Automatic recognition of sedimentary microfacies based on Adaboost algorithm: Taking the Shanxi Formation in Q zone of Longdong gas field as an example
-
摘要:
在油气田开发中,沉积微相识别对于明确沉积背景及单砂体刻画起着重要的作用。陇东气田地质条件复杂,主力气藏深度大、产层单一,仅山1段底部产气,对于多种资料交叉共同分析沉积微相,仅依靠人工判别沉积微相,过程复杂且容易出错,很难在沉积微相和测井数据之间建立精确的对应关系。为了充分利用测井资料,提高沉积微相划分的效率,提出一种基于Adaboost算法的沉积微相自动识别方法,为后期气田开发沉积背景及单砂体刻画提供更准确的依据。在研究中,对测井曲线进行优选,并进行预处理,运用数学统计法提取了6个特征参数作为训练的输入集,把沉积微相的类型作为训练的输出结果标签,从已解释的沉积微相数据中选取共1210组作为训练样本,其中组建的训练样本共约968组,组建测试样本242组。研究结果显示,应用该方法的训练效果和测试结果的准确性分别达到96.45%,90.4%,可以验证该方法在陇东气田Q区应用效果较好。
-
关键词:
- 沉积微相 /
- Adaboost算法 /
- 测井 /
- 自动识别 /
- 陇东气田
Abstract:In oil and gas field development, sedimentary micro-phase identification plays an important role in clarifying the sedimentary background and single sand body delineation. Only the bottom of Shan 1 section produces gas. For the analysis of sedimentary microfacies through multiple data intersections, relying solely on manual discrimination of sedimentary microfacies is a complex and error prone process, making it difficult to establish an accurate correspondence between sedimentary microfacies and logging data. Therefore, in order to make full use of the logging data and improve the efficiency of sediment microphase delineation, this paper proposes an automatic identification of sediment microphases based on Adaboost algorithm to provide a more accurate basis for sediment background and single sand body delineation for later gas field development. In the study, optimization and preprocessing of logging curves were carried out, and six feature parameters were extracted using mathematical statistical methods as the input set for training. The type of sedimentary microfacies was used as the output result label for training, and a total of 1210 groups are selected as training samples from the interpreted sedimentary microphase data, of which a total of about 968 groups of training samples are formed and 242 groups of test samples are formed. The results of the study show that the accuracy of the training results and test results of the application of the method reaches 96.45% and 90.4%, respectively, which can be verified that the method is better applied in Q area of Longdong gas field.
-
-
表 1 不同机器学习方法分析
Table 1 Analysis of different machine learning methods
机器学习
方法算法原理 优点 局限性 BP神经
网络通过自身的训练,学习某种规则,在给定
输入值时得到最接近期望输出值的结果是具有很强的非线性映射能力和柔性的网络结构 学习速度慢,容易陷入局部极小值,网络层数、神经元个数的选择没有相应的理论指导,网络推广能力有限 K-means
算法输入聚类个数k及包含 n个数据对象的
数据库,输出满足方差最小标准k个
聚类的一种算法根据较少的已知聚类样本的类别对树进行剪枝
确定部分样本的分类,具有优化迭代功能,针对部分
小样本可以降低总的聚类时间复杂度K值的选定难,初始聚类中心的选择不准确,当数据量大的时候,算法消耗时间久 贝叶斯算法 利用已知的先验概率和新的观测数据
来更新后验概率,最后实现分类的处理高维数据和缺失数据,具有良好的
泛化能力和鲁棒性是基于独立性假设,现实中预测问题很难完全独立 支持向
量机对数据进行二元分类的广义线性分类器 在高维空间中非常高效,即使在数据维度比样本
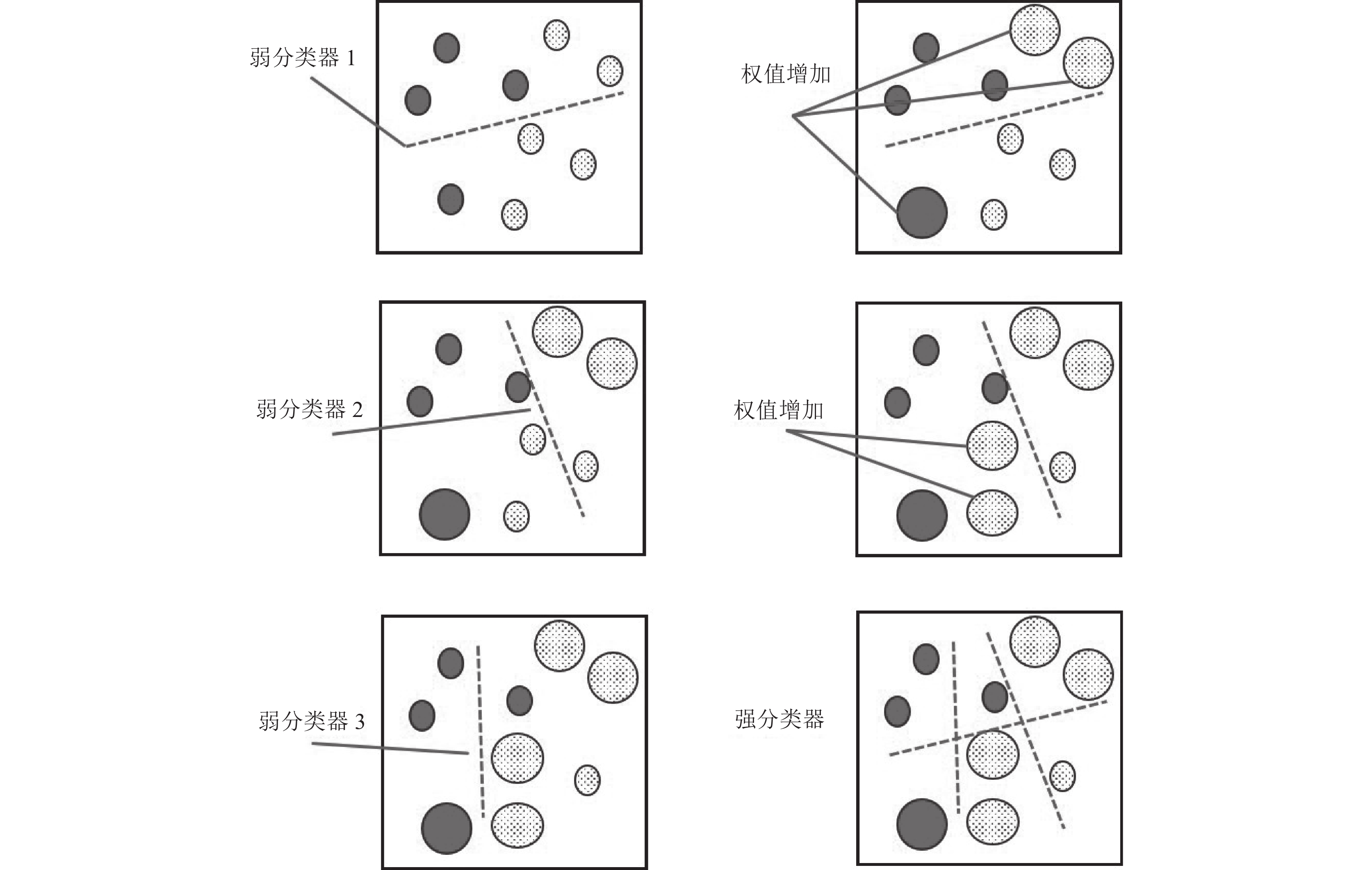
数量大的情况下仍然有效对大量的训练样本进行分类很困难,而且参数调整的过程很繁琐 Adaboost算法 是一种二元分类器,从弱分类器的
线性组合中构建一个强分类器训练集样本的权重更偏向于难以识别的样本,
为了得到下一个最弱的分类器,对被误分类的样本
进行进一步的学习,直到样本被正确分类得到强分类器的过程需要时间 表 2 研究区三角洲前缘亚相的伽马测井曲线类型
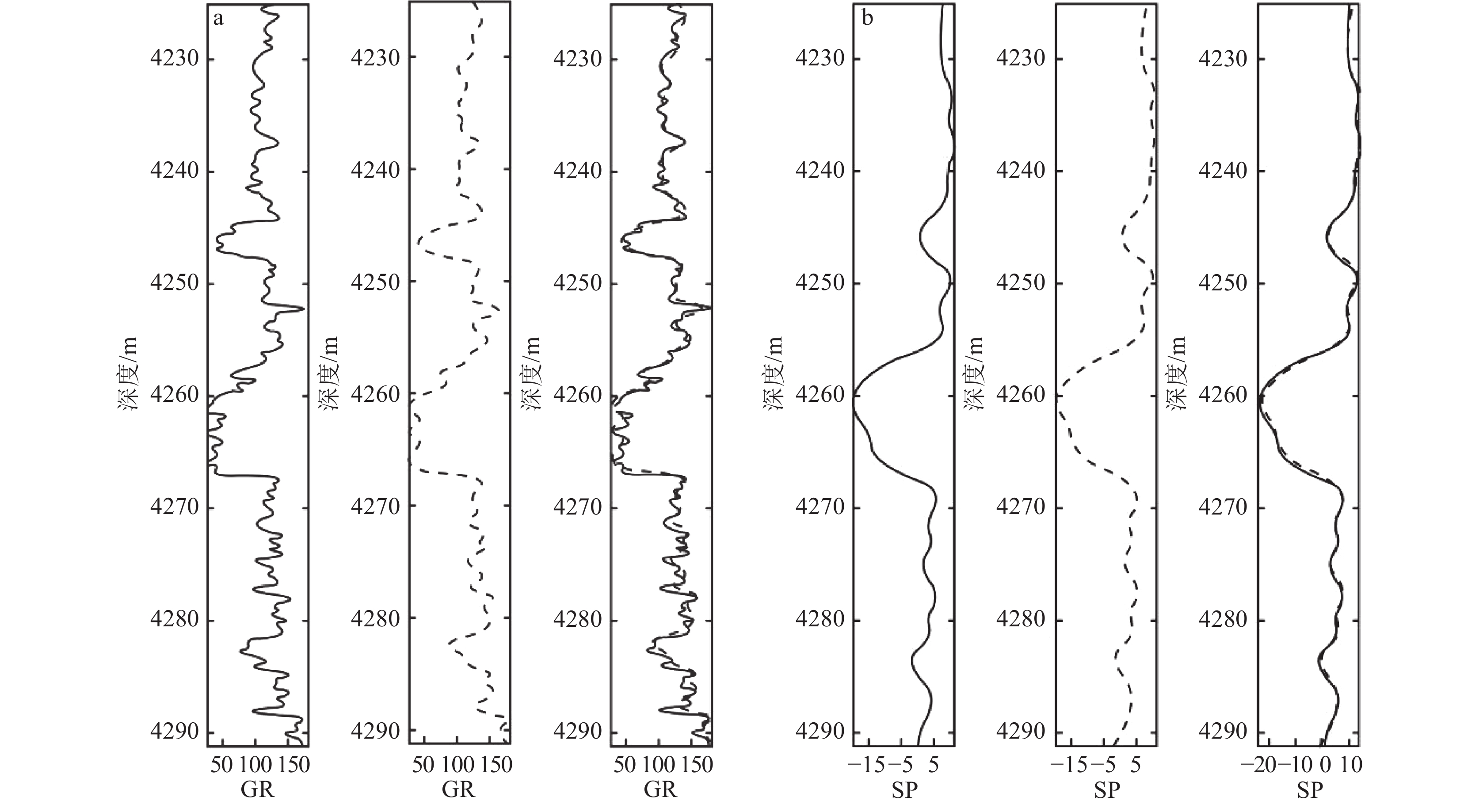
Table 2 Gamma logging curve types of delta front subfacies in the study area
曲线形态 箱形 漏斗形 钟形 下部漏斗形,上部为钟形 呈低幅微齿状 微相类型 水下分流河道 河口坝 分流河道侧翼 前缘席状砂 分流间湾 曲线 表 3 山1段三角洲前缘相测井曲线数值范围
Table 3 Numerical range of logging curves for delta front facies in Shan 1 section
沉积微相 测井曲线数值范围 自然电位/ mV 自然伽马/ API 深侧向电阻率/ (Ω·m) 浅侧向电阻率/ (Ω·m) 水下分流河道 −30.4 ~ −20.3 24.3 ~ 52.1 15.17 ~ 63.14 14.25 ~ 66.34 河口坝 −20.6 ~ −6.8 68.5 ~ 124.6 14.99 ~ 25.02 15.19 ~ 24.87 席状砂 −25.3 ~ 2.7 50.6 ~ 108.2 8.31 ~ 63.85 8.38 ~ 56.15 分流河道侧翼 −15.7 ~ 6.9 43.2 ~ 118.5 23.77 ~ 220.32 20.96 ~ 224.814 分流间湾 10.4 ~ 30.7 101.3 ~ 168.5 13.67 ~ 31.24 12.93 ~ 28.91 表 4 山1段各类沉积微相自然伽马特征参数平均值
Table 4 Average values of natural gamma characteristic parameters for various sedimentary microfacies in Shan 1 section
沉积微相 测井平均值V 相对重心W 变差方差根GS 平均斜率K 水下分流河道 0.41 0.48 0.27 0.059 河口坝 0.57 0.63 0.26 0.037 席状砂 0.52 0.47 0.28 0.087 分流河道侧翼 0.51 0.35 0.32 0.027 分流间湾 0.50 0.48 0.26 0.106 表 5 模型部分预测结果
Table 5 Model part prediction results
井名 V W GS K GR平均值 沉积微相 预测结果 Q1 0.52 0.41 0.30 −0.17 52.06 水下分流河道 水下分流河道 Q10 0.54 0.38 0.29 0.04 70.77 分流河道侧翼 分流河道侧翼 Q10 0.54 0.68 0.32 0.10 110.70 河口坝 河口坝 Q12 0.58 0.63 0.28 −0.03 88.53 河口坝 河口坝 Q12 0.52 0.32 0.91 0.04 81.36 分流河道侧翼 分流河道侧翼 Q12 0.50 0.57 0.24 −0.01 117.54 分流间湾 分流间湾 Q15 0.40 0.56 0.25 −0.01 37.94 水下分流河道 水下分流河道 Q15 0.72 0.60 0.20 −0.11 135.96 河口坝 分流间湾 Q22 0.59 0.66 0.32 0.01 103.27 河口坝 河口坝 Q27 0.47 0.60 0.23 0.08 45.59 水下分流河道 水下分流河道 Q27 0.47 0.60 0.23 0.08 45.59 水下分流河道 水下分流河道 Q27 0.42 0.63 0.23 −0.10 88.64 河口坝 河口坝 Q30 0.29 0.65 0.26 0.03 30.53 水下分流河道 水下分流河道 Q30 0.59 0.42 0.29 0.03 124.30 分流间湾 河口坝 Q20 0.29 0.27 0.28 −0.05 72.14 分流河道侧翼 分流河道侧翼 Q20 0.56 0.53 0.23 −0.08 126.05 分流间湾 分流间湾 Q24 0.49 0.52 0.27 0.05 27.31 水下分流河道 水下分流河道 Q25 0.50 0.59 0.25 0.01 33.47 水下分流河道 水下分流河道 Q26 0.44 0.52 0.27 −0.06 127.18 分流间湾 分流间湾 Q23 0.40 0.64 0.27 −0.04 41.28 水下分流河道 水下分流河道 Q13 0.49 0.60 0.22 0.03 111.67 河口坝 河口坝 Q18 0.42 0.44 0.31 0.01 153.23 分流间湾 分流间湾 Q19 0.18 0.42 0.25 0.02 28.76 水下分流河道 水下分流河道 Q19 0.47 0.59 0.26 0.07 151.07 分流间湾 分流间湾 Q6 0.62 0.61 0.25 0.05 79.87 河口坝 河口坝 -
Bhattacharya S, Mishra S. 2018. Applications of machine learning for facies and fracture prediction using bayesian network theory and random forest: Case studies from the Appalachian basin, USA[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 170: 1005−1017.
Li L Y, Wei J C, Yin H Y, et al. 2018 . Influence of sedimentary facies on reservoir quality and distribution of diagenetie feantures in the Funing Formation, Wanglong Zhuang oilfield, Subei Basin , Eastern China [J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 11: 432.
曹莹, 苗启广, 刘家辰, 等. 2013. AdaBoost算法研究进展与展望[J]. 自动化学报, 39(6): 745−758. 陈欢庆, 朱筱敏. 2008. 精细油藏描述中的沉积微相建模进展[J]. 地质科技情报, (2): 73−79. 陈靖. 2022. 基于录测井资料的沉积微相定量识别方法研究——以渤中26-X构造为例[J]. 石油地质与工程, 36(5): 21−27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2022.05.004 国景星, 陈铭. 2018. 基于支持向量机的浊积扇沉积微相自动识别[J]. 甘肃科学学报, 30(2): 25−31. 韩文龙, 王延斌, 高向东, 等. 2016 . 基于BP神经网络的沉积微相识别[J]. 煤炭技术. 35(12): 114−116. 韩玉娇. 2022. 基于AdaBoost机器学习算法的大牛地气田储层流体智能识别[J]. 石油钻探技术, 50(1): 112−118. 李艳华, 王红涛, 王鸣川, 等. 2017 . 基于PCA和KNN的碳酸盐岩沉积相测井自动识别[J]. 测井技术, 41(1): 57−63. 梁云, 门昌骞, 王文剑. 2023. 基于模型决策树的AdaBoost算法[J]. 山东大学学报(理学版), 58(1): 67−75. 罗歆, 闫建平, 王军, 等. 2023. 基于FMI图像深度学习的砂砾岩体沉积微相识别方法——以东营凹陷北带Y920区块沙四上亚段为例[J]. 沉积学报, 41(4): 1138−1152. 罗仁泽, 周洋, 康丽侠, 等. 2022. 基于DMC-BiLSTM的沉积微相智能识别方法[J]. 石油物探, 61(2): 253−261, 338. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2022.02.007 邱晨, 闫建平, 钟光海, 等. 2023 . 深层页岩气地层沉积微相细分类型测井识别与应用——以四川盆地泸州地区五峰组−龙马溪组为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 34(3): 1−13. 苏建龙, 蒲勇, 缪志伟, 等. 2020. 元坝地区灯影组四段丘滩体相控储层预测[J]. 石油物探, 59(4): 607−615. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2020.04.011 王宇喆. 2017. Sufyan油田AbuGabra组沉积微相识别方法[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 36(3): 44−48. 夏辉, 王龙, 张道锋, 等. 2022. 鄂尔多斯盆地庆阳气田二叠系山西组1段层序结构与沉积演化及其控制因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 43(6): 1397−1412, 1488. 赵忠军, 刘烨, 王凤琴, 等. 2016 . 基于支持向量机的辩状河测井沉积微相识别[J]. 测井技术, 40(5) : 637−642. 张苗燕. 2018 .基于Adaboost的铁路扣件完损性检测方法研究[D].兰州交通大学硕士学位论文. -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 杨旭明,文鹏帆,张春亢,张显云,康雅敬. 基于GTWR-LightGBM模型的京津冀地区近地面SO2浓度估算. 环境科学与技术. 2024(10): 204-215 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 叶烨,叶晗迪,鲍杰利. 基于改进Adaboost算法的分布式光伏发电孤岛检测方法. 机电技术. 2024(05): 14-17+33 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: