Sulfur isotopic composition and its source of Jiaodong gold deposit
-
摘要:
胶东是全球第三大金矿集中区,矿床主要分布于胶西北、栖蓬福、牟乳等成矿区,矿化类型以蚀变岩型和石英脉型为主。由于金主要赋存于黄铁矿等硫化物中,这些硫化物的硫同位素组成对反映成矿物质来源具有重要指示意义。按照成矿区域、赋矿深度、矿化类型和含硫矿物对有关硫同位素数据进行了分类统计对比。分析表明,金矿床的δ34S值为-14.0‰~15.1‰,各典型金矿床的δ34S平均值在5.5‰~13.0‰之间,主要集中在6.0‰~10.0‰。δ34S值呈现如下规律性变化:牟乳成矿区>胶莱盆地东北缘>胶西北成矿区>栖蓬福成矿区,硫化物石英脉型>蚀变岩型>石英脉型,浅部矿>深部矿,黄铁矿>闪锌矿>黄铜矿>方铅矿。研究认为,金矿床中的硫为混合来源,由早前寒武纪变质岩系、晚中生代花岗岩类和地幔端元的多源同位素混合而成。硫同位素组成的变化主要与上述端元的混合比例有关,被较多晚中生代花岗岩物质混染的金矿床δ34S值较高,成矿深度较大、地壳物质混染较少的金矿床δ34S值较低。金矿形成于一次集中爆发的成矿事件,成矿过程中硫同位素体系已基本达到均一。
Abstract:Jiaodong is the third largest gold deposit concentration area in the world, with gold reserves of more than 5000 tons.The gold deposits are mainly distributed in the Northwest Jiaodong, Qi-Peng-Fu, Mu-Ru and other metallogenic regions.The metallogenic types are mainly fracture zone altered rock-type(Jiaojia-type), quartz vein-type(Linglong-type), and their transition types.Since gold mainly occurs in pyrite and other sulfides, the sulfur isotopic composition of these sulfides can reflect the source of ore-forming materials.In this paper, the sulfur isotopic compositions are classified and statistically compared according to the metallogenic regions, ore bearing depth, metallogenic types and sulfur-containing minerals.The δ34S value of gold deposits ranges from -14.0‰ to 15.1‰, with an average value of 5.5‰ to 13.0‰, and mainly concentrated in 6.0‰~10.0‰.The δ34S value shows the following rules: Mu-Ru metallogenic region > Northeast margin of Jiaolai Basin metallogenic region > Northwest Jiaodong metallogenic region > Qi-Peng-Fu metallogenic region, sulfide quartz vein-type > altered rock-type > quartz vein-type, shallow deposit > deep deposit, pyrite > sphalerite > chalcopyrite > galena.The study shows that the sulfur of the gold deposit is a mixed source, which is composed of multi-source isotopes of Early Precambrian metamorphic rock series, Late Mesozoic granitoids and Mantle material.The change of sulfur isotopic composition is mainly related to the type of country rock and sulfur source.The δ34S value of the gold deposit mixed with much late Mesozoic granite materials is relatively high, but the gold deposit in depth mixed with less crustal materials is relatively low.The sulfur isotope system in the metallogenic process is uniformity and controlled by one centralized explosion metallogenic event.
-
胶东是中国最重要的金矿集中区,其黄金储量和产量均居全国首位,已累计探明黄金储量超过5000 t[1]。金成矿具有“同时性、爆发性”的特征[2-4],目前大多数学者认为胶东金矿成矿时代集中在早白垩世(约120 Ma),且金的形成时代与华北克拉通破坏的高峰期一致,但对金矿成矿物质来源的认识一直存在争议。关于胶东金矿的物质来源,有地质勘查工作者强调新太古代变质基底的贡献和成矿物质的继承演化[5-6];有学者认为,前寒武纪变质基底很难作为金的主要来源,金矿的成矿流体和物质可能与古太平洋板片俯冲后撤导致的软流圈地幔上涌,交代岩石圈地幔有关[7-8];也有学者认为,克拉通破坏型金矿的成矿物质来源与滞留在地幔过渡带的俯冲板片脱水对Au等亲硫元素迁移的影响有关[9];还有学者提出,胶东型金矿是与岩浆热液有关的独特的脉状金矿床,成矿物质来源于岩浆热液或下地壳物质的部分熔融[10];部分学者认为,成矿物质是多源性的,除来自于地幔外,也来源于基性岩脉和花岗岩体[11-12]。
Au元素的来源、迁移和富集机理一直是金成矿作用研究的核心科学问题,硫同位素示踪则是研究成矿物质来源的重要途径,因此,前人对胶东金矿的硫同位素组成进行了大量测试,并分析了硫的来源。许多研究者认为,硫源主要继承了赋矿围岩的硫同位素特征,初始来源于胶东早前寒武纪变质杂岩,最终来源于晚中生代花岗岩类[6, 10];也有研究者认为,胶东金矿高的硫同位素组成与扬子克拉通新元古代高硫沉积地层俯冲到华北克拉通岩石圈地幔有关[13],或认为34S可能来源于板块俯冲过程中的脱挥发分作用[14];还有研究认为,硫以幔源岩浆硫为主,并混染了壳源硫[15-19]。以往的研究注重于通过金矿床与围岩对比,或可能的源区岩石的硫同位素特征来解释硫的来源,缺乏对不同金矿床之间硫同位素变化的系统研究,以及对硫同位素来源及演化的进一步揭示。本文较全面地整理了前人对胶东29个金矿床硫同位素组成的测试结果,分类对比了不同矿床硫同位素组成数值的差异,探讨了硫的来源及其变化原因。
1. 区域地质背景
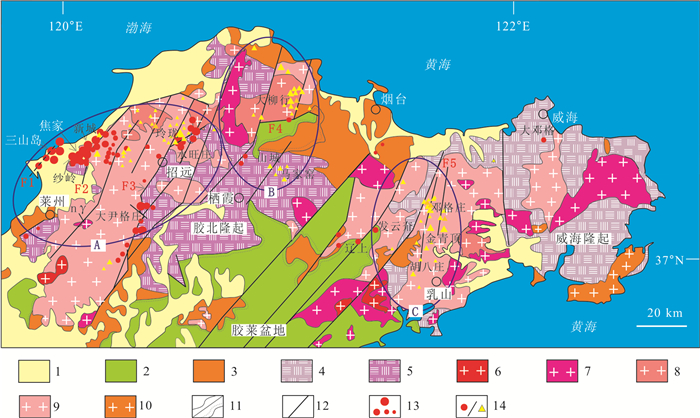
胶东地区的大地构造位置处于华北克拉通东南缘和大别-苏鲁造山带北东端,主要由胶北地体和苏鲁地体组成。胶北地体主要由胶北隆起和胶莱盆地构成,苏鲁地体在该区称为威海隆起[20]。胶北隆起主要由前寒武纪基底变质岩系和中生代花岗质侵入岩组成[21-23]。前寒武纪基底变质岩系主要为太古宙花岗绿岩带和古—新元古代变质地层;中生代花岗质侵入岩主要包括侏罗纪—白垩纪的玲珑、郭家岭、栾家河、昆嵛山、艾山、伟德山等岩体。胶东地区断裂构造发育,金矿床主要受NNE—NE向断裂带控制,主要成矿断裂带包括三山岛、焦家、招平、牟乳断裂等。按照矿床分布的空间特点,胶东地区的金矿床被划分为胶西北、栖蓬福、牟乳等金成矿区[1](图 1)。胶莱盆地为晚中生代形成的陆相盆地,由下白垩统莱阳群和上白垩统青山群、王氏群3套沉积序列组成:下部莱阳群为一套绿色、杂色河湖相碎屑岩系,中部青山群为一套陆相基性—中酸性火山沉积岩系,上部王氏群为一套红色河湖相碎屑岩系[24]。
![]() 图 1 胶东地区区域地质及金矿床分布图(据参考文献[1]修改)1—第四系; 2—白垩系; 3—元古宇; 4—新元古代含榴辉岩的花岗质片麻岩; 5—新太古代胶东变质杂岩; 6—白垩纪崂山型花岗岩; 7—白垩纪伟德山型花岗岩; 8—白垩纪郭家岭型花岗岩; 9—侏罗纪玲珑型花岗岩; 10—三叠纪花岗岩类; 11—整合/不整合地质界线; 12—断层; 13—特大/大/中/小型金矿床; 14—蚀变岩型/石英脉型金矿床; A—胶西北成矿区; B—栖蓬福成矿区; C—牟乳成矿区(包括胶莱盆地东北缘); F1—三山岛断裂; F2—焦家断裂; F3—招平断裂; F4—西林-陡崖断裂; F5—金牛山断裂Figure 1. Regional geological sketch map and distribution of gold deposits in Jiaodong area
图 1 胶东地区区域地质及金矿床分布图(据参考文献[1]修改)1—第四系; 2—白垩系; 3—元古宇; 4—新元古代含榴辉岩的花岗质片麻岩; 5—新太古代胶东变质杂岩; 6—白垩纪崂山型花岗岩; 7—白垩纪伟德山型花岗岩; 8—白垩纪郭家岭型花岗岩; 9—侏罗纪玲珑型花岗岩; 10—三叠纪花岗岩类; 11—整合/不整合地质界线; 12—断层; 13—特大/大/中/小型金矿床; 14—蚀变岩型/石英脉型金矿床; A—胶西北成矿区; B—栖蓬福成矿区; C—牟乳成矿区(包括胶莱盆地东北缘); F1—三山岛断裂; F2—焦家断裂; F3—招平断裂; F4—西林-陡崖断裂; F5—金牛山断裂Figure 1. Regional geological sketch map and distribution of gold deposits in Jiaodong area胶东金矿的工业类型主要包括破碎带蚀变岩型(焦家式)和石英脉型(玲珑式)2类,二者累计资源储量占胶东金资源总量的94%[25]。另外,还有二者的过渡类型(破碎带石英网脉型、硫化物石英脉型),以及少量层间滑动带型、蚀变砾岩型、盆缘断裂角砾岩型、黄铁矿碳酸盐脉型等金矿化类型[25-29]。
破碎带蚀变岩型(焦家式)金矿床受规模较大的区域性断裂构造控制,主矿体一般产于主断裂面下盘,矿化连续稳定,矿体规模大、形态较简单,围岩蚀变主要发育黄铁绢英岩化、硅化、钾化等。该类型金矿床的矿石自然类型主要有浸染状黄铁绢英岩化碎裂岩型、细脉浸染状黄铁绢英岩化花岗质碎裂岩型和细脉浸染状黄铁绢英岩化花岗岩型。
石英脉型(玲珑式)金矿床受主干断裂伴生、派生的低级别、低序次陡倾角断裂控制。矿床由单条或多条石英脉组成,矿体形态较复杂,往往成群成带发育,单个矿体规模一般较小,Au品位较高。围岩蚀变以黄铁绢英岩化为主。
硫化物石英脉型(邓格庄式)金矿床受陡倾的张性断裂构造控制,矿体以含金硫化物石英脉单脉为主,部分矿区可出现石英脉群,矿体规模往往不大,多为陡倾斜脉状(倾角60°~85°),矿石Au品位较高。围岩蚀变主要有黄铁矿化、绢云母化、硅化、绢英岩化。该类型金矿石区别于石英脉型金矿石的最主要特征是富含黄铁矿(含硫一般大于等于8%)。
胶东金矿床中的金主要呈自然金矿物(如银金矿、金银矿等)独立产出于载金矿物(如黄铁矿、石英等)的裂隙、晶隙或包裹于其中。对焦家金矿带2690粒金颗粒的统计结果显示,金矿物赋存状态有裂隙金、晶隙金及包体金3种,矿床浅部以裂隙金(51.30%)和晶隙金(41.12%)为主,而深部以晶隙金(65.78%)和包体金(21.11%)为主。
2. 典型矿床地质特征
2.1 焦家深部金矿床
焦家深部金矿床受焦家主干断裂控制,断裂上盘主要为新太古代变质岩系,下盘主要为侏罗纪玲珑花岗岩,且玲珑花岗岩中发育较多脉岩,主要有伟晶岩、细晶岩、石英闪长玢岩、闪长玢岩、辉绿玢岩和煌斑岩脉。焦家断裂在该段总体走向为23°左右,倾向NW,倾角22°~40°。断裂沿走向及倾向均呈舒缓波状展布,膨胀夹缩、分支复合特征较明显。蚀变带宽18~124 m不等,发育连续的主裂面,矿化蚀变发育,且具有明显的分带性。共圈定4个矿体群,包括99个矿体,其中Ⅰ号矿体规模最大,资源量约占总储量的90%,矿体走向长580~1160 m,斜深790~2470 m,最大控制垂深1120 m,呈似层状、大脉状产出,具分支复合等特点,走向约30°,倾向NW,倾角16°~30°,厚度1~38 m,Au品位1.01×10-6~11.97×10-6[15]。
2.2 水旺庄金矿床
水旺庄金矿床位于招平断裂带北段,矿床浅部为新太古代TTG岩系,深部为侏罗纪玲珑花岗岩,矿体主要赋存于主裂面下的黄铁绢英岩化碎裂岩带和黄铁绢英岩化花岗质碎裂岩带中。浅部矿体受控于破头青断裂,深部矿体受控于九曲蒋家断裂[30-31]。破头青断裂地表宽350~450 m,局部地段宽达800 m。总体走向60°,倾向SE,倾角28°~45°。共圈出70个金矿体和101个金矿化体,其中2号矿体和53号矿体是最重要的金矿体,分别占深部资源量的85.11%和13.34%,矿体走向长80~2560 m、斜深80~2080 m,呈大脉状、透镜状产出,倾向100°~150°,倾角16°~32°,平均厚度1.20~10.41 m,Au平均品位4.13×10-6[16, 32]。
2.3 乳山金矿床
乳山金矿床位于牟乳成矿带中段,是牟乳成矿带中规模最大的金矿。矿体主要产于昆嵛山二长花岗岩中,矿区可见少量荆山群变质岩呈椭球状残留体零星出露,发育煌斑岩、花岗伟晶岩脉等。共圈出16个金矿体,其中Ⅱ号矿体为主矿体,其资源量占矿床总量的90%以上。Ⅱ号矿体呈较规则的脉状产出,沿走向和倾向均呈舒缓波状,脉体厚度几厘米至数米,受NNE—NE向将军石-曲河庄断裂控制,赋矿标高120~1220 m,总体走向5°~30°,倾向SE,倾角65°~90°。矿体与煌斑岩脉有较密切的空间关系,常被煌斑岩脉穿切或穿切煌斑岩脉[33]。
2.4 辽上金矿床
辽上金矿床位于胶莱盆地东北缘地区,发育于郭城断裂下盘。矿体受NE向断裂构造控制,发育于古元古代荆山群与晚侏罗世二长花岗岩接触带附近,主要赋矿围岩为荆山群大理岩、变粒岩等,晚侏罗世花岗岩中发育大量煌斑岩脉。共圈定7条矿化蚀变带、56个金矿体,其中Ⅲ-9号矿体占矿床资源总量的50.7%。矿体总体走向37°左右,倾向SE,倾角5°~55°,走向长80~550 m,斜深42~271 m,多呈透镜状、似层状、脉状、楔状、马鞍状等产出,具分支复合现象,厚度1.36~42.93 m,Au品位1.36×10-6~ 22.68×10-6[34]。
3. 硫同位素组成及变化
近年,随着金矿研究的不断深入和测试技术的进步,前人试图对矿体成矿过程进行精细刻画,大量的同位素分析手段被用于成矿过程的研究,特别是对黄铁矿微区原位硫同位素组成进行了大量研究[35-42]。本文统计了胶东地区29个代表性金矿床的856个硫同位素组成数据(表 1,其中395个数据由LA-MC-ICPMS原位微区硫同位素分析方法测得,461个数据为传统的硫化物单矿物溶样法测得)及各类围岩的82个硫同位素组成数据(表 2,溶样法)。
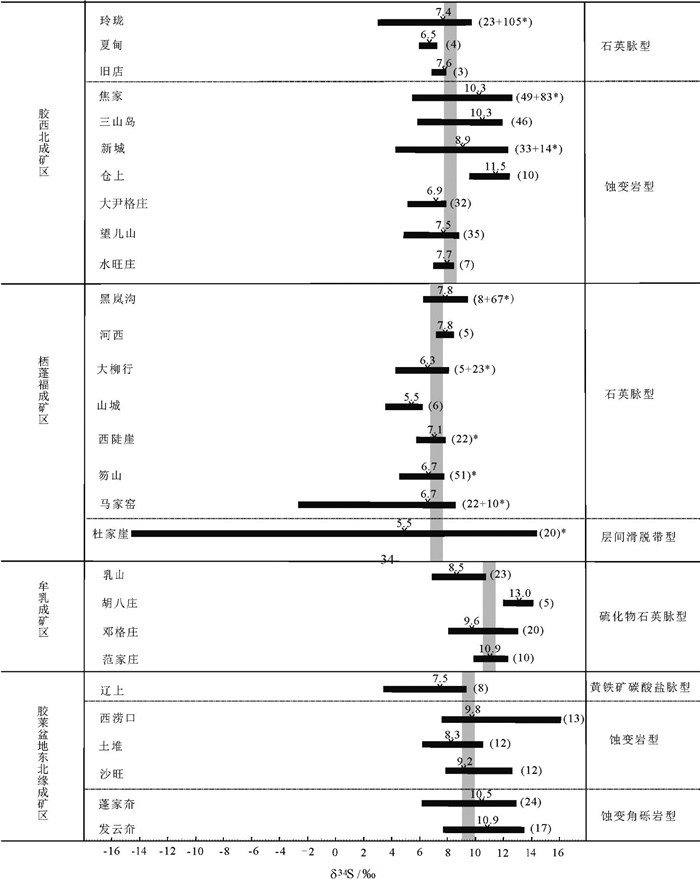
表 1 胶东典型金矿床硫同位素组成Table 1. Sulfur isotopic compositions of typical gold deposits in Jiaodong area成矿区 矿床 矿床类型 δ34S值/‰ 范围/‰ 平均值/‰ 样品数/件 参考文献 胶西北 玲珑 石英脉型 7.8, 7.0, 8.3, 7.8, 7.9, 7.7, 8.3, 7.6, 8.5, 7.5, 7.0, 8.6, 7.2, 6.4, 7.3, 7.4;3.3, 2.9, 3.4, 4.3, 4.5, 4.4, 5.7;(8.3, 7.8, 7.9, 7.4, 7.4, 6.2, 6.3, 6.5, 6.3, 6.1, 8.5, 7.0, 6.3, 6.9, 7.2, 6.4, 6.4, 6.9, 7.2, 4.9, 6.8, 5.3, 7.1, 6.1, 7.9, 6.6, 6.8, 5.8, 5.9, 8.1, 7.3, 6.0, 5.9, 6.4, 6.9;7.7, 8.0, 8.3, 8.1, 8.4, 8.9, 8.6, 7.6, 8.1, 8.5, 9.4, 8.8, 8.1, 7.9, 8.2, 8.4, 8.0, 7.2, 9.4, 8.4, 8.5, 8.0, 8.5, 7.9, 7.4, 7.0, 7.6, 6.7, 7.1, 6.5, 6.3, 9.4, 9.8, 8.8, 8.6, 9.3, 9.5, 8.1, 8.2, 8.6, 8.6, 8.2, 8.4, 8.6, 8.5, 8.2, 9.1, 8.1, 8.3, 8.5, 8.8, 9.2, 7.0, 8.1, 8.2, 9.1, 8.3, 8.2, 8.8, 9.2, 9.6, 8.5, 8.1, 8.0, 8.4, 8.6, 8.9, 5.9, 4.2, 4.0)* 2.9~9.8 7.4 23+105* [43-44, 45*-46*] 夏甸 6.5, 7.3, 6.0, 6.5 6.0~7.3 6.5 4 [47] 旧店 7.9, 6.9, 8.0 6.9~8.0 7.6 3 本文 焦家 蚀变岩型 11.0, 10.5, 9.5, 10.2, 8.6, 9.5, 11.3, 8.8;11.4, 11.5, 11.3, 10.1;11.2, 11.0, 11.1, 10.8, 11.5, 10.9, 11.3, 10.8, 10.9, 10.6, 11.01;8.3, 9.7, 8.4, 8.8, 7.9, 7.0, 6.5, 7.1, 8.6;11.1, 12.6, 11.5, 11.1, 11.2, 11.4, 11.4, 11.2;7.5, 7.8, 8.0, 9.3, 7.8, 9.3, 8.9, 9.7, 9.8;(10.4, 10.2, 11.2, 11.2, 10.4, 9.8, 10.0, 10.6, 9.5, 10.6, 11.1, 11.4, 11.0, 10.1, 11.0, 11.4, 10.9, 10.3, 10.9, 10.1, 11.9, 11.0, 11.5, 10.1, 12.2, 11.4, 9.1, 12.5, 9.6, 11.2, 11.2, 10.5, 11.0, 8.8, 10.3, 11.2, 10.8, 11.2, 11.3, 10.3, 10.8, 11.9, 11.6, 10.2, 9.7, 9.7, 9.8, 9.9, 9.4, 11.0, 10.3, 11.1, 11.6, 10.7, 10.9, 11.8, 10.9, 11.6, 10.2, 10.2, 9.6, 10.8, 10.8, 10.6, 6.3, 5.5, 7.6, 8.3;10.7, 11.7, 11.3, 8.5, 8.7, 10.6, 12.7, 8.8, 11.0, 10.3, 11.8, 12.7, 10.5, 11.2, 12.1)* 5.5~12.7 10.3 49+83* [15, 48-52, 53*-54*] 三山岛 10.9, 10.9, 11.5, 11.5, 11.2, 10.9, 5.8, 8.7, 10.9, 10.9;11.5, 11.1, 11.8, 11.1, 11.0, 10.7, 9.7, 7.8;12.0, 12.0, 11.7, 11.9, 11.5;8.5, 8.4, 9.3, 9.2, 8.0, 10.5, 10.4;9.7, 11.7, 11.6, 11.8, 7.7;10.6, 10.2, 8.6, 11.9, 11.4, 9.5, 9.3, 10.2, 9.4, 9.4, 11.4 5.8~12.0 10.3 46 [49, 55-59] 新城 9.8, 9.2, 9.9, 9.5, 10.5, 10.6, 10.5, 8.4, 9.9, 8.8, 8.5, 8.3, 8.9, 9.1, 9.4, 8.7, 9.7, 7.7, 8.3, 8.2, 7.6, 8.0, 5.7, 7.0, 6.7, 7.5, 6.9, 7.9, 8.1, 7.7, 5.8, 4.3, 5.7;(11.0, 10.7, 9.7, 12.4, 8.9, 12.2, 10.9, 8.7, 11.4, 10.8, 8.3, 11.3, 8.7, 10.9)* 4.3~12.4 8.9 33+14* [54*, 60] 仓上 12.0, 11.1, 9.6, 10.5;11.7, 12.4, 11.3, 12.5, 11.7, 12.2 9.6~12.5 11.5 10 [49, 61] 大尹格庄 7.2, 7.2, 7.5, 7.4, 7.5, 7.3, 7.2, 7.3, 6.8, 6.9, 7.1, 6.8, 6.6, 6.8, 6.9, 5.0, 4.6, 4.6, 7.0, 7.2, 7.3, 5.5, 5.9, 7.4, 6.8;7.9, 7.5, 7.5, 7.2, 7.8, 6.8, 7.6 4.6~7.9 6.9 32 [49, 62] 望儿山 7.1, 8.7, 7.8, 6.3, 8.2, 7.6, 7.2, 7.4, 7.2, 6.3, 6.8, 8.6, 4.8, 6.7, 7.4, 7.0, 8.1, 6.6, 6.6, 7.5, 8.3, 8.9, 8.4, 6.4, 7.0, 6.6, 6.6, 7.8, 7.5, 7.3;8.7, 8.9, 8.5, 8.7, 8.5 4.8~8.9 7.5 35 [49, 63] 水旺庄 7.5, 8.0, 7.5, 8.1, 7.0, 8.5, 7.4 7.0~8.5 7.7 7 [16] 栖蓬福 石英脉型 黑岚沟 7.2, 6.8, 6.7, 6.9, 9.5, 8.0, 8.4, 6.3;(6.8, 6.6, 6.9, 7.1, 7.1, 7.0, 7.0, 7.2, 7.0, 7.0, 7.1, 7.2, 7.9, 7.2, 7.2, 7.5, 7.7, 7.6;7.7, 7.8, 7.5, 7.7, 7.4, 7.7, 7.6, 7.7, 7.3, 7.7, 7.1, 6.9, 7.6, 7.8, 7.7, 7.7, 7.2, 7.1, 7.4;8.5, 8.4, 8.3, 8.3, 8.5, 8.5, 8.4, 8.3, 8.4, 8.3, 8.3, 8.6, 8.8, 8.4, 8.6, 8.3, 8.1, 8.4, 8.4, 8.2, 8.2, 8.3, 8.7, 8.2, 8.7, 8.4, 8.5, 8.3, 8.4, 8.5)* 6.3~9.5 7.8 8+67* [40*, 43] 河西 7.6, 7.4, 7.5, 8.0, 8.5 7.4~8.5 7.8 5 [43] 大柳行 8.2, 6.4, 6.8, 6.8, 8.2;(4.3, 4.8, 4.9, 4.9, 5.0, 5.1, 5.1, 5.8, 5.9, 6.1, 6.4, 6.5, 6.5, 6.6, 6.6, 6.8, 6.8, 6.8, 6.8, 6.8, 7.0, 7.1, 7.2)* 4.3~8.2 6.3 5+23* [41*, 43] 山城 3.7, 5.5, 6.2, 6.4, 6.0, 5.1 3.7~6.4 5.5 6 [64] 西陡崖 5.8, 5.9, 6.0, 6.2, 6.2, 6.6, 6.9, 6.9, 6.9, 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 7.3, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6, 7.7, 7.7, 7.7, 7.8, 7.9 5.8~7.9 7.0 22* [41*] 笏山 7.1, 7.1, 7.2, 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.6, 7.7, 7.8, 7.9;5.7, 5.8, 6.0, 6.1, 6.1, 6.2, 6.2, 6.3, 6.3, 6.3, 6.3, 6.3, 6.4, 6.4, 6.4, 6.4, 6.4, 6.4, 6.5, 6.5, 6.5, 6.5, 6.5, 6.6, 6.6, 6.6, 6.6, 6.6, 6.6, 6.6, 6.7, 6.7, 6.7, 6.7, 6.7, 6.7, 6.7, 6.8, 6.8, 6.9, 7.0 5.7~7.9 6.7 51* [39] 马家窑 8.7, 8.8, 8.4, 8.4, 7.8, 7.7, 7.3, 7.4, 6.5, 7.0, 5.4, 7.9, 5.8, 7.4, 7.7, 7.7, 7.6, 5.5, 4.3, 5.3, 7.8, 7.9;(6.9, 7.6, 7.9, 8.6, 5.6, 5.3, 5.5, 5.5, -2.5, 4.4)* -2.5~8.8 6.6 22+10* [41*, 64] 杜家崖 层间滑脱带型 5.6, 7.1, 5.8, 4.5, 5.5, 9.2, -14.0, -3.8, 8.2, 7.7, -6.8, 5.5, 7.9, 7.4, 15.1, 10.4, 8.6, 7.3, 9.5, 8.8 -14.0~15.1 5.5 20* [65] 牟乳 乳山 硫化物石英脉型 7.2, 7.9, 10.6, 8.0, 10.7, 9.7, 8.3, 8.8, 9.6;9.7, 9.8, 6.8, 9.4, 7.6, 8.2;7.0, 8.7, 8.3, 7.4, 8.3, 8.5, 7.9, 8.3 6.8~10.7 8.5 23 [5, 66-67] 胡八庄 13.5, 11.9, 14.1, 12.6, 12.8 11.9~14.1 13.0 5 [68] 邓格庄 8.6, 10.4, 8.0, 8.4, 8.6;9.3, 9.0, 9.6, 9.3, 9.3, 8.8;10.1, 8.4, 10.0, 10.4, 10.8, 10.0, 10.4, 13.0, 9.0 8.0~13.0 9.6 20 [5, 49, 69] 范家庄 10.9, 11.4, 10.3, 12.3, 10.9, 10.7, 11.2, 9.8, 10.8, 10.4 9.8~12.3 10.9 10 [70] 胶莱盆地东北缘 辽上 黄铁碳酸盐脉型 3.4, 7.4, 8.0, 9.4, 8.4, 7.7, 9.1, 7.3 3.4~9.4 7.5 8 [71] 西涝口 蚀变岩型 7.8, 7.6, 8.8, 8.7, 8.6, 9.0, 8.9, 9.4, 9.5, 9.5, 16.2, 15.4, 7.6 7.6~16.2 9.8 12 [72] 土堆 9.7, 10.5, 8.5, 9.1;8.0, 8.2, 6.2, 7.0, 8.0, 7.5;8.2, 8.0 6.2~10.6 8.3 12 [72-74] 沙旺 9.1, 10.8, 10.0, 12.7;8.2, 9.6, 7.9, 8.5, 8.4;7.2, 8.0, 10.3 7.9~12.7 9.2 12 蓬家夼 蚀变角砾岩型 10.9, 11.5, 11.2;9.7, 10.4, 10.3, 10.7, 11.3;13.0, 12.7, 11.6, 10.6, 10.9;10.5, 11.3, 9.9, 11.0, 11.2, 10.8, 10.7, 10.8;6.2, 7.5, 8.3 6.2~13.0 10.5 24 [49, 75-78] 发云夼 蚀变砾岩型 10.7, 11.1, 10.9, 11.1, 10.9;12.6, 13.0, 13.6, 12.9, 12.8, 10.4, 10.4, 10.4, 10.1;8.6, 7.7, 8.7 8.6~13.6 10.9 17 [49, 79-80] 注:*数据为LA-MC-ICPMS原位微区硫同位素分析方法获得 表 2 胶东金矿主要赋矿围岩硫同位素组成Table 2. Sulfur isotopic compositions of surrounding rock of gold deposits in Jiaodong area地层/岩石 δ34S /‰ 变化范围/‰ 平均值/‰ 样品数/件 参考文献 胶东岩群 1.0, 1.5, 1.1, 1.7, 1.3, 1.0;5.6, 8.2, 10.8, 12.4, 15.4;6.9, 9.4, 7.8;1.8, 2.1;6.1, 7.8, 7.5, 7.0, 7.4, 7.3, 2.2, 1.2, 0.0, 1.7;7.8, 7.5, 7.0, 7.4, 7.3, 6.1, 2.2, 1.2, 0.0, 1.7 0.0~15.4 5.0 36 [41, 45, 60-61, 81-82] 荆山群 10.7, 9.9, 9.8, 9.3, 9.8, 9.8, 10.0, 8.2, 12.0 8.2~12.0 9.9 9 [76] 粉子山群 11.3, 13.0, 10.6, 11.4, 13.0, 12.0, 13.6 10.6~13.6 12.1 7 [45] TTG岩系 2.4, 2.3, 2.8, 3.0, 1.0, 1.6 1.0~3.0 2.2 6 [45] 昆嵛山花岗岩 15.3, 3.8;14.9, 8.5, 3.9 3.8~15.3 9.3 5 [83-84] 郭家岭花岗岩 6.0, 7.2, 7.8, 6.4, 9.2, 16.0, 7.4 6.0~16.0 8.6 7 [60] 玲珑花岗岩 7.9, 8.2, 8.3, 8.4, 8.2, 8.0 7.9~8.4 8.1 6 [49] 中基性脉岩 5.3~10.8 6.9 6 [61] 3.1 不同区域金矿床的硫同位素组成及变化
3.1.1 硫同位素组成
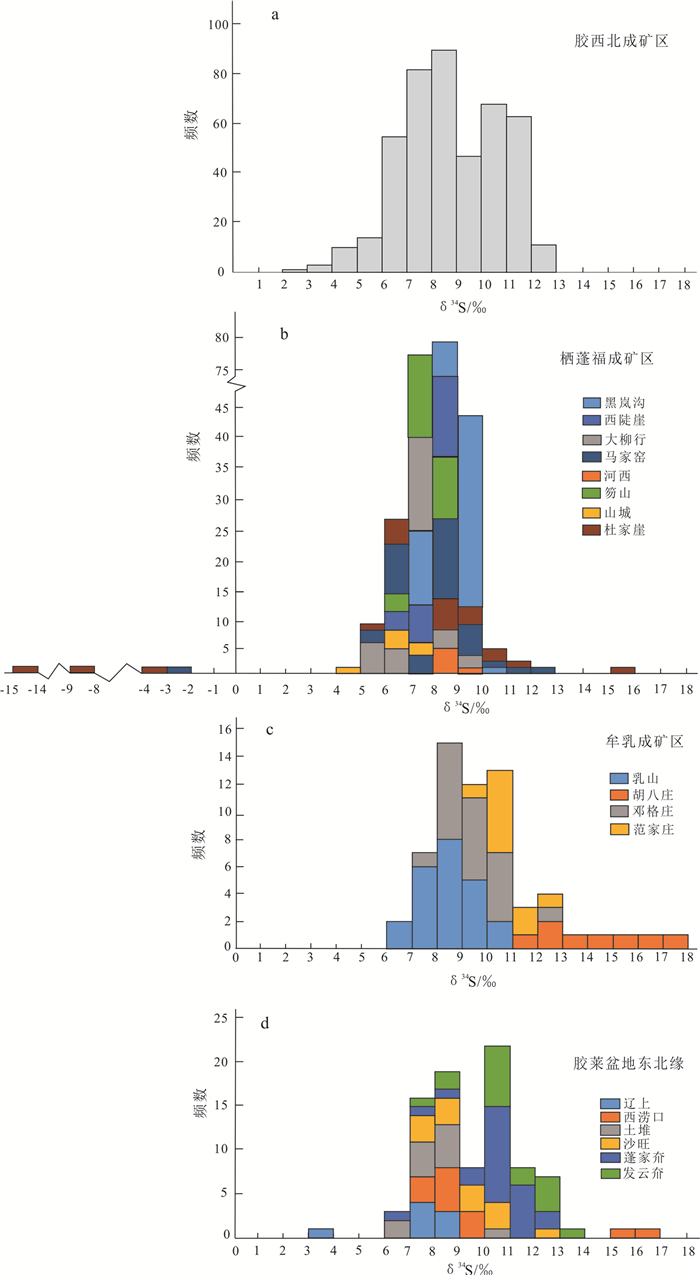
综合胶东29个典型金矿床的硫同位素组成数据可以看出,金矿床的δ34S值变化范围较大,为-14.0‰~15.1‰,除个别样品外,绝大部分正向偏离陨石硫,各矿床的δ34S平均值为5.5‰~13.0‰。根据金矿床分布特点和成矿地质条件差异,按照胶西北、栖蓬福、牟乳和胶莱盆地东北缘4个成矿区分别统计分析硫同位素组成特征。
胶西北成矿区是胶东最重要的金成矿区,绝大部分超大型、大型金矿床集中发育在该区的三山岛、焦家和招平断裂带中,矿化类型以破碎带蚀变岩型和石英脉型为主。统计发现,该区444件样品的δ34S值在4.3‰~12.7‰之间,主要集中在6.0‰~10.0‰之间,呈现出富集34S的特征(图 2-a)。其中,位于胶西北成矿区西部三山岛断裂带中的三山岛和仓上金矿床的δ34S值较高,位于中部焦家断裂带上的焦家、新城、马塘等金矿床次之,位于东部招平断裂带中的玲珑、水旺庄、大尹格庄、夏甸、旧店等金矿床的δ34S值较低,呈现出自西向东δ34S值渐趋降低的变化趋势。
栖蓬福成矿区的金矿床以石英脉型矿床为主,239件样品的δ34S值在-14.0‰~15.1‰之间,平均值在5.5‰~8.5‰之间(表 1;图 2-b),除马家窑和杜家崖金矿床的4件样品中出现δ34S负值外,其他测试数值均为正值。其中,杜家崖金矿床的δ34S值介于-14.0‰~15.1‰之间,是胶东地区变化范围最大的金矿床;山城和杜家崖金矿床的δ34S平均值均为5.5‰,是胶东δ34S值最低的金矿床。相比而言,分布于栖蓬福成矿区西北部的蓬莱黑岚沟、河西和大柳行金矿床的δ34S值略高,而东南部的栖霞山城、西陡崖、笏山、马家窑、杜家崖金矿床的δ34S值偏低,区域上呈现出由北西向南东降低的趋势。
牟乳成矿区的金矿床以硫化物石英脉型为主,δ34S值在6.8‰~14.1‰之间,平均值在8.5‰~13.0‰之间(表 1;图 2-c),其中胡八庄金矿床的δ34S值(11.9‰~14.1‰,平均值为13.0‰)是胶东金矿硫同位素组成最高的。
胶莱盆地东北缘的金矿床类型以蚀变岩型(包括蚀变砾岩)为主,有少量黄铁矿碳酸盐脉型(辽上金矿床)、盆缘断裂角砾岩型(蓬家夼金矿床)等特殊矿化类型。该区金矿床的δ34S值在3.4‰~16.2‰之间,平均值在7.5‰~10.9‰之间(表 1;图 2-d)。相比而言,赋存于胶莱盆地中的发云夼金矿床δ34S值最高,而辽上金矿床的δ34S值偏低。
3.1.2 硫同位素组成的区域变化
对上述不同成矿区各矿床的硫同位素组成对比发现,牟乳成矿区金矿床的δ34S值较高,δ34S值最高的胡八庄金矿床位于该区;栖蓬福成矿区金矿床的δ34S值较低,胶东地区3个δ34S值最低的金矿床均位于该成矿区;胶莱盆地东北缘金矿床的δ34S值高于胶西北及栖蓬福成矿区金矿床,而略低于牟乳成矿区金矿床。即δ34S值由牟乳成矿区→胶莱盆地东北缘→胶西北成矿区→栖蓬福成矿区渐趋降低(图 3)。根据各成矿区所处的大地构造位置分析,苏鲁超高压变质带边缘的金矿床δ34S值较高,胶莱盆地边缘次之,胶北隆起的金矿床δ34S值较低。在胶北隆起中,隆起区中部早前寒武纪变质岩系出露区(栖霞地区)的金矿床δ34S值最低。
3.2 不同成矿深度硫同位素组成及变化
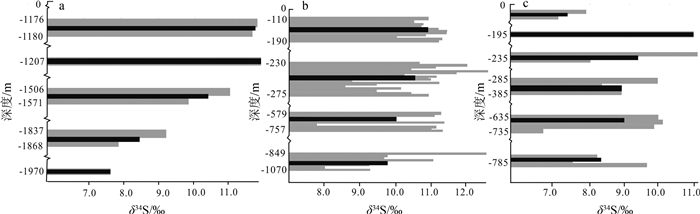
通过焦家、纱岭和乳山金矿床的硫同位素组成分析发现,各金矿床的浅部矿体δ34S值较高,而深部矿体较低,即由浅到深,矿床的δ34S值呈现减小的趋势(表 3;图 4)。其中焦家金矿床-110~-275 m深度29件样品的δ34S值为8.6‰~12.7‰,平均值为10.8‰[48-50, 54];-579~-757 m深度9件样品的δ34S值为7.5‰~11.5‰,平均值为10.1‰[15, 52];-849~-1070 m深度8件样品的δ34S值为8.0‰~12.6‰,平均值为9.8‰[15, 52]。纱岭金矿床-1100~-1600 m深度5件样品的δ34S值为9.8‰~11.8‰,平均值为11.2‰;-1800~-2000 m深度3件样品的δ34S值为7.7‰~9.2‰,平均值为8.3‰,深部的平均值较浅部的小2.9‰[17]。乳山金矿床0~-385 m深度8件样品的δ34S值为7.2‰~10.7‰,平均值为8.9‰;-635~-700 m深度7件样品的δ34S值为6.8‰~9.8‰,平均值为8.7‰[5, 66]。
表 3 胶东典型金矿床深部和浅部硫同位素组成Table 3. Sulfur isotopic composition in different depths of typical gold deposits in Jiaodong area矿床 深度/m 矿床类型 δ34S值/‰ 变化范围/‰ 平均值/‰ 样品数/件 参考文献 焦家 -110~-275 蚀变岩型 11.4, 11.5, 11.3, 10.1;11.0, 10.5, 9.5, 10.2, 8.6, 9.5, 11.3, , 8.8;10.8, 10.9, 10.6, 11.0, 11.3, 10.9, 11.5, 10.8, 11.1, 11.0, 11.2;(10.3, 11.8, 12.7, 10.5, 11.2, 12.1)* 8.6~12.7 10.8 23+6* [48-50, 54*] 焦家 -579~-757 11.4, 11.2, 7.5 7.8, 11.5, 7.8, 11.2, 11.1, 11.4 7.5~11.5 10.1 9 [15, 52] 焦家 -849~-1070 9.3, 8.0, 9.3, 8.9, 11.1, 9.7, 9.8, 12.6 8.0~12.6 9.8 8 纱岭 -1100~-1600 11.7, 11.6, 11.8, 10.9, 9.8 9.8~11.8 11.2 5 [15, 52] 纱岭 -1800~-2000 9.2, 7.9, 7.7 7.7~9.23 8.2 3 [17] 乳山 0~-385 硫化物石英脉型 7.2, 7.9, 10.6, 8.0, 10.7, 9.7, 8.3, 8.8, 7.2~10.7 8.9 8 [5, 66] 乳山 -635~-700 9.7, 9.8, 6.8, 9.4, 7.6, 8.2, 9.6 6.8~9.8 8.7 7 注:*数据为LA-MC-ICPMS原位微区硫同位素分析方法获得 前人研究表明,胶东各矿床的成矿深度有差异,如大尹格庄和夏甸金矿床的成矿深度较大,分别为9.2~14.0 km[85]和8.8~12.6 km[86],玲珑金矿床的成矿深度略小,为5.4~9.0 km[87],辽上金矿床的成矿深度最小,为2.97~3.24 km[88]。各矿床δ34S平均值为:夏甸6.5‰、大尹格庄6.9‰、玲珑7.4‰、辽上7.5‰(表 1)。比较而言,成矿深度较大的金矿床δ34S值较小,随着成矿深度变浅,δ34S趋于增大。
3.3 不同类型金矿床硫同位素组成及变化
胶东金矿的主要工业类型为破碎带蚀变岩型(焦家式)和石英脉型(玲珑式),另外,还有二者的过渡类型(破碎带石英网脉型、硫化物石英脉型),以及少量的其他矿化类型(层间滑动带型、蚀变砾岩型、盆缘断裂角砾岩型、黄铁矿碳酸盐脉型等)[25, 28]。蚀变岩型金矿主要分布于胶西北的三山岛、焦家和招平3条成矿断裂带中,典型的蚀变岩型金矿床(如仓上、三山岛、新城、马塘、焦家、夏甸、大尹格庄、水旺庄等)的δ34S平均值为6.5‰~11.1‰,δ34S值最小的是夏甸金矿床,最大的为大尹格庄金矿床。石英脉型金矿主要分布于胶西北和栖蓬福成矿区,其中胶西北成矿区玲珑金矿床的δ34S值为2.9‰~9.8‰,望儿山金矿床的δ34S值为4.8‰~8.9‰,旧店金矿床的δ34S值为6.9‰~8.0‰;栖蓬福成矿区黑岚沟金矿床的δ34S值为6.3‰~9.5‰,栖霞山城、西陡崖和马家窑金矿床的δ34S值为-2.5‰~ 8.8‰,石英脉型金矿的δ34S平均值为5.5‰~7.8‰,黑岚沟金矿的δ34S值较大,山城和杜家崖金矿床的δ34S平均值最低。硫化物石英脉型金矿分布于牟乳成矿区,δ34S平均值为8.5‰~13.0‰,乳山金矿床的δ34S值较低,胡八庄金矿床的最高。黄铁矿碳酸岩脉型金矿的δ34S值在3.4‰~9.4‰之间,平均值为7.5‰。蚀变砾岩型金矿的δ34S值在6.2‰~13.6‰之间,平均值为10.5‰~10.9‰。层间滑脱带型金矿δ34S值在-14.0‰~15.1‰之间,变化范围大。相比而言,硫化物石英脉型和蚀变砾岩型金矿的δ34S值较高,其次为蚀变岩型,石英脉型最低(图 3),即硫化物石英脉型和蚀变砾岩型>蚀变岩型>石英脉型。
3.4 不同硫化物硫同位素组成
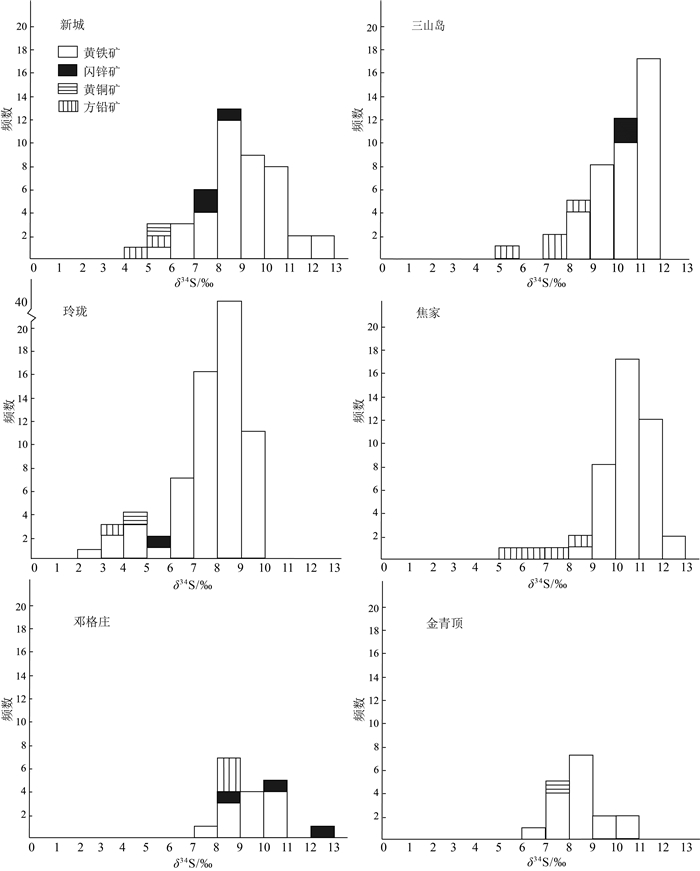
6个金矿床的不同金属硫化物的硫同位素组成数据(表 4)显示,主要硫化物的δ34S值分别为:黄铁矿2.9‰~12.6‰、闪锌矿5.9‰~13.0‰、黄铜矿4.2‰~7.9‰、方铅矿4.0‰~9.0‰,大致呈现出黄铁矿>闪锌矿>黄铜矿>方铅矿的变化趋势。就单个矿床而言,不同硫化物的δ34S值也总体呈现黄铁矿>闪锌矿>黄铜矿>方铅矿的变化趋势(图 5)。
表 4 不同硫化物硫同位素组成Table 4. Sulfur isotopic composition of different sulfide矿床 δ34S值/‰(变化范围) 参考文献 黄铁矿 闪锌矿 黄铜矿 方铅矿 焦家 11.0, 10.5, 9.5, 10.2, 8.6, 9.5, 11.3, 8.8;11.4, 11.5, 11.3, 10.1;11.2, 11.0, 11.1, 10.8, 11.5, 10.9, 11.3, 10.8, 10.9, 10.6, 11.01;8.3, 9.7, 8.4, 8.8, 7.9, 7.0, 6.5, 7.1, 8.6;11.1, 12.6, 11.5, 11.1, 11.2, 11.4, 11.4, 11.2;7.5, 7.8, 8.0, 9.3, 7.8, 9.3, 8.9, 9.7, 9.8;(10.4, 10.2, 11.2, 11.2, 10.4, 9.8, 10.0, 10.6, 9.5, 10.6, 11.1, 11.4, 11.0, 10.1, 11.0, 11.4, 10.9, 10.3, 10.9, 10.1, 11.9, 11.0, 11.5, 10.1, 12.2, 11.4, 9.1, 12.5, 9.6, 11.2, 11.2, 10.5, 11.0, 8.8, 10.3, 11.2, 10.8, 11.2, 11.3, 10.3, 10.8, 11.9, 11.6, 10.2, 9.7, 9.7, 9.8, 9.9, 9.4, 11.0, 10.3, 11.1, 11.6, 10.7, 10.9, 11.8, 10.9, 11.6, 10.2, 10.2, 9.6, 10.8, 10.8, 10.6;10.7, 11.7, 11.3, 8.5, 8.7, 10.6, 12.7, 8.8, 11.0, 10.3, 11.8, 12.7, 10.5, 11.2, 12.1)*(6.5~12.7) 6.3, 5.5, 7.6, 8.3
(5.5~8.3)[15, 48-52, 53*-54*] 三山岛 10.9, 10.9, 11.5, 11.5, 11.2, 10.9;11.5, 11.1, 11.8, 11.1, 11.0, 10.7, 9.7;12.0, 12.0, 11.7, 11.9, 11.5;8.5, 8.4, 9.3, 9.2, 8.0, 10.5, 10.4;9.7, 11.7, 11.6, 11.8;10.6, 10.2, 8.6, 11.9, 11.4, 9.5, 9.3, 10.2, 9.4, 9.4, 11.4(8.0~12.6) 10.9, 10.9 5.8, 8.7, 7.7, 7.8
(5.8~8.7)[49, 55-59] 玲珑 7.8, 7.0, 8.3, 7.8, 7.9, 7.7, 8.3, 7.6, 8.5, 7.5, 7.0, 8.6, 7.2, 6.4, 7.3, 7.4;3.3, 2.9, 3.4, 4.3, 4.5, 4.4, 5.7;(8.3, 7.8, 7.9, 7.4, 7.4, 6.2, 6.3, 6.5, 6.3, 6.1, 8.5, 7.0, 6.3, 6.9, 7.2, 6.4, 6.4, 6.9, 7.2, 4.9, 6.8, 5.3, 7.1, 6.1, 7.9, 6.6, 6.8, 5.8, 5.9, 8.1, 7.3, 6.0, 5.9, 6.4, 6.9;7.7, 8.0, 8.3, 8.1, 8.4, 8.9, 8.6, 7.6, 8.1, 8.5, 9.4, 8.8, 8.1, 7.9, 8.2, 8.4, 8.0, 7.2, 9.4, 8.4, 8.5, 8.0, 8.5, 7.9, 7.4, 7.0, 7.6, 6.7, 7.1, 6.5, 6.3, 9.4, 9.8, 8.8, 8.6, 9.3, 9.5, 8.1, 8.2, 8.6, 8.6, 8.2, 8.4, 8.6, 8.5, 8.2, 9.1, 8.1, 8.3, 8.5, 8.8, 9.2, 7.0, 8.1, 8.2, 9.1, 8.3, 8.2, 8.8, 9.2, 9.6, 8.5, 8.1, 8.0, 8.4, 8.6, 8.9)*(2.9~9.8) 5.9* 4.2* 4.0* [43, 44, 45*-46*] 新城 9.8, 9.2, 9.9, 9.5, 10.5, 10.6, 10.5, 8.4, 9.9, 8.8, 8.5, 8.3, 8.9, 9.1, 9.4, 8.7, 9.7, 7.7, 8.3, 8.2, 7.6, 8.0, 5.7, 7.0, 6.7, 7.5, 6.9;(11.0, 10.7, 9.7, 12.4, 8.9, 12.2, 10.9, 8.7, 11.4, 10.8, 8.3, 11.3, 8.7, 10.9)*(5.7~12.4) 7.9, 8.1, 7.7
(7.7~8.1)5.8 4.3, 5.7
(4.3~5.7)[54*, 60] 邓格庄 10.4, 8.0, 8.4;9.3, 9.0, 9.6, 9.3, 9.3, 8.8;10.1, 10.8, 10.8(8.0~10.8) 8.6, 10.4, 13.0
(8.6~13.0)8.6, 8.4, 9.0
(8.4~9.0)[5, 49, 69] 乳山 7.2, 10.6, 8.0, 10.7, 9.7, 8.3, 8.8, 9.6;7.0, 8.7, 8.3, 7.4, 8.3, 8.5, 7.9, 8.3;9.7, 9.8, 6.8, 9.4, 7.6, 8.2(7.0~10.6) 7.9 [5, 66-67] 注:*数据为LA-MC-ICPMS原位微区硫同位素分析方法获得 已有研究表明,从热液系统中结晶出的各种硫化物和硫酸盐的硫同位素组成主要取决于热液中总硫浓度和同位素组成、温度、pH值、氧逸度(fO2)、离子强度等[89]。在热力学平衡状态下,体系的硫同位素组成达到平衡时,各硫化物中34S富集的顺序为辉钼矿>黄铁矿>闪锌矿(磁黄铁矿)>黄铜矿>铜蓝>方铅矿>辰砂>辉铜矿(辉锑矿)>辉银矿。胶东金矿主要硫化物的34S含量变化趋势符合这一顺序,表明硫同位素在成矿体系中基本达到分馏平衡,硫化物的硫同位素组成代表了成矿流体中的硫同位素组成[90]。
4. 讨论
4.1 硫的来源
胶东地区已探明的金资源量大于5000 t,如此巨量金的来源一直是地质工作者研究的重点,许多研究者基于对硫同位素的研究探讨金矿床的成矿物质来源,然而对于硫的来源至今没有达成一致认识。前人分别提出,胶东金矿的硫来源于华北克拉通陆壳的早前寒武纪变质杂岩和晚中生代花岗岩类[6, 10]或富34S的岩浆岩[91-92]、扬子克拉通新元古代高硫沉积地层[13]、太平洋板块俯冲过程中的脱挥发分作用[14]或俯冲带高氧逸度的地幔脱气作用[4]、被陆壳混染了的幔源岩浆[15-17]等认识。
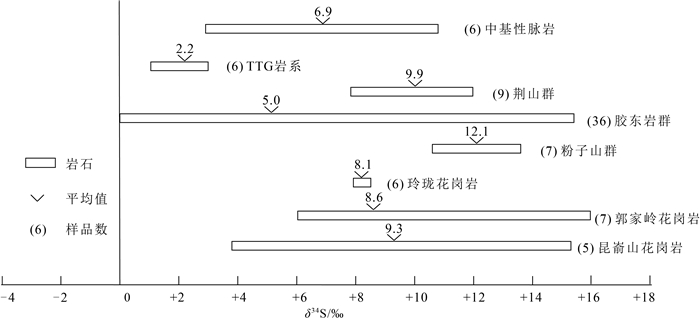
胶东金矿的主要赋矿围岩为晚中生代花岗岩类,其次为早前寒武纪变质岩系,矿床中常有较多的中基性脉岩。为了揭示金矿床中硫的来源,前人对金矿的主要赋矿围岩进行了硫同位素组成测试(表 4)。统计结果表明,新太古代TTG岩系的δ34S值最低且变化范围小,为1.0‰~3.0‰;新太古代胶东岩群的δ34S值变化范围大,为0~15.4‰,平均5.0‰;荆山群和粉子山群是δ34S值最高的围岩类型,为8.2‰~13.6‰;晚中生代花岗岩类的δ34S值仅次于荆山群和粉子山群,为3.8‰~16.0‰;中基性脉岩的δ34S值略低于晚中生代花岗岩,且变化范围小于后者,为5.3‰~10.8‰。赋矿围岩的δ34S值总体呈现荆山群和粉子山群>中生代花岗岩>中基性脉岩>胶东群>TTG岩系的特征(图 6)。
对比研究发现,金矿床与赋矿围岩的硫同位素组成有良好的对应关系,以荆山群为主要围岩的蓬家夼、西涝口等金矿床的δ34S值最高,赋存于晚中生代花岗岩围岩中的乳山、邓格庄、黑岚沟、旧店、玲珑等金矿床的δ34S值次之,以TTG岩系为主要赋矿围岩的马家窑、山城等金矿床的δ34S值最低(表 1)。这说明,金矿床的硫同位素组成与其赋矿围岩有关,成矿流体与赋矿围岩发生了充分的水-岩相互作用,围岩中的硫被活化并萃取到成矿流体中。
通过对比金矿床与赋矿围岩的硫同位素组成特征发现,二者的δ34S值非常接近,且绝大多数金矿床的δ34S值小于赋矿围岩,如胶西北的新城、牟乳的金青顶和胶莱盆地东北缘的辽上等金矿床的δ34S最低值分别为4.3‰、3.0‰和3.4‰,明显小于围岩的δ34S值,说明成矿过程中有较低δ34S值的组分参与。对不同矿化类型金矿床的硫同位素研究表明,石英脉型金矿的δ34S值最低,这是由于石英脉型金矿是大规模流体在扩容带快速充填成矿的,流体与围岩的相互作用时间较短,而蚀变岩型金矿是成矿流体沿裂隙较多的围岩缓慢渗流交代成矿的,成矿流体与围岩经历了充分的水-岩相互作用[2],即石英脉型金矿的δ34S值更接近于原始成矿流体系统的同位素组成。石英脉型金矿同样表现出在高δ34S值的围岩中矿床的δ34S值相应较高的特点,如以晚中生代花岗岩为主要围岩的玲珑和黑岚沟金矿床的δ34S值,明显高于以TTG岩系和胶东群为主要围岩的马家窑和山城金矿床,说明石英脉型金矿的硫同位素组成同样受到围岩的影响,成矿流体中有更低δ34S值的硫源参与。由于幔源岩浆的δ34S值一般较低,而且胶东中基性脉岩的δ34S值低于绝大部分金矿床,因此认为,金矿硫同位素组成中有幔源的成分,是来自地幔的原始岩浆流体在上侵过程中混染了大量地壳硫的混合硫。由于赋矿围岩主要是正向偏离陨石硫的晚中生代花岗岩类及新太古代TTG岩系。因此,金矿床的硫同位素组成以富34S为特征,个别富32S的金矿床与其混染了低δ34S值的胶东变质杂岩有关。
上述分析表明,胶东金矿的硫同位素组成中有幔源硫的存在,成矿物质中有幔源组分,这与前人根据胶东金矿床中其他同位素组成研究得出的认识一致。金矿床中碳酸盐矿物的碳同位素研究表明,其δ13C值与火成岩/岩浆系统和地幔碳储库的值非常接近[93],指示成矿流体中的碳源自岩浆系统或地幔。铅同位素组成值投点于下地壳与地幔演化线之间,且与赋矿围岩的铅具有较大范围的重叠,指示铅主要来源于地壳,可能混合有地幔物质[94-95]。矿石中黄铁矿流体包裹体氦-氩同位素特征显示,其具有壳幔混合来源特征,计算的成矿流体中地幔端元流体的比例主要在40%以下[15, 96-97]。
4.2 硫同位素变化的原因
胶东主要金矿床硫同位素组成具有正向偏离陨石硫的特征,但是各矿床的硫同位素组成又有明显的变化,并且在区域分布、矿化类型、深度位置等方面表现出一定的规律性变化。前人已初步认识到这种规律性变化并做出了相应的解释,如提出胶西北成矿区自东向西δ34S值递增[82]和从石英脉型-破碎带蚀变岩型金矿δ34S值相对略有增高[49, 52],并认为分别是由于海水硫和表生硫参与了成矿作用所致[61, 82],石英脉型矿石基本代表了成矿原始流体系统的同位素组成,而蚀变岩型矿石在成矿时与围岩中的硫发生了同位素交换导致δ34S值增高[49]。
综合分析各种因素,笔者认为,胶东金矿硫同位素组成的变化主要受围岩类型和硫源的制约。硫同位素组成的区域性变化主要与围岩类型有关:牟乳成矿区金矿床的围岩主要是富34S的昆嵛山花岗岩,相应地该区金矿床的δ34S值最高;胶莱盆地东北缘金矿床的赋矿围岩较复杂,主要有晚中生代花岗岩、新太古代荆山群和中生代莱阳群,围岩的δ34S值较高,金矿床的δ34S值也较高;栖蓬福成矿区的栖霞地区主要由相对贫34S的早前寒武纪TTG岩系和胶东岩群组成,金矿床的δ34S值是胶东最低的;胶西北成矿区金矿床的赋矿围岩主要是δ34S值中等的玲珑花岗岩和郭家岭花岗岩,对应金矿床的δ34S值高于栖蓬福地区而低于牟乳成矿区和胶莱盆地东北缘地区。胶西北成矿区的三山岛、焦家金矿床的34S含量较高,可能与其所在的破碎蚀变带规模大、浅表部流体混入较多有关,或与其位置接近变质地层, 混合了较多与海相变质地层——荆山群、粉子山群有关的表生硫有关[61, 82]。
石英脉型金矿与蚀变岩型金矿硫同位素值存在差异,一方面是由于二者的成矿方式及水-岩相互作用的程度不同[2],另一方面与成矿深度及与地表的连通性有关。在胶西北地区,蚀变岩型金矿赋存于断裂构造的主断裂带中,石英脉型金矿赋存于断裂下盘的次级裂隙中[2],说明石英脉型金矿形成深度较深。本次研究显示,蚀变岩型金矿由浅部至深部δ34S值降低,深部的δ34S值与石英脉型金矿接近,也说明石英脉型金矿成矿深度较大。由于蚀变岩型金矿的控矿断裂带规模大、切割深、破碎程度高,有利于水-岩相互作用的充分进行及表生硫的下渗和混合,造成δ34S值增高;随着深度加大,表生硫的混入量减少,δ34S值逐渐降低。而石英脉型金矿的控矿裂隙规模小、与地表连通性差,加之快速充填成矿及成矿深度较大,不利于大气降水的渗入和表生硫的混入,水-岩相互作用不充分,因此保留了较多的幔源组分,导致δ34S值偏低。
胶东金矿床以富δ34S为特点,但在马家窑、杜家崖金矿床中,部分δ34S值呈负值。另外,栖霞十里堡银矿床的δ34S值在-5.7‰~-2.1‰之间,平均值为-4.3‰[61]。位于胶东东部苏鲁超高压变质带中的范家埠金矿床δ34S值为-5.5‰~-9.1‰,其硫同位素组成特征与含油气盆地热卤水的相近,因此认为其成矿流体可能来源于中生代胶莱盆地[98],但胶莱盆地东北缘金矿床的δ34S值并未显示负值特征。对比发现,这几个矿床有一些共同特征,如赋矿围岩均为早前寒武纪变质岩,其中杜家崖金矿直接赋存于粉子山群大理岩中;矿物组合除黄铁矿外,还有较多方铅矿、闪锌矿等多金属硫化物;矿床周边一般都会有铅锌、铜、钼等有色金属矿相伴产出。鉴于早前寒武纪变质岩的硫同位素组成变化较大,且常出现重硫的亏损,而方铅矿、闪锌矿、黄铜矿等有幔源物质的贡献。因此认为,金矿床中的δ34S负值特征是原始地幔硫与亏损34S的变质岩不同比例混合的结果。
矿床中黄铁矿、闪锌矿、黄铜矿、方铅矿的δ34S值依次降低的变化特征说明,成矿过程中的硫同位素体系已达到均一,这些矿物是在一次成矿事件的较短时间内形成的。根据对金矿床中矿脉穿插关系与矿物共生组合的研究,胶东金矿成矿作用一般可划分为黄铁矿-绢云母-石英、石英-黄铁矿-金、石英-多金属硫化物-金、石英-碳酸盐4个阶段[10, 15],金主要出现于第2和3阶段,黄铁矿贯穿于第1~3阶段,方铅矿、黄铜矿、闪锌矿等硫化物为第3阶段的产物。硫同位素特征指示,4个矿化阶段是在同一成矿事件较短的时间段内形成的,说明胶东大量金矿是在较短时间内集中爆发成矿的。这与近年对胶东金矿的高精度同位素测年限定的成矿时间(120±2 Ma)[99]吻合。
5. 结论
(1) 胶东金矿的δ34S值为-14.0‰~15.1‰,各典型矿床的平均值在5.5‰~13.0‰之间,主要集中在6.0‰~10.0‰之间。δ34S值在区域分布、矿化类型、深度位置方面等表现出牟乳成矿区>胶莱盆地东北缘>胶西北成矿区>栖蓬福成矿区,硫化物石英脉型>蚀变岩型>石英脉型,矿床浅部>矿床深部,黄铁矿>闪锌矿>黄铜矿>方铅矿的特点。
(2) 金矿床中的硫为混合来源,是来自于地幔岩浆的流体在上升过程中混染了大量地壳物质,由地幔、华北克拉通地壳中的早前寒武纪变质岩系和晚中生代花岗岩类等多种来源的硫同位素混合而成。
(3) 硫同位素组成的变化主要与围岩类型和不同端元混合的比例有关,成矿物质受晚中生代花岗质岩浆混染较多的金矿床的δ34S值较高。金成矿过程中硫同位素体系已基本达到均一,金矿是一次成矿事件集中爆发形成的。
致谢: 感谢两位匿名审稿专家的宝贵意见。 -
图 1 胶东地区区域地质及金矿床分布图(据参考文献[1]修改)
1—第四系; 2—白垩系; 3—元古宇; 4—新元古代含榴辉岩的花岗质片麻岩; 5—新太古代胶东变质杂岩; 6—白垩纪崂山型花岗岩; 7—白垩纪伟德山型花岗岩; 8—白垩纪郭家岭型花岗岩; 9—侏罗纪玲珑型花岗岩; 10—三叠纪花岗岩类; 11—整合/不整合地质界线; 12—断层; 13—特大/大/中/小型金矿床; 14—蚀变岩型/石英脉型金矿床; A—胶西北成矿区; B—栖蓬福成矿区; C—牟乳成矿区(包括胶莱盆地东北缘); F1—三山岛断裂; F2—焦家断裂; F3—招平断裂; F4—西林-陡崖断裂; F5—金牛山断裂
Figure 1. Regional geological sketch map and distribution of gold deposits in Jiaodong area
表 1 胶东典型金矿床硫同位素组成
Table 1 Sulfur isotopic compositions of typical gold deposits in Jiaodong area
成矿区 矿床 矿床类型 δ34S值/‰ 范围/‰ 平均值/‰ 样品数/件 参考文献 胶西北 玲珑 石英脉型 7.8, 7.0, 8.3, 7.8, 7.9, 7.7, 8.3, 7.6, 8.5, 7.5, 7.0, 8.6, 7.2, 6.4, 7.3, 7.4;3.3, 2.9, 3.4, 4.3, 4.5, 4.4, 5.7;(8.3, 7.8, 7.9, 7.4, 7.4, 6.2, 6.3, 6.5, 6.3, 6.1, 8.5, 7.0, 6.3, 6.9, 7.2, 6.4, 6.4, 6.9, 7.2, 4.9, 6.8, 5.3, 7.1, 6.1, 7.9, 6.6, 6.8, 5.8, 5.9, 8.1, 7.3, 6.0, 5.9, 6.4, 6.9;7.7, 8.0, 8.3, 8.1, 8.4, 8.9, 8.6, 7.6, 8.1, 8.5, 9.4, 8.8, 8.1, 7.9, 8.2, 8.4, 8.0, 7.2, 9.4, 8.4, 8.5, 8.0, 8.5, 7.9, 7.4, 7.0, 7.6, 6.7, 7.1, 6.5, 6.3, 9.4, 9.8, 8.8, 8.6, 9.3, 9.5, 8.1, 8.2, 8.6, 8.6, 8.2, 8.4, 8.6, 8.5, 8.2, 9.1, 8.1, 8.3, 8.5, 8.8, 9.2, 7.0, 8.1, 8.2, 9.1, 8.3, 8.2, 8.8, 9.2, 9.6, 8.5, 8.1, 8.0, 8.4, 8.6, 8.9, 5.9, 4.2, 4.0)* 2.9~9.8 7.4 23+105* [43-44, 45*-46*] 夏甸 6.5, 7.3, 6.0, 6.5 6.0~7.3 6.5 4 [47] 旧店 7.9, 6.9, 8.0 6.9~8.0 7.6 3 本文 焦家 蚀变岩型 11.0, 10.5, 9.5, 10.2, 8.6, 9.5, 11.3, 8.8;11.4, 11.5, 11.3, 10.1;11.2, 11.0, 11.1, 10.8, 11.5, 10.9, 11.3, 10.8, 10.9, 10.6, 11.01;8.3, 9.7, 8.4, 8.8, 7.9, 7.0, 6.5, 7.1, 8.6;11.1, 12.6, 11.5, 11.1, 11.2, 11.4, 11.4, 11.2;7.5, 7.8, 8.0, 9.3, 7.8, 9.3, 8.9, 9.7, 9.8;(10.4, 10.2, 11.2, 11.2, 10.4, 9.8, 10.0, 10.6, 9.5, 10.6, 11.1, 11.4, 11.0, 10.1, 11.0, 11.4, 10.9, 10.3, 10.9, 10.1, 11.9, 11.0, 11.5, 10.1, 12.2, 11.4, 9.1, 12.5, 9.6, 11.2, 11.2, 10.5, 11.0, 8.8, 10.3, 11.2, 10.8, 11.2, 11.3, 10.3, 10.8, 11.9, 11.6, 10.2, 9.7, 9.7, 9.8, 9.9, 9.4, 11.0, 10.3, 11.1, 11.6, 10.7, 10.9, 11.8, 10.9, 11.6, 10.2, 10.2, 9.6, 10.8, 10.8, 10.6, 6.3, 5.5, 7.6, 8.3;10.7, 11.7, 11.3, 8.5, 8.7, 10.6, 12.7, 8.8, 11.0, 10.3, 11.8, 12.7, 10.5, 11.2, 12.1)* 5.5~12.7 10.3 49+83* [15, 48-52, 53*-54*] 三山岛 10.9, 10.9, 11.5, 11.5, 11.2, 10.9, 5.8, 8.7, 10.9, 10.9;11.5, 11.1, 11.8, 11.1, 11.0, 10.7, 9.7, 7.8;12.0, 12.0, 11.7, 11.9, 11.5;8.5, 8.4, 9.3, 9.2, 8.0, 10.5, 10.4;9.7, 11.7, 11.6, 11.8, 7.7;10.6, 10.2, 8.6, 11.9, 11.4, 9.5, 9.3, 10.2, 9.4, 9.4, 11.4 5.8~12.0 10.3 46 [49, 55-59] 新城 9.8, 9.2, 9.9, 9.5, 10.5, 10.6, 10.5, 8.4, 9.9, 8.8, 8.5, 8.3, 8.9, 9.1, 9.4, 8.7, 9.7, 7.7, 8.3, 8.2, 7.6, 8.0, 5.7, 7.0, 6.7, 7.5, 6.9, 7.9, 8.1, 7.7, 5.8, 4.3, 5.7;(11.0, 10.7, 9.7, 12.4, 8.9, 12.2, 10.9, 8.7, 11.4, 10.8, 8.3, 11.3, 8.7, 10.9)* 4.3~12.4 8.9 33+14* [54*, 60] 仓上 12.0, 11.1, 9.6, 10.5;11.7, 12.4, 11.3, 12.5, 11.7, 12.2 9.6~12.5 11.5 10 [49, 61] 大尹格庄 7.2, 7.2, 7.5, 7.4, 7.5, 7.3, 7.2, 7.3, 6.8, 6.9, 7.1, 6.8, 6.6, 6.8, 6.9, 5.0, 4.6, 4.6, 7.0, 7.2, 7.3, 5.5, 5.9, 7.4, 6.8;7.9, 7.5, 7.5, 7.2, 7.8, 6.8, 7.6 4.6~7.9 6.9 32 [49, 62] 望儿山 7.1, 8.7, 7.8, 6.3, 8.2, 7.6, 7.2, 7.4, 7.2, 6.3, 6.8, 8.6, 4.8, 6.7, 7.4, 7.0, 8.1, 6.6, 6.6, 7.5, 8.3, 8.9, 8.4, 6.4, 7.0, 6.6, 6.6, 7.8, 7.5, 7.3;8.7, 8.9, 8.5, 8.7, 8.5 4.8~8.9 7.5 35 [49, 63] 水旺庄 7.5, 8.0, 7.5, 8.1, 7.0, 8.5, 7.4 7.0~8.5 7.7 7 [16] 栖蓬福 石英脉型 黑岚沟 7.2, 6.8, 6.7, 6.9, 9.5, 8.0, 8.4, 6.3;(6.8, 6.6, 6.9, 7.1, 7.1, 7.0, 7.0, 7.2, 7.0, 7.0, 7.1, 7.2, 7.9, 7.2, 7.2, 7.5, 7.7, 7.6;7.7, 7.8, 7.5, 7.7, 7.4, 7.7, 7.6, 7.7, 7.3, 7.7, 7.1, 6.9, 7.6, 7.8, 7.7, 7.7, 7.2, 7.1, 7.4;8.5, 8.4, 8.3, 8.3, 8.5, 8.5, 8.4, 8.3, 8.4, 8.3, 8.3, 8.6, 8.8, 8.4, 8.6, 8.3, 8.1, 8.4, 8.4, 8.2, 8.2, 8.3, 8.7, 8.2, 8.7, 8.4, 8.5, 8.3, 8.4, 8.5)* 6.3~9.5 7.8 8+67* [40*, 43] 河西 7.6, 7.4, 7.5, 8.0, 8.5 7.4~8.5 7.8 5 [43] 大柳行 8.2, 6.4, 6.8, 6.8, 8.2;(4.3, 4.8, 4.9, 4.9, 5.0, 5.1, 5.1, 5.8, 5.9, 6.1, 6.4, 6.5, 6.5, 6.6, 6.6, 6.8, 6.8, 6.8, 6.8, 6.8, 7.0, 7.1, 7.2)* 4.3~8.2 6.3 5+23* [41*, 43] 山城 3.7, 5.5, 6.2, 6.4, 6.0, 5.1 3.7~6.4 5.5 6 [64] 西陡崖 5.8, 5.9, 6.0, 6.2, 6.2, 6.6, 6.9, 6.9, 6.9, 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 7.3, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6, 7.7, 7.7, 7.7, 7.8, 7.9 5.8~7.9 7.0 22* [41*] 笏山 7.1, 7.1, 7.2, 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.6, 7.7, 7.8, 7.9;5.7, 5.8, 6.0, 6.1, 6.1, 6.2, 6.2, 6.3, 6.3, 6.3, 6.3, 6.3, 6.4, 6.4, 6.4, 6.4, 6.4, 6.4, 6.5, 6.5, 6.5, 6.5, 6.5, 6.6, 6.6, 6.6, 6.6, 6.6, 6.6, 6.6, 6.7, 6.7, 6.7, 6.7, 6.7, 6.7, 6.7, 6.8, 6.8, 6.9, 7.0 5.7~7.9 6.7 51* [39] 马家窑 8.7, 8.8, 8.4, 8.4, 7.8, 7.7, 7.3, 7.4, 6.5, 7.0, 5.4, 7.9, 5.8, 7.4, 7.7, 7.7, 7.6, 5.5, 4.3, 5.3, 7.8, 7.9;(6.9, 7.6, 7.9, 8.6, 5.6, 5.3, 5.5, 5.5, -2.5, 4.4)* -2.5~8.8 6.6 22+10* [41*, 64] 杜家崖 层间滑脱带型 5.6, 7.1, 5.8, 4.5, 5.5, 9.2, -14.0, -3.8, 8.2, 7.7, -6.8, 5.5, 7.9, 7.4, 15.1, 10.4, 8.6, 7.3, 9.5, 8.8 -14.0~15.1 5.5 20* [65] 牟乳 乳山 硫化物石英脉型 7.2, 7.9, 10.6, 8.0, 10.7, 9.7, 8.3, 8.8, 9.6;9.7, 9.8, 6.8, 9.4, 7.6, 8.2;7.0, 8.7, 8.3, 7.4, 8.3, 8.5, 7.9, 8.3 6.8~10.7 8.5 23 [5, 66-67] 胡八庄 13.5, 11.9, 14.1, 12.6, 12.8 11.9~14.1 13.0 5 [68] 邓格庄 8.6, 10.4, 8.0, 8.4, 8.6;9.3, 9.0, 9.6, 9.3, 9.3, 8.8;10.1, 8.4, 10.0, 10.4, 10.8, 10.0, 10.4, 13.0, 9.0 8.0~13.0 9.6 20 [5, 49, 69] 范家庄 10.9, 11.4, 10.3, 12.3, 10.9, 10.7, 11.2, 9.8, 10.8, 10.4 9.8~12.3 10.9 10 [70] 胶莱盆地东北缘 辽上 黄铁碳酸盐脉型 3.4, 7.4, 8.0, 9.4, 8.4, 7.7, 9.1, 7.3 3.4~9.4 7.5 8 [71] 西涝口 蚀变岩型 7.8, 7.6, 8.8, 8.7, 8.6, 9.0, 8.9, 9.4, 9.5, 9.5, 16.2, 15.4, 7.6 7.6~16.2 9.8 12 [72] 土堆 9.7, 10.5, 8.5, 9.1;8.0, 8.2, 6.2, 7.0, 8.0, 7.5;8.2, 8.0 6.2~10.6 8.3 12 [72-74] 沙旺 9.1, 10.8, 10.0, 12.7;8.2, 9.6, 7.9, 8.5, 8.4;7.2, 8.0, 10.3 7.9~12.7 9.2 12 蓬家夼 蚀变角砾岩型 10.9, 11.5, 11.2;9.7, 10.4, 10.3, 10.7, 11.3;13.0, 12.7, 11.6, 10.6, 10.9;10.5, 11.3, 9.9, 11.0, 11.2, 10.8, 10.7, 10.8;6.2, 7.5, 8.3 6.2~13.0 10.5 24 [49, 75-78] 发云夼 蚀变砾岩型 10.7, 11.1, 10.9, 11.1, 10.9;12.6, 13.0, 13.6, 12.9, 12.8, 10.4, 10.4, 10.4, 10.1;8.6, 7.7, 8.7 8.6~13.6 10.9 17 [49, 79-80] 注:*数据为LA-MC-ICPMS原位微区硫同位素分析方法获得 表 2 胶东金矿主要赋矿围岩硫同位素组成
Table 2 Sulfur isotopic compositions of surrounding rock of gold deposits in Jiaodong area
地层/岩石 δ34S /‰ 变化范围/‰ 平均值/‰ 样品数/件 参考文献 胶东岩群 1.0, 1.5, 1.1, 1.7, 1.3, 1.0;5.6, 8.2, 10.8, 12.4, 15.4;6.9, 9.4, 7.8;1.8, 2.1;6.1, 7.8, 7.5, 7.0, 7.4, 7.3, 2.2, 1.2, 0.0, 1.7;7.8, 7.5, 7.0, 7.4, 7.3, 6.1, 2.2, 1.2, 0.0, 1.7 0.0~15.4 5.0 36 [41, 45, 60-61, 81-82] 荆山群 10.7, 9.9, 9.8, 9.3, 9.8, 9.8, 10.0, 8.2, 12.0 8.2~12.0 9.9 9 [76] 粉子山群 11.3, 13.0, 10.6, 11.4, 13.0, 12.0, 13.6 10.6~13.6 12.1 7 [45] TTG岩系 2.4, 2.3, 2.8, 3.0, 1.0, 1.6 1.0~3.0 2.2 6 [45] 昆嵛山花岗岩 15.3, 3.8;14.9, 8.5, 3.9 3.8~15.3 9.3 5 [83-84] 郭家岭花岗岩 6.0, 7.2, 7.8, 6.4, 9.2, 16.0, 7.4 6.0~16.0 8.6 7 [60] 玲珑花岗岩 7.9, 8.2, 8.3, 8.4, 8.2, 8.0 7.9~8.4 8.1 6 [49] 中基性脉岩 5.3~10.8 6.9 6 [61] 表 3 胶东典型金矿床深部和浅部硫同位素组成
Table 3 Sulfur isotopic composition in different depths of typical gold deposits in Jiaodong area
矿床 深度/m 矿床类型 δ34S值/‰ 变化范围/‰ 平均值/‰ 样品数/件 参考文献 焦家 -110~-275 蚀变岩型 11.4, 11.5, 11.3, 10.1;11.0, 10.5, 9.5, 10.2, 8.6, 9.5, 11.3, , 8.8;10.8, 10.9, 10.6, 11.0, 11.3, 10.9, 11.5, 10.8, 11.1, 11.0, 11.2;(10.3, 11.8, 12.7, 10.5, 11.2, 12.1)* 8.6~12.7 10.8 23+6* [48-50, 54*] 焦家 -579~-757 11.4, 11.2, 7.5 7.8, 11.5, 7.8, 11.2, 11.1, 11.4 7.5~11.5 10.1 9 [15, 52] 焦家 -849~-1070 9.3, 8.0, 9.3, 8.9, 11.1, 9.7, 9.8, 12.6 8.0~12.6 9.8 8 纱岭 -1100~-1600 11.7, 11.6, 11.8, 10.9, 9.8 9.8~11.8 11.2 5 [15, 52] 纱岭 -1800~-2000 9.2, 7.9, 7.7 7.7~9.23 8.2 3 [17] 乳山 0~-385 硫化物石英脉型 7.2, 7.9, 10.6, 8.0, 10.7, 9.7, 8.3, 8.8, 7.2~10.7 8.9 8 [5, 66] 乳山 -635~-700 9.7, 9.8, 6.8, 9.4, 7.6, 8.2, 9.6 6.8~9.8 8.7 7 注:*数据为LA-MC-ICPMS原位微区硫同位素分析方法获得 表 4 不同硫化物硫同位素组成
Table 4 Sulfur isotopic composition of different sulfide
矿床 δ34S值/‰(变化范围) 参考文献 黄铁矿 闪锌矿 黄铜矿 方铅矿 焦家 11.0, 10.5, 9.5, 10.2, 8.6, 9.5, 11.3, 8.8;11.4, 11.5, 11.3, 10.1;11.2, 11.0, 11.1, 10.8, 11.5, 10.9, 11.3, 10.8, 10.9, 10.6, 11.01;8.3, 9.7, 8.4, 8.8, 7.9, 7.0, 6.5, 7.1, 8.6;11.1, 12.6, 11.5, 11.1, 11.2, 11.4, 11.4, 11.2;7.5, 7.8, 8.0, 9.3, 7.8, 9.3, 8.9, 9.7, 9.8;(10.4, 10.2, 11.2, 11.2, 10.4, 9.8, 10.0, 10.6, 9.5, 10.6, 11.1, 11.4, 11.0, 10.1, 11.0, 11.4, 10.9, 10.3, 10.9, 10.1, 11.9, 11.0, 11.5, 10.1, 12.2, 11.4, 9.1, 12.5, 9.6, 11.2, 11.2, 10.5, 11.0, 8.8, 10.3, 11.2, 10.8, 11.2, 11.3, 10.3, 10.8, 11.9, 11.6, 10.2, 9.7, 9.7, 9.8, 9.9, 9.4, 11.0, 10.3, 11.1, 11.6, 10.7, 10.9, 11.8, 10.9, 11.6, 10.2, 10.2, 9.6, 10.8, 10.8, 10.6;10.7, 11.7, 11.3, 8.5, 8.7, 10.6, 12.7, 8.8, 11.0, 10.3, 11.8, 12.7, 10.5, 11.2, 12.1)*(6.5~12.7) 6.3, 5.5, 7.6, 8.3
(5.5~8.3)[15, 48-52, 53*-54*] 三山岛 10.9, 10.9, 11.5, 11.5, 11.2, 10.9;11.5, 11.1, 11.8, 11.1, 11.0, 10.7, 9.7;12.0, 12.0, 11.7, 11.9, 11.5;8.5, 8.4, 9.3, 9.2, 8.0, 10.5, 10.4;9.7, 11.7, 11.6, 11.8;10.6, 10.2, 8.6, 11.9, 11.4, 9.5, 9.3, 10.2, 9.4, 9.4, 11.4(8.0~12.6) 10.9, 10.9 5.8, 8.7, 7.7, 7.8
(5.8~8.7)[49, 55-59] 玲珑 7.8, 7.0, 8.3, 7.8, 7.9, 7.7, 8.3, 7.6, 8.5, 7.5, 7.0, 8.6, 7.2, 6.4, 7.3, 7.4;3.3, 2.9, 3.4, 4.3, 4.5, 4.4, 5.7;(8.3, 7.8, 7.9, 7.4, 7.4, 6.2, 6.3, 6.5, 6.3, 6.1, 8.5, 7.0, 6.3, 6.9, 7.2, 6.4, 6.4, 6.9, 7.2, 4.9, 6.8, 5.3, 7.1, 6.1, 7.9, 6.6, 6.8, 5.8, 5.9, 8.1, 7.3, 6.0, 5.9, 6.4, 6.9;7.7, 8.0, 8.3, 8.1, 8.4, 8.9, 8.6, 7.6, 8.1, 8.5, 9.4, 8.8, 8.1, 7.9, 8.2, 8.4, 8.0, 7.2, 9.4, 8.4, 8.5, 8.0, 8.5, 7.9, 7.4, 7.0, 7.6, 6.7, 7.1, 6.5, 6.3, 9.4, 9.8, 8.8, 8.6, 9.3, 9.5, 8.1, 8.2, 8.6, 8.6, 8.2, 8.4, 8.6, 8.5, 8.2, 9.1, 8.1, 8.3, 8.5, 8.8, 9.2, 7.0, 8.1, 8.2, 9.1, 8.3, 8.2, 8.8, 9.2, 9.6, 8.5, 8.1, 8.0, 8.4, 8.6, 8.9)*(2.9~9.8) 5.9* 4.2* 4.0* [43, 44, 45*-46*] 新城 9.8, 9.2, 9.9, 9.5, 10.5, 10.6, 10.5, 8.4, 9.9, 8.8, 8.5, 8.3, 8.9, 9.1, 9.4, 8.7, 9.7, 7.7, 8.3, 8.2, 7.6, 8.0, 5.7, 7.0, 6.7, 7.5, 6.9;(11.0, 10.7, 9.7, 12.4, 8.9, 12.2, 10.9, 8.7, 11.4, 10.8, 8.3, 11.3, 8.7, 10.9)*(5.7~12.4) 7.9, 8.1, 7.7
(7.7~8.1)5.8 4.3, 5.7
(4.3~5.7)[54*, 60] 邓格庄 10.4, 8.0, 8.4;9.3, 9.0, 9.6, 9.3, 9.3, 8.8;10.1, 10.8, 10.8(8.0~10.8) 8.6, 10.4, 13.0
(8.6~13.0)8.6, 8.4, 9.0
(8.4~9.0)[5, 49, 69] 乳山 7.2, 10.6, 8.0, 10.7, 9.7, 8.3, 8.8, 9.6;7.0, 8.7, 8.3, 7.4, 8.3, 8.5, 7.9, 8.3;9.7, 9.8, 6.8, 9.4, 7.6, 8.2(7.0~10.6) 7.9 [5, 66-67] 注:*数据为LA-MC-ICPMS原位微区硫同位素分析方法获得 -
宋明春, 宋英昕, 丁正江, 等. 胶东金矿床: 基本特征和主要争议[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2018, 26(4): 406-422. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ201804006.htm 宋明春, 林少一, 杨立强, 等. 胶东金矿成矿模式[J]. 矿床地质, 2020, 39(2): 215-236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202002002.htm 翟明国, 范宏瑞, 杨进辉, 等. 非造山带型金矿——胶东型金矿的陆内成矿作用[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(1): 85-98. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.01.005 朱日祥, 范宏瑞, 李建威, 等. 克拉通破坏型金矿床[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2015, 45(8): 95-114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201508006.htm 应汉龙. 胶东金青顶、邓格庄金矿床含金石英的40Ar/39Ar快中子活化年龄[J]. 黄金科学技术, 1994, 2(4): 24-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ404.004.htm 李士先, 刘长春, 安郁宏, 等. 胶东金矿地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007. 蒋少涌, 戴宝章, 姜耀辉, 等. 胶东和小秦岭: 两类不同构造环境中的造山型金矿省[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(11): 2727-2738. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200911004.htm Wang Z C, Xu Z, Cheng H, et al. Precambrian metamorphic crustal basement cannot provide much gold to form giant gold deposits in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2021, 354: 106045. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2020.106045
朱日祥, 孙卫东. 大地幔楔与克拉通破坏型金矿[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2021, 51(9): 1444-1456. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK202109003.htm 杨立强, 邓军, 王中亮, 等. 胶东中生代金成矿系统[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(9): 2447-2467. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409001.htm 薛建玲, 李胜荣, 孙文燕, 等. 胶东邓格庄金矿床流体包裹体氦、氩同位素组成及其成矿物质来源示踪[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2013, 43(2): 400-414. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201302010.htm 张德全, 徐洪林, 孙桂英. 山东牟平邓格庄金矿的地球化学特征及成因[J]. 矿床地质, 1997, 16(3): 204-213. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ703.001.htm Deng J, Yang L Q, Groves D I, et al. An integrated mineral system model for the gold deposits of the giant Jiaodong province, eastern China[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2020, 208: 103274. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103274
Feng K, Fan H R, Groves D I, et al. Geochronological and sulfur isotopic evidence for the genesis of the post-magmatic, deeply sourced, and anomalously gold-rich Daliuhang orogenic deposit, Jiaodong, China[J]. Mineral Deposita, 2020, 55: 293-308. doi: 10.1007/s00126-019-00882-8
李杰, 宋明春, 梁金龙, 等. 焦家深部金矿床成矿流体来源: 来自黄铁矿微量元素及S-He-Ar同位素的约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(1): 297-313. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202001023.htm 李杰, 张丽鹏, 宋明春, 等. 胶东水旺庄金矿床成矿机制: 来自S-H-O同位素和流体包裹体的制约[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(5): 1569-1584. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202105003.htm 姜梦瑶. 胶东纱岭金矿床成矿机制及构造背景分析[D]. 河北地质大学硕士学位论文, 2019: 36-38. 张义东. 胶东水旺庄金矿床深部地质特征及成因机制研究[D]. 河北地质大学硕士学位论文, 2018: 27-29 安梦莹. 胶东招平断裂带南段金矿成矿作用及成矿规律[D]. 河北地质大学硕士学位论文, 2021: 30-39. Li S Z, Kusky T M, Zhao G C, et al. Two Stage Triassic Exhumation of HPUHP Terranes in the Western Dabie Orogen of China: Constraints from Structural Geology[J]. Tectonophysics, 2010, 490: 267-293. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2010.05.010
宋明春. 胶东金矿深部找矿主要成果和关键理论技术进展[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(9): 1758-1771. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.09.017 Song M C, Li J, Yu X F, et al. Metallogenic Characteristics and Tectonic Setting of the Jiaodong Gold Deposit, China[J]. Solid Earth Sciences, 2021, 6(4): 385-405. doi: 10.1016/j.sesci.2021.07.002
Li J, Li C Y, Song M C, et al. Mineralization of the Shangjiazhuang Mo deposit in the Jiaodong peninsula, China: constraints from S-H-O isotopes and fluid inclusions[J]. Solid Earth Sciences, 2021, 6(4): 370-384. doi: 10.1016/j.sesci.2021.08.001
宋明春, 李杰, 李世勇, 等. 鲁东晚中生代热隆-伸展构造及其动力学背景[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2018, 48(4): 941-964. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201804001.htm 宋明春, 李三忠, 伊丕厚, 等. 中国胶东焦家式金矿类型及其成矿理论[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2014, 44(1): 87-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201401008.htm 李杰. 胶东地区钼-铜-铅锌多金属矿成矿作用及成矿模式—兼论与胶东金成矿作用的关系[D]. 成都理工大学博士学位论文, 2012: 1-127. 李杰, 宋春明, 李世勇, 等. 胶东大邓格金多金属矿床地质地球化学特征及意义[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(1): 221-237. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2016.01.016 李国华, 丁正江, 纪攀, 等. 胶莱盆地东北缘地区金矿特征及找矿方向[J]. 地质与勘探, 2016, 52(6): 1029-1036. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201606003.htm 丁正江, 孙丰月, 刘福来, 等. 胶东中生代动力学演化及主要金属矿床成矿系列[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(10): 3045-3080. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201510011.htm 刘国栋, 温桂军, 刘彩杰, 等. 招平断裂北段水旺庄深部超大型金矿床的发现、特征和找矿方向[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2017, 25(3): 38-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ201703006.htm 刘国栋, 宋国政, 鲍中义, 等. 胶东招平断裂北段深部找矿新突破及对断裂空间展布的新认识[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2019, 43(2): 226-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201902003.htm 鲍中义, 孙忠全, 刘国栋, 等. 破头青断裂水旺庄矿区矿床地质特征及找矿方向[J]. 山东国土资源, 2014, 30(2): 31-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDDI201402009.htm 赛盛勋. 胶东牟乳金矿带构造-流体-成矿及动力学[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 博士学位论文, 2020: 25-26. 薄军委, 丁正江, 宋明春, 等. 胶东辽上金矿床C、O、S、Pb同位素组成及矿床成因[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2021, 40(2): 321-336. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2021.02.010 Liang J L, Li J, Sun W D, et al. Source of ore-forming fluids of the Yangshan gold field, western Qinling orogen, China: Evidence from microthermometry, noble gas isotopes and in situ sulfur isotopes of Au-carrying pyrite[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 105: 404-422. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.12.029
Liang J L, Li J, Liu X M, et al. Multiple element mapping and in-situ S isotopes of Au-carrying pyrite of Shuiyindong gold deposit, southwestern China using NanoSIMS: Constraints on Au sources, ore fluids, and mineralization processes[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 123: 103576. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103576
Zhao J, Liang J L, Li J, et al. Gold and sulfur sources of the Taipingdong Carlin-type gold deposit: Constraints from simultaneous determination of sulfur isotopes and trace elements in pyrite using nanoscale secondary ion mass spectroscopy[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 117: 1-11.
Yang L Q, Deng J, Wang Z L, et al. Relationships between Gold and Pyrite at the Xincheng Gold Deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Implications for Gold Source and Deposition in a Brittle Epizonal Environment[J]. Economic Geology, 2016, 111(1): 105-126. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.111.1.105
Yang K F, Jiang P, Fan H R, et al. Tectonic transition from a compressional to extensional metallogenic environment at ~120Ma revealed in the Hushan gold deposit, Jiaodong, North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 160: 408-425.
Feng K, Fan HR, Hu FF, et al. Involvement of anomalously As-Au-rich fluids in the mineralization of the Heilan'gou gold deposit, Jiaodong, China: evidence from trace element mapping and in-situ sulfur isotope composition[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 160: 304-321. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.12.023
田杰鹏. 胶东栖蓬福矿集区中生代金多金属矿区域成矿作用[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 博士学位论文, 2020: 90-97. 朱照先, 赵新福, 林祖苇, 等. 胶东金翅岭金矿床黄铁矿原位微量元素和硫同位素特征及对矿床成因的指示[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(3): 945-959. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202003019.htm 侯明兰, 蒋少涌, 姜耀辉, 等. 胶东蓬莱金成矿区的S-Pb同位素地球化学和Rb-Sr同位素年代学研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(10): 2525-2533. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200610012.htm 王磊. 山东玲珑金矿流体包裹体及同位素特征研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 硕士学位论文, 2010: 84-85. 林祖苇. 胶东玲珑金矿田石英脉型与蚀变岩型矿体黄铁矿矿物学和地球化学的对比及对成因的指示[D]. 中国地质大学(武汉) 硕士学位论文, 2019: 64-66. 程韩宇. 胶东玲珑金矿和焦家金矿地球化学特征对比研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 硕士学位论文, 2019: 49-53. 杜佛光. 胶东招远夏甸金矿地球化学与矿床成因研究[D]. 南京大学硕士学位论文, 2019: 45-51. 陈阳阳. 山东焦家金矿床地球化学特征及矿床成因探讨[D]. 长安大学硕士学位论文, 2017: 59-61. 毛景文, 李厚民, 王义天, 等. 地幔流体参与胶东金矿成矿作用的氢氧碳硫同位素证据[J]. 地质学报, 2005, 79(6): 839-857. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2005.06.013 庞绪成. 山东焦家金矿矿床地球化学特征及深部矿体预测研究[D]. 成都理工大学博士学位论文, 2005: 74-76. 张佳楠. 山东莱州焦家金矿床矿化富集规律及矿床成因探讨[D]. 吉林大学硕士学位论文, 2012: 37-38. 宋明春, 宋英昕, 沈昆, 等. 胶东焦家深部金矿矿床地球化学特征及有关问题讨论[J]. 地球化学, 2013, 42(3): 274-289. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2013.03.009 马亮. 胶东地区中生代岩石圈快速减薄过程中岩浆与金成矿事件的地球化学研究[D]. 南京大学博士学位论文, 2013: 129-131. Mills S E, Tomkins A G, Weinberg R F, et al. Anomalously silver-rich vein-hosted mineralisation in disseminated-style gold deposits, Jiaodong gold district, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 68: 127-141. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.12.014
罗栋. 胶东三山岛金矿床成矿流体演化[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 硕士学位论文, 2014: 80-85. 郭春影. 胶东三山岛-仓上金矿带构造-岩浆-流体金成矿系统[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 博士学位论文, 2009: 90-94. 姜晓辉, 范宏瑞, 胡芳芳, 等. 胶东三山岛金矿中深部成矿流体对比及矿床成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(5): 1327-1340. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201105009.htm 刘亚洲. 三山岛金矿床成矿流体特征与水-岩反应热力学模拟[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 博士学位论文, 2019: 70-72. Wen B J, Fan H R, Hu F F, et al. Fluid evolution and ore genesis of the giant Sanshandao gold deposit, Jiaodong gold province, China: Constrains from geology, fluid inclusions and H-O-S-He-Ar isotopic compositions[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 176: 96-112.
张潮, 刘育, 刘向东, 等. 胶西北新城金矿床硫同位素地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(9): 2495-2506. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409004.htm 黄德业. 胶东金矿成矿系列硫同位素研究[J]. 矿床地质, 1994, 13(1): 75-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ401.007.htm 张瑞忠, 王中亮, 王偲瑞, 等. 胶西北大尹格金矿床成矿机理: 载金黄铁矿标型及硫同位素地球化学约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(8): 2451-2464. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201608015.htm 郭林楠. 胶东型金矿床成矿机理[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 博士学位论文, 2016: 120-125. 王佳良, 孙丰月, 王力, 等. 山东栖霞马家窑金矿床地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 黄金, 2013, 34(6): 14-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ201306006.htm 吕文杰. 胶东烟台市福山区杜家崖金矿床成因矿物学与找矿[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 博士学位论文, 2010: 54-56. 陈海燕. 胶东金青顶金矿成因矿物学与深部远景研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 硕士学位论文, 2010: 46-50. 李旭芬. 胶东牟平-乳山金矿带金青顶金矿矿床成因与找矿方向研究[D]. 长安大学博士学位论文, 2011: 86-87. 蔡亚春, 范宏瑞, 胡芳芳, 等. 胶东胡八庄金矿成矿流体、稳定同位素及成矿时代研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(5): 1341-1351. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201105010.htm 薛建玲, 李胜荣, 庞振山, 等. 胶东邓格庄金矿成矿流体、成矿物质来源与矿床成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(5): 1453-1468. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201805017.htm 张铭, 谭俊, 王怀洪, 等. 山东范家庄金矿床S、Pb同位素组成及对成矿物质来源的示踪[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(4): 124-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201904013.htm 纪攀. 胶东辽上金矿床地质特征及成因研究[D]. 吉林大学硕士学位论文, 2016: 45-46. 孙兴丽. 山东胶莱盆地西涝口金矿床的特征和成因[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 博士学位论文, 2014: 101. 李红梅, 魏俊浩, 王启, 等. 山东土堆—沙旺金矿床同位素组成特征及矿床成因讨论[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(6): 791-802. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201006004.htm 陈昌昕. 山东郭城土堆—沙旺金矿床地质特征及矿床成因研究[D]. 吉林大学硕士学位论文, 2015: 50-51. 孙丰月, 石准立, 冯本智. 胶东金矿地质及幔源C-H-O流体分异成岩成矿[M]. 吉林: 吉林人民出版社, 1995. 张竹如, 陈世桢. 胶东金成矿域胶莱盆地中超大型金矿床找矿远景[J]. 地球化学, 1999, 28(3): 203-212. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1999.03.001 赵玉灵, 杨金中, 沈远超. 胶东蓬家夼金矿床稳定同位素地球化学特征研究[J]. 矿物岩石, 2000, 20(40): 19-24 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS200004003.htm 孙丽伟. 胶东乳山蓬家夼金矿床地质特征及矿化富集规律研究[D]. 吉林大学硕士学位论文, 2015: 60-64. 曾庆栋, 沈远超, 刘铁兵, 等. 胶莱盆地发云夼金矿床硫、铅同位素地球化学[J]. 矿床地质, 2002, 21(S): 759-762. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2002S1203.htm 陈扬. 山东牟平宋家沟金矿床地质特征及成因研究[D]. 吉林大学硕士学位论文, 2015: 54-55. 裘有守. 我国变质岩区内生金矿成矿特征及尚待解决的问题之刍见[J]. 贵金属地质, 1992, 4: 252-262. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJSD199204007.htm 王义文, 朱奉三, 宫润谭. 构造同位素地球化学—胶东金矿集中区硫同位素再研究[J]. 黄金, 2002, 23(4): 3-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ200204000.htm 安家桐, 于东斌, 沈昆, 等. 山东牟平—乳山地区金矿控矿条件的研究. 中国金矿主要类型区域成矿条件文集(胶东地区)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1988: 1-45. 张时淦. 山东金牛山成矿带金矿床基本特征及成因探讨[J]. 中国地质科学院沈阳地质矿产研究所所刊, 1990, 21: 68-81. https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ199007001007.htm Chai P, Zhang Z Y, Hou Z Q. Geological and Fluid Inclusion Constraints on Gold Deposition Processes of the Dayingezhuang Gold Deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(4): 955-971. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.13849
Chai P, Hou Z Q, Zhang Z Y. Geology, Fluid Inclusion and Stable Isotope Constraints on the Fluid Evolution and Resource Potential of the Xiadian Gold Deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula[J]. Resource Geology, 2017, 67(3): 341-359. doi: 10.1111/rge.12134
Guo L N, Deng J, Yang L Q, et al. Gold deposition and resource potential of the Linglong gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula: Geochemical comparison of ore fluids[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 120.10.1016/j. oregeorev. 2020.103434.
Li J J, Zhang P P, Li G H, et al. Formation of the Liaoshang gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China: Evidence from geochronology and geochemistry[J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 10.1002/gj. 3718.
张德会, 赵仑山. 地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2013, 416-418. 郑永飞, 陈江峰. 稳定同位素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000: 1-316. Hoefs J. Stable isotope geochemistry(Sixth Edition)[M]. Springer, 2009: 72.
Ionov D A, Dupuy C, O'Reilly S Y, et al. Carbonated peridotite xenoliths from Spitsbergen: Implications for trace element signature of mantle carbonate metasomatism[J]. Earth and Planetary of Science Letters, 1993, 119: 283-297. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(93)90139-Z
Tan J, Wei J H, Li Y J, et al. Origin and geodynamic significance of fault-hosted massive sulfide gold deposits from the Guocheng-Liaoshang metallogenic belt, eastern Jiaodong Peninsula: Rb-Sr dating, and H-O-S-Pb isotopic constraints[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65: 687-700. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.06.007
Song M C, Deng J, Yi P H, et al. The kiloton class Jiaojia gold deposit in eastern Shandong Province and its genesis[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(3): 801-824. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12239
张良, 刘跃, 李瑞红, 等. 胶东大尹格庄金矿床铅同位素地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(9): 2468-2480. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409002.htm 张连昌, 沈远超, 李厚民, 等. 胶东地区金矿床流体包裹体的He、Ar同位素组成及成矿流体来源示踪[J]. 岩石学报, 2002, 18(4): 559-565. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200204014.htm 张运强, 李胜荣, 陈海燕, 等. 胶东金青顶金矿床成矿流体来源的黄铁矿微量元素及He-Ar同位素证据[J]. 中国地质, 2012, 39(1): 195-204. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.01.019 李建威, 毕诗健, Paulo V. 胶东苏鲁地体范家埠金矿成矿作用与矿床成因浅析: 兼与胶北地体金矿对比[J]. 高校地质学报, 2010, 16(2): 125-142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2010.02.001 Zhang L, Weinberg R F, Yang L Q, et al. Mesozoic Orogenic Gold Mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: A Focused Event at 120 ±2 Ma During Cooling of Pregold Granite Intrusions[J]. Economic Geology, 2020, 115(2): 415-441. doi: 10.5382/econgeo.4716
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 吴净,郭佳怡,张明礼,王延华. 湖泊氮沉积研究热点与发展趋势. 南京师大学报(自然科学版). 2025(01): 18-27 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘欣月,李海波,刘胜山,何文杰,董浩,程艳,乔俊豪,徐银. 大冶湖沉积物氮磷形态分布特征及生态风险评价. 环境科学学报. 2024(06): 161-173 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. Bo Han,Zhen Ma,Liang-jun Lin,Hong-wei Liu,Yi-hang Gao,Yu-bo Xia,Hai-tao Li,Xu Guo,Feng Ma,Yu-shan Wang,Ya-long Zhou,Hong-qiang Li. Planning and construction of Xiong'an New Area(city of over 5 million people):Contributions of China's geologists and urban geology. China Geology. 2024(03): 382-408 .  必应学术
必应学术
4. 杨关绍,温雯雯,王旭,郭雯,王明果,黄林培,孔令阳,李蕊,陈光杰,王教元. 异龙湖草——藻型稳态转换的碳氮磷化学计量特征及埋藏量估算. 地理学报. 2024(11): 2830-2848 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 雷晓玲,韩程远,魏泽军,杨程,李璐. 多级雨水塘径流污染特征及底泥氮、磷污染风险评价研究. 环境科学与管理. 2023(06): 173-178 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 邱坚,原璐彬,邢书语,刘鑫,丁益华,田苗苗. 镇江市金山湖沉积物磷元素分布特征研究. 环境监控与预警. 2023(06): 85-92 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)



 下载:
下载: