Structural patterns and influencing factors of the upper wall of the nappe in the Karamay-Wuerhe fault zone, northwestern Junggar Basin
-
摘要:
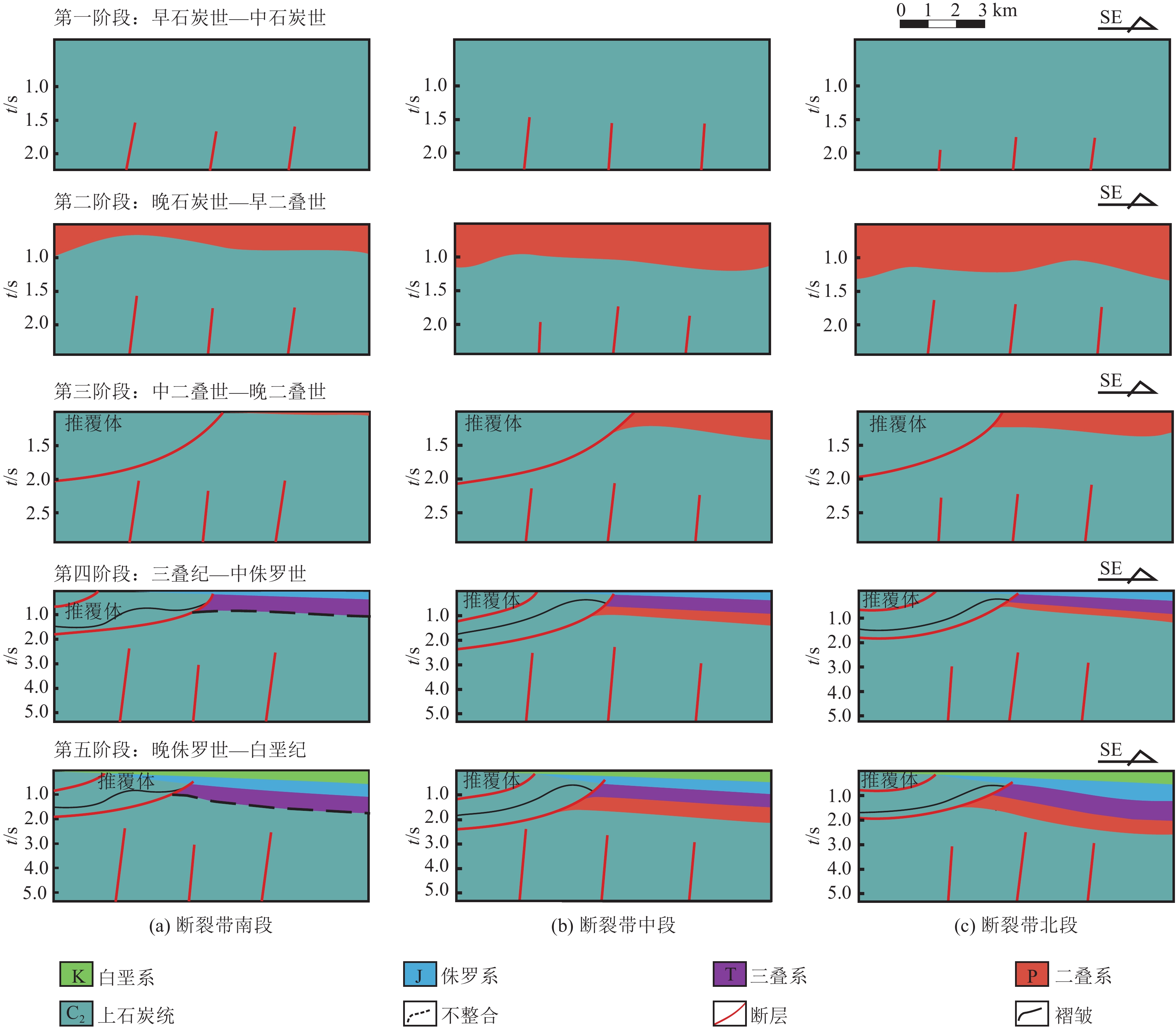
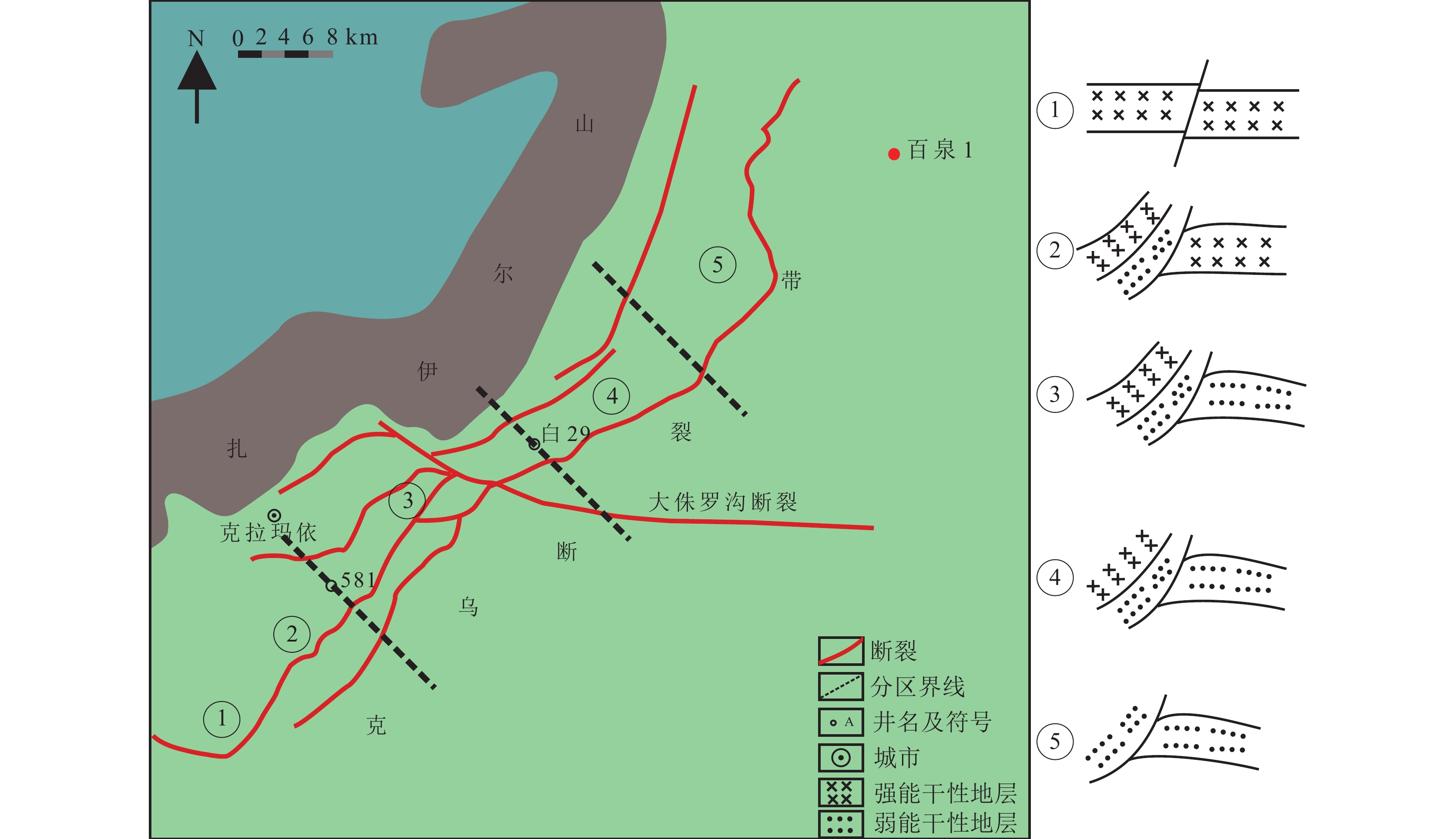
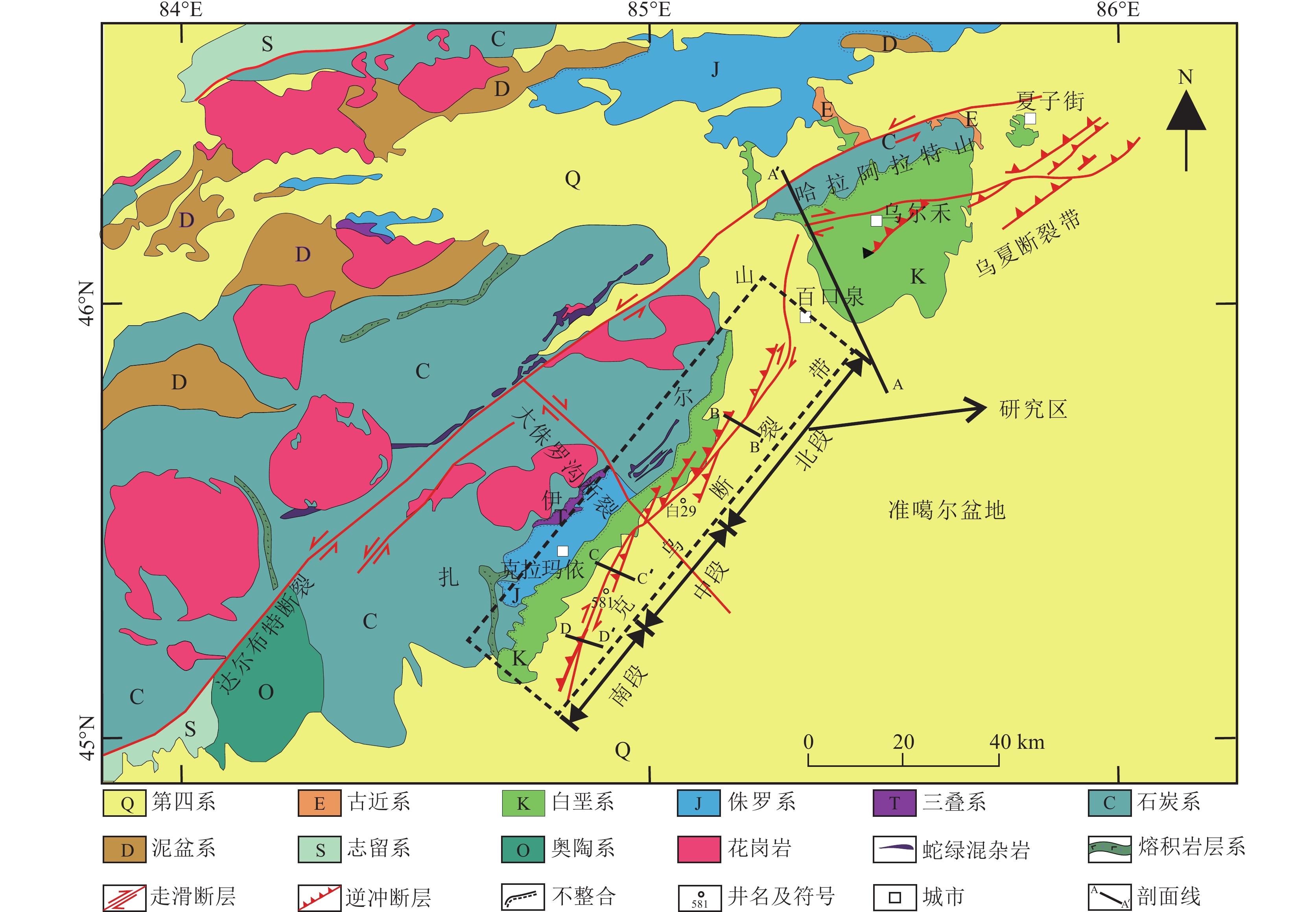
准噶尔盆地西北缘克拉玛依−乌尔禾断裂带(克−乌断裂带)及其周缘发现了大量的油气藏,尤其是推覆体上盘伴随着勘探程度及地质认识不断深化,已呈现出“百里油区”的态势。然而,受多期构造活动及断裂带内部复杂的岩性组合影响,石炭系内幕地层构造样式展现出多种类型及复杂的空间展布样式,因此需要对构造样式及成因进一步探讨。综合地震和钻井资料,结合区域构造格局,梳理了准噶尔盆地西北缘克−乌断裂带上盘构造变形特征与影响因素;根据构造样式与推覆体内的岩性组合类型,将克−乌断裂带推覆体上盘划分出南段、中段和北段3个变形单元;明确了上盘石炭系5期主要构造阶段,分段恢复了推覆体上盘构造演化期次及样式。综合上述研究,认为克−乌断裂带上、下盘原始岩性组合关系是造成上盘石炭系内幕地层原始形变差异的主要因素,上盘石炭系内幕地层岩性组合差异是造成原生构造保存的主要因素。上述因素共同造成了圈闭条件沿克−乌断裂带自南向北变化。该研究为克−乌断裂带上盘油气勘探提供指导,同时也为类似条件地区的油气勘探提供借鉴。
Abstract:Many oil and gas reservoirs have been discovered in the Karamay-Wuerhe (Ke-Wu) fault zone and its periphery in the northwestern margin of Junggar Basin. With the deepening of exploration level and geological understanding, the upper wall of nappe has already presented a situation of "Baili Oildom". However, due to the influence of multi-period tectonic activities and complex lithological assemblages inside the fault zone, the structural patterns show various types and complex spatial distribution patterns. Therefore, it is necessary to further explore the structural patterns and genesis. Based on seismic data, drilling data and regional tectonic framework, this study summarizes the structural deformation characteristics and influencing factors of the upper wall of the Ke-Wu fault zone in the northwestern margin of the Junggar Basin; the upper wall of the nappe of the Ke-Wu fault zone is divided into three deformation units: namely southern, central and northern segments; the five main tectonic stages of the Carboniferous strata on the upper side are clarified, and the stages and styles of tectonic evolution have been restored. In summary, the main factor for the difference in the original deformation of the Carboniferous inner strata is the original lithological assemblage relationship. And the difference of the lithologic assemblage in the upper wall is the main factor for the preservation of the original structure. The above factors together result in different trap conditions from south to north along the Ke-Wu fault zone. This study has guidance for future hydrocarbon exploration of the upper wall of the Ke-Wu fault zone and other similar areas.
-
-
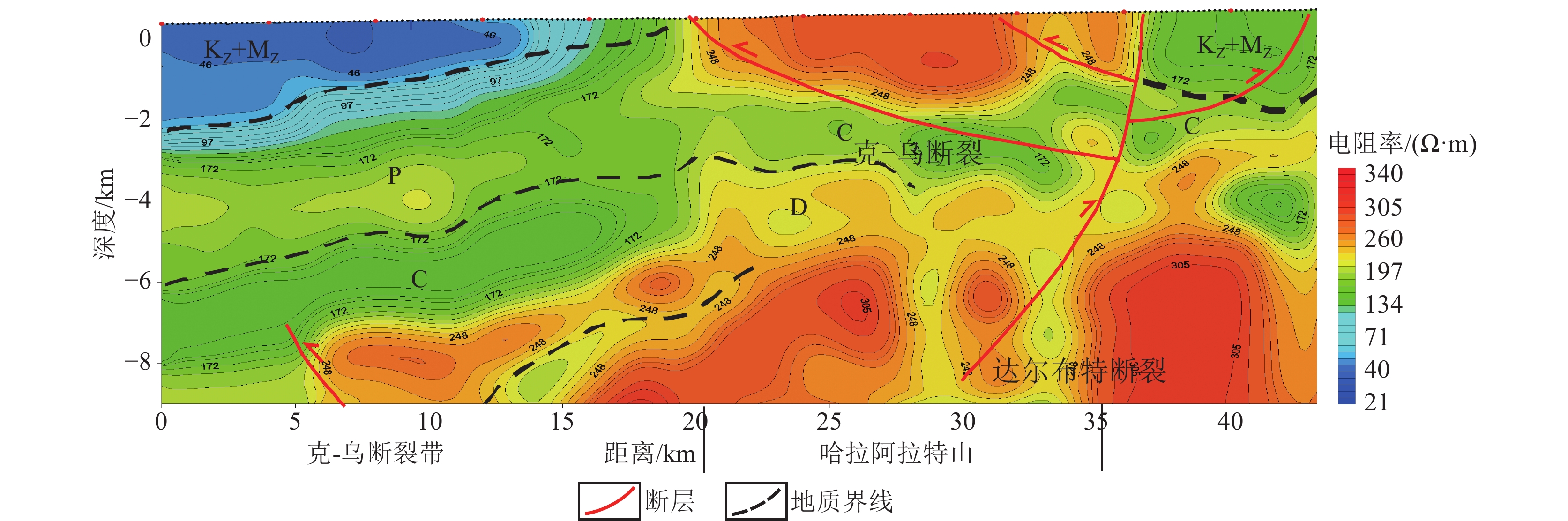
图 2 克−乌断裂带地区反演电阻率剖面(A-A'剖面位置见图1)
KZ+MZ—新生界与中生界;P—二叠系;C—石炭系;D—泥盆系
Figure 2. Inversion resistivity profile of Ke-Wu fault zone
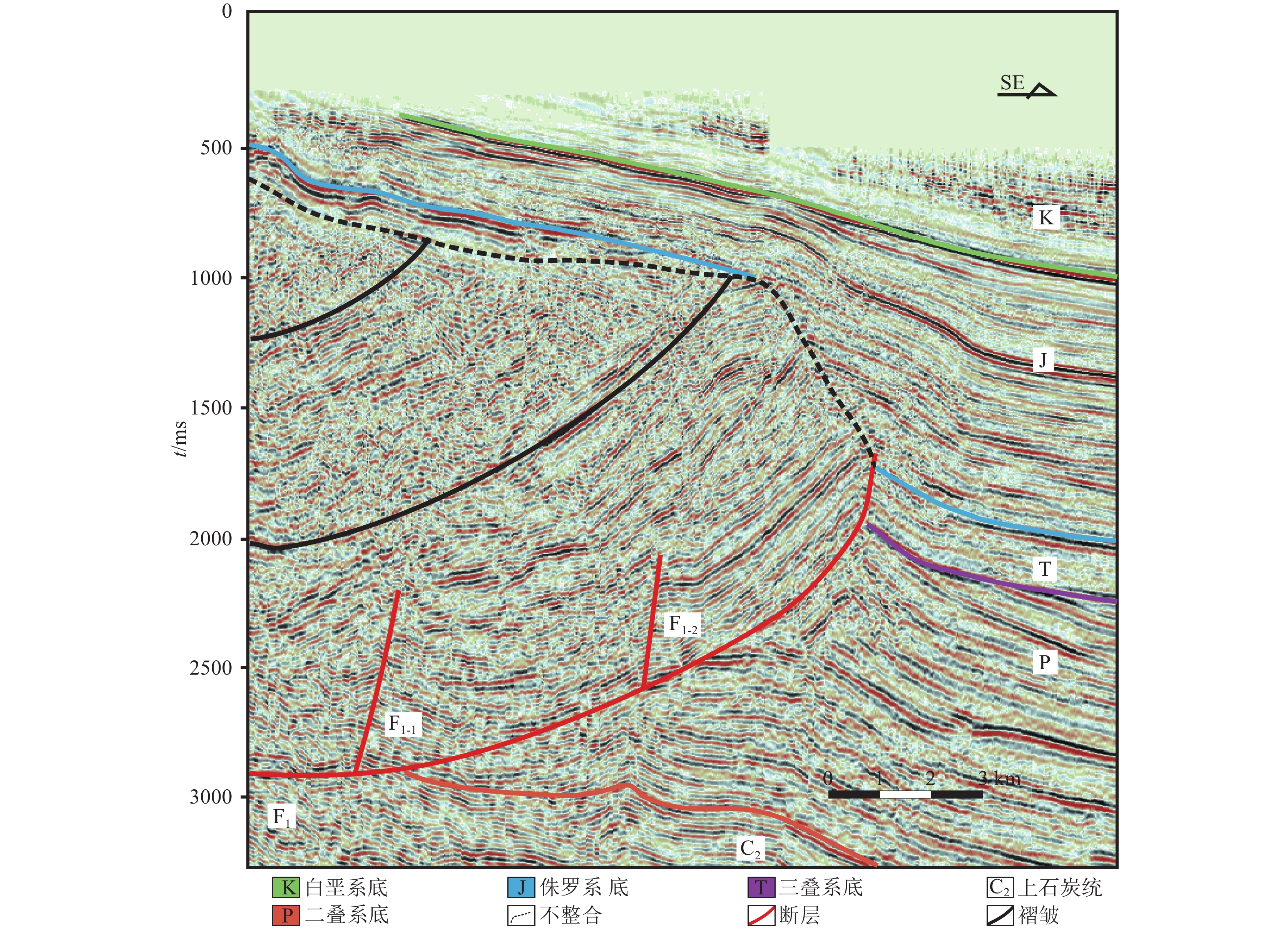
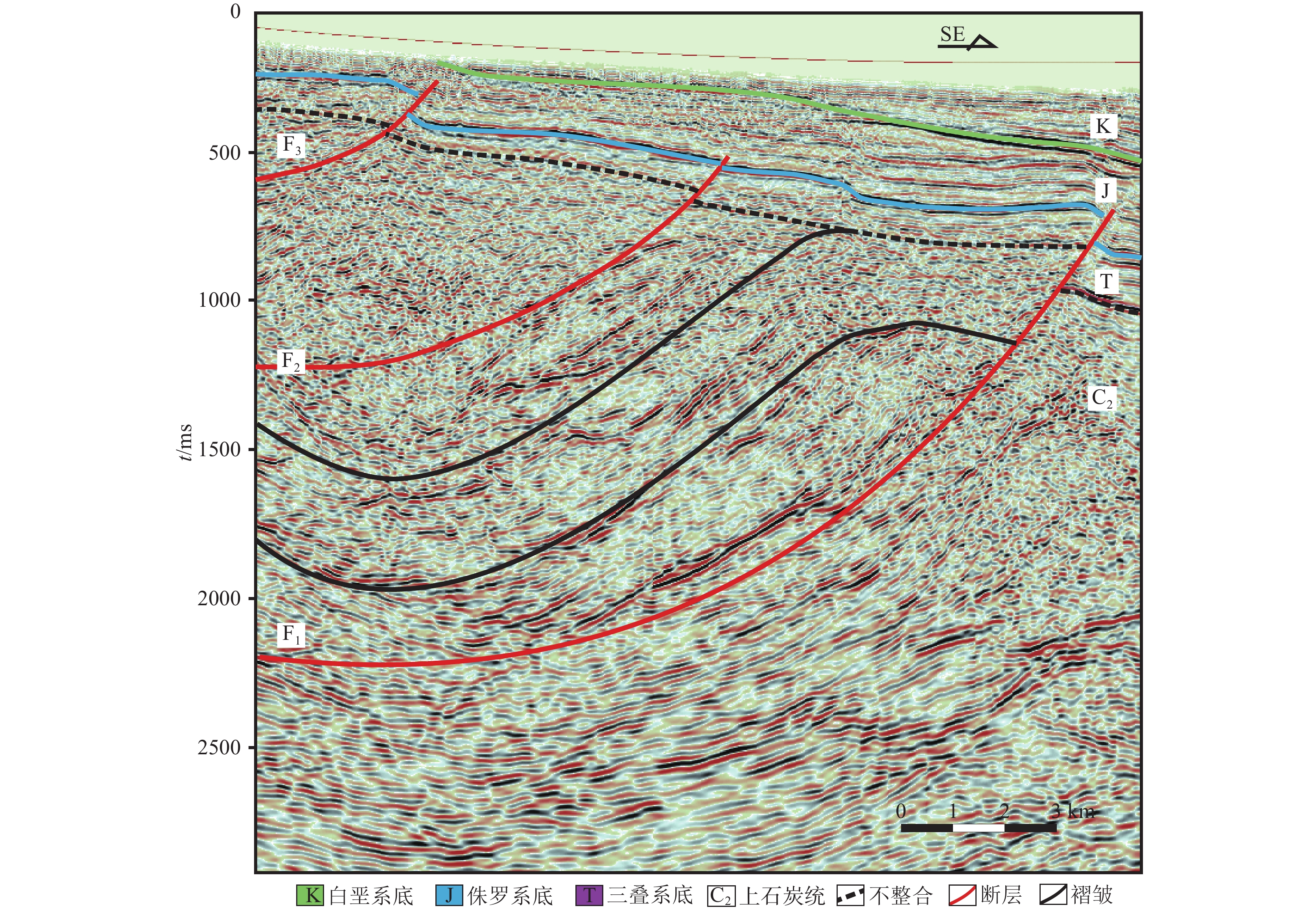
图 4 克−乌断裂带中段地震解释剖面(C-C'剖面位置见图1)
Figure 4. Seismic section of the central part of Ke-Wu fault zone
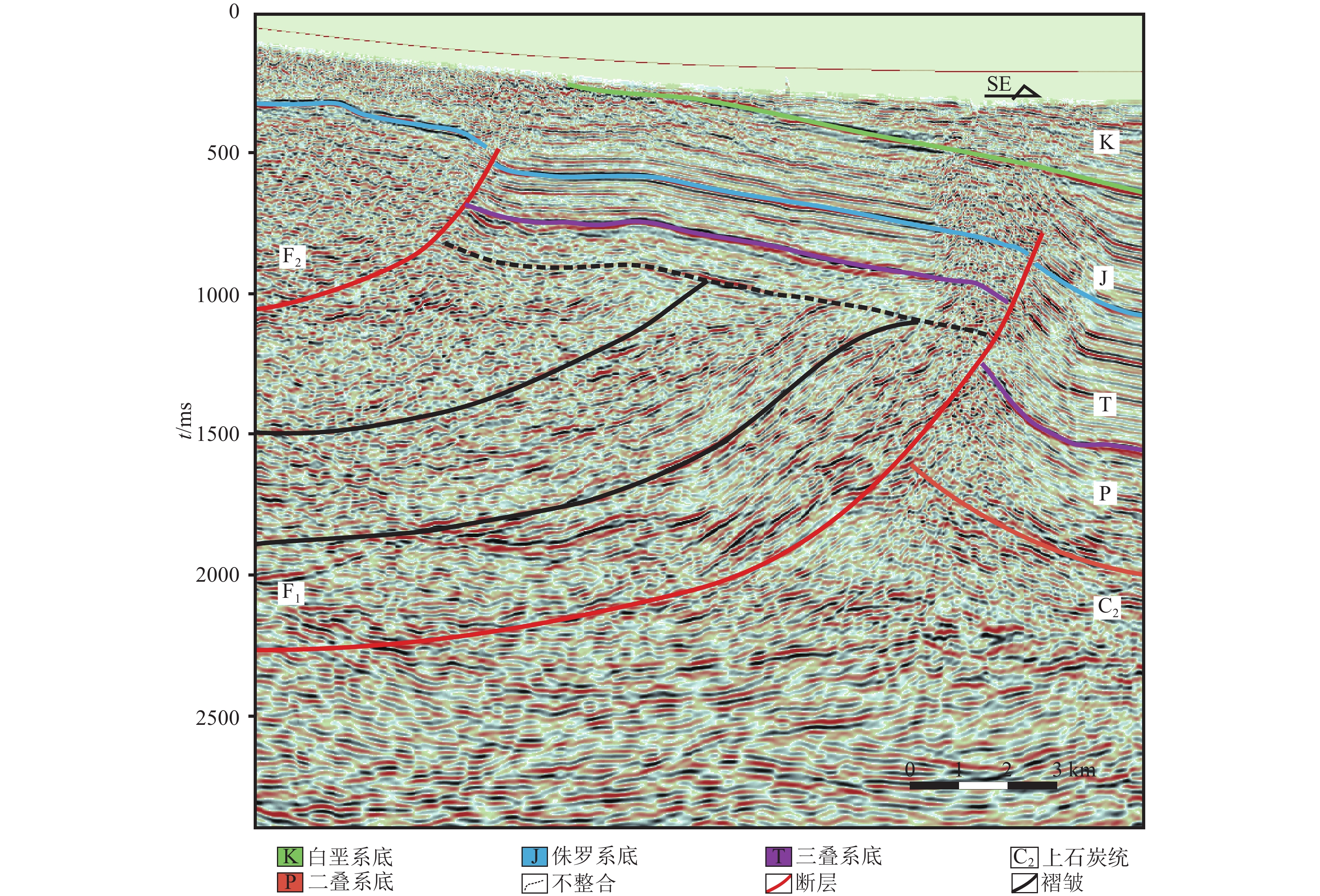
图 5 克−乌断裂带南段地震解释剖面(D-D'剖面位置见图1)
Figure 5. Seismic section of the southern part of Ke-Wu fault zone
表 1 克−乌断裂带上盘构造样式
Table 1 Structural patterns of the hanging wall of Ke-Wu fault zone
主要类型 剖面样式 构造样式 分布区域 构造−地层
要素改造断展褶皱 

克−乌断裂带北段 扎伊尔山推覆−哈拉阿拉特山走滑垂向叠合区
弱能干性上盘−弱能干性下盘断弯褶皱 

克−乌断裂带中段 扎伊尔山推覆控制区
过渡性上盘−过渡性下盘挤压褶皱 

扎伊尔山推覆控制区
强能干性−过渡性上盘−过渡性下盘地层刚性破裂 

克−乌断裂带南段 扎伊尔山推覆控制区
强能干性上盘−强能干性下盘
-
Buckman S, Aitchison J C. 2004. Tectonic evolution of Palaeozoic terranes in West Junggar, Xinjiang, NW China[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 226(1): 101−129. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2004.226.01.06
Choulet F, Chen Y, Cogné J, et al. 2013. First Triassic palaeomagnetic constraints from Junggar (NW China) and their implications for the Mesozoic tectonics in Central Asia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 78: 371−394. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.01.023
Jahn B, Windley B, Natal'In B, et al. 2004. Phanerozoic continental growth in Central Asia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 23: 599−603. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(03)00124-X
Şengör A M C, Natal'In B A, Burtman V S. 1993. Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Palaeozoic crustal growth in Eurasia[J]. Nature, 364(6435): 299−307. doi: 10.1038/364299a0
Xiao W, Han C, Yuan C, et al. 2008. Middle Cambrian to Permian subduction-related accretionary orogenesis of Northern Xinjiang, NW China: Implications for the tectonic evolution of central Asia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 32(2/4): 102−117. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2007.10.008
蔡忠贤, 陈发景, 贾振远. 2000. 准噶尔盆地的类型和构造演化[J]. 地学前缘, (4): 431−440. 陈发景, 汪新文, 汪新伟. 2005. 准噶尔盆地的原型和构造演化[J]. 地学前缘, (3): 77−89. 程怀蒙, 张胜业. 2015. 西准噶尔达尔布特断裂电性特征及成像[J]. 地球物理学进展, 30(6): 2440−2447. 陈石, 郭召杰. 2010. 达拉布特蛇绿岩带的时限和属性以及对西准噶尔晚古生代构造演化的讨论[J]. 岩石学报, 26(8): 2336−2344. 陈石, 郭召杰, 漆家福, 等. 2016. 准噶尔盆地西北缘三期走滑构造及其油气意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 37(3): 322−331. 陈书平, 漆家福, 于福生, 等. 2007. 准噶尔盆地南缘构造变形特征及其主控因素[J]. 地质学报, (2): 151−157. 陈宣华, 聂兰仕, 丁伟翠, 等. 2015. 西准噶尔走滑断裂系元素分布特征及其成矿意义[J]. 岩石学报, 31(2): 371−387. 陈宣华, 陈正乐, 白彦飞, 等. 2016. 中亚成矿域西部巴尔喀什−准噶尔成矿带晚古生代成矿作用大爆发[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 38(3): 285−305. 管树巍, 李本亮, 侯连华, 等. 2008. 准噶尔盆地西北缘下盘掩伏构造油气勘探新领域[J]. 石油勘探与开发, (1): 17−22. 何登发, 张磊, 吴松涛, 等. 2018. 准噶尔盆地构造演化阶段及其特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 39(5): 845−861. 靳军, 王剑, 刘金, 等. 2018. 准噶尔盆地克−百断裂带石炭系深部岩性岩相及时空分布特征[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 48(2): 238−245. 林伟, 孙萍, 薛振华, 等. 2017. 西准噶尔达拉布特断裂带中段晚古生代构造分析[J]. 岩石学报, 33(10): 2987−3001. 李宗浩, 刘海磊, 卞保力, 等. 2018. 准噶尔盆地西北缘掩伏带构造特征及勘探潜力分析[J]. 特种油气藏, 25(5): 56−60. 孟家峰, 郭召杰, 方世虎. 2009. 准噶尔盆地西北缘冲断构造新解[J]. 地学前缘, 16(3): 171−180. 秦克章. 2000. 新疆北部中亚型造山与成矿作用[D]. 中国科学院研究生院(地质与地球物理研究所)博士学位论文. 邱争科, 李婷, 杨兴, 等. 2020. 准噶尔盆地克−百断裂带石炭系内幕成藏特征[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 42(5): 39−47. 曲国胜, 马宗晋, 陈新发, 等. 2009. 论准噶尔盆地构造及其演化[J]. 新疆石油地质, 30(1): 1−5. 邵雨, 汪仁富, 张越迁, 等. 2011. 准噶尔盆地西北缘走滑构造与油气勘探[J]. 石油学报, 32(6): 976−984. 隋风贵. 2015. 准噶尔盆地西北缘构造演化及其与油气成藏的关系[J]. 地质学报, 89(4): 779-793. 王平在, 何登发, 雷振宇, 等. 2002. 中国中西部前陆冲断带构造特征[J]. 石油学报, (3): 8, 11−17. 谭开俊, 张帆, 吴晓智, 等. 2008. 准噶尔盆地西北缘盆山耦合与油气成藏[J]. 天然气工业, (5): 10−13,136. 吴孔友, 瞿建华, 王鹤华. 2014. 准噶尔盆地大侏罗沟断层走滑特征、形成机制及控藏作用[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 38(5): 41−47. 汪仁富. 2012. 准噶尔盆地西北缘克拉玛依−夏子街走滑构造[D]. 浙江大学博士学位论文. 杨庚, 王晓波, 李本亮, 等. 2011. 准噶尔西北缘斜向挤压构造与走滑断裂[J]. 地质科学, 46(3): 696−708. 尤绮妹. 1983. 准噶尔盆地西北缘推复构造的研究[J]. 新疆石油地质, (1): 6−16. 张弛, 黄萱. 1992. 新疆西准噶尔蛇绿岩形成时代和环境的探讨[J]. 地质论评, (6): 509−524. 张琴华, 魏洲龄, 孙少华. 1989. 西准噶尔达尔布特断裂带的形成时代[J]. 新疆石油地质, (1): 35−38. 张晓杰. 2016. 准噶尔盆地西北缘横断层特征及其在油气成藏中作用[D]. 中国石油大学(华东)硕士学位论文. 张元元, 曾宇轲, 唐文斌. 2021. 准噶尔盆地西北缘二叠纪原型盆地分析[J]. 石油科学通报, 6(3): 333−343. 张越迁, 汪新, 刘继山, 等. 2011. 准噶尔盆地西北缘乌夏走滑构造及油气勘探意义[J]. 新疆石油地质, 32(5): 447−450. 赵瑞斌, 李进云, 石树中, 等. 1997. 达尔布特断裂中段构造活动性[J]. 内陆地震, (4): 295−301. -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 杨旭明,文鹏帆,张春亢,张显云,康雅敬. 基于GTWR-LightGBM模型的京津冀地区近地面SO2浓度估算. 环境科学与技术. 2024(10): 204-215 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 叶烨,叶晗迪,鲍杰利. 基于改进Adaboost算法的分布式光伏发电孤岛检测方法. 机电技术. 2024(05): 14-17+33 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: