Zircon U-Pb age, petrogenesis and tectonic model of Miocene quartz monzonite in Zuozuoxiang area, Western Lhasa terrane
-
摘要:
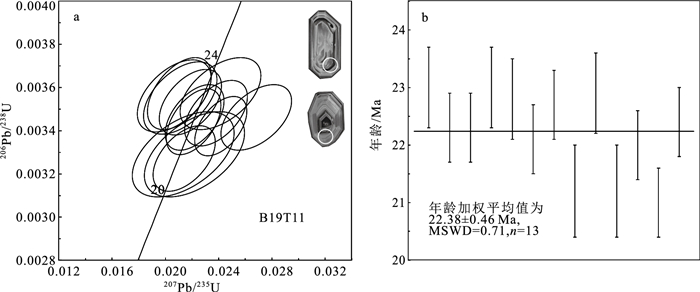
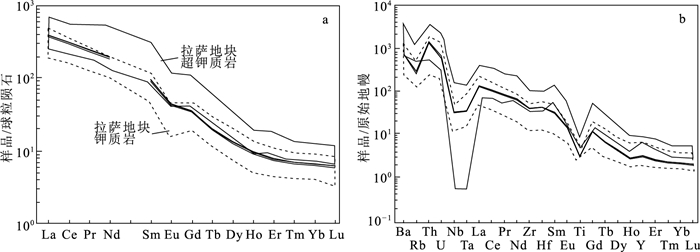
中新世的岩浆活动对于判别青藏高原新生代的构造演化具有重要意义,本文在拉萨地体西部左左乡地区新厘定出一套中新世石英二长岩。通过LA-ICP-MS测年,获得锆石206Pb/238U年龄为22.38±0.46 Ma(n=13,MSWD=0.71),此年龄可代表石英二长岩的形成时代。全岩化学成分显示,其具有高的SiO2(65.87%~66.90%)、K2O(6.19%~6.41%)含量、K2O/Na2O值(1.7~1.8)及低的MgO(1.71%~1.76%)含量,岩石类型属于拉萨地体中新世钾质中酸性岩系列。依据岩石高的Mg#(56.5~57.8)值、Nb/Ta(16.0~16.4)值、Cr(46.0×10-6~48.9×10-6)、Ni(32.6×10-6~34.8×10-6)含量及大量的暗色包体,推测左左乡中新世石英二长岩形成于壳源岩浆与幔源岩浆的混合。依据区域内的隆升研究结果,推测印度板片分段俯冲及撕裂模型相比于岩石圈地幔对流减薄模型、增厚岩石圈拆沉模型、俯冲印度板片断裂模型能够更合理地解释拉萨地体中新世钾质-超钾质火山岩的成因。
-
关键词:
- 拉萨地体 /
- 中新世 /
- 钾质中酸性岩 /
- 印度板片撕裂 /
- LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年
Abstract:The Miocene magmatism is of great significance to distinguish the Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau.In this paper, a new set of Miocene quartz monzonite has been redefined in Zuozuoxiang area, western Lhasa terrane.Zircon U-Pb dating shows that the age of quartz monzonite is 22.38±0.46 Ma.Whole rock geochemical test shows that quartz monzonite has high SiO2 (65.87%~66.90%), K2O(6.19%~6.41%)contents, K2O/Na2O(1.7~1.8)ratios and low MgO(1.71%~1.76%)contents, belonging to potassic intermediate-acid rock.According to the high Mg#(56.5~57.8), Nb/Ta(16.0~16.4), Cr(46.0×10-6~48.9×10-6), Ni(32.6×10-6~34.8×10-6)and a large number of dark inclusions in the rocks, we believe that Miocene quartz monzonite from Zuozuoxiang area was formed by partial melting of thickened lower crust with the addition of mantle material.In addition, based on the results of uplift studies, we believe that the tearing of Indian plate is more suitable for the interpretation of Miocene potassic-ultrapotassic rocks in Lhasa terrane than the convective thinning of lithospheric mantle, the delamination of thickened lithosphere and the break-off of Indian plate.
-
Keywords:
- Lhasa terrane /
- Miocene /
- Potassic rocks /
- Tearing of Indian plate /
- LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating
-
20世纪80年代,人们开始认识到地下空间在城市建设中的重要地位,并明确提出了地下空间资源的概念。国内对地下空间资源开发利用适宜性评价的研究起步较晚,最早由北京及一些沿海城市提出并实施了地下空间开发适宜性评价(祝文君,1992;廖建三等,2006),之后郑州市、宁波市、济南市、苏州市、南宁市、石家庄市、上海市、雄安新区等城市和地区也相继开展了这项工作(徐军祥等,2012;潘朝等,2013;刘健等,2014;夏友等,2014;张晶晶等,2016;吴炳华等,2017;郝爱兵等,2018;Gao et al., 2023)。目前,城市地下空间开发利用适宜性评价常用的评价方法有层次分析法、模糊综合评判法、综合指数法、可拓法、灰色综合评价法等(柳昆等,2011;胡宁,2012;岳志辉,2013;林才秀,2018;董英等,2020;张晓波等,2023),其中层次分析法是应用最广泛的一种方法,其最核心的工作是评价指标的选取,而这项工作要基于大量地质环境背景资料的收集、整理、分析。受区域地质环境影响,评价指标的选取和量化标准差异较大。本文系统梳理了大连市金普新区的基础地质、水文地质、工程地质、环境地质等资料,筛选出5大类17个评价指标,构建了基于层次分析法和多目标线性加权函数模型的评价方法体系,并对浅层(0~15 m)、次深层(15~30 m)、深层(30~50 m)地下空间进行了地质条件适宜性评价,为国土空间规划提供基础数据支撑。
1. 地质概况
1.1 地形地貌与地质构造
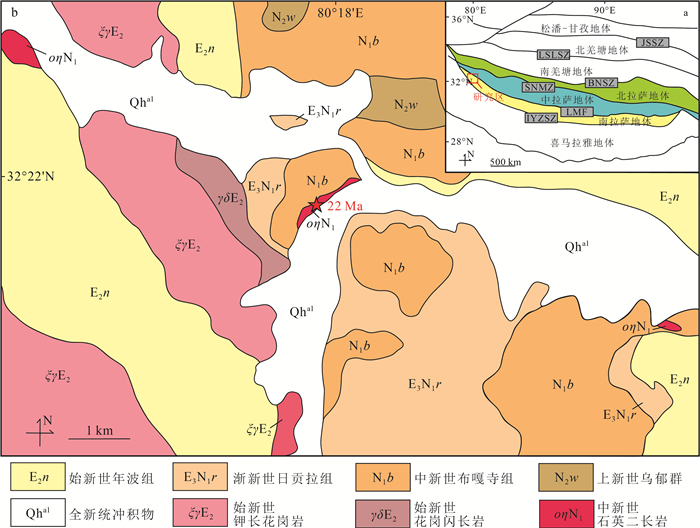
金普新区位于辽东半岛南部,为千山山脉向西南的延伸段,西临渤海,东濒黄海,形成两海之间丘陵起伏的地形,属于构造剥蚀低丘地貌。地形较复杂,地势起伏较大,坡度在0~61.7%之间,最高点为南部的大黑山主峰,海拔633.1 m。大地构造位置为中朝准地台,位于辽东台隆和华北断坳2个二级构造单元的交接部位。主要构造体系有东西向和北东—北北东向构造,局部有北西向构造。金州断裂和董家沟断裂从境内穿过。根据收集的资料,金州断裂在中更新世有活动,董家沟断裂在中更新世也有活动(图 1)。研究区除石河街道抗震设防烈度为8度外,其他均为7度。
1.2 水文地质
区内登沙河、邓屯河、大魏家河、青云河水库、卧龙水库和鸽子塘水库的下游地面高程较低,存在洪水淹没危险。地下水按含水介质类型分为松散岩类孔隙水、碳酸盐岩类裂隙岩溶水和基岩裂隙水3类。除河流两岸及沿海地段地下水位埋深小于3 m外,其他地区一般介于3~25 m之间。三十里堡、大魏家、大小窑湾、金州湾等地段含水层富水性较大,单井涌水量大于1000 m3/d,易引起基坑突涌、坑壁渗水等;其他区域单井涌水量均小于1000 m3/d,适宜工程建设。
1.3 工程地质
区内地基土承载力总体上中间高、两侧低,与地貌有密切联系。在中部低山丘陵地区,出露岩性主要为石灰岩、石英砂岩、片麻岩、花岗岩、辉绿岩、页岩等,地基土承载力在300~4500 kPa之间,可满足多层或高层建筑天然地基要求;区内东、西部坡洪积扇裙、冲洪积平原地段,粉质粘土、中粗砂等地基土承载力一般为150~240 kPa,可满足多层或高层建筑天然地基要求;在青云河、登沙河、旗杆河、邓屯河沿线,龙口水库上游及海积平原部分地段,地基承载力一般为60~150 kPa,尤其是在青云河、登沙河上游和龙口水库上游,部分沿海地段分布有填土、淤泥质土和红粘土,地基承载力在60~80 kPa之间,需进行地基处理方可作为持力层。
在三十里堡河、大魏家河、北大河、寨子河、登沙河、旗杆河等河流中下游存在轻微—中等砂土液化区,主要在15 m以浅的地层中,仅三十里堡河、北大河入海口处在15~20 m范围存在砂土液化区。
1.4 环境地质
区内存在的主要地质环境问题有地质灾害、海水入侵和岩溶。对地下空间开发利用影响最大的地质灾害是采空塌陷。金州石棉矿、董家沟煤矿、大湾煤矿、复州湾粘土矿虽已闭坑多年,但地面塌陷仍时有发生,对工程建设影响大。地质灾害易发区主要地质灾害有崩塌、滑坡、泥石流(图 2),主要影响与浅层地下空间相连接的地上建筑结构。
海水入侵面积共115.77 km2,较突出的有7个地段:马桥子街道海中龙眼、登沙河街道范家屯-大吴家屯、大魏家街道、复州湾街道、大李家街道许家屯、七顶山马圈子、炮台镇孤山后屯(图 3),最大Cl-含量为2522 mg/L,对钢筋混凝土结构具腐蚀作用。
总体上在金州断裂以西的炮台、复州湾、石河、三十里堡、七顶山、大魏家、二十里堡及董家沟断裂以南的友谊、拥政、中长、光明、先进、湾里、大孤山、大窑湾、董家沟、金石滩、大李家等街道,岩溶较发育,钻孔中常见溶洞、溶孔及溶隙,大的溶洞直径达0.3~2 m,顺层理和构造节理发育,呈扁豆状和串珠状溶洞,对地下空间开发影响较大。其他区域岩溶不发育。
2. 技术手段与数据
为全力支撑金普新区发展和总体规划,中国地质调查局于2018—2020年在金普新区全域开展了1:5万水文地质、工程地质调查工作。完成水文地质钻探992 m,工程地质钻探4038 m,水质全分析320组,土壤分析150组,综合物探测井1580 m,获取了土体物理力学参数、地下水位及水质等数据,为工程地质、水文地质、不良地质作用、水土腐蚀性评价等提供了丰富的基础数据。
3. 地下空间开发利用适宜性评价
层次分析法(Analytic Hierarchy Process,AHP)于20世纪70年代由美国Saaty教授提出,是一种定性与定量分析相结合的多目标决策分析方法(梁宗巨等,1989)。它使复杂的系统整体分解清晰,把多目标、多准则的决策化为多层次、单目标的两两对比,然后只要进行简单的数学运算即可(欧刚,2008)。
由于层次分析法计算步骤简单明确,容易被决策者了解和掌握,在多目标规划领域具有广泛的应用价值。因此,本文采用层析分析法构建了评价指标体系,并结合专家调查法确定了各指标权重。
3.1 评价指标及量化取值
对于不同的城市,其地质条件不同,地下空间开发地质条件适宜性评价指标及量化取值亦不同。本文通过对大连金普新区地质概况的分析得出,影响地下空间开发利用的地质条件因素包括地形地貌、工程地质、水文地质、不良地质条件和地质灾害、活动断裂和地震效应五大类。从数据获取难易程度及指标科学性、完备性、重复性等方面综合考虑,筛选出17个评价指标,采用层次分析法构建了地下空间开发地质条件适宜性评价指标体系。结合金普新区的地质环境特征,咨询了省内知名专家,并参考相关规范、标准,确定了各指标量化取值标准(表 1)。
表 1 地下空间开发地质条件适宜性评价指标分级标准Table 1. Classification standard for suitability evaluation index of geological conditions for underground space development序号 一级指标 二级指标 评价指标分级标准 考虑层位 1分(适宜性差) 2分(适宜性较差) 3分(较适宜) 4分(适宜) 1 地形地貌 地形形态 地形破碎,分割严重,非常复杂 地形分割较严重,复杂 地形变化较大,较完整 地形简单,完整 L1 2 地形坡度 ≥50% 25%~50% 10%~25% ≤10% L1 3 工程地质 岩土体特征 软土、填土 粘性土、砂土 较软岩、软岩、碎石土 坚硬岩、较硬岩 L1~L3 4 地基承载力 <80 kPa 80~150 kPa 150~200 kPa ≥200 kPa L1 5 岩体基本质量 Ⅴ Ⅳ Ⅲ Ⅰ、Ⅱ L1~L3 6 软土厚度 ≥5 m 2.5~5 m 0~2.5 m 0 L1~L2 7 水文地质 地下水埋深 <1 m 1~3 m 3~6 m ≥6 m L1 8 含水层富水性 ≥3000 m3/d 1000~3000 m3/d 100~1000 m3/d <100 m3/d L1~L3 9 地下水腐蚀性 强腐蚀 中等腐蚀 弱腐蚀 微腐蚀 L1~L3 10 土腐蚀性 强腐蚀 中等腐蚀 弱腐蚀 微腐蚀 L1~L3 11 洪水淹没可能性 洪水淹没深度或用地标高低于设防洪水位超过1.0 m 洪水淹没深度或用地标高低于设防洪水位(0.5~1.0)m 洪水淹没深度或用地标高低于设防洪水位<0.5 m 无洪水淹没或用地标高高于设防标高 L1~L3 12 不良地质作用和地质灾害 海水入侵程度 严重入侵 中度入侵 轻度入侵 未入侵 L1~L3 13 岩溶发育程度 强渗透性岩体(T=200~400 m3/d) 中等渗透性岩体(T=10~200 m3/d) 低渗透性岩体(T<10 m3/d) 非碳酸盐岩体 L1~L3 14 地质灾害易发程度 高易发 中易发 低易发 不易发 L1~L3 15 活动断裂和地震效应 砂土液化 严重液化 中等液化 轻微液化 不液化 L1~L2 16 活动断裂 强烈全新活动断裂 微弱、中等全新活动断裂 非全新活动断裂 无活动断裂 L1~L3 17 抗震设防烈度 >Ⅸ度区 Ⅸ度区 Ⅶ、Ⅷ度区 ≤Ⅵ度区 L1~L3 注:L1为浅层(0~15 m)地下空间影响指标,L2为次深层(15~30 m)地下空间影响指标,L3为深层(30~50 m)地下空间影响指标 3.2 确定指标权重
首先通过层次分析法-专家问卷调查法(朱茵等,1999),按Saaty 1~9标度(表 2)对评价指标进行两两比较,得出各自的判断矩阵。
表 2 层次分析定权法的判断矩阵标度及其含义Table 2. The judgment matrix scale and meaning of AHP weighting method标度 含义 1 表示2个因素相比,具有同等重要性 3 表示2个因素相比,一个比另一个稍微重要 5 表示2个因素相比,一个比另一个明显重要 7 表示2个因素相比,一个比另一个强烈重要 9 表示2个因素相比,一个比另一个极端重要 2,4,6,8 上述两相邻判断之中间值,表示重要性判断之间的过渡性 倒数 因素i与j比较判断得到bij,因素j与i比较判断得到bji=1/bij 然后利用公式(1)作一致性检验。
CI=λmax (1) 式中:CI为一致性指标,λmax为最大特征根,n为矩阵阶数,RI为平均随机一致性指标(取值见表 3),CR为随机一致性比率。只有当CR<0.10时,判断矩阵才具有满意的一致性,所获取值才较合理。
表 3 层次分析法的平均随机一致性值Table 3. The mean random consistency value of AHP矩阵阶数(n) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 平均一致性指标值RI 0.00 0.00 0.52 0.89 1.11 1.25 1.35 1.40 1.45 最后分别得到浅层地下空间L1(0~15 m)、次深层地下空间L2(15~30 m)、深层地下空间L3(30~50 m)的各指标权重(表 4)。
表 4 评价指标权重Table 4. The weight of evaluation index序号 一级指标 二级指标 权重 L1 L2 L3 1 地形地貌 地形形态 0.05 2 地形坡度 0.15 3 工程地质 岩土体特征 0.066 0.104 0.117 4 地基承载力 0.047 5 岩体基本质量 0.009 0.063 0.070 6 软土厚度 0.028 0.021 7 水文地质 地下水埋深 0.018 8 含水层富水性 0.011 0.038 0.038 9 地下水腐蚀性 0.004 0.013 0.013 10 土腐蚀性 0.004 0.013 0.013 11 洪水淹没可能性 0.014 12 不良地质作用和地质灾害 海水入侵程度 0.028 0.035 0.035 13 岩溶发育程度 0.083 0.104 0.104 14 地质灾害易发程度 0.139 0.174 0.174 15 活动断裂和地震效应 砂土液化 0.027 0.034 16 活动断裂 0.188 0.236 0.255 17 抗震设防烈度 0.135 0.168 0.182 3.3 评价模型
由于多目标线性加权函数法(郭骏瀚等,2023)综合考虑了各因子的权重,且易于GIS的图层叠加分析,因此建立了基于多目标线性加权函数法的评价模型,见公式(2)。
S=\sum\limits_{j=1}^m\left(\sum\limits_{i=1}^n A_i B_i\right) C_j (2) 式中:S为评价目标总得分(0≤S≤1);Ai为第i个单项指标的量化分值;Bi为第i个单项指标的权重;Cj为第j个主题的权重。
依据数学模型公式(2),利用MapGIS的空间分析模块进行图层叠加分析和属性运算,最终生成自然划分的新单元,每个新单元的属性值都不相同。根据评价目标总得分S按表 5的等级划分标准对地下空间开发适宜性进行等级划分。
表 5 评价结果等级划分标准Table 5. Criteria for grading evaluation results评价得分 S<1.5 1.5≤S<2.5 2.5≤S<3.5 S≥3.5 评价等级 适宜性差 适宜性较差 较适宜 适宜 3.4 评价结果
根据以上评价方法,得到浅层、次深层、深层地下空间地质条件适宜性评价图(图 4—图 6)。评价结果表明,浅层地下空间开发适宜区位于区内中东部(表 6)。较适宜区主要位于区内西部、南部及东部河流沿线,适宜性较差区主要位于西部、南部,这些地区面临岩溶发育、含水层富水性中等—丰富、地下水埋深浅等问题,尤其是西部的大魏家、七顶山、三十里堡岩溶发育,溶洞直径达0.3~2 m。适宜性差区分别位于湾里街道、董家沟街道、复州湾街道和大黑山。大黑山海拔633.1 m,是金普新区境内最高的山峰,地形坡度大,不适宜浅层地下空间开发;其他4个区分别是金州石棉矿、董家沟煤矿、大湾煤矿、复州湾粘土矿的采空区,矿山虽已闭坑多年,但地面塌陷仍时有发生,对工程建设影响大。
表 6 金普新区地下空间开发地质条件适宜性评价分区Table 6. Suitability evaluation zoning table of underground space development in Jinpu New Area工程建设层位 适宜性分区 面积/km2 占比/% 空间分布 主要地质环境问题 浅层地下空间
L1适宜区 602.28 35.22 研究区中东部 — 较适宜区 832.44 48.68 研究区西部、南部及东部的河流沿线 岩溶较发育、含水层富水性中等、地下水埋深浅、活动断裂 适宜性较差区 238.38 13.95 研究区西部、南部 岩溶发育,含水层富水性丰富,地形坡度较大 适宜性差区 36.82 2.15 湾里、董家沟、复州湾、大黑山 采空区、地形破碎 次深层地下
空间L2适宜区 923.27 53.99 研究区中东部 — 较适宜区 567.80 33.21 研究区西部、南部及登沙河中下游 岩溶较发育,含水层富水性中等,活动断裂 适宜性较差区 211.16 12.35 研究区西部、南部 岩溶发育,含水层富水性丰富 适宜性差区 7.69 0.45 湾里、董家沟、复州湾 采空区 深层地下空间
L3适宜区 977.25 57.15 研究区中东部 — 较适宜区 517.85 30.29 研究区西部、南部及登沙河中下游 岩溶较发育,含水层富水性中等,活动断裂 适宜性较差区 207.13 12.11 西研究区西部、南部 岩溶发育,含水层富水性丰富 适宜性差区 7.69 0.45 湾里、董家沟、复州湾 采空区 次深层地下空间适宜区位于区内中东部。较适宜区主要位于区内西部、南部及登沙河中下游,适宜性较差区主要位于区内西部和南部,存在的主要地质环境问题是岩溶发育、含水层富水性中等—丰富、活动断裂。适宜性差区分别是湾里街道、董家沟街道、复州湾街道的采空区。
深层地下空间评价结果与次深层相比差别不大,均有4个适宜性差区,分别是湾里街道、董家沟街道、复州湾街道的采空区。适宜性较差区面积有所减少,适宜区面积有所增加,这主要是由于金普新区第四系埋藏较浅,30 m以下大部分区域为基岩,不存在软土和砂土液化问题,且随着深度的增加,岩体基本质量由Ⅲ级变为Ⅴ级。因此,总体上工程地质性质变好,适宜地下空间开发利用。
4. 结论
(1) 金普新区总体上地质条件较好,适宜区和较适宜区占比重较大,主要位于金州断裂以东;适宜性差和较差区主要位于金州断裂以西。其中浅层地下空间适宜性差和较差区总面积占全区的16.10%,存在的主要地质环境问题是采空区、岩溶发育、含水层富水性丰富、地形破碎;次深层、深层地下空间适宜性差和较差区总面积分别占全区的12.80%、12.56%,存在的主要地质环境问题均是采空区、岩溶发育、含水层富水性丰富。
(2) 金普新区存在采空区、岩溶、软土、砂土液化等不良工程地质问题,在控制性详细规划和重大工程建设中应加以重视,建议做大比例尺的详细勘察。
(3) 金州断裂是海域-金州地震带的控震断裂带,建议对其进行专项调查,查明其位置、断裂带宽度及活动性,划定工程安全避让距离。
致谢: 感谢吉林大学青藏高原科研团队所有成员。感谢审稿专家对本文的建议。 -
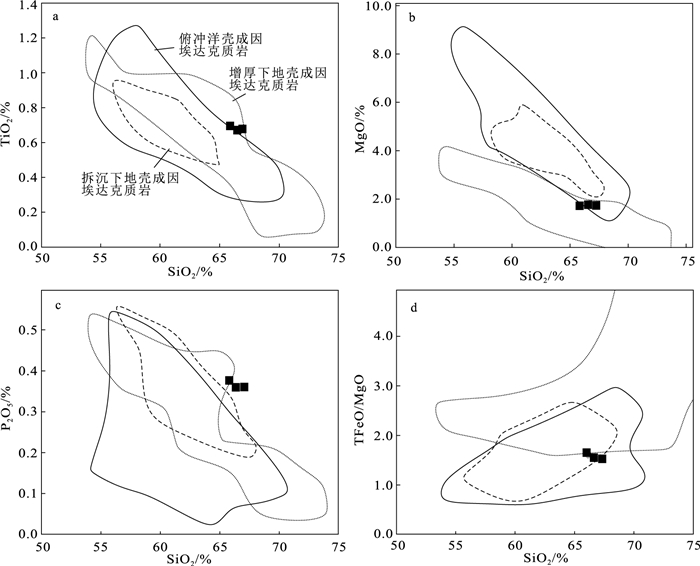
图 6 左左乡中新世石英二长岩成因判别图解
a—SiO2-TiO2图解;b—SiO2-MgO图解;c—SiO2-P2O5图解;d—SiO2-TFeO/MgO图解[28]
Figure 6. Genetic discrimination diagram of Miocene quartz monzonite in Zuozuoxiang area
表 1 左左乡中新世石英二长岩锆石U-Th-Pb同位素数据
Table 1 U-Th-Pb isotope composition of zircon in the Miocene quartz monzonite at Zuozuoxiang area
编号 元素/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 同位素年龄/Ma Th U Pb 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 1 1437 750 4.16 1.92 0.0211 0.0016 0.0036 0.0001 21.00 2.00 23.00 0.70 2 1751 905 5.06 1.93 0.0222 0.0015 0.0035 0.0001 22.00 1.00 22.30 0.60 3 1497 679 4.05 2.20 0.0268 0.0018 0.0035 0.0001 27.00 2.00 22.30 0.60 4 1341 551 3.43 2.43 0.0241 0.0020 0.0036 0.0001 24.00 2.00 23.00 0.70 5 314 363 4.08 0.87 0.0568 0.0037 0.0088 0.0003 56.00 4.00 57.00 2.00 6 1151 581 3.30 1.98 0.0211 0.0018 0.0036 0.0001 21.00 2.00 22.80 0.70 7 4444 1147 8.27 3.87 0.0221 0.0014 0.0034 0.0001 22.00 1.00 22.10 0.60 8 857 1026 6.87 0.83 0.0353 0.0019 0.0055 0.0002 35.00 2.00 35.30 1.00 9 1923 778 4.86 2.47 0.0219 0.0015 0.0035 0.0001 22.00 2.00 22.70 0.60 10 2391 964 5.47 2.48 0.0213 0.0025 0.0033 0.0001 21.00 3.00 21.20 0.80 11 1225 594 3.46 2.06 0.0207 0.0018 0.0036 0.0001 21.00 2.00 22.90 0.70 12 291 366 13.08 0.79 0.2546 0.0147 0.0288 0.0008 230.00 12.00 183.00 5.00 13 750 641 2.91 1.17 0.0222 0.0025 0.0033 0.0001 22.00 2.00 21.20 0.80 14 5634 1605 10.91 3.51 0.0242 0.0013 0.0034 0.0001 24.00 1.00 22.00 0.60 15 240 307 5.22 0.78 0.1057 0.0144 0.0148 0.0007 102.00 13.00 94.00 4.00 16 4363 1509 8.85 2.89 0.0214 0.0015 0.0033 0.0001 22.00 2.00 21.00 0.60 17 250 258 7.85 0.97 0.1534 0.0087 0.0229 0.0006 145.00 8.00 146.00 4.00 18 241 642 18.19 0.38 0.2173 0.0106 0.0273 0.0007 200.00 9.00 173.00 5.00 19 107 102 11.27 1.04 0.6624 0.0510 0.0837 0.0028 516.00 31.00 518.00 16.00 20 5113 1292 9.47 3.96 0.0238 0.0016 0.0035 0.0001 24.00 2.00 22.40 0.60 表 2 左左乡中新世石英二长岩主量、微量和稀土元素含量
Table 2 Analytical results of major, trace and rare earth elements of Miocene quartz monzonite in Zuozuoxiang area
编号 B19T11H1 B19T11H2 B19T11H3 编号 B19T11H1 B19T11H2 B19T11H3 SiO2 66.90 65.87 66.41 La 90.7 95.2 94.3 Al2O3 14.69 14.36 14.79 Ce 186.3 197.0 195.0 MgO 1.76 1.71 1.73 Pr 22.6 24.1 23.8 Na2O 3.65 3.47 3.60 Nd 87.9 94.1 92.6 K2O 6.30 6.19 6.41 Sm 14.2 15.1 15.0 P2O5 0.36 0.38 0.36 Eu 2.5 2.6 2.6 TiO2 0.68 0.69 0.67 Gd 7.2 7.4 7.4 CaO 2.16 2.80 2.33 Tb 0.7 0.8 0.8 TFe2O3 3.00 3.07 2.98 Dy 3.3 3.5 3.4 MnO 0.05 0.05 0.05 Ho 0.5 0.6 0.6 烧失量 0.79 1.69 0.95 Er 1.2 1.3 1.3 Cr 46.8 48.9 46.0 Tm 0.2 0.2 0.2 Ni 32.6 34.8 33.0 Yb 1.1 1.1 1.1 Rb 477.0 476.7 476.7 Lu 0.2 0.2 0.2 Sr 627.3 524.6 699.3 Hf 13.6 13.8 13.7 Y 12.9 13.6 13.5 Ta 1.5 1.5 1.5 Zr 458.4 466.6 471.5 Pb 87.4 97.4 97.7 Nb 23.4 24.6 24.2 Th 113.9 122.7 117.7 Cs 25.4 27.8 27.0 U 12.4 14.1 12.4 Ba 1837.0 2090.2 2090.6 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 -
赵志丹, 莫宣学, Nomade S, 等. 青藏高原拉萨地块碰撞后超钾质岩石的时空分布及其意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22: 787-794. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200604003.htm Foley S F, Venturelli G, Green D H. The ultrapotassic rocks: characteristics, classification, and constraints for petrogenetic models[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 1987, 24(2): 81-134. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(87)90001-8
Chen J L, Zhao W X, Xu J F, et al. Geochemistry of Miocene trachytes in Bugasi, Lhasa block, Tibetan Plateau: Mixing products between mantle- and crust-derived melts?[J]. Gondwana Research, 2012, 21: 112-122. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.06.008
陈建林, 许继峰, 康志强, 等. 青藏高原西南部查孜地区中新世钾质火山岩地球化学及其成因[J]. 地球化学, 2007, 36: 457-466. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200705003.htm 孙晨光, 赵志丹, 莫宣学, 等. 青藏高原拉萨地块西部中新世赛利普超钾质岩石的地球化学与岩石成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23: 2715-2726. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.11.004 刘栋, 赵志丹, 朱弟成, 等. 青藏高原拉萨地块西部雄巴盆地后碰撞钾质-超钾质火山岩年代学与地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(7): 2045-2059. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201107014.htm 刘栋. 青藏高原后碰撞钾质-超钾质岩石的地球化学特征与岩石成因[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2017. Chung S L, Lo C H, Lee T Y, et al. Diachronous uplift of the Tibetan plateau starting 40 Myr ago[J]. Nature, 1998, 394: 769-773. doi: 10.1038/29511
Turner S, Arnaud N, Liu J, et al. Post-collision, shoshonitic volcanism on the Tibetan Plateau: Implications for convective thinning of the lithosphere and the source of ocean island basalts[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1996, 37: 45-71. doi: 10.1093/petrology/37.1.45
Chen J L, Zhao W X, Xu J F, et al. Geochemistry of Miocene trachytes in Bugasi, Lhasa block, Tibetan Plateau: Mixing products between mantle- and crust-derived melts?[J]. Gondwana Research, 2012, 21: 112-122. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.06.008
侯增谦, 赵志丹, 高永丰, 等. 印度大陆板片前缘撕裂与分段俯冲: 来自冈底斯新生代火山-岩浆作用证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(4): 761-774. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200604001.htm Hao L L, Wang Q, Wyman D A, et al. First identification of postcollisional A-type magmatism in the Himalayan-Tibetan orogeny[J]. Geology, 2019, 47: 187-190.
Chung S L, Lo C H, Lee T Y, et al. Diachronous uplift of the Tibetan plateau starting 40 Myr ago[J]. Nature, 1998, 394: 769-773. doi: 10.1038/29511
Wang C S, Dai J G, Zhao X X, et al. Outward-growth of the Tibetan Plateau during the Cenozoic: a review[J]. Tectonophysics, 2014, 621: 1-43. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2014.01.036
Yin A, Harrison T M. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2000, 28: 211-280. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211
李才, 翟庆国, 董永胜, 等. 青藏高原羌塘中部榴辉岩的发现及其意义[J]. 科学通报, 2006, 51(1): 70-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200601013.htm Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y L, et al. The origin and pre-Cenozoic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23: 1429-1454. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.002
Yuan H L, Gao S, Liu X M, et al. Accurate U-Pb Age and Trace Element Determinations of Zircon by Laser Ablation- Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry[J]. Geostandards and Geoana-lytical Research, 2004, 28: 353-370. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2004.tb00755.x
Ludwig K R. User's Manual for Isoplot 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, Berkeley, 2003.
于红. 陕西商南松树沟橄榄岩矿物地球化学特征及成因机理示踪[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2011. 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23: 1217-1238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.06.001 Lee C T A, Tang M. How to make a copper porphyry ore deposit[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2020, 529: 115868. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2019.115868
Baker M B, Hischmann M M, Ghiorso M S, et al. Compositions of near solidus predictive melts from experiments and thermodynamic calculations[J]. Nature, 1995, 375: 308-311. doi: 10.1038/375308a0
Defant M J, Drummond M S. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere[J]. Nature, 1990, 347(6294): 662-665. doi: 10.1038/347662a0
Castillo P R, Janney P E, Solidum R U. Petrology and geochemistry of Camiguin Island, southern Philippines: insights to the source of adakites and other lavas in a complex arc setting[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 1999, 134(1): 33-51.
Rapp R P, Watson E B. Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8-32 kbar: implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36: 891-931. doi: 10.1093/petrology/36.4.891
Chen J L, Xu J F, Kang Z Q, et al. Origin of Cenozoic alkaline potassic volcanic rocks at Konglongxiang, Lhasa terrane, Tibetan Plateau: products of partial melting of a mafic lower-crustal source?[J]. Chemical Geology, 2010, 273: 286-299. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2010.03.003
Münker C, Pfnder J A, Weyer S, et al. Evolution of planetary cores and the earth-moon system from Nb/Ta systematics[J]. Science, 2003, 301(5629): 84-87. doi: 10.1126/science.1084662
Pfnder J A, Münker C, Stracke A, et al. Nb/Ta and Zr/Hf in ocean island basalts: Implications for crust-mantle differentiation and the fate of niobium[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 254(1-2): 158-172. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2006.11.027
黄思华, 陈建林, 曾云川, 等. 拉萨地块西北部早白垩世岩浆岩地球化学特征及其对高原南部早期地壳生长的指示[J]. 地球化学, 2020, 49: 21-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX202001002.htm 李勇, 张士贞, 李奋其, 等. 西藏拉萨地块西段狮泉河地区晚侏罗世花岗岩年代学、地球化学与岩石成因[J]. 地球科学, 2020. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.102. Wang Q, Xu J F, Jian P, et al. Petrogenesis of Adakitic Porphyries in an Extensional Tectonic Setting, Dexing, South China: Implications for the Genesis of Porphyry Copper Mineralization[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2006, 47(1): 119-144. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egi070
Bouilhol P, Jagoutz O, Hanchar J M, et al. Dating the India-Eurasia collision through arc magmatic records[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2013, 366: 163-175. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2013.01.023
Lippert P C, van Hinsbergen D J J, Dupont-Nivet G. Early Cretaceous to present latitude of the central proto-Tibetan Plateau: A paleomagnetic synthesis with implications for Cenozoic tectonics, paleogeography, and climate of Asia[J]. Geol. Soc. Am. Spec. Pap., 2014, 507: 1-21.
Tapponnier P, Xu Z, Roger F, et al. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet Plateau[J]. Science, 2001, 294: 1671-1677. doi: 10.1126/science.105978
Turner S, Arnaud N, Liu J, et al. Post-collision, shoshonitic volcanism on the Tibetan Plateau: Implications for convective thinning of the lithosphere and the source of ocean island basalts[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1996, 37: 45-71. doi: 10.1093/petrology/37.1.45
Hao L L, Wang Q, Wyman D A, et al. First identification of postcollisional A-type magmatism in the Himalayan-Tibetan orogeny[J]. Geology, 2019, 47: 187-190.
Wang R, Richards J P, Zhou L M, et al. The role of Indian and Tibetan lithosphere in spatial distribution of Cenozoic magmatism and porphyry Cu-Mo deposits in the Gangdesebelt, southern Tibet[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2015, 150: 68-94. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.07.003
Copley A, Avouac J P, Royer J Y. India-Asia collision and the Cenozoic slowdown of the Indian plate: Implications for the forces driving plate motions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research B: Solid Earth, 2010, 115: B03410.
Kirstein L A. Thermal evolution and exhumation of the Ladakh Batholith, northwest Himalaya, India. Tectonophysics, 2011, 503(3/4): 222-233.
Ding L, Xu Q, Yue Y, et al. The Andeantype Gangdese Mountains: paleoelevation record from the Paleocene-Eocene Linzhou Basin[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2014, 392: 250-264. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2014.01.045
Enkelmann E, Ehlers T A, Zeitler P K, et al. Denudation of the Namche Barwa antiform, eastern Himalaya[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 307: 323-333. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2011.05.004
Dai J G, Wang C S, Hourigan J, et al. Exhumation history of the Gangdese Batholith, Southern Tibetan Plateau: evidence from apatite and zircon(U-Th)/He thermochronology[J]. J. Geol., 2013, 121(2): 155-172. doi: 10.1086/669250
Ji W Q, Wu F Y, Liu C Z, et al. Early Eocene crustal thickening in southern Tibet: New age and geochemical constraints from the Gangdese batholith[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 53: 82-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.08.020
Harrison T M, Copeland P, Kidd W S F, et al. Raising Tibet[J]. Science, 1992, 255: 1663-1670. doi: 10.1126/science.255.5052.1663
Chung S L, Chu M F, Zhang Y, et al. Tibetan tectonic evolution inferred from spatial and temporal variations in post-collisional magmatism[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2005, 68: 173-196.
Chen Y, Li W, Yuan X H, et al. Tearing of the Indian lithospheric slab beneath southern Tibet revealed by SKS-wave splitting measurements[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 413: 13-24. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2014.12.041
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 张培兴,韩健健,靳天禄,周娜,李金霞,刘帅,周静文. 综合地质与经济因素的城市地下空间开发潜力探析. 价值工程. 2025(02): 80-82 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 鲜于慧玲,李红,王幸文. 吉林省大安市耕地后备资源开发适宜性研究. 世界地质. 2025(01): 164-178 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张静,崔健,马诗敏,代雅建,朱巍. 基于层次分析法与频率比模型的采空塌陷危险性评价. 地质与勘探. 2024(01): 88-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 卜吉武,李家乐,姜亚东,娜仁花. 基于层次分析法的赤峰市地质灾害易发性评价. 环境与发展. 2024(01): 20-27 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: