Petrogenesis of porphyries in Baxi copper deposit in East Junggar, NW China and its enlightenment to mineral prospecting
-
摘要:
新疆坝西铜矿位于东准噶尔琼河坝矿集区,是新发现的斑岩型铜矿。主要赋矿围岩为石英闪长岩、花岗闪长岩和石英二长闪长岩。锆石U−Pb测年显示,花岗闪长岩和石英闪长岩均形成于337 Ma,属早石炭世晚期。花岗闪长岩和石英闪长岩都具有高硅、中低钾,属钙碱性系列,富钙、富铝,为准铝质—弱过铝质。富集轻稀土及大离子亲石元素,亏损Nb、Ta、Ti等高场强元素,具有弱的负Eu异常,表现出弧花岗岩特征和某些埃达克岩特性。结合区域研究,初步认为形成于东准噶尔岩浆活动相对“宁静期”的坝西含矿石英闪长岩和花岗闪长岩,应与早期俯冲的弧物质的部分熔融有关,并发生了岩浆混合作用,且伴随有一定程度的结晶分异,同时也形成斑岩型铜矿,此时应处于从俯冲增生到后造山伸展的转换阶段。琼河坝地区除志留纪—泥盆纪发育大量矿产外,石炭纪也是一个重要的成矿期,值得关注。本次研究对北疆及邻区的晚古生代后碰撞斑岩矿产的找矿勘查工作具有重要的指示意义。
Abstract:The recently discovered Baxi porphyry copper deposit is located in the Qiongheba ore−concentration area in East Junggar, Xinjiang. The ore−bearing porphyry are mainly composed of quartz diorite, quartz monzodiorite and granodiorite. Zircon U−Pb dating yielded two similar late Early Carboniferous ages of 337 Ma for quartz diorite and granodiorite. Quartz diorites and granodiorites are high SiO2, CaO, Al2O3, and low K2O contents, belonging the calc−alkaline, aluminum−weakly peraluminous. They are rich in LREE and LILE, such as Nb, Ta and Ti with weak negative Eu anomaly and high Sr and low Y contents, showing arc granitic characters with some Adakite futures. Combined with the regional research, we suggest the diorites and granodiorites in the Baxi porphyry copper deposit formed by partial melting of former subduction arc with magmatic mixing and following crystallization differentiation during the tectonic transition period from subduction to post−orogenic setting in Late Paleozoic. Porphyry copper deposits also formed in this period. In other words, except the Silurian−Devonian large−scale metallogenic stage, Carboniferous is also an important metallogenic stage in the Qiongheba area. It indicates that we should more attention on Late Paleozoic post−collision porphyry deposits in mineral exploration in northern Xinjiang and adjacent areas.
-
Keywords:
- Qiongheba /
- Carboniferous /
- porphyry copper deposit /
- tectonic setting transition /
- East Junggar
-
中亚造山带作为世界上最大的显生宙增生造山带(Chen et al., 2000),也是世界上重要的矿产资源集中分布区,包括大量与增生作用密切相关的斑岩铜矿(申萍,2015)。自西向东由哈萨克斯坦,经西准噶尔(Ji et al., 2018)、东准噶尔、南蒙古,到内蒙古北部,再到中国东北北部,在中亚造山带南部形成一条规模宏大的斑岩铜矿带,这些斑岩铜(钼、金)矿形成时代主要为早中古生代(申萍,2015;高俊等,2019)。中国境内的东准噶尔地区,位于该巨型成矿带的中段,也发现了一系列的斑岩铜矿,特别是琼河坝地区(郭丽爽等,2009;屈迅等,2009;王登红等,2009;杜世俊等,2010;张永等,2010;王磊等,2018;王斯林等,2018),如蒙西铜矿、琼河坝铜矿、桑南铜矿、铜华岭铜矿、和尔赛铜矿等,已成为一个重要的矿集区。这些斑岩铜矿与整个中亚造山带南部斑岩铜矿带一样,形成时代也主要集中在晚志留世—早泥盆世(郭丽爽等,2009;杜世俊等,2010),因此斑岩铜矿勘查也围绕着该时期的侵入岩和含火山岩地层展开。尽管部分学者认为北疆地区在二叠纪仍存在俯冲,但是多数学者认为整个大洋的消失应该在晚石炭世之前。不同于青藏高原的后碰撞斑岩成矿,北疆的造山后斑岩成矿显然不是重点。然而,随着勘查的进一步深入,在坝西地区新近发现一处斑岩铜矿(王斯林等,2017,2018;Xiao et al., 2018;张铭鸿等,2021),其赋矿斑岩侵入中泥盆统,成岩成矿时代应该晚于中泥盆世,前人获得矿区石英闪长岩的年龄为早石炭世(Xiao et al., 2018),与琼河坝主体的成矿时代不一致。本文对该矿区的两类赋矿围岩开展了年代学和地球化学研究,探讨其岩石成因,为北疆地区晚古生代的斑岩勘查提供重要信息。
1. 地质背景
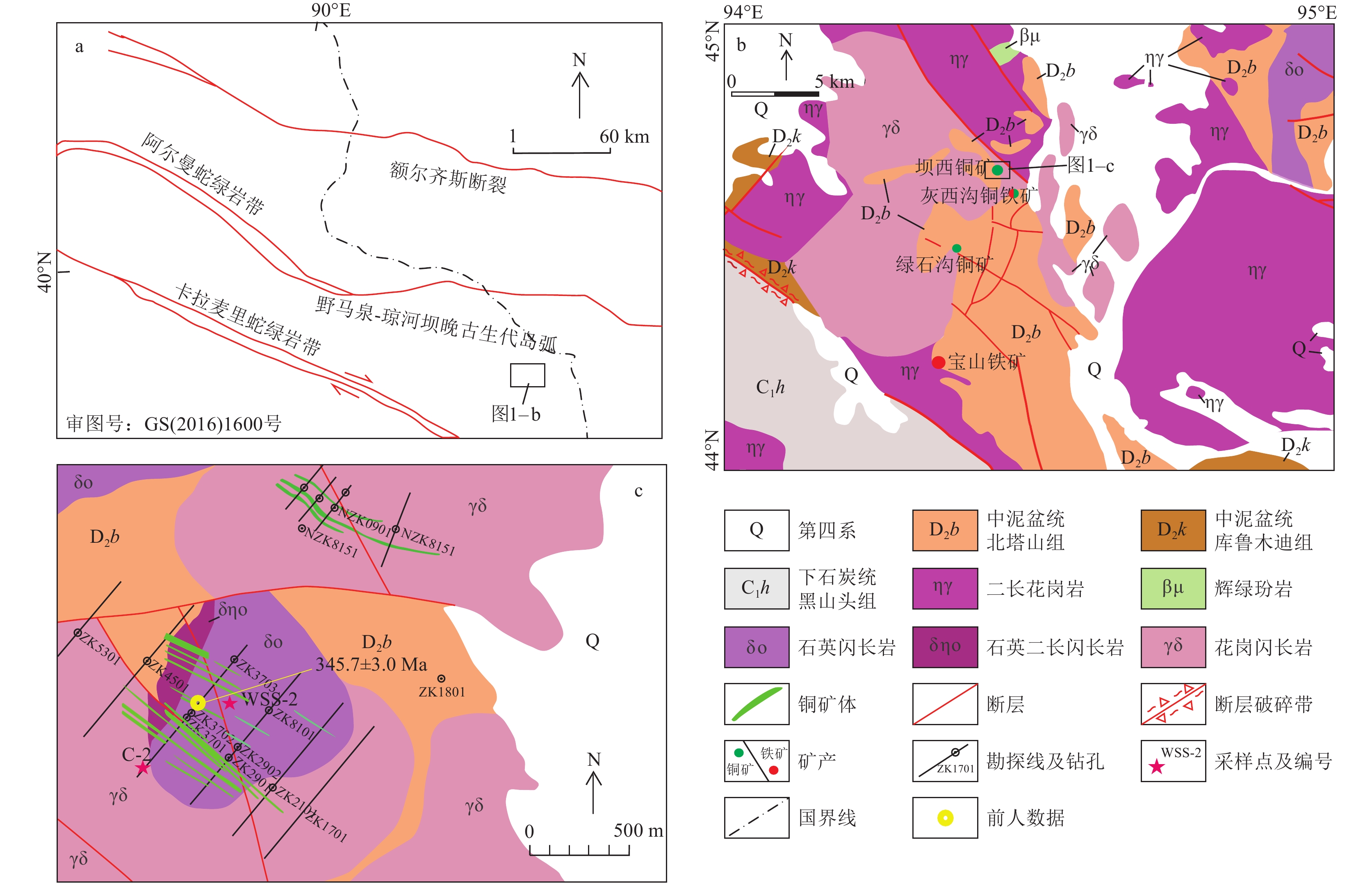
东准噶尔地区位于北疆(新疆北部阿尔泰、准噶尔和天山)准噶尔盆地东部,夹持于阿尔泰和东天山之间,被认为是图瓦−蒙古山弯构造的最南缘(Xiao et al., 2012)。主要为泥盆纪—二叠纪的火山−沉积地层,分布少量侏罗系,新生界及第四系广泛分布。关于该地区的构造环境,一直存在争论(童英等,2010;Long et al., 2012),有观点认为是在古生代东准噶尔洋向北俯冲导致的一系列洋内增生(童英等,2010;Long et al., 2012; Han et al., 2018),也有观点认为,晚古生代晚期已处于后碰撞环境(张海祥等,2004,2008;Han et al., 2018;孟秋熠,2020)。坝西铜矿位于东准噶尔东南部琼河坝矿集区,距伊吾县北东约160 km,构造上属于谢米斯台−野马泉−琼河坝古生代岛弧带的一部分,是环准噶尔北部斑岩铜矿带的重要组成部分(图1–a)。该地区出露的地层主要有中—上奥陶统荒草坡群(O2-3h)含化石的火山碎屑岩;中泥盆统北塔山组(D2b)海相中基性火山岩及中酸性火山碎屑岩夹碳酸盐岩地层和库鲁木迪组(D2k)砂岩、灰质粉砂岩、生物灰岩夹少量火山岩;下石炭统黑山头组(C1h)滨海、浅海相碎屑岩和中性火山岩;上二叠统红雁池组陆相中—基性火山熔岩。区内岩浆活动较强烈,中酸性侵入岩广泛分布,主要形成于古生代。
![]() 图 1 东准噶尔地质简图(a)、区域地质图(b)及矿区地质简图(c)(年龄数据据张铭鸿等,2021)Figure 1. Geotectonic position(a), regional geological (b) and mine geological (c) maps of the Baxi copper deposit
图 1 东准噶尔地质简图(a)、区域地质图(b)及矿区地质简图(c)(年龄数据据张铭鸿等,2021)Figure 1. Geotectonic position(a), regional geological (b) and mine geological (c) maps of the Baxi copper deposit2. 矿区地质及成矿特征
坝西铜矿位于绿石沟铜矿、灰西沟铜矿和宝山铁矿北部(图1–b),可分为南、北2个矿区,主体在南部。区内地层为中泥盆统北塔山组(侯可军等,2013),主要分布于矿区中部及西北角,为一套中性浅海相火山熔岩及火山凝灰岩,岩性主要为安山质晶屑凝灰岩、安山质角砾晶屑岩屑凝灰岩、沉凝灰岩和安山岩,普遍具角岩化、青磐岩化(绿帘石化、绿泥石化和碳酸盐化)蚀变。
矿区侵入岩发育,外围主要为花岗闪长岩,包括南、北2个侵入体,中部则以石英闪长岩和石英二长闪长岩为主,其中,石英二长闪长岩分布面积较小(图1–c),同时发育辉绿岩脉和闪长玢岩脉。南部矿区3类侵入岩在接触带附近相互穿插,还可以见到过渡类型,尤其是石英闪长岩和石英二长闪长岩之间,矿物组成略有变化,粒度变化并不规律。3类岩石均侵入中泥盆统北塔山组中。
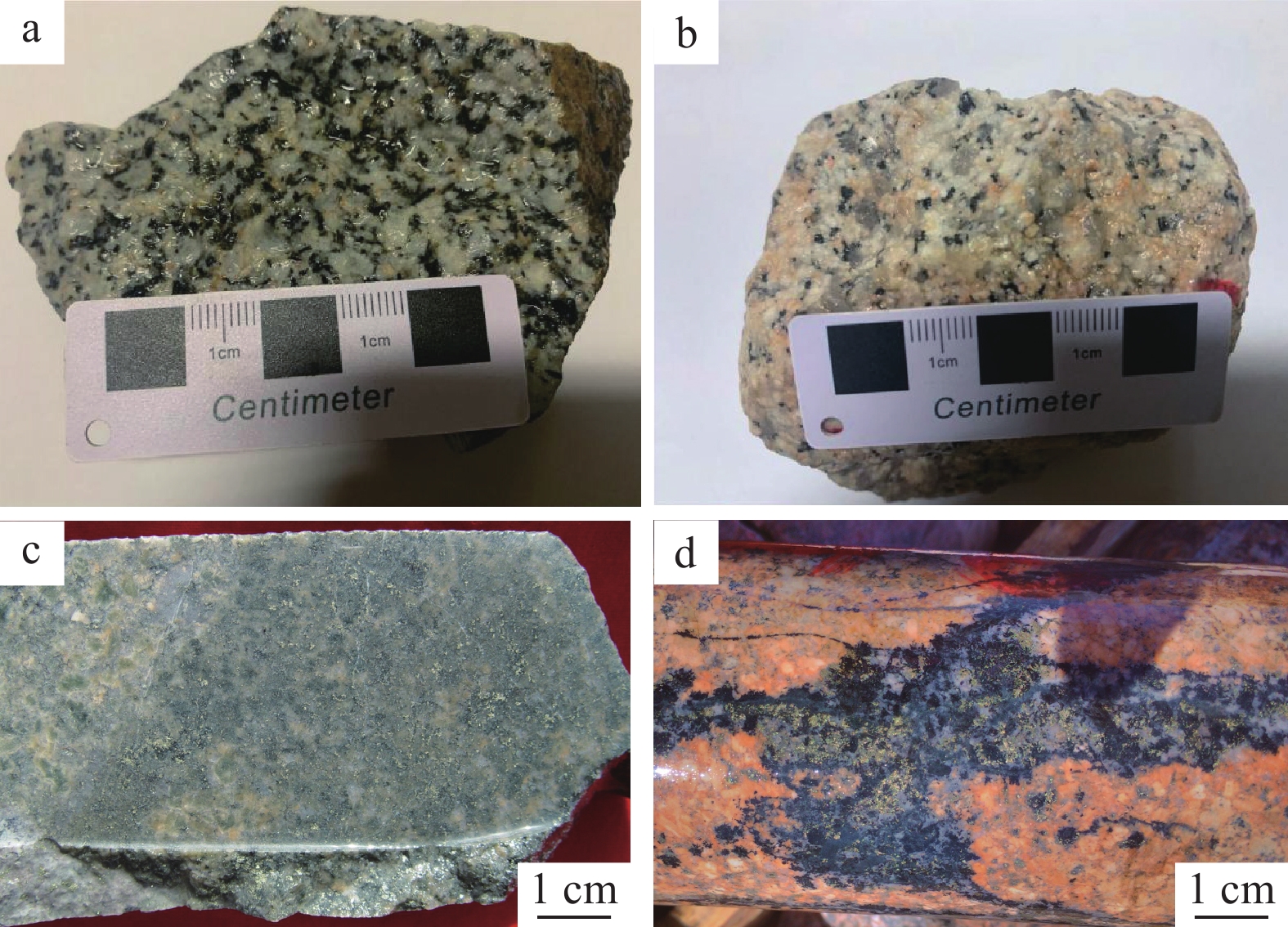
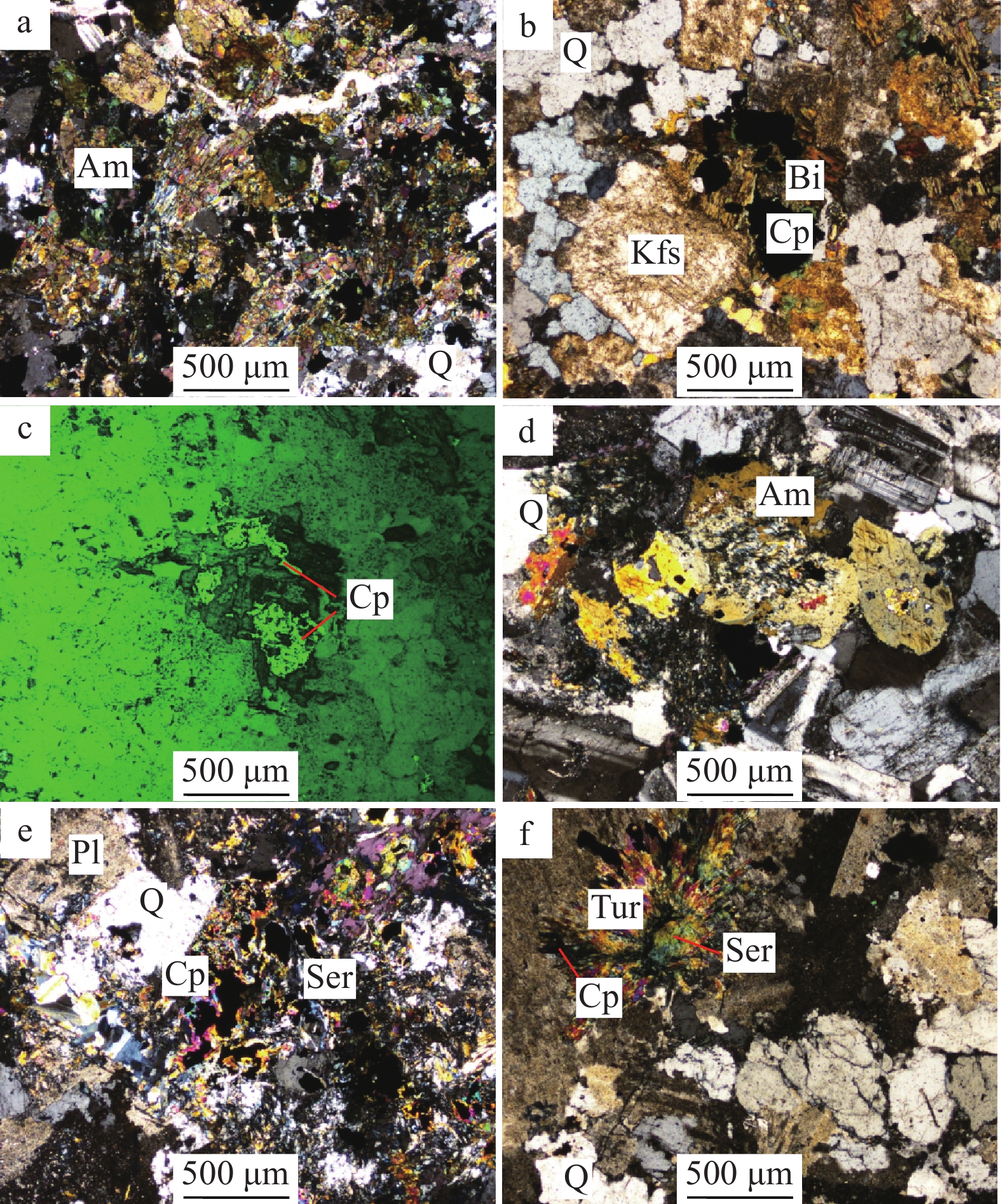
石英闪长岩为细—中粒结构,局部可见斜长石粗斑晶,呈似斑状结构(图2–a)。主要矿物组成:斜长石(55%~60%)普遍自形,主要为板状—板柱状,多呈等粒结构,但有时粒径也相差达2~4倍,使岩石呈现不等粒—似斑状结构(图2–a),双晶和环带结构普遍存在;钾长石(10%~12%)主要呈半自形,多数等粒,与斜长石呈相嵌结构;石英(15%)完全呈他形,且粒度明显小于长石,分布于长石粒间;角闪石(3%)多蚀变,为板片状,与黑云母密切伴生,分布于长石粒间;黑云母(10%)分布广泛,多呈长条状分布于长石粒间,有时也呈片状零星分布(图版Ⅰ–a)。
花岗闪长岩为中粒结构,浅肉红色,暗色矿物普遍较少,局部可见角闪石聚集,岩石颜色较深(图2–b)。主要矿物组成为石英(15%~20%)、斜长石(50%~55%)、钾长石20%~25%,暗色矿物主要为角闪石(5%~8%)(图版Ⅰ–b)。
矿区构造以断裂为主,按走向大致可分为NW向和EW向2组,其中NW向断裂形成较早,规模较大,活动较强烈,常伴随有一定的热液活动和蚀变,发育串珠状石英脉,见孔雀石化、褐铁矿化。EW向断裂形成较晚,常切割NW向断裂带,其中的岩石也较破碎,有泥化、次生石英岩化、孔雀石化、褐铁矿化。
坝西铜矿体主要产于石英闪长岩(图2–c)中,在花岗闪长岩(图2–d)和石英二长闪长岩中也有分布,多呈细脉状、浸染状、细脉−浸染状。矿化元素主要是Cu,其次是Mo,矿化只发生在蚀变岩石中。黄铜矿较多分布于角闪石和黑云母蚀变强烈部位,黄铜矿常单独呈短小细脉分布于蚀变岩中,有时也和绢云母或石英构成细脉,个别还有含黄铜矿的绿泥石细脉。
矿化岩石的蚀变作用非常普遍,主要蚀变有长石的高岭土化、角闪石等暗色矿物的绿泥石化、绿帘石化、绢云母化、硅化、电气石化、沸石化和碳酸盐化。矿化蚀变总体表现为以矿体为中心,从内向外依次为钾化(黑云母化)−硅化、绢英岩化带(绢云母+绿泥石)−泥化带(沸石化+高岭土化+高岭石化+碳酸盐化)−青磐岩化带,显示出典型的斑岩铜矿特征。石英闪长岩中的角闪石等暗色矿物普遍蚀变,与磁铁矿和硫化物密切伴生(图版Ⅰ–a),磁铁矿和黄铁矿的产出与黑云母蚀变关系密切(图版Ⅰ–b,c)。在石英闪长岩中暗色矿物多被绢云母交代(图版Ⅰ–d),在强粘土化的石英闪长岩中可见铜矿化与绢云母化关系密切(图版Ⅰ–e),在花岗闪长岩中可见电气石呈放射状分布在绢云母化−粘土化的长石边部,并产生少量黄铜矿(图版Ⅰ–f)。
3. 样品与测试方法
3.1 样品特征
本次选择与成矿相关的石英闪长岩和花岗闪长岩进行锆石U−Pb测年和地球化学分析。这2类岩石的地球化学分析样品分别来自于钻孔岩心和野外露头。石英闪长岩锆石U−Pb测年样品(WSS-2)采自矿区西南含矿岩体中部(图1–c)。岩石呈浅黄色,细—中粒结构到似斑状结构。斜长石和钾长石所占比例为3∶1,斜长石普遍自形,晶体粒径明显大于钾长石,钾长石多为他形;石英(15%~25%)呈他形不等粒结构;角闪石和黑云母(10%)并存,但前者稍占优势。副矿物有榍石、磷灰石、锆石、磁铁矿等。
花岗闪长岩锆石U−Pb测年样品(C-2)采自矿区西南含矿岩体南端(图1–c)。岩石呈灰白色,具半自形粒状结构,块状构造。主要矿物有斜长石(50%),呈自形板柱状,环带结构发育;钾长石(5%),多呈半自形—他形;石英(15%~20%),呈他形粒状;黑云母(<5%)和角闪石(15%~25%)均发生了蚀变(图2–c,d)。副矿物有榍石、磷灰石、锆石、磁铁矿等。
3.2 测试方法
3.2.1 锆石U−Pb测年
锆石单矿物分离及透射光、反射光和阴极发光照相在河北省区域地质调查院完成。首先,将原岩样品粉碎,经常规重选和电磁选后,在双目镜下挑选锆石。然后,将完整的典型锆石颗粒置于DEVCON环氧树脂中,待固结后抛磨,使锆石内部充分暴露,进行锆石显微(反射光和透射光)照相和阴极发光(CL)照相。
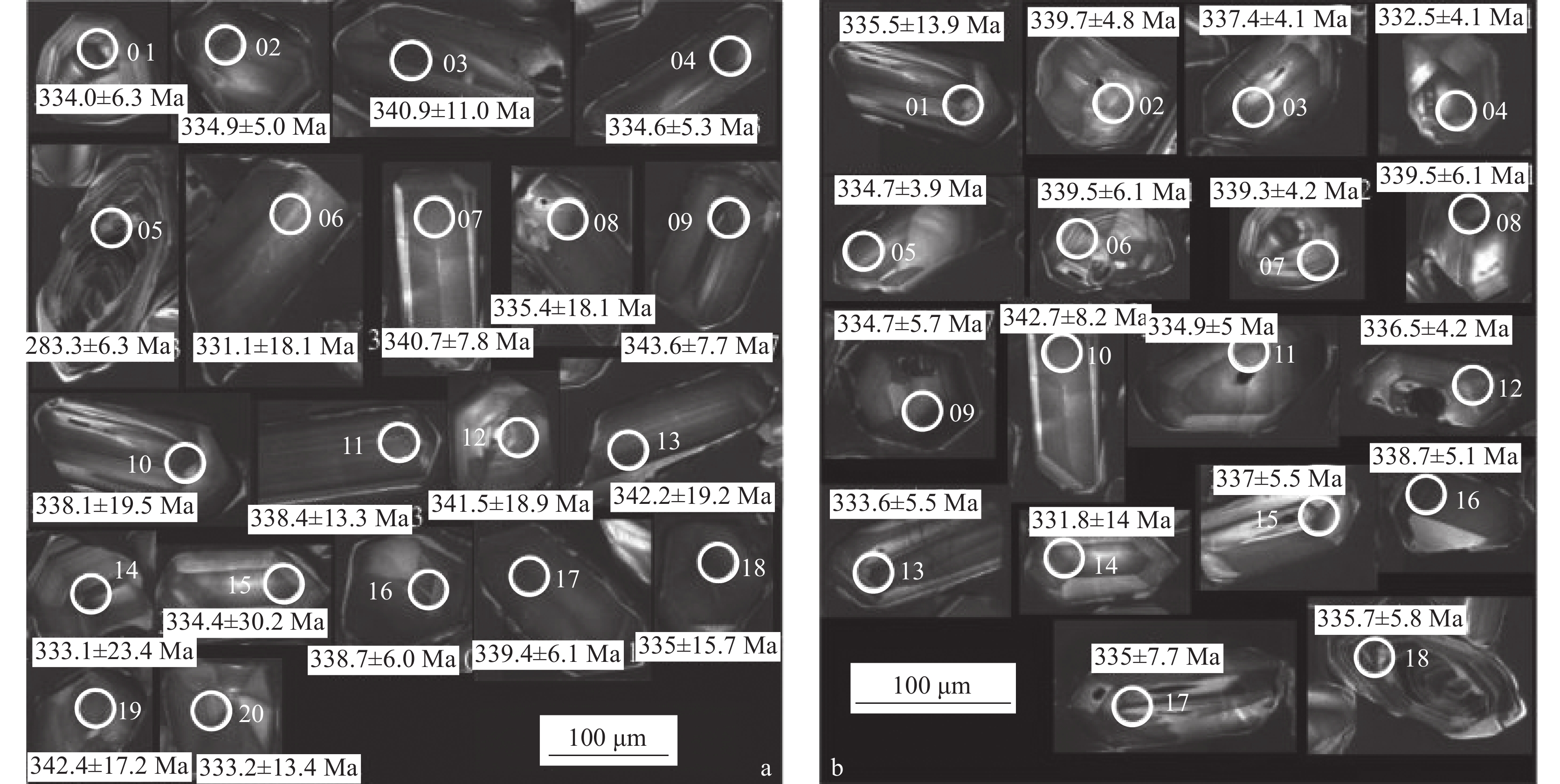
石英闪长岩(图3–a)与花岗闪长岩(图3–b)样品的锆石均呈自形粒状和柱状,无色透明,CL图像显示大部分锆石晶形较完整,少量较破碎,极少量为浑圆椭球状。其中,石英闪长岩的锆石长50~150 μm,部分具有非常明显的振荡环带韵律结构,部分具有扇状分带结构;花岗闪长岩的锆石长50~200 μm,大部分锆石内部结构均匀,振荡环带韵律结构非常明显,部分具有扇状分带结构。这2类岩石中的部分锆石具有暗色包裹体或继承核,本次选取了晶形完好、无核无包裹体的锆石进行测试分析。
锆石U−Pb同位素分析在北京燕都中实测试技术有限公司实验室完成。激光剥蚀系统为New Wave UP213(黄岗等,2016),ICP-MS为布鲁克M90。激光剥蚀的斑束为30 μm,激光剥蚀过程中采用氦气作载气、氩气为补偿气以调节灵敏度。每个时间分辨分析数据包括约15 s的空白信号和50 s的样品信号。U−Pb同位素定年采用锆石标准91500作外标进行同位素分馏校正,每分析5~10个样品点,分析2次91500。数据处理采用中国地质大学刘勇胜(2014)编写的ICPMSDataCal程序和Ludwig(2012)的Isoplot程序进行分析和作图,采用208Pb对普通铅进行校正。利用NIST612作为外标计算锆石样品的Pb、U、Th含量。具体操作方法可见参考文献(孟秋熠,2020)。
3.2.2 地球化学分析
样品的主量和微量元素分析在国家地质实验测试中心完成。首先取0.2 g样品粉末进行Lithium metaborate/tetrabortate 融合和硝酸稀释溶解,将样品/助溶剂的融合物于马弗炉上在1050℃的温度下加热15 min。提取熔融物,倒入100 mL由去离子水和ACS级纯度硝酸配置的5%浓度的HNO3中。将溶液摇晃2 h使其充分溶解,取其一部分置于聚丙分析管内。通过电感耦合等离子光谱分析(ICP-AES)进行主量元素和Ba、SC、Cu、Zn、Ni含量分析。在ICP-MS上进行其他微量及稀土元素含量分析。对于贵金属的分析,称取0.5 g样品,置于3 mL高温的(95℃)王水中进行溶解,通过ICP-MS进行分析。所有的分析以OS-18为标准样,精度均优于±3%。
4. 测试结果
4.1 锆石U−Pb年龄
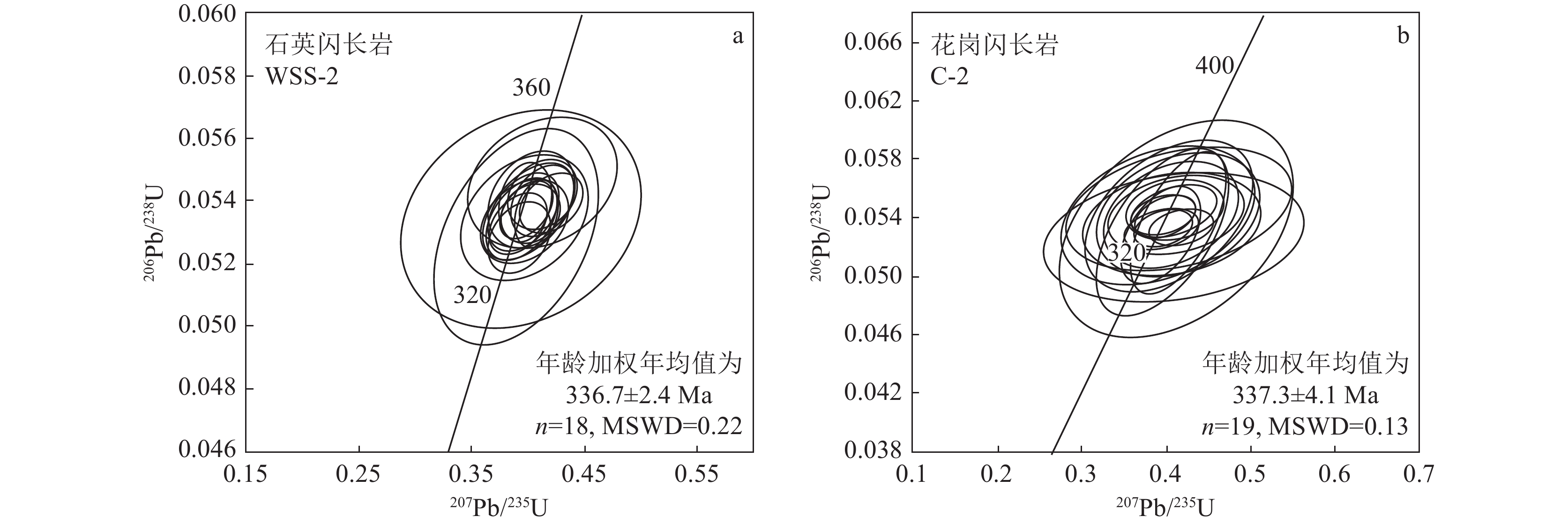
锆石U−Pb同位素分析测试结果列于表1。其中,石英闪长岩所有测试结果都落在谐和线附近,呈集中分布(图4–a),206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为336.7±2.4 Ma(MSWD=0.22,n=18),代表石英闪长岩的形成年龄。花岗闪长岩共进行了20个测点分析,1个样品因高含量204Pb而未获得结果,19个测点集中分布,落在谐和线附近,206Pb/238U年龄为335~342 Ma,206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为337.3±4.1 Ma(MSWD=0.13,n=19,图4−b),代表花岗闪长岩的形成年龄。
表 1 坝西铜矿含矿花岗闪长岩(C-2)和石英闪长岩(WSS-2) LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Th−Pb同位素分析结果Table 1. LA−ICP−MS zircon U−Th−Pb data of granodiorite (C-2) and quartz diorite (WSS-2) in the Baxi copper deposit样号 含量/10−6 Th/U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 208Pb/232U 1σ 206Pb /238U 年龄/Ma 1σ Pb Th U C-2-1 6.50 45.80 111.60 0.41 0.06 0.00 0.39 0.03 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 334.0 6.3 C-2-2 5.90 38.30 99.80 0.38 0.06 0.00 0.42 0.03 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 334.9 5.0 C-2-3 5.20 37.40 85.80 0.43 0.06 0.01 0.41 0.05 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 340.9 11.0 C-2-4 5.40 34.20 93.30 0.36 0.06 0.00 0.40 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 334.6 5.3 C-2-5 3.70 24.20 65.10 0.37 0.06 0.01 0.41 0.06 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 341.5 18.9 C-2-7 4.60 33.20 80.40 0.41 0.06 0.01 0.41 0.10 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 331.1 18.1 C-2-8 6.10 52.10 100.40 0.51 0.06 0.01 0.41 0.04 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 340.7 7.8 C-2-9 5.40 44.60 89.20 0.50 0.06 0.01 0.40 0.06 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 335.4 18.1 C-2-10 8.40 67.20 136.60 0.49 0.05 0.00 0.41 0.04 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 343.6 7.7 C-2-11 4.70 28.30 79.60 0.35 0.06 0.01 0.42 0.04 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 338.1 19.5 C-2-12 6.50 45.90 111.20 0.41 0.06 0.01 0.40 0.07 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 338.4 13.3 C-2-13 4.00 27.90 66.60 0.42 0.06 0.01 0.42 0.09 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 342.4 17.2 C-2-14 5.00 36.60 85.40 0.42 0.05 0.01 0.41 0.06 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 342.2 19.2 C-2-15 6.90 57.40 112.70 0.50 0.06 0.01 0.40 0.07 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 335.0 15.7 C-2-16 4.30 34.70 75.30 0.46 0.05 0.01 0.40 0.05 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 333.1 23.4 C-2-17 4.40 29.30 80.40 0.36 0.05 0.01 0.41 0.09 0.05 0.00 0.00 0.00 334.4 30.2 C-2-18 8.90 63.80 151.30 0.42 0.05 0.00 0.40 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 338.7 6.0 C-2-19 5.30 43.70 89.70 0.48 0.05 0.00 0.40 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 339.4 6.1 C-2-20 18.90 215.40 302.20 0.71 0.05 0.01 0.39 0.03 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 332.2 13.4 WSS-2-1 9.50 107.50 146.70 0.73 0.06 0.01 0.39 0.07 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 335.5 13.9 WSS-2-2 18.80 187.30 290.70 0.64 0.06 0.00 0.41 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 339.7 4.8 WSS-2-3 22.00 241.70 332.80 0.72 0.05 0.00 0.40 0.01 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 337.4 4.1 WSS-2-4 17.40 206.70 265.60 0.77 0.05 0.00 0.39 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 332.5 4.1 WSS-2-5 13.70 152.50 208.80 0.73 0.05 0.00 0.39 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 334.7 3.9 WSS-2-6 28.30 322.80 423.20 0.76 0.05 0.00 0.40 0.03 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 339.5 6.1 WSS-2-7 14.60 151.90 223.90 0.67 0.06 0.00 0.42 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 339.3 4.2 WSS-2-8 14.60 149.80 224.30 0.66 0.05 0.00 0.40 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 338.2 4.1 WSS-2-9 16.30 184.80 245.40 0.75 0.06 0.00 0.40 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 334.7 5.7 WSS-2-10 18.30 201.90 270.50 0.74 0.06 0.01 0.41 0.04 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 342.7 8.2 WSS-2-11 14.80 142.20 226.20 0.62 0.05 0.00 0.39 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 334.9 5.0 WSS-2-13 17.00 186.90 253.90 0.73 0.05 0.00 0.40 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 336.5 4.2 WSS-2-14 10.40 115.20 156.80 0.73 0.05 0.00 0.39 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 333.6 5.5 WSS-2-15 14.70 165.10 217.70 0.75 0.05 0.00 0.39 0.05 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 331.8 14.0 WSS-2-17 8.80 75.50 134.80 0.56 0.06 0.00 0.41 0.03 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 337.0 5.5 WSS-2-18 14.40 123.40 217.80 0.56 0.05 0.00 0.40 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 338.7 5.1 WSS-2-19 17.10 209.40 243.60 0.85 0.05 0.01 0.39 0.04 0.05 0.00 0.00 0.00 335.0 7.7 WSS-2-20 11.90 118.90 178.30 0.66 0.06 0.00 0.42 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.00 0.00 335.7 5.8 表 2 坝西铜矿赋矿岩石主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果Table 2. Major, trace and rare elements compositions of the ore-bearing rocks from the Baxi copper deposit元素 WSS-3 BX-GSY1 BX-GSY2 C-2 BX-GSY3 BX-GSY4 BX-GSY5 D008-2 石英闪长岩 石英闪长岩 黑云母辉石石英闪长岩 花岗闪长岩 花岗闪长岩 花岗闪长岩 黑云母花岗闪长岩 黑云母花岗闪长岩 SiO2 60.3 60 56.87 62.97 63.61 63.66 63.97 61.33 TiO2 0.55 0.58 0.79 0.59 0.51 0.46 0.46 0.61 Al2O3 17.85 17.7 17.22 15.95 16.12 17.52 17.37 16.19 Fe2O3 2.42 6.34 8.26 2.35 5.5 4.19 4.29 3.09 FeO 2.87 2.94 3.99 3.41 2.68 2.46 2.01 3.2 MnO 0.12 0.14 0.15 0.16 0.08 0.13 0.12 0.08 MgO 2.43 2.48 3.43 2.23 2.18 1.52 1.48 2.67 CaO 5.87 5.46 6.64 4.99 4.47 4.28 4.13 4.87 Na2O 4.36 4.37 3.4 3.4 3.58 4.62 4.73 3.54 K2O 0.84 1.31 1.41 2 2.3 1.72 1.8 2.16 P2O5 0.18 0.18 0.2 0.14 0.13 0.17 0.17 0.15 H2O + 1.08 0.11 0 1.09 0.11 0.1 0.12 1.23 烧失量 1.28 0.79 0.87 0.89 0.66 1.92 1.04 1.1 总计 100.15 102.4 103.23 100.17 101.93 102.75 101.69 100.22 La 11.9 13.6 12 12.7 14.2 15.8 14 12.8 Ce 25 30 29.3 28.5 32.9 34.3 32.2 27.9 Pr 3.42 3.6 3.6 4.26 3.9 4.1 3.8 4.2 Nd 12.8 14.8 16.2 16 15.7 16.7 15.4 15.6 Sm 3.14 3.2 4 4.36 3.5 3.5 3.4 4.49 Eu 1.07 1 1 1.02 0.86 1.1 1 0.99 Gd 3.18 2.7 3.5 4.57 3 3 2.8 4.61 Tb 0.48 0.47 0.68 0.77 0.56 0.51 0.5 0.75 Dy 2.98 2.9 4.1 4.53 3.4 3 3 4.72 Ho 0.53 0.63 0.9 0.79 0.74 0.64 0.64 0.82 Er 1.95 1.7 2.5 3.05 2.1 1.8 1.8 3.02 Tm 0.28 0.28 0.41 0.47 0.37 0.31 0.31 0.45 Yb 2 1.9 2.6 2.96 2.2 2.1 2 3.18 Lu 0.24 0.29 0.4 0.37 0.35 0.31 0.32 0.38 Y 18.2 16 22.7 29 19.3 17.4 16.4 28.7 Rb 16.5 44.7 41.3 Ba 477 786 701 Nb 3.84 4.29 3.86 Ta 0.21 0.25 0.22 Zr 93.3 99.7 152 Hf 2.63 3.33 4.41 Th 2.23 3.69 3.62 V 141 139 170 Cr 12.5 8.73 11 Co 15 16.3 12.9 Ni 9.66 7.2 8.89 U 0.88 1.24 1.37 ∑REE 68.97 77.07 81.19 84.35 83.78 87.17 81.17 83.91 δEu 1.02 1.03 0.8 0.69 0.79 1.01 0.96 0.66 DI 57.56 55.8 45.48 61.91 62.23 66.03 67.51 60.69 A/CNK 0.95 0.96 0.9 0.95 0.98 1.02 1.01 0.95 A/NK 2.21 2.06 2.42 2.05 1.92 1.85 1.78 1.98 注:主量元素含量单位为%;稀土和微量元素含量单位为10−6 4.2 岩石地球化学特征
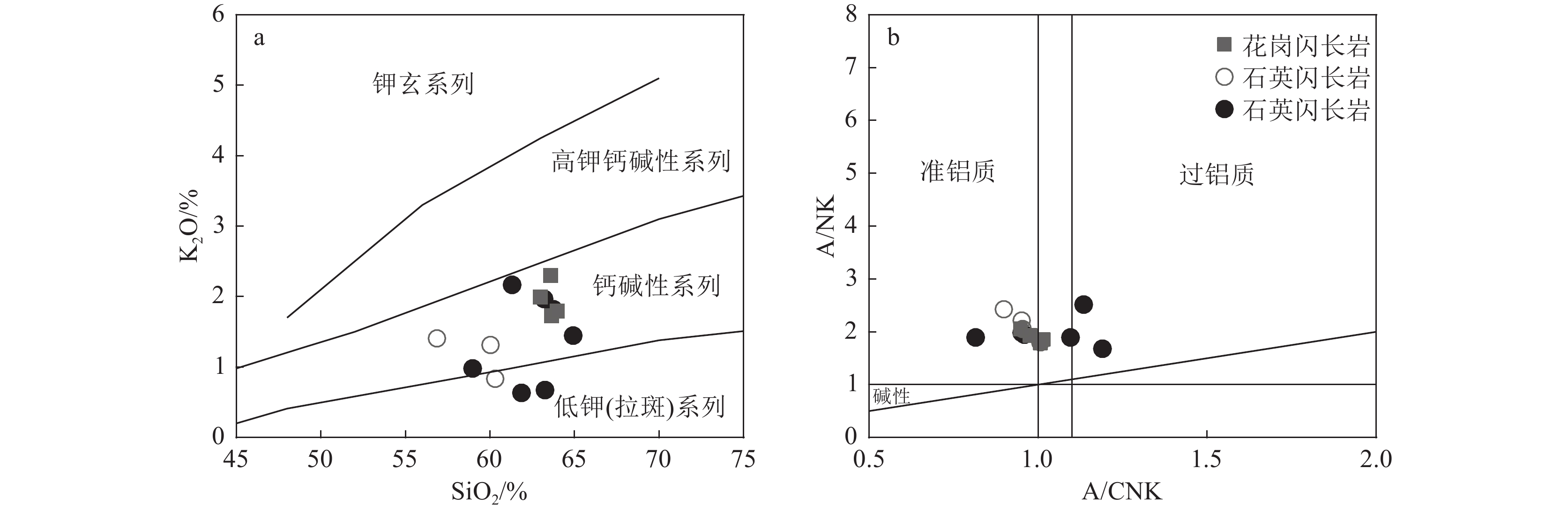
岩石化学成分测试结果见表2。花岗闪长岩SiO2含量为62.97%~63.97%,K2O+Na2O含量为5.40%~6.53%,里特曼指数σ为1.43~2.04,在SiO2−K2O图解(图5–a)中大部分样品点落入钙碱性系列;Al2O3含量为15.95%~17.52%,CaO含量为4.13%~6.64%,属准铝质或弱过铝质(A/CNK=0.95%~1.02,A/NK=1.85~2.05)(图5–b);具有低的MgO含量(1.48%~3.43%)和P2O5含量(0.13%~0.20%)。石英闪长岩中的硅(SiO2=56.87%~61.33%)和碱含量(K2O+Na2O=4.81%~5.98%)相对花岗闪长岩均较低,而铝含量较高(Al2O3=16.19%~17.85%),主体也属钙碱性系列(图5–a),但全部属于准铝质(A/CNK=0.90~0.97,A/NK=1.98~2.42),Xiao et al.(2018)、张铭鸿等(2021)获得石英闪长岩相对宽泛的分析结果,部分落在过铝质区(图5–b)。
![]() 图 5 坝西铜矿花岗闪长岩和石英闪长岩SiO2−K2O图解(a)和A/CNK−A/NK图解(b)(空心圆石英闪长岩数据为本文数据;实心圆石英闪长岩数据据Xiao et al., 2018; 张铭鸿等,2021)Figure 5. Diagrams of SiO2-K2O (a) and A/CNK-A/NK (b) for granodiorite and quartz diorite from the Baxi copper deposit
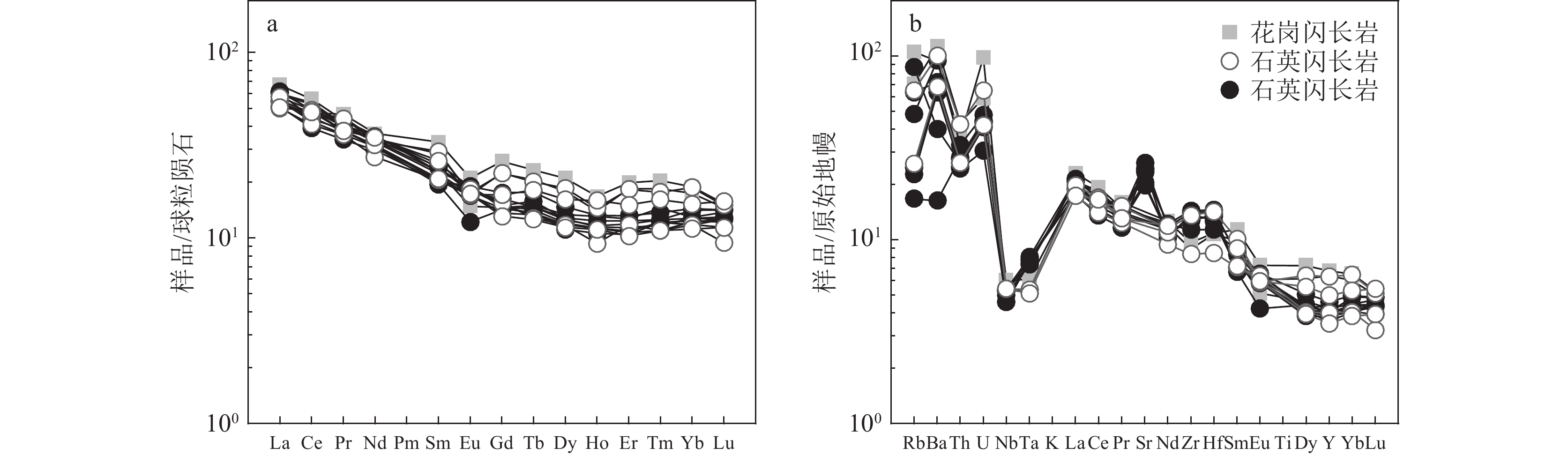
图 5 坝西铜矿花岗闪长岩和石英闪长岩SiO2−K2O图解(a)和A/CNK−A/NK图解(b)(空心圆石英闪长岩数据为本文数据;实心圆石英闪长岩数据据Xiao et al., 2018; 张铭鸿等,2021)Figure 5. Diagrams of SiO2-K2O (a) and A/CNK-A/NK (b) for granodiorite and quartz diorite from the Baxi copper deposit含矿石英闪长岩和花岗闪长岩的稀土元素含量均不高,总量(∑REE)介于68.97×10−6~87.17×10−6之间,变化范围较小,轻稀土元素(LREE)含量为57.33×10−6~75.50×10−6,重稀土元素(HREE)含量为10.87×10−6~19.88×10−6。在球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分曲线中,样品差异不大,呈右倾型(图6–a)。岩石LREE/HREE值介于3.51~6.47之间,显示轻稀土元素富集、重稀土元素含量亏损。δEu值为0.66~1.03,仅3个样品δEu>1,δEu平均值为0.85,总体上表现为Eu负异常;(La/Yb)N值为2.89~5.40,平均4.07,轻稀土元素相对富集,轻、重稀土元素分馏较明显;(La/Sm)N值介于1.63~2.84之间。在微量元素原始地幔蛛网图(图6–b)上,大离子亲石元素U、La、Hf及K、Rb、Ba等较富集,Th、Nb、Ta、Ti高场强元素相对亏损。这与前人获得的石英闪长岩稀土和微量元素特征总体一致(图6–b)。
![]() 图 6 坝西铜矿花岗闪长岩和石英闪长岩稀土元素配分模式图(a)及微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化值据Sun et al., 1989;空心圆石英闪长岩数据为本文数据;实心圆石英闪长岩数据据Xiao et al., 2018; 张铭鸿等,2021)Figure 6. Chondrite normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive-mantle normalized trace element spidergrams (b) for granodiorite and quartz diorite from the Baxi copper deposit .
图 6 坝西铜矿花岗闪长岩和石英闪长岩稀土元素配分模式图(a)及微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化值据Sun et al., 1989;空心圆石英闪长岩数据为本文数据;实心圆石英闪长岩数据据Xiao et al., 2018; 张铭鸿等,2021)Figure 6. Chondrite normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive-mantle normalized trace element spidergrams (b) for granodiorite and quartz diorite from the Baxi copper deposit .5. 讨 论
5.1 成岩成矿时代
本次对坝西斑岩铜矿赋矿围岩中的石英闪长岩和花岗闪长岩锆石U−Pb测年结果显示,石英闪长岩锆石U−Pb年龄为336.6±2.4 Ma,与前人测年结果(345.7 Ma,Xiao et al., 2018)基本一致,属早石炭世侵位的产物;花岗闪长岩锆石U−Pb年龄为337.3±4.1 Ma,与本文石英闪长岩测年结果一致(337 Ma)。该结果与两者在野外呈相互穿插关系相一致,且与矿区辉钼矿Re-Os测年结果(338.9±4.6 Ma,另文发表)一致,符合斑岩铜矿成岩成矿时代一致性的特点。
东准噶尔及邻区的岩浆事件主要发生在早中古生代(志留纪—泥盆纪)和晚古生代中晚期(喻亨祥等,1998;李锦轶等,1990,2000;杨富全等,2001;李雷,2012;赵建新等,2017;Gao et al., 2018),是中亚成矿域内大规模斑岩矿产的聚集区之一(Gao et al., 2018a, b;Gu et al., 1996;熊小林等,2005;Windley et al., 2007; 杨志明等,2009)。早石炭世岩浆活动较弱。之前的勘查与研究显示,东准噶尔成矿期主要为早中古生代(志留纪—泥盆纪)。琼河坝地区除北山金矿形成于晚古生代外(346 Ma),其他矿产均形成于志留纪—泥盆纪,如蒙西铜矿、琼河坝铜矿、桑南铜矿、铜华岭铜矿及和尔赛铜矿,且形成时代较集中(420~390 Ma)(王登红等,2009;屈迅等,2009;张永等,2010;Ji et al., 2018; 王斯林等,2018;王磊等,2018;高俊等,2019)。本次研究表明,除早古生代的峰期成矿事件外,东准噶尔地区还存在一期北山金矿、坝西铜矿这样的晚古生代成矿事件,对后期的矿产勘查具有重要的指示意义。
5.2 成因及对矿产勘查的启示
坝西铜矿石英闪长岩和花岗闪长岩主量元素含量相近,低硅、低钾,属于钙碱性系列花岗岩类,钙、铝含量中等,显示出准铝质或弱过铝质花岗岩的特点,与典型I型花岗岩类一致。在Harker图解上,赋矿围岩显示出2个不同的演化序列,各自成较好的线性关系,暗示这2类岩石并不是同一种岩浆分异的产物,可能是岩浆混合的产物,同时,无论花岗闪长岩还是石英闪长岩均可见暗色微粒包体,暗示了岩浆混合作用的存在。赵建新等(2017)获得石英闪长岩的锆石Hf同位素分析结果(εHf(t)=+13.66~+15.56),与本区同期花岗岩类同位素特征一致,显示年轻幔源物质是其主要的物质来源。
矿区2类岩石的稀土元素总量均较低,且相对富集轻稀土元素,负Eu异常较弱,表明斜长石分离结晶作用不明显,分异指数较低也指示了这一点。在微量元素蛛网图中,岩石相对富集大离子亲石元素,亏损Nb、Ta、Ti等高场强元素,暗示有明显的榍石的分离结晶。综合看,虽然这些赋矿花岗岩类显示出弧花岗岩的特征,如相对高的Y(16.0×10−6~28.7×10−6)和Yb(1.90×10−6~3.18×10−6)含量,以及低的Sr/Y和(La/Yb)N值,但它们具有埃达克岩的地球化学特征,如高硅(SiO2>56%)、低镁(MgO<3%)、高锶(Sr>400×10−6),表明它们可能与典型的弧花岗岩有所区别。
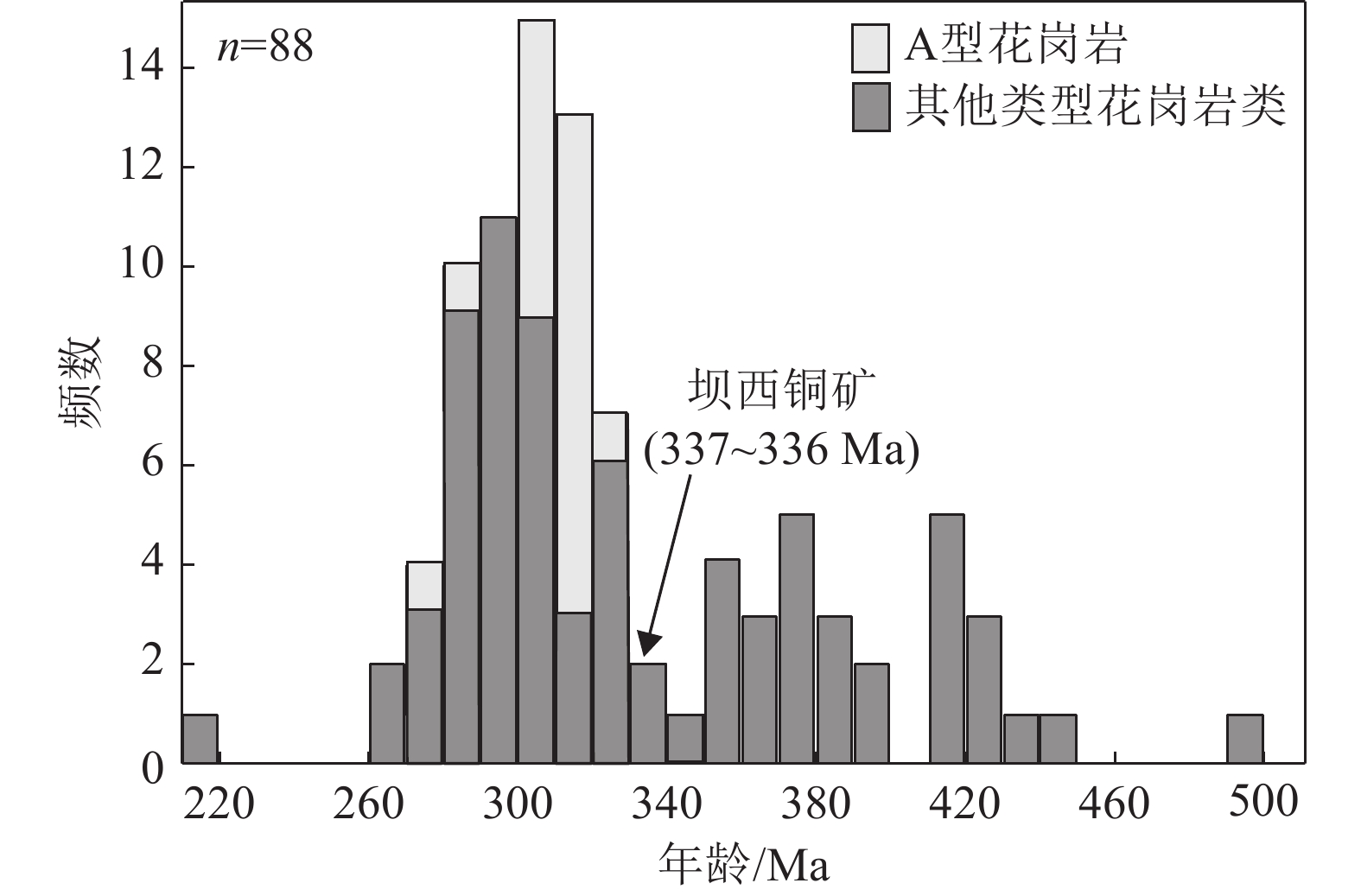
值得注意的是,东准噶尔地区大量发育的早古生代弧岩浆作用,在早石炭世(360~330 Ma)似乎出现一个岩浆“宁静期”(肖文交等,2006),随后(330~270 Ma)发育大规模的碱性(A型)花岗岩(图7)(侯增谦等,2006;张招崇等,2010),并且发育时间从北到南是同步的,不具有时空迁移性(卢鹏等,2021),揭示了区域性造山后伸展背景。东准噶尔地区石炭纪沉积相由滨海、浅海相向浅海相—陆相转变,北疆地区全区性的晚石炭世不整合也为此提供了证据,表明早石炭世应是从泥盆纪的俯冲挤压环境向晚石炭世后造山伸展环境转变的重要时期,只是缺乏碰撞相关的证据,实际上整个中亚造山带构造演化晚期均缺失碰撞的直接证据,但早石炭世是一个重要的构造体制转换期。形成于早石炭世晚期的坝西岩体应是这种构造体制转换期的产物,并不是直接与俯冲作用有关,而是早期的弧物质发生部分熔融,为这些石英闪长岩和花岗岩闪长岩岩浆提供了重要物质来源,因此这些岩石均显示出弧花岗岩的特征,但又与之不同。同时,这些早期的弧物质也是成矿物质的重要来源,或者说早期的俯冲促成了成矿物质的初步富集,在构造转换阶段的初期进一步富集成矿。像坝西铜矿这种出现于岩浆活动“宁静期”之后,岩浆作用渐强的关键时期的斑岩铜矿,虽然不一定是后碰撞成矿,但其与冈底斯大规模后碰撞斑岩在成岩成矿物质来源、演化特征方面具有很多的相似之处(侯增谦等,2006;张招崇等,2010;Xiao et al., 2012),需要注意这种早期俯冲阶段的成矿物质富集,在后期再富集(活化)成矿的(斑岩)矿产,不仅对琼河坝地区的找矿工作有重要的指示意义,也有助于深化整个北疆乃至中亚造山带南缘的构造转换阶段—后碰撞斑岩铜矿形成机制的认识。
6. 结 论
(1)新疆东准噶尔坝西斑岩铜矿赋矿围岩形成于早石炭世晚期,石英闪长岩和花岗闪长岩锆石U−Pb年龄分别为336.6±2.4 Ma和337.3±4.1 Ma,二者形成时代基本一致,表明在琼河坝地区除早古生代的成岩成矿事件外,还存在一期晚古生代的成岩成矿事件。
(2)坝西岩体形成于从早古生代的俯冲增生到晚石炭世—早二叠世后造山伸展的构造体制转换期,早期的弧物质为这些岩浆作用和成矿作用提供了重要物质来源,岩浆混合作用是岩体形成的重要机制。
致谢:本文在实验测试过程中得到中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所杨岳清老师的帮助,新疆维吾尔自治区地质矿产勘查开发局第六地质大队在野外调查、资料收集等方面提供了帮助,审稿老师认真审阅本文并提出了建设性意见,在此表示衷心的感谢。
-
图 1 东准噶尔地质简图(a)、区域地质图(b)及矿区地质简图(c)(年龄数据据张铭鸿等,2021)
Figure 1. Geotectonic position(a), regional geological (b) and mine geological (c) maps of the Baxi copper deposit
图 5 坝西铜矿花岗闪长岩和石英闪长岩SiO2−K2O图解(a)和A/CNK−A/NK图解(b)(空心圆石英闪长岩数据为本文数据;实心圆石英闪长岩数据据Xiao et al., 2018; 张铭鸿等,2021)
Figure 5. Diagrams of SiO2-K2O (a) and A/CNK-A/NK (b) for granodiorite and quartz diorite from the Baxi copper deposit
图 6 坝西铜矿花岗闪长岩和石英闪长岩稀土元素配分模式图(a)及微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化值据Sun et al., 1989;空心圆石英闪长岩数据为本文数据;实心圆石英闪长岩数据据Xiao et al., 2018; 张铭鸿等,2021)
Figure 6. Chondrite normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive-mantle normalized trace element spidergrams (b) for granodiorite and quartz diorite from the Baxi copper deposit .
表 1 坝西铜矿含矿花岗闪长岩(C-2)和石英闪长岩(WSS-2) LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Th−Pb同位素分析结果
Table 1 LA−ICP−MS zircon U−Th−Pb data of granodiorite (C-2) and quartz diorite (WSS-2) in the Baxi copper deposit
样号 含量/10−6 Th/U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 208Pb/232U 1σ 206Pb /238U 年龄/Ma 1σ Pb Th U C-2-1 6.50 45.80 111.60 0.41 0.06 0.00 0.39 0.03 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 334.0 6.3 C-2-2 5.90 38.30 99.80 0.38 0.06 0.00 0.42 0.03 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 334.9 5.0 C-2-3 5.20 37.40 85.80 0.43 0.06 0.01 0.41 0.05 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 340.9 11.0 C-2-4 5.40 34.20 93.30 0.36 0.06 0.00 0.40 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 334.6 5.3 C-2-5 3.70 24.20 65.10 0.37 0.06 0.01 0.41 0.06 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 341.5 18.9 C-2-7 4.60 33.20 80.40 0.41 0.06 0.01 0.41 0.10 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 331.1 18.1 C-2-8 6.10 52.10 100.40 0.51 0.06 0.01 0.41 0.04 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 340.7 7.8 C-2-9 5.40 44.60 89.20 0.50 0.06 0.01 0.40 0.06 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 335.4 18.1 C-2-10 8.40 67.20 136.60 0.49 0.05 0.00 0.41 0.04 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 343.6 7.7 C-2-11 4.70 28.30 79.60 0.35 0.06 0.01 0.42 0.04 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 338.1 19.5 C-2-12 6.50 45.90 111.20 0.41 0.06 0.01 0.40 0.07 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 338.4 13.3 C-2-13 4.00 27.90 66.60 0.42 0.06 0.01 0.42 0.09 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 342.4 17.2 C-2-14 5.00 36.60 85.40 0.42 0.05 0.01 0.41 0.06 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 342.2 19.2 C-2-15 6.90 57.40 112.70 0.50 0.06 0.01 0.40 0.07 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 335.0 15.7 C-2-16 4.30 34.70 75.30 0.46 0.05 0.01 0.40 0.05 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 333.1 23.4 C-2-17 4.40 29.30 80.40 0.36 0.05 0.01 0.41 0.09 0.05 0.00 0.00 0.00 334.4 30.2 C-2-18 8.90 63.80 151.30 0.42 0.05 0.00 0.40 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 338.7 6.0 C-2-19 5.30 43.70 89.70 0.48 0.05 0.00 0.40 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 339.4 6.1 C-2-20 18.90 215.40 302.20 0.71 0.05 0.01 0.39 0.03 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 332.2 13.4 WSS-2-1 9.50 107.50 146.70 0.73 0.06 0.01 0.39 0.07 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 335.5 13.9 WSS-2-2 18.80 187.30 290.70 0.64 0.06 0.00 0.41 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 339.7 4.8 WSS-2-3 22.00 241.70 332.80 0.72 0.05 0.00 0.40 0.01 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 337.4 4.1 WSS-2-4 17.40 206.70 265.60 0.77 0.05 0.00 0.39 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 332.5 4.1 WSS-2-5 13.70 152.50 208.80 0.73 0.05 0.00 0.39 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 334.7 3.9 WSS-2-6 28.30 322.80 423.20 0.76 0.05 0.00 0.40 0.03 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 339.5 6.1 WSS-2-7 14.60 151.90 223.90 0.67 0.06 0.00 0.42 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 339.3 4.2 WSS-2-8 14.60 149.80 224.30 0.66 0.05 0.00 0.40 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 338.2 4.1 WSS-2-9 16.30 184.80 245.40 0.75 0.06 0.00 0.40 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 334.7 5.7 WSS-2-10 18.30 201.90 270.50 0.74 0.06 0.01 0.41 0.04 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 342.7 8.2 WSS-2-11 14.80 142.20 226.20 0.62 0.05 0.00 0.39 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 334.9 5.0 WSS-2-13 17.00 186.90 253.90 0.73 0.05 0.00 0.40 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 336.5 4.2 WSS-2-14 10.40 115.20 156.80 0.73 0.05 0.00 0.39 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 333.6 5.5 WSS-2-15 14.70 165.10 217.70 0.75 0.05 0.00 0.39 0.05 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 331.8 14.0 WSS-2-17 8.80 75.50 134.80 0.56 0.06 0.00 0.41 0.03 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 337.0 5.5 WSS-2-18 14.40 123.40 217.80 0.56 0.05 0.00 0.40 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.01 0.00 338.7 5.1 WSS-2-19 17.10 209.40 243.60 0.85 0.05 0.01 0.39 0.04 0.05 0.00 0.00 0.00 335.0 7.7 WSS-2-20 11.90 118.90 178.30 0.66 0.06 0.00 0.42 0.02 0.05 0.00 0.00 0.00 335.7 5.8 表 2 坝西铜矿赋矿岩石主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 2 Major, trace and rare elements compositions of the ore-bearing rocks from the Baxi copper deposit
元素 WSS-3 BX-GSY1 BX-GSY2 C-2 BX-GSY3 BX-GSY4 BX-GSY5 D008-2 石英闪长岩 石英闪长岩 黑云母辉石石英闪长岩 花岗闪长岩 花岗闪长岩 花岗闪长岩 黑云母花岗闪长岩 黑云母花岗闪长岩 SiO2 60.3 60 56.87 62.97 63.61 63.66 63.97 61.33 TiO2 0.55 0.58 0.79 0.59 0.51 0.46 0.46 0.61 Al2O3 17.85 17.7 17.22 15.95 16.12 17.52 17.37 16.19 Fe2O3 2.42 6.34 8.26 2.35 5.5 4.19 4.29 3.09 FeO 2.87 2.94 3.99 3.41 2.68 2.46 2.01 3.2 MnO 0.12 0.14 0.15 0.16 0.08 0.13 0.12 0.08 MgO 2.43 2.48 3.43 2.23 2.18 1.52 1.48 2.67 CaO 5.87 5.46 6.64 4.99 4.47 4.28 4.13 4.87 Na2O 4.36 4.37 3.4 3.4 3.58 4.62 4.73 3.54 K2O 0.84 1.31 1.41 2 2.3 1.72 1.8 2.16 P2O5 0.18 0.18 0.2 0.14 0.13 0.17 0.17 0.15 H2O + 1.08 0.11 0 1.09 0.11 0.1 0.12 1.23 烧失量 1.28 0.79 0.87 0.89 0.66 1.92 1.04 1.1 总计 100.15 102.4 103.23 100.17 101.93 102.75 101.69 100.22 La 11.9 13.6 12 12.7 14.2 15.8 14 12.8 Ce 25 30 29.3 28.5 32.9 34.3 32.2 27.9 Pr 3.42 3.6 3.6 4.26 3.9 4.1 3.8 4.2 Nd 12.8 14.8 16.2 16 15.7 16.7 15.4 15.6 Sm 3.14 3.2 4 4.36 3.5 3.5 3.4 4.49 Eu 1.07 1 1 1.02 0.86 1.1 1 0.99 Gd 3.18 2.7 3.5 4.57 3 3 2.8 4.61 Tb 0.48 0.47 0.68 0.77 0.56 0.51 0.5 0.75 Dy 2.98 2.9 4.1 4.53 3.4 3 3 4.72 Ho 0.53 0.63 0.9 0.79 0.74 0.64 0.64 0.82 Er 1.95 1.7 2.5 3.05 2.1 1.8 1.8 3.02 Tm 0.28 0.28 0.41 0.47 0.37 0.31 0.31 0.45 Yb 2 1.9 2.6 2.96 2.2 2.1 2 3.18 Lu 0.24 0.29 0.4 0.37 0.35 0.31 0.32 0.38 Y 18.2 16 22.7 29 19.3 17.4 16.4 28.7 Rb 16.5 44.7 41.3 Ba 477 786 701 Nb 3.84 4.29 3.86 Ta 0.21 0.25 0.22 Zr 93.3 99.7 152 Hf 2.63 3.33 4.41 Th 2.23 3.69 3.62 V 141 139 170 Cr 12.5 8.73 11 Co 15 16.3 12.9 Ni 9.66 7.2 8.89 U 0.88 1.24 1.37 ∑REE 68.97 77.07 81.19 84.35 83.78 87.17 81.17 83.91 δEu 1.02 1.03 0.8 0.69 0.79 1.01 0.96 0.66 DI 57.56 55.8 45.48 61.91 62.23 66.03 67.51 60.69 A/CNK 0.95 0.96 0.9 0.95 0.98 1.02 1.01 0.95 A/NK 2.21 2.06 2.42 2.05 1.92 1.85 1.78 1.98 注:主量元素含量单位为%;稀土和微量元素含量单位为10−6 -
Chen B, Jahn B M, Wilde S, et al. 2000. Two contrasting Paleozoic magmatic belts in northern Inner Mongolia, China: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Tectonophysics, 328(1): 157−182.
Du S J, Qu X, Deng G, et al. 2010. Chronology and tectonic setting of the intrusive bodies and associated porphyry copper deposit in Hersai area, eastern Junggar.[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(10): 2981−2996(in Chinese with English abstract).
Gao F L, Gui X M, Li T Z, et al. 2018. Rock−forming and ore−forming ages and geochemistry of the Layikeleke porphyry Cu(Mo) deposit in East Junggar of Xinjiang and their geological significance[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 37(6): 1113−1124.
Gao J, Klemd R, Zhu M, et al. 2018a. Large−scale porphyry−type mineralization in the Central Asian metallogenic domain: A review[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 165: 7−36. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.10.002
Gao J, Qin K Z, Zhou M F, et al. 2018b. Large−scale porphyry−type mineralization in the Central Asian Metallogenic Domain: Geodynamic background, magmatism, fluid activity and metallogenesis[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 165: 1−6. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.08.023
Gao J, Zhu M T, Wang X S, et al. 2019. Large−scale porphyry−type mineralization in the Central Asian metallogenic domain: tectonic background, fluid feature and metallogenic deep dynamic mechanism[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 93(1): 24−71(in Chinese with English abstract).
Gu L X, Yan Z F. 1996. Geology and genesis of peraluminous granites in East Tianshan Upper Paleozoic island arc belt[J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 15(1): 33−43. doi: 10.1007/BF03166794
Guo L S, Zhang R, Liu Y L, et al. 2009. Zircon U−Pb age of Tonghualing intermediate−acid intrusive rocks, Eastern Junggar, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 45(5): 819−824(in Chinese with English abstract).
Han Y, Zhao G. 2018. Final amalgamation of the Tianshan and Junggar orogenic collage in the southwestern Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Constraints on the closure of the Paleo−Asian Ocean[J]. Earth−Science Reviews, 186: 129−152. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.09.012
Hou K J, Qin Y, Li Y H, et al. 2013. In situ Sr−Nd Isotopic Measurement of Apatite Using Laser Ablation Multi−collector Inductively Coupled Plasma−Mass Spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 32(4): 547−554(in Chinese with English abstract).
Hou Z Q, Qu X M, Yang Z S, et al. 2006. Metallogenesis in Tibetan collisional orogenic belt: Ⅲ. Mineralization in post−collisional extension setting[J]. Mineral Deposits, 25(6): 629−651(in Chinese with English abstract).
Huang G, Niu G Z, Wang X L, et al. 2016. Early Silurian adakitic rocks of East Junggar, Xinjiang: Evidence from zircon U−Pb age, geochemistry and Sr−Nd−Hf isotope of the quartz diorite[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 35(5): 751−767(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ji J Q, Chen J F, Han B F. 2018. Zircon U−Pb ages and tectonic implications of Paleozoic plutons in northern West Junggar, North Xinjiang, China[J]. Lithos, 115(1/4): 137−152.
Liu Y S. 2014. The manual of ICPMSDataCal for LA-ICP-MS/LA-MCICP-MS data processing[R]. State Key Laboratory of Geological Processes and Mineral Resources, China University of Geosciences: 1–40(in Chinese).
Ludwig K R. 2012. User’s manual for Isoplot 3.75: A geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley, California: Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication.
Li J T, Zhu B Q. 1990. Main characteristics of late paleozoic platetectonics in the southern part of East Junggar, Xinjiang[J]. Geological Review, 36(4): 305−316(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li J T, Xiao X C, Chen W. 2000. Late Ordovician continental basement of the eastern Junggar Basin in Xinjiang, NW China: Evidence from the Laojunmiao metamorphic complex on the northeast basin margin[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 19(3): 297−302(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li L. 2012. Study on the Granitic Magmatism and Tectonic Significance of the Silurian in the Eastern Junggar Region, Xinjiang[D]. Master's Thesis of Northwest University(in Chinese with English abstract).
Long X, Yuan C, Sun M, et al. 2012. Geochemistry and U−Pb detrital zircon dating of Paleozoic graywackes in East Junggar, NW China: Insights into subduction−accretion processes in the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Gondwana Research, 21(2/3): 637−653. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.05.015
Lu P, Tong Y, Meng Q Y, et al. 2021. Petrogenesis and tectonic setting of the Late Permian A−type granitic dyke swarm in Ulungur, East Junggar[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 40(1): 58−70(in Chinese with English abstract).
Meng Q Y. 2020. Spatiotemporal distribution and mineralization of Paleozoic granites in East Junggar[D]. Master's Thesis of China University of Geosciences(Beijing)(in Chinese with English abstract).
Qu X, Xu X W, Liang G L, et al. 2009. Geological and geochemical characteristics of the Mengxi Cu−Mo deposit and its constraint to tectonic setting of the Qiongheba magmatic arc in eastern Junggar, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(4): 765−776(in Chinese with English abstract).
Shen P. 2015. The magmatic oxygen fugacity of porphyry copper deposits in the Central Asian Metallogenic Domain and its control on the scale of ore deposits[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2015(S1): 497(in Chinese).
Sun S S, Mcdonough W F. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publications, 42(12): 313−345.
Tong Y, Wang T, Hong D W, et al. 2010. Spatial and temporal distribution of the Carboniferous−Permian granitoids in northern Xinjiang and its adjacent areas, and its tectonic significance[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 29(6): 619−641(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang D H, Li H Q, Ying L J, et al. 2009. Copper and gold metallogenic epoch and prospecting potential in Qiongheba area of Yiwu County, Xinjiang[J]. Mineral Deposits, 28(1): 73−82(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang L, Chen A D. 2018. Discussion on geophysical characteristics and prospecting of Bashang copper deposit in Xinjiang[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 496(4): 107−109(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang S L, Qu S Z, Xu M S, et al. 2017. Geophysical characteristics and prospecting direction of Daxi copper depoasits[J]. Xingjiang Geology, 35(2): 201−206(in Chinese).
Wang S L, Guo Y, Gao K. 2018. Geological characteristics and metallogenic prospect analysis of Daxi copper deposit in Yiwu County, Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Youse Jinshu, 41(1): 22−24(in Chinese).
Windley B F, Alexeiev, Xiao W J, et al. 2007. Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 164(12): 31−47.
Xiao W J, Han C M, Yuan C, et al. 2006. Unique Carboniferous−Permian tectonic−metallogenic framework of Northern Xinjiang (NW China): Constraints for the tectonics of the southern Paleoasian Domain[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(5): 1062−1076(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xiao W, Windley B F, Han C, et al. 2018. Late Paleozoic to Early Triassic multiple roll−back and oroclinal bending of the Mongolia collage in Central Asia[J]. Earth−Science Reviews, 186: 94−128. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.09.020
Xiao W, Li S, Santosh M, et al. 2012. Orogenic belts in Central Asia: Correlations and connections[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 49: 1−6. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.03.001
Xiong X L, Cai Z Y, Niu H C, et al. 2005. The Late Paleozoic adakites in eastern Tianshan area and their metallogenetic significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(3): 967−976(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang F Q, Wu H, Han J L. 2001. Metallogenic series and metallogenic egularity of metallic ore deposits in East Zhungeer, Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 19(1): 54−58(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Z M, Hou Z Q. 2009. Porphyry Cu deposits in collisional orogen setting: A preliminary genetic model[J]. Mineral Deposits, 28(5): 515−538(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yu H X, Wu G Q, Liu J Y. 1998. Two types of granite and two metallogenic series in eastern Junggar Region of Xinjiang[J]. Geotectonica Et Metallogenia, 22(2): 119−127(in Chinese).
Zhang H X, Niu H C, Hiroaki Sato, et al. 2004. Late Paleozoic Adakite and Nb−enriched Basalt from Northern Xinjiang: Evidence for the Southward Subduction of the Paleo−Asian Ocean[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 10(1): 106−113(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang H X, Shen X M, Ma L , et al. 2008. Geochronology of the Fuyun adakite, North Xinjiang and its constraint to the initiation of the Paleo−Asian Ocean subduction[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(5): 1054−1058(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang M H, Yao Y, Cheng Z G, et al. 2021. Early Carboniferous quartz diorite in the Baxi copper deposit, East Junggar: Insight into potential for porphyry copper deposits[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 40(1): 153−168(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Y, Liang G L, Wu Q Y, et al. 2010. Characteristics and formation mechanism of the veins in Mengxi porphyry Cu−Mo deposit, eastern Junggar, Xinjiang, China.[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(10): 2997−3006(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Z C, Dong S Y, H H, et al. 2009. Geology and geochemistry of the Permian intermediate−acid intrusions in the southwestern Tianshan, Xinjiang, China: implications for petrogenesis and tectonics[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 28(12): 1827−1839 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao J X, Tong Y, Meng G X, et al. 2017. Zircon U−Pb age and petrogenesis of the Lüshigou high Ba−Sr quartz−monzonite in East Junggar, Xinjiang, and its geological significance[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 36(5): 743−754(in Chinese with English abstract).
杜世俊, 屈迅, 邓刚, 等. 2010. 东准噶尔和尔赛斑岩铜矿成岩成矿时代与形成的构造背景[J]. 岩石学报, 26(10): 2981−2996. 高俊, 朱明田, 王信水, 等. 2019. 中亚成矿域斑岩大规模成矿特征: 大地构造背景, 流体作用与成矿深部动力学机制[J]. 地质学报, 93(1): 24−71. 郭丽爽, 张锐, 刘玉琳, 等. 2009. 新疆东准噶尔铜华岭中酸性侵入体锆石U−Pb年代学研究[J]. 北京大学学报: 自然科学版, 45(5): 819−824. 侯可军, 秦燕, 李延河, 等. 2013. 磷灰石Sr−Nd同位素的激光剥蚀−多接收器电感耦合等离子体质谱微区分析[J]. 岩矿测试, 32(4): 547−554. 侯增谦, 曲晓明, 杨竹森, 等. 2006. 青藏高原碰撞造山带: Ⅲ 后碰撞伸展成矿作用[J]. 矿床地质, 25(6): 629−651. 黄岗, 牛广智, 王新录, 等. 2016. 新疆东准噶尔早志留世埃达克岩−来自锆石U−Pb年龄、地球化学及Sr−Nd−Hf同位素的证据[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 35(5): 751−767. 李锦轶, 肖序常, 汤耀庆, 等. 1990. 新疆东准噶尔卡拉麦里地区晚古生代板块构造的基本特征[J]. 地质论评, 36(4): 305−316. 李锦轶, 肖序常, 陈文. 2000. 准噶尔盆地东部的前晚奥陶世陆壳基底——来自盆地东北缘老君庙变质岩的证据[J]. 中国区域地质, 19(3): 297−302. 李雷. 2012. 新疆东准噶尔地区志留纪花岗岩浆作用及构造意义研究[D]. 西北大学硕士学位论文. 刘勇胜. 2014. LA-ICP-MS/LA-MC-ICP-MS 数据处理软件ICPMSDataCal(V9. 5) 使用手册[R]. 中国地质大学地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室: 1–40. 卢鹏, 童英, 孟秋熠, 等. 2021. 东准噶尔北缘乌伦古地区晚二叠世A型花岗质岩墙成因及构造背景[J]. 地质通报, 40(1): 58−70. 孟秋熠. 2020. 东准噶尔古生代花岗岩时空分布规律与成矿作用[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文. 屈迅, 徐兴旺, 梁广林, 等. 2009. 蒙西斑岩型铜钼矿地质地球化学特征及其对东准噶尔琼河坝岩浆岛弧构造属性的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 25(4): 765−776. 申萍. 2015. 中亚成矿域斑岩铜矿岩浆氧逸度及其对矿床规模的控制[J]. 矿物学报, (S1): 497. 童英, 王涛, 洪大卫, 等. 2010. 北疆及邻区石炭—二叠纪花岗岩时空分布特征及其构造意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 29(6): 619−641. 王登红, 李华芹, 应立娟, 等. 2009. 新疆伊吾琼河坝地区铜、金矿成矿时代及其找矿前景[J]. 矿床地质, 28(1): 73−82. 王磊, 陈安德. 2018. 关于新疆坝西铜矿地球物理特征及找矿探讨[J]. 世界有色金属, 496(4): 107−109. 王斯林, 屈栓柱, 徐敏山, 等. 2017. 坝西铜矿地质地球物理特征及找矿方向[J]. 新疆地质, 35(2): 201−206. 王斯林, 郭燕, 高科. 2018. 新疆伊吾县坝西铜矿地质特征及成矿远景分析[J]. 新疆有色金属, 41(1): 22−24. 肖文交, 韩春明, 袁超, 等. 2006. 新疆北部石炭纪—二叠纪独特的构造−成矿作用: 对古亚洲洋构造域南部大地构造演化的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 22(5): 1062−1076. 熊小林, 蔡志勇, 牛贺才, 等. 2005. 东天山晚古生代埃达克岩成因及铜金成矿意义[J]. 岩石学报, 21(3): 967−976. 杨富全, 吴海, 韩金良. 2001. 新疆东准噶尔金属矿床成矿系列及成矿规律[J]. 新疆地质, 19(1): 54−58. 杨志明, 侯增谦. 2009. 初论碰撞造山环境斑岩铜矿成矿模型[J]. 矿床地质, 28(5): 515−538. 喻亨祥, 吴郭泉, 刘家远. 1998. 新疆东准噶尔地区两类花岗岩与两个成矿系列[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 22(2): 119−127. 张海祥, 沈晓明, 马林, 等. 2008. 新疆北部富蕴县埃达克岩的同位素年代学及其对古亚洲洋板块俯冲时限的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 24(5): 1054−1058. 张海祥, 牛贺才, Sato H, 等. 2004. 新疆北部晚古生代埃达克岩、富铌玄武岩组合: 古亚洲洋板块南向俯冲的证据[J]. 高校地质学报, 10(1): 106−113. 张铭鸿, 姚勇, 程志国, 等. 2021. 新疆东准噶尔坝西早石炭世石英闪长岩及其对斑岩铜矿的指示意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 40(1): 153−168. 张永, 梁广林, 吴倩怡, 等. 2010. 东准噶尔蒙西斑岩铜钼矿床脉体特征及其形成机制[J]. 岩石学报, 26(10): 2997−3006. 张招崇, 董书云, 黄河, 等. 2010. 西南天山二叠纪中酸性侵入岩的地质学和地球化学: 岩石成因和构造背景[J]. 地质通报, 28(12): 1827−1839. 赵建新, 童英, 孟贵祥, 等. 2017. 新疆东准噶尔绿石沟高Ba−Sr石英二长岩的锆石U−Pb年龄、成因及地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 36(5): 743−754.



 下载:
下载: