Spatio-temporal variation of soil conservation in the upper reaches of the Tarim River Basin based on RUSLE model
-
摘要:
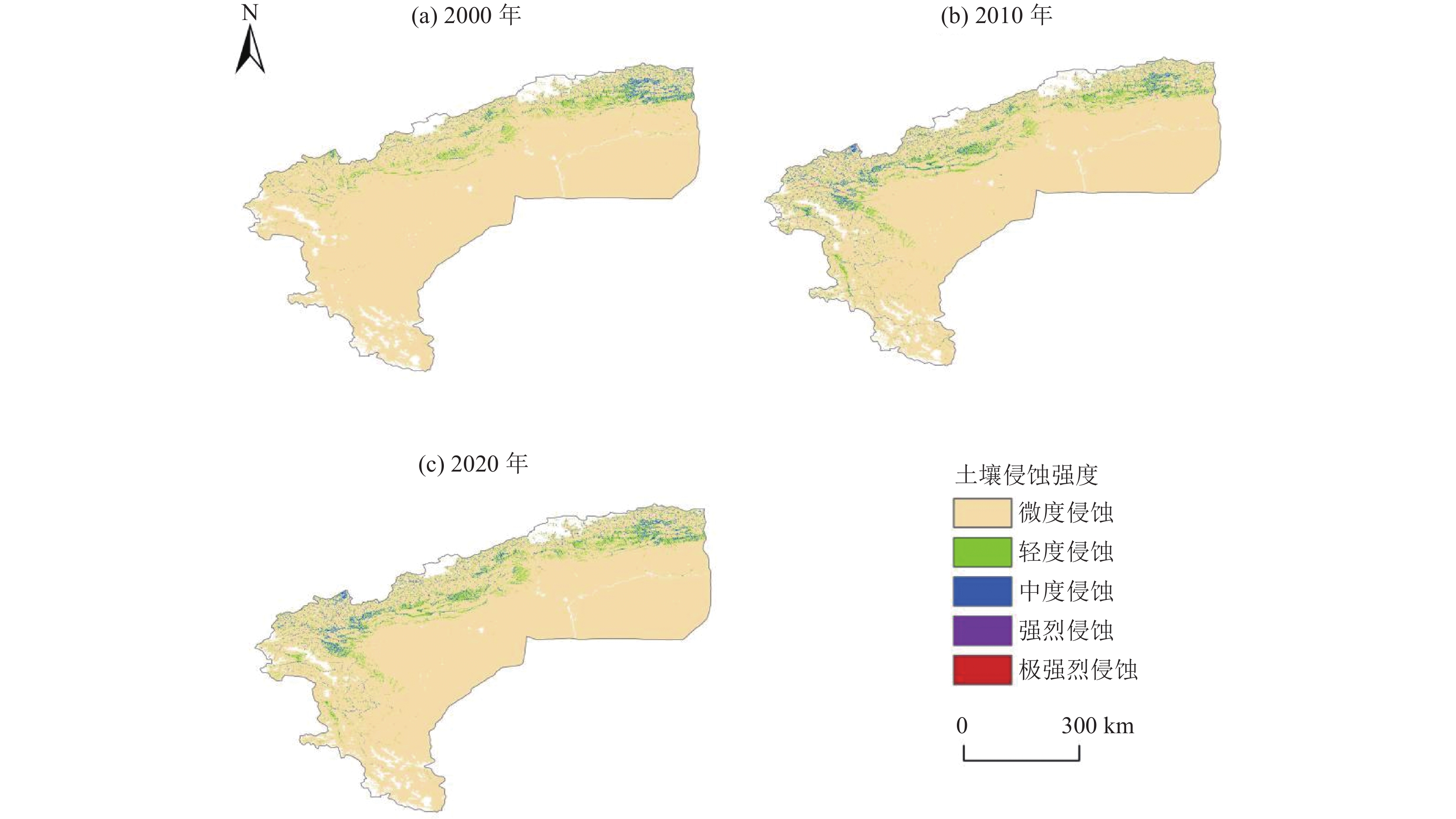
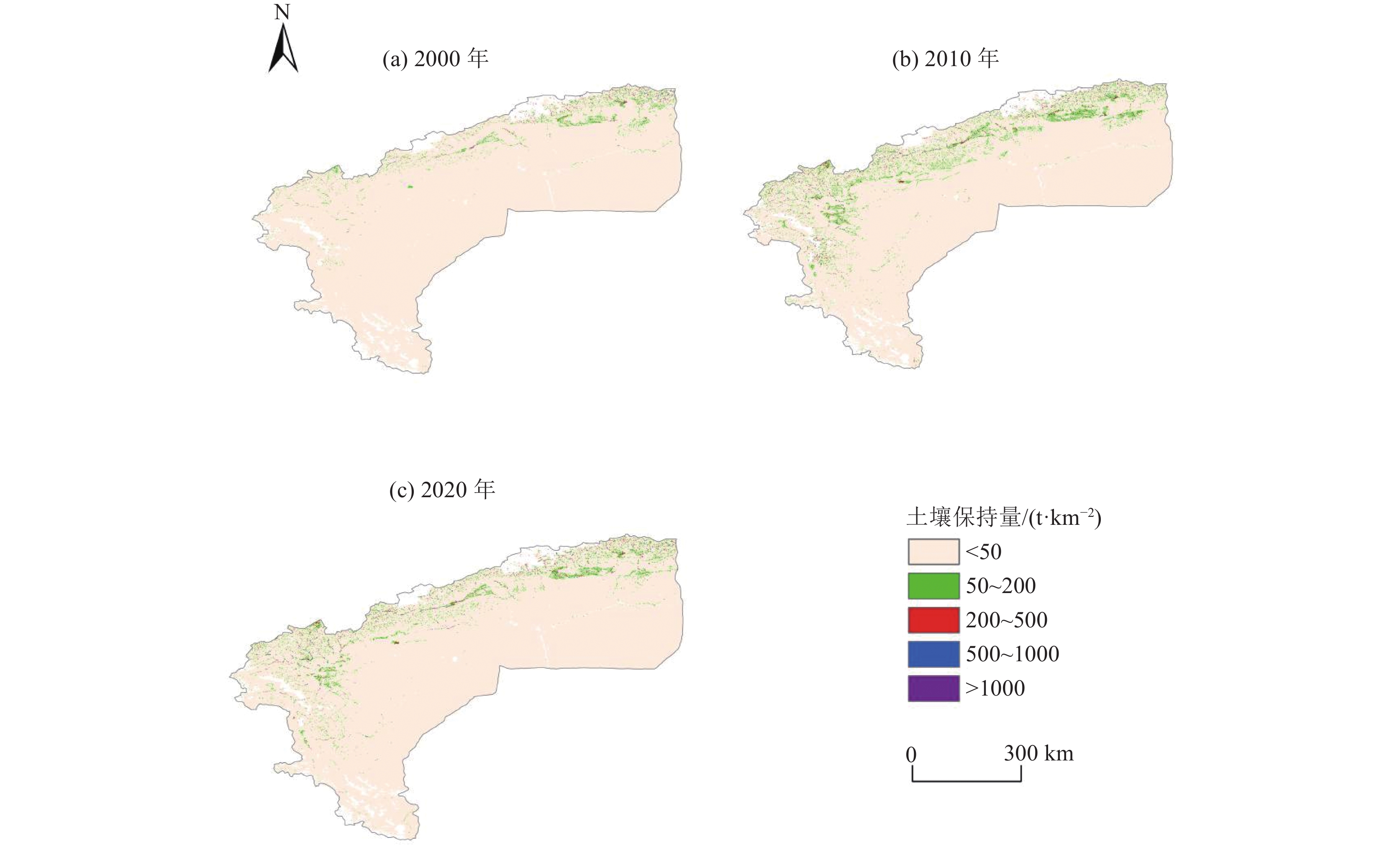
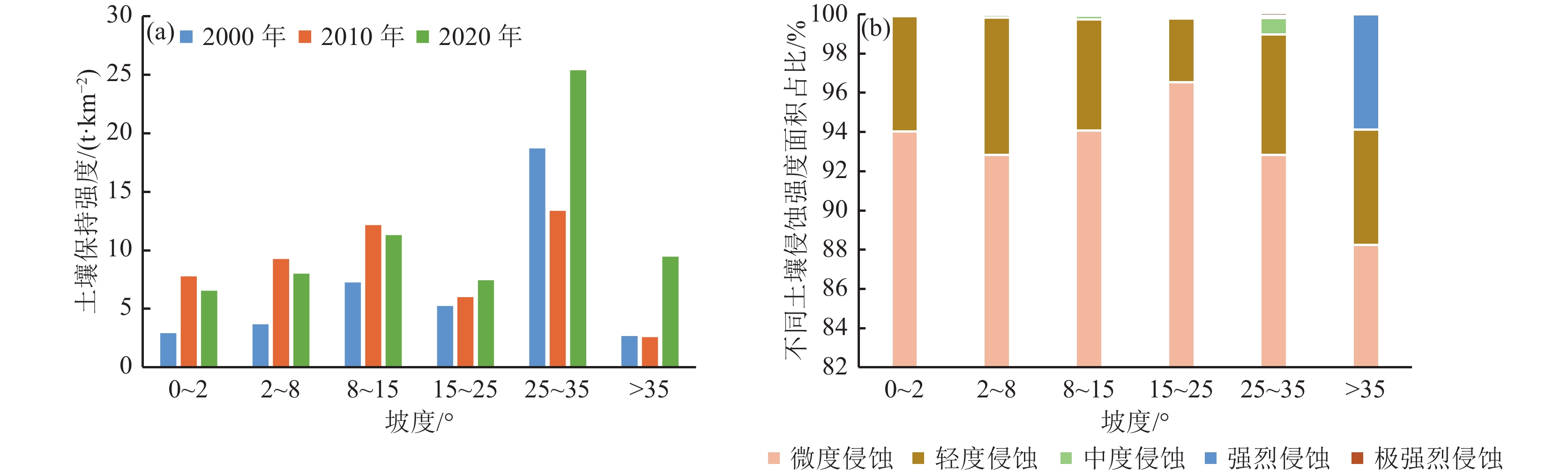
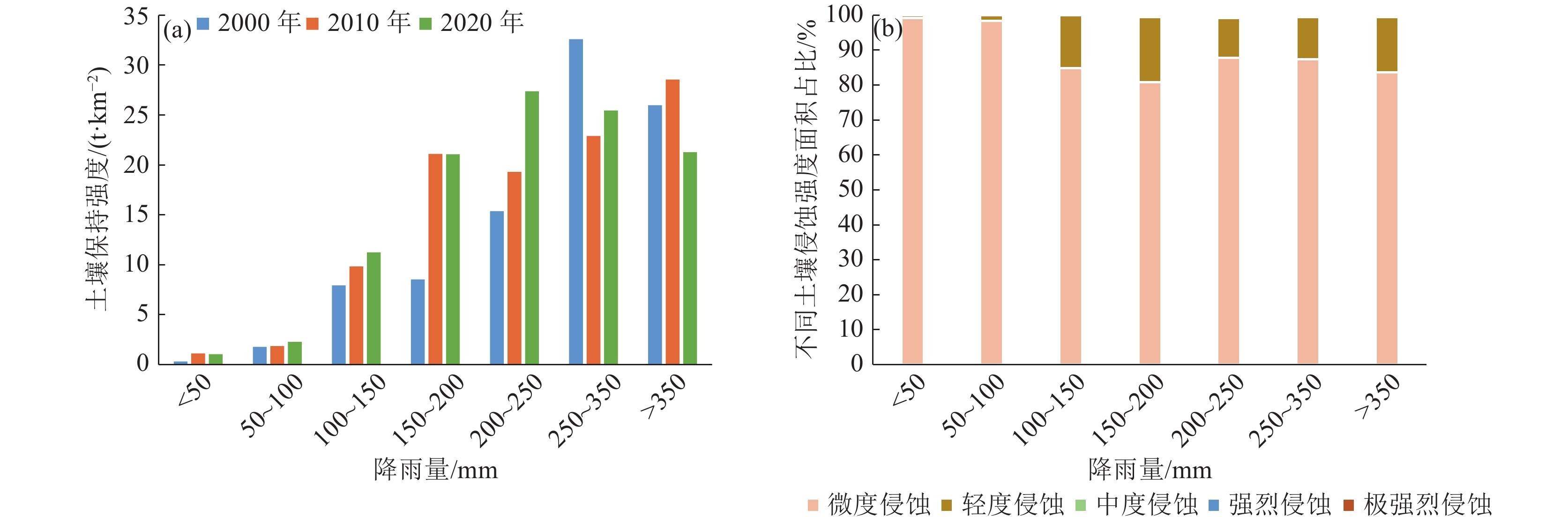
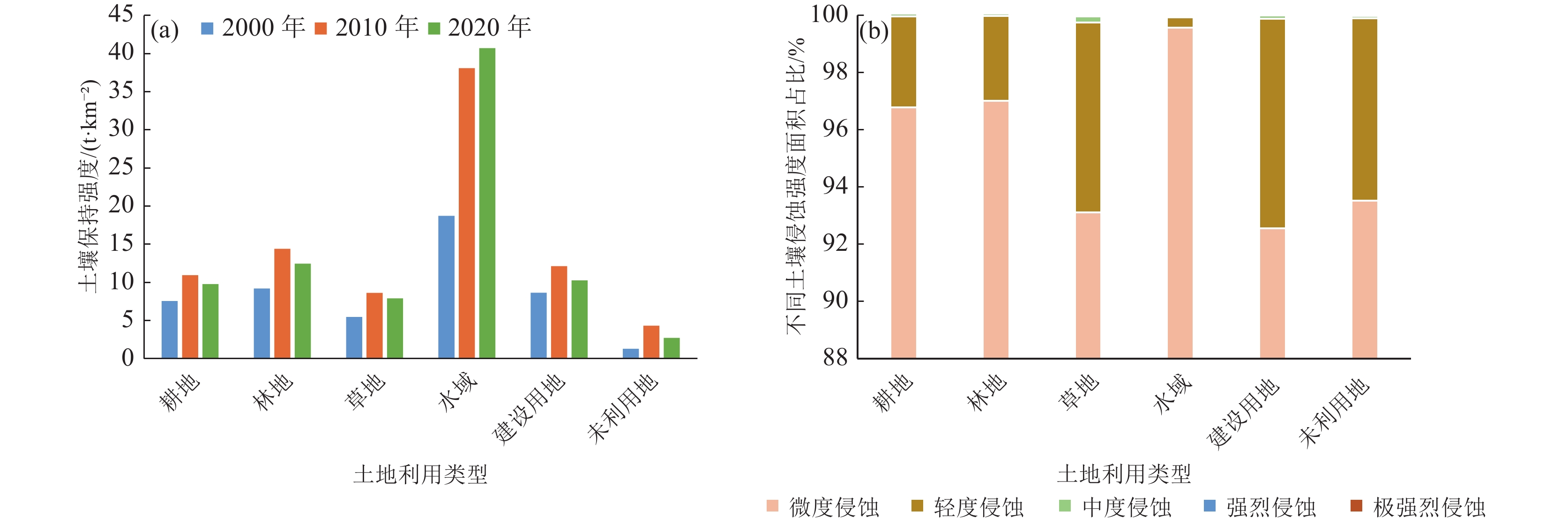
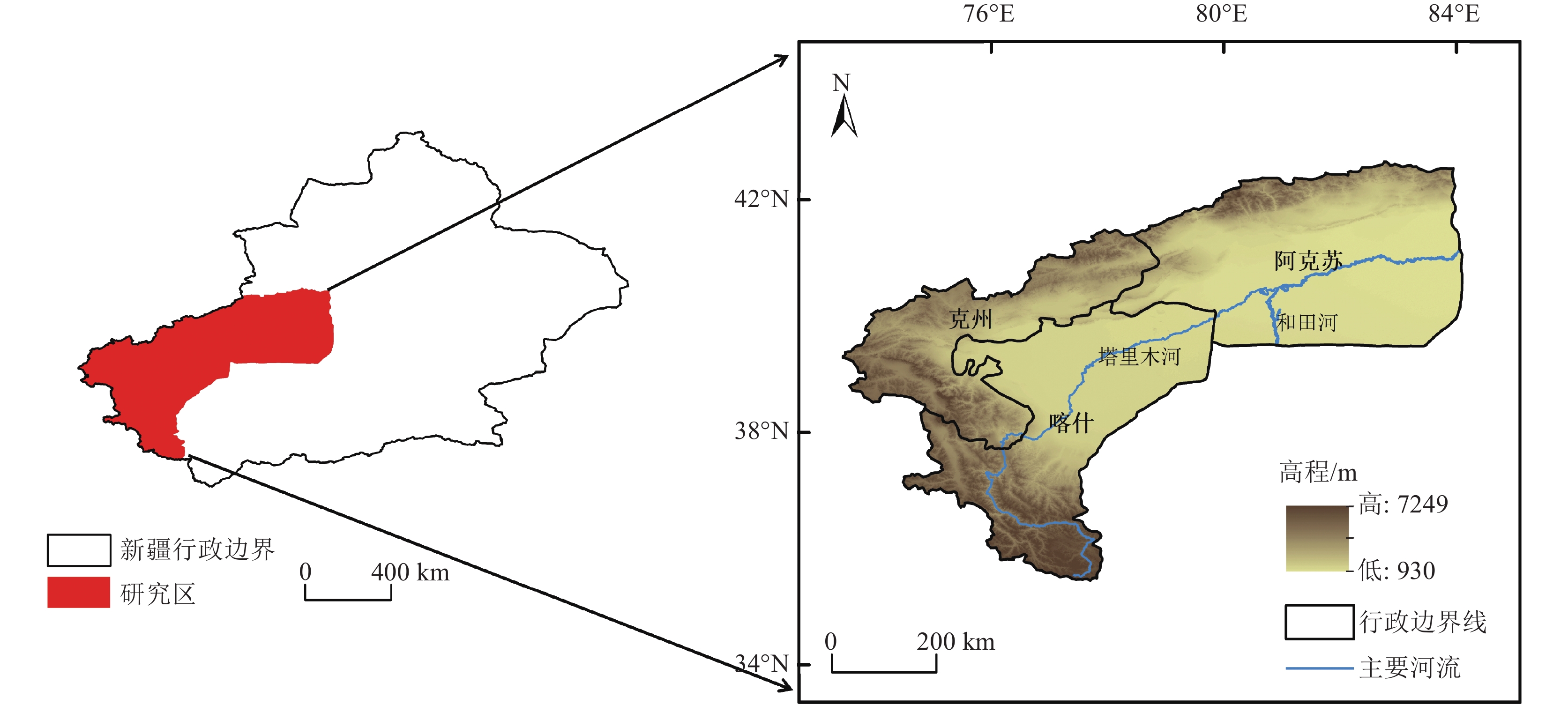
新疆塔里木河流域是中国重点生态保护区,流域土壤保持量的研究有利于水土保持功能区划和水土保持治理措施布局,对于区域生态修复与维护有重要作用。以塔里木河流域上游区为研究对象,基于该区域2000—2020年的降雨、土壤、地形等数据,采用修正通用土壤流失方程(RUSLE模型),估算2000—2020年流域土壤在水力侵蚀下的土壤侵蚀量和土壤保持量,分析其时空变化规律,并就土壤保持对其影响因子的敏感性展开分析。结果表明:流域以微度和轻度土壤侵蚀为主,在2000—2020年的土壤侵蚀面积总体呈减少趋势;土壤保持空间分布呈现中间高、四周低格局,且2000—2020年的土壤保持强度在一定程度上得到增强;降雨、地形和土地利用是土壤保持变化的主要驱动因子,且土壤保持能力随着降水量和植被覆盖总体呈现梯度增长趋势。评价结果揭示了研究区土壤保持时空分布特征,以及土壤保持对驱动因子的敏感性,可为流域水土侵蚀防治和生态修护提供指导依据。
Abstract:The Tarim River Basin in Xinjiang is a key ecological reserve in China, and the study of soil conservation in the basin is beneficial to the functional zoning of soil and water conservation and the layout of soil and water conservation management measures, and plays an important role in regional ecological restoration and maintenance. Based on the rainfall, soil and topography data of the upper Tarim River Basin from 2000 to 2020, the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE model) is used to estimate the soil erosion and soil conservation of the watershed soils under hydraulic erosion from 2000 to 2020, analyse their spatial and temporal variation patterns, and conduct a sensitivity analysis on the soil conservation to its influencing factors. The results show that soil erosion and soil retention in the basin are characterised by micro- and micro-erosion. The results show that: soil erosion in the watershed is mainly slight and mild, and the area of soil erosion is generally decreasing from 2000 to 2020; the spatial distribution of soil conservation shows a pattern of high in the middle and low in the surroundings, and the intensity of soil conservation is enhanced to a certain extent from 2000 to 2020; rainfall, topography and land use are the main driving factors of soil conservation changes, and the soil conservation capacity is increasing with the amount of The results of the evaluation reveal that the soil conservation capacity of the study area is increasing in a gradient with the amount of precipitation and vegetation cover in general. The evaluation results reveal the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of soil conservation in the study area, as well as the sensitivity of soil conservation to the driving factors, and the results of the study can provide guidance for the control of soil erosion and ecological conservation in the watershed.
-
Keywords:
- RUSLE rnodel /
- soil conservation /
- driving force /
- spatiotemporal pattern /
- Tarim River Basin
-
-
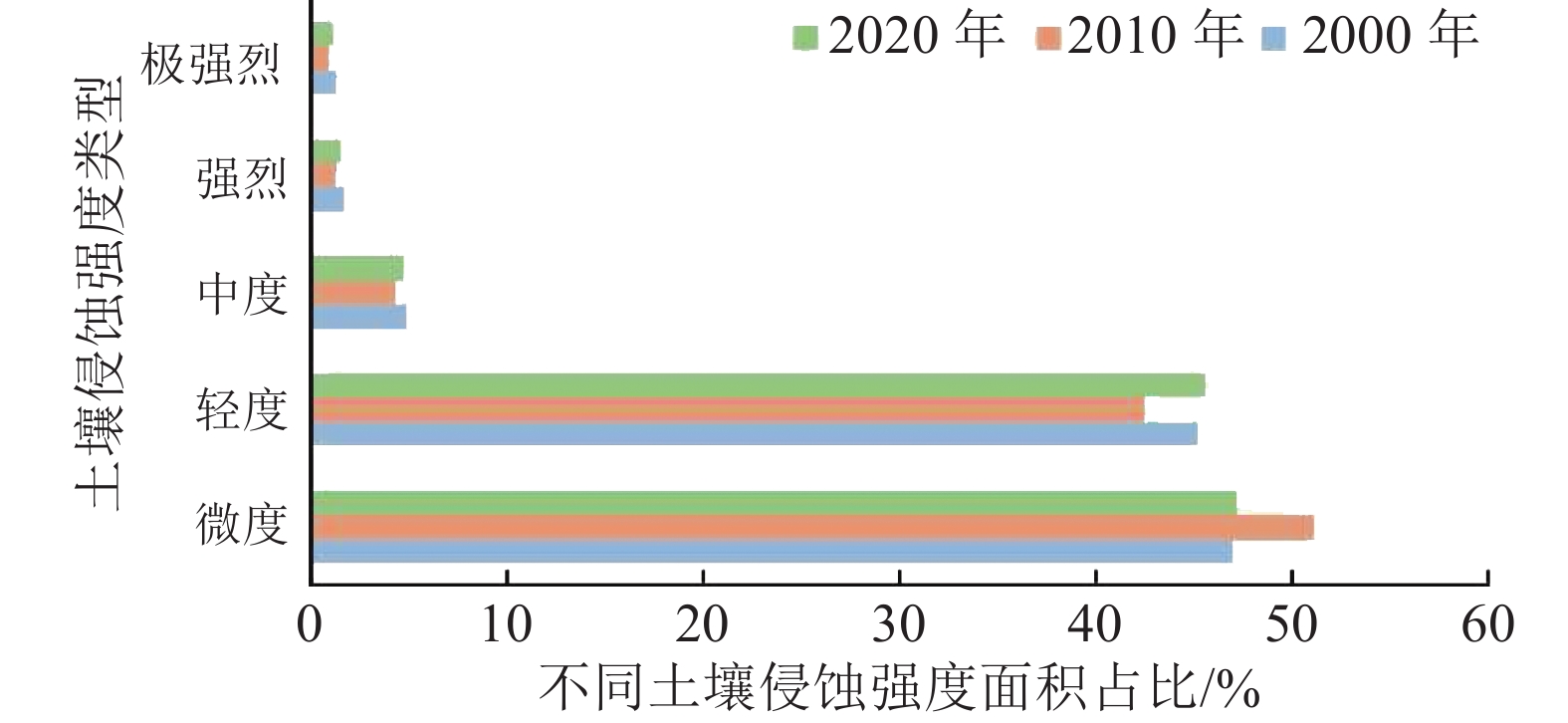
表 1 研究区不同土壤侵蚀强度面积变化量
Table 1 The variation of area of different soil erosion intensity in the study area
km² 时段 微度 轻度 中度 强烈 极强烈 2000—2010年 − 6471.74 6218.77 142.49 40.60 21.41 2010—2020年 1334.74 − 965.89 − 36.22 − 12.71 − 12.35 2000—2020年 − 5137.01 5252.88 106.27 27.89 9.06 -
Borrelli P, Märker M, Panagos P, et al. 2014. Modeling soil erosion and river sediment yield for an intermountain drainage basin of the Central Apennines, Italy[J]. Catena, 114: 45−58. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2013.10.007
De R A P J , Wesseling C G , Ritsema C J. 1996. LISEM: A single−event physically based gydrological and soil erosion model for drainage basins. I: Theroy, input and output[J]. Hydrological Processes, 10(8): 1107−1117.
Laflen J M, Lane L J, Foster G R. 1991. WEPP: A new generation of erosion prediction technology[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 46(1): 34−38.
Morgan R P C, Quinton J N, Smith R E, et al. 1998. The European Soil Erosion Model (EUROSEM): a dynamic approach for predicting sediment transport from fields and small catchments[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 23(6): 527−544. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9837(199806)23:6<527::AID-ESP868>3.0.CO;2-5
Niyonsenga J D, Mugabowindekwe M, Mupenzi C. 2020. Spatial analysis of soil erosion sensitivity using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation model in Nyamasheke District, Western Province of Rwanda[J]. Transactions in Gis, 25(2): 735−750.
Rao E, Ouyang Z Y, Yu X X, et al. 2014. Spatial patterns and impacts of soil conservation service in China[J]. Geomorphology, 207: 64−70. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2013.10.027
Renard K G, Foster G R, Weesies G A, et al. 1997. Predicting soil erosion by water: a guide to conservation planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE)[M]. Agricultural Handbook.
Williams J R. 1990. The Erosion−Productivity Impact Calculator (EPIC) Model: A Case History[J]. Philosophical Transactions:Biological Sciences, 329(1255): 421−428. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1990.0184
Wischmeier W H, Smith D D. 1985. Rainfall energy and its relationship to soil loss[J]. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 39(2): 285−291.
白云岗, 洪传勋, 宋郁东, 等. 2005. 塔里木河下游水土保持生态修复研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 12(4): 256−257,263. 蔡崇法, 丁树文, 史志华, 等. 2000. 应用USLE模型与地理信息系统IDRISI预测小流域土壤侵蚀量的研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 14(2): 19−24. 韩强, 薛联青, 刘远洪, 等. 2017 塔里木河中上游土地利用变化的径流响应[J]. 干旱区地理, 40(6): 1165−1170. 郝姗姗, 李梦华, 马永强, 等. 2019. 黄土丘陵区土壤侵蚀因子敏感性分析[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 17(2): 77−86. 贾振宇, 王世曦, 刘学, 等. 2021. 辽河保护区土壤保持功能时空变化及其影响因素分析[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 11(4): 686−692. 蒋春丽, 张丽娟, 张宏文, 等. 2015. 基于RUSLE模型的黑龙江省2000—2010年土壤保持量评价[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 23(5): 642−649. 雷泳南. 2020. 基于GIS的福建省水土保持功能重要性评价[J]. 水土保持通报, 40(5): 262−267,341. 李佳蕾, 孙然好, 熊木齐, 等. 2021. 中国5年间隔水蚀区土壤侵蚀数据集的研发(2000—2015)[J]. 全球变化数据学报(中英文), 5(2): 203−212,322−331. 李玉建, 侍克斌, 吴培军. 2010. 塔里木河下游水土保持与生态修复措施[J]. 人民黄河, 32(5): 77−78. 刘宝元, 张科利, 焦菊英. 1999. 土壤可蚀性及其在侵蚀预报中的应用[J]. 自然资源学报, 14(4): 345−350. 刘雨曈. 2022. 塔里木河流域水土流失动态变化分析[J]. 水生态学杂志, 43(3): 105−112. 刘月, 赵文武, 贾立志. 2019. 土壤保持服务: 概念、评估与展望[J]. 生态学报, 39(2): 32−440. 水利部水土保持司. 2008. 土壤侵蚀分类分级标准 SL190-2007 [S]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社 宋艺, 孙培新, 郭凯. 2004. 塔里木河上中游的水土流失及防治对策[J]. 中国水土保持, (7): 11−12. 谭炳香, 李增元, 王彦辉, 等. 2005. 基于遥感数据的流域土壤侵蚀强度快速估测方法[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 20(2): 215−220. 田宇, 朱建华, 李奇, 等. 2020. 三峡库区土壤保持时空分布特征及其驱动力[J]. 生态学杂志, 39(4): 1164−1174. 王晓峰, 程昌武, 尹礼唱, 等. 2020. 新疆生态系统服务时空变化及权衡协同关系[J]. 生态学杂志, 39(3): 990−1000. 薛联青, 张卉, 张洛晨, 等. 2017. 基于改进RVA法的水利工程对塔里木河生态水文情势影响评估[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 45(3): 189−196. 于萌. 2019. 新疆地区土壤侵蚀强度变化趋势及原因分析[J]. 中国水土保持, 453(12): 36−37. 张超, 王治国, 凌峰, 等. 2016. 水土保持功能评价及其在水土保持区划中的应用[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 14(5): 90−99. 章文波, 付金生. 2003. 不同类型雨量资料估算降雨侵蚀力[J]. 资源科学, (1): 35−41. 赵帮元, 张建国, 张栋, 等. 2020. 土壤侵蚀因子变化对县域水土流失动态变化的影响[J]. 中国水土保持, (3): 30−33,5. 中华人民共和国生态环境部. 2017. 关于印发《生态保护红线划定指南》的通知[N/OL]. (2017-07-20 2022-09-01].https://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/bgt/201707/t20170728_418679.htm.
邹雅婧, 闫庆武, 谭学玲, 等. 2019. 渭北矿区土壤侵蚀评估及驱动因素分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 42(6): 1387−1394. -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 杨旭明,文鹏帆,张春亢,张显云,康雅敬. 基于GTWR-LightGBM模型的京津冀地区近地面SO2浓度估算. 环境科学与技术. 2024(10): 204-215 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 叶烨,叶晗迪,鲍杰利. 基于改进Adaboost算法的分布式光伏发电孤岛检测方法. 机电技术. 2024(05): 14-17+33 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: