Grain size features of the modern tidal−flat sediment on the north bank of Hangzhou Bay and the implication of sea-level reconstruction
-
摘要:
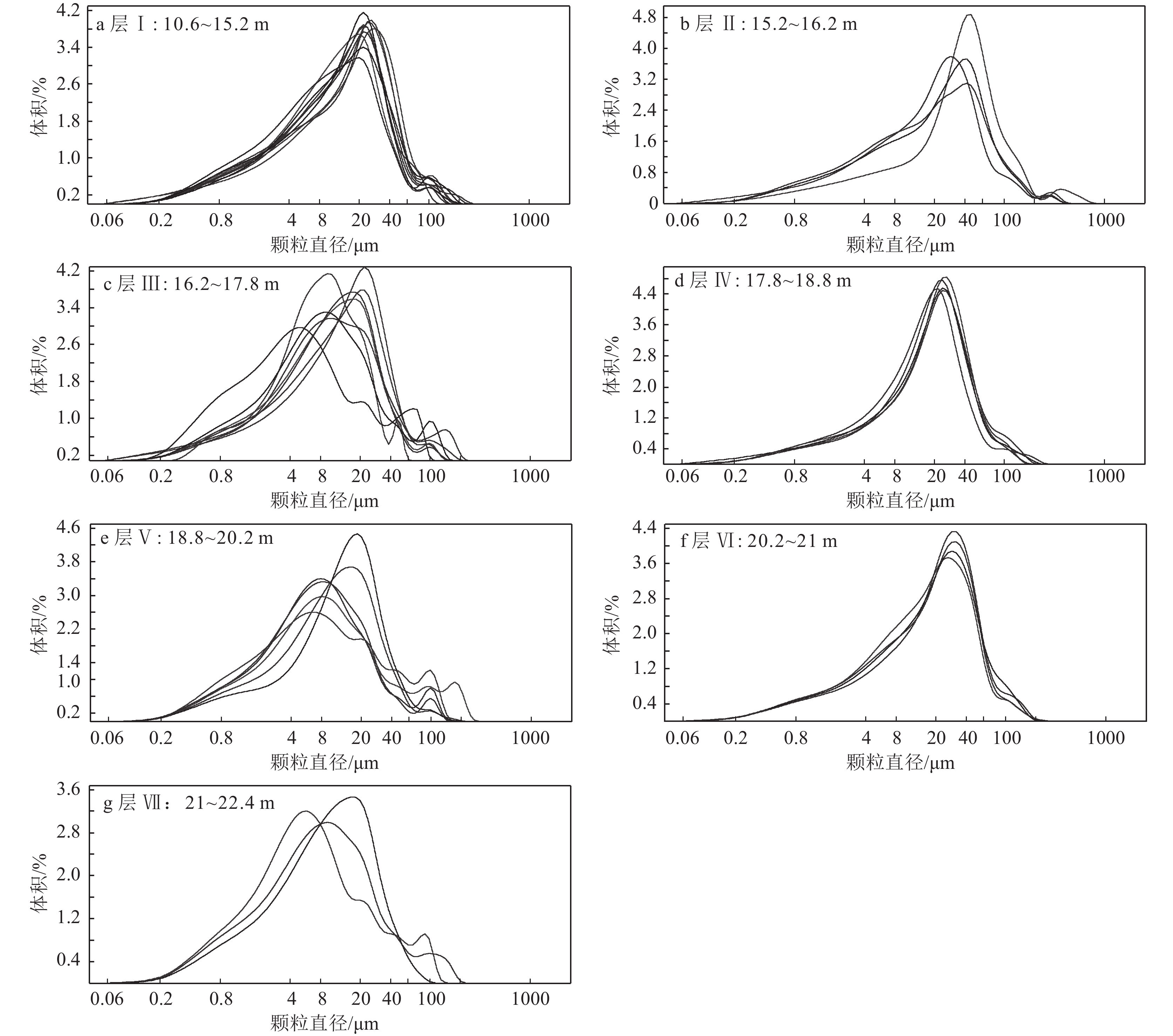
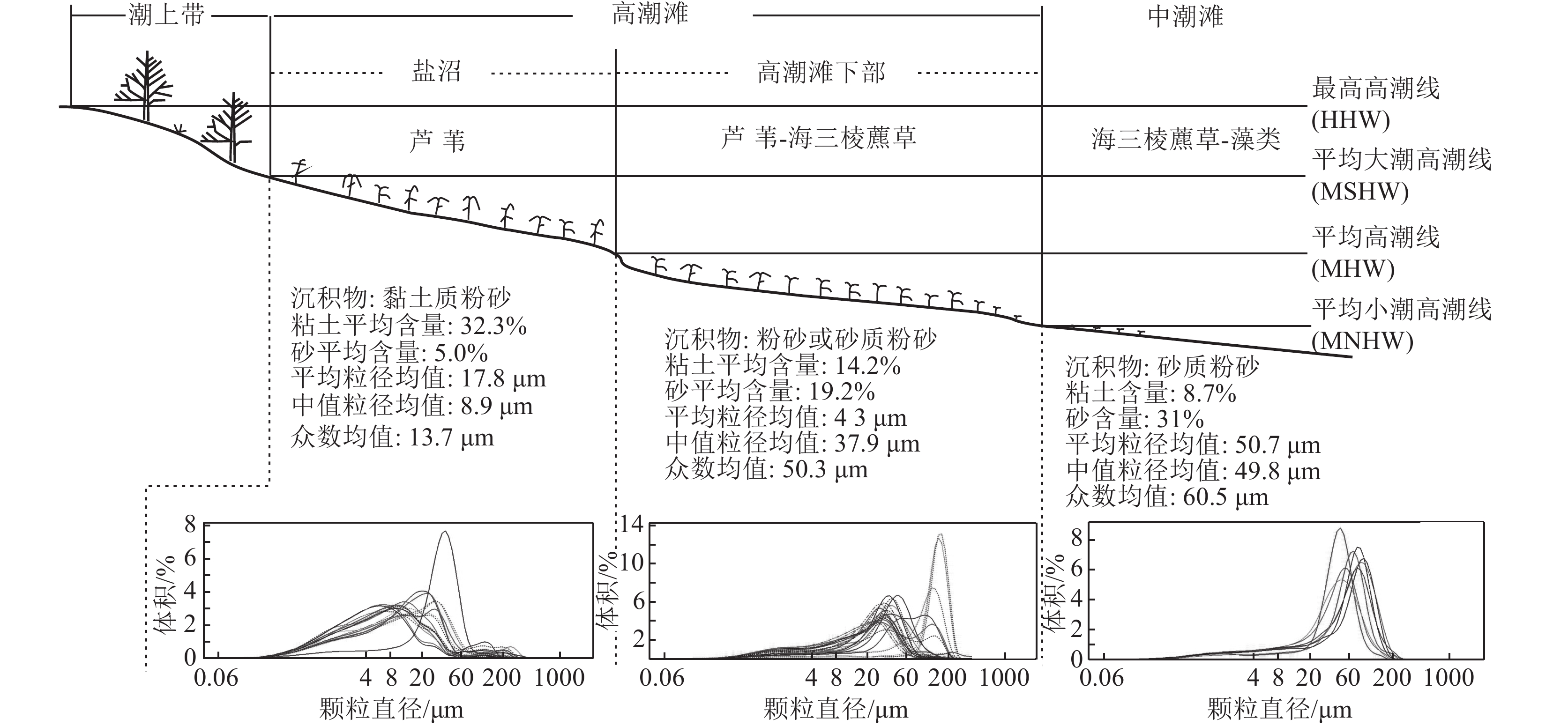
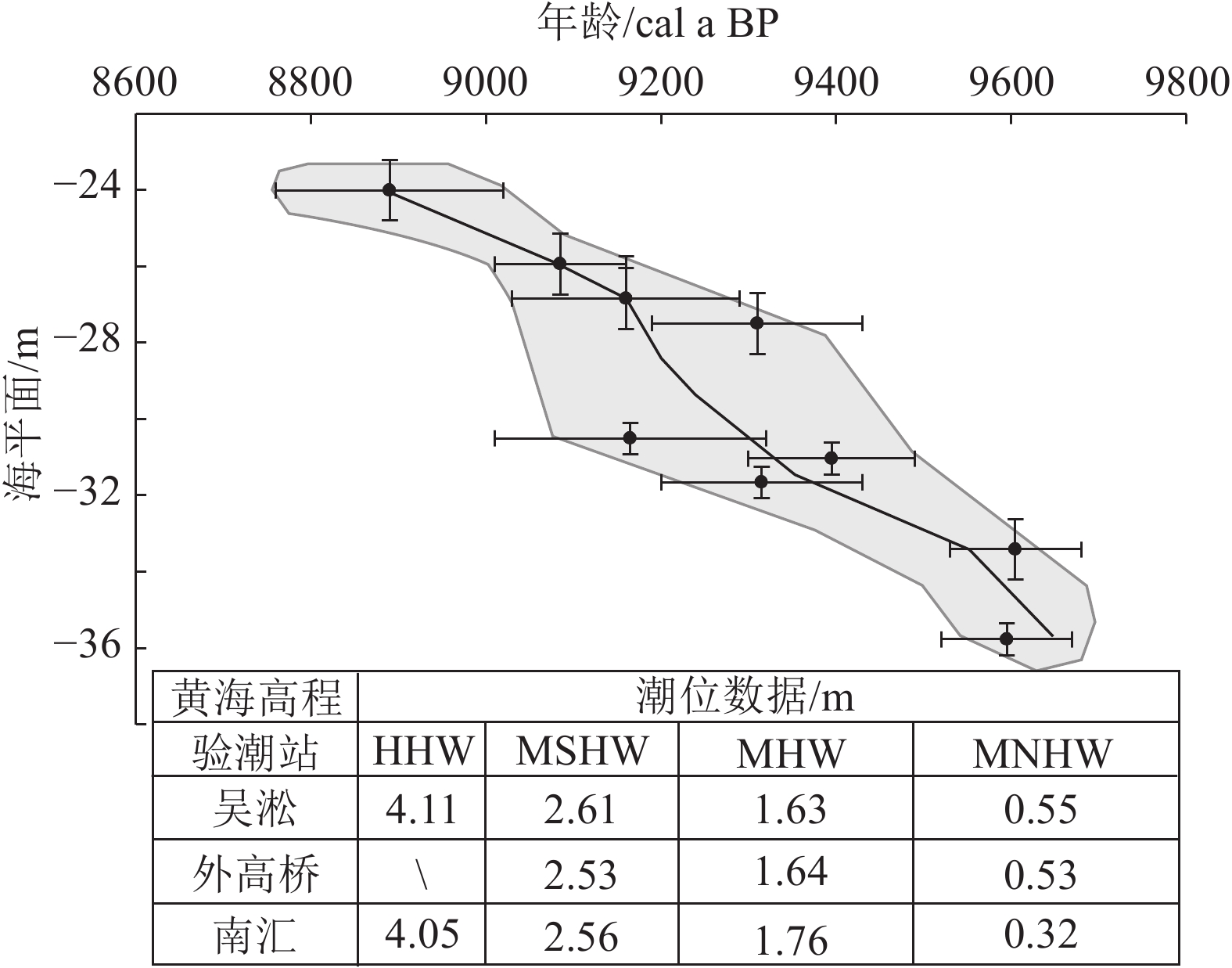
对杭州湾北岸3处现代潮滩沉积物进行高精度粒度分析,查找研究区潮滩不同微相的粒度特征和差异,提取基于粒度分析的潮滩微相识别敏感指标,并将其应用到该区域的全新世钻孔潮滩沉积物中,识别钻孔潮滩沉积微相,据此建立研究区全新世早期的海平面曲线。研究表明:杭州湾北岸现代高潮滩盐沼沉积物粘土含量明显高于高潮滩下部和中潮滩,而砂含量与之相反;高潮滩盐沼平均粒径等粒度参数明显小于中、高潮滩的粒度参数;盐沼沉积物粒度频率曲线峰态宽缓,明显区别于高潮滩下部和中潮滩。上述现代潮滩微相粒度敏感指标可成功应用到钻孔潮滩沉积微相划分中,并建立了该区域全新世早期海平面曲线。曲线显示,9700~8700 cal a BP期间海平面上升约11.6 m,海平面上升速率可达1.2 cm/a。现代潮滩不同位置沉积物粒度参数的规律性差异可作为潮滩微相识别的有效指标,为古潮滩沉积微相识别和古海平面重建提供参考依据。
Abstract:In this paper we take detail analyses on the sediment grain size for three tidal flat sections to set up the diagnostic indexes for recognization of tidal flat facies along the north bank of the Hangzhou Bay. The study also examined the application of the diagnostic indexes for distinguishing salt marsh, upper and lower tidal flats in a Holocene sediment core HZK11. The results show that clay and sand components could be the diagnostic indexes for distinguishing salt marsh, upper and lower tidal flats. Salt marsh volume curves are different from the upper and lower tidal plat. The parameters (Mode, Median and Mode) are effective indexes to identify salt marsh upper and lower tidal flat sediments.Above diagnostic sediment components, grain size parameters and volume curves are applied successfully to identify the exact tidal plat facies in boreholes and can be used to reconstruct relative sea-level which demonstrates sea-level rise of around 1.2 cm/a from 9700 cal a BP to 8700 cal a BP.
-
Keywords:
- grain size analysis /
- diagnostic indexes /
- tidal flat facies /
- sea-level /
- Hangzhou Bay
-
石英砂岩是一种固结的砂质岩石,其中石英及硅质岩屑含量达90%以上,来源于各种岩浆岩、沉积岩和变质岩,伴生矿物为长石、云母、岩屑、重矿物和粘土矿物,胶结物主要为硅质胶结。其特点是规模大、开采条件较好、易于破碎分级和大规模生产,但胶结物成分较复杂,杂质较多(汪灵等, 2019)。石英砂岩是一种大宗非金属矿,用途非常广泛,是近百种工业产品的原料,主要用于玻璃工业、填料领域及生产有机硅化合物和其他工业用石英砂硅质矿物等高新技术产业领域(颜玲亚等, 2020)。由于石英砂岩含铁硅质、胶结质深入石英颗粒缝隙,一般须经过选矿提纯才能为工业利用。近年来,湖南玻璃工业和新能源产业发展很快,湖南省正在重点打造高性能电子玻璃产业基地,需要大量的高纯石英砂岩矿提供原材料。
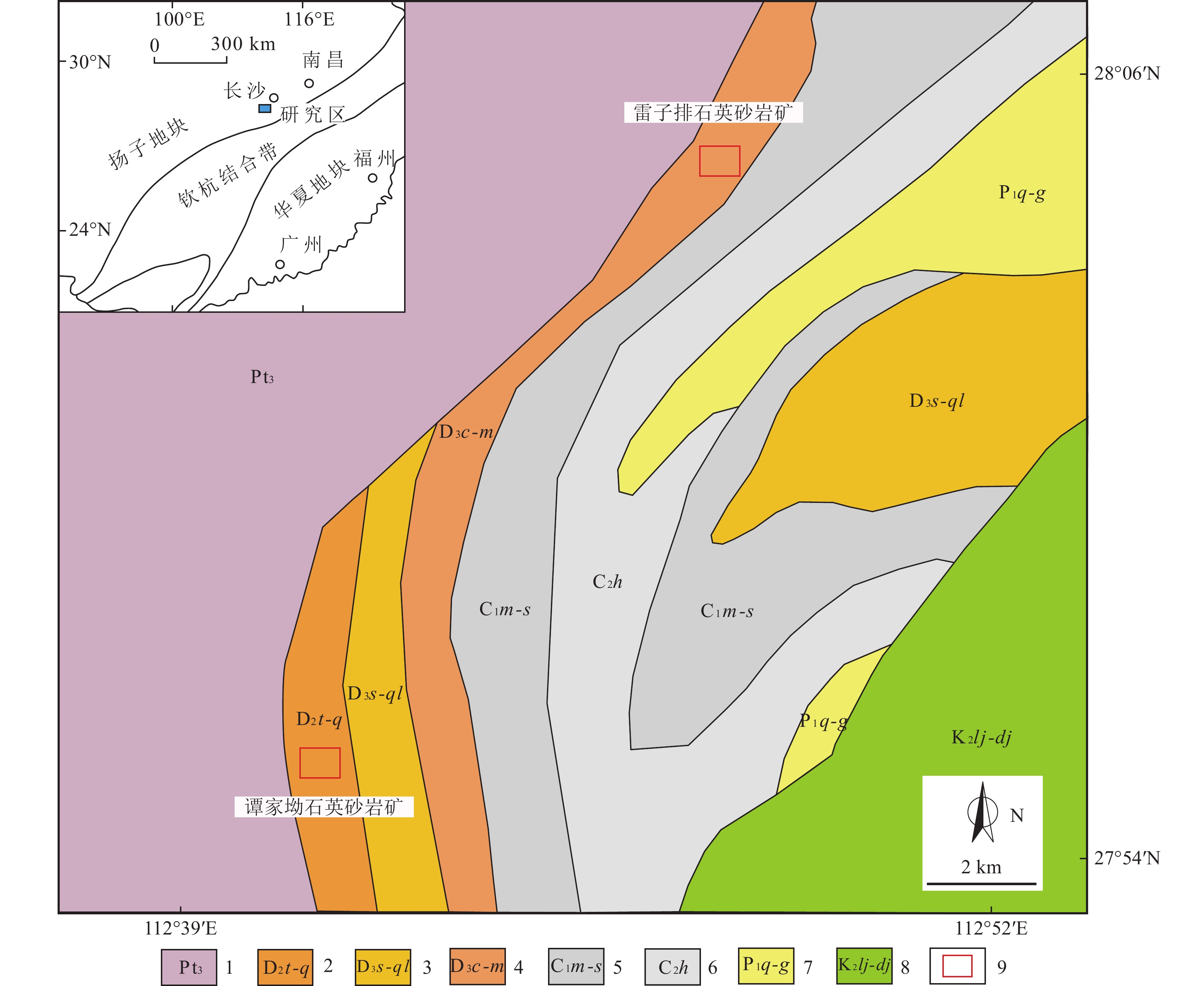
湖南省石英砂岩矿资源丰富,著名的有湘潭县雷子排大型石英砂岩矿、湘潭县谭家坳中型石英砂岩矿、溆浦县谭家湾大型石英砂岩矿,醴陵市浦口镇十八坡玻璃用大型石英砂砾岩矿、衡东县甘溪镇石岗坳中型石英砂岩矿、衡东县白莲镇白莲村小型石英砂岩矿等。目前发现的大型石英砂岩矿床主要产于扬子地台沉积盖层中,产出层位以泥盆系为主,其次有石炭系等,矿层往往赋存在浅海相或海陆交互相沉积地层中。前人(谭建农, 2000; 梁玉明等, 2017; 吴少飞等, 2019)对典型石英砂岩矿的地质特征及赋矿层位做了系统总结,但对矿石矿物组成及杂质赋存状态研究较少。谭家坳石英砂岩矿床于20世纪60年代开采,赋矿地层为泥盆系跳马涧组,后续在该地层相继发现多个石英砂岩矿床。本文以湘潭县谭家坳石英砂岩矿床为例,对其矿物组成、胶结物及杂质特征进行了研究,并结合区域地质背景对矿床成因进行了初步探讨,以期还原湖南地区石英砂岩矿的成矿作用。
1. 区域地质背景
谭家坳石英砂岩矿位于湖南省湘潭市,大地构造位于“钦杭结合带”中段湘潭—衡阳一线扬子地块与华夏地块的接合带附近,即钦杭结合带北东部位(严加永等, 2019)。钦杭带大致经历了新元古代早期扬子地块与华夏地块的碰撞、南华纪的裂解、加里东期的汇聚和碰撞,于印支期结束了海相沉积史,同时形成一系列横跨褶皱,叠加在加里东期褶皱之上。燕山期研究区地壳运动主要表现为断块运动,形成断陷盆地和少量火山盆地(杨明桂等, 2009)。岩浆活动较强烈,形成大量的加里东期、印支期及燕山期花岗岩(龚雪婧等, 2023)。
区域出露的地层由老至新主要有中元古界冷家溪群,中泥盆统跳马涧组、云台观组、棋子桥组,上泥盆统佘田桥组、七里江组、长龙界组、锡矿山组、欧家冲组、孟公坳组,下石炭统马栏边组、天鹅坪组、石磴子组,上石炭统黄龙组,另分布有少量二叠系和白垩系(图1)。其中,中泥盆统跳马涧组、云台观组是石英砂岩矿的含矿地层,主要由杂色砂岩、砂质页岩、石英砂砾岩组成。
区域岩浆岩较发育,东北部为加里东期宏夏桥和板杉铺岩体,主要由花岗闪长岩、石英闪长岩、二长花岗岩组成(李建华等, 2015);西部为印支期歇马、紫云山岩体,主要由黑云母二长花岗岩、二长花岗岩组成(鲁玉龙等, 2017);南部为燕山期衡山复式岩体,由南岳岩体和白石峰岩体组成,南岳岩体主要为花岗闪长岩,白石峰岩体主要为二云母花岗岩(蔡富成等, 2021)。
2. 矿床地质特征
谭家坳石英砂岩矿赋矿地层为中泥盆统跳马涧组。矿体呈层状、似层状产出,SiO2平均含量达95.29%,矿体资源量(原332+333)500 × 104 t以上,为中型的玻璃用石英砂岩矿床,属于优质玻璃原材料。
中泥盆统跳马涧组广泛分布于湘中—湘南区,均与上下层位呈高角度不整合接触,岩性主要为紫红色砂质泥岩、砂质页岩、泥质粉砂岩夹细砂岩及灰白色石英砾岩、石英砂岩。其中,跳马涧组下段以石英砂岩为主,上段以(粉)砂质泥页岩为主。
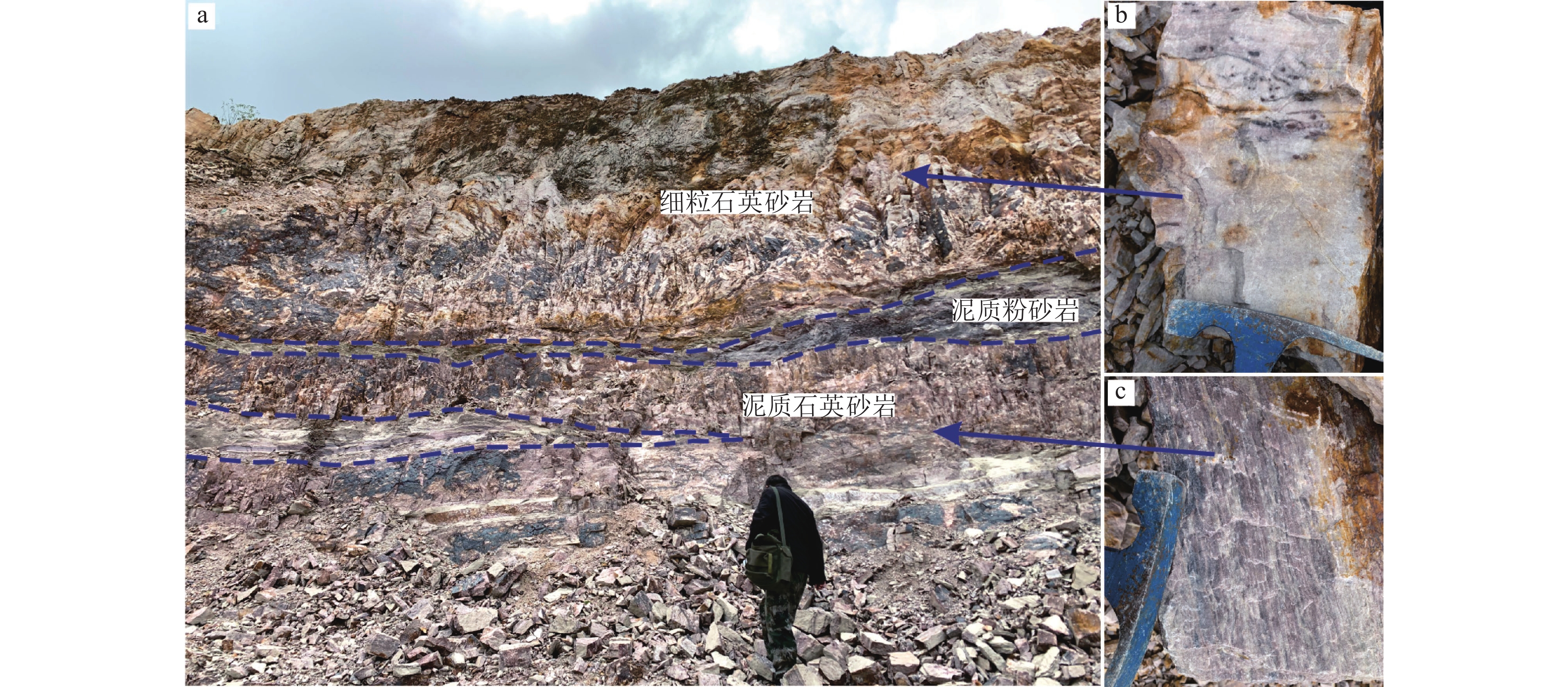
跳马涧组下段为谭家坳石英砂岩矿赋矿层位,其岩性为灰白色中细粒石英砂岩,灰白色—黄灰色中细粒石英砂岩,夹紫红色泥质粉砂岩及泥质石英砂岩(图2–a),该段厚108~124 m,大体可分上中下三部分。下部岩性主要为灰白色细粒石英砂岩,次为黄灰色—灰白色中厚层状细中粒石英砂岩夹厚层石英砂岩,底部为紫红色中厚层石英砾岩,砾岩厚度一般小于1 m,粒径小于2 cm;中部为灰白色中细粒石英砂岩夹灰绿色泥质粉砂岩及紫红色泥质粉砂岩,或为互层,泥质石英砂岩褐铁矿化较强烈,沿裂隙面分布(图2–c)。上部岩性主要为灰白色细粒石英砂岩(图2–b),其次为中细粒石英砂岩,另外含少量紫红色泥质粉砂岩透镜体。总体上,从下到上石英砂岩SiO2含量逐渐升高,褐铁矿化则随之减弱。
跳马涧组上段为矿体顶板,厚度不均匀,与下段呈整合接触。本段岩性主要为灰白色—紫灰色细粒石英砂岩,其次为灰紫含铁泥质石英砂岩、紫红色泥质粉砂岩等,呈透镜体产出。由下而上泥质成分逐渐增加,顶部主要为紫红色泥质粉砂岩。
矿体走向近南北向,倾向北西,产状330°~350°∠15°~25°,呈层状产出,平面上呈近南北向的弯曲带状。矿体规模较大,控制走向延伸 800 m,倾向延伸100~500 m,矿体厚度为 30~100 m,平均厚度为55 m。矿体中主要矿物成分SiO2含量为90.1%~98.9%,平均95.29%。矿石中石英分布均匀,杂质主要为Al2O3、Fe2O3,经水洗后Al2O3含量小于1%,Fe2O3含量在0.1%~0.15%之间。
3. 矿石特征
3.1 矿石矿物组成
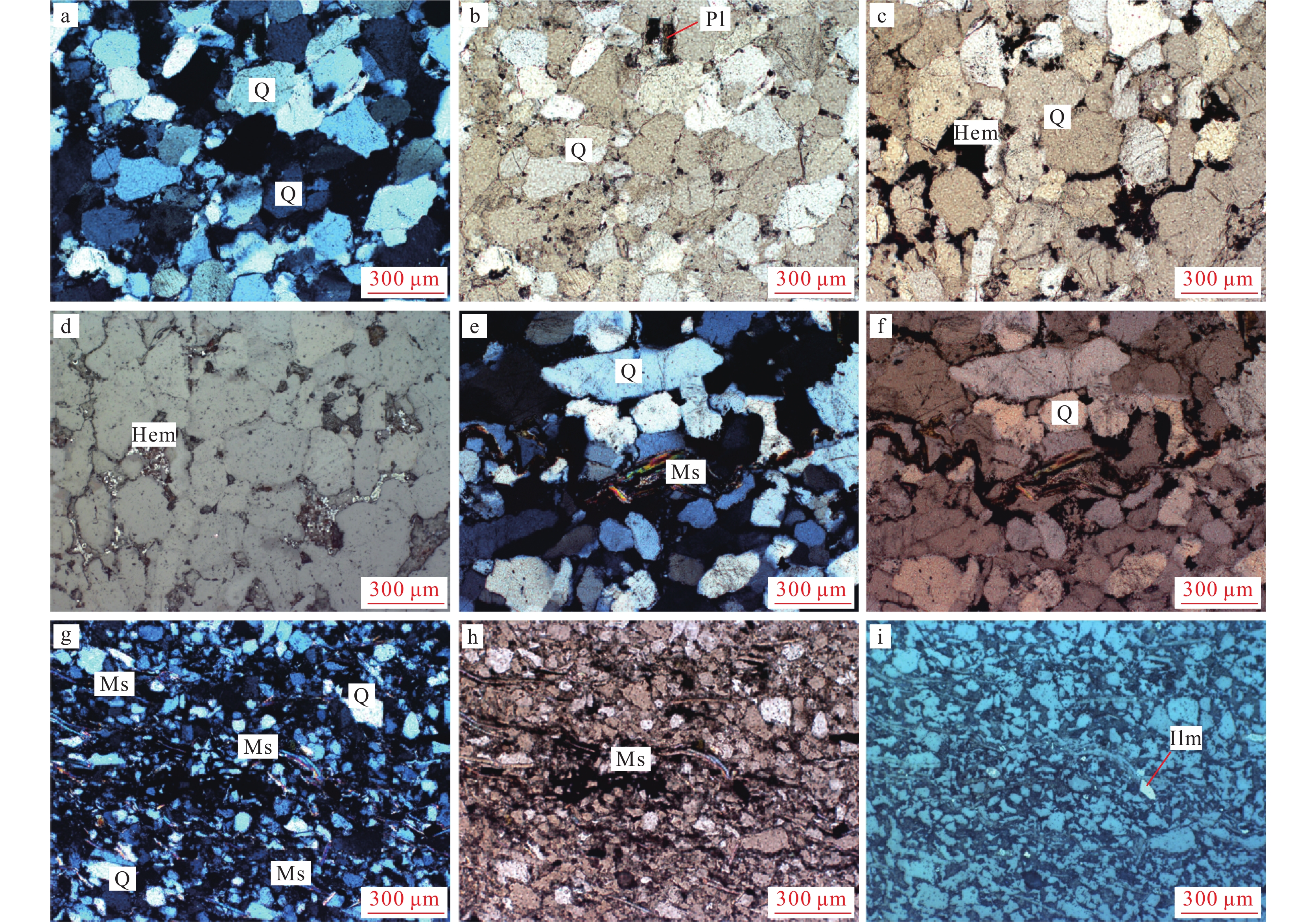
矿石主要为细粒、中细粒石英砂岩,矿石矿物主要为石英。石英以碎屑颗粒状胶结在一起,石英含量大于90%,偶见长石晶屑,其中石英颗粒最大粒径为0.8 mm,主要粒径在0.2~0.5 mm之间,粗细混杂分布,无规律,石英颗粒以次圆状至不规则次棱角状为主,形状较不规则。石英颗粒间的粘土、云母等胶结物含量为5%~8%,主要由硅铝泥质杂基、少许硅质胶结物和白云母组成(图版Ⅰ–a~f)。胶结物主要为硅铝质,分布在石英颗粒间或石英裂隙中,接触式胶结。胶结物中局部含有黑色粒状杂质,含量小于1%,主要成分为赤铁矿(图版Ⅰ–d),其特征是呈不规则粒状无序分布在胶结物中,边界不清晰,赤铁矿化程度不等,呈渐变过渡接触。
细粒石英砂岩中夹少量泥质石英砂岩(图版Ⅰ–g~i),主要由石英、白云母、粘土等矿物组成,泥质石英砂岩中石英含量普遍小于细粒石英砂岩。石英粒径普遍小于0.1 mm,白云母呈细鳞片状产出,含量在10%左右,由于重结晶,白云母定向散布穿插于石英粒间。同时也造成泥质石英砂岩的机械强度不高、较容易破碎。石英颗粒间的粘土等填隙物含量在10%左右,另外可见少量的金红石颗粒。
3.2 矿石结构构造
矿石构造主要为块状构造,其次为厚层状构造。矿石结构以他形晶粒状结构为主,其次为砾状结构、砂状结构、网脉状结构、填隙状结构等。他形晶粒状结构的矿石由他形晶粒石英组成。砾状结构、砂状结构的矿石主要为石英砾岩、砂砾岩、砂岩,其碎屑主要为石英晶屑,偶见角闪石岩岩屑、炭质页岩屑、石英粉砂岩屑等,充填物主要为微晶或细晶石英、玉髓、绢云母、高岭石等。充填物中有时还见褐铁矿、绿泥石、白云母等。网脉状结构、填隙状结构的矿石中,石英晶屑之间通常结构紧密、无间隙,或间隙中为玉髓、微晶石英等;局部石英颗粒之间有间隙,并被白云母、高岭石、玉髓等充填,低倍镜下呈现网脉状、填隙状等形态。
3.3 矿石的化学成分
谭家坳石英砂岩矿体中细粒石英砂岩矿石的全岩主量元素定量分析在北京大学教育部重点实验室完成。测试采用熔片法X-射线荧光光谱法(XRF)分析,首先称取0.5 g样品放入坩埚,然后加入适量硼酸高温熔融成玻璃片,最后在X射线荧光光谱仪(XRF-1500)上采用外标法测定氧化物含量。主要氧化物的分析相对误差小于2%,分析结果见表1。
表 1 谭家坳石英砂岩矿体主量元素分析结果Table 1. Major elements analysis results of Tanjiaao quartz sandstone ore body% 样品编号 SiO2 Fe2O3 Al2O3 Cr2O3 MgO CaO K2O Na2O TiO2 烧失量 总量 TJA-1 95.53 0.85 1.28 0.001 0.01 0.12 0.31 0.04 0.03 0.98 99.15 TJA-2 96.14 1.09 1.07 0.001 0.02 0.1 0.21 0.03 0.05 0.68 99.39 TJA-3 94.21 1.41 1.45 0.001 0.05 0.14 0.13 0.01 0.05 1.24 98.69 平均 95.29 1.12 1.27 0.001 0.03 0.12 0.22 0.03 0.04 0.97 99.08 主量元素分析结果显示:矿石的SiO2含量平均为95.29%,接近普通石英砂产品的要求(SiO2>98.2%);Al2O3含量平均为1.27%,高于普通石英砂产品的要求(Al2O3≤0.7%)及超纯石英砂产品(Al2O3≤0.5%)的要求;Fe2O3含量平均为1.12%,其含量与普通石英砂产品的要求(Fe2O3≤0.075%)、超纯石英砂产品(电子玻璃用石英砂产品)的要求(Fe2O3≤0.01%~0.12%)还相差甚远(《矿产资源工业要求》编委会,2010);K2O和CaO的平均含量分别为0.22%及0.12%,Na2O和TiO2的平均含量分别为0.03%及0.04%,MgO的平均含量为0.03%。含Al、Fe杂质是影响矿石品质的最主要因素,因此需要对杂质赋存状态及特征进行分析。
3.4 杂质赋存状态及特征
本次研究选择TESCAN扫描电子显微镜(SEM)对谭家坳石英砂岩样品进行微观形貌观察,首先对探针片进行镀碳处理,其加速电压为16 kV,电流16 nA。将选择好的目标矿物或区域用扫描电镜配置的布鲁克QUANTAX 能谱仪(EDS)进行微区原位成分分析。
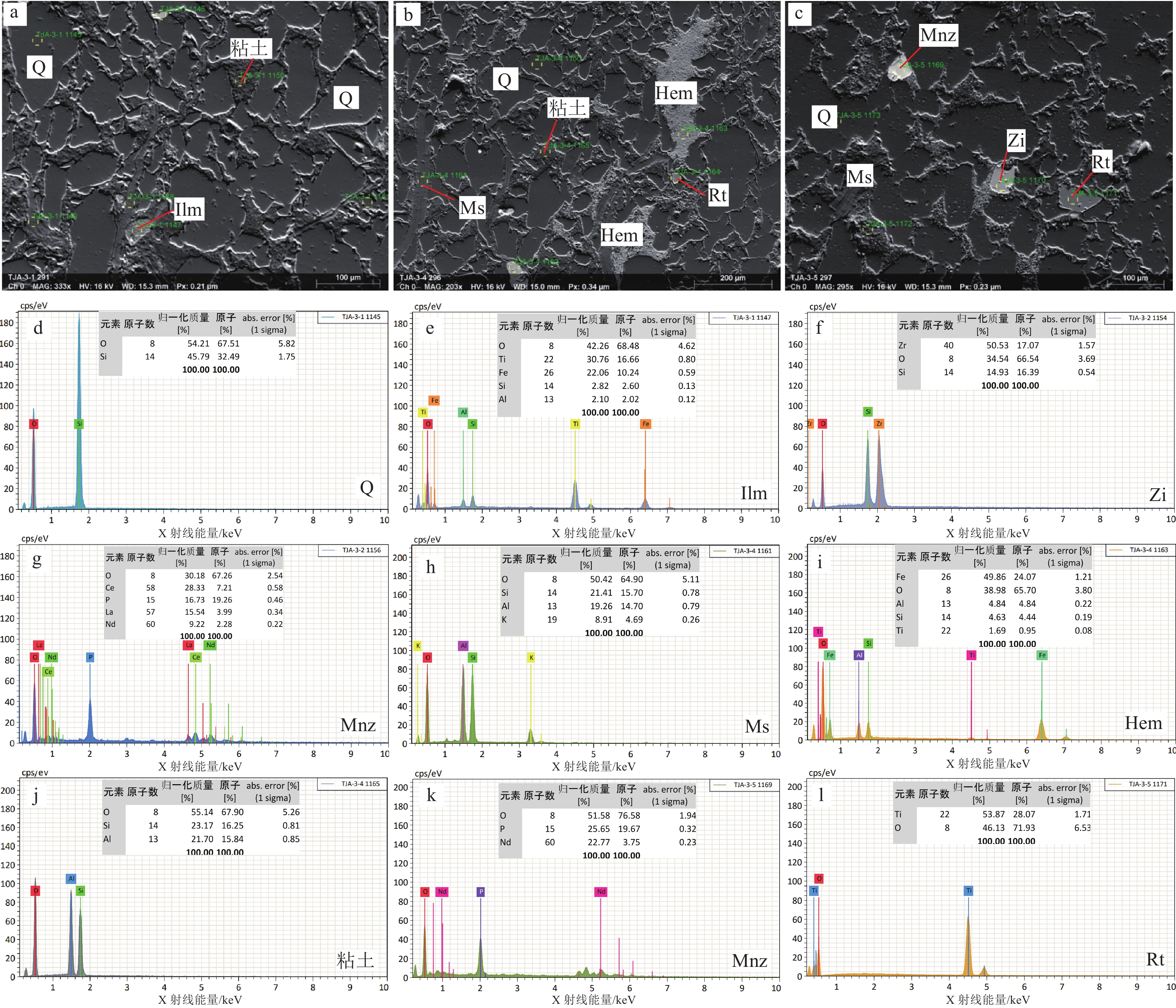
由谭家坳石英砂岩探针片样的SEM-EDS分析结果(图3)可以看出,石英颗粒间及晶体裂缝存在溶蚀坑,局部可见细小的溶蚀坑呈蜂窝状密集分布,而较大者已被颗粒细小的粘土矿物充填(图3–a,b)。EDS分析结果表明,石英只含有 O、Si 两种元素,且O、Si摩尔分数之比接近 2∶1(图3–d),与石英的理论化学式一致,说明矿石中石英的纯度很高,且晶体结构中不含类质同象杂质。
粘土矿物和白云母为矿石中Al的赋存矿物。其中粘土矿物由 O、Si、Al等元素组成(图3–j),其中O含量为55.14%,Si含量为23.17%,Al含量为21.70%,推测主要由高岭石等矿物组成。白云母主要分布于石英颗粒之间,呈不规则带状,由O、Si、Al、K等元素组成(图3–h),其中O含量为50.42%,Si含量为21.41%,Al含量为19.26%,K含量为8.91%。
赤铁矿和钛铁矿为矿石中Fe的赋存矿物。其中赤铁矿主要分布于石英颗粒之间(图3–b,i),由Fe、O等元素组成,含有少量Al、Si、Ti元素,其中Fe含量为49.86%,O含量为38.98%,野外观察发现,由于发生了氧化作用,可见赤铁矿沿裂隙呈薄膜状产出。钛铁矿主要分布于石英颗粒之间(图3–a,e),由Fe、Ti、O等元素组成,含有少量Al、Si元素,其中Fe含量为22.06%,Ti含量为30.76%,O含量为42.26%。
矿石中偶见锆石、独居石、金红石等矿物(图3–c,f,l),大小在40~80 μm之间,分布于石英颗粒间,其中独居石主要含有La、Ce、Nd等稀土元素(图3–g,k)。
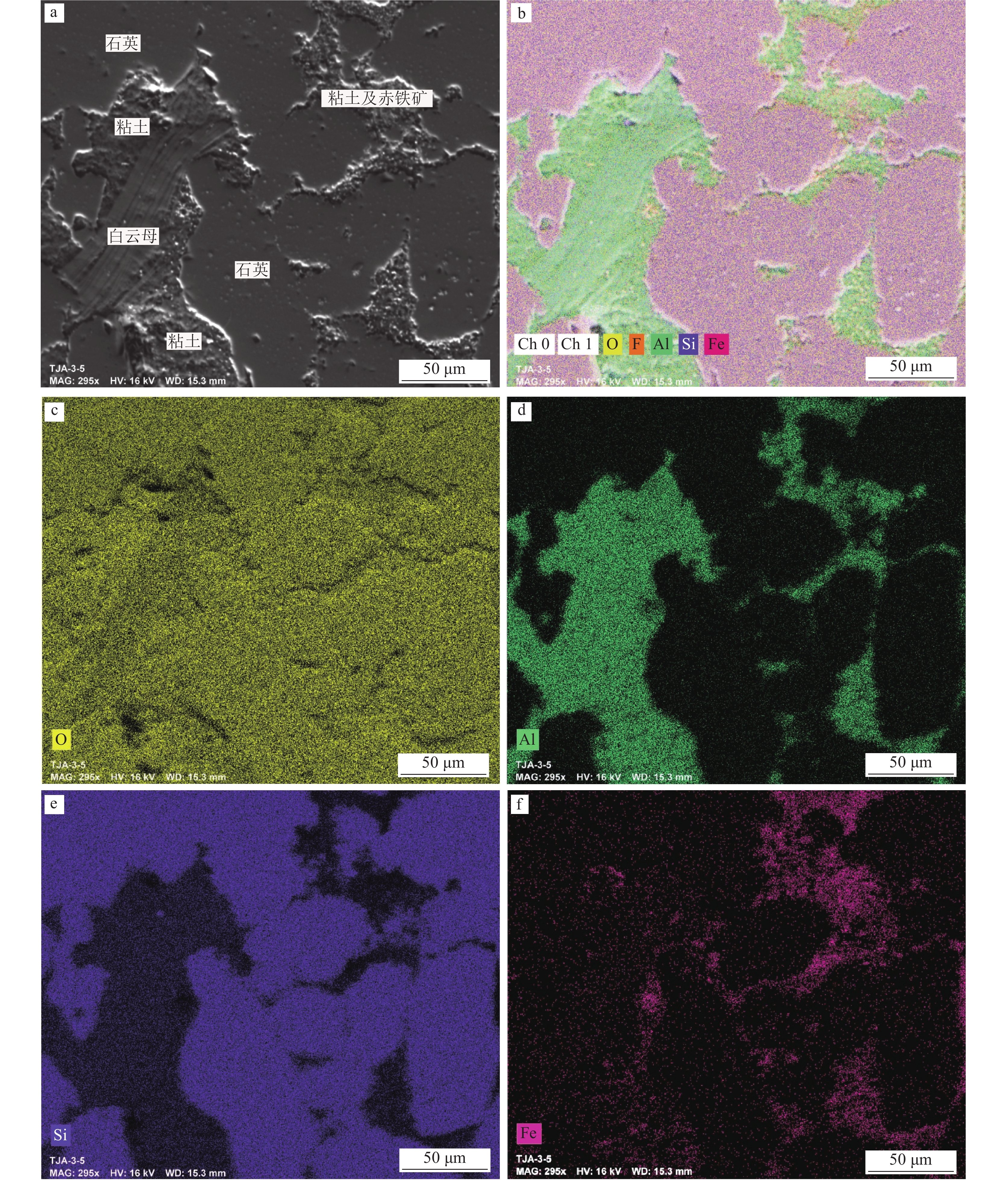
对典型石英颗粒及其胶结物区域进行原位微区扫面(mapping)分析(图版Ⅱ)可以发现,胶结物中Al、Fe杂质元素主要以白云母、粘土、赤铁矿等矿物形式产出,其中赤铁矿与粘土密切共生。单点EDS研究得出,粘土矿物主要为高岭土,推测赤铁矿为含铁质的粘土矿物氧化而成。因此,Al、Fe杂质元素主要呈填隙物形态存在于石英颗粒间,部分呈镶边状紧密黏附在石英颗粒周边,利于分选解离。
4. 讨 论
4.1 成矿物质来源
矿石的矿物组成在追溯成矿物质来源方面具有重要作用。矿石中的石英以碎屑颗粒状胶结在一起,除石英外,还含有白云母、锆石、钛铁矿、独居石、金红石等矿物。矿石的碎屑物中含有斜长石和白云母,胶结物主要为铁质及粘土矿物,由此推断石英砂岩的原岩之一为岩浆岩。镜下见矿石主要由细粒、中细粒石英组成,粒径一般在0.2~0.5 mm之间,分选性相对较好,磨圆度多为次圆—次棱角状,胶结方式为孔隙—压嵌型。显微镜下石英均见波状消光现象,少量铁质胶结物及锆石、钛铁矿等重矿物不均匀分布,而泥质石英砂岩中白云母定向散布穿插于石英粒间。这种具有较高含量的SiO2和结构较成熟的石英砂岩是水流及波浪对沉积物反复冲刷淘洗的产物。因此,从矿石矿物组成可以得出,石英砂岩的原岩为中酸性岩体,而研究区东北部大面积分布的加里东期花岗闪长岩体、石英闪长岩体、二长花岗岩体可能是矿体的母岩之一(司荣军等, 2004)。
通常情况下,搬运距离越远,成熟度越高,分选性越好。石英砂岩屑显示出较好的分选性和磨圆度、较富集的石英及特有的杂质矿物组合。跳马涧组直接不整合于中元古界之上,其间有近 6 亿年的沉积间断,表明这套石英砂岩并不是直接来源于花岗岩的风化、沉积、固结,而是来源于先前存在的砂岩,是多旋回改造的产物(张欣平等, 1992)。区域上,中泥盆统跳马涧组石英砂岩平行不整合覆盖在较厚的中元古界冷家溪群之上,后者主要由变质细砂岩、砂质板岩、变质砂岩组成,反映了中泥盆世稳定克拉通环境下地壳多次均匀上升-沉降的历史(王子正等, 2019),每一个旋回都为石英的进一步分选和富集创造了条件(陈光艳等, 2021)。
4.2 沉积环境
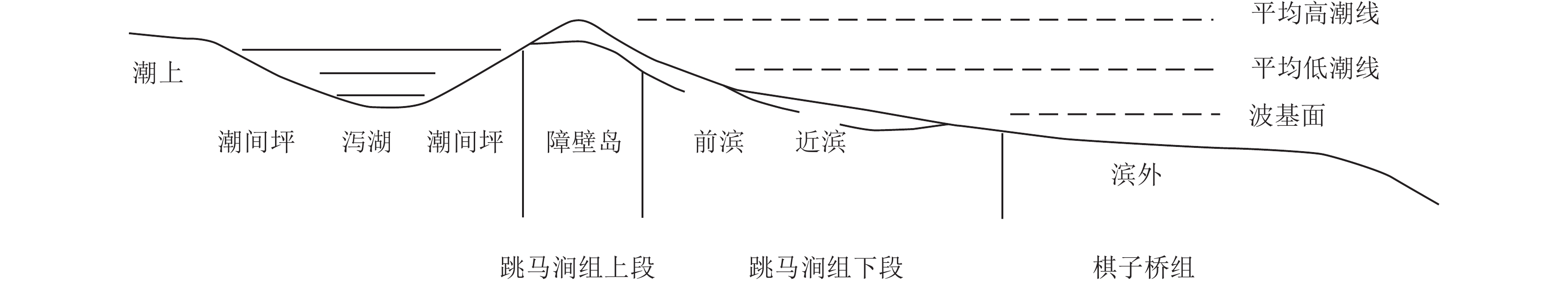
前人研究认为,跳马涧组古沉积环境属于滨海环境(王刚田等, 1984)。滨海沉积环境可进一步划分为海岸沙丘、后滨带、前滨带、临滨带等(陈建强等, 2015)。其中,前滨带位于平均高潮线与平均低潮线之间的冲浪带,是无障壁海岸环境中能量最高的部位,地形相对平坦,受潮汐的作用,以沉积中—细石英砂岩为主,磨圆度、分选性极好且纯净,砂岩的成分和结构成熟度极高。生物化石较贫乏,多见生物碎片,局部可见重矿物富集,沉积构造以发育海滩环境所特有的冲洗交错层理为主,次为平行层理,浪成波痕、菱形波痕、冲刷痕、泡沫痕、流痕等浅水沉积构造标志也非常发育(周邦国等, 2018)。由镜下观察可知,谭家坳矿石中石英颗粒绝大多数以细粒为主,中粒次之,且石英分选性较好,多数为次圆—次棱角状。石英晶屑之间通常结构紧密、无间隙,或间隙中为玉髓、微晶石英等;局部石英颗粒之间有间隙,并被白云母、高岭石、玉髓等充填,也可见重矿物局部富集。研究区跳马涧组石英砂岩普遍发育平行层理和交错层理(图2–c),局部可见石英砂岩呈波痕构造,另外矿物组成伴有钛铁矿、金红石、锆石。由以上特征可以推断,研究区石英砂岩应属于滨海沉积环境,且与前滨亚相沉积物的特点极符合。因此,综合分析认为,跳马涧组石英砂岩沉积环境为滨海环境中的前滨亚相。
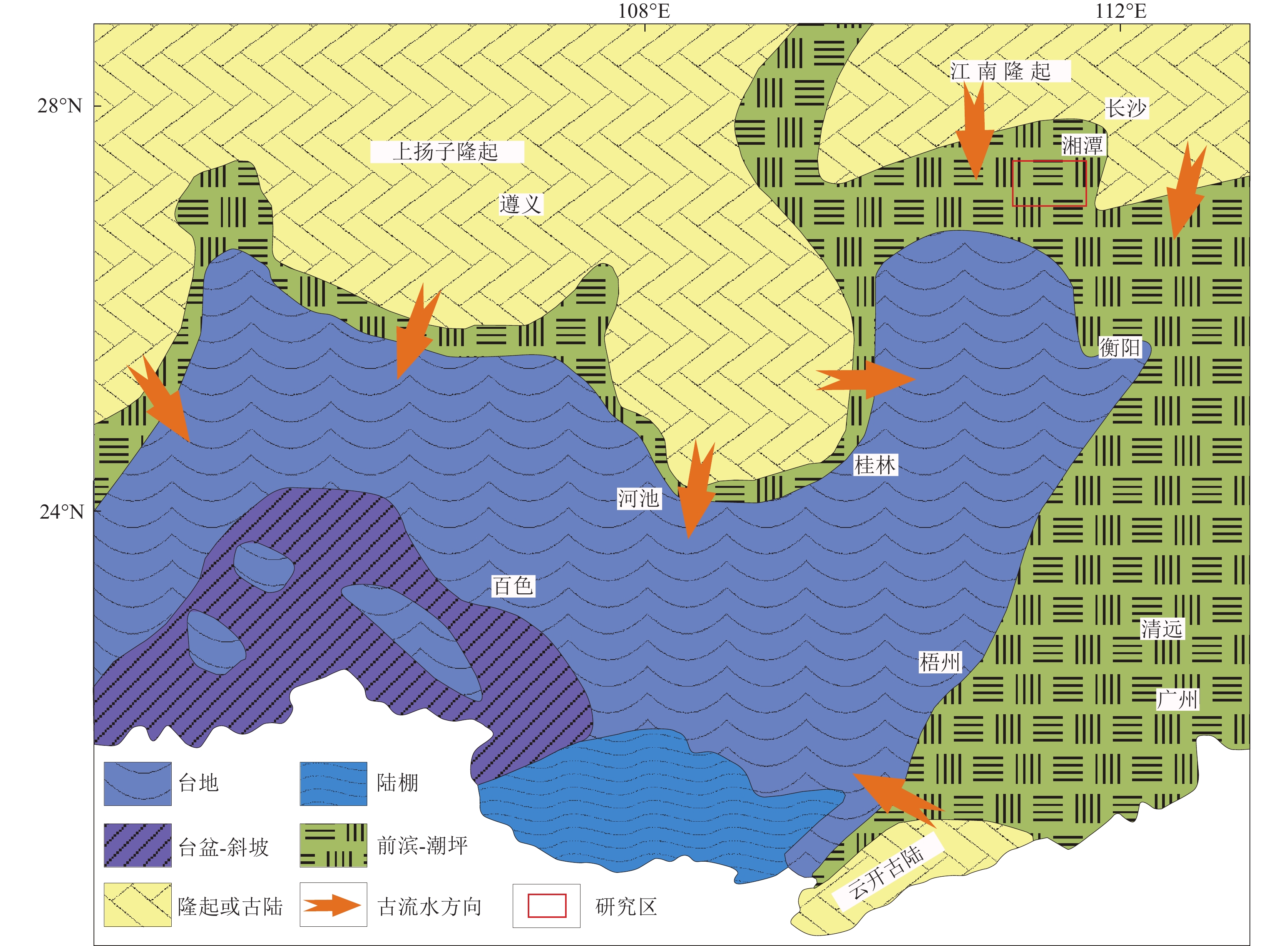
江南造山带新元古代沉积物中广泛含有新元古代—太古宙末期岩浆锆石(Li et al., 2014; Shu et al., 2015;Xu et al., 2018; Yao et al., 2019; 陈家驹等, 2021),江山−绍兴断裂北西侧早古生代前陆盆地中除上述岩浆锆石外,还含有早古生代岩浆锆石(Xu et al., 2012, 2016; Yao et al., 2015; 杨树锋等, 2019; 马学平等, 2010)。早泥盆世早期,湘中、湘南广大地区上升遭受剥蚀,发生了多次由南向北的海侵,表现为碳酸盐岩的沉积范围增大,碎屑物质向北沉积(图4)。早泥盆世晚期,广西入侵的海水浸及桂林进入湘西南一带,沉积了滨海相的源口组碎屑岩。中泥盆世早期,海水由西南继续向东北浸漫,北达湘潭韶山一带, 接受来自江南造山带的物源供给,沉积了前滨—近滨相碎屑岩(Yuan et al., 2023)。跳马涧期,海侵扩大达湘西新晃直至岳阳一线,在前滨和潮间坪带沉积了砾质、砾砂质、砂质、砂泥质、粉砂质、细砂质等碎屑沉积。
![]() 图 4 华南湘桂地区中泥盆世早期岩相古地理图(据刘宝珺, 1994修改)Figure 4. Lithofacies paleogeography map of early Middle Devonian in Hunan and Guangxi
图 4 华南湘桂地区中泥盆世早期岩相古地理图(据刘宝珺, 1994修改)Figure 4. Lithofacies paleogeography map of early Middle Devonian in Hunan and Guangxi4.3 矿床成因
刘宝珺等(1995)认为华南存在江南古陆与华夏古陆,两者在晋宁期沿江山-绍兴断裂带碰撞缝合,但向湘、粤、桂方向开启,形成“加里东”残洋盆地。由晋宁期至加里东期,盆地沉积中心不断向南西迁移,最终于广西运动或东吴运动关闭。矿区所在的区域晚古生代—中生代三叠纪是继加里东构造运动的全面海退之后产生的新一轮巨型沉积旋回(张岳桥等, 2012)。
中泥盆世之前,矿区所在的区域广泛出露中元古代地层及加里东期岩浆岩,遭受长期风化剥蚀,为石英砂岩提供了物质来源,泥盆纪中期,区域普遍接受前滨相沉积,跳马涧组主要受潮汐的作用,其演化过程如图5所示:在海岸线陆地(障壁岛)一侧,发育辫状河流,沉积物主要是河流带来的陆源物质,这些物质经过长距离的搬运、磨蚀和分选,成岩后就形成了成熟度较高的石英砂岩,受波浪的一定作用,经多个旋回的搬运、分选、沉积,沉积的砂岩成熟度较高,石英较纯,并在分选条件较好的部位形成石英砂岩矿床。中泥盆世晚期,湘中、湘南广大地区沉积了近滨环境的砂泥质、粉砂质、细砂质沉积,在湘潭、醴陵等地海水中富含氧,致使岩石普遍为紫色、紫红色调。跳马涧组沉积结束后进入滨外浅海,开始了棋梓桥组的泥灰岩沉积,总的演化为海进过程。
![]() 图 5 湖南省湘潭地区跳马涧组沉积模式图(据张欣平等, 1992)Figure 5. Sedimentary model of Tiaomajian Formation in Xiangtan area, Hunan Province
图 5 湖南省湘潭地区跳马涧组沉积模式图(据张欣平等, 1992)Figure 5. Sedimentary model of Tiaomajian Formation in Xiangtan area, Hunan Province5. 结 论
(1)湖南省谭家坳石英砂岩矿SiO2含量平均高达95.29%,Al2O3含量平均为1.27%,Fe2O3含量平均为1.12%,胶结物中Al、Fe杂质元素主要以白云母、粘土、赤铁矿等矿物形式产出,并呈填隙物形态存在于石英颗粒间,利于分选解离。
(2)谭家坳石英砂岩多为细粒石英砂岩,纯度较高,磨圆度多为次圆—次棱角状,胶结方式为孔隙—压嵌型,矿物成熟度和结构成熟度也极高,反映出滨海环境中的前滨亚相的沉积特点。
(3)区域广泛出露的元古宙地层及加里东期岩浆岩,为研究区石英砂岩提供了物质来源,经多个旋回的搬运、分选、沉积,形成了中泥盆统跳马涧组石英砂岩,并在分选条件较好的部位形成石英砂岩矿床。
致谢:感谢湖南省地质科学院相关人员对本项目的大力支持,感谢审稿专家细心审阅并提出建设性意见。
-
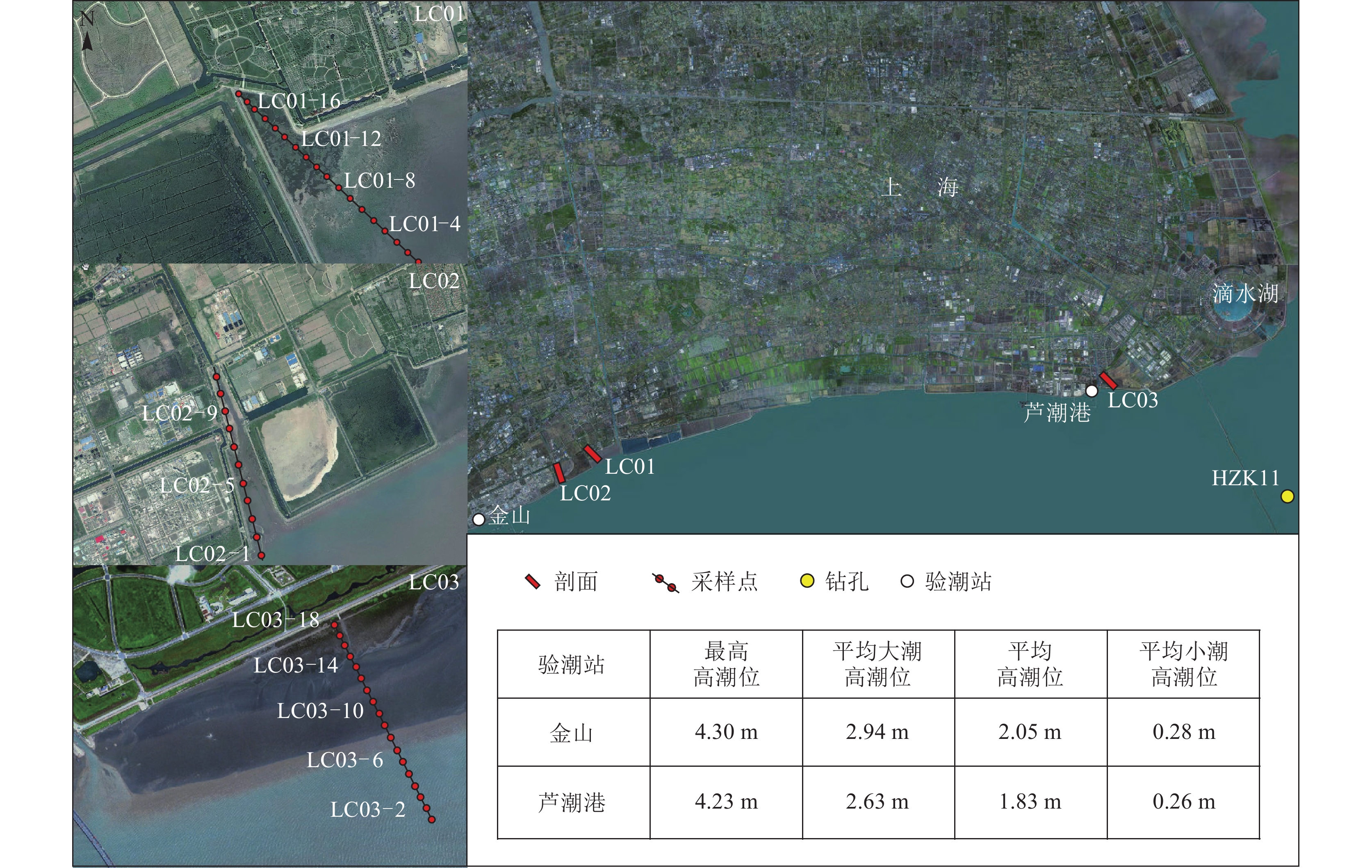
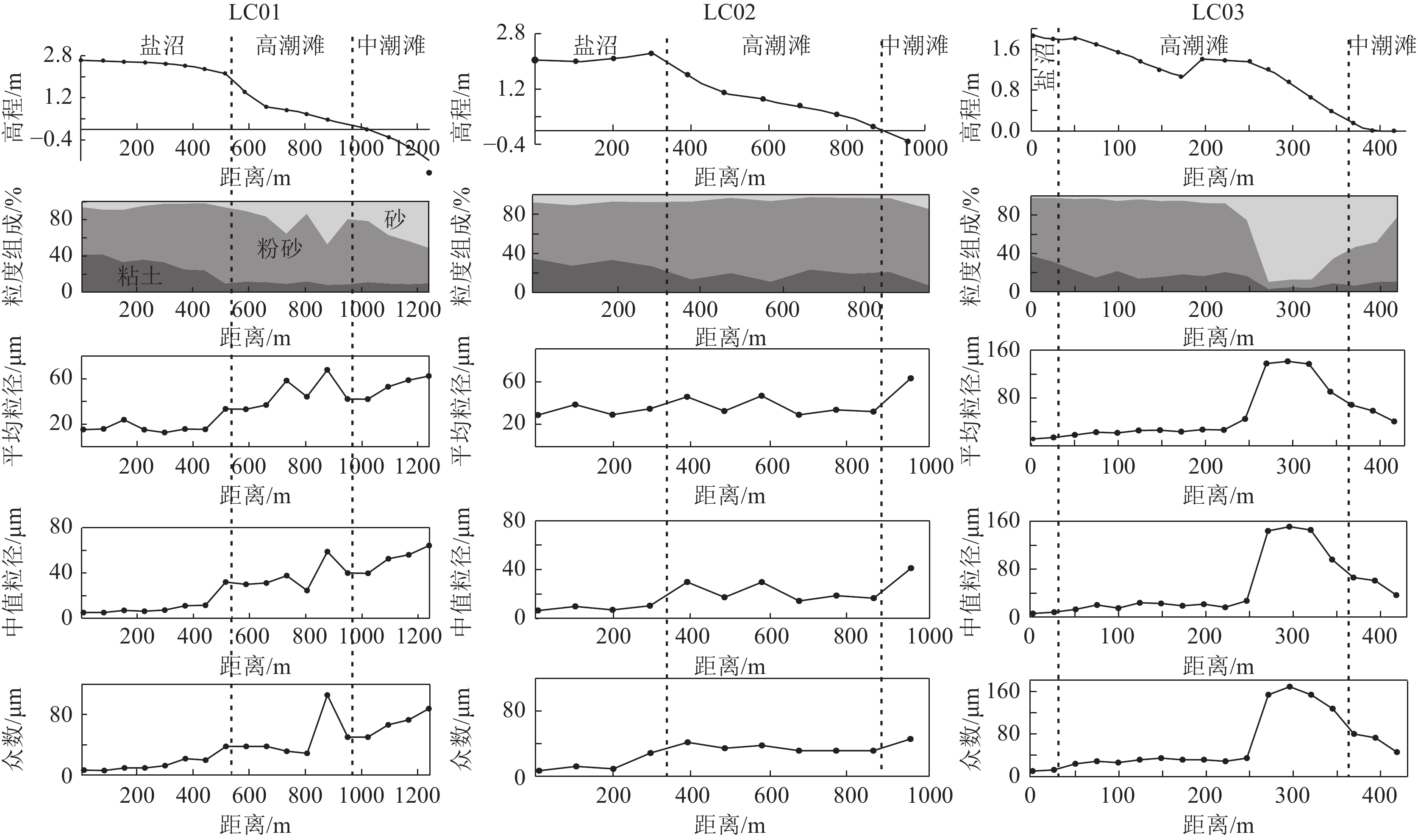
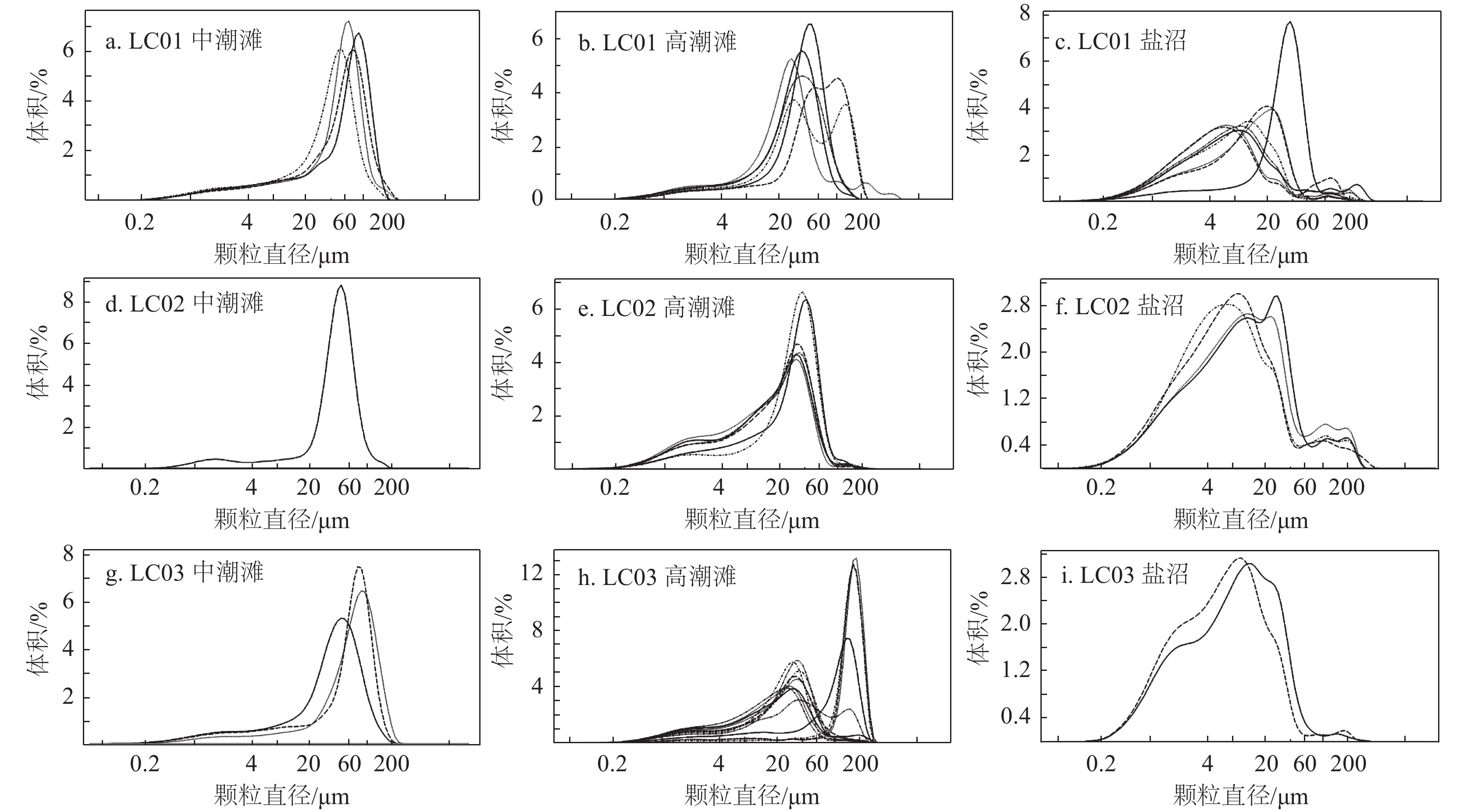
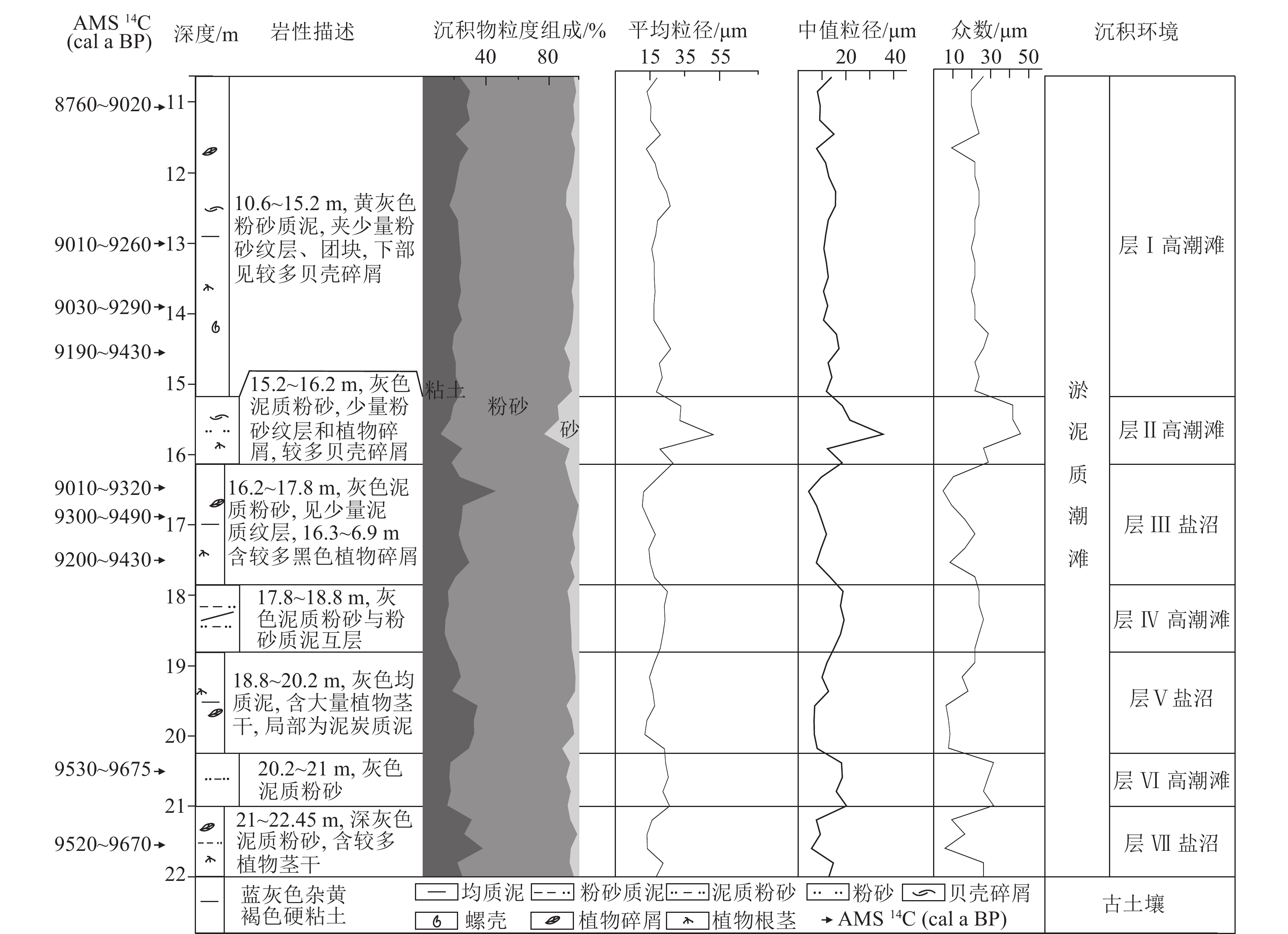
表 1 LC01 ~ LC03潮滩沉积物粒度参数
Table 1 Grain size distribution of tidal−flat sediments in LC01 ~ LC03
沉积相 剖面 粘土/% 粉砂/% 砂/% 平均粒径/µm 中值粒径/µm 众数/µm 极值 均值 极值 均值 极值 均值 极值 均值 极值 均值 极值 均值 盐沼 LC01 9.9~42.1 30.8 49.4~83.9 64.2 1.6~8.9 5.0 12.6~33.4 18.3 5.1~32.1 10.7 5.9~38.0 15.4 LC02 27.1~35.3 30.9 57.2~65.7 61.1 6.9~10.4 8.0 19.4~25.9 22 6.6~10.5 8.5 7.1~28.7 14.4 LC03 31.7~37.9 34.8 60.2~66.5 63.4 1.8~1.9 1.9 11.7~14.3 13 6.2~8.5 7.4 10.3~12.4 11.3 高潮滩 LC01 8.3~12.1 10.3 44.8~78.1 66.3 10.1~47 23.4 33.1~67.9 47.1 24.6~59 37.1 28.7~105.9 48.7 LC02 11.3~23.7 18.2 74.1~82.5 77.7 2.2~6.8 4.1 19.6~31.3 24.4 14.4~29.9 21.2 31.5~41.7 34.8 LC03 3~22.8 14.1 7.5~82.8 55.8 2.4~89.5 30.2 18.4~141 57.4 13.1~151 55.3 23.8~168.9 67.3 中潮滩 LC01 9.1~11.2 10 38.9~67.5 51.8 21.3~51.1 38.2 42~62.4 54 39.8~64.3 53.2 50.2~87.9 69.4 LC02 7.4 7.4 78.2 78.2 14.4 14.2 42 42 41.2 41.2 45.8 45.8 LC03 6.5~10.9 9.2 40.3~68.4 50.1 20.7~53.2 40.6 41~68.6 56.1 37.1~66.4 54.9 45.8~80.1 66.3 表 2 HZK11孔沉积物粒度参数
Table 2 Grain size distribution of sediments in HZK11
分层 粘土/% 粉砂/% 砂/% 平均粒径/µm 中值粒径/µm 众数/µm 极值 均值 极值 均值 极值 均值 极值 均值 极值 均值 极值 均值 层Ⅰ 17.3~30.5 23.7 67.2~74.7 71.9 1.6~9.2 4.4 12.8~26.8 18.9 7.8~17.1 12.3 9.4~28.7 21.9 层Ⅱ 11.6~25.5 18.7 66.3~72.7 68.8 5.8~22.1 12.5 20.7~51.2 32.9 12.3~35.5 21.3 26.1~45.8 36.8 层Ⅲ 21~47.2 27.7 49.1~76.5 69 0~6.3 3.2 10.5~19.5 15.1 4.4~13.4 9.3 4.9~21.7 13.7 层Ⅳ 14.3~17.4 15.9 76.5~81.1 78.7 4.4~7.2 5.4 20.8~24.9 22.9 14.9~19.2 17.7 21.7~26.1 23.9 层Ⅴ 19.1~35.3 28.2 56.9~78.7 67.2 2~10.6 4.6 12~23.3 16.4 6.7~12.7 9 6.5~21.7 12.2 层Ⅵ 15.9~18.2 17.3 74.9~77.1 76.4 5~7.9 6.4 22.3~26.2 24.5 16~20.2 18.2 26.1~31.5 29.5 层Ⅶ 22.4~38.7 29 56.3~72.5 67 0.8~5.7 4 13.2~22.5 16.7 5.6~14.7 10 5.9~26.1 16.8 表 3 HZK11孔沉积物对古海平面的指示意义和古海平面位置
Table 3 Relative sea-level reconstructed using sea-level indicatoes of core HZK11
实验室编号 标高H/m 测年材料 沉积环境 测试年龄 校正年龄 (2σ) 指示意义 古海平面(SL) a BP 误差 cal a BP 可信度 指示位置 标高/m 标高/m 误差 β-345615 −22.93 植物碎屑 高潮滩下部 8080 40 8760~9020 0.99 MNHW-MHW 1.07±0.6 −24.0 0.60 β-345617 −24.86 植物碎屑 高潮滩下部 8180 40 9010~9160 0.72 MNHW-MHW 1.07±0.6 −25.93 0.60 β-345618 −25.76 植物碎屑 高潮滩下部 8250 40 9030~9290 1 MNHW-MHW 1.07±0.6 −26.83 0.60 β-345619 −26.41 植物碎屑 高潮滩下部 8320 40 9190~9430 0.88 MNHW-MHW 1.07±0.6 −27.48 0.60 β-345620 −28.21 植物碎屑 盐沼 8240 60 9010~9320 0.96 MHW-MSHW 2.12±0.45 −30.33 0.45 β-345621 −28.74 植物碎屑 盐沼 8430 40 9300~9490 1 MHW-MSHW 2.12±0.45 −30.86 0.45 β-345622 −29.36 植物碎屑 盐沼 8330 40 9200~9430 0.92 MHW-MSHW 2.12±0.45 −31.48 0.45 β-345623 −32.33 植物碎屑 高潮滩下部 8670 40 9530~9680 1 MNHW-MHW 1.07±0.6 −33.40 0.60 β-345624 −33.47 植物碎屑 盐沼 8640 40 9520~9670 0.99 MHW-MSHW 2.12±0.45 −35.59 0.45 注:MHW—平均高潮位;MNHW—平均小潮高潮位;MSHW—平均大潮高潮位 -
Bard E, Hamelin B, Arnold M, et al. 1996. Deglacial sea−level record from Tahiti corals and the timing of global meltwater discharge[J]. Nature, 382: 241−244. doi: 10.1038/382241a0
Bird M I, Fifield L K, Teh T S, et al. 2007. An inflection in the rate of early mid−Holocene eustatic sea−level rise: A new sea−level curve from Singapore[J]. Estuarine Coastal & Shelf Science, 71(3/4): 523−536.
Bird M I, Fifield L K, Teh T S, et al. 2009. An inflection in the rate of early mid−Holocene eustatic sea−level rise: a new sea−level curve from Singapore[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 71: 523–536.
Bird M, Austin W E N, Wurster C M, et al. 2010. Punctuated eustatic sea−level rise in the early mid−Holocene[J]. Geology, 38: 803−806.
Chappell J, Polach H. 1991. Post−glacial sea−level rise from a coral record at Huon Peninsula, Papua New Guinea[J]. Nature, 349: 147−149. doi: 10.1038/349147a0
Chen Z, Stanley D J. 1998. Rising sea level on eastern China’s Yangtze Delta[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 14: 360−366.
Fairbanks R G. 1989. A 17000−year glacio−eustatic sea level record: influence of glacial melting rates on the Younger Dryas event and deep−ocean circulation[J]. Nature, 342: 637−642. doi: 10.1038/342637a0
Gehrels W R. 1999. Middle and Late Holocene sea−level changes in eastern Maine reconstructed from foraminiferal saltmarsh stratigraphy and AMS 14C dates on basal peat[J]. Quaternary Research, 52: 350−359. doi: 10.1006/qres.1999.2076
Hijma M P, Cohen K M. 2010. Timing and magnitude of the sea−level jump preluding the 8200 yr event[J]. Geology, 38(3): 275−278. doi: 10.1130/G30439.1
Liu J P, Milliman J D, Gao S. 2004. Holocene development of the Yeoow River’s sub−aqueous delta, North Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 209: 45−67. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2004.06.009
Saito Y. 1998. Sea levels of the last glacial in the East China Sea continental shel[J]. Quaternary Research, 37: 235−242. doi: 10.4116/jaqua.37.235
Shennan I. 1986. Flandrian sea−level changes in the Fenland II: Tendencies of sea−level movement, altitudinal changes, and local and regional factors[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 1: 155−179. doi: 10.1002/jqs.3390010205
Tamura T, Saito Y, Sieng S, et al. 2009. Initiation of the Mekong River delta at 8 ka: evidence from the sedimentary succession in the Cambodian lowland[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 28(3/4): 327−344. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2008.10.010
Törnqvist T E. 2004. Deciphering Holocene sea−level history on the U. S. Gulf Coast: A high−resolution record from the Mississippi Delta[J]. Geological Society of America, 116: 1026−1039. doi: 10.1130/B2525478.1
Wang Z H, Saito Y, Zhan Q, et al. 2018. Three - Di- mensional Evolution of the Yangtze River Mouth, China during the Holocene: Impacts of Sea Level, Climate and Human Activity[J]. Earth−Science Reviews, 185: 938−955.
Wang Z, Zhan Q, Long H, et al. 2013. Early to mid−Holocene rapid sea−level rise and coastal response on the southern Yangtze delta plain, Chinae[J]. Journal of Quaternary Scienc, 28(7): 659−672. doi: 10.1002/jqs.2662
Wang Z, Zhuang C, Saito Y, et al. 2012. Early mid−Holocene sea−level change and coastal environmental response of the southern Yangtze delta plain, China: implications for the rise of Neolithic culture[J]. Quaternary Science Review, 35: 51−62. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2012.01.005
Yang S, Milliman J, Li P, et al. 2011. 50000 dams later: erosion of the Yangtze River and its delta[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 75(1): 14−20.
Yu S Y, Berglund B E, Sandgren P. 2007. Evidence for a rapid sea−level rise 7600 yr ago[J]. Geology, 35: 891−894.
Zhan Q, Wang Z H, Xie Y, et al. 2012. Assessing C/N and Δ13C as Indicators of Holocene Sea Level and Freshwater Discharge Changes in the Subaqueous Yangtze Delta, China[J]. The Holocene, 22(6): 697−704. doi: 10.1177/0959683611423685
Zong Y. 2004. Mid−Holocene sea−level highstand along the Southeast Coast of Chinal[J]. Quaternary Internationa, 117: 55−67.
高晓琴, 王张华, 李琳, 等. 2012. 长江口现代潮滩表层沉积物磁性特征和铁硫化物在潮滩微相的分布[J]. 古地理学报, 14(5): 673−684. 国家海洋局. 2012. 2011年中国海平面公报[R]. 北京: 国家海洋局. 李琳, 王张华, 吴绪旭, 等. 2013. 长江口北支潮滩不同沉积微相有机地球化学元素分布[J]. 古地理学报, 15(1): 95–104. 水利部长江水利委员会. 2021. 长江泥沙公报[M]. 武汉: 长江出版社. 汪品先, 章纪军, 赵泉鸿, 等. 1988. 东海底质中的有孔虫和介形虫[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社. 战庆, 王张华. 2014. 利用盐沼泥炭重建长江三角洲北部全新世中期海平面[J]. 古地理学报, 16(4): 548−556. 赵亚楠, 王张华, 吴绪旭, 等. 2015. 长江口现代潮滩沉积物粒度特征及其在沉积相识别中的应用[J]. 古地理学报, 17(3): 405−416. -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 雷聪聪,高琪,王文宝,李卫星,马军,闫振军. 阿拉善地块北缘雅干中酸性火山岩LA-ICP-MS年龄、地球化学特征及其对区域构造演化的制约. 地质通报. 2025(Z1): 459-476 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: