Evaluation on geological suitability of development and utilization of underground space resources in Xiong’an New Area
-
摘要:
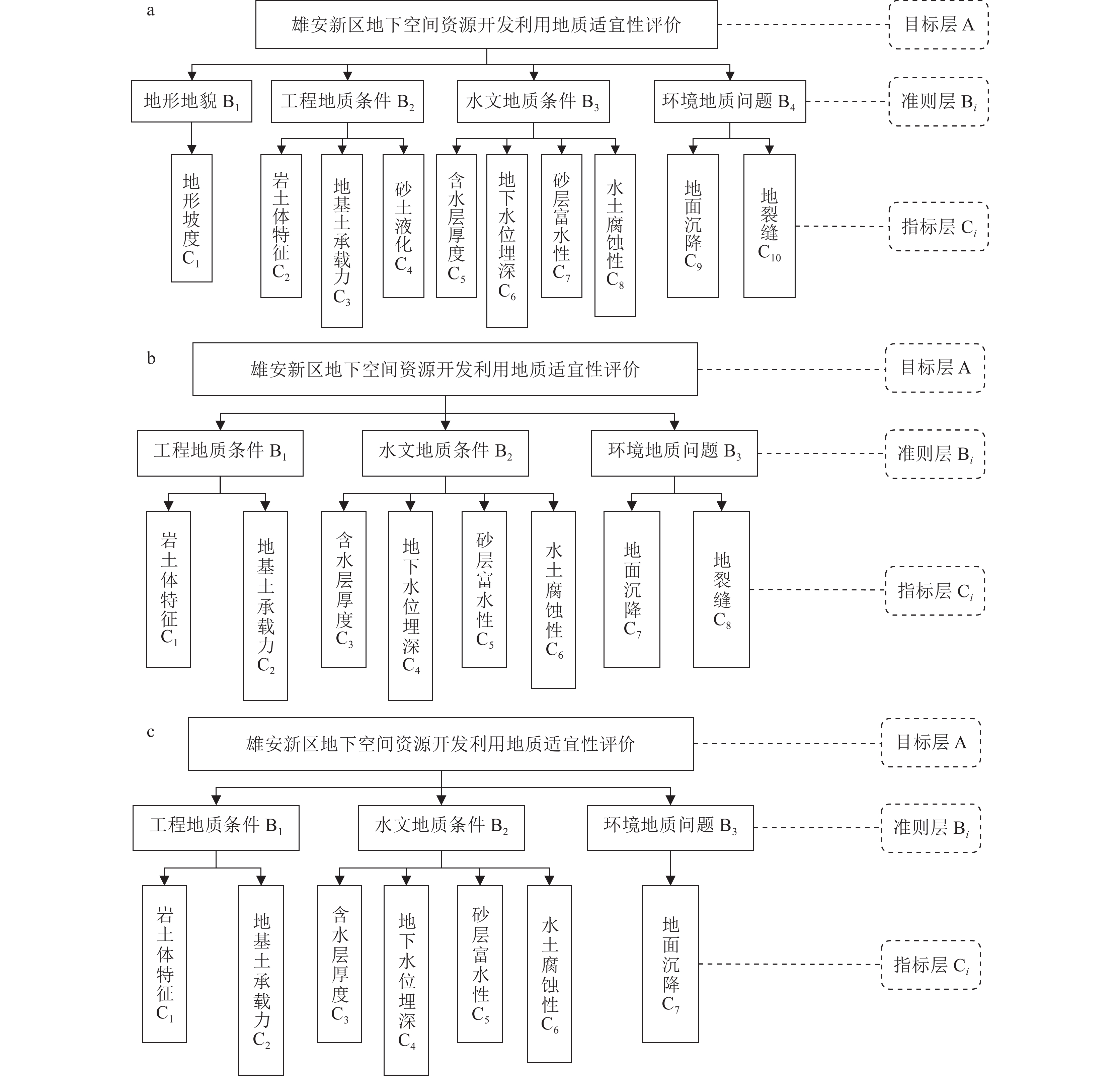
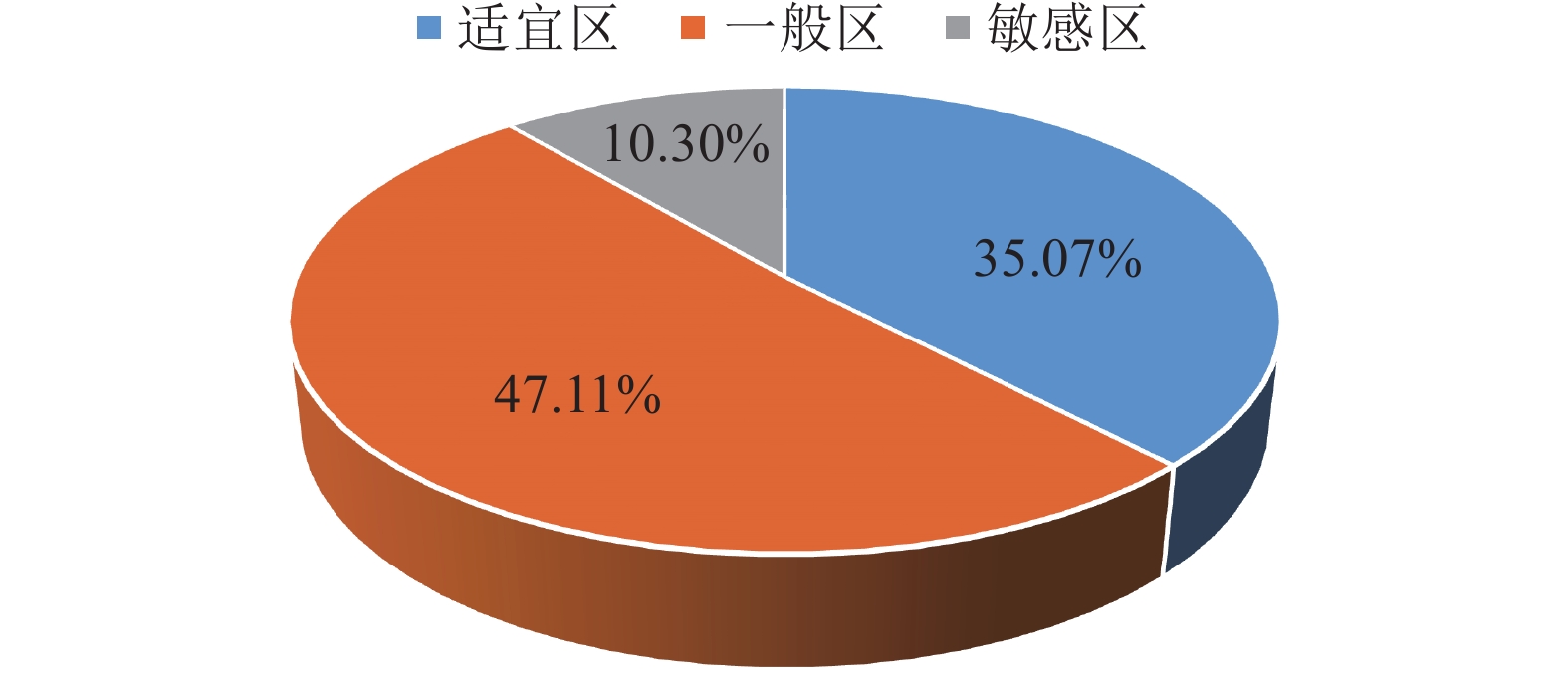
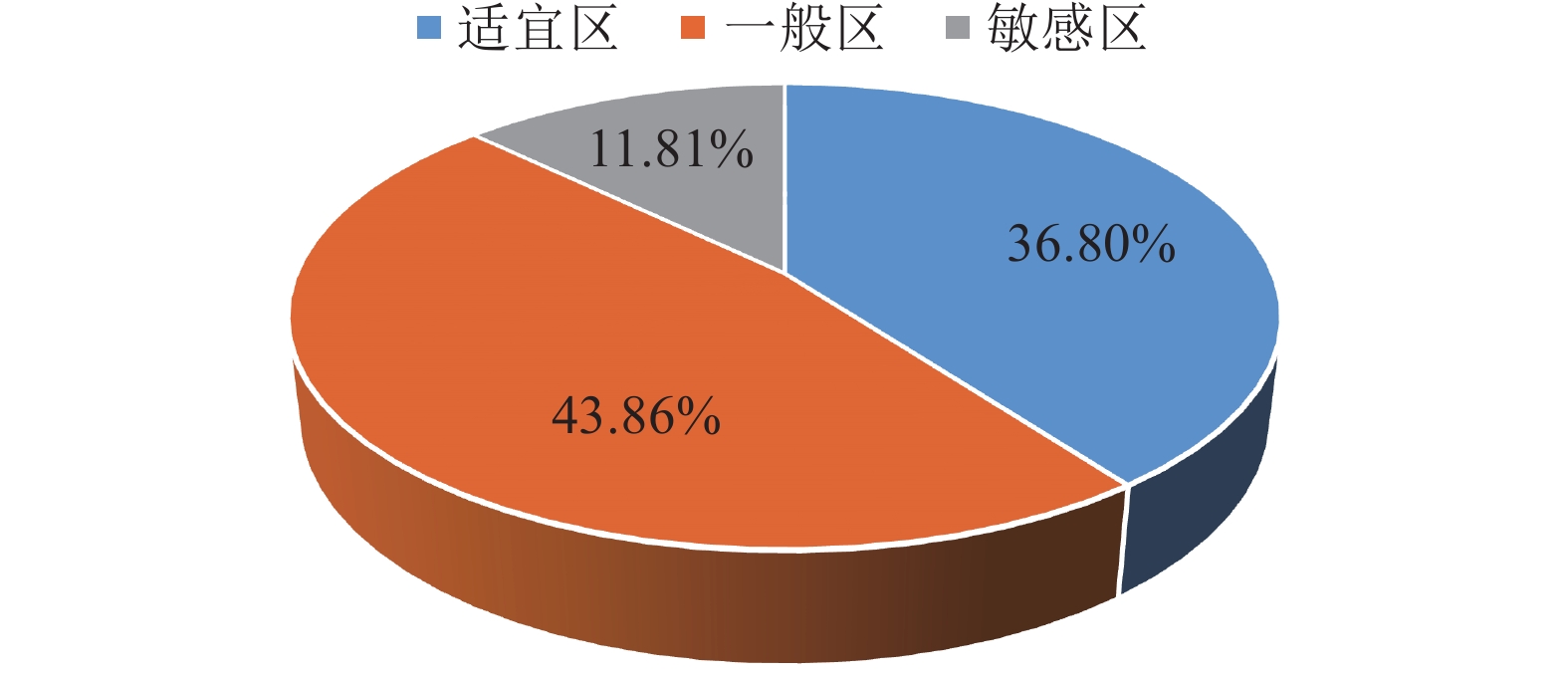
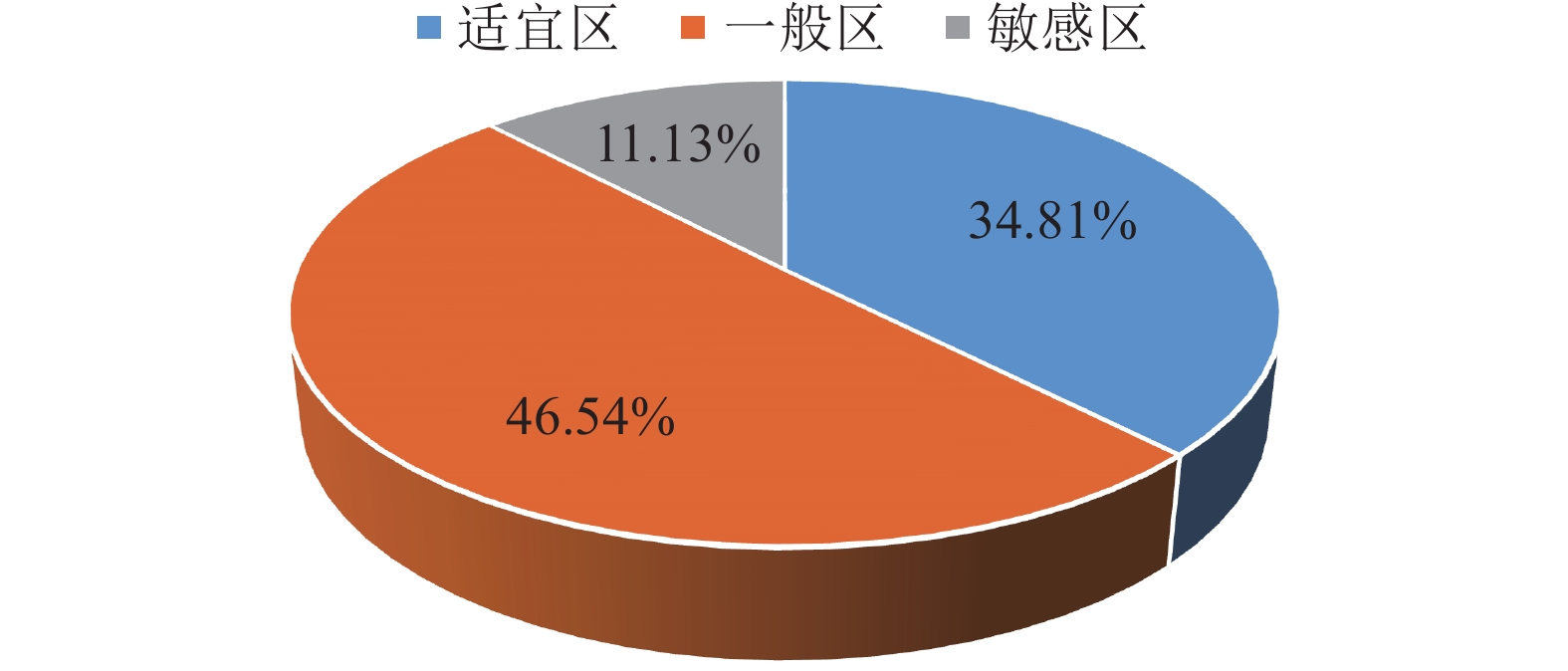
雄安新区开发作为千年大计、国家大事,地下空间资源的开发利用可促进新区高质量建设与可持续发展。通过层次分析法,建立了雄安新区地下空间资源开发利用地质适宜性评价指标体系,对雄安新区浅层、次深层、深层地下空间地质适宜性进行了评价。研究结果表明,雄安新区地下空间资源开发利用的地质适宜性评价指标可划分为五大类10个指标,主要影响指标为含水砂层、地面沉降、液化砂土、水土腐蚀性等;按浅层、次深层和深层将评价结果划分为适宜区、一般区和敏感区,其中适宜区和一般区总面积约占新区面积的 80%,说明雄安新区地下空间资源开发利用地质适宜性整体较好。该评价结果为雄安新区高质量建设及可持续发展提供了可靠的技术支撑。
Abstract:Xiong’an New Area development is a grand project and a national event. The development and utilization of underground space resources can promote high-quality construction and sustainable development of the New Area. This paper establishes the evaluation index system of geological environment suitability for the development and utilization of underground space resources through the analytic hierarchy process and evaluates the geological environment suitability of underground space resources at different depths. The results show that the evaluation indexes can be divided into five categories and 11 indexes for the development and utilization of underground space in Xiong’an New Area. The main influence indexes are water-bearing sand layer, land subsidence, liquefied sand and corrosion of soil and water, etc. According to shallow, sub-deep and deep underground space, the suitability evaluation results were divided into suitable areas, less suitable areas and sensitive areas. The total area of suitable areas and less suitable areas accounted for about 80% of the New Area, indicating that the overall geological suitability of underground space development and utilization is good in Xiong’an New Area. The evaluation results provide reliable technical support for the high-quality construction and sustainable development in Xiong’an New Area.
-
-
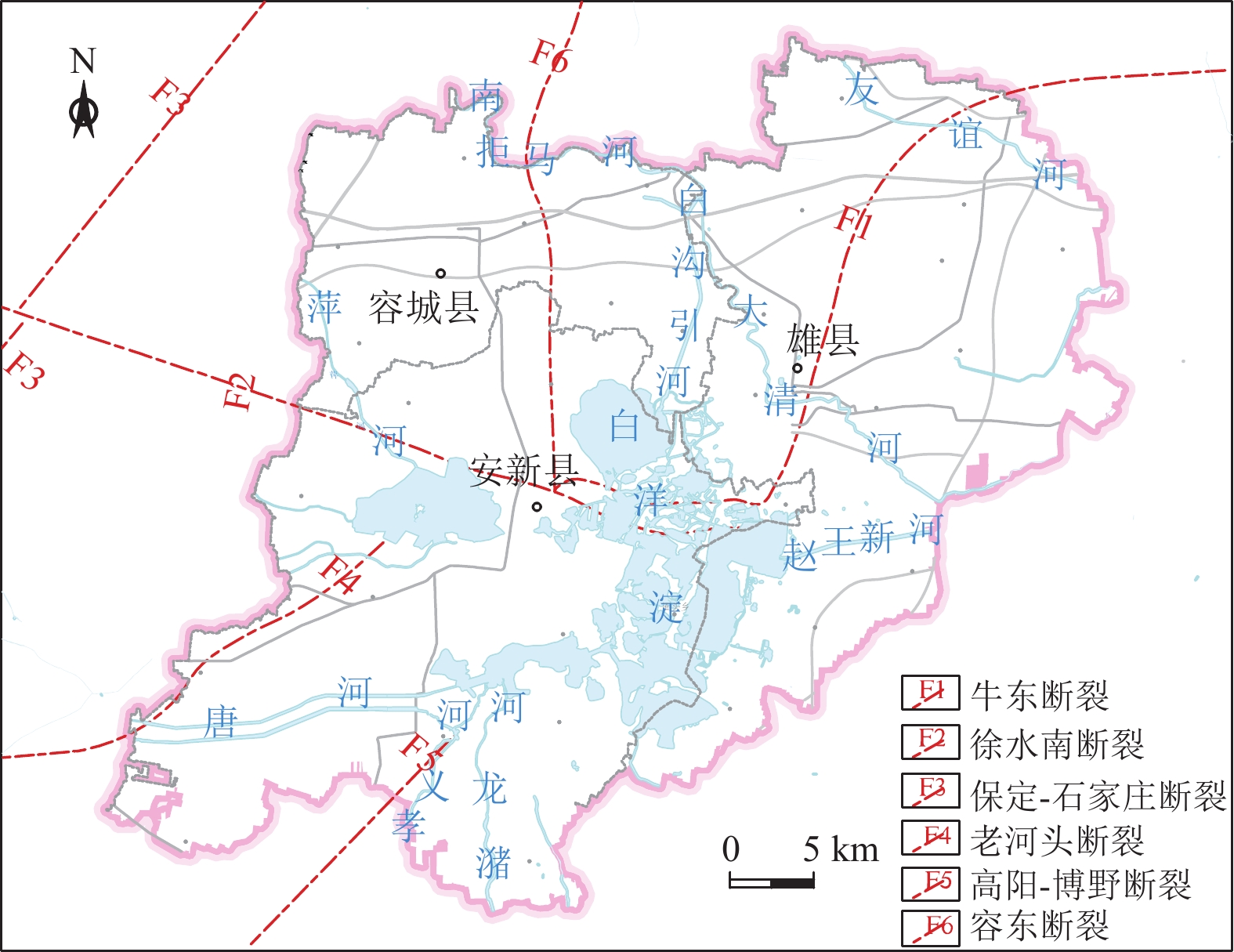
图 3 雄安新区主要断裂分布图(据马震等,2021)
Figure 3. Distribution map of major faults in Xiong’an New Area
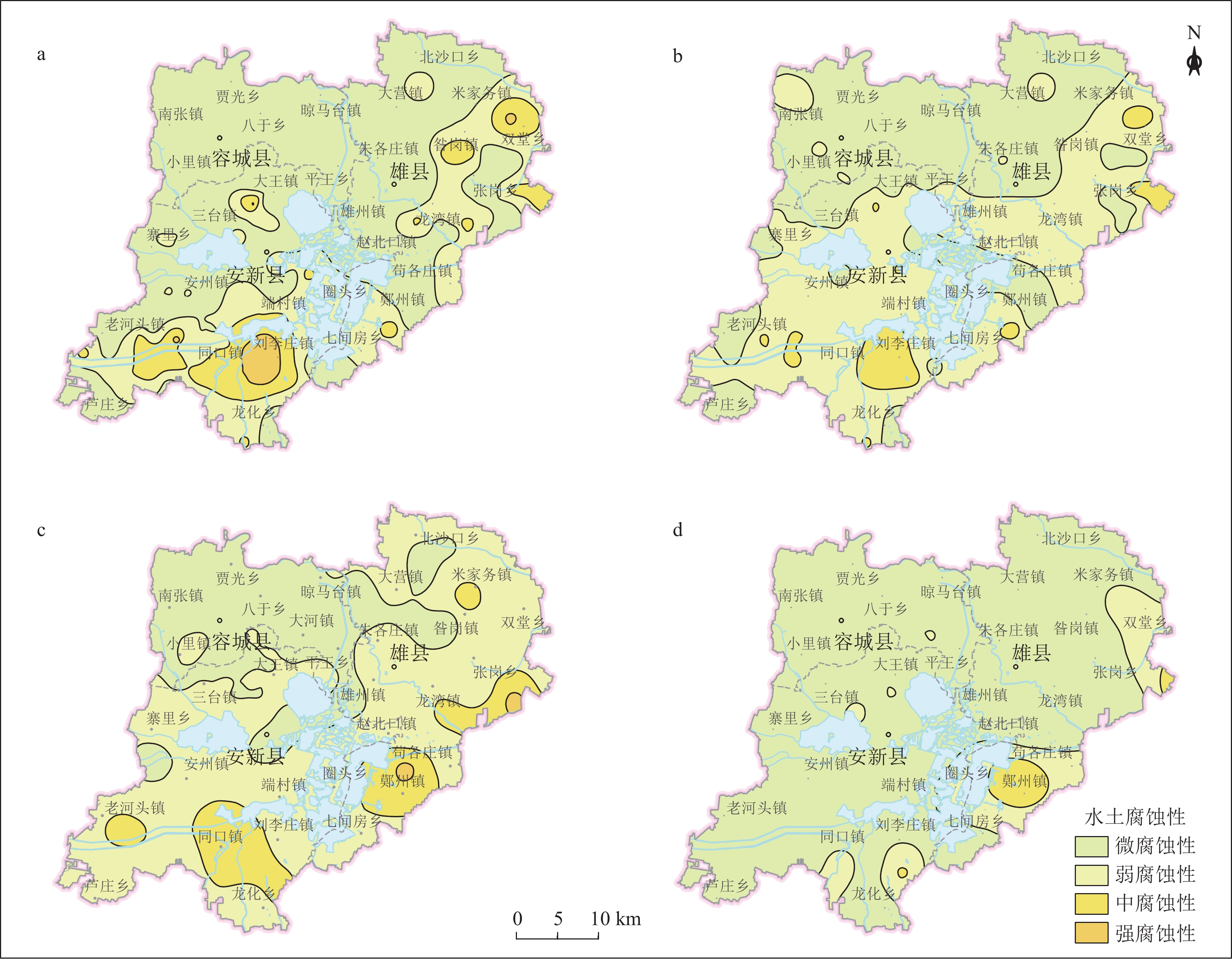
表 1 雄安新区地下空间开发利用地质适宜性评价指标分级标准
Table 1 Classification standard of suitability evaluation index for the development and utilization of underground space in Xiong’an New Area
目标层 准则层 指标层 分级标准 优良(1.0) 一般(0.5) 差(0.0) 地下空间资源开发利用
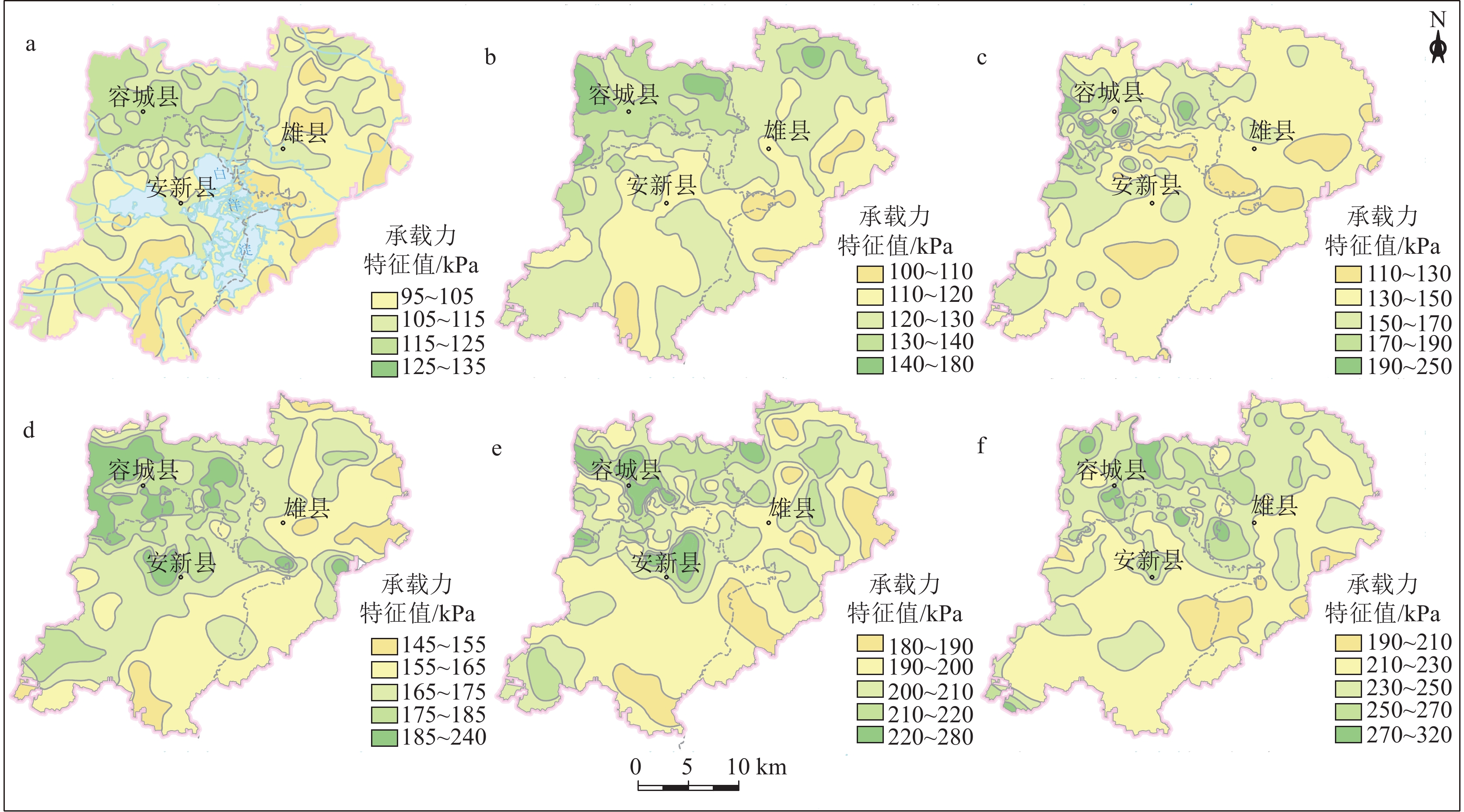
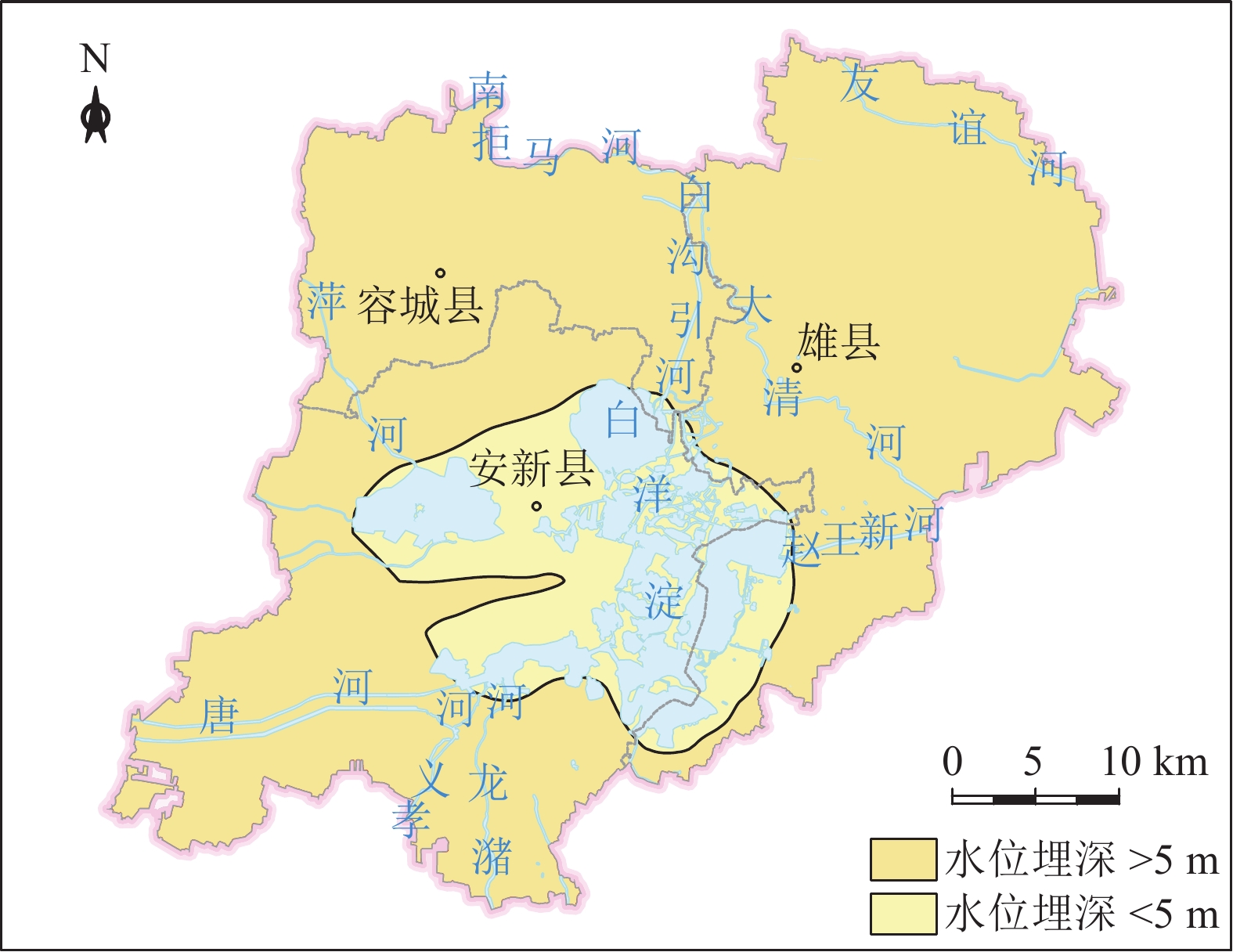
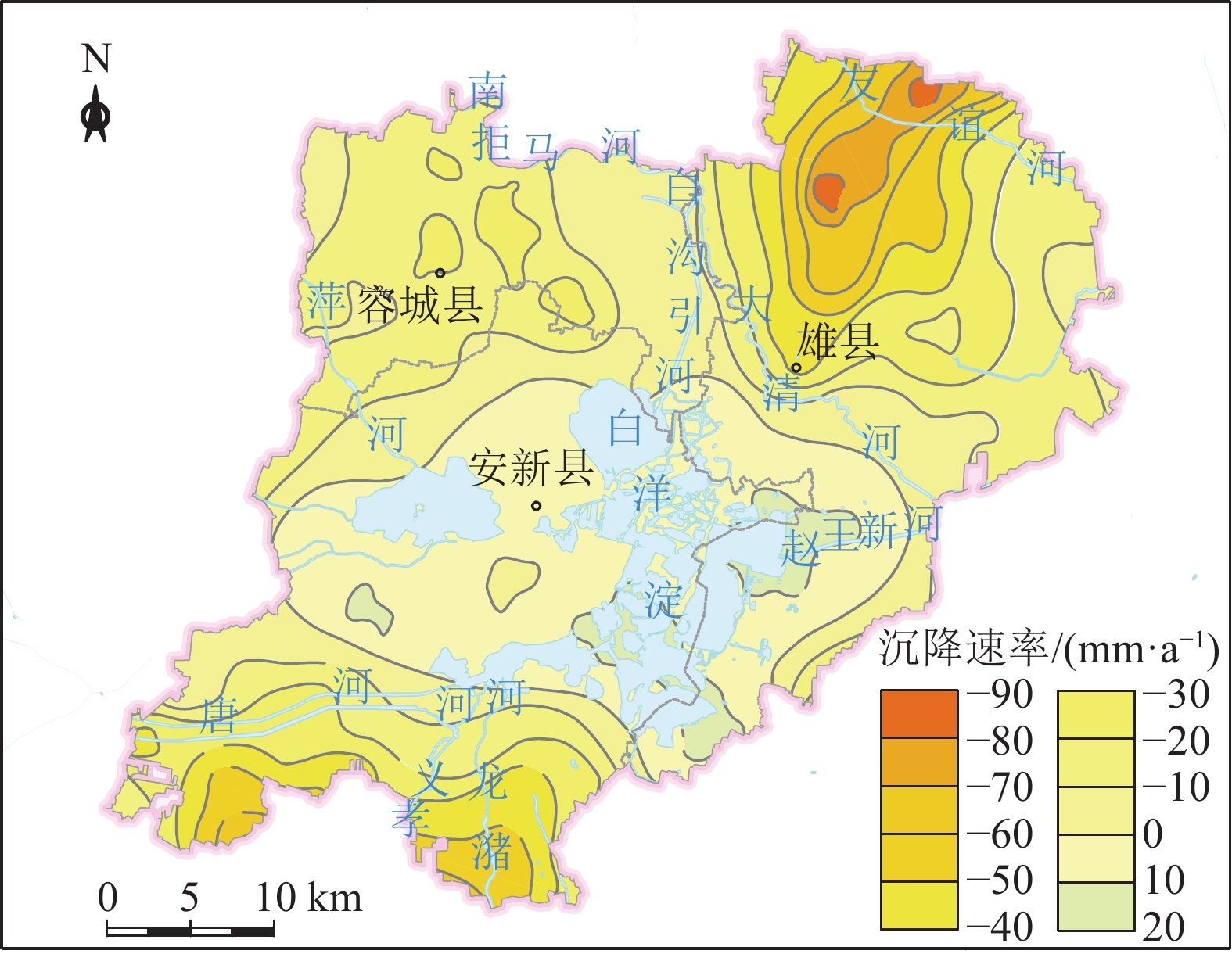
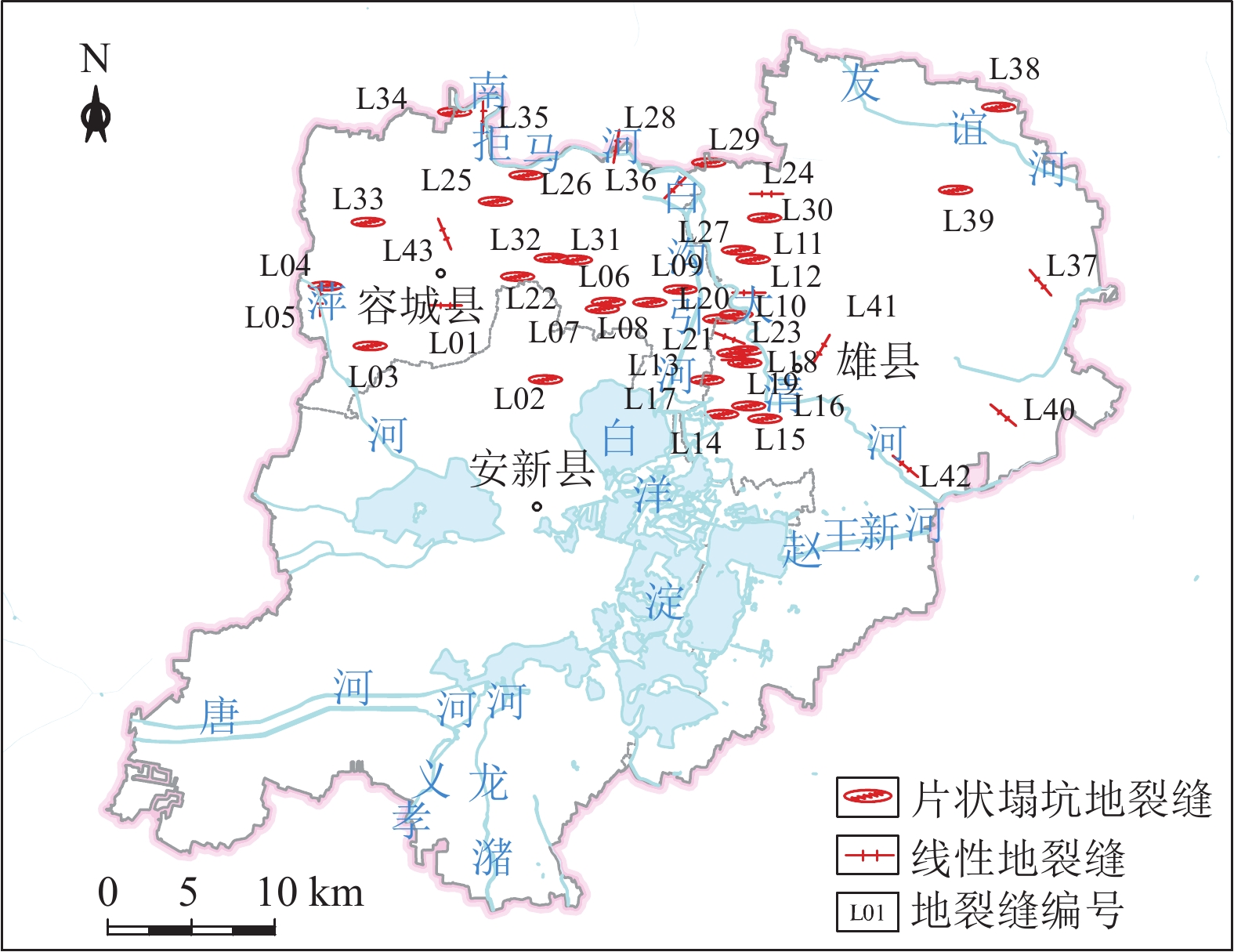
地质适宜性分层评价地形地貌 地形坡度/° <15 15~25 >25 工程地质条件 岩土体组合特征 单层、双层 三层 多层 岩土体承载力/kPa >160 90~160 <90 砂土液化 ≤6 6~18 >18 水文地质条件 地下水位埋深/m >10 5~10 <5 含水层厚度/m <3 3~9 >9 含水层富水性/(m3·d−1) <100 100~1000 >1000 水土腐蚀性 弱 中 强 环境地质问题 地面沉降速率/(mm·a−1) <30 30~50 >50 地裂缝 无或稀疏 较密集 密集 表 2 判断矩阵标度及其含义
Table 2 Identification and meaning of judging matrix
标度 表示含义 1 两个因素Ai与Aj相比,具有同等重要性 3 两个因Ai与Aj相比,Ai比Aj稍微重要 5 两个因Ai与Aj相比,Ai比Aj比较重要 7 两个因Ai与Aj相比,Ai比Aj明显重要 9 两个因Ai与Aj相比,Ai比Aj强烈重要 2,4,6,8 上述相邻判断1~3、3~5、5~7、7~9的中值 倒数 若Ai与Aj相比重要性为aij,则Aj与Ai相比为aji=1/aij 表 3 判断矩阵随机一致性指标
Table 3 Stochastic consistency index of judgment matrix
矩阵阶数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 RI 0.00 0.00 0.58 0.89 1.12 1.25 1.36 1.41 1.45 表 4 目标层-准则层判断矩阵A~B及一致性检验结果
Table 4 Judgment matrix of A~B and result of consistency test
目标层A 地形地貌B1 工程地质条件B2 水文地质条件B3 环境地质问题B4 权重Wi 地形地貌B1 1 1/5 1/4 1/2 0.0809 工程地质条件B2 5 1 1 3 0.4005 水文地质条件B3 4 1 1 3 0.3788 环境地质问题B4 2 1/3 1/3 1 0.1397 λmax=4.001,CI=0.00033,CR=0.00037<0.1 表 5 B2判断矩阵及一致性检验结果
Table 5 Judgment matrix of B2 and result of consistency test
工程地质条件B2 岩土体组合特征C2 岩土体承载力C3 砂土液化C4 权重Wi 岩土体组合特征C2 1 3 2 0.5499 岩土体承载力C3 1/3 1 1 0.2098 砂土液化C4 1/2 1 1 0.2402 λmax=3.0183,CI=0.00915,CR=0.016<0.1 表 6 B3判断矩阵及一致性检验结果
Table 6 Judgment matrix of B3 and result of consistency test
水文地质条件B3 地下水位埋深C5 含水层厚度C6 含水层富水性C7 水土腐蚀性C8 权重Wi 地下水位埋深C5 1 1/3 1/5 2 0.1153 含水层厚度C6 3 1 1 3 0.3816 含水层富水性C7 5 1 1 3 0.4035 水土腐蚀性C8 1/2 1/3 1/3 1 0.0995 λmax=4.1576,CI=0.0525,CR=0.0590<0.1 表 7 浅层地下空间评价指标权重取值
Table 7 Weight values of evaluation indexes of shallow underground space
指标层 地形地貌 工程地质条件 水文地质条件 环境地质问题 综合权重Wi WB1=0.0809 WB2=0.4005 WB3=0.3788 WB3=0.1397 地形坡度 1.0000 0.0809 岩土体组合特征 0.5499 0.2202 岩土体承载力 0.2098 0.0840 砂土液化 0.2402 0.0962 地下水位埋深 0.1153 0.0437 含水层厚度 0.3816 0.1446 含水层富水性 0.4035 0.1528 水土腐蚀性 0.0995 0.0377 地面沉降速率 0.8000 0.1118 地裂缝 0.2000 0.0279 表 8 次深层地下空间评价指标权重取值
Table 8 Weight values of evaluation indexes of sub-deep underground space
指标层 工程地质条件 水文地质条件 环境地质问题 综合权重Wi WB2=0.4286 WB3=0.4286 WB3=0.1429 岩土体组合特征 0.6500 0.2786 岩土体承载力 0.3500 0.1500 地下水位埋深 0.1153 0.0494 含水层厚度 0.3816 0.1636 含水层富水性 0.4035 0.1729 水土腐蚀性 0.0995 0.0426 地面沉降速率 0.8000 0.1143 地裂缝 0.2000 0.0286 表 9 深层地下空间评价指标权重取值
Table 9 Weight values of evaluation indexes of deep underground space
指标层 工程地质条件 水文地质条件 环境地质问题 综合权重Wi WB2=0.4286 WB3=0.4286 WB3=0.1429 岩土体组合特征 0.6500 0.2786 岩土体承载力 0.3500 0.1500 地下水位埋深 0.1153 0.0494 含水层厚度 0.3816 0.1636 含水层富水性 0.4035 0.1729 水土腐蚀性 0.0995 0.0426 地面沉降速率 1.000 0.1429 表 10 雄安新区地下空间开发利用地质适宜性评价
Table 10 Suitability evaluation on the development and utilization of underground space in Xiong’an New Area
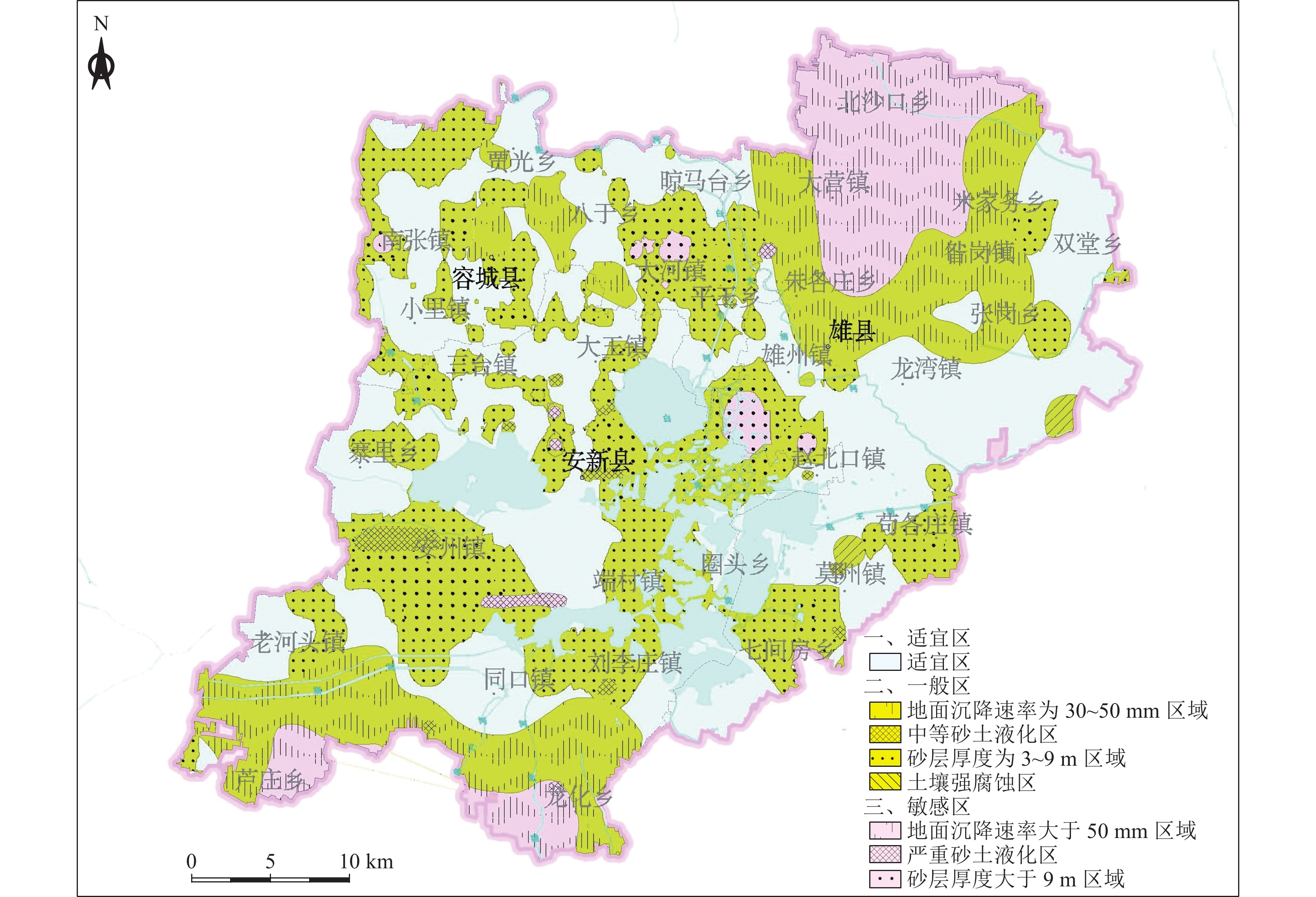
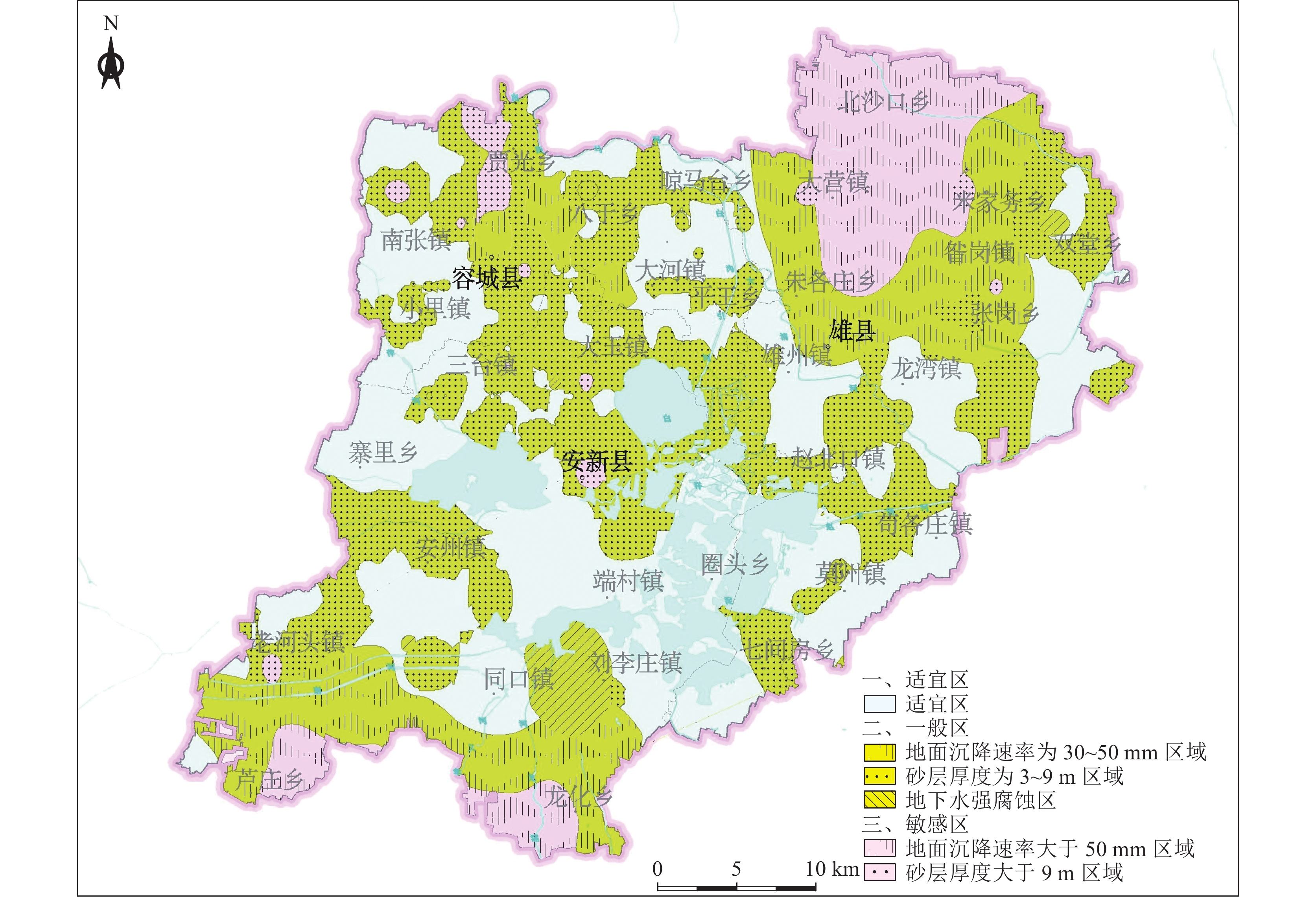
层位 适宜性分区 分布 开发利用建议 浅层地下空间
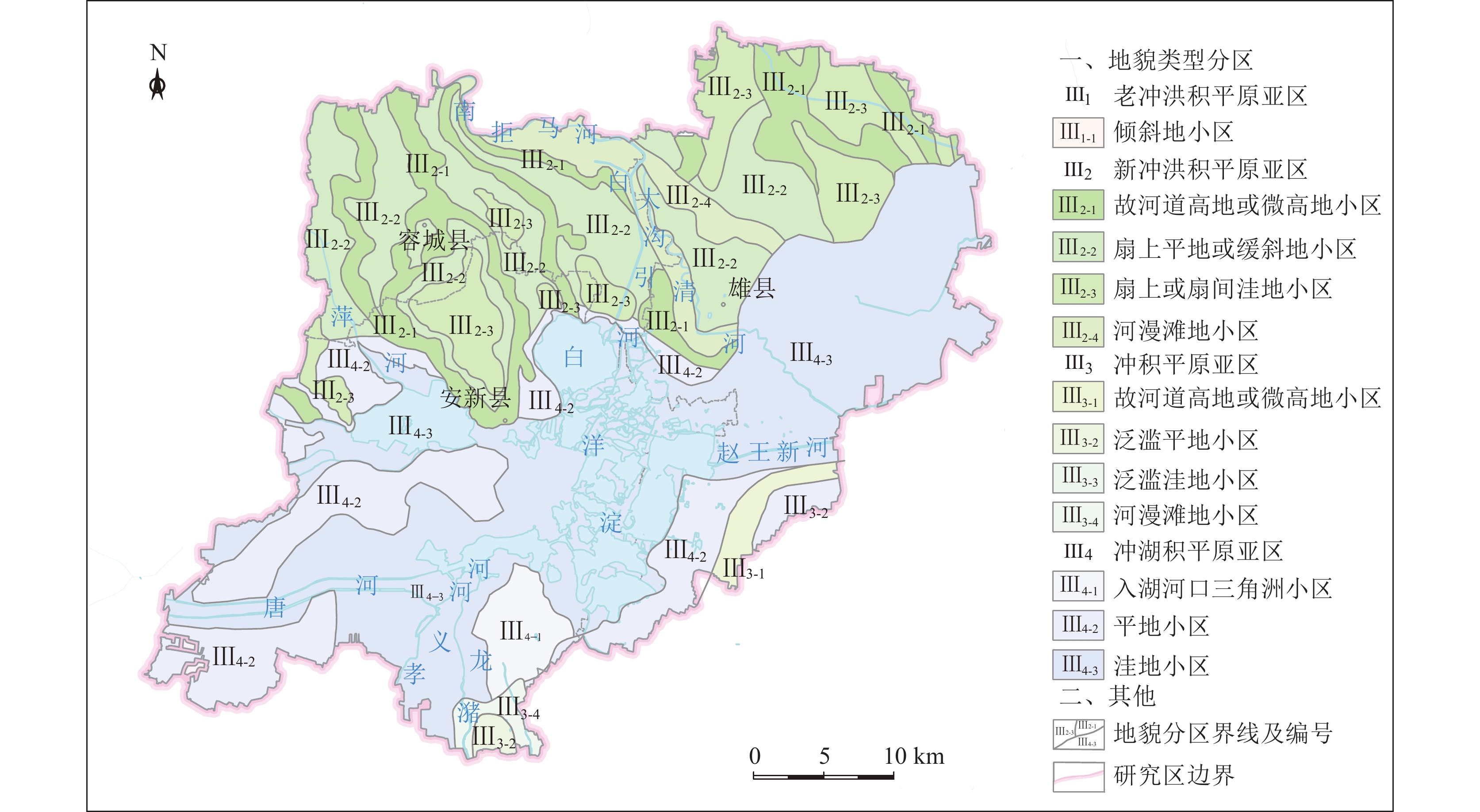
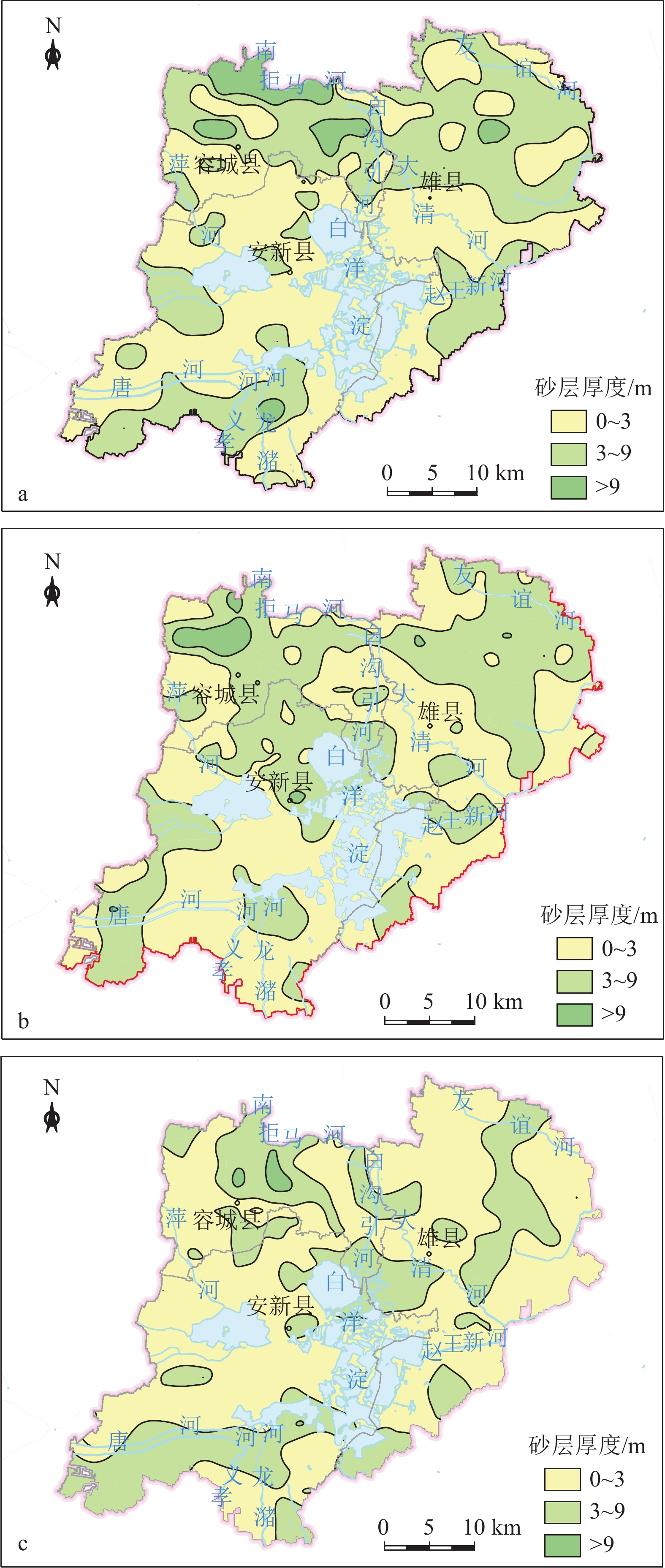
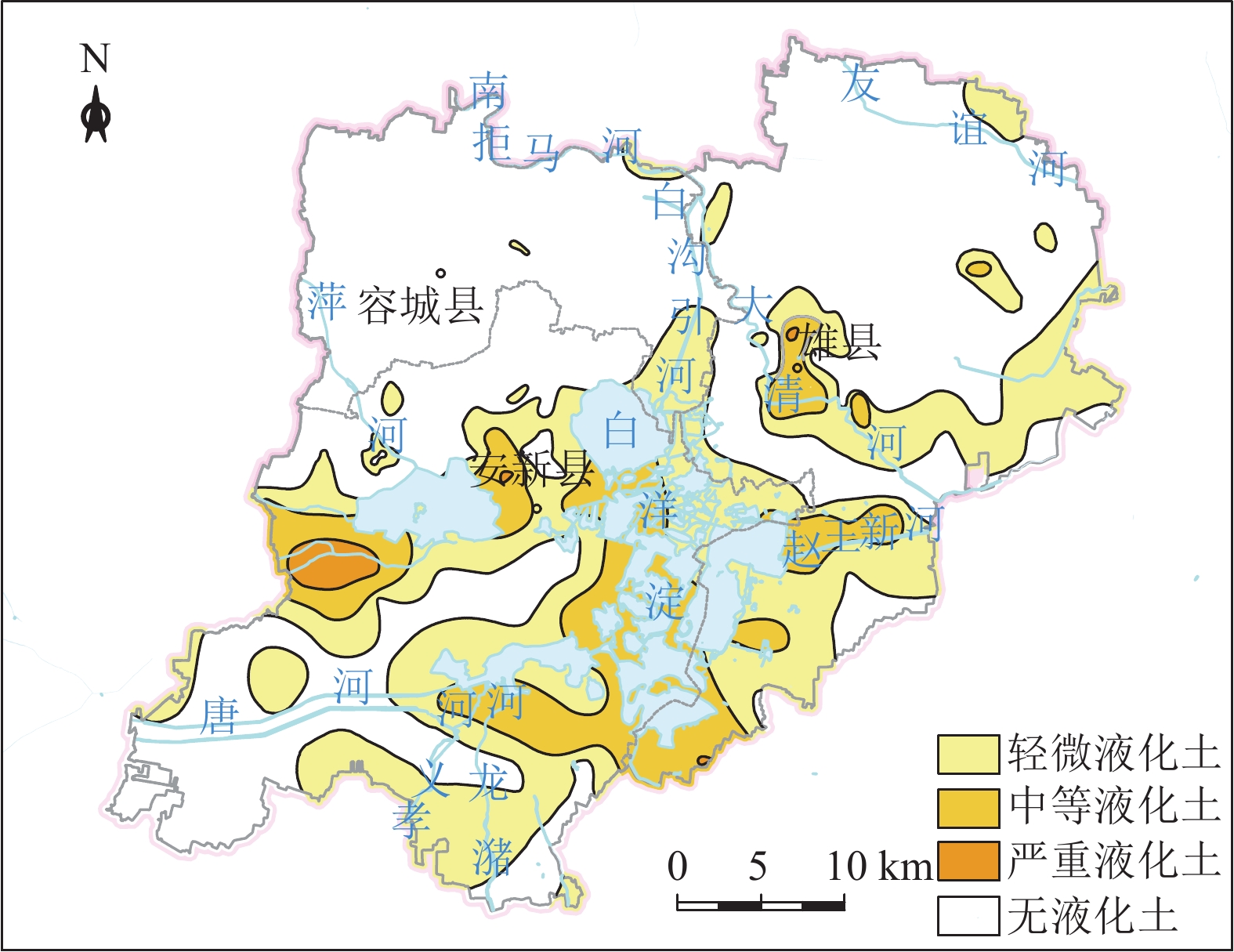
(0~30 m)敏感区 含水砂层厚度大于9 m的区域呈点状分布于容城县
大河镇以北、雄县雄州镇西南区域,地面沉降速率大
于50 mm的区域位于雄县北部的大营镇以东、北沙口
乡以南、龙化乡以西、芦庄乡以东区域。安新县西北
部、端村镇西部区域存在严重砂土液化区地下空间开发利用应避开敏感区,若无法规避,应开展专题研究确定抗坑底突涌、含水层保护、抗液化处理等措施 一般区 含水砂层厚度介于3~9 m之间的区域广泛分布全区;平
王乡东北部、大王镇西南和南部、三台镇东南部、安新
县县城、安州镇西北部存在中等砂土液化区;地面沉降
速率介于30~ 50 mm之间的区域分布在雄县北部、容城
县八于乡、安新县南部芦庄乡北部和龙化乡北部;雄县
鄚州镇东北部存在土壤强腐蚀区地下空间开发利用在一般区开展时,应通过采取抗坑底突涌、预防不均匀地面沉降、抗液化处理、地下水腐蚀防护等措施确保地下空间开发建设的安全 适宜区 除上述2类地区外的区域 次深层地下空间(30~50 m) 敏感区 含水砂层厚度大于9 m的区域呈片状分布于容城县大
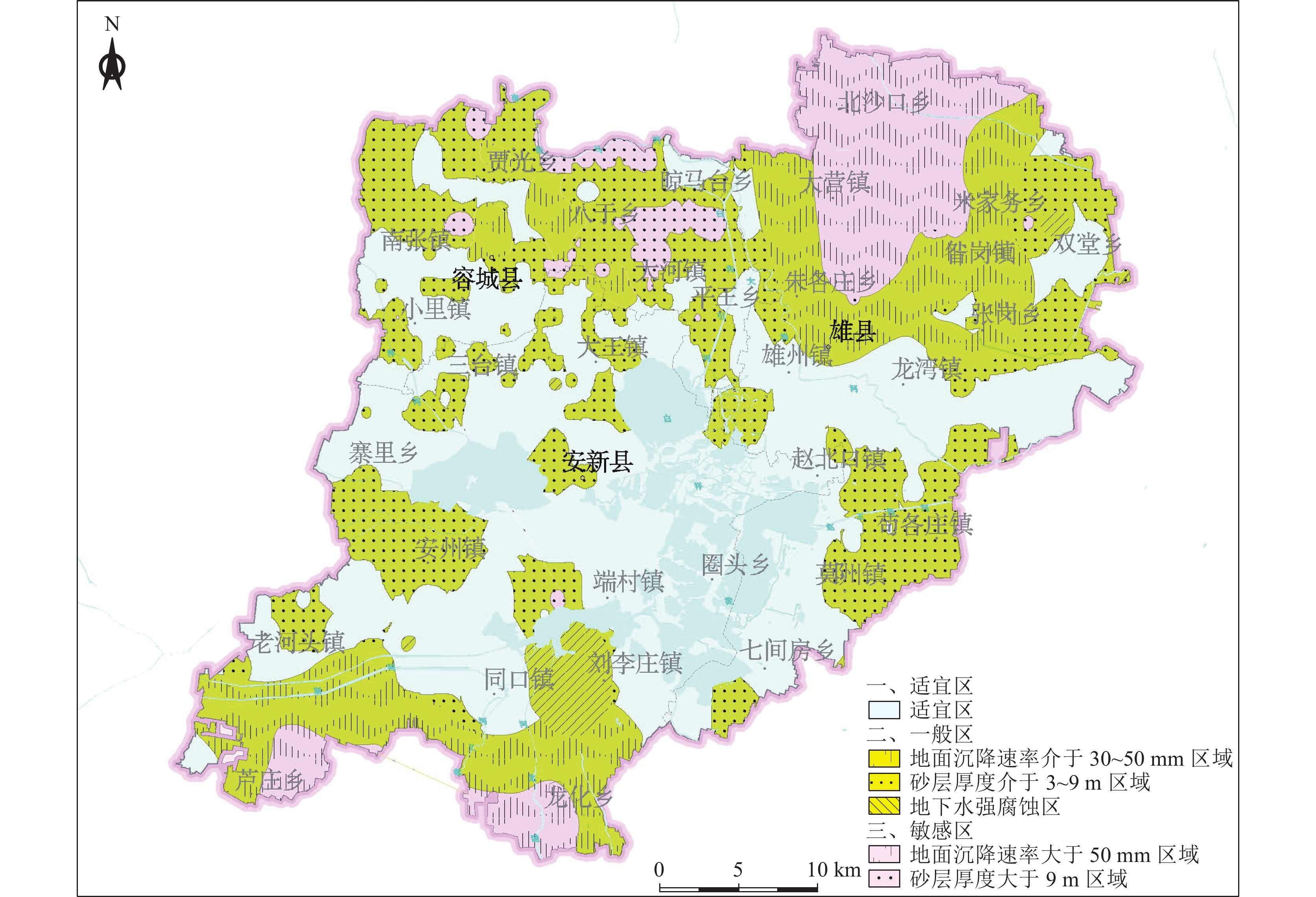
河镇以北、南拒马河南岸,地面沉降速率大于50 mm的
区域位于雄县北部的大营镇以东、北沙口乡以南、安
新县芦庄乡以东、龙化乡以西地下空间开发利用应避开敏感区,若无法规避,应开展专题研究确定抗坑底突涌、含水层保护等措施 一般区 含水砂层厚度介于3~9 m之间的区域广泛分布全区;地
面沉降速率介于30~50 mm之间的区域主要位于雄县以
北、容城县北部、安新县南部龙化乡和芦庄乡;刘李庄
镇存在地下水强腐蚀区地下空间开发利用在一般区开展时,应通过采取抗坑底突涌、预防不均匀地面沉降、地下水腐蚀防护等措施确保地下空间开发建设
的安全适宜区 除上述2类地区外的区域 深层地下空间
(50~70 m)敏感区 含水砂层厚度大于9 m区域呈片状分布于容城县贾光
乡一带、南张镇以北、安新县县城,地面沉降速率大于
50 mm的区域位于雄县北部的大营镇以东、北沙口乡以
南、安新县龙化乡以西、芦庄乡以东区域地下空间开发利用应避开敏感区,若无法规避,应开展专题研究确定抗坑底突涌、含水层保护等措施 一般区 含水砂层厚度介于3~9 m之间的区域广泛分布全区;地
面沉降速率介于30~50 mm之间的区域主要分布在雄县
以北、安新县芦庄乡和龙化乡;刘李庄镇存在地下水强
腐蚀区地下空间开发利用在一般区开展时,应通过采取抗坑底突涌、预防不均匀地面沉降、地下水腐蚀防护等措施确保地下空间开发建设的
安全适宜区 除上述2类地区外的区域 -
Admiraal H, Cornaro A. 2016. Why underground space should be included in urban planning policy and how this will enhance an urban underground future[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 55: 214−220. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2015.11.013
Chen Z L, Chen J Y, Liu H, et al. 2018. Present status and development trends of underground space in Chinese cities: evaluation and analysis[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 71: 253−270. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2017.08.027
Edelenbos J, Monnikhof R, Haasnoot J, et al. 1998. Strategic study on the utilization of underground space in the Netherlands[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 13(2): 159−165. doi: 10.1016/S0886-7798(98)00043-1
Li X Z, Li C, Parriaux A, et al. 2016. Multiple resources and their sustainable development in Urban Underground Space[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 55: 59−66.
Nathan D, Mark B, John D, et al. 2018. Going underground: An exploration of the interfaces between underground urban transport infrastructure and its environment[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 81: 450−462. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2018.08.027
Saaty T L. 1997. A scaling method for priorities in hierarchical structures[J]. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 15(3): 234−281.
Saaty T L. 1990. How to make a decision: The analytic hierarchy process[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 48(1): 9−26. doi: 10.1016/0377-2217(90)90057-I
Wout B. 2016. Urban underground space: Solving the problems of today’ s cities[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 55: 245−248. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2015.11.012
Zhou D K, Li X Z, Wang Q, et al. 2019. GIS−based urban underground space resources evaluation toward three−dimensional land planning: A case study in Nantong, China[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 84(1): 1−10.
蔡鹤生, 周爱国, 唐朝晖. 1998. 地质环境质量评价中的专家—层次分析定权法[J]. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 23(3): 299−302. 程光华, 王睿, 赵牧华, 等. 2019. 国内城市地下空间开发利用现状与发展趋势[J]. 地学前缘, 26(3): 39−47. 葛伟亚, 王睿, 张庆, 等. 2021. 城市地下空间资源综合利用评价工作构想[J]. 地质通报, 40(10): 1601−1608. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2021.10.001 郭朝斌, 王志辉, 刘凯, 等. 2019. 特殊地下空间应用与研究现状[J]. 中国地质, 46(3): 482−492. doi: 10.12029/gc20190304 郭骏瀚, 刘凯, 邓岳飞, 等. 2023. 基于熵权优化法的地下空间资源地质适宜性评价[J]. 地质通报, 42(2/3): 385−396. 郝爱兵, 吴爱民, 马震, 等. 2018. 雄安新区地上地下工程建设适宜性一体化评价[J]. 地球学报, 39(5): 513−522. 韩博, 夏雨波, 裴艳东, 等. 2020. 雄安新区地下空间工程地质特征及环境地质效应[J]. 工程勘察, 48(3): 1−8. 蒋杰, 葛伟亚, 马青山, 等. 2021. 南昌市中心城区地下空间开发地质适宜性评价[J]. 地质通报, 40(5): 734−744. 李鹏岳, 王东辉, 李胜伟, 等. 2021a. 山前冲积平原型城市地下空间开发利用地质适宜性评价——以成都市为例[J]. 地质通报, 40(10): 1644−1655. 李鹏岳, 韩浩东, 王东辉, 等. 2021b. 城市地下空间资源开发利用适宜性评价现状及发展趋势[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 41(1): 121−128. 李晓昭, 王睿, 顾倩, 等. 2019. 城市地下空间开发的战略需求[J]. 地学前缘, 26(3): 32−38. 刘宏伟, 王国明, 马传明, 等. 2022. 沉积平原区地下空间开发利用适宜性评价指标体系研究——以北京通州区和河北廊坊北三县为例[J]. 华北地质, 45(4): 68−74. 龙睿, 张发旺, 栾崧, 等. 2020. 广州市城区地下空间开发利用适宜性评价研究[J]. 西北地质, 53(4): 194−206. 马邦闯, 谭飞, 焦玉勇, 等. 2020. 基于粗糙集与AHP的地下空间开发地质适宜性评价模型构建方法研究[J]. 安全与环境工程, 27(6): 153−159. 马震, 夏雨波, 李海涛, 等. 2021. 雄安新区自然资源与环境-生态地质条件分析[J]. 中国地质, 48(3): 677−696. 马震, 黄庆彬, 林良俊, 等. 2022. 雄安新区多要素城市地质调查实践与应用[J]. 华北地质, 45(1): 58−68. 潘朝, 吴立, 左清军, 等. 2013. 基于模糊数学的武汉市地下空间开发地质适宜性评价[J]. 安全与环境工程, 20(2): 19−23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1556.2013.02.005 彭建, 柳昆, 郑付涛, 等. 2010. 基于AHP的地下空间开发利用适宜性评价[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 6(4): 688−694. 王兰化, 马武明, 李明明, 等. 2015. 天津滨海新区地下空间开发适宜性评价[J]. 地质调查与研究, 38(4): 299−304. 王成善, 周成虎, 彭建兵, 等. 2019. 论新时代我国城市地下空间高质量开发和可持续利用[J]. 地学前缘, 26(3): 1−8. 夏友, 马传明. 2014. 郑州市地下空间资源开发利用地质适宜性评价[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 10(3): 493−497. 夏雨波, 郭旭, 韩博, 等. 2021. 雄安新区水土质量与地质调查评价项目成果报告[R]. 中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心. 夏雨波, 郭旭, 王冰, 等. 2022. 雄安新区水土腐蚀性地质成因研究[J]. 华北地质, 45(3): 69−76. 邢怀学, 窦帆帆, 葛伟亚, 等. 2022. 城市地下空间开发利用地质适宜性三维评价指标体系研究——以杭州市为例[J]. 地质论评, 68(2): 607−614. 杨木壮, 张建峰, 郑先昌. 2009. 城市地下空间开发利用的潜在不利影响及其对策[J]. 现代城市研究, 24(8): 24−28. 杨文采, 田钢, 夏江海, 等. 2019. 华南丘陵地区城市地下空间开发利用前景[J]. 中国地质, 46(3): 447−454. 谭飞, 汪君, 焦玉勇, 等. 2021. 城市地下空间适宜性评价研究国内外现状及趋势[J]. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 46(5): 1896−1908. 张明阳, 王一鸣, 叶文荣, 等. 2020. 温州市规划区地下空间开发地质环境适宜性评价[J]. 土木工程学报, 53(S1): 378−384. 张晓波, 刘凯, 蒋鹏, 等. 2023. 基于约束条件的深圳市南山S区地下空间开发地质适宜性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 50(4): 213−224. 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 2010. GB 50011—2010: 建筑抗震设计规范[S]. 邹承杰. 2018. 河北省容城县中更新世以来的钻孔沉积物地球化学特征及古气候演化[D]. 河北地质大学硕士学位论文.



 下载:
下载: