Zircon U-Pb ages, petrogenesis and tectonic setting of basic rocks in Gudui area, southern Tibet
-
摘要:
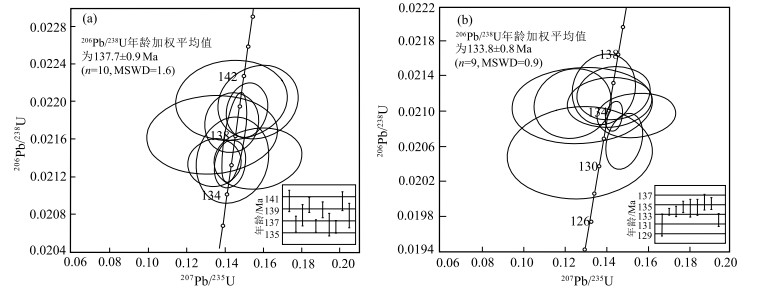
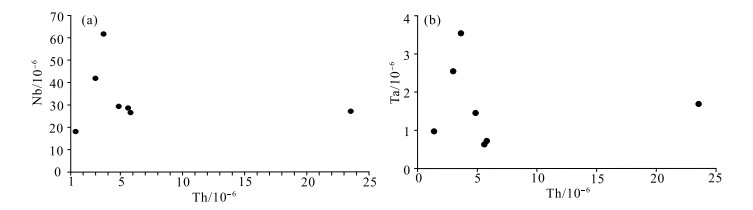
藏南古堆地区处于喜马拉雅带北东段, 雅鲁藏布江缝合带南部, 措美大火成岩省东南部, 区内基性岩分布较广泛, 主要呈脉状侵位于侏罗纪—三叠纪地层中。为探讨古堆地区基性岩的成因及其构造动力学背景, 对区内基性岩进行了锆石U-Pb年龄、岩石地球化学等研究。结果表明, SHRIMP锆石206Pb/238U同位素测年得出辉绿岩年龄加权平均值为137.7±0.9 Ma;辉长岩年龄加权平均值为133.8±0.8 Ma, 其形成时代为早白垩世, 与措美大火成岩省OIB型基性岩形成时代相近(130~136 Ma)。岩石地球化学证据表明, 基性岩具有高TiO2和P2O5特点, 不具有Nb-Ta槽特征, 微量元素比值(Ce/Zr、Zr/Nb、Zr/Y、Th/Yb)及稀土元素配分模式与板内洋岛玄武岩(OIB)相似。综合研究表明, 古堆地区基性岩源于富集地幔, 并且基性岩浆在上侵过程中未受到地壳混染, 其形成于板内构造环境, 可能是Kerguelen地幔柱早期活动的产物。对古堆地区基性岩的研究, 为近一步认识藏南地区早白垩世基性岩的成因及其大地构造背景提供了地质年代学和岩石地球化学方面的证据。
Abstract:The Gudui area in southern Tibet is located in the northeast section of the Himalaya belt, the south of the Yarlung Zangbo River suture zone, and the southeast of the cuomei large igneous province.The basic rocks in the area are widely distributed, mainly located in the Jurassic-Triassic strata.In order to explore the origin and structural dynamic background of basic rocks in Gudui area, zircon U-Pb chronology and rock geochemistry of basic rocks in the area are studied in this paper.The results show that the SHRIMP zircon 206Pb/238U isotopic dating shows that the weighted average age of diabase is 137.7±0.9 Ma, and the weighted average age of gabbro is 133.8±0.8 Ma, its formation age is early Cretaceous, which is similar to that of OIB basic rocks in Cuomei igneous Province(130~136 Ma).Rock geochemical evidence shows that the basic rocks have high TiO2 and P2O5 characteristics, not Nb-Ta groove characteristics, and the trace element ratios(Ce/Zr, Zr/Nb, Zr/Y, Th/Yb)and rare earth distribution patterns are similar to those of intraplate ocean island basalt(OIB).The comprehensive study shows that the basic rocks in gudui area originated from the enriched mantle, and the basic magma was not contaminated by the crust during the upwelling process.It was formed in the intraplate tectonic environment and may be the product of the early activities of the Kerguelen mantle plume.Through this study of basic rocks in Gudui area, geological chronology and rock geochemistry evidence are provided for further understanding the genesis and tectonic background of Early Cretaceous basic rocks in the southern Tibet.
-
额尔古纳地块得尔布干NE向成矿带是中国重要的铅锌矿集区(带)之一,该成矿带地处大兴安岭西坡、额尔古纳地块与兴安地块的交汇部位(图 1-a),从南到北发育甲乌拉、查干布拉根、东珺、得耳布尔、比利亚谷等多个大、中型铅锌银多金属矿床(Li et al., 2016; 赵岩等, 2017)。二道河子铅锌矿床位于NE向得尔布干深大断裂北西侧,额尔古纳地块得尔布干成矿带中段(图 1)(段明新等, 2014; 赵岩等, 2018),是该成矿带的典型铅锌矿床之一。近年来,不少学者在赋矿围岩火山岩、火山碎屑岩详细研究的基础上,结合区域及矿床地质特征,对二道河子矿床的构造格架、成矿流体、矿床成因等开展了研究(李进文等, 2011; Yan et al., 2015; 成来顺等, 2016; 李兴等, 2016; 刘艳荣等, 2019; 2023 Xu et al., 2020; 党顺安等, 2022),获得了许多重要成果。但是,对该矿床成矿时代的研究较薄弱,前人主要通过赋矿围岩塔木兰沟组晶屑岩屑凝灰岩中的锆石U-Pb年龄间接制约成矿年龄(李进文等, 2011; Yan et al., 2015),缺乏对二道河子矿床直接而精确的定年,严重制约了对该矿床成矿动力学背景、矿床成因等方面的认识。
![]() 图 1 二道河子矿床大地构造位置图(a)和区域地质图(b) (据段明新等, 2014修改)1—地质界线;2—断层;3—铅锌银矿床;K1b—下白垩统白音高老组;J3mk—上侏罗统满克头鄂博组;J2tm—中侏罗统塔木兰沟组;γδ52—燕山期花岗闪长岩;λπ52—燕山期流纹斑岩;Qπ52—燕山期石英斑岩;γδ42—海西期花岗闪长岩;F1—牡丹江断裂;F2—敦化-密山断裂;F3—伊通-依兰断裂;F4—西拉木伦-长春断裂;F5—贺根山-黑河断裂;F6—塔源-喜桂图断裂Figure 1. Tectonic map(a) and regional geological map(b)of the Erdaohezi Pb-Zn-Ag deposit
图 1 二道河子矿床大地构造位置图(a)和区域地质图(b) (据段明新等, 2014修改)1—地质界线;2—断层;3—铅锌银矿床;K1b—下白垩统白音高老组;J3mk—上侏罗统满克头鄂博组;J2tm—中侏罗统塔木兰沟组;γδ52—燕山期花岗闪长岩;λπ52—燕山期流纹斑岩;Qπ52—燕山期石英斑岩;γδ42—海西期花岗闪长岩;F1—牡丹江断裂;F2—敦化-密山断裂;F3—伊通-依兰断裂;F4—西拉木伦-长春断裂;F5—贺根山-黑河断裂;F6—塔源-喜桂图断裂Figure 1. Tectonic map(a) and regional geological map(b)of the Erdaohezi Pb-Zn-Ag deposit近年来,随着现代测试技术的发展,国内外众多地质学家都尝试用成矿体系的矿石矿物或脉石矿物进行直接定年(李文博等, 2002; 陈文等, 2011; 王银之等, 2015; Hnatyshin et al., 2016; Niu et al., 2020)。其中,硫化物Rb-Sr等时线定年是铅锌矿床近年来发展最快的直接定年方法,且取得了一定成果(杨红梅等, 2012; Yang et al., 2019; 张哲铭等, 2019)。Xu et al.(2020)对二道河子矿床2个矿带的闪锌矿、方铅矿、黄铁矿等硫化物进行了Rb-Sr年龄测试,获得Rb-Sr年龄为130.5±3.6 Ma,但其选择的硫化物样品来自不同矿带的不同成矿阶段,较难保证样品的同源性和同时性;此外,选取的深色闪锌矿内常含有大量的黄铜矿和磁黄铁矿包体,这些都可能会对测试结果产生影响。因此,为了更全面精确地确定二道河子矿床铅锌矿化的时间,本文在详细研究矿床地质特征的基础上,重点对Ⅲ号矿带主成矿阶段的共生闪锌矿和黄铁矿进行了Rb-Sr等时线年龄测定,结合与成矿同时或略晚的安山玢岩脉的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年,准确厘定了该矿床的形成时间,并探讨成矿构造背景。
1. 矿区地质概况与矿床地质特征
二道河子矿床矿区出露地层主要为中侏罗统塔木兰沟组中酸性火山沉积岩建造和第四系。矿区构造主要为NE向得尔布干深大断裂及一系列NW—NNW向、NE向和SN向次级断裂,其中NE向得尔布干断裂为主要导矿构造,NW—NNW向次级断裂在矿区内形成3条断裂破碎带,是主要的赋矿构造,NE向和SN向断裂通常破坏矿体。矿区侵入岩为安山玢岩脉,按产状可见NW向和NE向2组,其中NW向岩脉呈透镜状沿断裂构造侵位于晶屑岩屑凝灰岩或岩性界面处,与矿体近平行,局部插入矿体中,部分岩脉可见微弱矿化(图 2-a、b),其与成矿作用有密切关系;NE向岩脉截断或切穿矿体,但对矿体破坏不大,无矿化(李兴等, 2016)。
矿床地质研究揭示,矿体主要赋存于塔木兰沟组晶屑岩屑凝灰岩和安山岩的NW向断裂破碎带或岩性界面处,区内分布有Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ 3条矿化带(图 3),各矿化带内分别有11条、28条和57条矿体。矿体呈脉状、透镜状和不规则状发育,总体走向262°~347°,沿走向长50~250 m,倾向NE,倾角50°~80°,局部反倾,个别矿体近直立,倾向延伸40~550 m。二道河子矿床已经探明的铅锌资源量为43.47×104 t,Ag资源量为366.89 t,其中Pb、Zn、Ag的平均品位分别为2.18%、2.79%和52.95 g/t。
![]() 图 3 二道河子铅锌矿床矿区地质图(据李兴等, 2016修改)1—第四系坡积物、冲积物;2—塔木兰沟组安山岩;3—塔木兰沟组岩屑晶屑凝灰岩;4—塔木兰沟组凝灰岩;5—地质界线;6—不整合地质界线;7—断层及编号;8—矿体;9—断裂破碎带及编号Figure 3. Geological map of the Erdaohezi Pb-Zn deposit
图 3 二道河子铅锌矿床矿区地质图(据李兴等, 2016修改)1—第四系坡积物、冲积物;2—塔木兰沟组安山岩;3—塔木兰沟组岩屑晶屑凝灰岩;4—塔木兰沟组凝灰岩;5—地质界线;6—不整合地质界线;7—断层及编号;8—矿体;9—断裂破碎带及编号Figure 3. Geological map of the Erdaohezi Pb-Zn deposit矿石构造主要为浸染状构造(图版Ⅰ-a)、致密块状构造(图版Ⅰ-b)、脉状构造(图版Ⅰ-c)、网脉状构造(图版Ⅰ-d),其次为条带状构造(图版Ⅰ-e)和角砾状构造(图版Ⅰ-f)。矿石结构为自形—他形粒状结构(图版Ⅰ-g~j)、环带结构(图版Ⅰ-h)、交代结构(图版Ⅰ-i、j)、乳滴状结构(图版Ⅰ-j~k)、脉状-网脉状结构(图版Ⅰ-l)等。矿石中金属矿物主要为方铅矿、闪锌矿和黄铁矿,其次为黄铜矿、毒砂、磁黄铁矿、银矿物等,非金属矿物主要为石英、绢云母、绿泥石、方解石等。根据矿脉之间的穿插关系和矿石结构构造,该矿床的热液成矿期可划分为3个成矿阶段:①石英-黄铁矿阶段(Ⅰ),细粒自形黄铁矿颗粒和石英呈浸染状分布在围岩和石英脉中(图版Ⅰ-a),该阶段矿化较弱,是热液成矿作用的早期。②石英-多金属硫化物阶段(Ⅱ),该阶段是主要的成矿阶段,其内发育大量的硫化物(图版Ⅰ-b~d),主要以脉状、浸染状赋存在围岩和石英脉中。③石英-方解石-黄铁矿阶段(Ⅲ),该阶段是热液成矿作用的晚期,呈细脉状穿插交代其他成矿阶段。围岩蚀变有硅化、绢云母化、绿泥石化、碳酸盐化等,其中,前3种蚀变与矿化关系密切。
![]() 图版Ⅰa.浸染状、脉状构造,阶段Ⅰ黄铁矿呈浸染状分布在凝灰岩中,被阶段Ⅱ铅锌矿脉穿插;b.致密块状构造,阶段Ⅱ硫化物致密均匀分布;c.脉状构造,阶段Ⅱ闪锌矿脉穿插阶段Ⅰ黄铁矿化凝灰岩;d.脉状、角砾状构造,阶段Ⅲ石英-黄铁矿脉穿插阶段Ⅱ方铅矿脉和阶段Ⅰ黄铁矿化凝灰岩;e.条带状构造,阶段Ⅱ硫化物呈条带状穿插交代阶段Ⅰ黄铁矿化凝灰岩;f.角砾状构造,阶段Ⅱ硫化物角砾被石英胶结;g.自形粒状结构;h.环带结构,黄铁矿具核-边环带;i.半自形、他形粒状结构和尖角交代结构,他形粒状方铅矿呈尖角状交代半自形、他形粒状黄铁矿;j.尖角交代结构和乳滴状结构,他形粒状方铅矿呈尖角状交代闪锌矿和黄铁矿,黄铜矿呈乳滴状分布于闪锌矿中;k.乳滴状结构,磁黄铁矿和黄铜矿呈乳滴状分布于闪锌矿中;l.脉状、网脉状结构和尖角交代结构,方铅矿呈尖角状、脉状穿插交代早期黄铁矿。g~l的拍摄条件均为反射光(单偏光)。Sul—硫化物;Py—黄铁矿;Sp—闪锌矿;Gn—方铅矿;Cp—黄铜矿;Po—磁黄铁矿;Q—石英图版Ⅰ.
图版Ⅰa.浸染状、脉状构造,阶段Ⅰ黄铁矿呈浸染状分布在凝灰岩中,被阶段Ⅱ铅锌矿脉穿插;b.致密块状构造,阶段Ⅱ硫化物致密均匀分布;c.脉状构造,阶段Ⅱ闪锌矿脉穿插阶段Ⅰ黄铁矿化凝灰岩;d.脉状、角砾状构造,阶段Ⅲ石英-黄铁矿脉穿插阶段Ⅱ方铅矿脉和阶段Ⅰ黄铁矿化凝灰岩;e.条带状构造,阶段Ⅱ硫化物呈条带状穿插交代阶段Ⅰ黄铁矿化凝灰岩;f.角砾状构造,阶段Ⅱ硫化物角砾被石英胶结;g.自形粒状结构;h.环带结构,黄铁矿具核-边环带;i.半自形、他形粒状结构和尖角交代结构,他形粒状方铅矿呈尖角状交代半自形、他形粒状黄铁矿;j.尖角交代结构和乳滴状结构,他形粒状方铅矿呈尖角状交代闪锌矿和黄铁矿,黄铜矿呈乳滴状分布于闪锌矿中;k.乳滴状结构,磁黄铁矿和黄铜矿呈乳滴状分布于闪锌矿中;l.脉状、网脉状结构和尖角交代结构,方铅矿呈尖角状、脉状穿插交代早期黄铁矿。g~l的拍摄条件均为反射光(单偏光)。Sul—硫化物;Py—黄铁矿;Sp—闪锌矿;Gn—方铅矿;Cp—黄铜矿;Po—磁黄铁矿;Q—石英图版Ⅰ.2. 样品及测试方法
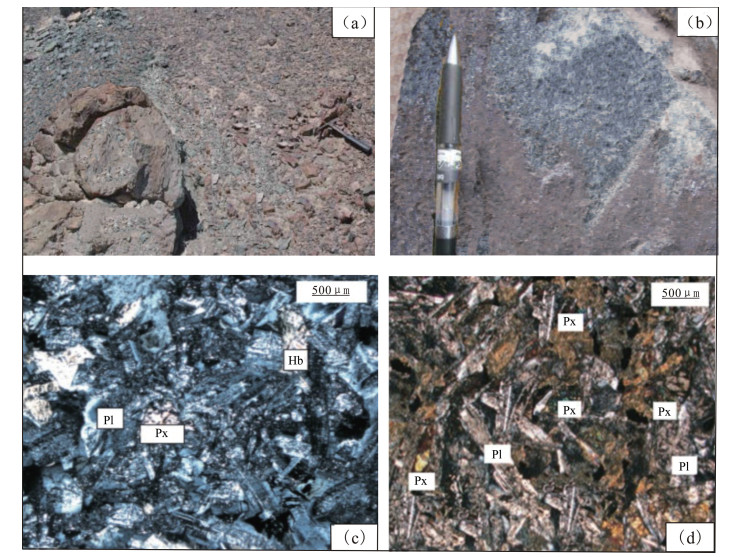
显微岩相学观察发现,黄铁矿和闪锌矿主要分布在石英-多金属硫化物阶段,其中,黄铁矿颗粒较纯净,早期黑色闪锌矿中含有大量乳滴状黄铜矿和磁黄铁矿,晚期红褐色闪锌矿则较干净。为保证样品的同源性、等时性及纯度,本次挑选的8个硫化物样品(5个闪锌矿和3个黄铁矿)均为二道河子矿床Ⅲ号矿带、主成矿阶段的共生黄铁矿和红褐色闪锌矿。锆石U-Pb定年样品采自Ⅲ号矿带730中段的安山玢岩脉,岩石呈斑状结构、块状构造,由斑晶和基质组成(图 2-b)。斑晶含量10%~15%,其中斜长石斑晶含量7%~10%,多发生绢云母化和碳酸盐化;暗色矿物斑晶含量3%~5%,全部蚀变成绿泥石,局部可见铁质,推测原矿物为角闪石。基质含量为85%~90%,成分为长石、角闪石和少量隐晶质等。
黄铁矿和闪锌矿的Rb、Sr含量可能低于0.1×10-6,为确保实验成功,首先在南京南太地质测试所采用电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) 进行草测,确认样品Rb、Sr含量较高并足以进行同位素组成测试。硫化物的Rb、Sr同位素组成测试在该所采用热电离同位素质谱仪(VG354型)上完成,具体测试过程及步骤见文献(Wang et al., 2007; 赵岩等, 2017)。测试中使用美国NBS987标样:87Sr/86Sr同位素比值为0.710236±0.000007,Sr的全流程空白为5×10-9~7×10-9g,87Sr/86Sr同位素比值用87Sr/86Sr=0.1194进行标准化,λRb=1.42×10-11 a-1。等时线年龄用Isoplot 3.7进行计算(Ludwig, 2003)。采用常规方法完成单颗粒锆石的挑选和制靶,然后在日内瓦大学对其进行透射光、反射光和阴极发光(CL)图像采集。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素测定在长安大学成矿作用及动力学实验室完成,仪器为美国Agilent公司的7700X型电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)和美国Photon Machines公司的Analyte Excite 193nm气态准分子激光剥蚀系统,激光束斑直径为35 μm,频率为8 Hz,激光能量密度为5.9 J/cm2,详细的仪器参数和测试过程见栾燕等(2019)。采用Glitter程序对锆石的同位素比值及元素含量进行计算,年龄计算及谐和图绘制采用Isoplot 3.7完成(Ludwig, 2003)。
3. 测试结果
二道河子矿床硫化物的Rb、Sr含量和同位素组成测试结果见表 1。硫化物Rb含量为0.081×10-6~2.632×10-6,Sr含量为0.661×10-6~3.186×10-6,Rb、Sr之间没有明显的相关性(图 4-a);87Rb/86Sr值为0.103~3.984,87Sr/86Sr值为0.711196~ 0.719006。样品中如果Rb和Sr发生丢失或有外来Rb和Sr的加入,那么在Rb/Sr与87Rb/86Sr值和87Sr/86Sr值关系图解(图 4)中,样品点不会呈线性关系;反之,则表明样品具有良好的Rb、Sr封闭性,87Rb和放射成因 87Sr与样品初始Rb含量有关(杨郧城等, 2015)。本次采集样品的Rb/Sr和87Rb/86Sr值呈线性正相关(图 4-b),Rb/Sr和87Sr/86Sr值基本呈正相关关系,但有2件样品(730-15-2和610-7-4)存在偏差(图 4-c),推测可能是后期热液活动造成初始Rb和Sr含量的变化(杨郧城等, 2015; Liu et al., 2018)。剔除这2件样品后,其他样品的Rb/Sr值与87Sr/86Sr值呈良好的正相关关系,说明它们的同位素体系是相对封闭和均一的,拟合出的Rb-Sr等时线年龄为140.8±2.3 Ma,87Sr/86Sr初始比值为0.711042±0.000070,MSWD=1.06(图 5),代表了成矿年龄,即二道河子矿床形成于早白垩世。
表 1 二道河子矿床黄铁矿和闪锌矿Rb-Sr同位素测试结果Table 1. Rb-Sr isotopic results of pyrite and sphalerite from the Erdaohezi deposit样品编号 测试矿物 Rb/10-6 Sr/10-6 87Rb/86Sr 计算误差 87Sr/86Sr 计算误差 测试误差 (87Sr/86Sr)i Rb/Sr 730-15-1 闪锌矿 0.4028 1.8180 0.6435 0.01 0.712384 0.00005 0.000008 0.71110 0.222 730-15-2 闪锌矿 0.2975 1.1090 0.7804 0.01 0.713609 0.00005 0.000017 0.71205 0.268 650-4-4 闪锌矿 0.0813 2.3470 0.1026 0.01 0.711196 0.00005 0.000009 0.71099 0.035 610-7-3 闪锌矿 0.3469 1.0160 0.9923 0.01 0.713073 0.00005 0.000008 0.71109 0.341 610-7-4 闪锌矿 0.1972 0.6608 0.8807 0.01 0.712014 0.00005 0.000015 0.71025 0.298 690-4-4 黄铁矿 2.6320 1.9580 3.9840 0.01 0.719006 0.00005 0.000008 0.71103 1.344 650-7-2 黄铁矿 1.8050 3.1860 1.6710 0.01 0.714323 0.00005 0.000009 0.71098 0.567 610-7-3 黄铁矿 1.2730 1.3870 2.7630 0.01 0.716597 0.00005 0.000009 0.71107 0.918 本次挑选的样品锆石较干净、透明,颗粒大小不一,粒径大小为60~150 μm。形态上,锆石颗粒多呈短柱状或长柱状(其长短轴比介于1.2~3.5之间),大多较自形,少数颗粒有残缺,所有颗粒均具有不同程度的韵律环带和明暗相间的条带结构(图 6)。上述特征表明,它们应属岩浆成因锆石(吴元保等, 2004)。锆石U-Pb同位素组成和年龄数据见表 2。其中锆石的Th和U含量分别为111.63×10-6~ 809.24×10-6和134.66×10-6~807.70×10-6,Th、U之间具有较好的正相关性,Th/U值较高,介于0.42~1.44之间,多数大于0.5。16个分析点得到的 206Pb/238U年龄范围在133~144 Ma之间,最大的年龄误差为3 Ma。数据点在206Pb/238U-207Pb/235U年龄谐和图上均落在年龄谐和曲线上。由此得出,锆石206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为138.8±1.7 Ma,MSWD=2.8(95%置信度)(图 7)。
表 2 二道河子矿床安山玢岩锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果Table 2. Zircon U-Th-Pb data for andesitic porphyry from the Erdaoehzi deposit测点号 元素含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Pb Th U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 1 12.53 575.06 400.44 1.44 0.0498 0.0028 0.1540 0.0087 0.0224 0.0003 145 8 143 2 2 5.84 178.73 218.85 0.82 0.0457 0.0031 0.1377 0.0086 0.0222 0.0004 131 8 142 3 3 7.55 229.84 273.70 0.84 0.0498 0.0029 0.1525 0.0088 0.0224 0.0004 144 8 143 2 4 8.22 263.48 306.59 0.86 0.0499 0.0026 0.1474 0.0078 0.0215 0.0003 140 7 137 2 5 10.24 427.28 363.97 1.17 0.0476 0.0027 0.1377 0.0077 0.0210 0.0003 131 7 134 2 6 14.78 530.14 513.54 1.03 0.0523 0.0024 0.1597 0.0074 0.0222 0.0003 150 6 141 2 7 13.21 395.73 478.80 0.83 0.0488 0.0021 0.1509 0.0066 0.0223 0.0003 143 6 142 2 8 14.14 381.37 536.71 0.71 0.0484 0.0022 0.1463 0.0065 0.0219 0.0003 139 6 140 2 9 3.64 111.63 134.66 0.83 0.0530 0.0046 0.1544 0.0134 0.0213 0.0005 146 12 136 3 10 14.40 443.41 527.98 0.84 0.0495 0.0020 0.1480 0.0059 0.0216 0.0002 140 5 138 2 11 19.20 620.18 719.63 0.86 0.0491 0.0020 0.1437 0.0059 0.0212 0.0003 136 5 135 2 12 8.10 250.25 294.92 0.85 0.0516 0.0038 0.1594 0.0119 0.0226 0.0004 150 10 144 3 13 11.46 200.64 474.36 0.42 0.0531 0.0037 0.1539 0.0111 0.0209 0.0003 145 10 133 2 14 12.86 400.00 477.41 0.84 0.0506 0.0027 0.1499 0.0079 0.0215 0.0003 142 7 137 2 15 6.47 126.59 258.09 0.49 0.0523 0.0033 0.1565 0.0097 0.0219 0.0004 148 8 140 2 16 22.86 809.24 807.70 1.00 0.0501 0.0018 0.1509 0.0055 0.0218 0.0002 143 5 139 2 4. 讨论
4.1 成岩/成矿时代
前人对得尔布干成矿带典型铅锌多金属矿床的成岩、成矿年龄进行了大量研究(表 3)(李进文等, 2011; 张斌等, 2011; 李铁刚等, 2014; 吴涛涛等, 2014; Yan et al., 2015; 杨郧城等, 2015; Li et al., 2016; Niu et al., 2017;2020;杨梅等, 2017; Xu et al., 2018;2020;刘桂香等, 2018; 曹艳华等, 2020),其中赋矿围岩塔木兰沟组火山熔岩的年龄介于159.2~166.0 Ma之间(张斌等, 2011; 吴涛涛等, 2014; Xu et al., 2018),晶屑岩屑凝灰岩的锆石U-Pb年龄为161.0~164.2 Ma(李进文等, 2011; Yan et al., 2015; Xu et al., 2018),与成矿关系密切的中酸性次火山岩-浅成侵入岩的年龄为141.9~152.2 Ma(Niu et al., 2017; 杨梅等, 2017; 刘桂香等, 2018; 曹艳华等, 2020),成矿体系蚀变矿物绢云母/白云母的Ar-Ar年龄为131.9~137 Ma(Li et al., 2016; Niu et al., 2020),硫化物Rb-Sr年龄为130.2~142.7 Ma(李铁刚等, 2014; 杨郧城等, 2015; 赵岩等, 2017; Xu et al., 2020)。本次获得二道河子矿床硫化物的Rb-Sr等时线年龄为140.8±2.3 Ma,切穿矿体的安山玢岩脉锆石U-Pb年龄为138.8±1.7 Ma,进一步验证了晚侏罗世—早白垩世是大兴安岭西坡得尔布干成矿带铅锌多金属矿化的高峰期。该期矿化年龄明显较塔木兰沟组火山岩的成岩年龄晚20~30 Ma,而与安山玢岩的锆石U-Pb年龄非常接近,这也和野外安山玢岩与矿体平行、局部切穿矿体的地质现象吻合,表明它们之间具有密切的成因联系。因此,笔者推测,塔木兰沟组火山熔岩-碎屑岩可能仅为成矿提供了有利的存储空间,但并非成矿母岩;而晚于围岩就位的安山玢岩不但局部有矿化现象,其成岩时间也和成矿时间非常相近或重合,可能为矿化提供了物源或热源。
表 3 得尔布干成矿带铅锌多金属矿床岩石/矿石年龄Table 3. The results of isotopic dating for rock/ore samples of the Pb-Zn deposits in the Derbugan metallogenic belt矿床名称 测试岩石(矿物) 定年方法 年龄 资料来源 得耳布尔 粗面安山岩 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 167.0±2.0 Ma Xu et al., 2018 岩屑晶屑凝灰岩 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 164.8±1.6 Ma 闪锌矿 Rb-Sr等时线 141.6±1.9 Ma 赵岩等, 2017 比利亚谷 流纹质火山角砾熔岩 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 159.2±1.8 Ma 吴涛涛等, 2014 二道河子 岩屑晶屑凝灰岩 SHRIMP锆石U-Pb 164.2±2.3 Ma 李进文等, 2011 岩屑晶屑凝灰岩 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 161.0±3.1 Ma Yan et al., 2015 硫化物 Rb-Sr等时线 130.5±3.6 Ma Xu et al., 2020 东珺 玄武粗面安山岩 SHRIMP锆石U-Pb 166.0±3.7 Ma 张斌等, 2011 闪锌矿 Rb-Sr等时线 130.2±4.4 Ma 杨郧城等, 2015 甲乌拉 石英斑岩 SHRIMP锆石U-Pb 150.1±1.8 Ma Niu et al., 2017 正长斑岩 SHRIMP锆石U-Pb 148.8±2.2 Ma 二长岩斑岩 SHRIMP锆石U-Pb 145.3±1.9 Ma 花岗斑岩 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 141.9±0.5 Ma 曹艳华等, 2020 花岗斑岩 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 146.4±1.6 Ma 杨梅等, 2017 石英二长斑岩 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 152.2±1.5 Ma 刘桂香等, 2018 白云母 Ar-Ar等时线 131.88±0.83 Ma Niu et al., 2020 硫化物 Rb-Sr等时线 142.7±1.3 Ma 李铁刚等, 2014 查干布拉根 二长花岗斑岩 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 143±2 Ma Li et al., 2016 绢云母 Ar-Ar等时线 137±3 Ma 4.2 成矿构造背景
额尔古纳地块位于大兴安岭山脉的西侧,不少学者对该区晚侏罗世—早白垩世的构造背景进行了研究,目前仍存在不少争论。葛文春等(2007)和孙景贵等(2012)认为,大兴安岭地区及其邻区为一个整体,在中生代主要受古太平洋板块俯冲作用影响,晚侏罗世—早白垩世的大规模成矿作用形成于太平洋构造转折的晚期,受伸展构造应力场的制约(毛景文等, 2005; 周建波等, 2016)。但许文良等(2013;2019)通过总结中生代火山岩的岩石组合及时空分布特征,指出晚侏罗世—早白垩世早期松辽盆地以西地区主要受蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋俯冲作用的影响。蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋板块自早石炭世—晚二叠世开始持续向南俯冲(Sun et al., 2013),以往认为蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋盆的封闭和陆陆碰撞发生在晚三叠世,此后进入后碰撞或晚碰撞阶段(佘宏全等, 2012),但更多资料显示,蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋从西向东呈“剪刀式”逐渐闭合(Zhao et al., 1990; Fritzell et al., 2016),东部最后的闭合时间可持续到晚侏罗世—早白垩世,并在此后变为广泛的伸展作用(Van der Voo et al., 2015; Fritzell et al., 2016; Guo et al., 2017)。额尔古纳地块早白垩世广泛发育A型花岗岩(流纹岩)和碱性花岗岩(流纹岩),结合辽西地区晚侏罗世—早白垩世土城子组之前(159~139 Ma)自北向南的推覆事件(张长厚等, 2002; Zhang et al., 2008),判定额尔古纳地块在早白垩世处于蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋闭合后的加厚陆壳坍塌形成的伸展环境(孟恩等, 2011; 许文良等, 2013)。
二道河子矿床位于大兴安岭西坡额尔古纳地块,其成矿年龄为140.8±2.3 Ma,安山玢岩脉的锆石U-Pb年龄为138.8±1.7 Ma,均为早白垩世。因此,笔者初步认为,二道河子矿床及与成矿有关的同期次火山岩-浅成侵入岩均形成于蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋闭合后的后碰撞阶段。碰撞后的局部伸展作用导致岩石圈拆沉,软流圈上涌,早期俯冲的岩石圈地幔物质和下地壳发生部分熔融,形成大规模的岩浆活动,部分岩浆沿深大断裂上涌到地表,形成广泛分布的塔木兰沟组火山岩地层;此后,同来源的中酸性岩浆及热液流体上侵到已有的火山岩地层中,并在有利的构造部位沉淀,形成次火山岩-浅成侵入岩及铅锌多金属矿床。二道河子矿床属热液脉状铅锌多金属矿床。额尔古纳地块内的甲乌拉、比利亚谷、得耳布尔、东珺等铅锌多金属矿床与二道河子矿床的成矿地质背景相似,成矿时代接近,表明它们应为同一成矿事件的产物。
5. 结论
(1) 大兴安岭西坡二道河子矿床主成矿阶段硫化物的Rb-Sr同位素等时限年龄为140.8±2.3 Ma,与成矿关系密切的安山玢岩脉的锆石U-Pb年龄为138.8±1.7 Ma,结果表明该矿床形成于早白垩世,矿化时间与次火山岩(安山玢岩)热事件相近。
(2) 结合前人研究成果,推测二道河子矿床成矿与安山质岩浆作用有关,形成于蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋闭合后伸展环境。
致谢: 野外工作过程中,得到武警黄金第十一支队李武毅、陈武等诸多同仁的帮助;论文写作过程中,得到桂林理工大学地球科学学院罗先熔教授的指导;审稿专家提出宝贵的修改意见,在此一并表示衷心的感谢。 -
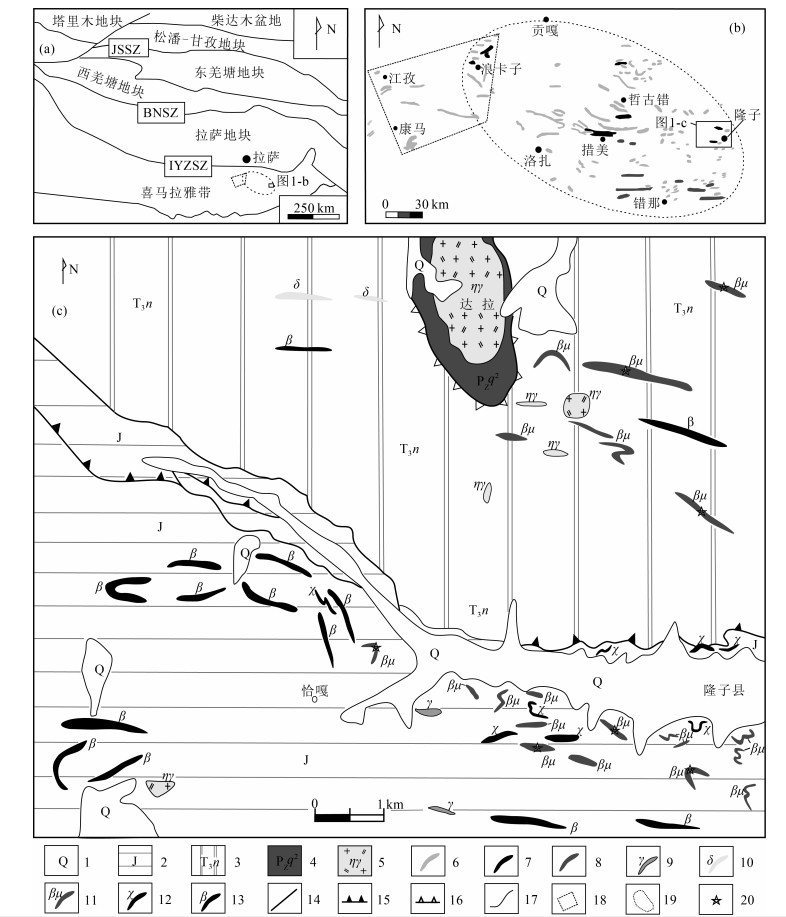
图 1 古堆地区地质简图
JSSZ—金沙江缝合带;BNSZ—班公湖-怒江缝合带;IYZSZ—印度河-雅鲁藏布江缝合带;1—第四系;2—侏罗系;3—三叠系涅如组;4—古生界曲德贡岩组;5—黑云母二长花岗岩;6—措美大火成岩省辉绿岩墙;7—措美大火成岩省辉长岩;8—措美大火成岩省玄武岩;9—花岗岩;10—闪长岩;11—辉绿、辉长岩;12—煌斑岩;13—火山岩;14—断层;15—逆冲推覆断裂;16—拆离断层;17—地质界线;18—最初提出的措美大火成岩省范围;19—后续新增的措美大火成岩省范围;20—采样点
Figure 1. Simplified geological map of Gudui area
表 1 古堆地区辉绿岩和辉长岩SHRIMP锆石U-Th-Pb分析结果
Table 1 SHRIMP zircon U-Th-Pb analysis results of diabase and gabbro in Gudui area
测试点号 206Pbc/% 含量/10-6 232Th/238U 207Pb*/206Pb* ±% 207Pb*/235U ±% 206Pb*/238U ±% 206Pb/238U
年龄/MaU Th 206Pb* 辉绿岩 1 1.21 549 1156 10.5 2.17 0.0473 13.6 0.14 13.6 0.0220 1.3 140.3 1.8 2 0.68 933 1914 17.3 2.12 0.0533 9.7 0.16 9.7 0.0214 1.0 136.5 1.4 3 1.71 585 1118 11.1 1.97 0.0447 16.9 0.13 17.0 0.0216 1.3 137.9 1.8 4 0.49 589 1061 11.1 1.86 0.0501 4.7 0.15 4.8 0.0219 0.9 139.7 1.2 5 0.83 835 2244 15.4 2.78 0.0457 6.8 0.13 6.8 0.0213 0.8 136.1 1.1 6 1.01 483 903 9.1 1.93 0.0479 6.3 0.14 6.4 0.0218 1.0 138.8 1.3 7 0.54 397 684 7.3 1.78 0.0488 8.6 0.14 8.8 0.0214 1.4 136.4 1.9 8 0.35 774 1972 14.2 2.63 0.0482 3.7 0.14 3.8 0.0213 0.8 136.0 1.0 9 0.64 427 799 8.1 1.93 0.0518 9.0 0.16 9.1 0.0220 1.1 140.3 1.6 10 0.30 1282 3840 23.9 3.09 0.0487 2.8 0.15 3.2 0.0216 1.5 137.9 2.1 辉长岩 1 2.28 210 92 3.8 0.44 0.0449 18.1 0.13 18.2 0.0205 1.7 130.8 2.2 2 0.00 1302 1962 23.4 1.51 0.0497 1.8 0.14 1.9 0.0209 0.5 133.6 0.7 3 1.74 1043 2010 19.1 1.93 0.0534 8.2 0.15 8.2 0.0209 0.8 133.6 1.1 4 2.04 991 2028 18.3 2.11 0.0485 9.5 0.14 9.6 0.0211 0.9 134.5 1.2 5 1.52 408 810 7.5 2.05 0.0439 17.0 0.13 17.1 0.0210 1.4 134.3 1.8 6 1.13 1020 2629 18.7 2.66 0.0427 10.2 0.12 10.2 0.0211 1.2 134.4 1.7 7 0.68 628 1343 11.5 2.21 0.0471 7.5 0.14 7.6 0.0212 1.2 135.5 1.6 8 1.31 818 2446 15.1 3.09 0.0490 8.2 0.14 8.3 0.0212 0.9 135.2 1.2 9 0.52 718 1567 12.8 2.26 0.0519 3.9 0.15 4.1 0.0207 1.0 131.8 1.3 表 2 古堆地区基性岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 2 Analysis results of major, trace and rare earth elements of basic rocks in Gudui area
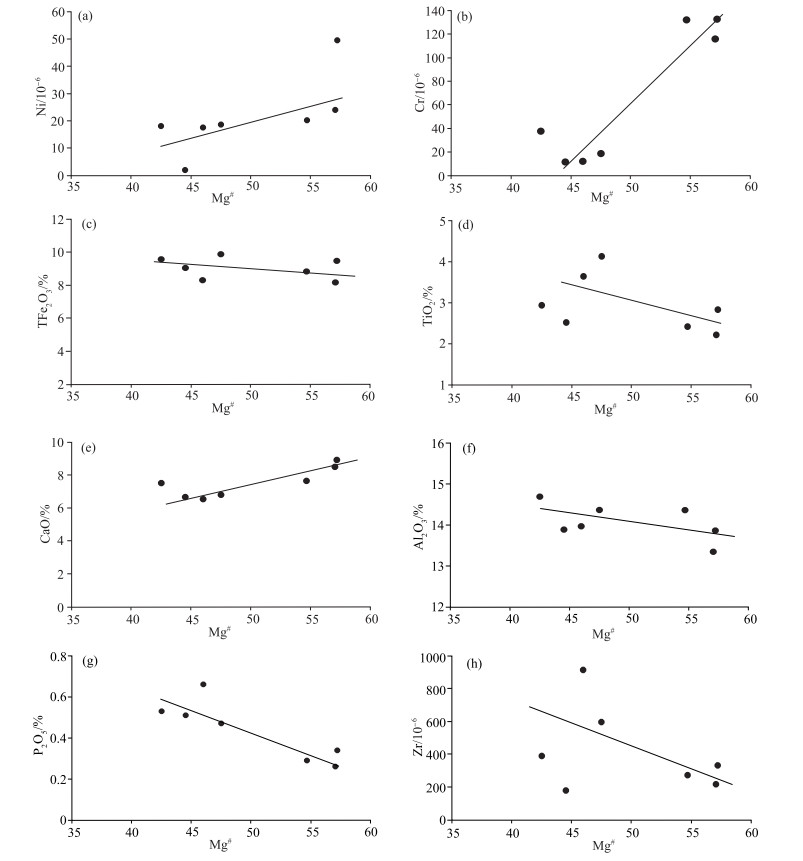
元素 辉长岩 辉绿岩 元素 辉长岩 辉绿岩 PM4QY002 11PM101 11PM102 11PM301 11PM302 11Q6 11Q8 PM4QY002 11PM101 11PM102 11PM301 11PM302 11Q6 11Q8 SiO2 52.14 49.85 48.76 49.18 48.14 51.70 50.61 Lu 0.69 0.48 0.31 0.49 0.54 0.74 0.72 TiO2 3.64 2.93 2.84 4.13 2.51 2.42 2.22 Y 48.98 34.71 35.19 36.53 42.41 55.17 49.69 Al2O3 13.96 14.68 13.86 14.36 13.88 14.36 13.34 ΣREE 325.49 128.53 265.92 184.2 235.31 220.31 191.63 Fe2O3 3.02 3.24 2.70 2.32 2.92 2.12 1.86 LREE 287.48 103.89 235.78 156.72 203.2 184.7 160.01 MnO 0.15 0.17 0.16 0.15 0.17 0.16 0.15 HREE 38.01 24.64 30.14 27.48 32.11 35.61 31.62 MgO 3.54 3.53 6.36 4.48 3.63 5.33 5.42 LREE/HREE 7.56 4.22 7.82 5.7 6.33 5.19 5.06 CaO 6.52 7.51 8.90 6.79 6.66 7.65 8.50 Na2O 3.84 3.82 3.07 4.39 2.83 2.74 2.46 (La/Yb)N 8.73 2.37 12.19 5.1 7.12 5.3 5.09 K2O 1.63 1.37 0.12 1.15 0.91 1.44 1.31 FeO 7.48 8.59 8.56 8.91 8.14 7.95 7.34 δEu 1.01 1.02 1.4 1.12 0.92 1.34 1.36 P2O5 0.66 0.53 0.34 0.47 0.51 0.29 0.26 Ba 433 501.5 155.7 205.8 201.8 355.4 279.4 Mg# 46.00 42.52 57.22 47.51 44.53 54.69 57.07 Co 40.8 24.2 45.5 52.2 36.5 43.83 41.65 烧失量 2.89 2.69 3.19 2.52 9.66 2.02 2.49 Cu 27 11.4 20.1 18.8 6 — — 总计 99.47 98.91 98.86 98.85 98.96 98.18 97.96 Ni 17.6 18.1 49.6 18.7 2 20.33 24.01 σ 3.27 3.93 1.77 4.97 2.72 2.01 1.87 Sc 19.6 17.6 26.8 23.6 16.7 26.3 25.4 Na2O+K2O 5.47 5.19 3.19 5.54 3.74 4.18 3.77 Sr 441.6 128.9 121.7 183.8 127.3 394.3 412.3 Zn 119.8 99.7 100.9 103 110.5 100.5 95.43 K2O/Na2O 0.42 0.36 0.04 0.26 0.32 0.53 0.53 Cr 12.2 37.5 132.6 18.8 11.8 131.7 115.8 Rb 22.2 125.3 5.0 20.4 26.1 50.3 49.92 A/CNK 0.70 0.68 0.65 0.69 0.72 0.72 0.73 Nb 61.7 27.15 18.19 41.99 29.24 26.44 28.56 La 57.72 10.69 38.74 24.02 37.03 37.34 32.84 Ta 3.54 1.69 0.97 2.54 1.45 0.72 0.63 Ce 119.2 44.51 94.78 65.64 85.91 78.77 68.17 W 0.68 2.64 0.91 0.62 0.41 2.11 1.59 Pr 15.94 6.37 13.7 9.15 11.56 10.23 8.78 Pb 13.8 26 5.7 13.7 20.9 21.65 24.77 Nd 75.72 32.31 69.13 45.03 54.38 43.64 37.5 Th 3.64 23.55 1.4 3 4.87 5.8 5.61 Sm 14.45 7.58 13.58 9.56 11.13 10.34 8.86 U 1.06 2.43 0.28 0.69 0.43 0.61 0.81 Eu 4.45 2.43 5.85 3.32 3.19 4.38 3.86 Sn 8.3 3.74 3.92 2.35 5 2.82 2.07 Gd 11.96 6.68 11.28 8.25 9.64 9.35 8.17 Zr 914.8 387.8 332.1 598.3 175.3 273.6 216.3 Tb 2.08 1.37 1.9 1.53 1.83 1.72 1.49 Li 17.2 39.8 35.7 31.5 74.1 36.92 25.66 Dy 10.39 7.13 8.67 7.69 9.14 10.39 9.08 Hf 12.8 10.2 5.4 6.8 7.3 7.21 10.82 Ho 2.04 1.47 1.59 1.57 1.83 2.05 1.83 V 237.8 139.7 271.4 312 256.4 273.2 257.3 Er 5.38 3.76 3.7 4.02 4.76 5.45 4.91 Au 0.1 0 0 0 0.07 0.82 0.88 Tm 0.73 0.52 0.41 0.55 0.64 0.86 0.79 Sb 1.12 0.72 0 0.57 0.54 0 0 Yb 4.74 3.23 2.28 3.38 3.73 5.05 4.63 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6,其中Au为10-9 -
西藏自治区地质矿产局.西藏自治区地质志[M]. 北京:地质出版社, 1993:449-450. 江思宏, 聂凤军, 胡朋, 等. 藏南基性岩墙群的地球化学特征[J]. 地质学报, 2007, 81(1): 60-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200701007.htm 童劲松, 刘俊, 钟华明, 等. 藏南洛扎地区基性岩墙群锆石U-Pb定年、地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(12): 1654-1664. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.12.019 周邦国, 张志, 李光明, 等. 藏南柯月铅锌矿床辉绿岩年代学及地球化学特征研究[J]. 矿物岩石, 2018, 38(1): 27-34. doi: 10.19719/j.cnki.1001-6872.2018.01.005 李永灿, 周清, 李应栩, 等. 藏南色岗辉绿岩墙群年代学及成因研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 2017, 23(1): 26-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201701003.htm 潘桂棠, 王立全, 朱弟成. 青藏高原区域地质调查中几个重大科学问题的思考[J]. 地质通报, 2004, 23(1): 12-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.01.007 钟华明, 童劲松, 夏军, 等. 藏南羊卓雍错南部桑秀组火山岩的特征及构造环境[J]. 地质通报, 2005, 24(1): 72-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2005.01.011 Zhu D C, Chuang S L, Mo X X. The 132 Ma Comei-Bunbury large igneous province: Remnants identified in present-day southeastern Australia[J]. Geology, 2009, 37: 583-586.
裘碧波, 朱弟成, 赵志丹, 等. 藏南措美残余大火成岩省的西延及其意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 26(7): 2207-2216. Hu X M, Jansa L, Chen L, et al. Provenance of Lower Cretaceous WÖlong volcaniclastics in the Tibetan Tethyan Himalaya: Implications for the final breakup of Eastern Gondwana[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2010, 223(3/4): 193-205.
张运昌, 陈彦, 杨青, 等. 西藏冈底斯带中部南木林地区林子宗群火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄和地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2019, 38(5): 719-732. https://www.cgsjournals.com/article/id/6153fe80ed73f876a05b5e01 聂凤军, 胡朋, 江思宏, 等. 藏南地区金和锑矿床(点)类型及其时空分布特征[J]. 地质学报, 2005, 79(3): 373-385. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2005.03.009 张刚阳. 藏南金锑多金属成矿带成矿模式与找矿前景研究[D]. 中国地质大学博士学位论文, 2012. Murphy M A, Harrison T M. The relationship between leucogranites and the South Tibet an detachment system, Rongbuk Valley, southern Tibet[J]. Geology, 1999, 27: 831-834.
周剑雄, 陈振宇. 锆石等测年矿物的电子探针及阴极射线致发光综合研究新方法[J]. 地质论评, 2002, 48(增刊): 31-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP2002S1007.htm Claoue-Long J C, Compston R W, Fanning C M. Two Carboniferous ages: A comparison of SHRIMP zircon dating with conventional zircon ages and 40Ar/39Ar analysis[C]//Berggren W A, Kent D V, Aubry M P, et al. Geochronology time scales and global stratigraphic coaelation: SEPM Special publication, 1995, 5(4): 3-31: Implications for the final breakup of Eastern Gondwana: Sedimentary Geology, 1995, 223(3/4): 193-205.
宋彪, 张玉海, 万渝生, 等. 锆石SHRIMP样品靶制作、年龄测定及有关现象讨论[J]. 地质论评, 2002, 48(增刊): 26-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP2002S1006.htm 吕晓春, 任冲, 成明, 等. 藏南隆子地区早白垩世双峰式火山岩的发现——来自SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年代学和岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 地质论评, 2016, 62(4): 945-954. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201604013.htm 陈雪峰, 刘希军, 许继峰, 等. 桂西那坡基性岩地球化学: 峨眉山地幔柱与古特提斯俯冲相互作用的证据[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2016, 40(3): 531-548. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201603010.htm 徐向珍, 杨经绥, 郭国林, 等. 雅鲁藏布江缝合带西段普兰蛇绿岩中地幔橄榄岩的岩石学研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(11): 3179-3196. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201111003.htm 曹光跃, 薛怀民, 刘哲, 等. 鲁西临朐地区早白垩世青山群火山岩的年代学、地球化学及岩石成因[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 92(3): 503-519. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201803006.htm Pearce J A. Trace element characteristics of lavas from destructive plate boundaries[C]//Thorpe R S. Andesites: Orogenic Andesites and Related Rocks. Chichester, England: John Wiley and Sons, 1982: 528-548.
丁枫, 高建国, 徐琨智. 西藏南部绒布地区基性岩脉岩石地球化学、年代学特征及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(2): 391-408. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202002004.htm Taylor S R, Mc Clennan S. The continental crust: Composition and evolution[M]. Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1985: 209-230.
张航, 柏勇, 徐争启, 等. 攀枝花大田地区辉绿岩脉岩石地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 2018, 38(4): 30-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS201804005.htm 郑吉林, 刘涛, 徐立明, 等. 大兴安岭嘎仙蛇绿混杂岩中超镁铁质岩地球化学、年代学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(4): 480-490. https://www.cgsjournals.com/article/id/6153fe63ed73f876a05b5d91 Halama R, Marks M, Brgmann G, et al. Crustal contamination of mafic magmas: evidence from a petrological, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Os-O isotope study of the proterozoic Isortoq dike swarm, South Greenland[J]. Lithos, 2004, 74: 199-232.
Sun S S, McDough W F. Chemical and isotope systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in ocean basins. Geol. Soc. London. Spec. Publ., 1989, 42: 313-345.
Weaver B L. The origin of ocean island basalt end-member compositions: trace element and isotopic constrains[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1991, 104: 381-297.
Lassiter J C, Depaolo D J. Plume lithosphere interaction in the generation of continental and oceanic flood basalts; chemical and isotopic constrains[C]//Mahoney J J, Coffin M F. Large igneous provinces; Continental, oceanic and planetary flood volcanism, Washington DC. American Geophysical Union Monograph, 2000, 100: 335-355.
Perfit M R, Gust D A, Bench A E. Chemical Characteristics of Island-Arc Basalts: Implications for Mantle Sources[J]. Chemical Geology, 1980, 30: 227-256.
贺新星, 肖龙, 王国灿, 等. 西准噶尔晚古生代中基性岩墙群岩石学成因及地质意义[J]. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(5): 777-796. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201505002.htm 董国臣, 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 等. 西藏冈底斯南带辉长岩及其所反映的壳幔作用信息[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(2): 203-210. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200802004.htm 王喜臣, 夏斌, 刘维亮, 等. 西藏蓬错蛇绿岩年代学、地球化学及岩石成因[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2018, 42(3): 550-569. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201803011.htm 张招崇, 王福生, 郝艳丽, 等. 峨眉山大火成岩省中苦橄岩与其共生岩石的地球化学特征及其对源区的约束[J]. 地质学报, 2004, 78(2): 171-180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200402004.htm 朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 等. 特提斯喜马拉雅桑秀组英安岩锆石SHRIMP年龄及其意义[J]. 科学通报, 2005, 50(4): 375-379. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB20050400C.htm 张雨轩, 解超明, 于云鹏, 等. 早侏罗世新特提斯洋俯冲作用——来自松多高镁闪长岩锆石U-Pb定年及Hf同位素的制约[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(8): 1387-1399. https://www.cgsjournals.com/article/id/6153fea9ed73f876a05b5efc 夏瑛, 朱弟成, 赵志丹, 等. 藏东南措美大火成岩省中OIB型镁铁质岩的全岩地球化学和锆石Hf同位素[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(5): 1588-1602. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201205023.htm 刘飞, 杨经绥, 连东洋, 等. 雅鲁藏布江缝合带西段北亚带的基性岩成因和构造意义[J]. 地球学报, 2015, 36(4): 441-454. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201504009.htm Kelemen P B, Hanghoj K, Greene A R, et al. One View of the geochemistry of Subduction—Related Magnmatic Arcs, with an Emphasis on Primitive Andesite and Lower Crust[J]. Treatise on Geochemistry, 2003, 3;593-659.
朱弟成, 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 等. 西藏南部二叠纪和早白垩世构造岩浆作用与特提斯演化: 新观点[J]. 地学前缘, 2009, 16(2): 1-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200902002.htm 朱弟成, 夏瑛, 裘碧波, 等. 为什么要提出西藏东南部早白垩世措美大火成岩省[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(11): 3659-3670. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201311001.htm Frey F A, McNaughton N J, Nelson D R, et al. Petrogenesis of the Bunbury basalt, weatern Australia: Interaction between the Kerguelen plume and Gondwana lithosphere?[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1996, 144(1/2): 163-183.
Ingle S, Scoates J S, Weis D, et al. Origin of Cretaceous continental basalts in southwestern Australia and eastern Indian: Insights from Os and Hf isotopes[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 209(1/2): 83-106.
杨高学, 李永军, 佟丽莉, 等. 西准噶尔蛇绿混杂岩中洋岛玄武岩研究新进展[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(2): 392-405. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201502014.htm 陈万峰, 王金荣, 张旗, 等. 洋岛和洋底高原玄武岩数据挖掘: 地球化学特征及其与MORB的对比[J]. 地质学报, 2017, 91(11): 2443-2455. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201711005.htm -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 何光武,蔡明海,胡鹏飞,肖俊杰,甘能俭,朱敏杰,吕堂安. 桂西北箭猪坡铅-锌-锑多金属矿床成因:来自闪锌矿微量、稀土元素及氢氧同位素的证据. 地质通报. 2024(Z1): 246-257 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 焦天龙,李进文,郭向国,佘宏全,任程昊,李长俭. 内蒙古二道河铅锌银矿床成矿流体、物质来源及成因探讨. 中国地质. 2024(02): 426-442 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 夏杰,卢友月,付建明,张遵遵,程顺波,李剑锋,宁勇云,冯经平,张吉梼. 南岭湘南吴家坪锡矿成岩成矿时代研究. 地质通报. 2024(04): 572-581 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: