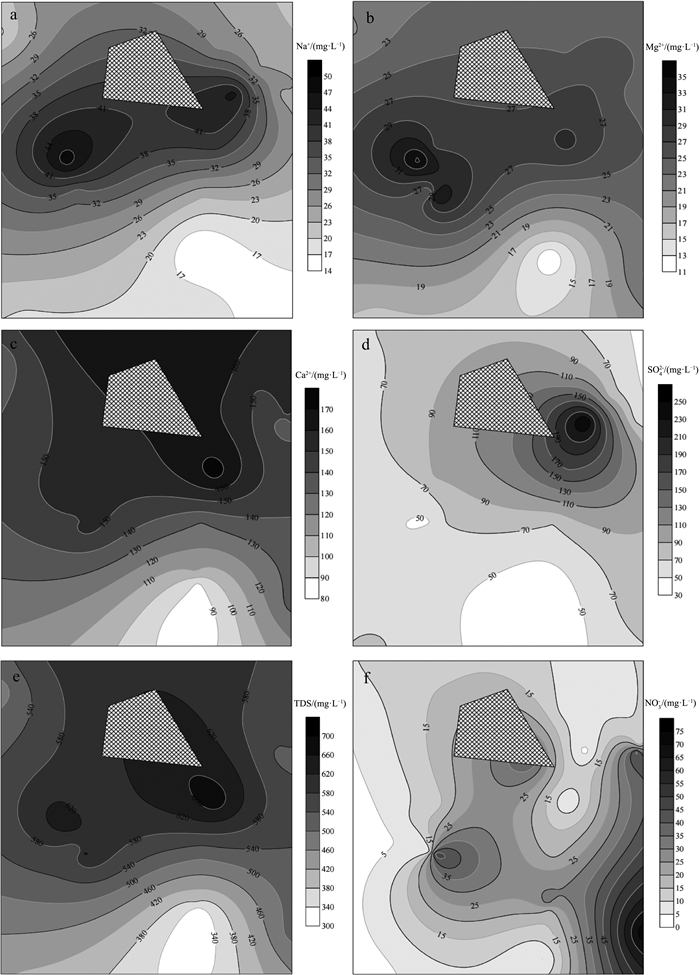
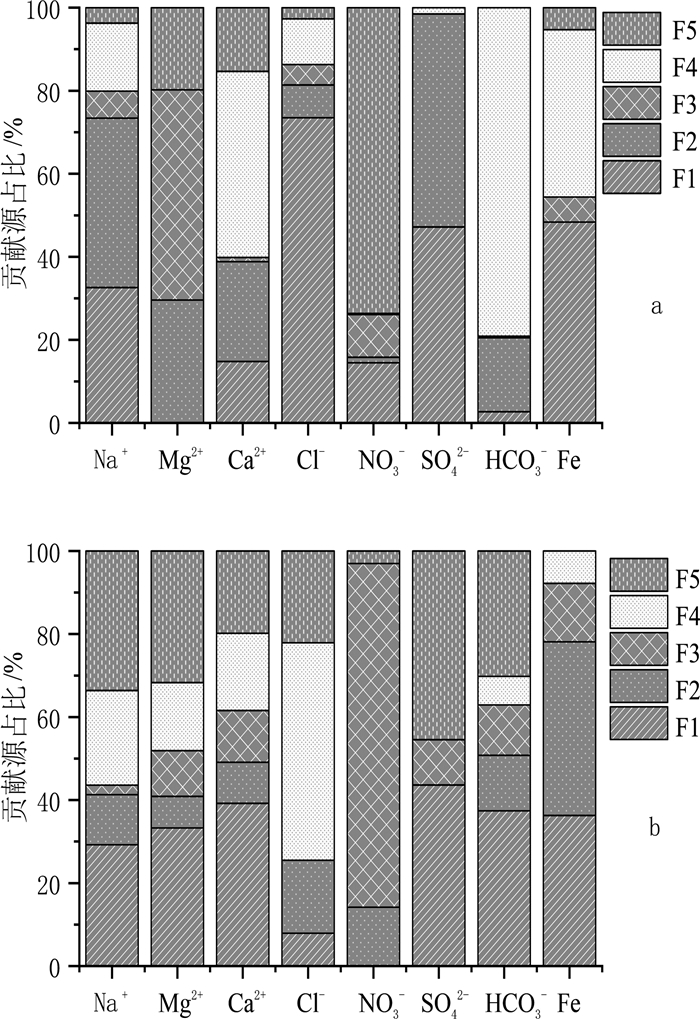
Source identification of chemical compounds in groundwater surrounding the landfill sites dumping construction and demolition waste
-
摘要:
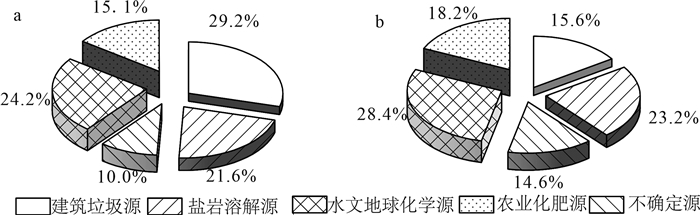
建筑垃圾是城市市政垃圾的重要组成部分,对其堆填处理可能造成场地及周围一定范围内的地下水污染。传统观念认为,建筑垃圾中多为惰性或无害成分,对地下水影响有限,缺乏关于建筑垃圾堆填对地下水水质造成影响的研究。选取2处建筑垃圾堆填场地,通过对场地周围地下水采样分析,得到场地周边地下水化学指标空间分布特征,并利用正定矩阵因子分解法(PMF)识别研究区地下水化学组分来源,从而定量评价建筑垃圾填埋对周边地下水水质变化的贡献。结果表明,建筑垃圾填埋会显著影响周边区域地下水组分的浓度和质量,尤其是TDS、TH、Ca2+、SO42-等组分显著受到影响,填埋时间越长、填埋体量越大,影响程度越深。两场地区域范围内Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+、SO42-和TDS 5个组分或指标的空间分布整体变化趋势较一致,均表现为垃圾填埋场附近沿地下水流下游方向的点位浓度较高,其他点位浓度较低,验证了建筑垃圾填埋对区域地下水质量的影响。PMF来源解析确定两场地周边地下水化学组分来源有建筑垃圾填埋、岩石风化溶解、水岩相互作用和农业活动,在场地一来源贡献占比分别为29.2%、21.6%、24.2%和15.1%,在场地二贡献占比分别为15.6%、23.2%、28.4%和18.2%。两场地周围地下水质量受人类活动影响程度较深,人为污染源正在成为地下水中离子组分的重要来源。
Abstract:Construction and demolition waste(CDW)accounts for a great portion of municipal solid waste, and the landfill treatment of CDW may cause groundwater pollution in the site and surrounding area.However, CDW is typically considered inert or harmless, presenting limited impact on groundwater quality, so that little research has been conducted on the impact of CDW landfills on groundwater.In this study, two CDW landfills were selected, and the spatial distribution of groundwater chemical components around the landfills were obtained by groundwater sampling and monitoring.The source of chemical components of groundwater in the study area was identified by using Positive Matrix Factorization(PMF)method.The contribution of CDW landfill to the deterioration of groundwater quality was quantitatively evaluated.Results show that the landfill of CDW can significantly affect the contents of hydro-chemical components and indexes in groundwater, especially total dissolved solid(TDS), total hardness(TH), Ca2+and SO42-.The spatial distribution of Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, SO42- and TDS in the two sites were similar in trend, that is, sampling sites near the landfills present greater concentrations of Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, SO42- and TDS, while sites far away from the landfills show lower concentration of those indexes.This distribution pattern suggests that CDW landfill probably have influence on the regional groundwater quality.The source apportionment results from PMF model suggest that sources of chemical components of groundwater around the two sites include CDW landfill leachate, rock weathering and dissolution, water-rock interaction and agricultural activities, with the corresponding contributions being 29.2%, 21.6%, 24.2% and 15.1%, respectively at Field 1 and 15.6%, 23.2%, 28.4% and 18.2%, respectively at Field 2.The quality of groundwater around the two sites is deeply affected by human activities, suggesting that anthropogenic pollution is becoming an important source of ion components in groundwater.
-
2021年5月22日凌晨2时04分,青海省果洛州玛多县黄河乡发生了7.4级地震,震源深度17 km,该地震发生在青藏高原巴颜喀拉地块东北部前人发现的全新世活断层,即昆仑山口-江错断裂带附近(张裕明等,1996;邓起东等,2002;2007)。青藏高原是中国最主要的地震活动区,尤其是青藏高原中部的巴颜喀拉块体周缘,近20年来发生了一系列强震事件,显示其构造运动正处于活跃期(程佳等,1997;闻学泽等,2011;Jia et al., 2012;徐锡伟等,2017)。巴颜喀拉地块位于青藏高原中北部,该地块呈西部狭长、东侧张开的倒三角形,北侧、西南侧、东南侧分别为柴达木-西秦岭褶皱带、羌塘地块和四川盆地(Meyer et al., 1998;张培震等,2003;徐锡伟等,2008;嘉世旭等,2017)。巴颜喀拉地块的现今运动主要受控于周边的大型活动断裂带,其北边界为昆仑断裂带(Kirby et al., 2000;杜方等,2013),东边界为兼右旋走滑分量的龙门山逆冲断裂(徐锡伟等,2002),南边界为玉树-鲜水河断裂带。作为南北地震带中段的重要组成部分,巴颜喀拉地块东缘现今的地震活动强烈,历史上曾发生过多次强震(许志琴等,1992;Densmore et al., 2007;邓起东等,2010;孟宪纲等,2014;杜方等,2018)。自21世纪初开始,沿巴颜喀拉地块边界又相继发生了多次强震,如2001年昆仑山口西Ms8.1地震、2008年汶川Ms8.0地震、2010年玉树Ms7.1地震和2013年芦山Ms7.0地震、2017年九寨沟Ms7.0地震。此次玛多7.4级地震的发生,表明目前巴颜喀拉块体仍然是中国大陆强震的主体活动地区之一。
玛多地震后,多家单位迅速组织了科考队奔赴现场,进行现场地震断层与次生灾害等的科学考察,在震中区一带先后发现了同震地表裂缝与伴生的地震地质灾害。笔者在玛多地震发生之后的第一时间,收集了玛多周边区域及地质构造、卫星遥感影像等资料,并沿此次地震的发震断裂昆仑山-江错断裂带进行了地震地表破裂与伴生次生灾害等的地表调查。本文主要对本次调查的结果进行介绍,并对相关问题进行讨论。
1. 区域地质背景
此次大地震发生区域在大地构造上隶属于北羌塘-三江造山系巴颜喀拉地块可可西里前陆盆地(图 1-a)。该前陆盆地呈北西西向展布于可可西里—巴颜喀拉一带,夹持于东昆仑断裂及可可西里南缘断裂之间。
研究区出露地层主要为巴颜喀拉山群昌马河组(T1-2č)、甘德组(T2gd)和清水河组(T3q), 另外在黄河流域及其支流第四纪沉积物广泛发育,类型有洪积物、冲积、风积、湖积等,而此次地震形成的地裂缝、砂土液化点、地震鼓包等均在第四系地质体中表现的更直观。区内有少量岩浆活动,在扎日加至东端的年宝玉则地区呈小岩株出露。
研究区断裂构造较发育,从北至南主要断裂有8条,分别为布青山南缘断裂(F1)、玛多-甘德断裂(F2)、玛曲-多确山断裂(F3)、卡木卡断裂(F4)、昆仑山口-江错断裂(F5)、甘德南缘断裂(F6)、卡巴纽尔多-鲜水河断裂(F7)、可可西里南缘断裂(F8)(图 1-b),其中F2-6断裂本次地震活动性明显。
玛多-甘德断裂西始昆仑山口西,经鄂陵湖北、玛多、甘德北延入甘肃,整体走向北西、倾向北东,呈向北东微凸的弧形,省内出露长度约780 km。地球物理资料反映,断裂切割深度为15 km,属韧-脆性壳型断裂,具多期活动特征。
昆仑山口-江错断裂西始昆仑山口西,经鄂陵湖南、玛多南部等地,向东延至甘德北,整体走向北西西、倾向南,为韧-脆性壳型断裂。该断层具有多期活动性,早期为浅—表部构造的逆冲推覆性质,后期为左行走滑,是一条区域性的地震活动带,2000年昆仑山口西8.1级地震带分布于该断裂带的西段(张裕明等,1996)。
玛曲-多确山断裂沿北西向延伸约76 km,倾向和倾角不明。沿断裂带水系发育,并呈直角状转弯,形成现代长垣状洼地,上游黄河干流经过,近代地震频繁发生,南侧平行排列的姊妹湖与负主断裂活动派生出羽状裂隙有关。断裂形成于中晚印支期,后期有复活。推测为隐伏正断层。
甘德南缘断裂区内出露长约60 km,断线走向北西,沿走向两端延伸迹象不明,倾角不明,性质可能为正断层。断层不仅切割下三叠统砂岩组,还控制中更新统冲洪积层及全新统风成砂的展布。北东侧为垄状、新月状砂丘,一直在活动,南西侧为已固定的风成砂堆积滩地及冲洪积层平地。沿断层线有断头河、湖泊呈线状排列等现象。断层可能形成于喜马拉雅期,现今活动性十分明显。
2. 地表破裂与次生灾害发育特征
本次工作针对玛多及周边地震区活动性断裂特征开展了遥感解译(刘文等,2021)和野外现场调查,截止2021年5月30日,在宽约75 km、长约230 km的调查区内,分别对玛多-甘德断裂(F2)、玛曲-多确山断裂(F3)、卡木卡断裂(F4)、昆仑山口-江错断裂(F5)、甘德南缘断裂(F6)5条活动断裂进行了定位调查,并在上述断裂地表新发现地裂缝653条、砂土液化和喷砂冒水点1237个、地震鼓包97个、塌陷坑2个(图 2)。
(1) 玛多-甘德断裂(F2)
该断裂为玛多-玛沁前陆隆起与可可西里前陆盆地的分界断裂,整体为走向北西向、向北微凸的弧形。本次在优云乡周边地区对该断裂活动性进行了调查。
该断裂呈北西向展布,断裂上、下盘地表均被第四系冲洪积物、风积物覆盖,局部表层草皮覆盖厚,断面产状难以判断。沿断裂处及周边地表发现不同规模的地裂缝共计35条(图版Ⅰ-a、b)。地裂缝依据走向大至可分成2组,第一组地裂缝走向在90°~150°之间,整体与断裂走向一致,地裂缝宽0.5~35 m,可见延伸15~300 m。第二组地裂缝与断裂走向近正交,走向在0°~40°之间,规模较小,宽0.4~12 m,可见延伸16~40 m。
(2) 玛曲-多确山断裂(F3)
本次在斗格恰-东葛纳青玛地区对该条断裂活动性进行了调查,共发现地裂缝75条、砂土液化和喷砂冒水点约522个、地震鼓包5个及塌陷坑2个。
地裂缝依据走向大致可分为2组:第一组地裂缝呈北西西—近东西向展布,走向为90°~150°,地裂缝宽0.15~300 m,长50~2200 m,个别地裂缝断续延伸大于5 km(图版Ⅰ-c);第二组地裂缝呈近南北—北东向展布,走向0°~60°,宽15.8~70 m,延伸280~850 m。
砂土液化和喷砂冒水点大多呈串珠状定向分布(图版Ⅰ-d),大小不等,单个砂土液化和喷砂冒水点大小在(2×4) cm~(90×50) cm之间。走向与地裂缝走向较一致,同样可根据砂土液化和喷砂冒水点展布方向分为2组。第一组走向在80°~150°之间,第二组走向在0~55°之间。
地震活动造成地面沉降,形成2处塌陷坑(图版Ⅰ-e),塌陷坑长轴走向均为130°,大小在(11.6×23)~(14.6×31.1) m之间,深0.85~1.2 m。
地震鼓包仅分布于D059点处,呈串珠状展布,走向181°,单个地震鼓包大小(15×8)~(30×45) cm,鼓包凸起高度10~20 cm,鼓包深度在10~25 cm之间(图版Ⅰ-f)。
(3) 卡木卡断裂(F4)
本次在卡格龙波格地区针对卡木卡断裂活动性开展了调查,共发现地裂缝12条。根据地裂缝走向可分为北西西向和北东—南西向2组,其中北西西向地裂缝走向为110°,整体宽约30 m、长约760 m、深0.5~0.9 m,北东—南西向地裂缝走向在236°~242°之间,宽50~100 m,长490~600 m,深0.1~0.9 m。
(4) 昆仑山口-江错断裂(F5)
本次沿扎陵湖南、多涌、鄂陵湖南、野马滩、黑河乡(玛查理镇)星星海、同布岗地区对该断裂活动性开展了调查,共发现地裂缝451条、砂土液化和喷砂冒水点688个、地震鼓包92个。
地裂缝依据走向可分为3组:第一组地裂缝整体呈近东西向或北西—南东向展布,走向在80°~140°之间,宽0.01~25 m,局部形成裂缝带宽达780 m,长0.3~500 m之间,个别地裂缝长达800 m,深0.12~1.5 m;第二组地裂缝呈北西—南东向或近南北向展布,裂缝走向320~350°,裂缝宽0.05~60 m,延伸在4~60 m之间,个别地裂缝长达800 m,深0.05~0.9 m;第三组地裂缝呈北东向展布,走向在30°~55°之间,裂缝宽0.7~5 m,延伸在35~500 m之间,深0.15~0.8 m(图版Ⅱ-a)。
砂土液化和喷砂冒水点多呈串珠状定向排列,绝大多数与近东西向或北西向地裂缝对应产出,走向以100°~120°之间居多,仅个别砂土液化和喷砂冒水点走向为10°或140°。单个砂土液化和喷砂冒水点大小在(0.01×0.06) m~(1.3×1.8) m之间,深0.03~0.6 m (图版Ⅱ-b)。
地震鼓包均沿北西—南东向地裂缝产出,其长轴走向在150°~160°之间,长轴在1.2~24 m之间,短轴在0.7~15 m之间(图版Ⅱ-c、d)。
(5) 甘德南缘断裂(F6)
西起哈日尼让马,经歇日科向南东延伸至地列一带,整体呈北西向展布,断层走向138°。断层上盘为活动风尘砂堆积、下盘为固定风尘砂及下—中三叠统昌马河组,断面北倾。断层沿线发育地裂缝、串珠状砂土液化和喷砂冒水点,断层活动性较为明显。
本次在歇日科地区共发现地裂缝80条、砂土液化和喷砂冒水点27个。其中地裂缝整体沿北西—南东向展布,地裂缝走向在110°~145°之间,宽0.3~ 100 m,宽2~650m之间,深0.02~0.4 m之间(图版Ⅱ-e)。砂土液化和喷砂冒水点整体沿地裂缝呈串珠状发育,走向120°~125°之间,其中单个砂土液化点大小在2×3cm~5×10cm之间,可见深度在10~15 cm之间(图版Ⅱ-f)。
3. 地震成因
据中国地震局网资料,本次玛多地震Ms7.4地震及余震集中分布于玛多-甘德断裂(F2)和昆仑山口-江错断裂(F5)之间。野外调查资料显示,在玛多-甘德断裂(F2)和昆仑山口-江错断裂(F5)之间,地表形成集中分布的地裂缝、砂土液化和喷砂冒水点、地震鼓包、塌陷坑等地质现象,由此判断,以F2和F5为界在区域上形成了一条宽约75 km、长约230 km的活动断裂带,其中玛曲-多确山断裂(F3)、卡木卡断裂(F4)、歇日科断裂(F6)断裂规模较小,属于该断裂带的次一级断裂。
玛多Ms7.4震源位置位于昆仑山口-江错断裂南侧,依据图 2中地裂缝、砂土液化和喷砂冒水点、地震鼓包及断裂带的空间展布特征分析,653条地裂缝总体呈北西—南东向展布,在西北段集中分布于鄂陵湖南侧,中段逐渐向玛曲、歇日科等地分散,而最东段分散更明显,在昌马河—优云乡一带均有发育,表明发震断层出现马尾状分支的现象;另外,在昌马河一带发育的地裂缝与玛多-甘德断裂带以一定角度斜交,地裂缝整体的走向与昆仑山口-江错断裂走向高度一致。因此认为,昆仑山口-江错断裂是本次强震的主要发震断层,断面整体南倾,性质为左旋走滑(图版Ⅱ-g、h)。
发震区位于巴颜喀拉地块,是夹持于北侧阿尼玛卿洋和南侧西金乌兰洋演化过程中的块体。自65 Ma以来,印度地块和塔里木地块以更大的应力向青藏高原挤压、俯冲,使高原大幅度抬升并经历了由“青藏运动序幕”、“青藏运动主幕”、“昆黄运动”及“共和运动”构成的剧烈、多幕次、后期显著加速的造山作用(李吉均等,1979;2015;崔之久等,1998;戴霜等,2005;张克信等,2013)。前人研究表明,巴颜喀拉地块东北部以块体挤压为主,东昆仑断裂带的滑动速率向东逐渐减小,意味着巴颜喀拉地块东部存在较强的内部变形。伴随青藏高原块体运动,青藏高原7级以上强震主要沿大型块体边界断裂带分布(邓起东等,2002;张培震等,2003),当块体前缘受到相对坚硬的盆地阻挡,板块内部会发生差异变形,形成一系列与边界性质相同的断裂并发生强震活动,玛多Ms7.4地震在此背景下发生。
4. 结论
(1) 在玛多县及周边宽约75 km、长约230 km的调查区内,共发现地裂缝653条、砂土液化和喷砂冒水点1237个、地震鼓包97个和塌陷坑2个。其分布特征显示:按走向可分为3组,分别为北西—南东(110°~130°)向、北东—南西(30°~55°)和北北西—南南东(320°~350°)向,主体以北西—南东为主,且形成时期最早(另2组有横切它的现象)、规模最大、地表延伸最长。
(2) 玛多地震地表破裂与独特次生灾害在西北段鄂陵湖南侧集中分布,于中段黄河乡一带逐渐向玛曲、歇日科等地分散,而最东段在昌马河—优云乡一带均有发育,分散最明显,表明发震断层出现马尾状分支的现象;在昌马河一带发育的地裂缝与玛多-甘德断裂带以一定角度斜交。
(3) 青海玛多“5.22 Ms7.4地震”的发震断裂为昆仑山口-江错断裂带(F5),断面整体南倾,性质为左旋走滑。此次大地震的发生是在印度板块向青藏高原挤压背景下,巴颜喀拉地块强烈向东挤出构造作用导致其北部走滑断裂发生左旋运动的结果。
致谢: 感谢审稿专家对论文修改与完善提出的宝贵意见。 -
表 1 研究区地下水化学测试指标
Table 1 Chemical species contents of groundwater in study area
测量指标 场地一 场地二 最小值 最大值 中位数 平均数 超标率 最小值 最大值 中位数 平均数 超标率 pH 7.07 8.00 7.45 7.46 0.0% 7.06 8.01 7.43 7.44 0.0% TDS 343.5 1649.1 716.4 769.4 14.3% 311.5 813.5 557.0 546.7 0.0% TH 269.0 1228.9 549.0 593.4 82.9% 264.2 627.0 480.9 457.1 60.0% Na+ 19.5 79.9 40.1 40.7 0.0% 14.0 48.8 26.7 27.8 0.0% Mg2+ 13.4 58.2 27.3 29.7 - 11.3 35.7 24.2 23.7 - Ca2+ 65.8 417.1 180.7 187.8 - 81.1 205.0 149.5 143.3 - HCO3- 253.4 1770.7 392.9 447.9 - 254.5 491.5 381.7 370.8 - SO42- 18.9 495.3 129.4 143.0 5.7% 31.6 253.1 71.6 85.3 5.0% Cl- 15.0 106.3 62.5 59.8 0.0% 13.8 139.9 23.8 38.9 0.0% NO3- 3.4 259.3 55.1 77.8 82.9% 11.8 80.4 44.2 41.8 75.0% Fe 0.114 0.617 0.197 0.232 20.0% 0.064 0.267 0.149 0.159 0.0% Al 0.002 1.905 0.029 0.141 11.4% 0.002 0.267 0.046 0.086 15.0% Cr 0.000 0.130 0.001 0.001 5.7% 0.001 0.017 0.004 0.006 0.0% As 0.001 0.013 0.006 0.006 11.4% 0.001 0.007 0.004 0.004 0.0% 注:除pH值外,其余单位为mg/L 表 2 两场地周边不同类别采样点位地下水化学组分浓度
Table 2 Descriptive statistics of groundwater chemical species contents in different types of sampling sites in surrounding of both fields
测试指标 场地一 场地二 场地上游 场地下游 其他 场地上游 场地下游 其他 中位数 对照值 平均数 中位数 平均数 中位数 平均数 中位数 对照值 平均数 中位数 平均数 中位数 平均数 TDS 425.4 578.2 441.8 809.9 693.0 742.4 759.9 491.0 587.0 590.7 614.5 653.2 529.8 553.8 TH 352.3 441.5 357.9 625.1 549.0 586.6 551.4 391.3 472.8 483.6 498.1 514.6 444.9 476.5 Na+ 24.7 31.0 25.3 43.4 40.2 39.4 34.9 22.9 24.9 26.1 34.7 39.6 27.0 26.7 Mg2+ 16.1 20.1 15.5 30.4 27.3 31.6 26.4 17.8 22.1 22.3 26.4 26.6 23.5 24.6 Ca2+ 116.3 143.1 119.0 199.3 180.7 182.0 183.3 126.9 152.3 156.3 155.3 161.5 138.8 148.5 HCO3- 271.2 308.5 278.2 509.8 427.2 384.4 384.6 299.6 406.6 409.3 358.3 335.2 365.8 377.2 SO42- 88.7 98.9 95.0 155.6 156.5 138.7 134.9 55.0 70.2 73.8 125.9 140.5 79.8 66.8 Cl- 29.8 46.2 31.5 59.9 66.8 62.9 54.1 34.2 25.8 23.0 53.2 67.6 38.7 23.6 NO3- 26.2 84.4 27.1 55.3 42.8 112.0 86.6 83.8 55.7 59.0 42.7 25.1 38.7 40.1 Al 0.053 0.046 0.050 0.063 0.030 0.030 0.029 0.018 0.144 0.152 0.117 0.117 0.064 0.044 Fe 0.130 0.220 0.140 0.222 0.203 0.251 0.190 0.117 0.198 0.213 0.177 0.166 0.147 0.139 Cr 0.003 0.004 0.003 0.018 0.005 0.009 0.007 0.006 0.009 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.004 As 0.006 0.005 0.006 0.007 0.007 0.005 0.006 0.005 0.003 0.002 0.006 0.007 0.004 0.004 注:所有数据的单位为mg/L -
孙佩文. 城市建筑装修垃圾产生量特性及管理对策研究[D]. 深圳大学硕士学位论文, 2020. 张亮, 洪智程, 冯一舰. 杭州市某典型建筑垃圾资源化处理项目的技术过程碳减排效益分析[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2022, 44(4): 506-509. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJWR202204015.htm 程颖卿. 协同治理视域下城市建筑垃圾处置对策研究[J]. 山西建筑, 2022, 48(13): 179-181. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZSX202213044.htm Chen H, Xu J, Li Y, et al. Trash to treasure: From construction waste to tellurium adsorbent materials[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 312.
Li H, Zhang Y, Wu L, et al. Recycled aggregates from construction and demolition waste as wetland substrates for pollutant removal[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 311: 127766. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127766
闫宏亮. 建筑垃圾循环再利用处理工艺改进研究[D]. 吉林大学硕士学位论文, 2019. 《全国地下水污染防治规划(2011—2020年)》讨论通过[J]. 环境保护与循环经济, 2011, 31(8): 34. Chen X J. China's water resources in 2020[J]. China Geology, 2021, 4(3): 536-538.
于丹凤, 李小月, 段华波, 等. 城市拆除和装修建筑垃圾重金属浸出特性分析[J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(1): 153-157. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJGC201901042.htm 郑佳. 北京西郊垃圾填埋场对地下水污染的预测与控制研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2009. 张清平. 堆存装修垃圾对土壤及地下水环境影响的研究[D]. 山东大学硕士学位论文, 2019. 赵起越, 李令军, 张立坤, 等. 建筑垃圾的危害、监测及管理[J]. 环境保护与循环经济, 2019, 39(7): 75-80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LNCX201907024.htm Timothy T, Thabet T, Kevin L, et al. Heavy metals in recovered fines from construction and demolition debris recycling facilities in Florida[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2004, 332(13): 1-11.
Robert H C, Deepika M, Rolf G. Barriers to Improving the Environmental Performance of Construction Waste Management in Remote Communities[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2017, 196: 830-837. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2017.08.014
Li Q, Zhang H, Guo S, et al. Groundwater pollution source apportionment using principal component analysis in a multiple land-use area in southwestern China. [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27: 9000-9011. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06126-6
Zhang M, Wang X, Liu C, et al. Quantitative source identification and apportionment of heavy metals under two different land use types: comparison of two receptor models APCS-MLR and PMF[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27: 42996-43010. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-10234-z
Hristova E, Veleva B, Georgieva E, et al. Application of Positive Matrix Factorization Receptor Model for Source Identification of PM10 in the City of Sofia, Bulgaria[J]. Atmosphere, 2020, 11(9): 890. doi: 10.3390/atmos11090890
Qi Y J Q, Liu X, Wang Z, et al. Comparison of receptor models for source identification of organophosphate esters in major inflow rivers to the Bohai Sea, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 265(Pt B): 114970.
Shin S M, Kim J Y, Lee J Y, et al. Enhancement of modeling performance by including organic markers to the PMF modeling for the PM2.5 at Seoul[J]. Air Quality, Atmosphere & Health, 2022, 15: 91-104.
Anaman R, Peng C, Jiang Z, et al. Identifying sources and transport routes of heavy metals in soil with different land uses around a smelting site by GIS based PCA and PMF[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 823: 153759. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153759
Li H Y. Application of positive matrix factorization to source apportionment of surface water quality of the Daliao River basin, northeast China[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2015, 187(3): 80. doi: 10.1007/s10661-014-4154-2
Zhang H, Chang S Q, Li H F, et al. Groundwater pollution source identification and apportionment using PMF and PCA-APCA-MLR receptor models in a typical mixed land-use area in Southwestern China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 741: 140483. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140483
平顶山市地方史志编纂委员会. 平顶山市志(上卷)[M]. 郑州: 河南省人民出版社, 1994. 杨家林, 王少辉. 浅析平顶山矿区地下水环境问题及防治措施[J]. 地下水, 2015, 37(5): 96-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU201505035.htm 连明涛, 李渡峰. 平顶山市城区地下水资源综合分析[J]. 河南水利, 2000, (6): 12-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNBD200006013.htm Pentti P, Unto T. Positive matrix factorization: A non-negative factor model with optimal utilization of error estimates of data values[J]. Environmetrics, 1994, 5(2): 111-126. doi: 10.1002/env.3170050203
Gary Norris R D. EPA Positive Matrix Factorization(PMF)5.0 Fundamentals and User Guide[S]. 2014: 1-105.
Zanotti C. Groundwater and surface water quality characterization through positive matrix factorization combined with GIS approach[J]. Water Research, 2019, 159: 122-134. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.04.058
Lapworth D J, Boving T B, Kreamer D K, et al. Groundwater quality: Global threats, opportunities and realising the potential of groundwater. [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 811: 152471. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152471
王罗春, 彭松, 赵由才. 建筑垃圾渗滤液实验室模拟研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2007, (11): 20-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS200711006.htm Silva R V, de Brito J, Dhir R K. Properties and composition of recycled aggregates from construction and demolition waste suitable for concrete production[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2014, 65: 201-217. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.04.117
Bijay M S, Takashi N, Tatsuru K, et al. Seasonal Groundwater Quality Status and Nitrogen Contamination in the Shallow Aquifer System of the Kathmandu Valley, Nepal[J]. Water, 2019, 11(10): 2184. doi: 10.3390/w11102184
Janet Y C L, Meng N C, Phaik E P, et al. Longitudinal assessment of rainwater quality under tropical climatic conditions in enabling effective rainwater harvesting and reuse schemes[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2016, 143: 64-75.
Mullaney J R, Lorenz D L, Arntson A D. Chloride in groundwater and surface water in areas underlain by the glacial aquifer system, northern United States[M]. Scientific Investigations Report, 2007: 2009-5086.
Tirumalesh K. Understanding the hydrochemical behavior of groundwater and its suitability for drinking and agricultural purposes in Pondicherry area, South India - A step towards sustainable development[J]. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 2016, 2/3: 143-153. doi: 10.1016/j.gsd.2016.08.001
丁爱中, 郝娜, 程莉蓉, 等. 四川德阳浅层地下水高含铁成因分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2009, 39(5): 868-873. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200905016.htm Wang H M. Geochemical Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Groundwater Fe in Seawater Intrusion Area[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2020, 231(7): 18-25.
Hu Q Y. Using multiple isotopes to identify sources and transport of nitrate in urban residential stormwater runoff[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2022, 194(3): 238-238.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 孟思晨,孟秋,陈启志,胡才博. 2021年5月22日青海玛多M_S7.4地震同震变形的数值模拟及其动力学启示. 中国科学院大学学报. 2024(01): 70-80 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘传正,梁宽,王秀英. 积石山M_s6.2级地震区大沙沟泥土流灾害链成因分析. 地质论评. 2024(03): 960-974 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王博,崔凤珍,刘静,周永胜,徐胜,邵延秀. 玛多M_S7.4地震断层土壤气特征与地表破裂的相关性. 地震地质. 2023(03): 772-794 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: