800~780Ma continental rift magmatism in the eastern part of the Jiangnan Orogen: Implications from~790Ma aluminous A-type granites in Zhejiang-Anhui-Jiangxi border area
-
摘要:
对江南造山带东段浙皖赣邻区的灵山花岗斑岩进行了同位素年代学和岩石地球化学研究。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄测定结果表明,灵山花岗斑岩形成于791.8±2.6Ma。在岩石地球化学组成上,灵山花岗斑岩具有高Si,高TFeO/(TFeO+MgO)值,低Mg、Ca、Mn和P,显示出过铝质的特征(A/CNK=1.04~1.18);微量元素富集Rb、Ga、Th、Zr、Y,贫Sr、P、Ti、Ba;稀土元素总量较高,轻、重稀土元素分异较明显,并表现出强烈的负Eu异常,这些特点与典型的铝质A型花岗岩一致。地球化学特征和前人研究成果表明,灵山花岗斑岩形成于陆内裂谷环境,最有可能来源于早期初生地壳的部分熔融。结合前人研究成果认为,800~780Ma的岩浆活动是华南新元古代一期重要的构造岩浆事件,该期岩浆活动不仅在华南新元古代盆地的形成过程中扮演了重要角色,而且在该时期构造环境的探讨、板溪期沉积旋回时限的标定等方面都发挥了重要作用。
Abstract:In this paper, the authors report geochronological and geochemical data obtained for Lingshan granite porphyries of the eastern Jiangnan Orogen in the Zhejiang-Anhui-Jiangxi border area. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of Lingshan granite porphyries shows that these rocks were crystallized at 791.8±2.6Ma. Lingshan granite porphyries are characterized by high Si, high TFeO/ (TFeO+MgO) ratio, low Mg, Ca, Mn, and P, and peraluminous nature (A/CNK=1.04~1.18); REE data show that the granite porphyries have high concentrations of Rb, Ga, Th, Zr, Y, but are depleted in Sr, P, Ti, Ba; additionally, the granite porphyries have high total REE concentrations and high LREE/HREE ratio, exhibiting strong negative Eu anomalies; these characteristics are consistent with features of the typical aluminous A-type granite. Geochemical analysis and results of previous researches show that the Lingshan granite porphyries were formed in a continental rift environment, and most likely derived from partial melting of juvenile crust. In combination with the previous study, the authors hold that the magmatic activities that occurred between 800 and 780 Ma not only played an important role in the formation of South China Neoproterozoic basin but also has important geological significance for the study of the tectonic environment during this period and calibration of sedimentary cycle during Banxi period.
-
早中新世后,随着青藏高原隆升,亚洲季风增强,中国北方大部地区逐渐脱离原有的行星气候控制的干旱气候状况,向今天的暖温带季风气候系统转变[1-2],其生态系统也由原来的草原及荒漠草原为主的植被景观,转变为森林草原-落叶阔叶林为主[2]。亚洲季风区的典型暖温带植被系统不仅对全球周期性气候变化具有明显的指示意义,而且对过去数百万年时间的气候转型具有较好的响应,因此,是近年来研究过去全球变化的重点[3-4]。
晚新近纪以来,全球气候经历了几次重要的调整过程,其中最重要的就是中更新世时期全球气候格局的调整,又称中更新世转型[5-6]。其特征为从“高频低幅”的早更新世气候向中更新世以来“低频高幅”的气候波动,其气候变化周期由40ka的地轴倾斜度周期,转变为100ka 的轨道偏心率周期[7]。期间全球气候降温,陆地表面大部分地区因此变得更加寒冷干燥,冰期时,形成北美、欧洲的冰盖,非洲撒哈拉沙漠形成,亚洲内陆环境进一步干旱化,冬季季风强度增加等[7-9]。研究中更新世气候格局的重新调整,以及转型前后气候周期性对华北地区植被的影响,有利于了解不同区域植被对全球气候环境变化的响应特征,为研究重大气候转型中的生态环境效应提供重要对比参照物[10]。
华北平原主要包括淮北平原、黄河平原和海河平原三大区块,位于中国北方地区的东部,属典型的季风区。华北平原北部海河下游地区的凹陷盆地中沉积了厚度大于5000m 的新生带地层[11],其中第四系厚280~410m,最厚约450m。目前,基于这些新生带地层,华北地区的古植被研究已有较多积累,如河北黄骅HB1、衡水HS1 及天津CQJ1 孔花粉谱[12-14],天津G2 孔[15]。但是由于地层中花粉鉴定数量偏少、地层年代学不完善,以及区域地貌、沉积环境等多元因素的影响,用高质量孢粉数据来探讨更新世以来华北地区植被转型与气候变化问题的研究并不多见。本次研究利用华北地区东部天津滨海新区沉积凹陷中G3 钻孔的岩心材料,通过古地磁年代序列及较高质量的孢粉分析数据重建区域植被历史,并结合已有的植被重建资料,探讨第四纪以来华北地区的植被演变特征及气候变化过程。
1. 研究区自然地理概况
位于北纬32°~40°、东经114°~121°的华北平原是中国东部最主要的平原,平均海拔低于50m,由黄河、海河、淮河等带来的泥沙沉积而成。华北平原属暖温带季风气候,四季变化明显,冬季寒冷、少雪;春季干旱,夏季气温高、湿度大、降水集中;全年平均气温8~15℃。年平均降水量南部淮河区800~1000mm,黄河下游600~700mm,海河下游为500~600mm,年降水量分配不平衡,多年平均水面蒸发量为1625mm,降水随季节变化显著,冬、春季少,夏季集中[16]。
研究区自然植被主要由暖温带落叶阔叶林组成。在现代植被中,阔叶类的落叶栎(Quercus)植被组成受纬向的温度效应控制非常明显,在南部为麻栎(Quercus acutissima)、栓皮栎(Quercus variabilis),向北逐渐过渡为蒙古栎(Quercus mongolica)和辽东栎(Quercus liaotungensis)。针叶类以松属(Pinus)占主要地位,以赤松(Pinus densiflora)为主。另外常见温带的枫桦(Betula costata)、五加(Eleutherococcussenticosus)、核桃楸(Juglans mandshurica Max.)、椴属(Tilia)等。华北平原,尤其是海河平原,湖泊和沼泽广布,沼泽植被以芦苇(Phragmites)、香蒲(Ty⁃pha)、水葱(Scirpus)、苔草(Carex)等为主[17]。
全新世晚期以来,由于人类活动的持续加强,华北地区原生落叶阔叶林遭到大规模破坏,形成了今天普遍的灌丛及灌丛草原,其中灌木以荆条、酸枣为主,草丛以黄背草和白羊草为建群种。
2. 研究材料与研究方法
2.1 钻孔地理位置与磁性地层
天津G3 钻孔(孔口坐标:北纬117°25′59.5″、东经38°49′57.6″)位于华北平原东部天津滨海地区的海河南侧,构造上属于黄骅坳陷中的板桥凹陷。孔口高程2.65m,孔深905m(图 1)。岩心直径100mm,全孔取心率90.0%以上。因此,取心率和岩心状况满足磁性地层学及其他研究的要求。
G3 孔200m 以上磁性地层中共有6 个极性段,包括3 个正极性段(N1~N3)和3 个负极性段(R1~R3),正极性段分别为N1(0~85.0m)、N2(95.5~105.9m)和N3(177~191.8m),负极性段分别为R1(85.0~95.5m)、R2(105.9~177.0m)和R3(191.8~212.5m)。其中N1(0~85.0m)以正极性为主,并且包含明显的全新世海相层,对应布容极性时(Brunhes),故确定N1(0~85.0m)对应C1n(0~0.781Ma)。85.0~212.5m(R1~R3)以负极性为主,对应松山极性时(Matuyama),其中,N2(95.5~105.9m)对应C1r.1n(0.988~1.072Ma),为贾拉米罗(Jaramillo)正极性亚时,奥尔都微(Olduvai)正极性亚时持续事件长,且强度大,在渤海湾沿岸其他钻孔中亦有出现,因此推断N3(177~191.8m)对应C2n(1.778~1.945Ma),为Olduvai正极性亚时(图 2)。
2.2 花粉分析方法
天津滨海新区大港G3 钻孔花粉样品取样深度在0~905m 之间,取样间隔岩性为粘土、亚粘土、亚砂土和砂。每个样品重量为100g,经盐酸和氢氟酸处理、直径7μm 筛网筛选提取花粉化石。花粉鉴定统计在400 倍日本OLYMPUS 光学生物显微镜下进行,每个样品鉴定统计的花粉数是观察统计3 个玻片以上得到的。
在取得的165 个样品的大部分中发现了花粉化石,但仅在160m 以上发现连续而丰富的花粉,160m以下花粉数量稀少,绝大多数样品中不足50 粒。160m 以上共42 个样品中花粉相对丰富,其中绝大多数样品鉴定粒数高于100 粒,样品平均粒数为218粒。本文选择具有连续有效花粉数据的0~160m 地层(0~1.7Ma),用Tilia 软件对花粉图谱进行百分比图谱的绘制(图 3)。
2.3 研究结果
在42 个有效样品中,共鉴定了9167 粒花粉,分属48 个科属。其中针叶乔木花粉有铁杉属(Tsu⁃ga)、冷杉属(Abies)、云杉属(Picea)和松属(Pinus),落叶阔叶乔木花粉有桦属(Betula)、鹅耳枥属(Car⁃pinus)、桤木属(Alnus)、栗属(Castanea)、落叶栎属(Quercus)、椴属(Tilia)、胡桃属(Juglans)、榆属(Ul⁃mus)、糙叶树属(Aphananthe)、枫香属(Liquidanber)、山核桃属(Carya)、无患子科(Sapindaceae),灌木植物花粉有嚼床科(Acanthaceae)、胡秃子科(Elaeagna⁃ceae)、榛属(Corylus)、虎榛子属(Ostryopsis)、麻黄属(Ephedra)、忍冬科(Caprifoliaceae)、蔷薇科(Rosace⁃ae)。草本植物花粉有旱生的地榆属(Sangnisorba)、葎草属(Humulus)、藜科(Chenopodiaceae)、菊科(Compositea)、蒿属(Artemisia)、茜草科(Rubiace⁃ae)、唇形科(Labiatea)、豆科(Leguminosae)、茄科(Solanaceae)、蓼属(Polygonum)、十字花科(Crcife⁃rae)、石竹科(Caryophllaceae)、伞形花科(Umbella⁃les)等,水生植物有禾本科(Gramineae)、泽泻科(Alismataceae)、香蒲属(Typha)、莎草科(Cyperace⁃ae)、荇菜属(Nymphoides)。蕨类植物孢子有石松科(Lycopodiaceae)、水龙骨属(Polypodium)、凤尾蕨属(Pteridium)、卷柏属(Selaginella)、水蕨科(Parkeria⁃ceae)、单缝孢子(Monolites)和三缝孢子(Trilites)。
通过Canoco 4.5 软件对G3 孔中孢粉属种排序(图 4),发现所有属种可分为4 个类群:①以云杉、松为代表的温性针叶林;②以栎属、榛属、栗属、胡桃等为主的落叶阔叶林;③以蒿属、藜科、禾本科和桦属为主的草原及疏林草原;④以榆属、蔷薇科、胡颓子和铁杉为主的暖温性灌丛。根据属种的分布规律推断,图 4 中第一主轴(横轴)指示湿度,第二主轴(纵轴)指示温度。
如图 3 所示,根据孢粉聚类分析结果,将G3 孔中花粉百分比图谱分为4 个带。
(1)孢粉带Ⅰ:松属-云杉属-藜属-菊科-蕨类组合(1.6~1.2Ma)
乔木平均为58.6%,以松(12.7%~84.2%)和云杉(0~10.6%)为主,早期有少量铁杉,后过渡为云杉,此外还包含含量较低的栎属、榆属、椴属、桦属、胡桃属等常见暖温性阔叶乔木;草本中藜科最多,平均为8.1%,菊科含量平均4.3%,最高14.3%,蒿属含量少于菊科,平均仅2.8%。蕨类孢子在本带含量较丰富,以石松为主,另外还有水龙骨、凤尾蕨等蕨类。
本段组合指示暖温带针阔叶混交林的特点,其中松属为主要建群种,其花粉的突出代表性使松属在此时具有绝对优势。其中重要的变化在1.5Ma 前后,针叶林成分由铁杉向云杉转变的过程,显示一次降温事件,由此又可以划分出2 个阶段,即Ⅰ -1(1.6~1.5Ma)和Ⅰ -2(1.5~1.2Ma)。草本组合显示,1.5Ma 以前,菊科含量较高,而到后期,禾本科含量逐渐增加,菊科花粉基本消失,显示了区域草地环境由湿转干的过程。
(2)孢粉带Ⅱ:松属-栎属-藜-蒿组合(1.2~0.7Ma)
本段乔木花粉整体比例下降,松属比例由上段的平均51%下降至15%左右,云杉、铁杉等针叶树基本消失,但落叶栎属比例由带Ⅰ的1.2%,显著上升为13.0%,同时桦属花粉也显著增加,另有少量栗属、榆属、胡桃属等阔叶树。草本花粉组成也发生重要改变,藜科、蒿属比例大幅度增加,并伴随禾本科与香蒲属花粉的增加。蒿属平均值由原来的2.7%增加为20.7%。
本段孢粉组合指示暖温带落叶阔叶林的植被特征。草本花粉,尤其是蒿属的比例大幅度增加,显示华北地区在该阶段林地消退与草原发展,指示该时期气候干旱化。
(3)孢粉带Ⅲ:栎属-松属-藜-蒿-香蒲组合(0.7~0.3Ma)
本段乔木花粉比例最低,松属平均值由15%进一步下降,栎属略有下降,伴随较多的桦属与少量云杉属、铁杉属,并出现了零星的枫香属、山核桃属花粉。草本中藜科和蒿属依然占据主导地位,显示草原继续发展,而香蒲比例大幅度上升,显示周边地区湖泊湿地的扩展。本段孢粉组合指示疏林草原的植被景观,同时,湖泊湿地开始大规模发育。
(4)孢粉带Ⅳ:松属-栎属-藜-蒿-香蒲组合(0.3~0Ma)
本段针叶乔木花粉比例回升,松属增加至22.1%,云杉、铁杉花粉含量也有显著增加,而阔叶类乔木比例下降,栎属略微下降,枫香属、山核桃属消失,出现少量椴属、栗属、榆属、胡桃属等阔叶树。草本主要变化为藜科比例下降和香蒲比例升高。本段孢粉组合指示以暖温带落叶阔叶林为主的植被景观,湖泊湿地持续发育。
3. 讨论
3.1 演变趋势
中更新世气候转型期间,全球冰量整体增加了约15%,平均温度显著下降。对于其转型时间,大部分研究显示其大约开始于1.2Ma[6],另一些研究认为稍晚,在约1.05Ma,或是0.9Ma 前后,另外有人认为这种转型也可能是以一种渐进的方式进行的,始于1.2Ma,到约0.6Ma 才完成转型[18]。
G3 孔指示的中国华北平原地区中更新世植被转型期,对应上述的孢粉带Ⅱ,显示华北地区植被转型开始发生于1.2Ma,主要表现为林地减少,喜湿的针叶林比例下降,较为干旱的落叶阔叶林增加,同时藜科、蒿属、禾本科等草地面积显著增加。这种变化在1.2Ma 左右的某个时间点发生,大致相当于深海O 同位素36 阶段。
黄骅HB1、衡水HS1、天津CQJ2 孔、天津G2 孔的1.28~2.80Ma 为暖温带落叶阔叶林的景观,整体上较暖湿。1.28Ma以来,典型暖温带阔叶乔木花粉比例减小,华北平原草地扩张,而黄骅HB1 孔与衡水HS1 孔在中更新世前后也发生了类似事件[12-15]。
尽管由于孢粉数据分辨率的问题,所有这些钻孔的花粉百分比变化在时间上没有完好吻合,但是1.2Ma 前后,中更新世转型期推动华北平原地区植被整体向干旱类型发展是具有普遍性的。
此后,大约在0.7Ma 前后又发生一次重大转型,林地进一步退化,区域植被由原来的落叶阔叶林向疏林草原转变,对应深海O 同位素18 阶段。之后这种趋势一直延续到0.3Ma 左右才发生转变。黄骅HB1 孔中,0.8~0.7Ma 以后以蒿属和香蒲属为主,草本花粉出现,并分别达到12.5% 和10.9%,衡水HS1孔中以蒿和藜科为代表的草本花粉在0.78Ma 后也显著增长,显示华北平原0.7~0.8Ma 前后草地植被显著扩张[12-14]。此后,在约0.3Ma,即大约O 同位素8 阶段以后,华北地区植被中林地比例再度增加,可能与深海O 同位素11 阶段以后的7 阶段,5 阶段等几次典型的高温期有关。
3.2 周期性气候变化的区域植被响应
尽管由于样品分辨率的问题,周期性气候变化导致的区域植被变化未能完全被花粉谱记录,以致花粉谱更多地指示了区域植被在万年尺度的长期发展趋势。但是,不论是1.2Ma 之前的40ka 轨道倾斜度周期性,还是1.2Ma 之后的100ka 轨道偏心率周期,周期性气候变化对植被的影响,在花粉谱中确有一定表现。
例如在孢粉带Ⅰ中,以松为代表的乔木花粉比例的波动变化为10%~80%,可能对应该时期由地轴倾斜度40ka 周期变化导致的区域植被的变化。在带Ⅳ 也有类似的波动响应。由此可见,不论是1.2Ma 之前40ka 周期的“ 高频低幅”变化,还是1.2Ma 之后,100ka 周期的“低频高幅”变化,对华北地区的植被都有显著影响。
如图 3 所示,华北地区植被在1.6~1.2Ma 期间在40ka 气候周期“高频低幅”的变化中,主要表现为松属、常绿栎、铁杉属、胡桃属的交替变化,指示了区域暖温性与温性植被林地类型的交替变化。而1.2Ma 之后随着草原植被的扩张,100ka 周期的“低频高幅”变化造成的华北地区区域植被的响应更多地表现为草原与森林的交替发展。
4. 结论
华北平原东北部天津G3 孔孢粉数据及周边地区已有花粉研究表明,华北平原地区1.6Ma 以来的植被演化主要可以分为4 个阶段:①1.6~1.2Ma 密闭度较高的暖温带针阔叶混交林;②1.2~0.7Ma 开阔的暖温带落叶阔叶林;③0.7~0.3Ma,阔叶疏林草原;④0.3Ma 至今,暖温带落叶阔叶林。
中国华北平原地区中更新世植被转型期对应于孢粉带Ⅱ,显示该转型始于1.2Ma,大致对应深海O 同位素36 阶段。主要特征为林地减少、喜湿的针叶林比例下降,较为干旱的落叶阔叶林增加,同时,藜科、蒿属、禾本科等草地面积显著增加。
大约在0.7Ma 前后又发生一次重大转型,林地进一步退化,区域植被由原来的落叶阔叶林向疏林草原转变,对应深海O 同位素18 阶段。
G3 孔代表的花粉谱显示,1.6Ma 以来气候周期性的变化对华北地区区域植被有较显著的影响。
在1.2Ma 之前,受40ka 轨道倾斜度气候周期性的影响,主要表现为植被林地类型的交替发展;在1.2Ma之后,受100ka 轨道偏心率气候周期性影响,主要表现为草原与森林交替发展。
-
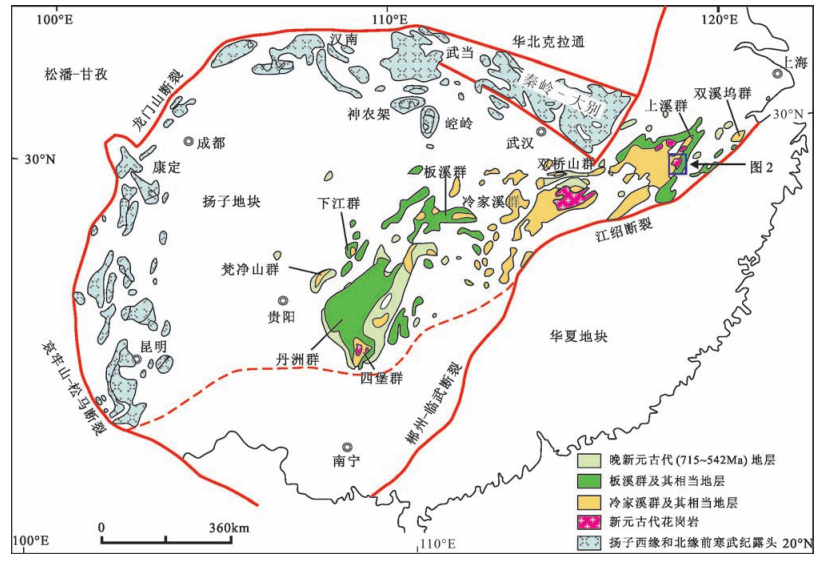
图 1 华南前寒武纪岩石分布(据参考文献[3]修改)
Figure 1. Geological map showing the distribution of Precambrian rocks in South China
图 6 灵山花岗斑岩A/CNK-A/NK图解(底图据参考文献[45])
Figure 6. A/CNK versus A/ NK plot for the Lingshan granite porphyries
图 7 灵山花岗斑岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)和原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)(原始地幔标准化数据、球粒陨石标准化数据据参考文献[46])
Figure 7. Chondrite-normalized REE distribution patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized spidergrams (b) for the Lingshan granite porphyries
图 8 江南造山带800~780Ma酸性岩10000×Ga/Al-(Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)图解(a)、10000×Ga/Al-Ce图解(b)、10000×Ga/Al-K2O/MgO图解(c)和1000×Ga/Al-TFeO/MgO图解(d)(底图均据参考文献[47];数据据参考文献[7, 16-17, 21, 23, 49])
Figure 8. 10000×Ga/Al versus Zr+Nb+Ce+Y diagram (a); 10000×Ga/Al-Ce diagram (b); 10000×Ga/Al-K2O/MgO diagram (c); 10000×Ga/Al-TFeO/MgO diagram (d) for 800~780Ma acid rocks in the Jiangnan Orogen
表 1 样品LN-3 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb年龄数据
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb zircon data of sample LN-3
测试点号 Th/U 同位素比值 同位素年龄/Ma 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 国土资源部沉积盆地与油气资源重点实验室 01 - 0.0664 0.0012 1.190 0.034 0.1301 0.0036 796.1 15.8 788.4 20.4 02 - 0.0656 0.0013 1.205 0.037 0.1333 0.0036 803.1 17.1 806.6 20.6 03 - 0.0689 0.0016 1.265 0.060 0.1335 0.0063 830.1 26.8 807.5 35.8 04 - 0.0705 0.0021 1.241 0.057 0.1297 0.0056 819.5 25.8 786.3 31.7 05 - 0.0692 0.0015 1.246 0.040 0.1301 0.0033 821.6 17.9 788.6 19.1 06 - 0.0675 0.0023 1.198 0.061 0.1295 0.0065 799.5 28.0 785.3 37.2 07 - 0.0672 0.0020 0.845 0.034 0.0903 0.0023 622.1 18.8 557.2 13.8 08 - 0.0644 0.0012 1.180 0.048 0.1318 0.0047 791.2 22.3 798.2 26.9 09 - 0.0658 0.0015 1.182 0.042 0.1314 0.0045 792.4 19.5 796.0 25.6 10 - 0.0648 0.0018 1.161 0.044 0.1297 0.0046 782.3 20.9 786.0 26.2 11 - 0.0688 0.0029 1.204 0.058 0.1287 0.0058 802.4 26.9 780.5 33.2 12 - 0.0638 0.0016 1.161 0.037 0.1321 0.0042 782.3 17.4 800.1 23.7 13 - 0.0711 0.0016 1.309 0.043 0.1332 0.0043 849.7 19.0 806.3 24.2 14 - 0.0641 0.0015 1.166 0.036 0.1310 0.0029 784.8 17.1 793.6 16.5 15 - 0.0650 0.0018 1.173 0.051 0.1303 0.0051 788.2 23.9 789.8 29.1 16 - 0.0688 0.0017 1.258 0.051 0.1312 0.0042 827.0 23.1 794.9 23.9 17 - 0.0664 0.0015 1.219 0.037 0.1314 0.0023 809.5 17.0 795.9 13.3 18 - 0.0940 0.0049 1.668 0.120 0.1277 0.0063 996.5 45.5 774.4 35.8 19 - 0.0668 0.0013 1.216 0.030 0.1313 0.0025 808.0 13.6 795.2 14.0 20 - 0.0653 0.0017 0.954 0.037 0.1054 0.0029 680.4 19.0 646.1 17.0 中国地质大学(武汉)地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室 01 0.54 0.0728 0.0017 1.196 0.028 0.1188 0.0012 798.5 12.9 723.7 6.8 02 0.58 0.0663 0.0017 1.188 0.027 0.1292 0.0015 795.1 12.7 783.2 8.6 03 0.66 0.0662 0.0013 1.191 0.023 0.1294 0.0009 796.3 10.6 784.5 5.0 04 0.44 0.0687 0.0016 1.270 0.028 0.1332 0.0010 832.6 12.7 806.1 5.8 05 0.56 0.0646 0.0013 1.178 0.024 0.1310 0.0009 790.2 11.2 793.8 5.4 06 0.46 0.0687 0.0018 1.249 0.032 0.1308 0.0011 822.8 14.6 792.2 6.3 07 0.60 0.0641 0.0015 1.156 0.026 0.1297 0.0010 780.1 12.4 786.2 5.9 08 0.39 0.0651 0.0014 1.198 0.027 0.1325 0.0013 799.5 12.4 801.9 7.2 09 0.36 0.0668 0.0013 1.192 0.023 0.1285 0.0008 797.0 10.8 779.2 4.8 10 0.67 0.0670 0.0014 1.213 0.025 0.1305 0.0012 806.5 11.7 790.7 6.6 11 0.36 0.0664 0.0018 1.208 0.032 0.1312 0.0011 804.3 14.9 795.0 6.0 12 0.58 0.0744 0.0019 1.452 0.038 0.1409 0.0012 910.7 15.9 850.0 6.8 13 0.32 0.0642 0.0013 1.184 0.026 0.1330 0.0013 793.3 12.2 805.2 7.3 14 0.49 0.0695 0.0013 1.086 0.023 0.1130 0.0013 746.4 11.0 690.3 7.4 15 0.60 0.0650 0.0013 1.167 0.023 0.1298 0.0010 785.3 10.8 786.6 5.4 16 0.48 0.0675 0.0014 1.212 0.026 0.1294 0.0010 805.9 11.9 784.7 5.7 17 0.32 0.0625 0.0013 1.128 0.026 0.1304 0.0016 766.8 12.5 790.1 9.1 18 0.39 0.0636 0.0013 1.147 0.024 0.1302 0.0009 776.0 11.4 788.8 5.1 19 0.44 0.0642 0.0015 1.157 0.027 0.1303 0.0011 780.8 12.7 789.5 6.2 20 0.42 0.0637 0.0014 1.169 0.027 0.1326 0.0011 786.4 12.6 802.6 6.2 21 0.39 0.0675 0.0016 1.207 0.031 0.1288 0.0012 803.6 14.2 781.0 7.0 22 0.55 0.0668 0.0019 1.225 0.036 0.1327 0.0016 812.2 16.3 803.1 9.1 23 0.46 0.0753 0.0014 0.949 0.018 0.0909 0.0006 677.5 9.2 560.8 3.6 24 0.54 0.0687 0.0014 1.260 0.025 0.1323 0.0009 827.8 11.3 801.0 5.0 表 2 灵山花岗斑岩主量、微量和稀土元素组成
Table 2 Major, trace elements and REE date for the Lingshan granite porphyries
样品号 LN-1 LN-2 LN-3 SiO2 78.05 79.83 79.14 TiO2 0.13 0.12 0.12 Al2O3 11.31 10.62 10.90 TFe2O3 1.54 1.22 1.44 MgO 0.08 0.10 0.10 CaO 0.14 0.01 0.04 Na2O 3.30 2.34 2.52 k2O 4.77 4.74 4.84 P2O5 0.012 0.009 0.009 MnO 0.02 0.02 0.01 H2O- 0.08 0.14 0.18 LOI 0.46 0.92 0.74 TOtal 99.90 100.07 100.04 Na2O+K2O 8.07 7.08 7.36 Zr 201 195 186 Nb 14.6 13.1 13.5 Sn 4.20 5.47 5.83 Cs 4.03 8.74 5.36 Ba 672 636 719 La 42.5 20.5 47.4 Ce 94.8 60.0 82.4 Pr 10.7 5.10 11.9 Nd 42.6 20.0 48.8 Sm 9.68 4.94 11.0 Eu 0.97 0.58 1.07 Gd 9.37 7.01 11.2 Tb 1.60 1.63 2.03 Dy 9.42 11.4 12.7 A/CNK 1.04 1.18 1.15 Li 14.0 32.2 24.4 Be 3.60 2.11 2.59 Sc 5.68 7.96 7.91 V 2.75 3.71 2.86 Cr 1.04 1.16 0.80 CO 0.37 0.30 0.32 Ni 0.44 0.66 0.30 Cu 7.22 10.4 5.87 Zn 52.0 55.6 60.4 Ga 16.8 16.9 16.2 Rb 179 195 187 Sr 17.0 21.5 24.4 Y 49.3 77.3 76.4 HO 1.84 2.63 2.71 Er 5.24 7.78 7.60 Tm 0.80 1.20 1.10 Yb 5.27 7.47 6.99 Lu 0.76 1.05 1.00 Hf 6.66 6.60 6.22 Ta 1.09 1.06 1.01 Tl 0.77 1.00 0.93 Pb 32.2 24.0 23.8 Th 17.3 16.4 15.7 U 3.26 3.35 4.34 1000xGa/Al 2.81 3.00 2.82 Zr+Nb+Ce+Y 360 346 358 TZr/℃ 814 827 819 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 -
Eby G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids:petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Lithos, 1990, 26:115-134. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(90)90043-Z Eby G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids:petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Lithos, 1990, 26:115-134. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(90)90043-Z
吴锁平, 王梅英, 戚开静. A型花岗岩研究现状及其评述[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2007, 26(1):57-66. http://www.airitilibrary.com/Publication/alDetailedMesh?docid=10006524-200701-26-1-57-66-a Zhao G C, Cawood P A. Precambrian Geology of China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2012, 222/223:13-54. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2012.09.017 Zhao G C, Cawood P A. Precambrian Geology of China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2012, 222/223:13-54. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2012.09.017
高林志, 戴传固, 刘燕学, 等.黔东南-桂北地区四堡群凝灰岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其地层学意义[J].地质通报, 2010, 29(9):1259-1267. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20100901&journal_id=gbc 高林志, 陈峻, 丁孝忠, 等.湘东北岳阳地区冷家溪群和板溪群凝灰岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄--对武陵运动的制约[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(7):1001-1008. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20110701&journal_id=gbc Li Z X, Wartho J A, Occhipinti S, et al. Early history of the eastern Sibao Orogen (South China) during the assembly of Rodinia:New mica 40Ar/39Ar dating and SHRIMP U-Pb detrital zircon provenance constraints[J]. Precambrian Research, 2007, 159:79-94. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2007.05.003 Li Z X, Wartho J A, Occhipinti S, et al. Early history of the eastern Sibao Orogen (South China) during the assembly of Rodinia:New mica 40Ar/39Ar dating and SHRIMP U-Pb detrital zircon provenance constraints[J]. Precambrian Research, 2007, 159:79-94. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2007.05.003
Li X H, Li W X, Li Z X, et al. 850-790Ma bimodal volcanic and intrusive rocks in northern Zhejiang, South China:A major episode of continental rift magmatism during the breakup of Rodinia[J]. Lithos, 2008, 102:341-357. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2007.04.007 Li X H, Li W X, Li Z X, et al. 850-790Ma bimodal volcanic and intrusive rocks in northern Zhejiang, South China:A major episode of continental rift magmatism during the breakup of Rodinia[J]. Lithos, 2008, 102:341-357. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2007.04.007
Li W X, Li X H, Li Z X. Middle Neoproterozoic syn-rifting volcanic rocks in Guangfeng, South China:petrogenesis and tectonic signi ficance[J]. Geological Magazine, 2008, 145:475-489. Li W X, Li X H, Li Z X. Middle Neoproterozoic syn-rifting volcanic rocks in Guangfeng, South China:petrogenesis and tectonic signi ficance[J]. Geological Magazine, 2008, 145:475-489.
Li W X, Li X H, Li Z X, et al. Obduction-type granites within the NE Jiangxi Ophiolite:Implications for the final amalgamation between the Yangtze and Cathaysia Blocks[J]. Gondwana Research, 2008, 13:288-301. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2007.12.010 Li W X, Li X H, Li Z X, et al. Obduction-type granites within the NE Jiangxi Ophiolite:Implications for the final amalgamation between the Yangtze and Cathaysia Blocks[J]. Gondwana Research, 2008, 13:288-301. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2007.12.010
Li X H, Li W X, Li Z X, et al. Amalgamation between the Yangtze and Cathaysia Blocks in South China:Constraints from SHRIMP U-Pb Zircon ages, geochemistry and Nd-Hf isotopes of the Shuangxiwu volcanic rocks[J]. Precambrian Research, 2009, 174:117-128. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2009.07.004 Li X H, Li W X, Li Z X, et al. Amalgamation between the Yangtze and Cathaysia Blocks in South China:Constraints from SHRIMP U-Pb Zircon ages, geochemistry and Nd-Hf isotopes of the Shuangxiwu volcanic rocks[J]. Precambrian Research, 2009, 174:117-128. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2009.07.004
Li W X, Li X H, Li Z X. Ca. 850Ma bimodal volcanic rocks in northeastern Jiangxi province, South China:initial extension during the breakup of Rodinia?[J]. American Journal of Science, 2010, 310:951-980. doi: 10.2475/09.2010.08 Li W X, Li X H, Li Z X. Ca. 850Ma bimodal volcanic rocks in northeastern Jiangxi province, South China:initial extension during the breakup of Rodinia?[J]. American Journal of Science, 2010, 310:951-980. doi: 10.2475/09.2010.08
Wang J, Li Z X. History of Neoproterozoic rift basins in South China:implications for Rodinia break-up[J]. Precambrian Research, 2003, 122:141-158. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00209-7 Wang J, Li Z X. History of Neoproterozoic rift basins in South China:implications for Rodinia break-up[J]. Precambrian Research, 2003, 122:141-158. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00209-7
Wang X L, Zhou J C, Qiu J S, et al. Geochemistry of the Meso-to Neoproterozoic basic-acid rocks from Hunan Province, South China:implications for the evolution of the western Jiangnan orogen[J]. Precambrian Research, 2004, 135:79-103. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2004.07.006 Wang X L, Zhou J C, Qiu J S, et al. Geochemistry of the Meso-to Neoproterozoic basic-acid rocks from Hunan Province, South China:implications for the evolution of the western Jiangnan orogen[J]. Precambrian Research, 2004, 135:79-103. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2004.07.006
Wang X L, Zhou J C, Qiu J S, et al. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon geochronology of the Neoproterozoic igneous rocks from Northern Guangxi, South China:Implications for tectonic evolution[J]. Precambrian Research, 2006, 145:111-130. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2005.11.014 Wang X L, Zhou J C, Qiu J S, et al. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon geochronology of the Neoproterozoic igneous rocks from Northern Guangxi, South China:Implications for tectonic evolution[J]. Precambrian Research, 2006, 145:111-130. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2005.11.014
Wang X L, Zhou J C, Griffin W L, et al. Detrital zircon geochronology of Precambrian basement sequences in the Jiangnan orogen:Dating the assembly of the Yangtze and Cathaysia Blocks[J]. Precambrian Research, 2007, 159:117-131. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2007.06.005 Wang X L, Zhou J C, Griffin W L, et al. Detrital zircon geochronology of Precambrian basement sequences in the Jiangnan orogen:Dating the assembly of the Yangtze and Cathaysia Blocks[J]. Precambrian Research, 2007, 159:117-131. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2007.06.005
Wang Q, Wyman D A, Li Z X, et al. Petrology, geochronology and geochemistry of ca. 780Ma A-type granites in South China:Petrogenesis and implications for crustal growth during the breakup of the supercontinent Rodinia[J]. Precambrian Research, 2010, 178:185-208. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2010.02.004 Wang Q, Wyman D A, Li Z X, et al. Petrology, geochronology and geochemistry of ca. 780Ma A-type granites in South China:Petrogenesis and implications for crustal growth during the breakup of the supercontinent Rodinia[J]. Precambrian Research, 2010, 178:185-208. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2010.02.004
Wang X L, Shu L S, Xing G F, et al. Post-orogenic extension in the eastern part of the Jiangnan orogen:Evidence from ca 800-760Ma volcanic rocks[J]. Precambrian Research, 2012, 222/223:404-423. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2011.07.003 Wang X L, Shu L S, Xing G F, et al. Post-orogenic extension in the eastern part of the Jiangnan orogen:Evidence from ca 800-760Ma volcanic rocks[J]. Precambrian Research, 2012, 222/223:404-423. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2011.07.003
Wang Y J, Zhang A M, Cawood P A, et al. Geochronological, geochemical and Nd-Hf-Os isotopic fingerprinting of an early Neoproterozoic arc-back-arc system in South China and its accretionary assembly along the margin of Rodinia[J]. Precambrian Research, 2013, 231:343-371. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2013.03.020 Wang Y J, Zhang A M, Cawood P A, et al. Geochronological, geochemical and Nd-Hf-Os isotopic fingerprinting of an early Neoproterozoic arc-back-arc system in South China and its accretionary assembly along the margin of Rodinia[J]. Precambrian Research, 2013, 231:343-371. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2013.03.020
Wang Y J, Zhang Y Z, Fan W M, et al. Early Neoproterozoic accretionary assemblage in the Cathaysia Block:Geochronological, LuHf isotopic and geochemical evidence from granitoid gneisses[J]. Precambrian Research, 2014, 249:144-161. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2014.05.003 Wang Y J, Zhang Y Z, Fan W M, et al. Early Neoproterozoic accretionary assemblage in the Cathaysia Block:Geochronological, LuHf isotopic and geochemical evidence from granitoid gneisses[J]. Precambrian Research, 2014, 249:144-161. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2014.05.003
Wang J, Zhou X L, Deng Q, et al. Sedimentary successions and the onset of the Neoproterozoic Jiangnan sub-basin in the Nanhua rift, South China[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2015, 104:521-539. doi: 10.1007/s00531-014-1107-5 Wang J, Zhou X L, Deng Q, et al. Sedimentary successions and the onset of the Neoproterozoic Jiangnan sub-basin in the Nanhua rift, South China[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2015, 104:521-539. doi: 10.1007/s00531-014-1107-5
Zheng Y F, Wu R X, Wu Y B, et al. Rift melting of juvenile arcderived crust:Geochemical evidence from Neoproterozoic volcanic and granitic rocks in the Jiangnan Orogen, South China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2008, 163:351-383. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2008.01.004 Zheng Y F, Wu R X, Wu Y B, et al. Rift melting of juvenile arcderived crust:Geochemical evidence from Neoproterozoic volcanic and granitic rocks in the Jiangnan Orogen, South China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2008, 163:351-383. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2008.01.004
Zhou J C, Wang X L, Qiu J S. Geochronology of Neoproterozoic Mafic Rocks and Sandstones from Northeastern Guizhou, South China:Coeval Arc Magmatism and Sedimentation[J]. Precambrian Research, 2009, 170:27-42. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2008.11.002 Zhou J C, Wang X L, Qiu J S. Geochronology of Neoproterozoic Mafic Rocks and Sandstones from Northeastern Guizhou, South China:Coeval Arc Magmatism and Sedimentation[J]. Precambrian Research, 2009, 170:27-42. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2008.11.002
薛怀民, 马芳, 宋永勤, 等.江南造山带东段新元古代花岗岩组合的年代学和地球化学:对扬子与华夏地块拼合时间与过程的约束[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(11):3215-3244. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201011006.htm 王自强, 高林志, 丁孝忠, 等."江南造山带"变质基底形成的构造环境及演化特征[J].地质论评, 2012, 58(3):401-413. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201203002.htm Zhao J H, Zhou M F, Yan D P, et al. Reappraisal of the ages of Neoproterozoic strata in South China:No connection with the Grenvillian orogeny[J]. Geology, 2011, 39(4):299-302. doi: 10.1130/G31701.1 Zhao J H, Zhou M F, Yan D P, et al. Reappraisal of the ages of Neoproterozoic strata in South China:No connection with the Grenvillian orogeny[J]. Geology, 2011, 39(4):299-302. doi: 10.1130/G31701.1
Zhao G C. Jiangnan Orogen in South China:Developing from divergent double subduction[J]. Gondwana Research, 2015, 27:1173-1180. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2014.09.004 Zhao G C. Jiangnan Orogen in South China:Developing from divergent double subduction[J]. Gondwana Research, 2015, 27:1173-1180. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2014.09.004
Li X H, Li Z X, Ge W C, et al. Neoproterozoic granitoids in South China:crustal melting above a mantle plume at ca. 825Ma[J]. Precambrian Research, 2003, 122:45-83. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00207-3 Li X H, Li Z X, Ge W C, et al. Neoproterozoic granitoids in South China:crustal melting above a mantle plume at ca. 825Ma[J]. Precambrian Research, 2003, 122:45-83. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00207-3
Yang C, Li X H, Wang X C, et al. Mid-Neoproterozoic angular unconformity in the Yangtze Block revisited:Insights from detrital zircon U-Pb age and Hf-O isotopes[J]. Precambrian Research, 2015, 266:165-178. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2015.05.016 Yang C, Li X H, Wang X C, et al. Mid-Neoproterozoic angular unconformity in the Yangtze Block revisited:Insights from detrital zircon U-Pb age and Hf-O isotopes[J]. Precambrian Research, 2015, 266:165-178. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2015.05.016
Li Z X, Li X H, Zhou H W, et al. Grencillian continental collision in south China:New SHRIMP U-Pb zircon results and implications for the configuration of Rodinia[J]. Geology, 2002, 30:163-166. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0163:GCCISC>2.0.CO;2 Li Z X, Li X H, Zhou H W, et al. Grencillian continental collision in south China:New SHRIMP U-Pb zircon results and implications for the configuration of Rodinia[J]. Geology, 2002, 30:163-166. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0163:GCCISC>2.0.CO;2
Li X H, Li Z X, Zhou H W, et al. U-Pb zircon geochronology, geochemisty and Nd isotopic study of the Neoproterozoic bimodal volcanic rocks in the Kangdian Rift of South China:implications for the initial rifting of Rodinia[J]. Precambrian Research, 2002, 113:135-154. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(01)00207-8 Li X H, Li Z X, Zhou H W, et al. U-Pb zircon geochronology, geochemisty and Nd isotopic study of the Neoproterozoic bimodal volcanic rocks in the Kangdian Rift of South China:implications for the initial rifting of Rodinia[J]. Precambrian Research, 2002, 113:135-154. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(01)00207-8
Li Z X, Li X H, Kinny P D, et al. Geochronology of Neoproterozoic syn-rift magmatism in the Yangtze Craton, South China and correlations with other continents:evidence for a mantle superplume that broke up Rodinia[J]. Precambrian Research, 2003, 122:85-109. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00208-5 Li Z X, Li X H, Kinny P D, et al. Geochronology of Neoproterozoic syn-rift magmatism in the Yangtze Craton, South China and correlations with other continents:evidence for a mantle superplume that broke up Rodinia[J]. Precambrian Research, 2003, 122:85-109. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00208-5
Li Z X, Bogdanova S V, Collins A S, et al. Assembly, configuration, and break-up history of Rodinia:a synthesis[J]. Precambrian Research, 2008, 160:179-210. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2007.04.021 Li Z X, Bogdanova S V, Collins A S, et al. Assembly, configuration, and break-up history of Rodinia:a synthesis[J]. Precambrian Research, 2008, 160:179-210. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2007.04.021
Wang X C, Li X H, Li W X, et al. Ca. 825Ma komatiitic basalts in South China:first evidence for >1500℃ mantle melts by a Rodinian mantle plume[J]. Geology, 2007, 35:1103-1106. doi: 10.1130/G23878A.1 Wang X C, Li X H, Li W X, et al. Ca. 825Ma komatiitic basalts in South China:first evidence for >1500℃ mantle melts by a Rodinian mantle plume[J]. Geology, 2007, 35:1103-1106. doi: 10.1130/G23878A.1
Wang X C, Li X H, Li W X, et al. The Bikou basalts in northwestern Yangtze Block, South China:remains of 820-810Ma continental flood basalts[J]. Geological Society of American Bulletin, 2008, 120:1478-1492. doi: 10.1130/B26310.1 Wang X C, Li X H, Li W X, et al. The Bikou basalts in northwestern Yangtze Block, South China:remains of 820-810Ma continental flood basalts[J]. Geological Society of American Bulletin, 2008, 120:1478-1492. doi: 10.1130/B26310.1
Zhou M F, Yan D P, Kennedy A K, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronological and geochemical evidence for Neoproterozoic arc-magmatism along the western margin of the Yangtze Block, South China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 196:51-67. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00595-7 Zhou M F, Yan D P, Kennedy A K, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronological and geochemical evidence for Neoproterozoic arc-magmatism along the western margin of the Yangtze Block, South China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 196:51-67. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00595-7
Zhou M F, Kennedy A K, Sun M, et al. Neoproterozoic Arc-Related Mafic Intrusions along the Northern Margin of South China:Implications for the Accretion of Rodinia[J]. The journal of Geology, 2002, 110:611-618. doi: 10.1086/341762 Zhou M F, Kennedy A K, Sun M, et al. Neoproterozoic Arc-Related Mafic Intrusions along the Northern Margin of South China:Implications for the Accretion of Rodinia[J]. The journal of Geology, 2002, 110:611-618. doi: 10.1086/341762
Zhou M F, Ma Y, Yan D P, et al. The Yanbian Terrane (Southern Sichuan Province, SW China):a Neoproterozoic arc assemblage in the western margin of the Yangtze Block[J]. Precambrian Research, 2006, 144:19-38. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2005.11.002 Zhou M F, Ma Y, Yan D P, et al. The Yanbian Terrane (Southern Sichuan Province, SW China):a Neoproterozoic arc assemblage in the western margin of the Yangtze Block[J]. Precambrian Research, 2006, 144:19-38. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2005.11.002
Zhou M F, Yan D P, Wang C L, et al. Subduction-Related Origin of the 750 Ma Xuelongbao Adakitic Complex (Sichuan Province, China):Implications for the Tectonic Setting of the Giant Neoproterozoic Magmatic Event in South China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 248:286-300. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2006.05.032 Zhou M F, Yan D P, Wang C L, et al. Subduction-Related Origin of the 750 Ma Xuelongbao Adakitic Complex (Sichuan Province, China):Implications for the Tectonic Setting of the Giant Neoproterozoic Magmatic Event in South China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 248:286-300. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2006.05.032
Zheng Y F, Zhang S B, Zhao Z F, et al. Contrasting zircon Hf and O isotopes in the two episodes of Neoproterozoic granitoids in South China:Implications for growth and reworking of continental crust[J]. Lithos, 2007, 96:127-150. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2006.10.003 Zheng Y F, Zhang S B, Zhao Z F, et al. Contrasting zircon Hf and O isotopes in the two episodes of Neoproterozoic granitoids in South China:Implications for growth and reworking of continental crust[J]. Lithos, 2007, 96:127-150. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2006.10.003
Zhang C L, Li H K, Santosh M. Revisiting the tectonic evolution of South China:interaction between the Rodinia superplume and plate subduction?[J] Terra Nova, 2013, 25(3):212-220. doi: 10.1111/ter.2013.25.issue-3 Zhang C L, Li H K, Santosh M. Revisiting the tectonic evolution of South China:interaction between the Rodinia superplume and plate subduction?[J] Terra Nova, 2013, 25(3):212-220. doi: 10.1111/ter.2013.25.issue-3
Liu Y S, Zong K Q, Kelemen P B, et al. Geochemistry and magmatic history of eclogites and ultramafic rocks from the Chinese continental scientific drill hole:Subduction and ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism of lower crustal cumulates[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 247(1/2):133-153. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Peter_Kelemen/publication/222191055_Geochemistry_and_magmatic_history_of_eclogues_and_ultramafic_rocks_from_the_Chinese_continental_scientific_drill_hole_Subduction_and_ultrahigh-pressure_metamorphism_of_lower_crustal_cumulates/links/00463525c48397ac5d000000.pdf?origin=publication_detail Liu Y S, Zong K Q, Kelemen P B, et al. Geochemistry and magmatic history of eclogites and ultramafic rocks from the Chinese continental scientific drill hole:Subduction and ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism of lower crustal cumulates[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 247(1/2):133-153. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Peter_Kelemen/publication/222191055_Geochemistry_and_magmatic_history_of_eclogues_and_ultramafic_rocks_from_the_Chinese_continental_scientific_drill_hole_Subduction_and_ultrahigh-pressure_metamorphism_of_lower_crustal_cumulates/links/00463525c48397ac5d000000.pdf?origin=publication_detail
Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Gao S, et al. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 257(1/2):34-43. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Yongsheng_Liu5/publication/222034389_In_situ_analysis_of_major_and_trace_elements_of_anhydrous_minerals_by_LAICPMSLAICPMS_without_applying_an_internal_standard/links/54067d610cf2c48563b2536f.pdf Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Gao S, et al. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 257(1/2):34-43. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Yongsheng_Liu5/publication/222034389_In_situ_analysis_of_major_and_trace_elements_of_anhydrous_minerals_by_LAICPMSLAICPMS_without_applying_an_internal_standard/links/54067d610cf2c48563b2536f.pdf
Hu Z C, Gao S, Liu Y S, et al. Signal enhancement in laser ablation ICP-MS by addition of nitrogen in the central channel gas[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2008, 23:1093-1101. doi: 10.1039/b804760j Hu Z C, Gao S, Liu Y S, et al. Signal enhancement in laser ablation ICP-MS by addition of nitrogen in the central channel gas[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2008, 23:1093-1101. doi: 10.1039/b804760j
Hu Z C, Liu Y S, Gao S, et al. A"wire"signal smoothing device for laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry analysis[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2012, 78:50-57. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2012.09.007 Hu Z C, Liu Y S, Gao S, et al. A"wire"signal smoothing device for laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry analysis[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2012, 78:50-57. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2012.09.007
Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5):635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2 Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5):635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42:313-345. Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and processes[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42:313-345.
Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell B W. A-type granites:geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95:407-419. doi: 10.1007/BF00402202 Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell B W. A-type granites:geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95:407-419. doi: 10.1007/BF00402202
吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等.花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(6):1217-1238. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK199001002.htm Yao J L, Shu L S, Santosh M. Neoproterozoic arc-trench system and breakup of the South China Craton:Constraints from NMORB type and arc-related mafic rocks, and anorogenic granite in the Jiangnan orogenic belt[J]. Precambrian Research, 2014, 247:187-207. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2014.04.008 Yao J L, Shu L S, Santosh M. Neoproterozoic arc-trench system and breakup of the South China Craton:Constraints from NMORB type and arc-related mafic rocks, and anorogenic granite in the Jiangnan orogenic belt[J]. Precambrian Research, 2014, 247:187-207. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2014.04.008
King P L, White A J R, Chappell B W, et al. Characterization and origin of aluminous A-type granites from the Lachlan Fold Belt, southeastern Australia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1997, 38(3):371-391. doi: 10.1093/petroj/38.3.371 King P L, White A J R, Chappell B W, et al. Characterization and origin of aluminous A-type granites from the Lachlan Fold Belt, southeastern Australia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1997, 38(3):371-391. doi: 10.1093/petroj/38.3.371
Chappell B W. Aluminium saturation in I-and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46:535-551. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00086-3 Chappell B W. Aluminium saturation in I-and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46:535-551. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00086-3
王强, 赵振华, 熊小林.桐柏-大别造山带燕山晚期A型花岗岩的厘定[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2000, 19(4):297-306. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200004001.htm Watson E B, Harrison T M. Zircon saturation revisited:temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983, 64:295-304. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(83)90211-X Watson E B, Harrison T M. Zircon saturation revisited:temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983, 64:295-304. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(83)90211-X
Collins W J, Beams S D, White A J, et al. Nature and origin of Atype granite with particular reference to Southeastern Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1982, 8:189-200. Collins W J, Beams S D, White A J, et al. Nature and origin of Atype granite with particular reference to Southeastern Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1982, 8:189-200.
Eby G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids:petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992, 20:641-644. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:CSOTAT>2.3.CO;2 Eby G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids:petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992, 20:641-644. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:CSOTAT>2.3.CO;2
Barbarin B. A review of the relationships between granitoid types:their origins and their geodynamic environments[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46:605-626. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00085-1 Barbarin B. A review of the relationships between granitoid types:their origins and their geodynamic environments[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46:605-626. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00085-1
Wu F Y, Sun D Y, Li H M, et al. A-type granites in northeastern China:age and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 187:143-173. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00018-9 Wu F Y, Sun D Y, Li H M, et al. A-type granites in northeastern China:age and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 187:143-173. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00018-9
Yang J H, Wu F Y, Chung S L, et al. A hybrid origin for Qianshan A-type granite, Northeast China:Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic evidence[J]. Lithos, 2006, 89:89-106. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2005.10.002 Yang J H, Wu F Y, Chung S L, et al. A hybrid origin for Qianshan A-type granite, Northeast China:Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic evidence[J]. Lithos, 2006, 89:89-106. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2005.10.002
汪正江, 王剑, 段太忠, 等.扬子克拉通内新元古代中期酸性火山岩的年代学及其地质意义[J].中国科学(D辑), 2010, 40(11):1543-1551. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201011009.htm 汪正江, 王剑, 谢渊, 等.重庆秀山凉桥板溪群红子溪组凝灰岩SHRIMP锆石测年及其意义[J].中国地质, 2009, 36(4):761-768. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200904003.htm 邓奇, 王剑, 汪正江, 等.扬子北缘西乡群大石沟组和三郎铺组凝灰岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2013, 43(3):797-808. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201303016.htm Yan Q R, Hanson A D, Wang Z Q, et al. Neoproterozoic Subduction and Rifting on the Northern Margin of the Yangtze Plate, China:Implications for Rodinia Reconstruction[J]. International Geology Review, 2004, 46:817-832. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.46.9.817 Yan Q R, Hanson A D, Wang Z Q, et al. Neoproterozoic Subduction and Rifting on the Northern Margin of the Yangtze Plate, China:Implications for Rodinia Reconstruction[J]. International Geology Review, 2004, 46:817-832. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.46.9.817
江新胜, 王剑, 崔晓庄, 等.滇中新元古代澄江组锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学研究及其地质意义[J].中国科学(D辑), 2012, 42(10):1496-1507. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201210005.htm Ernst R E, Wingate M T D, Buchan K L, et al. Global record of 1600-700Ma large igneous provinces (LIPs):Implications for the reconstruction of the proposed Nuna (Columbia) and Rodinia super-continents[J]. Precambrian Research, 2008, 160:159-178. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2007.04.019 Ernst R E, Wingate M T D, Buchan K L, et al. Global record of 1600-700Ma large igneous provinces (LIPs):Implications for the reconstruction of the proposed Nuna (Columbia) and Rodinia super-continents[J]. Precambrian Research, 2008, 160:159-178. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2007.04.019
汪正江, 王剑, 江新胜, 等.华南扬子地区新元古代地层划分对比研究新进展[J].地质论评, 2015, 61(1):1-22. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201501001.htm Wang X L, Zhao G C, Zhou J C, et al. Geochronology and Hf Isotopes of Zircon from Volcanic Rocks of the Shuangqiaoshan Group, South China:Implications for the Neoproterozoic Tectonic Evolution of the Eastern Jiangnan Orogen[J]. Gondwana Research, 2008, 14:355-367. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2008.03.001 Wang X L, Zhao G C, Zhou J C, et al. Geochronology and Hf Isotopes of Zircon from Volcanic Rocks of the Shuangqiaoshan Group, South China:Implications for the Neoproterozoic Tectonic Evolution of the Eastern Jiangnan Orogen[J]. Gondwana Research, 2008, 14:355-367. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2008.03.001
Li Z X, Evans D A D, Zhang S H. A 90° Spin on Rodinia:Possible Causal Links between the Neoproterozoic Supercontinent, Superplume, True Polar Wander and Low-Latitude Glaciation[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 220:409-421. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00064-0 Li Z X, Evans D A D, Zhang S H. A 90° Spin on Rodinia:Possible Causal Links between the Neoproterozoic Supercontinent, Superplume, True Polar Wander and Low-Latitude Glaciation[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 220:409-421. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00064-0
Huang X L, Xu Y G, Li X H, et al. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications of Neoproterozoic, Highly Fractionated A-Type Granites from Mianning, South China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2008, 165:190-204. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2008.06.010 Huang X L, Xu Y G, Li X H, et al. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications of Neoproterozoic, Highly Fractionated A-Type Granites from Mianning, South China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2008, 165:190-204. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2008.06.010
Li X H, Zhu W G, Zhong H, et al. The Tongde Picritic Dikes in the Western Yangtze Block:Evidence for Ca. 800Ma Mantle Plume Magmatism in South China during the Breakup of Rodinia[J]. The Journal of Geology, 2010, 118:509-522. doi: 10.1086/655113 Li X H, Zhu W G, Zhong H, et al. The Tongde Picritic Dikes in the Western Yangtze Block:Evidence for Ca. 800Ma Mantle Plume Magmatism in South China during the Breakup of Rodinia[J]. The Journal of Geology, 2010, 118:509-522. doi: 10.1086/655113
任光明, 庞维华, 孙志明, 等.扬子西缘登相营群基性岩墙锆石U-Pb年代学及岩石地球化学特征[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 40(1):66-79. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201301011.htm 林广春, 李献华, 李武显.川西新元古代基性岩墙群的SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄、元素和Nd-Hf同位素地球化学:岩石成因与构造意义[J].中国科学(D辑):地球科学, 2006, 36(7):630-645. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200607003.htm 李献华, 王选策, 李武显, 等.华南新元古代玄武质岩石成因与构造意义:从造山运动到陆内裂谷[J].地球化学, 2008, 37(4):382-398. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200804011.htm Wang X C, Li X H, Li W X, et al. Variable involvements of mantle plumes in the genesis of mid-Neoproterozoic basaltic rocks in South China:A review[J]. Gondwana Research, 2009, 15:381-395. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2008.08.003 Wang X C, Li X H, Li W X, et al. Variable involvements of mantle plumes in the genesis of mid-Neoproterozoic basaltic rocks in South China:A review[J]. Gondwana Research, 2009, 15:381-395. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2008.08.003
Deng Q, Wang J, Wang Z J, et al. Continental flood basalts of the Huashan Group, northern margin of the Yangtze block-implications for the breakup of Rodinia[J]. International Geology Review, 2013, 55(15):1865-1884. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2013.799257
王剑.华南新元古代裂谷盆地沉积演化--兼论与Rodinia解体的关系[M].北京:地质出版社, 2000. 王剑, 刘宝珺, 潘桂棠.华南新元古代裂谷盆地演化--Rodinia超大陆解体的前奏[J].矿物岩石, 2001, 21(3):135-145. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS200103020.htm 周汉文, 李献华, 王汉荣, 等.广西鹰扬关群基性火山岩的锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].地质论评, 2002, 48(增刊):22-25. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP2002S1005.htm 王剑, 李献华, Duan T Z, 等.沧水铺火山岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及"南华系"底界新证据[J].科学通报, 2003, 48(16):1726-1731. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200316002.htm 周金城, 王孝磊, 邱检生.江南造山带新元古代构造-岩浆演化[M].北京:科学出版社, 2014. 牟传龙, 林仕良, 余谦.四川会理天宝山组U-Pb年龄[J].地层学杂志, 2003, 27(3):216-219. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ200303010.htm 安徽省冶金地质局三三二地质队区测分队. 1:20万祁门幅、屯溪幅区域地质矿产调查报告.1971. 浙江省地质局区域地质测量队. 1:20万衢县幅区域地质矿产调查报告.1969.




 下载:
下载: