Sedimentary environment and organic matter enrichment model of black shale from Cretaceous Bayingebi Formation in Balongwula, Yingen-Ejin Banner Basin
-
摘要:
银额盆地早白垩世沉积的巴音戈壁组湖相页岩是一套重要的烃源岩。通过对巴隆乌拉剖面黑色页岩进行地球化学分析,研究其主量、微量和稀土元素特征,以及黑色页岩沉积的古环境及有机质富集模式。结果表明,Sr/Ba值为0.14~0.24,平均值为0.18,B/Ga值为3.89~6.51,平均值为5.03,相当B含量为230.88×10-6~375.99×10-6,平均值为294.95×10-6,古盐度为11.97‰~15.83‰,平均值为14.70‰;V/(V+Ni)值为0.67~0.84,平均值为0.74,Ceanom值为-0.113~0.018,平均值为-0.055;古气候指数(C)为0.80~1.34,平均值为1.06,化学蚀变指数(CIA)为75~81,平均值为79;古水深为4.16~88.04 m,平均值为33.40 m;P/Ti值为0.10~0.22,平均值为0.15,过剩钡(BaXS)为-46.5×10-6~144.5×10-6,平均值为38.85×10-6。综合各参数特征,研究区黑色页岩沉积于温暖、湿润、半咸水、缺氧的还原环境,沉积水体较深,具有低的古生产力条件。有机碳含量与沉积环境间相关性的研究表明,巴音戈壁组黑色页岩有机质富集是古盐度、氧化-还原条件、古气候、古生产力等因素共同作用的结果。研究结果可为银额盆地中生界沉积演化和油气资源评价提供理论支撑。
Abstract:The lacustrine shale of Early Cretaceous Bayingebi Formation is a suite of important source rocks resources in the Yingen-Ejin Banner basin.We studied the characteristics of the major elements, trace elements and rare earth elements, and the paleoenvironment and organic matter enrichment model of the black shale by the geochemical analysis of the Balongwula section.The results show that Sr/Ba value is 0.14~0.24, average value is 0.18, B/Ga value is 3.89~6.51, average value is 5.03, equivalent boron content is 230.88×10-6~375.99×10-6, average value is 294.95×10 -6, paleosalinity is 11.97‰~15.83‰, average value is 14.70‰; V/(V+Ni) value is 0.67~0.84, average value is 0.74, the Ceanom value is -0.113~0.018, average value is -0.055; the paleoclimate index(C) is 0.80~1.34, average value is 1.06, the chemical index alteration(CIA) is 75~81, average value is 79; the ancient water depth is 4.16~88.04 m, average value is 33.40 m; P/Ti value is 0.10~0.22, average value is 0.15, the excess barium(BaXS) is -46.5×10-6~144.5×10-6, average value is 38.85×10-6.Based on the characteristics of various parameters, the black shale in the study area is deposited in a warm and humid climate, with a sedimentary environment of deep lacustrine facies under an brackish water and anoxic condition.The paleoproductivity reflect a low initial paleoproductivity.The study on the correlation between organic carbon content and sedimentary environment shows that the organic matter enrichment in black shale of Bayingebi Formation is the result of the combined action of paleosalinity, oxidation-reduction conditions, paleoclimate and paleo-productivity.This will provide theoretical support for the sedimentary evolution of Mesozoic and the evaluation of oil and gas resources in Yingen-Ejin Banner Basin.
-
沉积岩中元素的分配除取决于元素本身的物理化学性质外,还受到古气候、古环境的极大影响,因此沉积岩中的元素记录了沉积时的古环境及其演化信息,可以利用元素含量及比值恢复古沉积环境[1-3]。页岩作为陆相沉积中最细粒的部分,记录了丰富的古气候、古环境、古生产力等信息[4]。前人得出一系列用微量元素及比值判别沉积环境的指标[5-7],同时沉积环境控制着烃源岩有机质的富集、发育和分布,对烃源岩进行地球化学古环境恢复,对于含油气盆地油气的勘探开发具有重要的意义[8]。
前人对银额盆地巴格毛德地区早白垩世油页岩进行了古环境分析,主要利用地球化学数据或孢粉资料,判定该地区早白垩世为干热与温湿交替过渡性气候[9-10]、温暖湿润气候[11]或半湿润—湿润气候[12],并进行了有机质富集条件分析[10, 13]。关于银额盆地巴隆乌拉地区的黑色页岩则研究较少,1:20万银根幅区域地质调查报告描述其为黑色油页岩①,“内蒙古自治区油页岩矿产资源调查评价(西部地区)”项目通过含油率分析,显示其未达到油页岩的工业品位②,因此本文认为其为黑色页岩。本文以银额盆地巴隆乌拉剖面为研究对象,对黑色页岩进行地球化学分析,定量或半定量地恢复水体的古盐度、氧化-还原条件、古气候、古水深及古生产力等;同时,通过分析有机碳含量与沉积环境间的关系,探讨巴音戈壁组黑色页岩有机质富集模式,为银额盆地中生界沉积演化研究和油气勘探开发提供理论支撑。
1. 地质概况
银根-额济纳旗盆地(简称银额盆地)位于内蒙古自治区西部,东西长约700 km,南北宽75~225 km,东连狼山,南接雅布赖山,西与北大山交界,北毗邻中蒙边界[9]。大地构造位置处于华北板块、塔里木板块、哈萨克斯坦板块和西伯利亚板块的交汇带[14],划分出4个隆起(绿园隆起、特罗西滩隆起、宗乃山隆起和楚鲁隆起)和7个坳陷(居延海坳陷、务桃亥坳陷、达古坳陷、苏红图坳陷、苏亥图坳陷、尚丹坳陷和查干坳陷)(图 1-a)。
巴隆乌拉剖面位于查干坳陷的西南部(图 1-b),出露地层为白垩系巴音戈壁组,可分为2个岩性段:下段为灰白色砾岩、砂砾岩;上段下部为黄褐色钙质细粒长石砂岩,中部为灰黑色薄层粉砂质灰岩,上部为灰黑色页岩夹褐色钙质粉砂质页岩、紫灰、紫红色页岩(图 2)。
2. 实验方法及测试结果
在巴隆乌拉剖面选取新鲜、未风化的露头,采集16件地球化学样品(地理坐标:北纬40°57′0.75″、东经105°44′58.13″),具体采样位置及编号见图 2。在自然资源部岩浆作用成矿与找矿重点实验室进行主量、微量及稀土元素分析,主量元素采用X射线荧光光谱法(XRF)测定,分析精度优于2%;微量及稀土元素采用电感耦合等离子质谱仪法(ICP-MS)测定,分析精度优于5%。选取其中8件样品进行全岩X-衍射和粘土矿物定量分析。
黑色页岩主量元素分析结果见表 1。SiO2含量为52.39%~57.60%,平均值为55.26%;Al2O3含量为20.65%~23.11%,平均值为22.07%;TFe2O3含量为4.63%~8.57%,平均值为6.40%;MgO含量为1.34%~2.06%,平均值为1.55%;K2O含量为2.76%~3.06%,平均值为2.91%;烧失量为6.89%~10.54%,平均值为8.85%,其余CaO、Na2O、TiO2、P2O5、MnO含量较低。
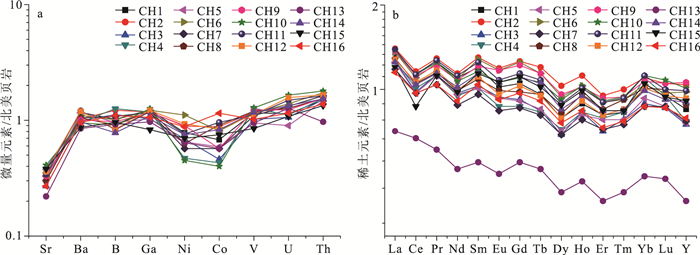
表 1 研究区黑色页岩主量元素分析结果Table 1. Major elements analysis of black shale in the study area样号 SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 FeO CaO MgO K2O Na2O TiO2 P2O5 MnO LOI CIA TOC P/Ti CH1 56.76 22.69 3.15 2.15 0.65 1.53 2.94 0.75 0.86 0.22 0.08 7.88 80 2.06 0.19 CH2 55.95 22.13 4.53 3.00 0.66 1.54 2.76 0.83 0.82 0.25 0.18 6.89 80 1.64 0.22 CH3 55.20 22.58 3.63 1.92 0.46 1.52 2.87 0.89 0.81 0.13 0.09 9.58 81 1.94 0.12 CH4 57.43 22.38 3.18 1.45 0.47 1.48 2.92 0.75 0.84 0.12 0.04 8.68 81 2.86 0.10 CH5 57.60 22.02 3.17 2.25 0.55 1.51 3.06 0.78 0.84 0.18 0.13 7.54 80 1.77 0.16 CH6 55.04 23.11 3.68 1.60 0.52 1.52 3.00 0.84 0.79 0.11 0.11 9.36 81 1.45 0.10 CH7 54.46 22.91 4.32 1.88 0.47 1.48 3.00 0.77 0.80 0.16 0.16 9.25 81 3.45 0.15 CH8 55.89 21.66 6.05 1.40 0.39 1.36 2.93 0.69 0.83 0.15 0.16 8.23 81 2.75 0.13 CH9 55.55 21.42 4.20 1.80 0.53 1.50 2.78 0.88 0.80 0.19 0.08 9.93 80 1.30 0.17 CH10 53.76 22.51 5.07 1.20 0.66 1.34 2.83 0.93 0.77 0.12 0.06 10.49 80 2.07 0.11 CH11 55.55 22.32 5.14 1.40 0.58 1.36 3.05 0.74 0.84 0.19 0.15 8.40 80 1.96 0.16 CH12 53.10 22.19 4.77 3.25 0.87 1.68 2.97 0.70 0.79 0.22 0.20 8.75 80 0.98 0.20 CH13 53.68 22.50 3.81 1.85 0.78 1.58 2.88 1.06 0.79 0.12 0.09 10.54 78 1.74 0.11 CH14 55.77 20.65 4.86 2.20 0.66 1.74 2.90 1.19 0.85 0.18 0.18 8.45 77 2.74 0.15 CH15 52.39 20.87 6.32 2.25 1.07 2.06 2.81 1.25 0.76 0.17 0.32 9.34 75 1.14 0.16 CH16 56.02 21.12 3.97 2.95 0.68 1.67 2.80 0.81 0.84 0.18 0.24 8.25 79 1.11 0.16 注:LOI为烧失量;CIA为化学蚀变指数,CIA=100×[Al2O3/(Al2O3+CaO*+Na2O+K2O)];TOC为有机碳含量;P/Ti为古生产力;主量元素含量单位为% 黑色页岩微量元素分析结果见表 2。北美页岩(NASC)标准化后的配分模式见图 3-a。巴隆乌拉剖面黑色页岩Sr、Ni和Co元素较北美页岩亏损,U和Th元素较北美页岩富集,Ba、B、Ga和V元素与北美页岩基本一致。
表 2 研究区黑色页岩微量元素分析结果Table 2. Trace elements analysis of black shale in the study area样号 Sr Ba B Ga Ni Co V U Th Sr/Ba B/Ga V/(V+Ni) h/m C BaXS CH1 110.00 642 132 28.20 52.90 13.00 151 4.21 18.00 0.17 4.68 0.74 26.28 0.89 83.00 CH2 113.00 567 159 27.20 60.60 16.70 154 4.70 18.50 0.20 5.85 0.72 46.01 1.30 34.00 CH3 116.00 547 145 23.70 47.20 8.79 132 3.91 18.10 0.21 6.12 0.74 9.52 0.95 20.50 CH4 102.00 530 164 27.20 32.20 8.16 165 4.11 18.60 0.19 6.03 0.84 7.18 0.80 -16.00 CH5 91.20 639 125 23.80 44.20 11.20 124 3.33 17.60 0.14 5.25 0.74 19.57 0.91 93.00 CH6 95.80 604 131 28.10 75.50 15.40 150 5.16 20.80 0.16 4.66 0.67 39.15 0.88 90.50 CH7 99.10 575 140 26.80 38.60 10.80 143 4.89 19.60 0.17 5.22 0.79 18.95 1.07 55.00 CH8 91.30 580 118 27.60 43.00 17.20 156 4.69 18.50 0.16 4.28 0.78 51.57 1.34 40.50 CH9 98.10 556 126 26.80 61.00 10.80 160 4.56 18.60 0.18 4.70 0.72 15.78 1.03 36.00 CH10 122.00 524 118 28.90 30.90 7.60 166 6.10 21.50 0.23 4.08 0.84 4.16 1.04 23.50 CH11 103.00 666 108 27.40 51.40 18.20 144 5.50 19.60 0.15 3.94 0.74 55.67 1.10 120.00 CH12 108.00 658 109 28.00 63.30 16.00 145 5.82 19.90 0.16 3.89 0.70 44.39 1.29 144.50 CH13 67.00 467 120 22.30 43.30 10.90 124 4.71 11.60 0.14 5.38 0.74 28.24 0.89 -46.50 CH14 79.70 533 101 25.10 51.00 15.70 152 4.95 18.40 0.15 4.02 0.75 43.38 1.09 -19.50 CH15 115.00 476 125 19.20 47.40 14.30 110 3.98 16.10 0.24 6.51 0.70 36.44 1.21 -18.00 CH16 82.40 527 143 24.40 60.00 21.90 133 4.24 16.50 0.16 5.86 0.69 88.04 1.19 -19.00 注:h为古水深;C为古气候指数,C =Σ(Fe+Mn+Cr+V+Co+Ni)/Σ(Ca+Mg+Sr+Ba+K+Na);BaXS为过剩钡,BaXS=Ba样品-Ti样品(Ba/Ti)PAAS,PAAS为后太古代澳大利亚页岩;微量元素含量单位为10-6 黑色页岩稀土元素分析结果见表 3。稀土元素总量(ΣREE)为117.35×10-6~236.72×10-6,平均值为205.37×10-6;轻稀土元素与重稀土元素比值(LREE/HREE)为3.39~4.78,平均值为3.99,相对富集轻稀土元素,用北美页岩(NASC)标准化后的配分模式见图 3-b,呈平缓的右倾斜曲线;(La/Yb)N值为1.15~1.43,平均值为1.29;(La/Ce)N值为1.05~1.38,平均值为1.23;δEuN值为0.90~0.96,平均值为0.93,未见正Eu异常;δCeN值为0.75~1.02,平均值为0.86,Ce具有轻微的负异常。
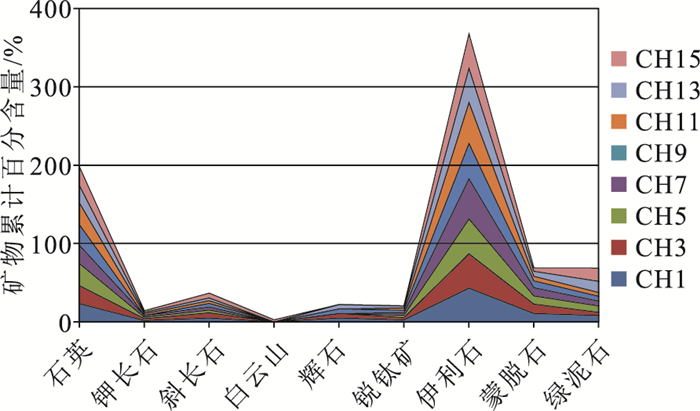
表 3 研究区黑色页岩稀土元素及北美页岩标准化计算结果Table 3. Rare earth elements analysis and NASC-normalized result of black shale in the study area样号 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb CH1 43.30 83.20 9.90 36.20 6.84 1.27 5.47 0.82 4.59 0.93 2.75 0.42 3.12 CH2 44.70 84.80 10.20 37.70 7.39 1.47 6.57 1.02 5.96 1.16 3.24 0.50 3.41 CH3 40.20 71.90 8.91 31.90 5.89 1.16 4.77 0.72 4.02 0.86 2.41 0.39 2.75 CH4 40.60 73.80 8.85 31.20 5.73 1.08 4.51 0.71 4.18 0.86 2.67 0.42 3.42 CH5 39.90 70.80 8.86 31.60 5.78 1.15 4.75 0.72 4.10 0.84 2.65 0.39 2.87 CH6 43.50 80.30 9.80 36.10 7.29 1.45 6.52 0.97 5.46 1.07 3.07 0.46 3.21 CH7 37.70 70.90 8.25 29.10 5.45 1.04 4.48 0.69 4.02 0.81 2.45 0.38 2.71 CH8 41.40 76.40 9.11 32.70 6.21 1.23 5.07 0.81 4.76 1.00 2.90 0.46 3.12 CH9 43.70 81.40 9.62 35.70 6.92 1.45 6.32 0.97 5.55 1.06 3.17 0.47 3.32 CH10 44.30 82.30 9.85 35.40 6.61 1.31 5.72 0.90 5.36 1.07 3.08 0.47 3.46 CH11 44.40 82.40 10.00 36.80 7.10 1.34 5.94 0.91 5.16 1.05 3.06 0.46 3.46 CH12 41.10 77.10 9.24 32.90 6.33 1.19 5.34 0.81 4.56 0.94 2.76 0.42 3.14 CH13 22.60 48.90 4.78 17.00 3.15 0.62 2.84 0.44 2.48 0.49 1.37 0.22 1.53 CH14 40.00 76.20 9.04 33.50 6.51 1.31 5.78 0.89 4.95 0.99 2.85 0.42 3.08 CH15 38.30 63.40 8.86 32.50 6.50 1.31 5.79 0.87 5.09 1.03 2.87 0.42 3.24 CH16 36.90 70.90 8.21 30.00 5.93 1.14 5.02 0.77 4.39 0.88 2.49 0.38 2.69 样号 Lu Y LREE HREE ΣREE LREE/HREE (La/Yb)N δEuN δCeN (La/Ce)N Ceanom CH1 0.46 22.90 180.71 41.44 222.15 4.36 1.34 0.91 0.88 1.19 -0.046 CH2 0.51 28.10 186.26 50.46 236.72 3.69 1.27 0.93 0.86 1.20 -0.053 CH3 0.41 20.30 159.96 36.63 196.59 4.37 1.42 0.96 0.83 1.28 -0.071 CH4 0.46 20.80 161.26 38.02 199.28 4.24 1.15 0.93 0.85 1.25 -0.060 CH5 0.42 20.40 158.09 37.14 195.23 4.26 1.35 0.96 0.82 1.29 -0.074 CH6 0.47 26.40 178.44 47.63 226.07 3.75 1.31 0.92 0.85 1.24 -0.063 CH7 0.42 20.80 152.44 36.76 189.20 4.15 1.35 0.92 0.88 1.21 -0.046 CH8 0.48 23.80 167.05 42.40 209.45 3.94 1.29 0.96 0.86 1.24 -0.057 CH9 0.51 28.50 178.79 49.87 228.66 3.59 1.28 0.96 0.86 1.22 -0.057 CH10 0.52 27.20 179.77 47.78 227.55 3.76 1.24 0.94 0.86 1.23 -0.055 CH11 0.48 26.80 182.04 47.33 229.37 3.85 1.24 0.91 0.85 1.23 -0.060 CH12 0.46 25.00 167.86 43.43 211.29 3.86 1.27 0.90 0.86 1.22 -0.051 CH13 0.23 10.70 97.05 20.29 117.35 4.78 1.43 0.92 1.02 1.05 0.018 CH14 0.44 24.30 166.56 43.71 210.27 3.81 1.26 0.94 0.87 1.20 -0.050 CH15 0.45 24.70 150.87 44.46 195.33 3.39 1.15 0.94 0.75 1.38 -0.113 CH16 0.41 21.30 153.08 38.34 191.42 3.99 1.33 0.92 0.89 1.19 -0.043 注:稀土元素含量单位为10-6 黑色页岩全岩X-衍射及粘土矿物定量分析结果见表 4。矿物成分主要为石英(22.1%~28.1%)、斜长石(3.5%~6.5%)和钾长石(1.7%~2.3%),少量辉石、锐钛矿和白云石;粘土矿物主要为伊利石(43.2%~52.3%)、蒙脱石(4.3%~11.8%)和绿泥石(4.2%~16.9%)(图 4)。
表 4 研究区黑色页岩全岩X-衍射及粘土矿物定量分析结果Table 4. Quantitative analysis results of X-diffraction and clay minerals of black shale in the study area% 样号 石英 钾长石 斜长石 白云石 辉石 锐钛矿 伊利石 蒙脱石 绿泥石 CH1 23.4 1.7 5.1 5.1 2.6 43.2 10.9 8.1 CH3 22.9 2.3 6.5 5.6 2.9 43.8 11.8 4.2 CH5 28.1 2.1 3.6 3.0 44.6 10.4 8.2 CH7 23.3 2.1 3.7 3.1 51.3 10.4 6.1 CH9 26.2 4.6 6.0 3.2 45.1 8.9 6.0 CH11 27.9 2.2 3.6 3.0 52.3 5.9 5.1 CH13 22.1 2.0 3.5 5.5 2.7 43.7 6.4 14.1 CH15 24.0 2.0 6.2 2.8 43.8 4.3 16.9 3. 沉积环境
3.1 古盐度
3.1.1 Sr/Ba值及Ba-Sr图解
Sr和Ba元素具有相似的化学性质,但Sr的迁移能力比Ba强,当水体盐度很低时,Sr、Ba均以重碳酸盐的形式出现,当水体盐度增大时,Ba首先以BaSO4的形式沉淀,留在水体中的Sr相对Ba富集,当水体盐度增大到一定程度时Sr才以SrSO4的形式沉淀。因而沉积物中Sr/Ba值与古盐度明显呈正相关性,可用来判断水体的古盐度[15]。同时,Ba-Sr图解也可以判别古盐度。该图解是麦列日克和普列多夫斯基进行粘土岩的沉积环境研究时提出来的,依据Ba元素与Sr元素的相关性,判别沉积物的古盐度[16]。
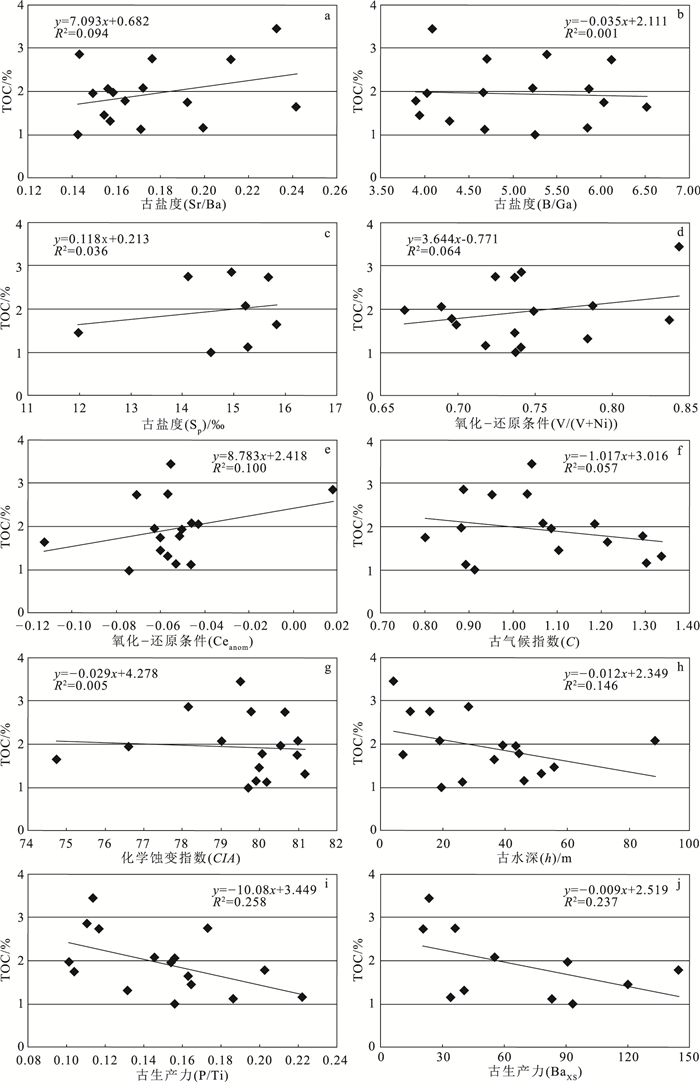
通常认为[17],Sr/Ba<0.6为淡水沉积,0.6≤Sr/Ba<1为半咸水沉积,Sr/Ba≥1为咸水沉积。研究区黑色页岩的Sr/Ba值为0.14~0.24,平均值为0.18(表 2;图 5),在Ba-Sr图上样品点全部落在半咸水区(图 6),综合分析认为,研究区黑色页岩为半咸水沉积。
3.1.2 B/Ga值
B和Ga元素的化学性质不同。硼酸盐溶解度大,能迁移,只有当水蒸发后才析出,Ga元素活动性低,易于沉淀,因此利用B/Ga值可以判断水体的古盐度[18]。
通常认为[17],B/Ga<4为淡水沉积,4≤B/Ga<7为半咸水沉积,B/Ga≥7为咸水沉积。研究区黑色页岩的B/Ga值为3.89~6.51,平均值为5.03(表 2;图 5),说明研究区黑色页岩主体为半咸水沉积。
3.1.3 B元素
B元素可以灵敏地反映盐度的变化,常被作为反映盐度的指标。Walker等[19-20]提出以伊利石理论K含量的8.5%来换算纯伊利石中的“校正B含量”,即校正B含量= 8.5×B测定值(10-6)/K2O(%),而伊利石的B含量又与K含量有关,为了在同等条件下进行对比,需计算相当于K2O为5%时的B含量,称为“相当B含量”,通常根据Walker的理论换算曲线,利用图解法求取(图 7)。同时相当B含量与校正B含量的图示关系可以换算成公式,即:相当B含量=11.8×校正B含量/[1.70×(11.8-K2O%)]。
Walker[20]研究认为,相当B含量<200×10-6为淡水—微咸水,200×10-6≤相当B含量<300×10-6为半咸水,300×10-6≤相当B含量<400×10-6为咸水,相当B含量≥400×10-6为超咸水。研究区黑色页岩的相当B含量为230.88×10-6~375.99×10-6,平均值为294.95×10-6(表 5;图 7),为半咸水—咸水沉积。
表 5 研究区黑色页岩粘土矿物含量及古盐度计算结果Table 5. Clay mineral content and paleosalinity of black shale in the study area样号 B/
10-6K2O/
%校正B
/10-6相当B
/10-6粘土矿物相对含量/% 校正粘土矿物/% B'/
10-6Couch古
盐度/‰I/S I Ch I S Ch CH1 132 2.94 381.63 298.98 70(25) 17 13 69.5 17.5 13.0 42.17 15.26 CH2 159 2.76 489.67 375.99 CH3 145 2.87 429.44 333.80 79(25) 14 7 73.3 19.8 7.0 43.61 15.67 CH4 164 2.92 477.40 373.16 CH5 125 3.06 347.22 275.76 66(25) 21 13 70.5 16.5 13.0 39.68 14.55 CH6 131 3.00 371.17 292.77 CH7 140 3.00 396.67 312.88 77(20) 14 9 75.6 15.4 9.0 42.02 15.22 CH8 118 2.93 342.32 267.88 CH9 126 2.78 385.25 296.46 74(20) 16 10 75.2 14.8 10.0 38.14 14.11 CH10 118 2.83 354.42 274.26 CH11 108 3.05 300.98 238.76 62(15) 30 8 82.7 9.3 8.0 30.91 11.97 CH12 109 2.97 311.95 245.22 CH13 120 2.88 354.17 275.60 66(15) 12 22 68.1 9.9 22.0 41.07 14.95 CH14 101 2.90 296.03 230.88 CH15 125 2.81 378.11 291.94 44(15) 30 26 67.4 6.6 26.0 44.20 15.83 CH16 143 2.80 434.11 334.80 注:I—伊利石;S—蒙脱石;Ch—绿泥石;I/S—伊/蒙混层,括号中数字为混层比;B'—Couch校正硼 利用B元素不仅可以定性分析古盐度,还能定量计算古盐度,常用的有Adamas(亚当斯)和Couch(科奇)公式[21-22]。Adamas公式适用于以伊利石为主的泥岩样品,Couch公式考虑了伊利石、蒙脱石、高岭石等多种粘土矿物的存在,以及各种粘土矿物吸附能力的差别。
通常认为,Sp<10‰为淡水—微咸水,10‰≤Sp<25‰为半咸水,25‰≤Sp<35‰为咸水,Sp≥35‰为超咸水[23]。研究区黑色页岩粘土矿物含量较高,主要为伊利石、蒙脱石和绿泥石,利用Couch公式计算较为符合实际情况,计算结果显示,研究区黑色页岩的古盐度为11.97‰~15.83‰,平均值为14.70‰(表 5;图 5),为半咸水沉积。
3.2 氧化-还原条件
元素在水体中的分异和富集受沉积水体氧化-还原条件的控制,因此沉积物中的元素变化记录了环境的变迁。运用这些特征元素的含量及其比值,可以得出当时水介质的氧化-还原条件[24-26]。
3.2.1 微量元素比值
Hatch等[27]和Jones等[28]指出,根据V/(V+Ni)值可判别沉积环境:V/(V+Ni)≥0.46指示还原环境,V/(V+Ni)<0.46代表氧化环境。研究区黑色页岩的V/(V+Ni)值为0.67~0.84,平均值为0.74(表 2;图 5),指示研究区黑色页岩沉积时为还原环境。
3.2.2 稀土元素
稀土元素中Ce异常值(Ceanom)能灵敏地反应沉积环境的氧化还原条件[29],其计算公式为:Ceanom=log[3CeN/(2LaN+NdN)],CeN、LaN、NdN分别代表元素Ce、La、Nd经北美页岩标准化的值。Ceanom大于-0.1,反映水体呈还原环境;Ceanom小于-0.1,反映水体呈氧化环境。研究区黑色页岩样品只有CH15的Ceanom值小于-0.1,其余样品均大于-0.1,为-0.113~0.018,平均值为-0.055(表 3;图 5),反映研究区黑色页岩沉积时主体为还原环境。
3.2.3 沉积岩颜色
沉积岩颜色是沉积的重要标志之一,尤其是泥质岩类的颜色,是判断沉积环境的重要标志[30]。通常灰色、黑色为还原环境中形成,而红色、紫红色则是在氧化环境中形成的。研究区页岩以深灰色、灰黑色为主(图 2),同时岩层中含自生黄铁矿晶粒,代表了水体较深、有机质较丰富,以还原环境为主的沉积特征。
3.3 古气候
3.3.1 古气候指数
元素在不同的气候条件下迁移富集规律不同,干燥的气候适合Ca、Mg等元素的富集,而潮湿的气候则适合Fe、Mn等元素的富集,因此定量引入古气候指数反映古气候条件[31],其计算公式为:C =Σ(Fe+Mn+Cr+V+Co+Ni)/Σ(Ca+Mg+Sr+Ba+K+Na)。
通常认为[31],C<0.1为干燥型气候,0.1≤C<0.2为半干燥型气候,0.2≤C<0.4为半潮湿型气候,C≥0.4为潮湿型气候。根据古气候指数计算公式得出,研究区黑色页岩古气候指数C值为0.80~1.34,平均值为1.06(表 2;图 5),指示研究区黑色页岩沉积时为潮湿型气候。
3.3.2 化学蚀变指数
根据泥岩的化学成分可以推断源区的风化作用,进而推断当时的气候条件。在风化作用过程中,稳定的阳离子易于保存(如Al3+、Ti4+),而不稳定的阳离子易于流失(如Na+、Ca2+、K+等)[32],元素的流失和富集程度取决于当时的化学风化强度[33]。Nesbit等[34]提出根据化学蚀变指数(CIA)来判断源区的风化程度,其计算公式为:CIA=100×[Al2O3/(Al2O3+CaO*+Na2O+K2O)],式中各元素采用摩尔分数,其中CaO*仅指硅质矿物中CaO的摩尔分数。CaO*的含量由Bock等的方法确定[35]:当CaO>Na2O时,CaO*=Na2O;当CaO≤Na2O时,CaO*=CaO。
通常认为[34],CIA为50~65,反映寒冷、干燥的气候条件下低等的化学风化作用;CIA为65~85,反映温暖、湿润气候条件下中等的化学风化作用;CIA为85~100,反映炎热、潮湿的热带亚热带条件下强烈的化学风化作用。研究区黑色页岩的化学蚀变指数(CIA)为75~81,平均值为79(表 1;图 5),指示巴音戈壁组黑色页岩沉积时为温暖、湿润的气候条件。
3.3.3 古生物标志
生物与其生活的环境是不可分割的统一体,根据地层中古生物化石的种类、大小、形态、完整性等,可以推测沉积时的古气候和古环境[36]。巴隆乌拉剖面巴音戈壁组上段产丰富的动植物化石①,包括脊椎动物、瓣鳃类、腹足类、叶肢介、介形虫、植物、孢粉等,其中植物化石有Elatocladus sp.,Brachyphyllum cf.obesum Hels,Sphenobdiera cf.longifolia,Baiera sp.,鱼化石有Leptolepiformis,Lycoptera wooduardi,说明当时的古气候适宜动植物的生存,为温暖、潮湿的气候条件。
3.4 古水深
传统的古水深研究多是根据岩性、沉积构造、沉积相、化石等定性推测。周洪瑞等[37]和吴智平等[38]提出定量计算最大古水深的方法,多位学者利用此方法取得了较好的效果[3, 39-40]。其计算公式为:
h=C/V3/2s Vs=Vo×NCo/(SCo−t×TCo) t=SLa/NLa 式中:h为古水深(m);C为常数(3.05×105);Vs为样品沉积时的沉积速率(m/Ma);Vo为正常环境的沉积速率,湖相泥岩沉积速率为(0.2~0.3)×103m/Ma;NCo为正常湖泊沉积物中Co的平均值(20×10-6);SCo为样品中Co的丰度(10-6);t为陆源输入的Co元素对样品的影响;TCo为陆源碎屑岩中Co的平均值(4.68×10-6);SLa为样品中La的丰度(10-6);NLa为陆源碎屑岩中La的平均值(38.99×10-6)。
利用微量元素Co的测试结果,经计算得出研究区黑色页岩沉积时的古水深为4.16~88.04 m,平均值为33.40 m(表 2;图 5),水深从下到上呈现振荡上升的趋势。目前,利用地球化学手段计算古水深尚不完善,仅能大致推测古水深的变化趋势[41]。
3.5 古生产力
3.5.1 P/Ti值
P元素是浮游生物的营养元素,可以指示沉积水体的古生产力。为了消除沉积有机质或自生矿物的影响,一般用P/Ti表征古沉积水体的初始生产力[42]。
通常认为[43],P/Ti<0.34为低生产力,0.34≤P/Ti<0.79为中等生产力,P/Ti≥0.79为高生产力。研究区黑色页岩P含量为480.7×10-6~1092.5×10-6,平均值为734.7×10-6;P/Ti值为0.10~0.22,平均值为0.15(表 1;图 5),指示研究区的古沉积水体为低生产力条件。
3.5.2 过剩钡(BaXS)
Ba元素一般以BaSO4的形式出现,它的沉积速率与古生产力具有对应关系[44],可以反映沉积水体的古生产力,一般用过剩钡(BaXS)来反映。其计算公式为:BaXS=Ba样品-Ti样品(Ba/Ti)PAAS,PAAS为后太古宙澳大利亚页岩,负值表示样品中Ba元素主要由陆源物质提供。
通常认为[45],BaXS<200×10-6为低生产力,200×10-6≤BaXS<1000×10-6为中等生产力,BaXS≥1000×10-6为高生产力。研究区黑色页岩过剩钡(BaXS)为-46.50×10-6~144.50×10-6,平均值为38.85×10-6(表 2;图 5),说明研究区的古沉积水体为低生产力条件。
4. 有机质富集模式
黑色页岩的形成受构造背景、热液活动、陆源输入、沉积环境、古生产力等因素影响,本文也从这几方面初步探讨银额盆地巴隆乌拉白垩系巴音戈壁组黑色页岩有机质的富集机制。
4.1 构造背景
查干坳陷是在晚古生代褶皱基底上发育起来的陆内断陷湖盆,沉积演化经历了断初、断陷和断坳3个阶段[46],早白垩世是盆地的主要发育时期,受北东向为主的正断裂控制[47]。巴音戈壁组下段为断初阶段,断陷发育强度较弱,规模较小,为低水位体系域,发育灰白色砾岩、砂砾岩;巴音戈壁组上段为断陷阶段,上段下部为水进体系域,发育黄褐色钙质细粒长石砂岩、灰黑色粉砂质灰岩,上段上部为高水位体系域,发育半深湖相灰黑色页岩夹褐色钙质粉砂质页岩,为坳陷最主要的烃源岩层。
通常认为,构造稳定区富集轻稀土元素,而构造活跃区贫轻稀土元素[48]。研究区黑色页岩轻稀土元素与重稀土元素比值(LREE/HREE)为3.39~4.78,平均值为3.99,相对富集轻稀土元素(表 3;图 3-b),表明该黑色页岩沉积时为稳定沉降的湖盆环境。热液活动会使沉积物具明显的正Eu异常,研究区黑色页岩的δEu值为0.90~0.96,平均值为0.93(表 3;图 3-b),Eu未见正异常,说明其未受到热液作用的影响。
4.2 陆源输入
页岩有机质的富集会受陆源碎屑输入的影响,元素Al、Ti、Th和Zr主要来自陆源碎屑,且后期成岩作用和风化作用对它们的影响微弱,因此可用来指示陆源输入[49]。研究区黑色页岩有机碳含量与Al、Ti、Th和Zr的相关性见图 8。有机碳含量与Al、Th和Zr的相关系数都较小,分别为0.012、0.001和0.025;有机碳含量与Ti的相关系数稍大,为0.315。总体来说,研究区巴音戈壁组陆源碎屑输入对有机质的富集影响微弱。
4.3 有机碳含量与沉积环境及古生产力的关系
有机质是生成油气的物质基础,常用有机碳含量(TOC)来评价烃源岩有机质丰度[50]。研究区16件烃源岩样品的TOC值为0.98%~3.45%,平均值为1.94%(表 1),达到好烃源岩的标准。利用黑色页岩有机碳含量与古盐度、氧化-还原条件、古气候、古水深及古生产力参数间的关系,分析巴音戈壁组黑色页岩有机质富集机制。
从图 9可以看出,巴音戈壁组黑色页岩有机碳含量与古盐度Sr/Ba、B/Ga、SP之间为弱的正相关性或无直接相关性,相关系数分别为0.094、0.001和0.036(图 9-a~c);与氧化-还原条件参数V/(V+Ni)和Ceanom之间为弱的正相关性,相关系数分别为0.064和0.100(图 9-d、e);与古气候指数(C)和化学蚀变指数(CIA)之间为弱的负相关性或无直接相关性,相关系数分别为0.057和0.005(图 9-f、g);与古水深(h)为负相关性,相关系数为0.146(图 9-h);与古生产力P/Ti和BaXS为负相关性,相关系数分别为0.258和0.237(图 9-i、j)。虽然有机碳含量与沉积环境各因素间的相关系数都较小,但与古盐度和氧化-还原条件为正相关性,其余为负相关性。半咸水和还原环境为有机质的保存提供了良好的条件;温暖、湿润的气候条件,虽然可以促进微生物的繁殖、增加水体的古生产力,但是大量的降水也会导致湖盆可容空间增大,稀释了沉降到水体底部的有机质浓度,导致有机质丰度降低[12]。
4.4 页岩有机质富集模式
有机质富集是复杂的物理化学过程,根据影响机制的不同,分为生产力模式型和保存模式型[42]。生产力模式型认为,有机质输入是其富集的主因,即古气候和古生产力等因素;保存模式型则认为,沉积环境是有机质富集的主要条件,即高盐度和缺氧的沉积环境等因素造成有机质的富集[51-52]。
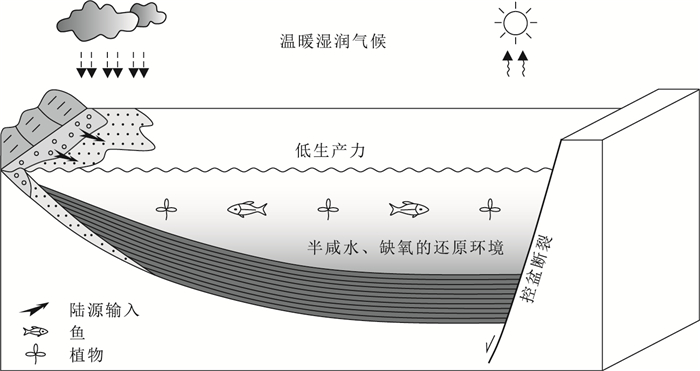
根据前述,研究区黑色页岩有机质富集受构造活动、热液活动及陆源输入影响微弱,有机碳含量与沉积环境及古生产力间的相关性研究表明,巴音戈壁组黑色页岩有机质富集是古盐度、氧化-还原条件、古气候、古生产力等因素共同作用的结果(图 10)。前人研究表明,绝大多数有机质在沉降过程中被降解,并统计了全球海洋的古生产力和海底沉积表层总有机碳含量的分布,发现古生产力与烃源岩分布的关系并不明显[53-54]。研究区黑色页岩形成时古沉积水体为低生产力条件,但半咸水、缺氧的还原环境提供了良好的保存条件,因此低生产力条件只要有机质能很好地保存,也能形成好的烃源岩。
5. 结论
(1) 研究区巴音戈壁组黑色页岩沉积时为温暖、湿润、半咸水、缺氧的还原环境,水深从下到上呈现振荡上升,沉积水体具有低生产力条件。
(2) 研究区黑色页岩有机质富集受构造活动、热液活动及陆源输入影响微弱,巴音戈壁组黑色页岩有机质富集是古盐度、氧化-还原条件、古气候、古生产力等因素共同作用的结果。
致谢: 文章撰写过程中得到中国地质调查局西安地质调查中心韩小锋、许海红高级工程师等的支持和帮助,审稿专家对本文提出了建设性的修改意见,在此一并表示衷心感谢。 -
表 1 研究区黑色页岩主量元素分析结果
Table 1 Major elements analysis of black shale in the study area
样号 SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 FeO CaO MgO K2O Na2O TiO2 P2O5 MnO LOI CIA TOC P/Ti CH1 56.76 22.69 3.15 2.15 0.65 1.53 2.94 0.75 0.86 0.22 0.08 7.88 80 2.06 0.19 CH2 55.95 22.13 4.53 3.00 0.66 1.54 2.76 0.83 0.82 0.25 0.18 6.89 80 1.64 0.22 CH3 55.20 22.58 3.63 1.92 0.46 1.52 2.87 0.89 0.81 0.13 0.09 9.58 81 1.94 0.12 CH4 57.43 22.38 3.18 1.45 0.47 1.48 2.92 0.75 0.84 0.12 0.04 8.68 81 2.86 0.10 CH5 57.60 22.02 3.17 2.25 0.55 1.51 3.06 0.78 0.84 0.18 0.13 7.54 80 1.77 0.16 CH6 55.04 23.11 3.68 1.60 0.52 1.52 3.00 0.84 0.79 0.11 0.11 9.36 81 1.45 0.10 CH7 54.46 22.91 4.32 1.88 0.47 1.48 3.00 0.77 0.80 0.16 0.16 9.25 81 3.45 0.15 CH8 55.89 21.66 6.05 1.40 0.39 1.36 2.93 0.69 0.83 0.15 0.16 8.23 81 2.75 0.13 CH9 55.55 21.42 4.20 1.80 0.53 1.50 2.78 0.88 0.80 0.19 0.08 9.93 80 1.30 0.17 CH10 53.76 22.51 5.07 1.20 0.66 1.34 2.83 0.93 0.77 0.12 0.06 10.49 80 2.07 0.11 CH11 55.55 22.32 5.14 1.40 0.58 1.36 3.05 0.74 0.84 0.19 0.15 8.40 80 1.96 0.16 CH12 53.10 22.19 4.77 3.25 0.87 1.68 2.97 0.70 0.79 0.22 0.20 8.75 80 0.98 0.20 CH13 53.68 22.50 3.81 1.85 0.78 1.58 2.88 1.06 0.79 0.12 0.09 10.54 78 1.74 0.11 CH14 55.77 20.65 4.86 2.20 0.66 1.74 2.90 1.19 0.85 0.18 0.18 8.45 77 2.74 0.15 CH15 52.39 20.87 6.32 2.25 1.07 2.06 2.81 1.25 0.76 0.17 0.32 9.34 75 1.14 0.16 CH16 56.02 21.12 3.97 2.95 0.68 1.67 2.80 0.81 0.84 0.18 0.24 8.25 79 1.11 0.16 注:LOI为烧失量;CIA为化学蚀变指数,CIA=100×[Al2O3/(Al2O3+CaO*+Na2O+K2O)];TOC为有机碳含量;P/Ti为古生产力;主量元素含量单位为% 表 2 研究区黑色页岩微量元素分析结果
Table 2 Trace elements analysis of black shale in the study area
样号 Sr Ba B Ga Ni Co V U Th Sr/Ba B/Ga V/(V+Ni) h/m C BaXS CH1 110.00 642 132 28.20 52.90 13.00 151 4.21 18.00 0.17 4.68 0.74 26.28 0.89 83.00 CH2 113.00 567 159 27.20 60.60 16.70 154 4.70 18.50 0.20 5.85 0.72 46.01 1.30 34.00 CH3 116.00 547 145 23.70 47.20 8.79 132 3.91 18.10 0.21 6.12 0.74 9.52 0.95 20.50 CH4 102.00 530 164 27.20 32.20 8.16 165 4.11 18.60 0.19 6.03 0.84 7.18 0.80 -16.00 CH5 91.20 639 125 23.80 44.20 11.20 124 3.33 17.60 0.14 5.25 0.74 19.57 0.91 93.00 CH6 95.80 604 131 28.10 75.50 15.40 150 5.16 20.80 0.16 4.66 0.67 39.15 0.88 90.50 CH7 99.10 575 140 26.80 38.60 10.80 143 4.89 19.60 0.17 5.22 0.79 18.95 1.07 55.00 CH8 91.30 580 118 27.60 43.00 17.20 156 4.69 18.50 0.16 4.28 0.78 51.57 1.34 40.50 CH9 98.10 556 126 26.80 61.00 10.80 160 4.56 18.60 0.18 4.70 0.72 15.78 1.03 36.00 CH10 122.00 524 118 28.90 30.90 7.60 166 6.10 21.50 0.23 4.08 0.84 4.16 1.04 23.50 CH11 103.00 666 108 27.40 51.40 18.20 144 5.50 19.60 0.15 3.94 0.74 55.67 1.10 120.00 CH12 108.00 658 109 28.00 63.30 16.00 145 5.82 19.90 0.16 3.89 0.70 44.39 1.29 144.50 CH13 67.00 467 120 22.30 43.30 10.90 124 4.71 11.60 0.14 5.38 0.74 28.24 0.89 -46.50 CH14 79.70 533 101 25.10 51.00 15.70 152 4.95 18.40 0.15 4.02 0.75 43.38 1.09 -19.50 CH15 115.00 476 125 19.20 47.40 14.30 110 3.98 16.10 0.24 6.51 0.70 36.44 1.21 -18.00 CH16 82.40 527 143 24.40 60.00 21.90 133 4.24 16.50 0.16 5.86 0.69 88.04 1.19 -19.00 注:h为古水深;C为古气候指数,C =Σ(Fe+Mn+Cr+V+Co+Ni)/Σ(Ca+Mg+Sr+Ba+K+Na);BaXS为过剩钡,BaXS=Ba样品-Ti样品(Ba/Ti)PAAS,PAAS为后太古代澳大利亚页岩;微量元素含量单位为10-6 表 3 研究区黑色页岩稀土元素及北美页岩标准化计算结果
Table 3 Rare earth elements analysis and NASC-normalized result of black shale in the study area
样号 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb CH1 43.30 83.20 9.90 36.20 6.84 1.27 5.47 0.82 4.59 0.93 2.75 0.42 3.12 CH2 44.70 84.80 10.20 37.70 7.39 1.47 6.57 1.02 5.96 1.16 3.24 0.50 3.41 CH3 40.20 71.90 8.91 31.90 5.89 1.16 4.77 0.72 4.02 0.86 2.41 0.39 2.75 CH4 40.60 73.80 8.85 31.20 5.73 1.08 4.51 0.71 4.18 0.86 2.67 0.42 3.42 CH5 39.90 70.80 8.86 31.60 5.78 1.15 4.75 0.72 4.10 0.84 2.65 0.39 2.87 CH6 43.50 80.30 9.80 36.10 7.29 1.45 6.52 0.97 5.46 1.07 3.07 0.46 3.21 CH7 37.70 70.90 8.25 29.10 5.45 1.04 4.48 0.69 4.02 0.81 2.45 0.38 2.71 CH8 41.40 76.40 9.11 32.70 6.21 1.23 5.07 0.81 4.76 1.00 2.90 0.46 3.12 CH9 43.70 81.40 9.62 35.70 6.92 1.45 6.32 0.97 5.55 1.06 3.17 0.47 3.32 CH10 44.30 82.30 9.85 35.40 6.61 1.31 5.72 0.90 5.36 1.07 3.08 0.47 3.46 CH11 44.40 82.40 10.00 36.80 7.10 1.34 5.94 0.91 5.16 1.05 3.06 0.46 3.46 CH12 41.10 77.10 9.24 32.90 6.33 1.19 5.34 0.81 4.56 0.94 2.76 0.42 3.14 CH13 22.60 48.90 4.78 17.00 3.15 0.62 2.84 0.44 2.48 0.49 1.37 0.22 1.53 CH14 40.00 76.20 9.04 33.50 6.51 1.31 5.78 0.89 4.95 0.99 2.85 0.42 3.08 CH15 38.30 63.40 8.86 32.50 6.50 1.31 5.79 0.87 5.09 1.03 2.87 0.42 3.24 CH16 36.90 70.90 8.21 30.00 5.93 1.14 5.02 0.77 4.39 0.88 2.49 0.38 2.69 样号 Lu Y LREE HREE ΣREE LREE/HREE (La/Yb)N δEuN δCeN (La/Ce)N Ceanom CH1 0.46 22.90 180.71 41.44 222.15 4.36 1.34 0.91 0.88 1.19 -0.046 CH2 0.51 28.10 186.26 50.46 236.72 3.69 1.27 0.93 0.86 1.20 -0.053 CH3 0.41 20.30 159.96 36.63 196.59 4.37 1.42 0.96 0.83 1.28 -0.071 CH4 0.46 20.80 161.26 38.02 199.28 4.24 1.15 0.93 0.85 1.25 -0.060 CH5 0.42 20.40 158.09 37.14 195.23 4.26 1.35 0.96 0.82 1.29 -0.074 CH6 0.47 26.40 178.44 47.63 226.07 3.75 1.31 0.92 0.85 1.24 -0.063 CH7 0.42 20.80 152.44 36.76 189.20 4.15 1.35 0.92 0.88 1.21 -0.046 CH8 0.48 23.80 167.05 42.40 209.45 3.94 1.29 0.96 0.86 1.24 -0.057 CH9 0.51 28.50 178.79 49.87 228.66 3.59 1.28 0.96 0.86 1.22 -0.057 CH10 0.52 27.20 179.77 47.78 227.55 3.76 1.24 0.94 0.86 1.23 -0.055 CH11 0.48 26.80 182.04 47.33 229.37 3.85 1.24 0.91 0.85 1.23 -0.060 CH12 0.46 25.00 167.86 43.43 211.29 3.86 1.27 0.90 0.86 1.22 -0.051 CH13 0.23 10.70 97.05 20.29 117.35 4.78 1.43 0.92 1.02 1.05 0.018 CH14 0.44 24.30 166.56 43.71 210.27 3.81 1.26 0.94 0.87 1.20 -0.050 CH15 0.45 24.70 150.87 44.46 195.33 3.39 1.15 0.94 0.75 1.38 -0.113 CH16 0.41 21.30 153.08 38.34 191.42 3.99 1.33 0.92 0.89 1.19 -0.043 注:稀土元素含量单位为10-6 表 4 研究区黑色页岩全岩X-衍射及粘土矿物定量分析结果
Table 4 Quantitative analysis results of X-diffraction and clay minerals of black shale in the study area
% 样号 石英 钾长石 斜长石 白云石 辉石 锐钛矿 伊利石 蒙脱石 绿泥石 CH1 23.4 1.7 5.1 5.1 2.6 43.2 10.9 8.1 CH3 22.9 2.3 6.5 5.6 2.9 43.8 11.8 4.2 CH5 28.1 2.1 3.6 3.0 44.6 10.4 8.2 CH7 23.3 2.1 3.7 3.1 51.3 10.4 6.1 CH9 26.2 4.6 6.0 3.2 45.1 8.9 6.0 CH11 27.9 2.2 3.6 3.0 52.3 5.9 5.1 CH13 22.1 2.0 3.5 5.5 2.7 43.7 6.4 14.1 CH15 24.0 2.0 6.2 2.8 43.8 4.3 16.9 表 5 研究区黑色页岩粘土矿物含量及古盐度计算结果
Table 5 Clay mineral content and paleosalinity of black shale in the study area
样号 B/
10-6K2O/
%校正B
/10-6相当B
/10-6粘土矿物相对含量/% 校正粘土矿物/% B'/
10-6Couch古
盐度/‰I/S I Ch I S Ch CH1 132 2.94 381.63 298.98 70(25) 17 13 69.5 17.5 13.0 42.17 15.26 CH2 159 2.76 489.67 375.99 CH3 145 2.87 429.44 333.80 79(25) 14 7 73.3 19.8 7.0 43.61 15.67 CH4 164 2.92 477.40 373.16 CH5 125 3.06 347.22 275.76 66(25) 21 13 70.5 16.5 13.0 39.68 14.55 CH6 131 3.00 371.17 292.77 CH7 140 3.00 396.67 312.88 77(20) 14 9 75.6 15.4 9.0 42.02 15.22 CH8 118 2.93 342.32 267.88 CH9 126 2.78 385.25 296.46 74(20) 16 10 75.2 14.8 10.0 38.14 14.11 CH10 118 2.83 354.42 274.26 CH11 108 3.05 300.98 238.76 62(15) 30 8 82.7 9.3 8.0 30.91 11.97 CH12 109 2.97 311.95 245.22 CH13 120 2.88 354.17 275.60 66(15) 12 22 68.1 9.9 22.0 41.07 14.95 CH14 101 2.90 296.03 230.88 CH15 125 2.81 378.11 291.94 44(15) 30 26 67.4 6.6 26.0 44.20 15.83 CH16 143 2.80 434.11 334.80 注:I—伊利石;S—蒙脱石;Ch—绿泥石;I/S—伊/蒙混层,括号中数字为混层比;B'—Couch校正硼 -
Algeo T J, Maynard J B. Trace-element behavior and redox facies in core shales of Upper Pennsylvanian Kansas-type cyclothems[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 206(3/4): 289-318.
张天福, 孙立新, 张云, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地北缘侏罗纪延安组、直罗组泥岩微量、稀土元素地球化学特征及其古沉积环境意义[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(12): 3454-3472. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.12.013 范萌萌, 卜军, 赵筱艳, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东南部延长组微量元素地球化学特征及环境指示意义[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 49(4): 633-642. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ201904016.htm 刘招君, 孟庆涛, 柳蓉, 等. 抚顺盆地始新统计军屯组油页岩地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(10): 2340-2350. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200910004.htm 陶树, 汤达祯, 周传祎, 等. 川东南—黔中及其周边地区下组合烃源岩元素地球化学特征及沉积环境意义[J]. 中国地质, 2009, 36(2): 397-403. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2009.02.013 Yuan K, Huang W H, Fang X X, et al. Geochemical characteristics and sedimentary environment of the Middle Devonian organic-rich shales in the Northwest of Guizhong Depression, Southwest China[J]. China Geology, 2020, 3(4): 567-574. doi: 10.31035/cg2020062
马中豪, 陈清石, 史忠汪, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地南缘延长组长7油页岩地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2016, 35(9): 1550-1558. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.09.022 马素萍, 夏燕青, 田春桃, 等. 南襄盆地泌阳凹陷湖相碳酸盐岩烃源岩沉积环境的元素地球化学标志[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2013, 32(4): 456-462. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2013.04.009 陈会军, 刘招君, 柳蓉, 等. 银额盆地下白垩统巴音戈壁组油页岩特征及古环境[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2009, 39(4): 669-675. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200904010.htm 武昕普, 柳蓉, 张坤, 等. 银额盆地下白垩统巴音戈壁组含油页岩岩系地球化学特征及有机质富集条件[J]. 世界地质, 2019, 38(4): 1021-1031. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2019.04.013 张明震, 吉利民, 戴霜. 银额盆地早白垩世孢粉记录的气候变化[C]//中国古生物学会第28届学术年会论文摘要集, 2015. 柳蓉, 闫旭, 刘招君, 等. 银额盆地下白垩统巴音戈壁组含油页岩岩系孢粉化石特征及地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2020, 50(2): 341-355. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202002004.htm Zhang K, Liu R, Liu Z J, et al. Influence of palaeoclimate and hydrothermal activity on organic matter accumulation in lacustrine black shales from the Lower Cretaceous Bayingebi Formation of the Yin'e Basin, China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2020, 560.
任纪舜, 王作勋, 陈炳蔚, 等. 从全球看中国大地构造: 中国及邻区大地构造图简要说明[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1999. 郑荣才, 柳梅青. 鄂尔多斯盆地长6油层组古盐度研究[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1999, 20(1): 20-25. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.1999.01.005 王涛, 胡能高, 杨家喜, 等. 东秦岭峡河岩群及有关问题讨论[J]. 中国区域地质, 1997, 16(4): 415-421. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD704.010.htm 王益友, 郭文莹, 张国栋. 几种地化标志在金湖凹陷阜宁群沉积环境中的应用[J]. 同济大学学报, 1979, 7(2): 51-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJDZ197902005.htm 李进龙, 陈东敬. 古盐度定量研究方法综述[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2003, 10(5): 1-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2003.05.001 Walker C T, Price N B, Wales S. Departure curves for computing paleosalinity from boron in illites and shales[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1963, 47(5): 833-841.
Walker C T. Evaluation of boron as a paleosalinity indicator and its application to offshore prospects[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1968, 52(5): 751-766.
Adams T D, Haynes J R, Walker C T. Boron in Holocene illites of the dovey estuary, wales, and its relationship to paleosalinity in cyclothems[J]. Sedimentology, 1965, 4: 189-195. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1965.tb01288.x
Couch E L. Calculation of paleosalinities from boron and clay mineraldata[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1971, 55(10): 1829-1837.
钟红利, 蒲仁海, 闫华, 等. 塔里木盆地晚古生代古盐度与古环境探讨[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 42(1): 74-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-274X.2012.01.017 Meyer E E, Quicksall A N, Landis J D, et al. Trace and race earth elemental investigation of a Sturtian cap carbonate, Pocatello, Idaho: evidence for ocean redox conditions before and during carbonate deposition[J]. Prccambrian Research, 2012, 192/195: 89-106. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2011.09.015
Maslov A V, Podkovyrow V N. Ocean redox state at 2500-500 Ma: Modern concepts[J]. Lithology and Mineral Resources, 2018, 53(3): 190-211. doi: 10.1134/S0024490218030057
夏鹏, 付勇, 杨镇, 等. 黔北镇远牛蹄塘组黑色页岩沉积环境与有机质富集关系[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(3): 947-956. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.03.019 Hatch J R, Leventhal J S. Relationship between inferred redox potential of the depositional environment and geochemistry of the Upper Pennsylvanian(Missourian)Stark Shale Member of the Dennis limestone, Wabaunsee County, Kansas, USA[J]. Chemical Geology, 1992, 99(1/3): 65-82.
Jones B J, Manning A C. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 111(1/4): 111-129.
Wright J, Schrader H, Holser W T. Palaeoredox variations in ancient oceans recorded by rare earth elements in fossil apatite[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1987, 51(3): 631-644. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(87)90075-5
刘宝君, 曾允孚. 岩相古地理基础和工作方法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1985. 杨万芹, 蒋有录, 王勇. 东营凹陷沙三下—沙四上亚段泥页岩岩相沉积环境分析[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 39(4): 19-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2015.04.003 Fedo C M, Nesbit H W, Young G M. Unravelling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleosoles, with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance[J]. Geology, 1995, 23(10): 921-924. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0921:UTEOPM>2.3.CO;2
Condie K C, Noll J P D, Conway C M. Geochemical and detrital mode evidence for two sources of Early Proterozoic sedimentary rocks from the Tonto Basin Supergroup, Central Arizona[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1992, 77(1/2): 51-76.
Nesbitt H W, Young G M. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites[J]. Nature, 1982, 299: 715-717. doi: 10.1038/299715a0
Bock B, Mclennan S M, Hanson G N. Geochemistry and provenance of the Middle Ordovician Austin Glen Member(Normanskill Formation)and the Taconian Orogeny in New England[J]. Sedimentology, 1998, 45: 635-655. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3091.1998.00168.x
姜在兴. 沉积学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2003. 周洪瑞, 王自强, 崔新省, 等. 华北地台南部中新元古界层系地层研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1999. 吴智平, 周瑶琪. 一种计算沉积速率的新方法——宇宙尘埃特征元素法[J]. 沉积学报, 2000, 18(3): 395-399. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2000.03.012 张才利, 高阿龙, 刘哲, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地长7油层组沉积水体及古气候特征研究[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2011, 22(4): 582-587. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201104004.htm 王峰, 刘玄春, 邓秀芹, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地纸坊组微量元素地球化学特征及沉积环境指示意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(6): 1265-1273. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201706017.htm 李继东, 付玉鑫, 蒋飞虎, 等. 银额盆地下白垩统巴音戈壁组泥岩地球化学特征与古环境意义[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 41(3): 48-56, 65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGXB202203007.htm 林晓慧, 詹兆文, 邹艳荣, 等. 准噶尔盆地东南缘芦草沟组油页岩元素地球化学特征及沉积环境意义[J]. 地球化学, 2019, 48(1): 67-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201901006.htm Algeo T J, Kuwahara K, Sano H, et al. Spatial variation in sediment fluxes, redox conditions, and productivity in the Permian-Triassic Panthalassic Ocean[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2011, 308(1/2): 65-83.
Paytan A, Kastner M. Benthic Ba fluxes in the central Equatorial Pacific, implications for the oceanic Ba cycle[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1996, 142(3/4): 439-450.
Pi D H, Liu C Q, Graham A, et al. Trace and rare earth element geochemistry of black shale and kerogen in the early Cambrian niutitang Formation in Guizhou Province, South China: Constraints for redox environments and origin of metal enrichments[J]. Precambrian Research, 2013, 225: 218-229. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2011.07.004
郭彦如. 银额盆地查干断陷闭流湖盆层序类型与层序地层模式[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2003, 14(6): 448-452. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2003.06.004 郑孟林, 李明杰, 曹春潮, 等. 北山—阿拉善地区白垩纪、侏罗纪盆地叠合特征[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2003, 27(4): 384-389. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2003.04.010 田巍, 王传尚, 白云山, 等. 湘中涟源凹陷上泥盆统佘田桥组页岩地球化学特征及有机质富集机理[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(11): 3794-3811. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201911019.htm Li Y F, Zhang T W, Ellis G S, et al. Depositional environment and organic matter accumulation of Upper Ordovician-Lower Silurian marine shale in the Upper Yangtze Platform, South China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2017, 466: 252-264. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2016.11.037
陆克政, 朱筱敏, 漆家福. 含油气盆地分析[M]. 东营: 中国石油大学出版社, 2006. Hofmann P, Ricken W, Schwark L, et al. Carbon-sulfur-iron relationships and 13C of organic matter for late Albian sedimentary rocks from North Atlantic Ocean: paleoceanographic implications[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2000, 163(3): 97-113.
Tyson R V. The "productivity versus preservation" controversy: Cause, flaws and resolution[J]. SEPM Spec. Publ., 2005, 82: 7-33.
丁修建, 柳广弟, 黄志龙, 等. 有机质供给和保存在烃源岩形成中的控制作用[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(5): 832-842. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201605009.htm Demaison G J, Moore G T. Anoxic environments and oil source bed genesis[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1980, 2(1): 9-31. doi: 10.1016/0146-6380(80)90017-0
宁夏回族自治区地质局. 1:20万银根幅区域地质调查报告. 1980. 西安地质矿产研究所. 内蒙古自治区油页岩矿产资源调查评价(西部地区)报告. 2008. -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 张培兴,韩健健,靳天禄,周娜,李金霞,刘帅,周静文. 综合地质与经济因素的城市地下空间开发潜力探析. 价值工程. 2025(02): 80-82 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 鲜于慧玲,李红,王幸文. 吉林省大安市耕地后备资源开发适宜性研究. 世界地质. 2025(01): 164-178 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张静,崔健,马诗敏,代雅建,朱巍. 基于层次分析法与频率比模型的采空塌陷危险性评价. 地质与勘探. 2024(01): 88-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 卜吉武,李家乐,姜亚东,娜仁花. 基于层次分析法的赤峰市地质灾害易发性评价. 环境与发展. 2024(01): 20-27 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: