Genesis of Jinqingding gold deposit in eastern Jiaodong Peninsula: constrain from trace elements of sulfide ore and wall-rock
-
摘要:
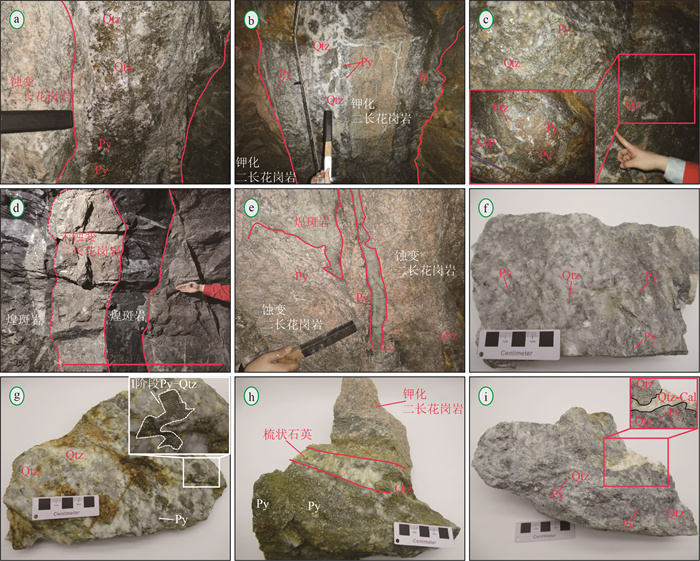
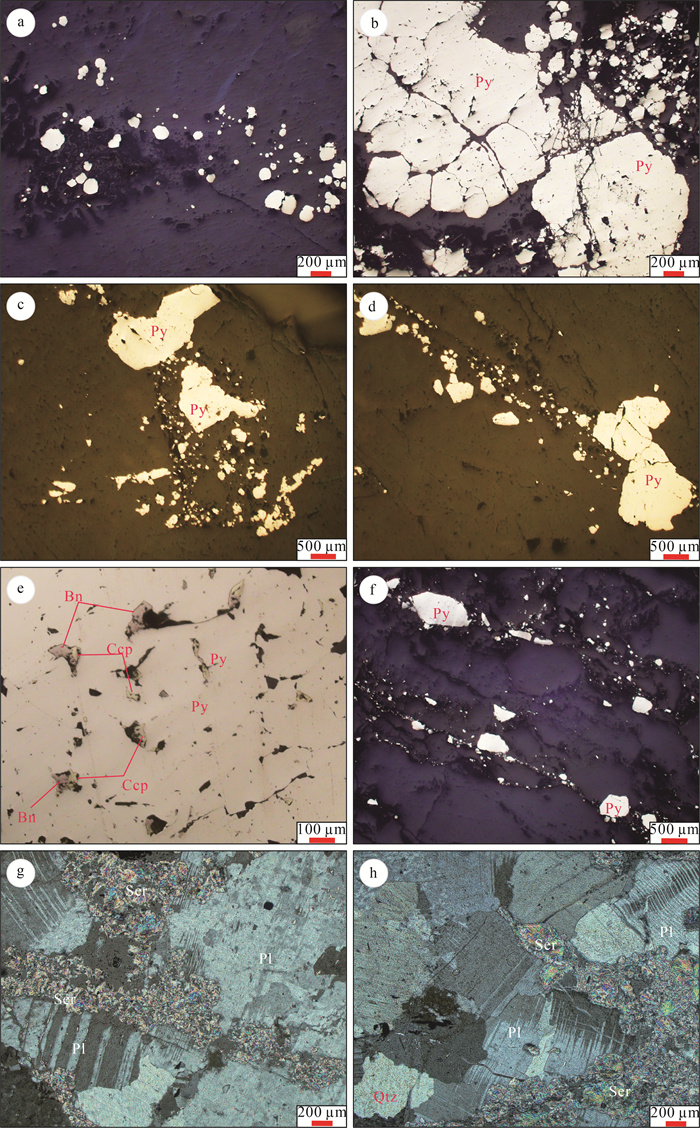
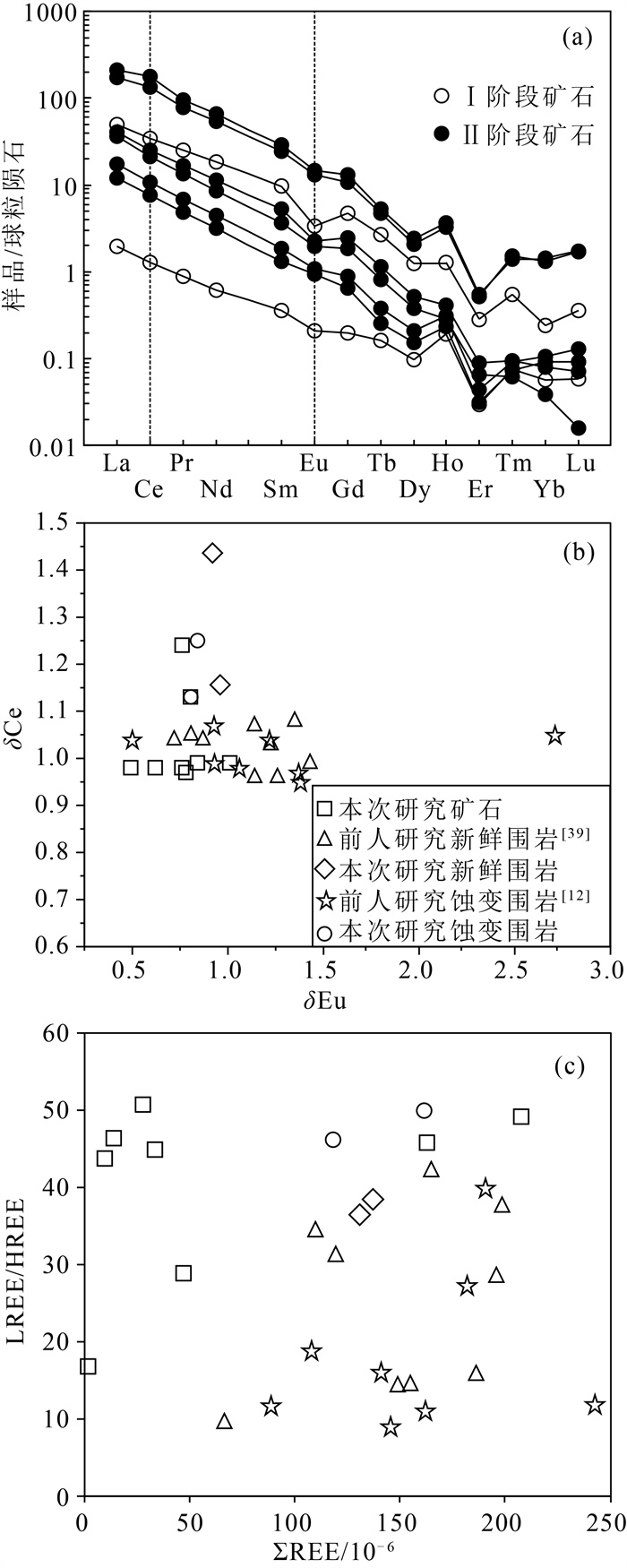
金青顶矿床是胶东东部牟平-乳山成矿带最大的金矿床(>35 t, 平均品位10 g/t), 矿化类型主要为硫化物石英脉型。在野外地质调查的基础上, 利用微量元素组成对金青顶矿床的成矿流体地球化学性质和成矿物质来源进行了研究, 并将金青顶矿床成因确定为受断裂控制的热液脉型金矿床。矿石稀土元素总量变化范围较大, 呈现出明显的轻稀土元素富集和重稀土元素亏损的特征(LREE/HREE=16.75~50.60), 负Eu异常显著, Ce异常不明显。Hf/Sm、Th/La、Nb/La等特征元素比值均小于1, 暗示成矿流体为富Cl体系。结合前人稳定同位素的研究, Ⅰ~Ⅱ阶段矿石δEu值逐渐减小, 可能有大气降水的加入, 说明金青顶矿床成矿流体为岩浆水和大气降水混合来源热液。硫化物矿石、蚀变和新鲜围岩Y/Ho值显示, 蚀变的围岩可为金成矿作用提供必要的成矿物质。
Abstract:The Jinqingding deposit is the largest gold deposit(> 35 t, average grade 10 g/t) within the Muping-Rushan metallogenic belt of eastern Jiaodong, and the main mineralization category is sulfide quartz-vein category.Based on the study of geological survey as well as trace element composition systematically, the geochemical characteristics of ore-forming fluid and source of ore-forming materials are constrained, and conducts the genesis of Jinqingding deposit as a hydrothermal vein-type gold deposit controlled by faults.In this study, the total rare earth elements(ΣREEs) in the ore varies widely, showing obvious light rare earth elements enrichment and heavy rare earth elements depletion(LREE/HREE=16.75~50.60), with strong negative Eu anomaly and insignificant Ce anomaly.The ratios of Hf/Sm, Th/La, and Nb/La are all less than 1, suggesting that the ore-forming fluid belongs to Cl-rich system.Combined with previous studies on stable isotopes, the δEu value of the ore from stage Ⅰ to Ⅱ gradually decreases in this study, and there may be the addition of meteoric water, indicating that the ore-forming fluid is a mixture of magmatic water and meteoric water.The Y/Ho ratio of sulfide ore, altered and fresh wall-rock implies that altered wall-rock can provide the necessary ore-forming material for gold mineralization.
-
青藏高原古生代—早中生代构造演化受控于古特提斯洋的裂解、扩张、俯冲等地质作用[1-2]。一般认为,龙木错-双湖-澜沧江洋代表了古特提斯洋的主洋盆[3]。但是,杨经绥等[4]在拉萨地块中东部的松多地区新发现了二叠纪榴辉岩,认为这些岩石可能代表了古特提斯洋俯冲形成的高压—超高压变质带。这一发现打破了对青藏高原特提斯域构造演化的传统认知,松多地区也因此成为研究的热点。自发现榴辉岩至今的十几年来,松多古特提斯缝合带的研究已经取得了一些进展[5-13]。但是前人的研究主要集中在榴辉岩上,对于蛇绿岩的研究相对匮乏,很大程度上制约了对松多古特提斯洋演化过程的认识,一些关于该缝合带的地质问题尚处于争议中,如松多地区蛇绿岩具有怎样的成因?反映了松多古特提斯洋怎样的演化过程[14-15]?想要解决这些问题,对松多地区蛇绿岩进行深入研究显得尤为重要。
蛇绿岩的产生与大洋的演化息息相关,大洋中脊玄武岩(MORB)型蛇绿岩可以直观地反映大洋的扩张过程,有助于估算洋脊扩张速率、反演大洋内部壳幔相互作用及动力学机制。而俯冲带(SSZ)型蛇绿岩可以将消亡的大洋与新生的洋壳有机联系起来,不仅可以帮助重塑区域构造演化过程,而且对理解板块俯冲带岩浆作用的地球动力学背景具有重要意义[16]。陈松永等[17-18]通过对松多地区蛇绿岩的研究,认为松多地区蛇绿岩主要有2类:一类为MORB型蛇绿岩,主要组成为分布在贡布爬拉和新达朗地区的基性火山岩;另一类为SSZ型蛇绿岩,主要组成为贡布爬拉超基性岩。前人通过对松多地区蛇绿岩中基性端元的初步研究,发现其时代为304~258 Ma,代表松多古特提斯洋的打开时间应早于304 Ma,其闭合应晚于258 Ma[15, 19];而且松多地区二叠纪蛇绿岩的地球化学特征存在从正常洋中脊玄武岩(N-MORB)—富集洋中脊玄武岩(E-MORB)—洋岛玄武岩(OIB)的连续演化,其成因极有可能与地幔柱/热点和大洋中脊之间的相互作用有关[19]。相较于松多地区MORB型蛇绿岩较深入的研究,前人对贡布爬拉SSZ型超基性岩关注很少,仅进行了初步报道。贡布爬拉超基性岩是否属于SSZ型蛇绿岩?松多地区是否存在SSZ型蛇绿岩?这些问题尚未得到解决。仅通过研究MORB型蛇绿岩中的基性岩揭示地幔熔融过程并不十分可靠,因为其仅代表大洋中脊岩浆作用的最终产物,且仅占洋壳总质量的10%~15%[20]。而蛇绿岩中的超基性岩端元,如深海橄榄岩等,可以提供更多关于地幔熔融、熔体抽取和熔融后岩浆作用的直接信息[21]。因此,松多地区蛇绿岩中超基性岩端元的研究,对松多地区蛇绿岩的重新厘定及松多古特提斯洋演化过程的认识具有重要意义。
本文以松多地区蛇纹石化橄榄岩(蛇纹岩)为研究对象,对其进行岩石学和地球化学分析,并进一步探讨其成因及意义。
1. 区域地质概况
拉萨地体位于班公湖-怒江缝合带和印度河-雅鲁藏布缝合带之间,其内部的构造划分主要存在2种不同的观点,一种是根据松多榴辉岩和帕那蓝片岩的研究,将拉萨地体分成南拉萨和北拉萨2个微地体[4];另一种将拉萨地体三分,将北拉萨细分为中拉萨和北拉萨,以洛巴堆-米拉山断裂带和狮泉河-永珠-嘉黎蛇绿岩带为界分为3个微板块,即南部、中部和北部拉萨地体[22]。南部和北部拉萨地体以新生地壳为主,部分地区可能存在前寒武纪结晶基底,而中部冈底斯板块是具有古元古代甚至太古宙结晶基底的条带状微陆块[22]。
研究区地处藏南工布江达县松多地区,大地构造位置处于中拉萨与南拉萨交界处,米拉山断裂带附近(图 1-a)。因紧邻洛巴堆-米拉山断裂带,断裂构造十分发育,褶皱变形复杂,构造样式多样,出露松多高压变质带、蛇绿混杂岩,以及发生强变质变形的部分松多岩组等,具构造混杂岩带的典型特征。松多高压变质带是目前青藏高原内部发现时间最新、保存程度较好、露头众多的高压变质带[23]。研究区高压变质岩主要位于松多乡、新达多、白朗、龙崖松多、吉朗、西朗等地区[5-13],岩石组合为榴辉岩、白云母片岩、石英岩等;蛇绿混杂岩主要包括原岔萨岗岩组绿片岩及其中产出的基性、超基性岩透镜体,岩性主要为蛇纹石化橄榄岩、玄武岩、辉长岩、堆晶岩、斜长花岗岩等[24];上石炭统—下二叠统松多岩组原岩主要为滨浅海-斜坡相的陆源碎屑砂泥岩,岩性主要包括变质石英砂岩、白云母石英片岩、绢云石英片岩、二云(长石)石英片岩及少量黑云石英片岩,可能属于一套类似裂陷盆地内的类复理石-复理石沉积建造,构造变形强烈、复杂,片理发育[25]。另外,受松多古特提斯洋及新特提斯洋演化事件的影响,研究区岩浆岩大规模展布,时代跨度为早石炭世—中新世,岩性组合具多样性特征(图 1-b)。
![]() JSSZ—西金乌兰-金沙江缝合带;LSLSZ—龙木错-双湖-澜沧江缝合带;BNSZ—班公湖-怒江缝合带;SNMZ—狮泉河-永珠-嘉黎蛇绿岩带;LMF—洛巴堆-米拉山断裂带;IYZSZ—印度河-雅鲁藏布缝合带;1—侏罗系-白垩系;2—石炭系-二叠系松多岩组;3—三叠纪岩浆岩;4—白垩纪岩浆岩;5—早侏罗世花岗岩;6—中生代地层;7—松多岩组变质石英砂岩;8—松多岩组石英岩;9—松多岩组白片岩;10—绿片岩;11—榴辉岩;12—洋岛玄武岩;13—超基性岩;14—堆晶岩;15—变质辉长岩;16—变质玄武岩;17—采样点;18—剖面位置Figure 1. Tectonic outline of the Tibetan Plateau(a), geological map of the Sumdo area(b)and sampling location map of ultramafic rocks(c)
JSSZ—西金乌兰-金沙江缝合带;LSLSZ—龙木错-双湖-澜沧江缝合带;BNSZ—班公湖-怒江缝合带;SNMZ—狮泉河-永珠-嘉黎蛇绿岩带;LMF—洛巴堆-米拉山断裂带;IYZSZ—印度河-雅鲁藏布缝合带;1—侏罗系-白垩系;2—石炭系-二叠系松多岩组;3—三叠纪岩浆岩;4—白垩纪岩浆岩;5—早侏罗世花岗岩;6—中生代地层;7—松多岩组变质石英砂岩;8—松多岩组石英岩;9—松多岩组白片岩;10—绿片岩;11—榴辉岩;12—洋岛玄武岩;13—超基性岩;14—堆晶岩;15—变质辉长岩;16—变质玄武岩;17—采样点;18—剖面位置Figure 1. Tectonic outline of the Tibetan Plateau(a), geological map of the Sumdo area(b)and sampling location map of ultramafic rocks(c)研究区超基性岩在龙崖松多、温木朗(原贡布爬拉超基性岩)等地均有发现(图 1-c),均呈构造岩片产出于绿片岩中,与绿片岩呈断层关系接触。在温木朗附近,发现一条较完整的蛇绿岩剖面,端元包括蛇纹石化橄榄岩、堆晶辉长岩、变质辉长岩及玄武岩,在蛇纹石化橄榄岩中还发现一条花岗岩侵入体(图 2),为典型的埃达克质花岗岩,其成因可能与俯冲的松多古特提斯洋板片的部分熔融有关,时代为266 Ma[15]。进一步研究表明,剖面中的变质辉长岩呈典型N-MORB的地球化学特征,形成时代为274 Ma[19]。
松多地区的超基性岩包括已完全蚀变的变质橄榄岩(蛇纹岩)和少量蚀变程度较低的方辉橄榄岩。方辉橄榄岩仅在龙崖松多地区存在小规模露头,风化面为灰白色,新鲜面为灰黑色,呈块状产出。蛇纹岩主要呈块状产出于绿片岩中,与绿片岩呈断层接触,出露范围较大,但单个露头规模较小,不超过30 m2,仅在温木朗地区存在大规模露头。受断层作用影响,蛇纹岩上各种擦痕、镜面现象十分明显,其与围岩接触部分发生强烈片理化(图版Ⅰ-a)。岩石风化面呈灰绿色,新鲜面呈墨绿色,偶尔可见球状风化现象(图版Ⅰ-b),表面蛇纹石呈纤维状(图版Ⅰ-c)。方辉橄榄岩的矿物成分主要为橄榄石(90%),裂理明显,破碎严重(图版Ⅰ-d),含少量斜方辉石(10%),镜下明显可见2组斜交解理(图版Ⅰ-e)。蛇纹岩蛇纹石化作用非常明显,矿物成分以纤维状的蛇纹石为主,不透明矿物主要为磁铁矿(图版Ⅰ-f)。
2. 测试方法
全岩主量、稀土和微量元素在中国地质大学(北京)地学实验中心实验室进行,分析仪器为美国利曼公司(LEEMAN LABS.INC)Prodigy型等离子发射光谱仪(ICP-OES)。SiO2的分析精度为1%,其他氧化物的分析精度在4%~10%之间。微量元素分析仪器为Agilent公司生产的四极杆ICP-MS7500a。采用两酸(HNO3+HF)高压反应釜(Bomb)溶样方法进行样品的化学预处理。质量监控标样为美国地质调查局(USGS)标准样品AGV2、中国地质测试中心岩石标样GSR-1和GSR-3、GSR-5。大多数元素的分析误差在5%以内。具体分析步骤与仪器参数详见参考文献[26]。
3. 地球化学特征
本次在温木朗(原贡布爬拉超基性岩,ST64)、屋烟朗(ST74)、龙崖松多(ST84)等地采集了10件超基性岩样品,样品分析结果见表 1。
表 1 松多超基性岩全岩地球化学分析结果Table 1. Whole rock composition of the ultramafic rocks in Sumdo样品编号 ST64H1 ST64H2 ST64H3 ST64H4 ST64H5 ST74H1 ST74H2 ST84H1 ST84H2 ST84H3 SiO2 40.36 44.26 37.65 41.34 38.30 43.28 39.15 40.90 37.59 41.14 TiO2 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.03 0.04 0.01 0.02 0.04 0.01 0.01 Al2O3 0.52 0.53 0.65 0.71 0.61 0.67 0.87 0.81 0.72 0.66 TFeO 9.41 9.19 12.98 8.78 11.69 5.63 7.73 8.75 9.19 8.33 MnO 0.17 0.12 0.18 0.15 0.14 0.06 0.23 0.12 0.14 0.10 MgO 39.08 36.52 39.50 39.21 39.83 36.69 42.48 40.91 42.89 39.82 CaO 0.08 0.00 0.01 0.21 0.06 0.09 0.08 0.72 0.35 0.10 Na2O 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.03 0.02 0.03 0.02 K2O 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.03 0.01 P2O5 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 烧失量 9.33 8.36 8.13 8.55 8.38 12.67 8.59 6.75 8.09 8.80 总计 99.01 99.03 99.14 99.00 99.08 99.12 99.19 99.04 99.05 99.01 Li 0.20 1.00 0.44 0.71 1.13 0.30 0.40 0.82 0.65 3.61 Sc 10.99 10.12 10.02 10.61 11.63 7.94 4.56 9.88 8.65 8.97 V 49.04 35.26 36.18 35.38 65.34 10.54 206.8 52.98 38.42 19.68 Cr 4708 3950 3940 4396 5628 1997 13052 3162 2878 3914 Co 130.9 124.6 142.3 127.6 139.5 87.9 123.3 137.1 124.5 123.0 Ni 1196 1173 1132 1209 1298 2112 2022 2574 2408 2424 Cu 3.24 4.58 4.30 3.28 4.08 4.49 2.94 0.84 1.84 5.66 Zn 65.68 47.90 64.56 57.12 52.02 45.36 113.6 47.90 49.22 62.52 Ga 2.05 2.07 1.93 2.21 3.19 0.73 2.27 1.14 0.98 1.05 Rb 1.68 0.86 1.11 0.88 0.99 0.42 1.40 2.25 19.58 14.08 Sr 0.4 0.3 0.3 0.2 0.4 1.7 428.6 363.2 238.2 354.8 Y 0.57 0.53 0.44 0.68 0.54 0.22 0.42 0.76 0.43 0.33 Zr 1.68 0.86 1.11 0.98 1.10 0.84 1.28 1.64 1.22 0.82 Nb 0.36 0.28 0.27 0.22 0.35 0.23 0.23 0.22 0.22 0.14 Cs 0.13 0.39 0.19 0.21 0.17 0.04 0.04 0.05 0.08 0.13 Ba 2.61 5.02 4.18 6.15 7.08 3.23 3.02 4.48 6.71 6.89 La 0.22 0.14 0.22 0.31 0.18 0.17 0.63 0.36 0.26 0.10 Ce 0.46 0.31 0.43 0.58 0.35 0.38 0.93 0.52 0.31 0.27 Pr 0.06 0.04 0.05 0.07 0.04 0.05 0.09 0.08 0.05 0.03 Nd 0.25 0.20 0.21 0.30 0.19 0.19 0.30 0.33 0.21 0.15 Sm 0.08 0.06 0.06 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.06 0.04 Eu 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.04 0.02 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.01 Gd 0.09 0.08 0.08 0.11 0.09 0.04 0.06 0.11 0.07 0.05 Tb 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.01 0.01 Dy 0.11 0.10 0.09 0.12 0.10 0.04 0.07 0.13 0.07 0.05 Ho 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.01 Er 0.06 0.06 0.05 0.07 0.07 0.03 0.04 0.08 0.05 0.04 Tm 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 Yb 0.06 0.06 0.05 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.04 0.10 0.06 0.05 Lu 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.01 0.01 Hf 0.04 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.02 Ta 0.03 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.01 Pb 0.61 0.29 0.38 0.32 0.36 0.37 0.44 0.94 0.41 0.38 Th 0.02 0.01 0.03 0.01 0.01 0.04 0.03 0.04 0.04 0.02 U 0.03 0.02 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.02 0.02 0.01 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 3.1 主量元素
超基性岩样品蚀变较强,烧失量较高(6.75%~ 12.67%),说明遭受了高度的水化过程。扣除烧失量重新计算主量元素含量后,SiO2含量在41.33%~50.06%之间,平均为44.76%,略低于全球深海橄榄岩平均值(45.6%)[21];TiO2含量在0.01%~0.05%之间,平均为0.03%;Al2O3含量在0.58%~0.96%之间,平均为0.75%,低于地幔岩和全球深海橄榄岩的平均值(分别为3.55%和1.29%)[21];MgO含量较高(40.28%~47.16%),平均为43.95%,与世界典型蛇绿岩中的方辉橄榄岩(39.6%~48.4%)相当,略高于全球深海橄榄岩(41.6%)[21];Mg#值为87.6~93.83,与世界典型蛇绿岩中的方辉橄榄岩值(88.6~92.1)基本一致[27];TFe2O3含量为6.51%~14.26%,平均为10.13%;Na2O、K2O、MnO和P2O5含量极低,分别平均为0.02%、0.01%、0.16%和0.01%。超基性岩亏损SiO2、CaO、Al2O3、TiO2、Na2O+K2O等易熔组分,明显低于原始地幔,MgO含量明显高于原始地幔[20],表明源岩具有一定程度的亏损。在ACM图解[27](图 3-a)中,样品点分布于变质橄榄岩区;在Al2O3-SiO2/MgO图解[28](图 3-b)中,样品点分布于橄榄岩区;在MgO-Al2O3图解[29](图 3-c)中,样品点分布于深海橄榄岩区域及附近。
3.2 稀土和微量元素
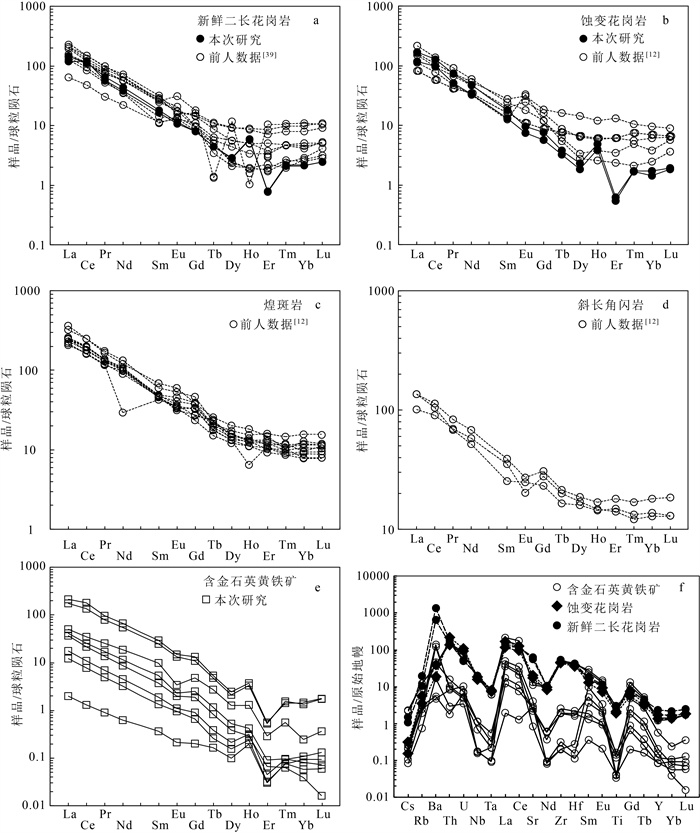
超基性岩样品稀土元素总量变化范围较大(4.04×10-6~9.31×10-6),高于球粒陨石值(3.292×10-6)[30],大部分低于原始地幔值(7.075×10-6)[31]。稀土元素配分曲线呈较宽缓的“U”型,(La/Yb)N =1.49~10.68,轻稀土元素较富集,轻、重稀土元素分异较明显;(La/Sm)N=1.41~6.43,轻稀土元素和中稀土元素存在轻微的分异;(Gd/Yb)N=0.79~1.22,重稀土元素分异不明显;δEu可以分为3组,分别为负异常(0.73)、无异常(0.90~1.07)和正异常(1.21~1.45),Eu的正异常表明岩石是幔源的,而Eu的负异常与斜长石的熔融作用或后期蚀变作用的叠加有关[32],反映了蚀变程度的不同。稀土元素丰度变化明显,表明熔融程度和亏损程度存在差异[33]。超基性岩的稀土元素配分曲线与典型蛇绿岩中变质橄榄岩的稀土元素配分曲线相似,落在深海地幔橄榄岩区域,而与弧前地幔橄榄岩明显不同;中稀土元素相较于重稀土元素和轻稀土元素亏损(图 4-a)。微量元素分布形式与全球深海橄榄岩基本一致[21]。由于蛇纹石化强烈,活动性元素Rb、Sr等含量有较大变化,具有明显的正U异常和Th、Nb负异常,大部分样品具有轻微的Zr、Hf负异常(图 4-b)。
4. 讨论
4.1 超基性岩原岩
超基性岩样品大部分蛇纹石化严重,几乎完全蚀变为蛇纹岩,原岩矿物组合极难识别,仅在龙崖松多地区保留了较好的原岩结构。前人通过对世界典型蛇绿岩中超基性岩的研究发现,MgO+TFeO和(m+f)/Si((Mg原子数+Fe原子数)/Si原子数)可以有效区别不同的原岩类型[21]。松多地区超基性岩的MgO+TFeO和(m+f)/Si值分别为49.0%~57.7%和1.36~1.48,与方辉橄榄岩(分别为51%~56%和1.55~1.90)一致(图 5)。该结果与镜下薄片鉴定和陈松永[17]的结果一致,笔者认为,松多地区的超基性岩属于方辉橄榄岩。
![]() 图 5 松多超基性岩(MgO+TFeO)-(m+f)/Si图解(贡布爬拉蛇纹岩数据据参考文献[17])
图 5 松多超基性岩(MgO+TFeO)-(m+f)/Si图解(贡布爬拉蛇纹岩数据据参考文献[17])
Lh—二辉橄榄岩;Hz—方辉橄榄岩:D—纯橄岩Figure 5. (MgO+TFeO)-(m+f)/Si diagram of the ultramafic rock in Sumdo在YbN-(Ce/Sm)N图解[29](图 6-a)中,样品点主要分布于深海橄榄岩和弧前橄榄岩区;在主量、微量元素-MgO图解(图 6-b~f)中,样品点基本落在深海橄榄岩区。同时,样品的Ga(0.73×10-6~3.19×10-6,平均为1.76×10-6)和Sc(1.56×10-6~11.63×10-6,平均为9.34×10-6)含量与深海橄榄岩一致(分别平均为1.98×10-6和10.30×10-6),与大洋地壳在成分上存在互补关系[21],结合样品高Mg#值和高Cr、Ni含量特征,笔者认为,样品是地幔橄榄岩部分熔融后的难熔残留体[21]。松多地区超基性岩的地球化学特征与亏损的深海橄榄岩十分相似,因此笔者认为,其原岩应为亏损的深海橄榄岩。
4.2 岩石成因
4.2.1 部分熔融特征
一般认为,地幔橄榄岩经历不同的部分熔融过程会导致其在矿物组合、矿物含量和全岩地球化学组成上存在差别[35-36],所以地幔橄榄岩的矿物含量和全岩地球化学特征可以为地幔橄榄岩的部分熔融提供证据。岩石圈地幔主要由尖晶石二辉橄榄岩和石榴子石二辉橄榄岩组成,在尖晶石二辉橄榄岩相部分熔融过程中,单斜辉石被认为是最先消耗的矿物[37-38],在无水条件下,地幔橄榄岩在经历大于25%的部分熔融后,其单斜辉石含量可由约15%降低为0%;如果为石榴子石相的地幔源区,单斜辉石可以保存至较高的部分熔融程度[34]。因此,地幔橄榄岩中单斜辉石含量可反映地幔橄榄岩的亏损及相对部分熔融程度。松多地区的超基性岩原岩为方辉橄榄岩,在龙崖松多地区变质程度较低的样品中也未发现单斜辉石的存在,表明松多地区的超基性岩可能为地幔橄榄岩在尖晶石相熔融后的难熔残留体。这与Yb-Ti图解[34](图 7-a)得到的结果一致。但是,样品的重稀土元素(HREE)含量明显低于深海橄榄岩(图 4),反映部分石榴子石相熔融的特征[21],这可能与松多古特提斯洋二叠纪地幔柱/热点活动引起的更高的地热梯度有关。更高的地热梯度使地幔橄榄岩更早的开始熔融,重稀土元素寄存在石榴子石中。
另外,重稀土元素受熔融程度控制,在后期变质过程中几乎不会受到影响[21]。为估算松多地区超基性岩的熔融程度,将松多地区超基性岩的原始地幔标准化稀土元素配分曲线与Niu[21]提出的批式熔融模式曲线(图 7-b)进行对比,发现松多地区超基性岩的熔融程度大于25%,经历了较高程度的批式熔融。
4.2.2 岩石-熔体反应
通常情况下,蛇绿岩中的地幔橄榄岩被认为是地幔经历了不同程度部分熔融亏损后的残余[39]。但松多地区超基性岩表现出轻稀土元素(LREE)富集的特征,证明其并非为简单的批式熔融残余体。前人将轻稀土元素的富集归因于岩石经历了俯冲带熔体/流体的改造,依据是俯冲带的玻安质熔体通常具有LREE、Zr和Sr富集的特征[40-41]。但在原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图中,样品并未表现出Zr、Hf的富集,而表现为轻微亏损,其地球化学特征与深海地幔橄榄岩非常相似,并非SSZ型的橄榄岩。太平洋洋中脊和印度洋洋中脊的深海橄榄岩同样表现出轻稀土元素富集的特征,为熔融残余的地幔在热力学边界层与后期上升的熔体渗透和交代的结果[21]。另外,流体/岩石的相互作用、强烈的蛇纹石化也可能导致轻稀土元素的富集[42]。熔体/岩石相互作用引起轻稀土元素富集时,高场强元素也会明显增加,而岩石发生蛇纹石化作用时,高场强元素含量变化不大,因为在含水流体中轻稀土元素溶解度比高场强元素高,而硅酸盐熔体中二者的溶解度几乎一致[21]。在La-Nb(图 8-a)和Zr-La图解(图 8-b)中,样品整体与深海橄榄岩趋势一致[21],随着轻稀土元素含量的增加,高场强元素含量略微增加,表明轻稀土元素的富集主要由流体作用或蛇纹石化作用所致,受硅酸盐熔体作用较小,这与野外观察到的强烈的蛇纹石化作用一致。
4.2.3 构造环境
前人对蛇绿岩构造环境的研究集中于上部洋壳端元,对下部地幔橄榄岩的研究较少,所以地幔橄榄岩构造环境的划分依据存在较大争议。一般认为,如果其形成于大洋中则与深海橄榄岩类似;形成于弧环境则与弧前橄榄岩类似。通过对比松多地区超基性岩与深海地幔橄榄岩和弧前地幔橄榄岩的主量、微量元素特征,笔者发现,松多地区超基性岩与深海橄榄岩相似,明显区别于弧前地幔橄榄岩。另外,松多地区超基性岩与堆晶岩、MORB型的变质辉长岩一起产出,互相呈断层接触关系;且其围岩为绿片岩,该绿片岩呈MORB/OIB的地球化学特征,被认为是松多古特提斯洋的大洋岩石圈残片[14-15, 19]。因此,笔者认为,松多地区超基性岩与周围堆晶岩和变质辉长岩一起,代表了一套较完整的MORB型蛇绿岩,形成于大洋中脊环境。
5. 对松多古特斯洋演化的启示
自发现榴辉岩至今,松多地区的榴辉岩已经得到了广泛的关注和深入的研究。前人根据松多榴辉岩、洋壳残片、后碰撞花岗岩等的研究,初步建立了松多古特提斯洋的演化模式:早石炭世—晚石炭世,松多古特提斯洋经历了从大陆裂谷—初始小洋盆—成熟大洋的发展阶段;二叠纪—早三叠世,松多古特提斯洋俯冲闭合;中晚三叠世—早侏罗世为碰撞造山-晚造山或后造山阶段[17]。然而,相较于榴辉岩等的深入研究,蛇绿岩各端元的研究程度较低,尤其是超基性岩端元。作为大洋岩石圈演化的直接产物,蛇绿岩可以有效地承载有关古大洋地幔动力学和大地构造过程的信息,为反演区域构造演化过程提供直接证据[16]。最近,有学者通过对松多地区蛇绿岩中的基性岩及洋岛的研究,提出松多古特提斯洋在二叠纪存在一次地幔柱/热点事件,并认为地幔柱/热点与大洋中脊之间的相互作用导致了松多地区地球化学特征复杂的基性岩的形成[19]。本文报道的超基性岩虽未获得年龄,但是前人从温木朗蛇纹岩(原贡布爬拉超基性岩)中的埃达克质花岗岩侵入体中获得266 Ma的年龄[15],再结合变质辉长岩274 Ma的年龄[24],笔者认为其形成时代应为早—中二叠世。同时,松多地区超基性岩的重稀土元素含量明显低于深海橄榄岩,反映了一定程度石榴子石的特征,表明其较早开始了批式熔融过程[21]。这种较早开始熔融的现象很可能是热点/地幔柱为其提供热量导致的。松多地区超基性岩的这一特征从侧面证明,松多古特提斯洋很可能在二叠纪存在地幔柱/热点的活动。
目前,前人关于蛇绿岩中超基性岩形成环境的认识主要包括以下3种:①形成于典型的SSZ型蛇绿岩中的超基性岩,如雅鲁藏布江中段的日喀则、萨嘎和桑桑蛇绿岩[43-45];②形成于MOR环境,后被SSZ改造的蛇绿岩中的超基性岩,如雅江带东段和西段的普兰蛇绿岩[46]、罗布莎蛇绿岩[47]和达机翁蛇绿岩[48];③形成于典型MOR环境的大洋深海橄榄岩,如雅江带西段的南公珠错蛇绿岩[49]。唐加-松多蛇绿混杂岩的重新厘定是继松多地区发现榴辉岩以来又一重要的发现,部分学者认为,松多地区的超基性岩属于SSZ型蛇绿岩中的端元,类似于Troodos蛇绿岩[17-18]。本次通过对松多地区超基性岩的研究,认为其应该形成于大洋中脊环境,属于典型的MORB型蛇绿岩,对松多地区蛇绿岩形成的构造环境和形成过程提出了新的认识。
6. 结论
(1) 松多地区超基性岩的原岩为深海橄榄岩。
(2) 松多地区超基性岩可能为尖晶石二辉橄榄岩地幔批式熔融后的难熔残留体,并具一定程度石榴子石相熔融的特征,熔融程度大于25%。
(3) 松多地区超基性岩可能形成于大洋中脊环境,为典型的MORB型蛇绿岩端元之一。
致谢: 感谢山东省第一地质矿产勘查院江海洋博士和乳山市自然资源局潘万伟工程师在野外取样过程中给予的帮助,审稿专家对本文提出了建设性意见,在此一并表示感谢。 -
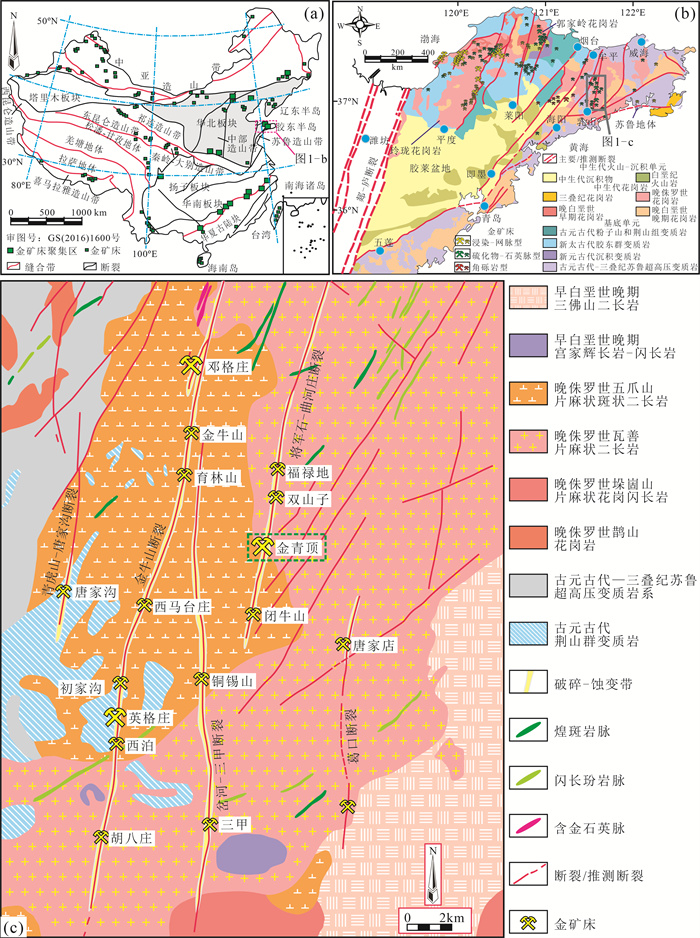
图 1 中国主要构造域及金矿床分布简图(a,据参考文献[19]修改)、胶东半岛地质及金矿床分布图(b,据参考文献[2]修改)和牟平-乳山成矿带地质及矿床分布图(c,据参考文献[11]修改)
Figure 1. Simplified map of China showing major tectonic domains(a) and locations of major gold deposits, geological map of the Jiaodong gold province(b) and geological map of the Muping-Rushan gold metallogenic belt(c)
表 1 金青顶金矿床硫化物矿石与围岩稀土元素组成
Table 1 Rare earth elements composition of sulfide ore and wall-rock in Jinqingding gold deposit
10-6 样品编号 20JQD- 1-1 20JQD- 1-2 20JQD- 2-1 20JQD- 2-2 20JQD- 3-1 20JQD- 3-2 20JQD- 5-1 20JQD- 5-2 20JQD- 8-1 20JQD- 8-2 20JQD- 9 20JQD- 10 Ⅱ阶段矿石 Ⅰ阶段矿石 Ⅱ阶段矿石 蚀变围岩 新鲜围岩 La 2.88 4.08 11.79 0.46 8.51 9.58 50.54 41.02 40.02 27.46 28.19 34.22 Ce 4.63 6.60 21.19 0.78 13.07 15.56 108.08 80.91 76.99 58.74 72.53 69.26 Pr 0.46 0.66 2.38 0.08 1.26 1.58 9.04 7.46 6.93 4.81 5.44 6.29 Nd 1.47 2.10 8.56 0.29 4.03 5.33 30.49 25.24 21.97 15.32 17.92 20.58 Sm 0.20 0.28 1.49 0.06 0.56 0.80 4.41 3.79 2.70 1.99 2.55 2.77 Eu 0.05 0.06 0.20 0.01 0.11 0.13 0.86 0.76 0.54 0.42 0.62 0.67 Gd 0.13 0.18 0.98 0.04 0.38 0.51 2.71 2.20 1.54 1.15 1.64 1.66 Tb 0.01 0.01 0.10 0.01 0.03 0.04 0.20 0.17 0.14 0.12 0.16 0.17 Dy 0.04 0.05 0.32 0.03 0.10 0.13 0.62 0.53 0.57 0.46 0.73 0.72 Ho 0.01 0.02 0.07 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.21 0.19 0.27 0.22 0.34 0.33 Er 0.01 0.01 0.05 / 0.01 0.01 0.09 0.09 0.10 0.09 0.13 0.13 Tm / / 0.01 / / / 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.06 0.05 Yb 0.02 0.02 0.04 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.24 0.22 0.28 0.24 0.37 0.36 Lu / / 0.01 / / / 0.04 0.04 0.05 0.05 0.06 0.06 Y 0.13 0.19 0.89 0.13 0.24 0.32 2.22 1.91 2.68 2.15 3.67 3.64 ΣREE 9.92 14.07 47.18 1.79 28.10 33.72 207.57 162.67 152.13 111.09 130.74 137.29 LREE/HREE 43.71 46.34 28.81 16.75 50.60 44.78 49.05 45.71 49.91 46.13 36.47 38.42 LaN/YbN 131.54 160.74 208.20 34.53 928.30 511.85 149.52 131.18 101.89 83.54 54.87 67.78 δEu 1.01 0.84 0.49 0.78 0.76 0.62 0.76 0.80 0.82 0.85 0.92 0.96 δCe 0.99 0.99 0.98 0.97 0.98 0.98 1.24 1.13 1.13 1.25 1.44 1.16 表 2 金青顶金矿床硫化物矿石与围岩微量元素组成
Table 2 Trace elements composition of sulfide ore and wall-rock in Jinqingding gold deposit
10-6 样品编号 20JQD- 1-1 20JQD- 1-2 20JQD- 2-1 20JQD- 2-2 20JQD- 3-1 20JQD- 3-2 20JQD- 5-1 20JQD- 5-2 20JQD- 8-1 20JQD- 8-2 20JQD- 9 20JQD- 10 Ⅱ阶段矿石 Ⅰ阶段矿石 Ⅱ阶段矿石 蚀变围岩 新鲜围岩 Cs 0.04 0.05 0.04 0.05 0.02 0.02 0.41 0.44 0.03 0.06 0.20 0.28 Rb 7.34 11.29 5.74 7.04 1.73 4.46 28.16 28.19 8.15 12.94 24.16 45.09 Ba 337.13 109.64 11.41 13.16 41.02 291.35 92.92 90.29 45.57 95.74 1562.78 3310.39 Th 0.26 0.46 0.24 0.05 0.08 0.30 4.76 4.23 6.40 3.98 4.56 5.34 U 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.05 0.03 0.04 0.63 0.59 0.87 0.75 0.40 0.42 Nb 0.17 0.28 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.27 4.54 4.88 4.52 3.89 4.90 4.93 Ta / 0.01 / / / / 0.09 0.08 0.11 0.10 0.11 0.12 La 2.88 4.08 11.79 0.46 8.51 9.58 50.54 41.02 40.02 27.46 28.19 34.22 Ce 4.63 6.60 21.19 0.78 13.07 15.56 108.08 80.91 76.99 58.74 72.53 69.26 Sr 18.63 18.47 29.36 20.83 6.06 16.17 80.67 95.49 147.21 125.37 401.84 459.54 Nd 0.17 0.28 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.27 4.54 4.88 4.52 3.89 4.90 4.93 Zr 7.55 9.90 0.78 0.79 1.23 7.28 171.59 195.07 170.80 178.54 188.42 205.48 Hf 0.20 0.23 0.03 0.01 0.02 0.17 4.45 4.59 3.82 4.10 4.17 4.51 Sm 0.20 0.28 1.49 0.06 0.56 0.80 4.41 3.79 2.70 1.99 2.55 2.77 Eu 0.05 0.06 0.20 0.01 0.11 0.13 0.86 0.76 0.54 0.42 0.62 0.67 Ti 53.26 73.40 17.46 18.40 14.97 63.45 869.63 886.42 954.11 854.40 1337.97 1218.07 Gd 0.13 0.18 0.98 0.04 0.38 0.51 2.71 2.20 1.54 1.15 1.64 1.66 Tb 0.01 0.01 0.10 0.01 0.03 0.04 0.20 0.17 0.14 0.12 0.16 0.17 Y 0.13 0.19 0.89 0.13 0.24 0.32 2.22 1.91 2.68 2.15 3.67 3.64 Yb 0.02 0.02 0.04 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.24 0.22 0.28 0.24 0.37 0.36 Lu / / 0.01 / / / 0.04 0.04 0.05 0.05 0.06 0.06 Y/Ho 25.3 25.3 19.1 27.1 22.5 22.0 24.7 22.3 26.6 24.6 28.2 28.6 Co 14.90 11.17 27.33 2.23 62.74 35.06 64.26 71.39 0.29 0.42 0.54 0.49 Ni / 1.96 2.45 0.96 3.97 2.79 3.88 6.79 0.19 0.34 0.20 0.17 Hf/Sm 0.98 0.83 0.02 0.22 0.03 0.21 1.01 1.21 / / / / Th/La 0.09 0.11 0.02 0.11 0.01 0.03 0.09 0.10 / / / / Nb/La 0.06 0.07 / 0.10 / 0.03 0.09 0.12 / / / / Y/Ho 25.32 25.30 19.13 27.06 22.49 21.97 24.66 22.32 / / / / Co/Ni / 5.71 11.18 2.31 15.81 12.58 16.56 10.51 / / / / Nb/Ta 56.04 36.78 12.27 34.30 30.76 59.81 52.06 57.98 / / / / Zr/Hf 38.53 42.12 25.94 65.61 73.71 42.07 38.59 42.48 / / / / -
Yang L Q, Deng J, Wang Z L, et al. Thermochronologic constraints on evolution of the Linglong Metamorphic Core Complex and implications for gold mineralization: a case study from the Xiadian gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 72: 165-178. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.07.006
Deng J, Yang L Q, Groves D I, et al. An integrated mineral system model for the gold deposits of the giant Jiaodong province, eastern China[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2020, 208: 103274. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103274
杨立强, 邓军, 王中亮, 等. 胶东中生代金成矿系统[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30: 2447-2467. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409001.htm 宋明春, 林少一, 杨立强, 等. 胶东金矿成矿模式[J]. 矿床地质, 2020, 39(2): 215-236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202002002.htm Goldfarb R J, Santosh M. The dilemma of theJiaodong gold deposits: Are they unique?[J]Geoscience Frontiers, 2014, 5: 139-153. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2013.11.001
Groves D I, Santosh M. The giant Jiaodong gold province: The key to a unified model for orogenic gold deposits?[J]Geoscience Frontiers, 2016, 7: 409-417. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2015.08.002
胡芳芳, 范宏瑞, 沈昆, 等. 胶东乳山脉状金矿床成矿流体性质与演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(5): 1329-1338. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200505001.htm 应汉龙. 胶东金青顶和邓格庄金矿床的同位素组成及其地质意义[J]. 贵金属地质, 1994, 3: 201-207. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJSD403.005.htm 胡芳芳, 范宏瑞, 杨进辉, 等. 胶东乳山金矿蚀变岩中绢云母40Ar/39Ar年龄及其对金成矿事件的制约[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2006, 2: 109-114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200602000.htm Li J W, Vasconcelos P M, Zhou M F, et al. Geochronology of the Pengjiakuang and Rushan gold deposits, eastern Jiaodong gold province, northeastern China: implications for regional mineralization and geodynamic setting[J]. Economic Geology, 2006, 101: 1023-1038. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.101.5.1023
Sai S X, Deng J, Qiu K F, et al. Textures of auriferous quartz-sulfide veins and 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of the Rushan gold deposit: Implications for processes of ore-fluid infiltration in the eastern Jiaodong gold province, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 117: 103254. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103254
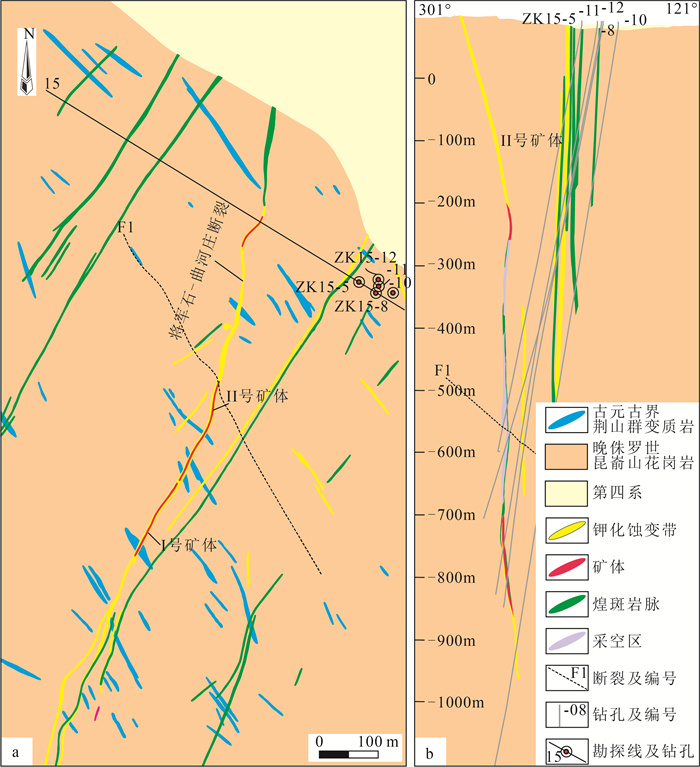
李旭芬. 胶东牟平-乳山金矿带金青顶金矿矿床成因与找矿方向研究[D]. 长安大学博士学位论文, 2011. 丁振举, 姚书振, 刘丛强, 等. 东沟坝多金属矿床喷流沉积成矿特征的稀土元素地球化学示踪[J]. 岩石学报, 2003, 4: 792-798. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200304021.htm 马玉波, 杜晓慧, 张增杰, 等. 青城子层状/脉状铅锌矿床稀土元素地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2013, 32(6): 1236-1248. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2013.06.010 郭林楠, 黄春梅, 张良, 等. 胶东罗山金矿床成矿流体来源: 蚀变岩型和石英脉型矿石载金黄铁矿稀土与微量元素特征约束[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(1): 121-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201901012.htm Li J, Cai W Y, Li B, et al. Paleoproterozoic SEDEX-type stratiform mineralization overprinted by Mesozoic vein-type mineralization in the Qingchengzi Pb-Zn deposit, Northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019, 184: 104009. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.104009
Li J, Wang K Y, Cai W Y, et al. Triassic gold-silver metallogenesis in Qingchengzi orefield, North China Craton: Perspective from fluid inclusions, REE and H-O-S-Pb isotope systematics[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 121: 103567. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103567
翟明国. 华北前寒武纪成矿系统与重大地质事件的联系[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29: 1759-1773. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201305023.htm Goldfarb R J, Qiu K F, Deng J, et al. Orogenic Gold Deposits of China[J]. Society of Economic Geologists Special Publications, 2019, 22: 263-324.
Yang J H, Wu F Y, Wilde S A. A review of the geodynamic setting of large-scale Late Mesozoic gold mineralization in the North China Craton: an association with lithospheric thinning[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2003, 23: 125-152. doi: 10.1016/S0169-1368(03)00033-7
Yang J H, Wu F Y. Triassic magmatism and its relation to decratonization in the eastern North China Craton[J]. Science in China, 2009, 52: 1319-1330. doi: 10.1007/s11430-009-0137-5
Li J, Cai W Y, Wang K Y, et al. Initial decratonization of the eastern North China Craton: New constraints from geochronology, geochemistry, and Hf isotopic compositions of Mesozoic igneous rocks in the Qingchengzi district[J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 55: 3796-3820. doi: 10.1002/gj.3635
Yang K F, Fan H R, Santosh M, et al. Reactivation of the Archean lower crust: implications for zircon geochronology, elemental and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic geochemistry of late Mesozoic granitoids from northwestern Jiaodong Terrane, the North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 2012, 146: 112-127.
王世进, 万渝生, 宋志勇, 等. 鲁东文登地区文登型(超单元)花岗岩体的SHRIMP锆石年代学[J]. 山东国土资源, 2012, 28(2): 1-5, 10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2012.02.002 Ma L, Jiang S Y, Dai B Z, et al. Multiple sources for the origin of Late Jurassic Linglong adakitic granite in the Shandong Peninsula, eastern China: zircon U-Pb geochronological geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic evidence[J]. Lithos, 2013, 162: 175-194.
张岳桥, 李金良, 张田, 等. 胶莱盆地及其邻区白垩纪—古新世沉积构造演化历史及其区域动力学意义[J]. 地质学报, 2008, 9: 1229-1257. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200809007.htm 朱日祥, 孙卫东. 大地幔楔与克拉通破坏型金矿[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2021, 51, doi: 10.1360/SSTe-2020-0305. Hou M L, Jiang Y H, Jiang S Y, et al. Contrasting origins of late Mesozoic adakitic granitoids from the northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, East China: implications for crustal thickening to delamination[J]. Geological Magazine, 2007, 144: 619-631. doi: 10.1017/S0016756807003494
Li X H, Fan H R, Zhang Y W, et al. Rapid exhumation of the northern Jiaobei Terrane, North China Craton in the Early Cretaceous: Insights from Al-in-hornblende barometry and U-Pb geochronology[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 160: 365-379. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.10.001
Song M C, Zhou J B, Song Y X, et al. Mesozoic Weideshan granitoid suite and its relationship to large-scale gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 55: 5703-5724. doi: 10.1002/gj.3607
王斌, 宋明春, 霍光, 等. 胶东晚中生代花岗岩的源区性质与构造环境演化及其对金成矿的启示[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2021, 40(2): 288-320. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2021.02.009 陈炳翰. 牟乳金矿带成矿作用地球化学[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2017. Zhang Y W, Hu F F, Fan H R, et al. Fluid evolution and gold precipitation in the Muping gold deposit(Jiaodong, China): insights from in-situ trace elements and sulfur isotope of sulfides[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 218: 106617. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2020.106617
胡芳芳, 范宏瑞, 杨进辉, 等. 胶东乳山含金石英脉型金矿的成矿年龄: 热液锆石SHRIMP法U-Pb测定[J]. 科学通报, 2004, (12): 1191-1198. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.12.014 郭敬辉, 陈福坤, 张晓曼, 等. 苏鲁超高压带北部中生代岩浆侵入活动与同碰撞-碰撞后构造过程: 锆石U-Pb年代学[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(4): 1281-1301. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200504025.htm 赛盛勋, 邱昆峰. 胶东乳山金矿床成矿过程: 周期性压力波动诱发的流体不混溶[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(5): 1547-1566. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202005014.htm 尹升, 张海芳, 王芳, 等. 山东金青顶金矿床Ⅱ号矿体成矿特征[J]. 山东国土资源, 2015, 31(11): 9-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2015.11.003 Liu Y S, Zong K Q, Kelemen P B, et al. Geochemistry and magmatic history of eclogites and ultramafic rocks from the Chinese continental scientific drill hole: Subduction and ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism of lower crustal cumulates[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 247(1/2): 133-153.
凌洪飞, 胡受奚, 孙景贵, 等. 胶东金青顶和大尹格庄金矿床花岗质围岩的蚀变地球化学研究[J]. 矿床地质, 2002, (2): 187-199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2002.02.011 陈海燕, 李胜荣, 张秀宝, 等. 胶东金青顶金矿床围岩蚀变特征与金矿化[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2012, 31(1): 5-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2012.01.002 Boynton W V. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteoritestudies[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1984: 63-114.
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Shannon R D. Revised Effective Ionic Radii and Systematic Studies of Interatomic Distances in Halides and Chalcogenides[J]. Acta Cryst, 1976, 32: 751-767. doi: 10.1107/S0567739476001551
Jiang S Y, Yu J M, Lu J J. Trace and rare-earth element geochemistry in tourmaline and cassiterite from the Yunlong tin deposit, Yunnan, China: implication for migmatitic-hydrothermal fluid evolution and ore genesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 209: 193-213. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.04.021
毕献武, 胡瑞忠, 彭建堂, 等. 黄铁矿微量元素地球化学特征及其对成矿流体性质的指示[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2004, (1): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2004.01.001 Mills R, Elderfield H. Rare earth elemen t geochemistry of hydrothermal deposits from the active TAG M ount, 26°N mid-Atlantic Ridge[J]. Geochimica et cosmochimica acta, 1995, 59(17): 3511-3524. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00224-N
Anenburg M, Mavrogenes J A, Frigo C, et al. Rare earth element mobility in and around carbonatites controlled by sodium, potassium, and silica[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6: eabb6570. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abb6570
Ayers J C, Watson E B. Apatite/fluid partitioning of rare-earth elements and strontium: Experimental results at 1.0 GPa and 1000℃ and application to models of fluid-rock interaction[J]. Chemical Geology, 1993, 110: 299-314. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(93)90259-L
Keppler H. Constraints from partitioning experiments on the composition of subduction zone fluids[J]. Nature, 1996, 380: 237-240. doi: 10.1038/380237a0
刘善宝. 山东乳山金青顶金矿田成矿规律及其成矿远景研究[D]. 长安大学博士学位论文, 2005. 翟建平, 胡凯, 陆建军. 乳山金矿床的成因机制—成矿流体和H, O, Sr同位素证据[J]. 科学通报, 1996, (12): 1119-1121. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1996.12.017 高太忠, 赵伦山, 杨敏之. 山东牟乳金矿带成矿演化机理探讨[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2001, (2): 155-160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2001.02.007 张运强, 李胜荣, 陈海燕, 等. 胶东金青顶金矿床成矿流体来源的黄铁矿微量元素及He-Ar同位素证据[J]. 中国地质, 2012, 39(1): 195-204. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.01.019 Bau M, Dulski P. Comparing yttrium and rare earths in hydrothermal fluids from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge: Implications for Y and REE behavior during near-vent mixing and for the Y/Ho ratio of Proterozoic seawater[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 155: 77-99. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(98)00142-9
王文元, 高建国, 侬阳霞, 等. 云南禄劝噜鲁铅锌矿床稀土元素和微量元素地球化学[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2017, 35(3): 418-430. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTXB201703014.htm 郭林楠. 胶东型金矿床成矿机理[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2016. Guo L N, Goldfarb R J, Wang Z L, et al. A comparison of Jiaojia- and Linglong-type gold deposit ore-forming fluids: Do they differ?[J]Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 88: 511-533. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.12.003
Guo L N, Deng J, Yang L Q, et al. Gold deposition and resource potential of the Linglong gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula: Geochemical comparison of ore fluids[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 120: 103434. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103434
Groves D I, Goldfarb R J, Gebre-Mariam M, et al. Orogenic gold deposits: a proposed classification in the context of their crustal distribution and relationship to other gold deposit types[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 1998, 13: 7-27. doi: 10.1016/S0169-1368(97)00012-7
Goldfarb R J, Groves D I, Gardoll S. Orogenic gold and geologic time: a synthesis[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2001, 18: 1-75. doi: 10.1016/S0169-1368(01)00016-6
曾国平, 向文帅, 吴发富, 等. 东北非与中国胶东造山型金矿对比及对非洲找矿勘查的启示[J]. 地质通报, 2022, 41(1): 48-59. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20220104&flag=1 -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 吴浩,徐祖阳,严维兵,郝宇杰,刘海永. 西藏中部聂尔错地区辉绿岩锆石U-Pb年龄与地球化学特征:对新特提斯洋板片断离的指示. 中国地质. 2023(06): 1804-1816 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: