Spatial heterogeneity characteristics of ground substrate in hilly area and its impact on vegetation ecology
-
摘要:
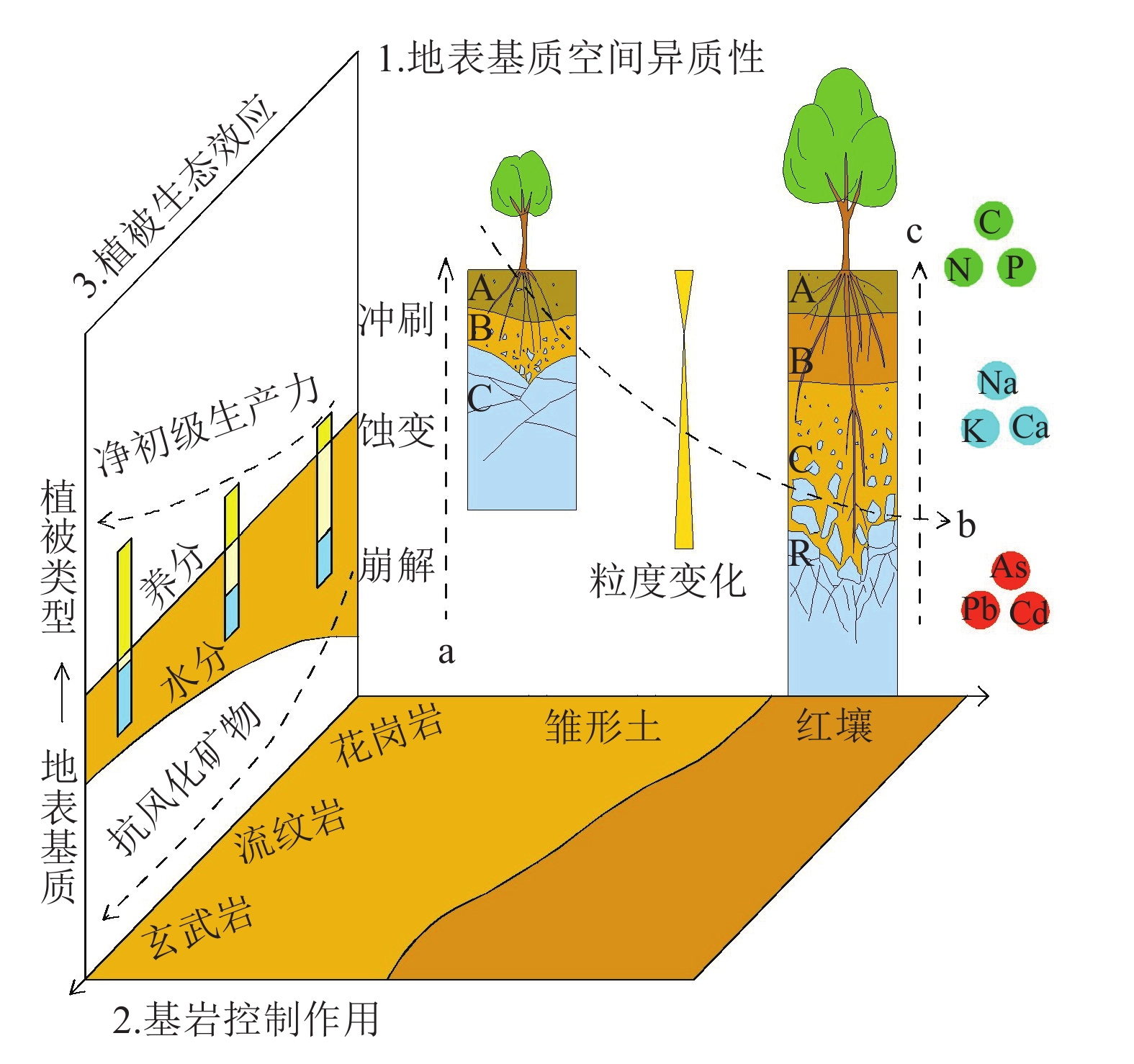
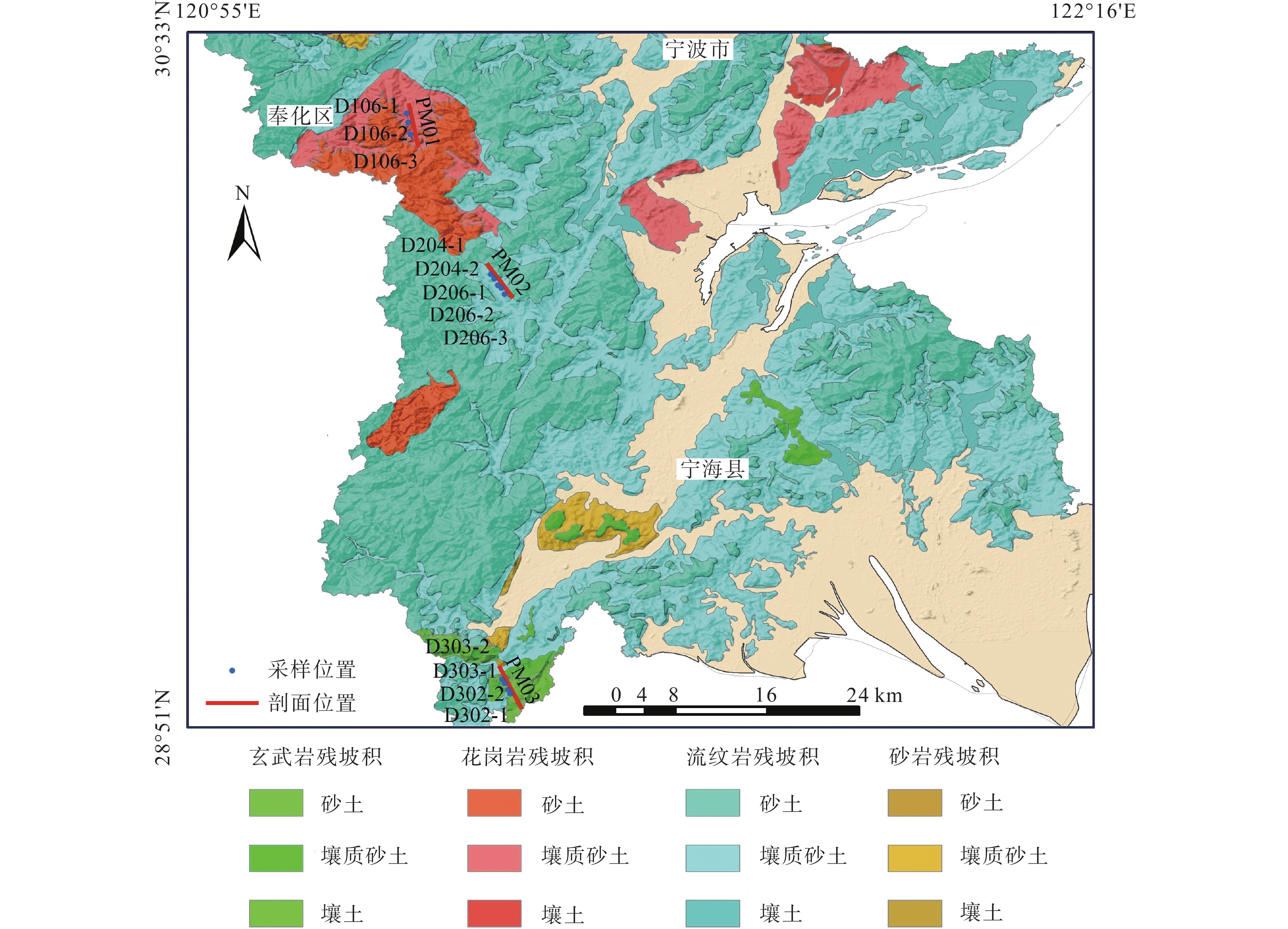
地表基质是地球表层孕育和支撑森林、草原、水、湿地等各类自然资源的基础物质,受地球关键带空间结构、元素特征等因素的影响,山丘区地表基质呈现明显的空间异质性特征,并显著影响着所属植被的空间分布和生态演化。研究地表基质空间异质性特征及其对植被生态的影响机理,对于进一步认识地球关键带结构及地表作用规律,支撑国土空间生态环境修复具有重要意义。以宁波山丘区地表基质为研究对象,采取剖面研究和样品测试的方法,从地表基质空间结构和元素特征角度,对花岗岩、流纹岩和玄武岩3类典型地表基质空间异质性进行了分析。研究发现,花岗岩类具有土质粗、透水性强等特点,流纹岩类具有土质较粗、浅表透气好等特点,玄武岩类具有土质细、通气性差等特点。此外,花岗岩类主量和微量元素较缺乏,流纹岩类富含Mo和Zn,玄武岩类富含Fe、Mg、Co、Cu、Zn等元素,且玄武岩CIA值明显高于花岗岩和流纹岩。结果表明,山丘区地表基质空间异质性主要受基岩的结构和元素组成影响,并对植被生长产生明显的生态效应。地表基质的空间结构主要影响水分的分布与运移,元素特征影响着养分的分布状况,由此引起的水分和养分的空间分布和丰度差异直接影响着植被生长。
Abstract:The ground substrate is the basic material of the Earth's surface layer that nurtures and supports various natural resources such as forests, grasslands, water and wetlands, etc. Influenced by the spatial structure of the Earth's key zones and elemental characteristics, the ground substrate of the hill area presents obvious spatial heterogeneity characteristics, and significantly influences the spatial distribution of the vegetation belonging to it and its ecological evolution.The study of the spatial heterogeneity characteristics of the ground substrate and its impact on vegetation ecology is of great significance for further understanding the structure and surface process laws of the Earth's critical zone, and supporting the restoration of the national territorial space ecological environment. Taking the ground substrate of Ningbo hill area as the research object, this paper analyzes the spatial heterogeneity of three typical surface matrices, namely granite, rhyolite and basalt, from the perspective of the spatial structure and elemental characteristics of the ground substrate by adopting the methods of sectional research and sample testing. It was found that the granite group is characterized by coarse soil and high permeability, the rhyolite group is characterized by coarser soil and good shallow−surface permeability, and the basalt group is characterized by fine soil and poor aeration. In addition, the main trace elements of granite type are deficient, rhyolite type is rich in Mo and Zn, basalt type is rich in Fe, Mg, Co, Cu and Zn, and the CIA value of basalt is significantly higher than that of granite and rhyolite. The results showed that the spatial heterogeneity of the ground substrate in the hilly area was mainly influenced by the structure and elemental composition of the bedrock, and had obvious ecological effects on the growth of vegetation. The spatial structure of the ground substrate mainly affects the distribution and transportation of water, and the elemental characteristics affect the distribution of nutrients, and the resulting differences in the spatial distribution and abundance of water and nutrients have a direct impact on the growth of vegetation.
-
-
表 1 各类指标测定方法
Table 1 Measurement methods for indicators
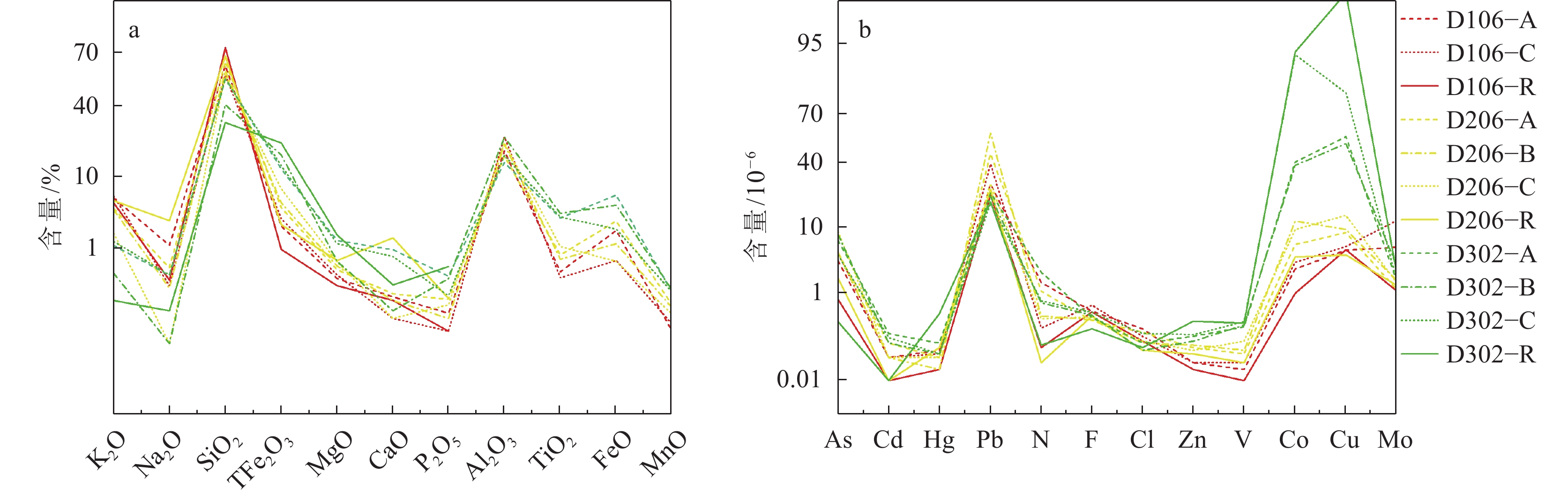
检测项目 分析方法 检测仪器 Al2O3、CaO、K2O、MgO、MnO、Na2O、SiO2、TFe2O3、P2O5、TiO2 X射线荧光光谱法 X射线荧光
光谱仪FeO 基准重铬酸钾溶液滴定 — As、Cd、Co、Cu、
Mo、Pb、V 、Zn电感耦合等离子体质谱法 等离子质谱仪 Cl 粉末压片-X射线
荧光光谱法X射线荧光
光谱仪F 离子选择电极法 离子选择性电极 Hg 蒸汽发生-冷原子荧光
光谱法原子荧光光谱仪 N 凯氏法 — 表 2 地表基质风化强度CIA指数
Table 2 CIA index of weathering strength of surface substrates
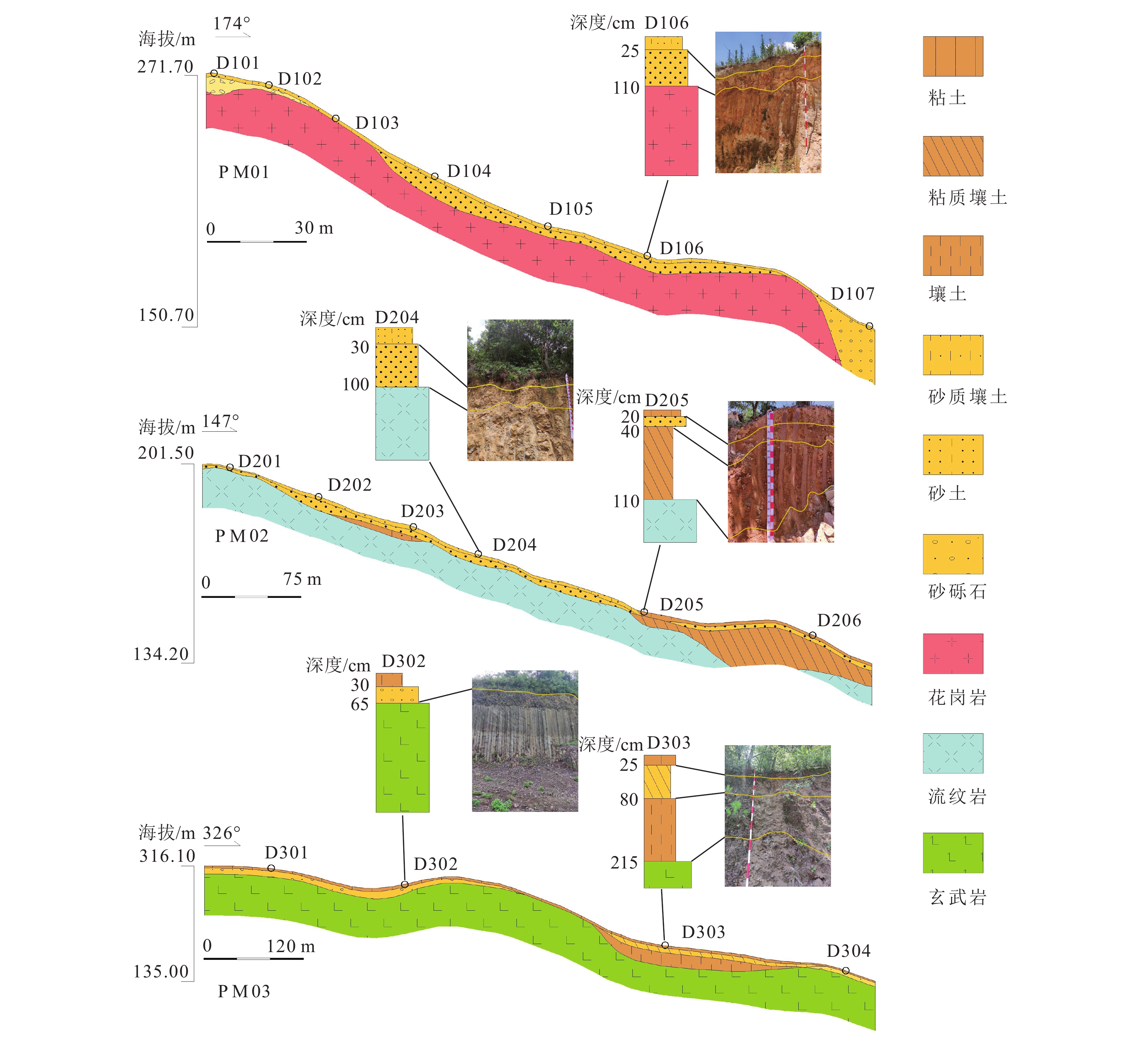
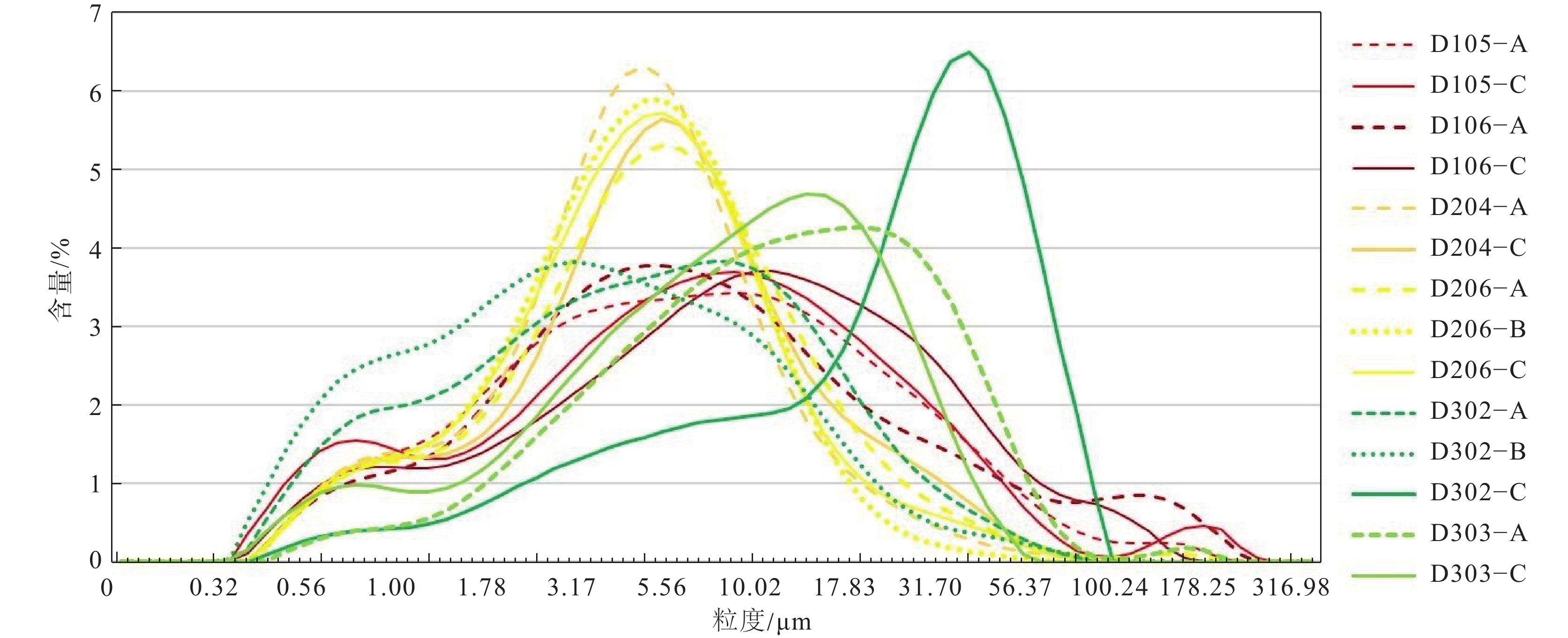
点位 层位 CIA 点位 层位 CIA D106 淋溶层 73.09 D206 淋溶层 77.98 母质层 79.68 淀积层 83.36 D204 淋溶层 74.95 母质层 92.29 母质层 77.03 D302 淋溶层 85.86 D303 淋溶层 97.62 淀积层 87.74 母质层 95.96 母质层 98.26 表 3 三种典型地表基质的植被适宜条件
Table 3 Vegetation suitability conditions for three typical ground substrate
地表基质
类型养分特征 水分制约 优势根系 适宜植被 花岗岩类 缺乏,富K、Mo 深层水分
较丰富垂直根系 松、杉、
灌木等流纹岩类 缺乏—中等,富K、Zn、P 上坡相对缺水,下
坡水分供给丰富垂直根系、辐射根系 槭、栎、竹、茶等多类
植被玄武岩类 多数元素丰富 水分充沛,
中层隔水辐射根系、串珠根系 杉、竹、茶等多类植被 -
Banwart S A, Chorver J, Gaillardet G, et al. 2013. Sustaining earth’s critical zone basic science and interdisciplinary solutions for global challenges[R]. United Kingdom: The University of Sheffield.
Bao Z W. 1992. A geochemical study of the granitoid weathering crust in Southeast China[J]. Geochimica, 21(2): 166−174 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Clair J S, Moon S, Holbrook W S, et al. 2015. Geophysical imaging reveals topographic stress control of bedrock weathering[J]. Science, 350(6260): 534−538. doi: 10.1126/science.aab2210
Ding Y J, Zhang S Q, Han T D, et al. 2014. Opportunities and challenges of studies across land surface processes to land surface system sciences[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 29(4): 443−455 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ge L S, Yang G C. 2020. New field of natural resources survey and monitoring: Ground substrate survey[J]. Natural Resource Economics of China, 33(9): 4−11 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Gu S Y, Wan G J, Miao J Q. 2003. Chemical weathering for dacite in Pingxiang, Guangxi[J]. Geochimica, 32(4): 328−334 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Hu Z L, Pan G X, Li L Q, et al. 2009. Changes in pools and heterogeneity of soil organic carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus under different vegetation types in Karst mountainous area of central Guizhou Province, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 29(8): 4187−4195 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Huang J T, Hou G C, Tao Z P, et al. 2008. Vegetation ecological areas of the Ordos Plateau and their hydrogeological significance[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 27(8): 1330−1334 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Jia L, Liu H, O Y Y, et al. 2022. Division scheme of surface substrate mapping units of mountainous−hilly area in South China based on geological formations research: example from Xinhui−Taishan area in Pearl River Delta[J]. Northwestern Geology, 55(4): 140−157 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Katemaher, Alexis N. 2019. Reactive transport processes that drive chemical weathering: frommaking space for water to dismantling continents[J]. Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 85(1): 349−380. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2018.85.12
Lan X C, Cheng L. 2017. Study on the regionalization of soil and water conservation in Ningbo City[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 15(1): 141−147 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li G, Henry L. 2016. Critical Zone research and observatories: Current status and future perspectives[J]. Vadose Zone Journal, 15(9): 1−14.
Li H, Reynolds J F, et al. 1995. On definition and quantification of heterogeneity[J]. Oikos, 73(2): 280−284. doi: 10.2307/3545921
Li X R. 2005. The impact of spatial heterogeneity changes in arid sandy soil on vegetation restoration[J]. Scientia Sinica(Terrae), (4): 361−370 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li X, Zhou X H, Xiang Z Q. 2023. Simply discussion on the work of ground substrate survey: Taking Hainan Island as an example[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 42(1): 68−75 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lin H. 2010. Earth’s Critical Zone and hydropedology: Concepts, characteristics, and advances[J]. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci., 14: 25−45. doi: 10.5194/hess-14-25-2010
Liu C Y, He M C. 2011. Research on the sensitive chemical weathering indices to rock weathering[J]. Earth and Environment, 39(3): 349−354 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu C. 2015. The mechanisms by grazing on grassland plant and soil spatial heterogeneity and their correlation[D]. Doctoral Dissertation of Northeast Normal University (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu L Y, Bian Z Q, Ding S Y. 2018. Effects of landscape spatial heterogeneity on the generation and provision of ecosystem services[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(18): 6412−6421 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu S, Li P, Feng Z. 2019. Eco−restoration research progress and strategy about wind−break and sand−fixation forest in BeiJing−TianJin−Hebei Metropolitan Region[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(1): 267−274 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Z, Huang X K, Xu H L, et al. 2020. Migration characteristics of elements in the rock−soil system and suitability evaluation of orange planting in Yaqueling area, Yichang, Hubei Province[J]. Geology in China, 47(6): 1853−1868.
Luo S, Zhang D M, Lu D B, et al. 2021. Evaluation of trace elements abundance and deficiency in cultivated soil and its influencing factors in Bijie City of Wumeng Mountain[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 40(9): 1570−1583 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ma T, Shen S, Deng Y M, et al. 2020. Theoretical approaches of survey on Earth's Critical Zone in basin: An example from Jianghan Plain, Central Yangtze River[J]. Earth Science, 45(12): 4498−4511 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ministry of Natural Resources. 2020. Notice of the general office of the ministry of natural resources printing and distributing “The ground substrate classification scheme (trial)”[EB/OL]. (2020-12-22) [2024-01-09]. http://gi.mnr.gov.cn/202012/t202012222596025.html (in Chinese).
Ministry of Natural Resources. 2020. Notice of the ministry of natural resources on issuing the overall plan for the construction of the Natural Resources Investigation and Monitoring System[EB/OL]. (2020-01-17) [2024-01-09]. http://gi.mnr.gov.cn/202001/t20200117_2498071.html (in Chinese).
Ning X B, Xiang W H, Fang X, et al. 2009. Chemical element concentration in calcite, calcareous soil and plants on the rocky desertification area in Huaxi, Guiyang[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 45(5): 34−41 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Pei X L, Han X L, Qian J L, et al. 2020. Soil fertility assessment indicators from the perspective of natural resources comprehensive observation[J]. Resources Science, 42(10): 1953−1964 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Priscia O, Jerôme V, Bernard D, et al. 1999. The effect of organic matter on chemical weathering: study of a small tropical watershed: nsimi−zoétélé site, cameroon[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 63(23): 4013−4035.
Richter D J, Mobley M. 2009. Monitoring earth’s critical zone[J]. Science, 326(20): 1067−1068.
Roering J J, Marshall J, Booth A M, et al. 2010. Evidence for biotic controls on topography and soil production[J]. Earth Planet Sci. Lett., 298: 183−190. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2010.07.040
Russell C P, Clifford R S, Leonard S S, et al. 2022. Forest vulnerability to drought controlled by bedrock composition[J]. Nature Geoscience, 9(15): 714−719.
Shao F L. 2012. Study on spatial heterogeneity relationship of vegetation structure and soil components in typical forest of northern Hebei mountains[D]. Doctoral Dissertation of Beijing Forestry University (in Chinese with English abstract).
Sharma A, Rajamani V. 2000. Weathering of gneissic rocks in the upper reaches of Cauvery river, south India: Implications to neotectonics of the region[J]. Chemical Geology, 166(3/4): 203−223. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00222-3
Shu L S. 2012. An analysis of principal features of tectonic evolution in South China Block[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 31(7): 1035−1053 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Titus J H, Nowak R S, Smith S D. 2002. Soil resource heterogeneity in the Mojave Desert[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 52(3): 269−292. doi: 10.1006/jare.2002.1010
Wang Z L, Wei Z G, Tao Y, et al. 2002. Distribution, migration and accumulation of rare earth elements (REE) in the rock−soil−Dicranopteris dichotoma (RSD) system[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 21(12): 881−889 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Z S, Zhang K B, Wang X. 2015. Spatial heterogeneity of vegetation in artificially fenced area in Liuyangpu of Yanchi County in Ningxia[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 13(5): 52−57 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xavier Z R, Jennifer M, Laura R, et al. 2015. Climatic and landscape controls on water transit times and silicatemineral weathering in the critical zone[J]. Water Resources Research, 51(8): 6036−6051. doi: 10.1002/2015WR017018
Xu W M, Song C Y, Li Q M. 2015. Relationship between soil resource heterogeneity and tree diversity in Xishuangbanna Tropical Seasonal Rainforest, Southwest China[J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 35(23): 7756−7762 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang S H, Song X D, Wu H Y, et al. 2024. A review and discussion on the Earth’s Critical Zone research: Status quo and prospect[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 61(2): 308−318 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yao X F, Yang J F, Zuo L Y, et al. 2022. Discussion on connotation and survey strategy of the ground substrate[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 41(12): 2097−2105 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yin Z Q, Hao A B, Wu A M, et al. 2022. The key progress in Chengde and the national proposal of the integrated survey of natural resources[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 41(12): 2087−2096 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yin Z Q, Qin X G, Zhang S J, et al. 2020. Preliminary study on classification and investigation of surface substrate[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 47(6): 8−14 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yu M G, Hong W T, Yang Z L, et al. 2021. Classification of Yanshanian volcanic cycle and the related mineralization in the coast area of southeastern China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 40(6): 845−863 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang G L, Song X D, Wu K N. 2021. A classification scheme for Earth’s Critical Zones and its application in China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 51(10): 1681−1692 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang G L, Wang Q B, Zhang F R, et al. 2013. Criteria for establishment of soil family and soil series in Chinese soil taxonomy[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 50(4): 826−834 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Z Y. 2017. Spatial distribution of vegetation and soil in temperate savanna ecosystem, Inner Mongolia[D]. Doctoral Dissertation of Chinese Academy of Forestry (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao J F, Liang Z M, Liu J T, et al. 2022. Variable runoff generation layer distributed hydrological model for hilly regions[J]. Advances in Water Science, 33(3): 429−441 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Q, Li T T, Zhang Q D. 2020. Soil nutrients'spatial heterogeneity and effects on vegetation distribution in Taiyue mountain[J]. Journal of Shanxi Normal University Natural Science Edition, 34(1): 79−84 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao X J, Wu T S, Zhong X Y, et al. 2020. Comprehensive evaluation of ecological risk of farmland soil in typical karst area of Guangxi area with high heavy metal background[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 48(22): 252−261 (in Chinese with English abstract).
包志伟. 1992. 华南花岗岩风化壳稀土元素地球化学研究[J]. 地球化学, 21(2): 166−174. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1992.02.008 丁永建, 张世强, 韩添丁, 等. 2014. 由地表过程向地表系统科学研究跨越的机遇与挑战[J]. 地球科学进展, 29(4): 443−455. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2014.04.0443 葛良胜, 杨贵才. 2020. 自然资源调查监测工作新领域: 地表基质调查[J]. 中国国土资源经济, 33(9): 4−11. 顾尚义, 万国江, 毛健全. 2003. 广西凭祥英安岩的化学风化作用研究[J]. 地球化学, 32(4): 328−334. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2003.04.004 胡忠良, 潘根兴, 李恋卿, 等. 2009. 贵州喀斯特山区不同植被下土壤C、N、P含量和空间异质性[J]. 生态学报, 29(8): 4187−4195. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.08.021 黄金廷, 侯光才, 陶正平, 等. 2008. 鄂尔多斯高原植被生态分区及其水文地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 27(8): 1330−1334. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.08.032 贾磊, 刘洪, 欧阳渊, 等. 2022. 基于地质建造的南方山地−丘陵区地表基质填图单元划分方案——以珠三角新会—台山地区为例[J]. 西北地质, 55(4): 140−157. 蓝雪春, 程岚. 2017. 宁波市水土保持区划研究[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 15(1): 141−147. 李响, 周效华, 相振群, 等. 2023. 地表基质调查的工作思路刍议: 以海南岛为例[J]. 地质通报, 42(1): 68−75. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2023.01.006 李新荣. 2005. 干旱沙区土壤空间异质性变化对植被恢复的影响[J]. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学), (4): 361−370. 刘晨. 2015. 放牧对草地植被、土壤空间异质性及其相互关系的调控机制[D]. 东北师范大学博士学位论文. 刘成禹, 何满潮. 2011. 对岩石风化程度敏感的化学风化指数研究[J]. 地球与环境, 39(3): 349−354. 刘绿怡, 卞子亓, 丁圣彦. 2018. 景观空间异质性对生态系统服务形成与供给的影响[J]. 生态学报, 38(18): 6412−6421. 刘硕, 李品, 冯兆忠. 2019. 京津冀防风固沙植被生态修复研究进展与对策[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(1): 267−274. 刘孜, 黄行凯, 徐宏林, 等. 2020. 湖北宜昌鸦鹊岭地区岩石−土壤元素迁移特征及柑橘种植适宜性评价[J]. 中国地质, 47(6): 1853−1868. doi: 10.12029/gc20200620 骆珊, 张德明, 卢定彪, 等. 2021. 乌蒙山区毕节市耕地土壤微量元素丰缺评价及其影响因素[J]. 地质通报, 40(9): 1570−1583. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2021.09.016 马腾, 沈帅, 邓娅敏, 等. 2020. 流域地球关键带调查理论方法: 以长江中游江汉平原为例[J]. 地球科学, 45(12): 4498−4511. 宁晓波, 项文化, 方晰, 等. 2009. 贵阳花溪石灰岩、石灰土与定居植物化学元素含量特征[J]. 林业科学, 45(5): 34−41. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7488.2009.05.005 裴小龙, 韩小龙, 钱建利, 等. 2020. 自然资源综合观测视角下的土壤肥力评价指标[J]. 资源科学, 42(10): 1953−1964. 邵方丽. 2012. 冀北山地典型森林植被与土壤成分的空间异质性关系研究[D]. 北京林业大学博士学位论文. 舒良树. 2012. 华南构造演化的基本特征[J]. 地质通报, 31(7): 1035−1053. 汪振立, 魏正贵, 陶冶, 等. 2002. 岩石−土壤−铁芒萁系统中稀土元素的分布、迁移和累积[J]. 地质通报, 21(12): 881−889. 王志述, 张克斌, 王晓. 2015. 盐池柳杨堡人工封育区植被空间异质性[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 13(5): 52−57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3007.2015.05.008 徐武美, 宋彩云, 李巧明. 2015. 西双版纳热带季节雨林土壤养分空间异质性对乔木树种多样性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 35(23): 7756−7762. 杨顺华, 宋效东, 吴华勇, 等. 2024. 地球关键带研究评述: 现状与展望[J]. 土壤学报, 61(2): 308−318. 姚晓峰, 杨建锋, 左力艳, 等. 2022. 地表基质的内涵辨析与调查思路[J]. 地质通报, 41(12): 2097−2105. 殷志强, 郝爱兵, 吴爱民, 等. 2022. 承德自然资源综合调查主要进展与全国自然资源综合调查总体思路[J]. 地质通报, 41(12): 2087−2096. 殷志强, 秦小光, 张蜀冀, 等. 2020. 地表基质分类及调查初步研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 47(6): 8−14. 余明刚, 洪文涛, 杨祝良, 等. 2021. 东南沿海燕山期火山活动旋回划分及其成矿规律[J]. 地质通报, 40(6): 845−863. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2021.06.003 张甘霖, 宋效东, 吴克宁. 2021. 地球关键带分类方法与中国案例研究[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 51(10): 1681−1692. 张甘霖, 王秋兵, 张凤荣, 等. 2013. 中国土壤系统分类土族和土系划分标准[J]. 土壤学报, 50(4): 826−834. doi: 10.11766/trxb201303180124 张志永. 2017. 内蒙古温带疏林草地生态系统植被−土壤的空间分异特征研究[D]. 中国林业科学研究院博士学位论文. 赵建飞, 梁忠民, 刘金涛, 等. 2022. 山丘区变动产流层分布式水文模型[J]. 水科学进展, 33(3): 429−441. 赵倩, 李婷婷, 张钦弟. 2020. 太岳山植物群落土壤养分空间异质性及其对植被分布的影响[J]. 山西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 34(1): 79−84. 赵辛金, 吴天生, 钟晓宇, 等. 2020. 广西典型岩溶区重金属高背景区农田土壤生态风险综合评价[J]. 江苏农业科学, 48(22): 252−261. 自然资源部. 2020a. 自然资源部关于印发《自然资源调查监测体系构建总体方案》的通知[EB/OL]. (2020-01-17) [2024-01-09]. http://gi.mnr.gov.cn/202001/t20200117_2498071.html. 自然资源部. 2020b. 自然资源部办公厅印发《地表基质分类方案(试行)》的通知[EB/OL]. (2020-12-22) [2024-01-09]. http://gi.mnr.gov.cn/202012/t202012222596025.html.



 下载:
下载: