Technical breakthrough and practice of ground penetrating radar in the exploration of Baiyangdian lake bottom stratum structure
-
摘要:
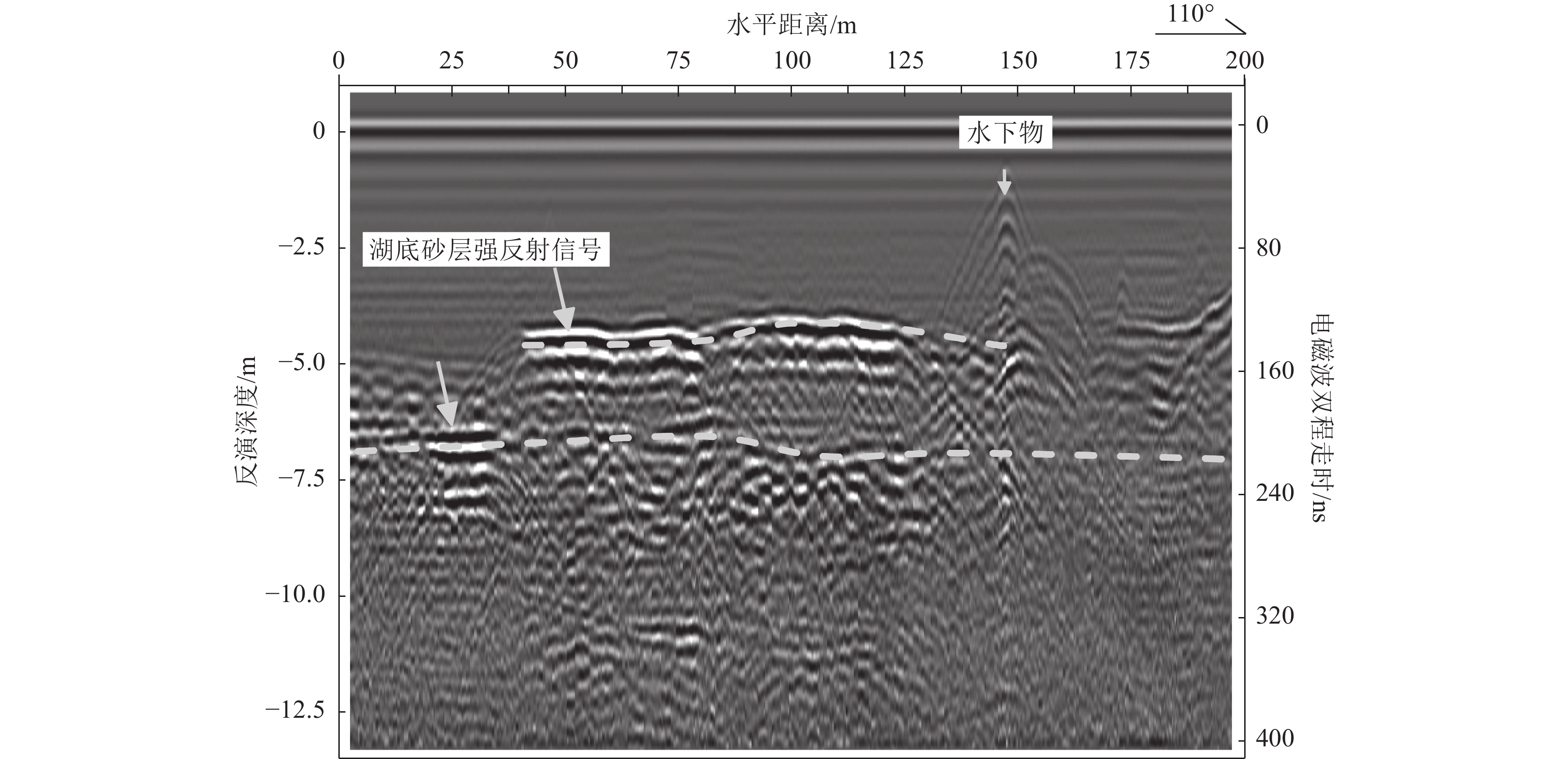
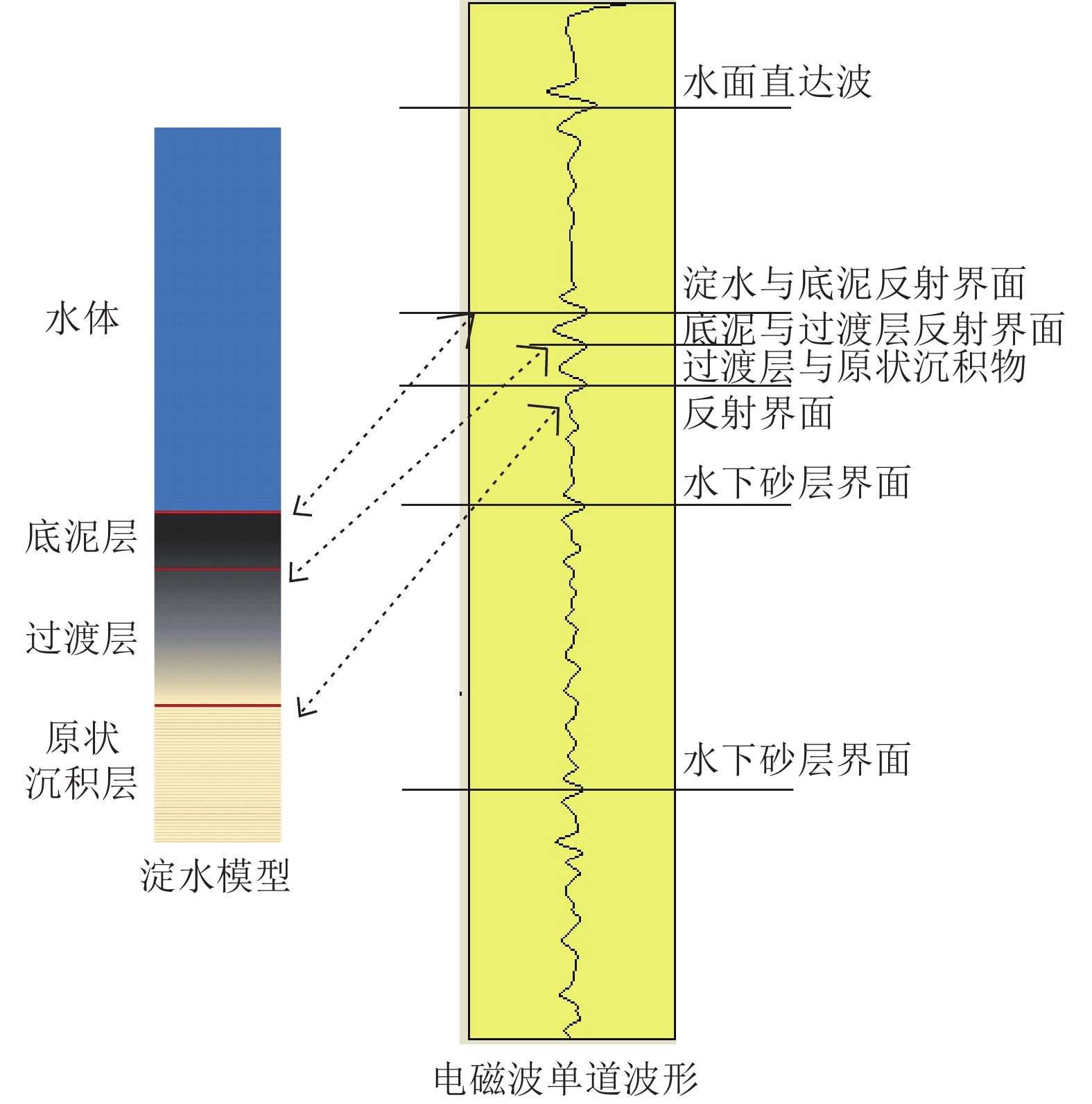
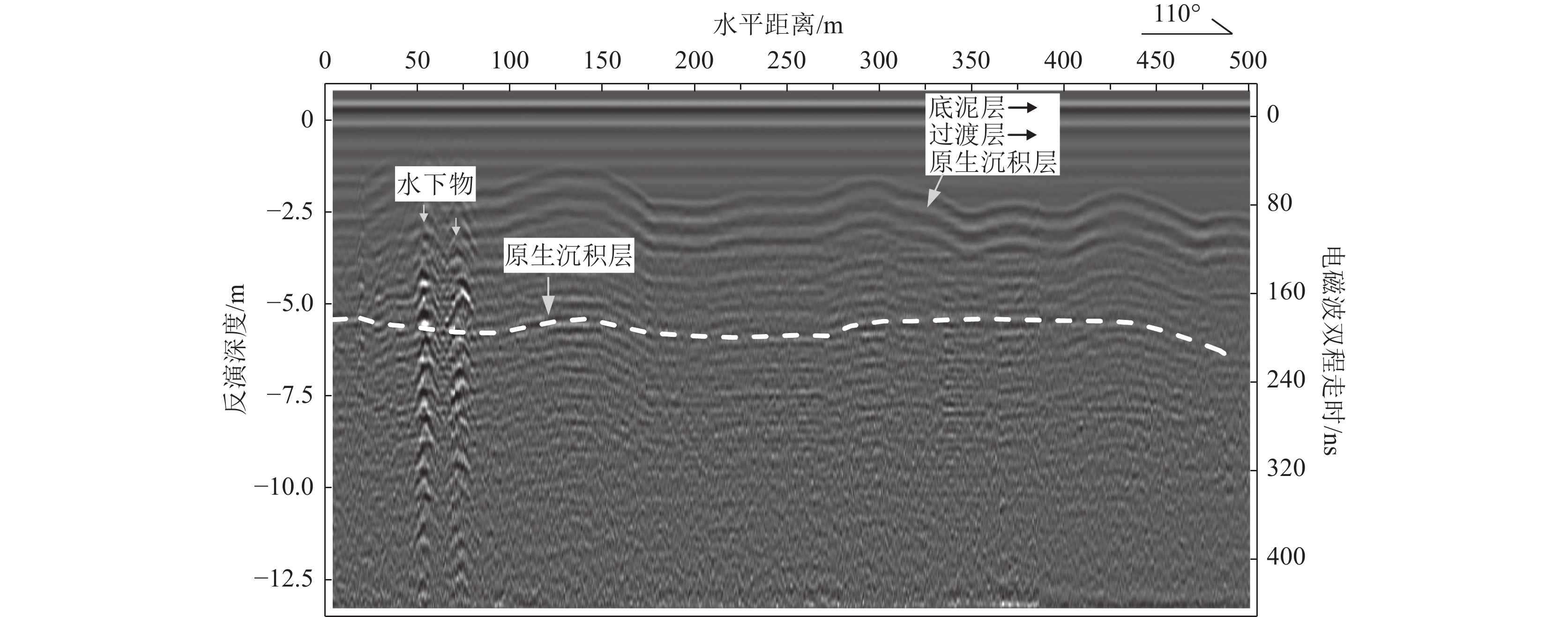
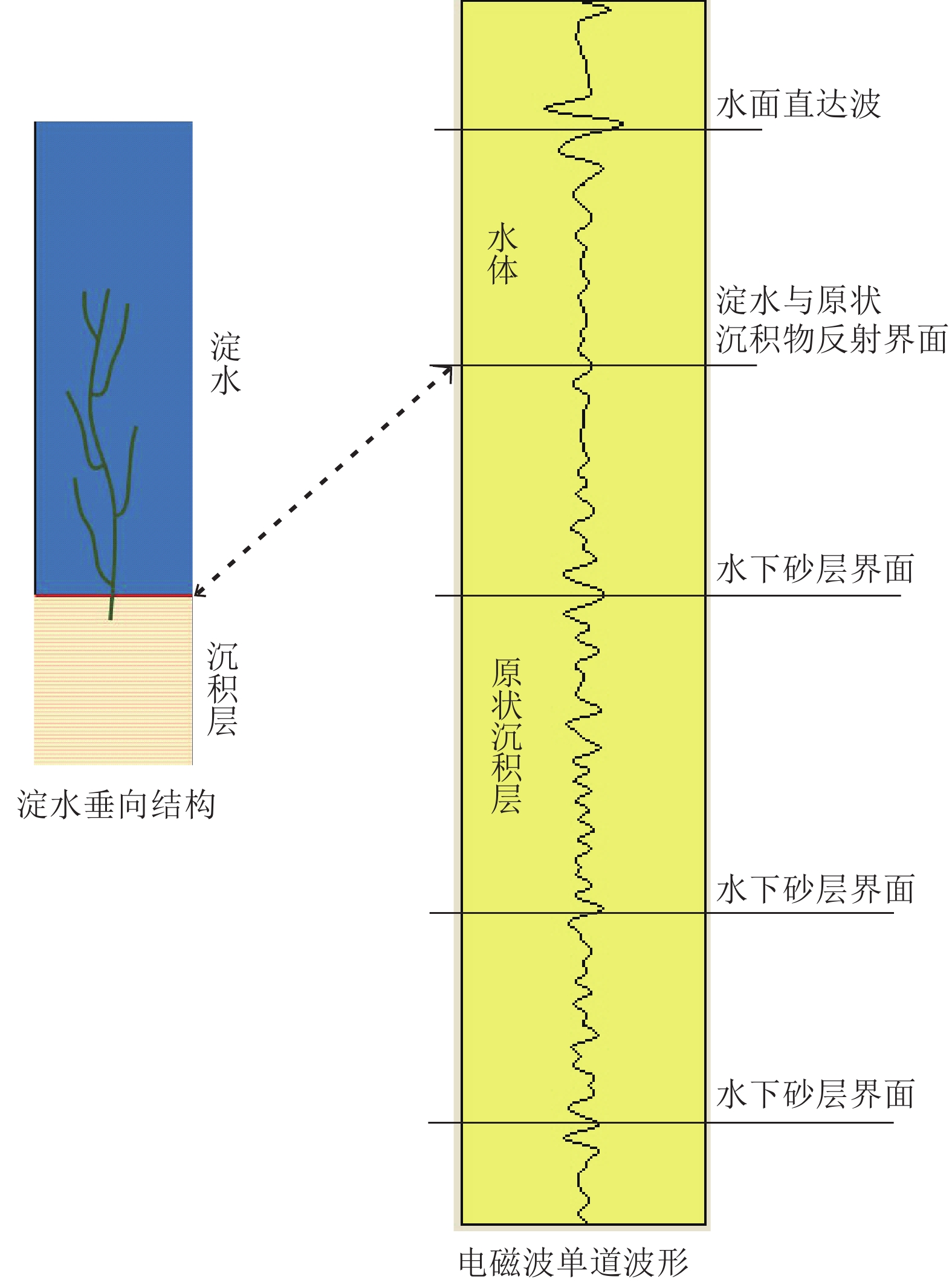
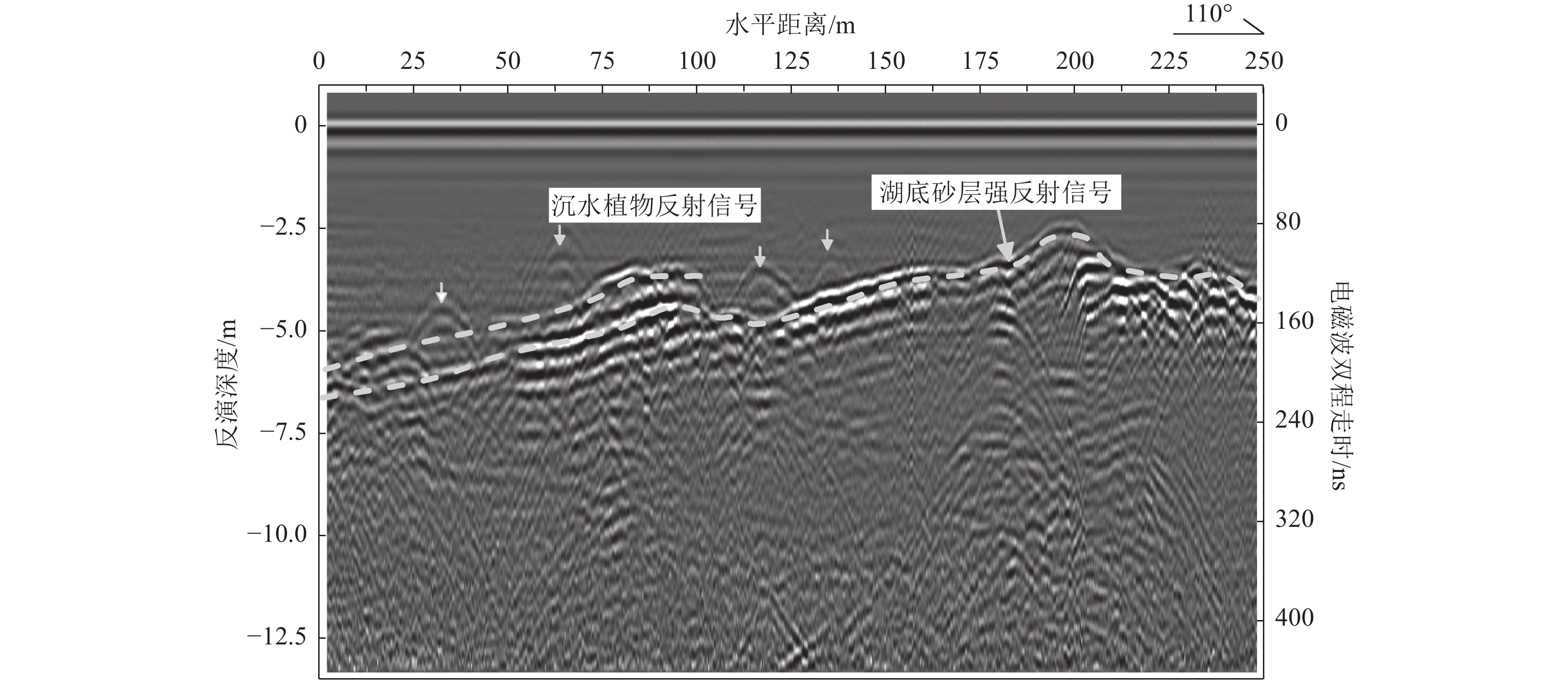
白洋淀湖底地层调查对于白洋淀生态地质调查、湖底生态清淤及湿地生态保护具有非常重要的现实意义。为系统探明白洋淀湖底地层结构,从区域尺度对湖底地层实现完整刻画,为钻探调查提供精确的靶区数据支撑,创新了探地雷达应用范围,采用船载方式,透过水体开展了湖底地层勘查。剖析白洋淀湖底结构探地雷达勘探技术难点,分析了含底泥和不含底泥2种情形下水上勘探电磁波的传播特征和湖底原生地层的地球物理响应条件,建立了淀水+淤泥层+湖底原生地层的湖底简化结构模型。通过对比国内外主流探地雷达系统不同硬件设备的勘探能力与适应条件,优选出双皮划艇搭载50 MHz低频组合天线的工作模式,结合适用于水下电磁波弱信号提取的数据处理技术,获得了白洋淀湖底15 m深度范围的地层结构数据。结果表明,此种工作模式适用于湖区水深小于5 m的水域,原生地层电磁波整体呈现弱反射特征,湖底15 m深度范围内存在2~3组砂层反射界面。淤泥层会大大削弱湖底原生地层的电磁波反射强度。存在厚砂层的水域,电磁波会形成强反射波组,砂层展布形态刻画清晰,砂层厚度变化在0~3 m之间。本项研究实现了湖底地层结构建模分析、天线勘探模式优选、数据处理过程优化等技术集成。该技术成果为白洋淀淀区地下水与地表水三维地质建模提供了基础依据,为湖底地层钻探勘查提供了靶区支撑,有力推动了白洋淀湿地水-陆一体化探测技术方法体系的构建。
Abstract:The investigation of the Baiyangdian lake bottom strata holds significant practical importance for the ecological geological survey, ecological silt removal, and wetland ecological protection of Baiyangdian. In order to systematically identify the stratigraphic structure of Baiyangdian lake at a regional scale and provide accurate target data support for drilling investigations, this paper introduces an innovative application range of ground penetrating radar (GPR) and conducts a ship-based stratigraphic survey through the water body. This study analyzes the technical challenges associated with exploring the lake bottom structure using GPR. It examines the characteristics of electromagnetic wave propagation and geophysical response conditions in two scenarios: with sediment and without sediment. A simplified model is established, consisting of diaster-water + silt layer + lake bottom primary formation. By comparing the exploration capability and adaptation conditions of different hardware equipment of mainstream ground penetrating radar systems at home and abroad, this paper optimizes the working mode by employing double kayaks equipped with a 50 MHz low-frequency combined antenna. Additionally, it combines suitable data processing technology for extracting weak signals from underwater electromagnetic waves. As a result, stratigraphic structure data at a depth of 15m are obtained for Baiyangdian lake. The findings indicate that this model is applicable to areas within the lake where water depth is less than 5 m; here, weak reflection characteristics are observed in electromagnetic waves emitted by primary formations at the lake bottom along with 2 ~ 3 groups of sand reflection interfaces at depths up to 15 m. The presence of silt layers significantly attenuates electromagnetic wave reflection intensity originating from primary strata at the lake bottom.
-
围限于东欧、西伯利亚、塔里木、华北等克拉通地块之间的中亚造山带是一个巨型造山拼贴体,主要由片岩-片麻岩地体、岩浆弧、弧相关盆地、增生杂岩、蛇绿混杂岩、海山等不同大地构造属性的地质体,经古亚洲洋长期俯冲和最终闭合,不断拼贴增生形成的 ( Şengör et al., 1993;肖文交等, 2019)。中亚造山带西起里海,东临西太平洋北侧,横跨哈萨克斯坦、乌兹别克斯坦、吉尔吉斯斯坦、中国、俄罗斯及蒙古国,东西长约5000 km,南北宽约1500 km,是全球规模最大的造山带之一。中亚造山带是典型的增生型造山带,在显生宙期间发生了强烈的壳幔相互作用和巨量的地壳增生,并形成了丰富的内生金属矿床,成为国际上探讨增生造山方式、大陆增生机制和增生成矿理论的核心区域 (李锦轶等, 1992; Jahn et al., 2000; 肖文交等, 2008; Xiao et al., 2015, 2018; 高俊等, 2019; Şengör et al., 2022)。自20世纪90年代起,中亚造山带成为国内外研究大陆增生的热点区域,一系列国内外研究项目的实施,使中亚造山带基础地质研究取得了重大进展(肖文交等, 2019)。
中亚造山带南缘,通常被称为天山-兴蒙造山带,记录了中亚岛弧与塔里木和华北克拉通的拼合过程,历来为造山带研究的焦点(李春昱等, 1984; Xiao et al., 2015; Song et al., 2024)。北山造山带位于中亚造山带南缘中段(图1),向西以星星峡断裂为界与天山造山带相连,向东与阿拉善和索伦构造带相连,北接南蒙古增生系统,向南以桥湾断裂为界与敦煌地块相连,横跨新疆东部、甘肃北部和内蒙西部。北山造山带构造演化关系到中亚造山带东西向构造衔接与对比,以及古亚洲洋构造域与南侧特提斯构造域的相互作用,其特殊的大地构造位置使其成为研究中亚造山带增生造山方式-时限及中国西北大地构造格局的关键。近年来,北山造山带构造演化逐渐成为学界重点关注的对象,尤其在蛇绿岩时代与构造背景、变质基底时代及构造属性、岩浆作用性质与时代、构造变形特征与时代等方面取得了许多新进展(Xiao et al., 2010; Qu et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2011, 2012a, b; Ao et al., 2012; Mao et al., 2012; Song et al., 2013a; Tian et al., 2013; 李舢, 2013; Liu et al., 2015; 贺振宇等, 2015; Zong et al., 2017; He et al., 2018b; Shi et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2018a, 2024b; Zheng et al., 2018; 宋东方等, 2018; Yuan et al., 2019; 辛后田等, 2020; 王国强等, 2021)。本文试图以岩浆活动期次和蛇绿混杂岩时空分布为主线,总结北山造山带近年来在基础地质方面的研究进展,并对其增生造山过程进行简要探讨。
![]() 图 1 北山造山带大地构造位置及构造单元划分简图(据Song et al., 2024修改)Figure 1. Tectonic location and sketch map of Beishan orogenic belt showing division of tectonic units
图 1 北山造山带大地构造位置及构造单元划分简图(据Song et al., 2024修改)Figure 1. Tectonic location and sketch map of Beishan orogenic belt showing division of tectonic units1. 构造单元基本特征
北山造山带分布有多条近东西向平行展布的韧性剪切带和蛇绿混杂岩带,自北向南分别为红石山-百合山蛇绿混杂岩、芨芨台子-石板井蛇绿混杂岩、红柳河-牛圈子-洗肠井蛇绿混杂岩、柳园-后红泉蛇绿混杂岩。根据蛇绿混杂岩的分布及岩性-构造特征,北山造山带可以划分为多个构造单元,自北至南分别为雀儿山岛弧、黑鹰山岛弧、马鬃山岛弧、双鹰山-花牛山岛弧和石板山岛弧( Xiao et al., 2010; Song et al., 2013a)(图1)。下面对各构造单元的基本特征进行简要介绍。
1.1 雀儿山岛弧
雀儿山岛弧位于红石山-百合山蛇绿混杂岩北侧,是北山造山带最北部的构造单元。主要由奥陶纪—石炭纪火山岩、侵入岩,以及火山碎屑岩、碳酸盐岩等组成,普遍经历了强烈的构造变形和中低级变质作用。奥陶纪咸水湖组火山岩为中酸性火山岩夹碎屑岩组合,主要岩性包括安山玄武岩、安山岩、英安岩、流纹岩、流纹质凝灰岩、沉凝灰岩、含砾岩屑长石砂岩等,流纹岩锆石U−Pb定年获得了462 ± 3 Ma的年龄(陈智斌等, 2020),指示中奥陶世岩浆作用。在中蒙边境大鱼山西侧火山-沉积岩地层中,采集到志留纪珊瑚、腹足、腕足等化石,证实红石山以北存在志留纪地层(王方成等, 2004)。泥盆纪雀儿山群为中酸性火山岩和火山碎屑岩,包括安山岩、英安岩、安山质晶屑凝灰岩、安山质火山角砾岩及安山质凝灰岩夹粉砂岩和灰岩。岩石地球化学分析显示这些火山岩属于低钾拉斑-钙碱性系列,亏损Nb、Ta、P、Ti等高场强元素,推测形成于洋壳俯冲的岛弧环境(任邦方等, 2019)。内蒙古哈珠东山雀儿山群火山岩获得锆石U−Pb年龄为387 ± 2 Ma,锆石εHf(t)值为+4.4~+15.0,指示幔源物质的贡献(任邦方等, 2019)。石炭纪地层包括绿条山组和白山组。早石炭世绿条山组由砂质板岩、硅质板岩、硅质岩、玄武岩和蚀变安山岩组成;晚石炭世白山组主要为一套中酸性熔岩夹少量火山碎屑岩,包括辉石安山岩、玄武安山岩、安山岩夹安山质火山碎屑岩及少量英安岩、流纹岩、灰岩、凝灰质砂岩等(卫彦升等, 2020)。雀儿山岛弧侵入岩包括中志留世石英闪长岩和早泥盆世花岗闪长岩、石英闪长岩、英云闪长岩等。中志留世石英闪长岩分布于百合山以北的碎石山和黄戈壁一带,其锆石U−Pb年龄为425 ± 4 Ma (辛后田等, 2020)。
1.2 红石山-百合山蛇绿混杂岩
红石山-百合山蛇绿岩带沿北山造山带北带红石山深大断裂断续出露,由甘肃红石山地区向东延伸至内蒙古西部百合山、蓬勃山、额勒根一带,两侧均以逆冲断层与相邻地质体分隔。在红石山地区,蛇绿混杂岩由不同成因的构造岩片构成,包括变质橄榄岩、堆晶辉长岩、玄武岩、硅质岩、复理石等,整体呈透镜状近东西向展布,与泥盆系、石炭系呈断层接触,其中玄武岩具有N-MORB地球化学属性(黄增保等, 2006)。红石山蛇绿混杂岩中的辉长岩LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb年龄为347 ± 3 Ma,表明存在早石炭世洋盆扩张活动(王国强等, 2014)。百合山蛇绿岩主要由变质橄榄岩、辉石橄榄岩、堆晶辉长岩、辉长岩、玄武岩、斜长花岗岩、硅质岩等组成,它们呈构造岩片逆冲叠置,整体仰冲于石炭纪绿条山组浊积岩之上。发育“岩块”-“基质”混杂结构,基质主要由蛇纹岩、砂板岩和绿泥片岩组成,岩块为超镁铁质岩、镁铁质岩、硅质岩、碳酸盐岩、火山岩等 (牛文超等, 2019)。岩石地球化学分析显示,辉长岩来源于受俯冲流体交代的亏损地幔,辉长岩LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb定年结果为345 ± 2 Ma,具有亏损的Sr−Nd同位素组成,(87Sr/86Sr)i值为0.70418~0.70711,εNd(t)值为+4.61~+7.28 (牛文超等, 2020)。斜长花岗岩锆石U−Pb定年获得了4组年龄加权平均值分别为433 ± 5 Ma、393 ± 3 Ma、342 ± 4 Ma、297 ± 2 Ma, 其中433 ± 5 Ma和393 ± 3 Ma两组年龄被解释为捕获的早古生代地层锆石年龄,342 ± 4 Ma年龄与蛇绿岩中的辉长岩年龄相似,代表了早期洋壳的形成年龄,而最年轻的一组年龄297 ± 2 Ma代表了斜长花岗岩的形成年龄(牛文超等, 2019)。额勒根蛇绿混杂岩是最近通过地质填图新发现的一套由玄武岩、斜长花岗岩、硅质岩和砂板岩构成的构造混杂岩,呈北西西向带状展布,宽2.5~8 km,延伸约25 km (张正平等, 2020)。玄武岩和斜长花岗岩均显示俯冲流体的加入,具有岛弧地球化学属性(张正平等, 2020)。根据岩浆岩的地球化学特征,多数学者认为,红石山-百合山蛇绿混杂岩为形成于俯冲带之上的SSZ型蛇绿岩,代表了弧后裂解的有限洋盆(牛文超等, 2019, 2020; 张正平等, 2020; 王国强等, 2021)。
1.3 黑鹰山-旱山岛弧
黑鹰山-旱山岛弧位于红石山-百合山蛇绿混杂岩和芨芨台子-石板井蛇绿混杂岩之间,主要由石炭系白山组火山岩和同期侵入岩、片麻岩构成。白山组火山岩主要由安山岩、英安岩、流纹岩及火山碎屑岩组成,总体为一套岛弧型钙碱性火山岩,同期侵入岩具有陆缘弧岩浆岩特征,岩浆岩自北向南具有从钙碱性岩浆到高钾钙碱性岩浆演化的趋势(贾元琴等, 2016; 任云伟等, 2019)。锆石U−Pb定年获得安山岩和流纹岩的形成时代为326 ± 1~314 ± 3 Ma (贾元琴等, 2016; 任云伟等, 2019)。辛后田等(2020)在大红山、哈珠、标山、风雷山、千条沟等地区白山组火山岩中获得了大量320~298 Ma的锆石U−Pb年龄,其中中基性火山活动时限为327~315 Ma,英安岩-流纹岩火山活动时限为320~298 Ma(辛后田等, 2020)。锆石年代学结果表明,白山组火山活动从早石炭世晚期一直持续到晚石炭世末,且以中酸性火山活动最强烈。此外,在哈珠地区报道了晚石炭世(306 ± 1 Ma)二长花岗岩、早二叠世(299 ± 2 Ma)花岗闪长岩和早二叠世(289 ± 1 Ma)钾长花岗岩,具有准铝质中钾钙碱性特征。花岗闪长岩和钾长花岗岩的锆石εHf(t)值为+9.6~+15.9和+4.7~+12.9,显示岩浆源区为新生地壳(李敏等, 2019)。此外,在旱山等地区,存在深变质的片麻岩,通常被认为是早前寒武纪的结晶基底(左国朝等, 1990),然而锆石微区U−Pb定年揭示,大多数片麻岩的形成时代为古生代(457~450 Ma),并不是早前寒武纪( Song et al., 2013b; Ao et al., 2016)。在明水以东50 km,出露大量片岩和片麻岩,包括黑云母斜长片麻岩、眼球状片麻岩、花岗片麻岩等,LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb定年揭示其形成时代为499~448 Ma (Song et al., 2013a)。这些新的年代学资料表明,片麻岩地体属于古生代岩浆弧的一部分,而不代表古老的陆块基底。
1.4 石板井-小黄山蛇绿混杂岩
石板井-小黄山断裂为倾向北北东的高角度逆断层(孟令顺等, 1995)。沿该断裂带在芨芨台子、石板井、小黄山等地区出露有蛇绿混杂岩,基于此,该构造带长期以来被认为是北山造山带的一级大地构造边界,代表了北侧明水-旱山微陆块(哈萨克斯坦板块)与南侧塔里木板块的缝合带(左国朝等, 1990; Zhang et al., 2012b)。芨芨台子蛇绿混杂岩由变质橄榄岩、堆晶辉长岩和基性火山岩组成,整体以一系列由北向南的逆冲岩片形式产出,岩片间夹硅质条带大理岩、石英片岩等(李向民等, 2012)。前人根据蛇绿岩外围地层为震旦系或奥陶系,认为芨芨台子蛇绿岩形成于早古生代(杨合群等, 2010)。李向民等(2012)对蛇绿岩中的辉长岩进行了LA−ICP−MS微区锆石U−Pb定年,获得了321 ± 6 Ma的年龄,认为该蛇绿岩形成于早石炭世。石板井蛇绿岩由蛇纹石化超基性岩、玄武岩、辉长岩、硅质岩、结晶灰岩等组成,发育“岩块-基质”混杂结构,整体构成一系列由南向北逆冲的构造岩片,就位于奥陶纪—志留纪地层中。此外,变质作用研究揭示,该蛇绿岩经历了热变质作用叠加中高压变质作用(周国庆等, 2001)。然而,该蛇绿混杂岩的形成时代和变质作用时代仍然没有得到很好限定。小黄山蛇绿岩由蛇纹岩、橄榄岩、辉石岩、辉长岩、辉绿岩、玄武岩等组成,超基性岩呈构造透镜体或串珠状沿小黄山断裂近东西向展布,蛇绿岩经历了强烈的变质变形,发育断层、褶皱、S-C组构、片理化等现象及“岩块-基质”构造混杂结构(宋泰忠等, 2008; Ao et al., 2016)。前人锆石U−Pb定年分别获得辉长岩和玄武岩年龄为345 ± 14 Ma和335 ± 4 Ma (Zheng et al., 2013),认为该蛇绿岩形成于早石炭世。最近对小黄山蛇绿岩中辉长岩SHRIMP锆石U−Pb定年获得了516 ± 8 Ma的年龄,属于早寒武世 (Shi et al., 2018)。玄武岩和辉长岩地球化学分析显示具有弧岩浆岩特征,其岩浆源区为受俯冲流体交代的地幔,认为小黄山蛇绿岩为形成于俯冲带之上的SSZ型蛇绿岩(Zheng et al., 2013; Shi et al., 2018),与俯冲板块后撤有关(Ao et al., 2016)。
1.5 马鬃山岛弧
马鬃山岛弧北以石板井-小黄山深大断裂为界,南以红柳河-牛圈子-洗肠井蛇绿混杂岩带为界,主要由片岩-片麻岩、公婆泉群火山岩、中酸性侵入岩等组成。其中,片岩-片麻岩包括云母石英片岩、绿泥石英片岩、斜长角闪岩、黑云斜长片麻岩、花岗片麻岩等,主要出露于双井子、勒巴泉和草呼勒哈德地区,其形成时代存在很大的争议。1∶20万地质图根据获得的化石证据,把这些变质杂岩填制为志留纪勒巴泉群,并划分为4个岩组(甘肃省地质局第二区域地质测量队, 1969)。后来的一些研究根据斜长角闪岩全岩Sm−Nd等时线定年和锆石U−Pb上交点年龄,认为这些变质杂岩原岩形成于新太古代—古元古代,并认为存在早前寒武纪结晶基底,称为马鬃山微陆块或马鬃山隆起(魏学平等, 1999, 2000)。详细的野外地质解析表明,这些变质杂岩普遍经历了强烈构造变形,发育透入性面理、同斜褶皱、不对称褶皱、S-C组构、斜长石旋转碎斑、拉伸线理等,表明这些变质杂岩为经历强烈剪切变形的构造岩(宋东方等, 2018)。对这些变质杂岩开展LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb定年,获得527~312 Ma的原岩年龄(Song et al., 2015),表明这些变质杂岩的原岩实质上为古生代岩浆岩,并不代表古老的结晶基底。在勒巴泉地区,笔者对变质杂岩进行了大比例尺的岩性-构造地质填图,识别出了变质碎屑岩、变质基性岩、变质硅质岩、大理岩等,整体形成了“岩块-基质”构造混杂结构,其中变质硅质岩呈薄层状产出,发育尖棱褶皱和紧闭褶皱,变质碎屑岩中发育大量无根钩状褶皱(图2)。因此,认为一部分变质杂岩实质上为形成于弧前的增生杂岩(Song et al., 2014)。
公婆泉群火山岩主要由流纹岩、安山岩、安山玢岩、玄武安山岩、火山角砾岩等组成。地球化学特征显示,安山岩和玄武安山岩为钙碱性系列岩石,具有明显的Nb、Ta亏损和Th、Pb、Sr富集,为形成于俯冲带的岛弧岩浆作用(Song et al., 2015)。对火山-沉积岩进行碎屑锆石U−Pb定年,获得了441 Ma、925 Ma、2470 Ma的年龄峰,指示早志留世火山作用(Song et al., 2015)。除火山岩外,马鬃山岛弧分布有大量的侵入体,包括寒武纪—早奥陶世(527~470 Ma)辉长岩-闪长岩、中—晚奥陶世(460~440 Ma)英云闪长岩-花岗闪长岩-二长花岗岩、晚志留世(430~420 Ma)钾长花岗岩-二长花岗岩、泥盆纪—早石炭世(405~365 Ma)花岗岩-辉长岩等(郑荣国等, 2012b; Song et al., 2015; Yu et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2017;辛后田等, 2020)。此外,在马鬃山岛弧最东端的东七一山地区报道了早石炭世(356 ± 2 Ma)埃达克质侵入体(Zhang et al., 2012b);在马鬃山岛弧西段的破城山地区,Tian et al.(2017)获得钙碱性火山岩和花岗闪长岩年龄分别为320 ± 3 Ma和309 ± 4 Ma,指示该岛弧岩浆作用持续到晚石炭世。
1.6 红柳河-牛圈子-洗肠井蛇绿混杂岩
该蛇绿混杂岩是北山造山带中延伸最长、出露宽度最大的蛇绿岩带,从新甘交界处的红柳河经甘肃玉石山、火石山、牛圈子,向东延伸至内蒙古西部月牙山、洗肠井地区。该蛇绿岩各岩性组分保存较完整,是北山地区研究最充分的蛇绿混杂岩。红柳河蛇绿混杂岩由基性—超基性杂岩及火山-沉积岩基质构成,前者呈透镜状展布,包括蛇纹石化橄榄岩、辉长岩、辉绿岩、玄武岩、斜长岩等,后者包括凝灰岩、粉砂岩、砂岩、硅质岩、结晶灰岩等(周国庆, 1988;于福生等, 2006)。该蛇绿岩中保存了大量的伸展构造,如堆晶辉长岩中发育丰富的辉长质糜棱面理、伸展褶辟理、小型韧性低角度正断层、韧-脆性共轭正断层、脆性正断层等伸展构造变形(郭召杰等, 2006)。前人对红柳河蛇绿岩开展了多种方法定年,获得辉长岩SHRIMP锆石U−Pb年龄为528 ± 3 Ma(Shi et al., 2018),伟晶辉长岩年龄为520 ± 6 Ma(Cleven et al., 2015),堆晶辉长岩年龄为516 ± 7 Ma (张元元等, 2008),获得辉长质糜棱岩角闪石和黑云母40Ar−39Ar坪年龄为496~295 Ma (郭召杰等, 2006)。此外,在红柳河二叠系中发现了块状和枕状玄武岩,40Ar−39Ar定年确定玄武岩的形成时代为300~280 Ma (潘金花等, 2008)。根据红柳河蛇绿岩中辉长岩和玄武岩具有岛弧岩浆岩的地球化学特征,该蛇绿岩被认为是形成于俯冲带之上的SSZ型蛇绿岩(Cleven et al., 2015; Shi et al., 2018)。
王立社等(2007)在甘肃北山火石山地区报道了新发现的蛇绿混杂岩,该混杂岩由蛇绿岩岩块和混杂岩基质组成。蛇绿岩岩块组成为纯橄岩、辉石橄榄岩、辉石岩、辉长岩、玄武岩、硅质岩等,基质为中—上志留统公婆泉群凝灰质砂岩夹碳酸盐岩和少量安山岩,发生了强烈构造变形。地球化学分析表明,辉长岩为钙碱性系列岩石,亏损高场强元素(Nb、Ta),并富集大离子亲石元素(Rb、Ba、Pb),轻稀土元素相对重稀土元素富集,具有岛弧岩浆岩地球化学属性,可能为形成于俯冲带之上的SSZ型蛇绿岩(Tian et al., 2014)。火石山蛇绿岩中辉长岩的LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb年龄为411 ± 4 Ma,为早泥盆世的产物(Tian et al., 2014)。牛圈子蛇绿岩出露于马鬃山煤窑北2 km处,主要由超镁铁质岩、辉长岩、堆晶辉长岩、斜长花岗岩、辉绿岩、枕状玄武岩及硅质岩组成,呈构造岩片向南逆冲(任秉琛等, 2001)。前人获得辉长岩LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb年龄为447 ± 4 Ma(武鹏等, 2012)和435 ± 2 Ma(Tian et al., 2014),斜长花岗岩U−Pb年龄为444 ± 2 Ma(Tian et al., 2014)。最近的锆石U−Pb定年获得辉长岩年龄为434 ± 3 Ma和354 ± 3 Ma,斜长花岗岩年龄为449 ± 2 Ma和430 ± 2 Ma,辉绿岩年龄为433 ± 3 Ma(Wang et al., 2017a)。地球化学分析显示,辉长岩、辉绿岩和斜长花岗岩形成于大洋中脊环境(Wang et al., 2017a)。
月牙山-洗肠井蛇绿混杂岩包括超镁铁质岩、辉长岩、辉绿岩、斜长花岗岩、枕状/块状玄武岩和深海硅质岩。超镁铁质岩主要为方辉橄榄岩,普遍发生蛇纹石化和强烈片理化,可见堆晶结构的橄榄辉石岩和辉长岩,辉长岩发生糜棱岩化、片理化(杨合群等, 2010; Ao et al., 2012; 郑荣国等, 2012a)。蛇绿岩组分与灰岩、绿泥石片岩、砂岩、板岩等发生构造混杂,形成“岩块-基质”结构,总体构成由北向南的逆冲构造(Ao et al., 2012)。蛇绿岩中的玄武岩和辉长岩表现为相对富集大离子亲石元素、亏损高场强元素,并具有不同程度的Nb、Ta负异常,与典型的岛弧火山岩地球化学特征相似,但另一方面又表现出与正常大洋中脊玄武岩相似的稀土元素配分模式,因此兼具岛弧火山岩和洋中脊玄武岩的成分特征(Ao et al., 2012; 郑荣国等, 2012a; Shi et al., 2018)。辉长岩的εNd(t)值介于+6.1~+8.2之间,(87Sr/86Sr)i值介于0.704633~0.705055之间,表明基性岩源区为亏损地幔(郑荣国等, 2012a; Shi et al., 2018)。对蛇绿岩中的岩浆岩进行锆石U−Pb定年,得出了较一致的早寒武世年龄,洗肠井蛇绿岩中斜长花岗岩的SHRIMP U−Pb年龄和SIMS U−Pb年龄分别为536 ± 7 Ma(侯青叶等, 2012)和533 ± 2 Ma(Ao et al., 2012),辉长岩的SHRIMP年龄为535 ± 6 Ma(Shi et al., 2018);月牙山蛇绿岩中辉长岩和斜长花岗岩的LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb年龄分别为527 ± 1 Ma和530 ± 1 Ma(胡新茁等, 2015)。
1.7 双鹰山-花牛山岛弧
双鹰山-花牛山构造带位于红柳河-牛圈子-洗肠井蛇绿混杂岩与柳园-后红泉蛇绿混杂岩之间。该构造带北段从西端玉石山经双鹰山−东端望旭山出露了一套变质沉积岩地层,前人划分为长城系古硐井群、蓟县系平头山组、青白口系大豁落山组及震旦系洗肠井群(甘肃省地质调查院, 2001),这些地层主要以逆冲断层的形式位于较年轻的沉积地层和侵入体之上( Zheng et al., 1996;Song et al., 2013c)。主要岩性为大理岩和结晶灰岩,夹石英片岩、石英岩、变质砂岩、板岩、千枚岩等。对这些变质沉积进行碎屑锆石U−Pb定年发现其主要的年龄峰值为约2500 Ma、约1760 Ma、约1450 Ma,最年轻的锆石年龄为中元古代晚期、新元古代晚期或古生代,表明它们可能是不同时代沉积的产物( Song et al., 2013c;余吉远等, 2018)。最新的碎屑颗粒和重矿物统计、全岩主量、微量元素地球化学分析、碎屑锆石U−Pb年代学和Hf同位素测试表明,古硐井群含有大量岩屑和长石碎屑,碎屑锆石年龄高度集中于470 Ma附近,且该区间锆石εHf(t)值多为正值,最年轻碎屑锆石年龄为444 ± 13 Ma,从而推测古硐井群可能形成于古生代的增生楔楔顶盆地,而不代表前寒武纪的稳定沉积盖层(霍宁等, 2022)。花牛山岛弧主要由奥陶纪—志留纪花牛山群火山-沉积岩、泥盆纪墩墩山组火山-沉积岩及相关侵入体构成。花牛山群包括蚀变玄武岩、安山玄武岩、英安岩、流纹岩、石英砂岩、长石砂岩、粉砂质泥岩、大理岩、板岩等,均发生了较低级的变质作用。变质英安岩LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb定年获得了晚奥陶世年龄455 ± 1 Ma,地球化学分析显示火山岩具有明显的弧岩浆岩特征,形成于活动大陆边缘(谢建强等, 2018)。在该岛弧东段的墩墩山地区,流纹岩和正长斑岩的形成时代分别为368 ± 3 Ma和371 ± 1 Ma,并表现出岛弧岩浆岩的地球化学特征(Guo et al., 2014, 2017)。侵入岩包括早泥盆世(415 ± 3 Ma)A型花岗岩(李舢等, 2009)、早泥盆世(397 ± 3 Ma)高钾钙碱性钾长花岗岩(李舢等, 2011)、晚泥盆世晚期(363 ± 1 Ma)钙碱性I型花岗岩、中三叠世(232 ± 1 Ma)A型花岗岩等(杨婧, 2019)。
1.8 柳园-后红泉蛇绿混杂岩
柳园-后红泉蛇绿混杂岩是北山造山带最南部的一条蛇绿岩带,从柳园镇地区向东经帐房山断续延伸至后红泉地区,大致沿柳园-大奇山-帐房山断裂带两侧断续分布约300 km(王国强等, 2021)。Mao et al. (2012)对柳园蛇绿混杂岩进行了详细的野外解析、岩石地球化学和年代学分析,该蛇绿岩混杂岩主要由超基性岩、辉长岩、块状和枕状玄武岩、硅质岩、凝灰岩等组成,这些不同岩性单元整体构成了由南西向北东方向的逆冲岩片。玄武岩具有较平坦的稀土元素配分型式,Sr−Nd同位素指示来自亏损地幔源区,微量元素显示受到俯冲流体的交代作用,因此柳园蛇绿岩被认为是形成于俯冲带之上的SSZ型蛇绿岩,并形成于弧前环境(Mao et al., 2012)。对与蛇绿岩混杂岩呈断层接触的二叠纪浊积岩进行全岩地球化学与物源分析,揭示它们为沉积于弧前盆地的海相碎屑岩(Guo et al., 2012)。蛇绿岩中的辉长岩LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb定年获得了早二叠世(286 ± 2 Ma)的年龄(Mao et al., 2012)。对于柳园超基性岩—基性岩的成因,也存在不同认识,除蛇绿混杂岩外,也有学者认为它们形成于大陆裂谷环境,是造山后板内裂解的产物( Zhang et al., 2011;Wang et al., 2017b)。对辉铜山和帐房山地区蛇绿岩中的辉长岩进行LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb定年,分别获得了晚奥陶世(446 ± 3 Ma)和晚泥盆世(363 ± 4 Ma)的年龄(余吉远等, 2012)。后红泉蛇绿混杂岩是最近通过野外地质填图识别出来的,主要由辉长岩、块状/枕状玄武岩、硅质岩等组成,它们呈“岩块”被砂岩基质包裹,其中玄武岩具有N-MORB或SSZ地球化学特征(Mao et al., 2023)。
1.9 石板山陆缘弧
石板山陆缘弧位于柳园-后红泉蛇绿混杂岩南侧,是北山造山带最南部的构造单元,以桥湾-小西弓韧性剪切带(或称疏勒河断裂)与南侧敦煌地块(或敦煌造山带)相隔。石板山弧主要由片岩-片麻岩、石炭纪—二叠纪火山-沉积岩及相关的侵入体组成。片岩-片麻岩地体由石英岩、大理岩、黑云石英片岩、角闪片岩、黑云斜长片麻岩、斜长角闪片麻岩、花岗片麻岩、混合岩化片麻岩等组成,主要分布于白墩子、石板墩、桥湾北、梧桐井等地区。对于该变质杂岩的形成时代和大地构造属性,目前存在较大的争议。前人称该变质杂岩为“北山杂岩”或“敦煌岩群”,并通过变质变形特征和岩性的区域对比,认为该变质杂岩形成于新太古代—古元古代,代表了北山造山带最老的早前寒武纪微陆块结晶基底(左国朝等, 1990)。近年来,在这些被称为“北山杂岩”的变质杂岩中陆续报道了约1400 Ma和930~870 Ma的花岗质片麻岩和花岗闪长岩(Liu et al., 2015; Yuan et al., 2015, 2019;贺振宇等, 2015;Wang et al., 2024b),认为北山造山带南部存在中—新元古代的微陆块。本次对这些变质杂岩进行了野外解析和年代学研究,发现它们经历了强烈的构造变形,锆石U−Pb定年显示,白墩子和石板墩正片麻岩的原岩形成于石炭纪—二叠纪(304~294 Ma),桥湾北变粒岩显示了二叠纪的单峰年龄(286~276 Ma),梧桐井北云母石英片岩最年轻的年龄峰值为428~427 Ma;锆石Hf同位素显示,奥陶纪—泥盆纪和石炭纪—二叠纪存在显著的地壳增生(Song et al., 2016)。Zheng et al. (2018)对穿山驯地区的变质杂岩进行了锆石U−Pb年代学研究,发现有的变质沉积岩样品显示古—中元古代的年龄峰值,有的样品则具有中二叠世的年龄峰,角闪岩显示二叠纪和三叠纪的年龄,从而认为北山杂岩可能源自哥伦比亚超大陆的增生边缘,在二叠纪—三叠纪经历了强烈增生造山事件,并不代表裂离自敦煌地块或塔里木地块的微陆块。此外,石板山构造带出露大量的花岗岩、花岗闪长岩、闪长岩、辉长岩、基性岩墙等侵入体,它们的形成时代为430 Ma(贺振宇等, 2014)及305~260 Ma(张文等, 2011; 冯继承等, 2012; Zheng et al., 2020),其中早古生代糜棱岩化花岗岩具有富集的Hf同位素组成(贺振宇等, 2014),二叠纪侵入体具有较亏损的Hf同位素组成,显示有更多地幔物质的加入(张文等, 2011; Zheng et al., 2020)。沙枣园复式岩体包括花岗闪长岩、石英闪长岩、二长花岗岩、正长花岗岩等,侵入时代为晚二叠世—早三叠世(252~246 Ma;赵宏刚等, 2020)。
2. 岩浆作用时空分布
2.1 前寒武纪岩浆作用
“北山杂岩”长期以来被认为是北山造山带最老的地质记录,代表了微陆块的早前寒武纪结晶基底,形成时代为新太古代—古元古代。多年来,不同的学者对北山变质杂岩的形成时代和大地构造属性进行了研究,获得了一些高精度年代学研究新进展。现有年代学资料显示,北山造山带最老的岩石为约1.4 Ga的花岗质片麻岩,分布于北山南带的旧井和穿山驯地区。贺振宇等(2015)在旧井地区测得一个黑云斜长片麻岩的LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb年龄为1408 ± 4 Ma,解释为原岩形成年龄,锆石具有正且高的εHf(t)值(+4.1~+9.9),Hf模式年龄(1.50~1.72 Ga)与锆石结晶年龄接近。Yuan et al. (2019)获得5个片麻岩或花岗闪长岩的锆石U−Pb年龄为1450~1401 Ma,并在晚古生代花岗岩中获得约1.4 Ga的继承锆石。Wang et al. (2024b)在穿山驯北西约14 km的北山杂岩中获得糜棱岩化花岗岩和眼球状花岗岩的锆石U−Pb年龄分别为1469 ± 14和1448 ± 13 Ma,被解释为岩体的结晶年龄,其锆石εHf(t)值分别为+3.6~+8.9和+1.7~+10.4。虽然近年来在北山北带的变质杂岩中也报道了一些中元古代的年龄,但这些样品中都存在一组古生代的年龄,暗示它们可能是古生代岩浆作用的产物,如张正平等(2017)报道内蒙古标山一带斜长角闪岩的锆石U−Pb年龄为1623 ± 21 Ma,但该样品实际上包括2组年龄,其中较年轻的一组显示早石炭世(360 ± 4 Ma)至早侏罗世(193 ± 3 Ma)年龄,表明该斜长角闪岩可能是晚古生代甚至中生代岩浆作用的产物;Wang et al. (2024b)在标山地区获得了斜长角闪岩年龄为1481 Ma,但该样品同样包含古生代的年龄。因此,需要更多的年代学工作来确定北山北带变质杂岩的形成时代。
北山造山带新元古代的岩浆记录较中元古代的岩浆记录多,主要分布于南带的双鹰山-花牛山和石板山构造带。在古堡泉地区,Liu et al. (2015)获得3个正片麻岩的原岩结晶年龄分别为905 ± 6 Ma、871 ± 9 Ma、871 ± 5 Ma,锆石εHf(t)值为−3.77~+5.29,全岩地球化学特征显示俯冲带大陆岩浆弧的特征。叶晓峰等(2013)获得花岗质片麻岩的年龄为902 ± 5 Ma,具有高钾钙碱性的特征,较高的εHf(t)值(−2.0~+1.0)表明有幔源新生物质的加入。Yuan et al. (2015)在古堡泉地区获得4个片麻岩的锆石U−Pb年龄分别为898 ± 4 Ma、 897 ± 2 Ma、892 ± 4 Ma和891 ± 4 Ma, 在石板山构造带获得花岗片麻岩的锆石年龄为933 ± 5 Ma,均解释为片麻岩原岩的结晶年龄,且这些片麻状花岗岩具有高钾钙碱性和轻稀土元素及大离子亲石元素相对富集的特征。Zong et al. (2017)获得古堡泉副片麻岩的锆石变质增生边年龄为898 ± 4 Ma和897 ± 2 Ma,旧井地区片麻岩的锆石变质边年龄为900 ± 3 Ma,被解释为麻粒岩相变质作用时代。姜洪颖等(2013)获得石板墩斜长角闪岩和白墩子片麻岩的原岩年龄为882 ± 4 Ma和881 ± 9 Ma,变质年龄为291 ± 4 Ma和294 ± 2 Ma。此外,在牛圈子西侧红山铁矿区具有拉斑玄武岩属性的辉长岩和安山质凝灰岩的锆石U−Pb年龄分别为765 ± 10 Ma和756 ± 23 Ma (王二腾等, 2024)。在北山造山带北部的标山地区,Wang et al. (2024b)报道了一个片麻状花岗岩的锆石U−Pb年龄为894 ± 6 Ma,锆石εHf(t)值为−2.6~+4.0。
2.2 早古生代岩浆作用
早古生代岩浆作用主要分布于北山造山带中部马鬃山岛弧和双鹰山-花牛山岛弧。在马鬃山岛弧三眼泉地区,原被认为是早前寒武纪的花岗质片麻岩(北山杂岩)形成于寒武纪—奥陶纪(500~450 Ma),锆石具有较富集的Hf同位素组成(εHf(t) = −9.9~−0.3),全岩成分显示轻稀土元素相对重稀土元素富集,大离子亲石元素相对高场强元素富集的特征(Song et al., 2013a)。北山中部广泛分布的公婆泉群火山岩具有典型的弧火山岩特征(Song et al., 2015),其形成时代为奥陶纪—志留纪,如阿民乌素一带钠长阳起岩的LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb年龄为475 ± 2 Ma(孟庆涛等, 2021)。夏尔陶勒地区原划分为前寒武纪“敦煌岩群”中的片麻状花岗闪长岩年龄为443 ± 9 Ma(王红杰等, 2020);在小黄山一带的片麻状花岗岩中获得443 ± 1 Ma和442 ± 2 Ma的锆石结晶年龄,时代为早志留世早期,岩石地球化学分析表明,花岗岩属于钙碱性系列,具有岛弧岩浆岩的特征(胡新茁等, 2024)。内蒙古北山基东一带侵入公婆泉群火山岩中的花岗闪长岩锆石U−Pb年龄为437 ± 1 Ma,具有Rb、Th、K等富集和Nb、Ta、P、Ti等相对亏损的特征(潘志龙等, 2021)。野马大泉一带I型角闪石花岗岩的锆石U−Pb年龄为441 ± 2和425 ± 2 Ma,具有正的εHf(t)值(−0.1~+7.6)(黄博涛等, 2021)。
花牛山岛弧早古生代岩浆作用包括晚奥陶世变质英安岩,锆石U−Pb年龄455 ± 1 Ma(谢建强等, 2018)。侵入体锆石年龄集中在晚奥陶世—志留纪,如赵泽辉等(2007)获得辉铜山钾长花岗岩和花岗闪长岩的侵位年龄分别为436 ± 9 Ma和423 ± 8 Ma;明舒井杂岩体中辉长岩、闪长岩、花岗岩的锆石U−Pb年龄分别为443 ± 1 Ma、437 ± 2 Ma、436 ± 2 Ma, 具有正的εHf(t)值(−1.1~+12.0)(李小菲等, 2015)。北山造山带北部雀儿山岛弧也有少量奥陶纪火山岩分布,咸水湖组流纹岩SHRIMP锆石U−Pb年龄为462 ± 3 Ma(陈智斌等, 2020)。
2.3 晚古生代岩浆作用
晚古生代岩浆岩在北山造山带大范围分布,尤其是在北山北带和南带。北山北带雀儿山群为一套泥盆纪钙碱性系列的中酸性火山岩组合,包括安山岩、英安岩、流纹岩等,其中流纹岩U−Pb年龄为387 ± 2 Ma(任邦方等, 2019),英安岩年龄为365 ± 2 Ma(管诰等, 2022)。黑鹰山岛弧白山组安山岩及浅成侵入的花岗斑岩锆石U−Pb年龄分别为300 ± 3 Ma和300 ± 2 Ma,具有活动大陆边缘弧的地球化学特征(杜庆祥等, 2023)。在红石山蛇绿混杂岩南侧的大红山地区发现一套强烈变形的泥盆纪英云闪长岩-花岗闪长岩-石英二长岩,具有弧花岗岩的特征,其形成时代为399~364 Ma(闫涛等, 2020)。小红山一带晚石炭世英云闪长岩-花岗闪长岩-奥长花岗岩的年龄为316 ± 2 Ma、311 ± 1 Ma、305 ± 2 Ma, 具有岛弧钙碱性花岗岩的特征(杨五宝等, 2020)。明水石英闪长岩LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb年龄为312 ± 2 Ma,锆石具有正εHf(t)值(+2.1~+4.5),全岩成分分析显示典型火山弧岩浆岩的地球化学特征(唐文轶等, 2024)。狼娃山二长花岗岩、红柳河槽正长花岗岩、跃进山北正长花岗岩、跃进山二长花岗岩的锆石U−Pb年龄分别为327 ± 2 Ma、327 ± 2 Ma、321 ± 2 Ma和310 ± 2 Ma,锆石具有正εHf(t)值(+5.9~+10.3),属于钙碱性弧花岗岩(白荣龙等, 2022b)。双尖山金矿区正长花岗岩锆石U−Pb年龄为318 ± 3 Ma,εHf(t)值为+6.6~+9.8(白荣龙等, 2022a)。标山东一带高钾钙碱性I型花岗岩的侵位时代为324 ± 3 Ma(刘广等, 2021)。在百合山蛇绿混杂岩带南清河沟—红柳峡地区新识别出一套低钾拉斑-钙碱性高镁辉长岩的形成时代为278 ± 1 Ma,具有正的全岩εNd(t)值(+5.6~+6.8),其岩浆起源于受俯冲流体交代的亏损地幔(张国震等, 2022)。
在北山造山带南带的花牛山岛弧和石板山岛弧分布有大量的晚古生代岩浆岩,尤其是石炭纪—二叠纪侵入体。杨镇熙等(2021a)在帐房山南黑头山一带识别出了具有埃达克岩特征的中酸性侵入体,其锆石U−Pb年龄为408 ± 3 Ma。泥盆纪中酸性火山岩主要分布于墩墩山地区,牛亚卓等(2020)获得火山岩夹层年龄为418 ± 1 Ma;李向民等(2011)获得安山岩锆石U−Pb年龄为367 ± 10 Ma;流纹岩和正长斑岩的锆石U−Pb年龄分别为368 ± 3和371 ± 1 Ma,这些岩石具有钙碱性地球化学特征并且具有正的锆石εHf(t)值(+1.4~+16.4)(Guo et al., 2014, 2017)。花牛山地区分布有早泥盆世的钾长花岗岩(397 ± 3 Ma)和A型花岗岩(415 ± 3 Ma)(李舢等, 2009, 2011),晚泥盆世二长花岗岩(368 ± 2 Ma)和花岗闪长岩(366 ± 2 Ma),锆石εHf(t)值为−3.1~+6.0,具有典型的Ⅰ型花岗岩特征(吕鑫等, 2022)。双峰山花岗闪长岩的形成时代为335 ± 2 Ma(孙新春等, 2021),花牛山闪长玢岩的形成时代为288 ± 8 Ma(王二腾等, 2022),辉铜山花岗岩早二叠世高钾花岗岩年龄为279~275 Ma(Li et al., 2013),音凹峡南中钾钙碱性黑云母花岗岩锆石U−Pb年龄为282 ± 3 Ma,具有正的εHf(t)值(+4.4~+7.8)(张文等, 2011)。树窝井、西涧泉及旧井地区侵入岩的年龄为285 ± 1 Ma, 269 ± 3 Ma, 266 ± 2 Ma和260 ± 1 Ma (张文等, 2010; Zhang et al., 2015a),半道山岩体侵位时代为285 ± 4 Ma (Zhang et al., 2012c)。花牛山—音凹峡一带存在大量辉绿岩脉,其形成时代为约282 Ma,被认为是软流圈与岩石圈地幔相互作用的产物(Zhang et al., 2015b)。罗东、坡北、旋窝岭基性—超基性岩体的侵位时代为282 ± 3 Ma,野外和地球化学特征指示其为形成于俯冲带的阿拉斯加型岩体(Ao et al., 2010)。帐房山南黑山头石英闪长岩锆石U−Pb年龄为268 ± 1 Ma(杨镇熙等, 2022)。此外,沿柳园—帐房山分布有二叠纪火山岩带,安山岩-英安岩-流纹岩的时代集中在294~268 Ma(牛亚卓等, 2018; 许伟等, 2019)。
2.4 中生代岩浆作用
中生代岩浆岩在北山造山带分布范围较小,主要分布于南带的花牛山和石板山构造带,且主要为三叠纪岩浆活动。柳园地区花牛山正长花岗岩、长流水正长花岗岩、白峡尼山二长花岗岩、大豁落山花岗闪长岩、柳园辉绿岩脉等侵入体的年龄集中在240~217 Ma( Li et al., 2012;李舢, 2013; 孙海瑞等, 2020)。小西弓石英正长斑岩年龄为248 ± 2 Ma(朱江等, 2015);碱湖子斑状花岗闪长岩锆石U−Pb年龄为249 ± 1 Ma和234 ± 1 Ma(杨镇熙等, 2021b)。胡小春等(2023)在帐房山南侧前红泉地区报道了三叠纪二长花岗岩,其锆石U−Pb年龄为239 ± 1 Ma,具有高钾钙碱性的特征。此外,在北山北带的小红山地区也报道了三叠纪岩浆活动,花岗斑岩的锆石U−Pb年龄为212 ± 2 Ma和206 ± 2 Ma(李敏等, 2020)。
综上,根据目前已发表的高精度同位素年代学资料,北山造山带的岩浆作用可以总体分为3个期次(图3),即中元古代岩浆作用(约1400 Ma)、新元古代岩浆作用(900~800 Ma)和早古生代—早中生代连续的岩浆作用(530~205 Ma)。
3. 增生造山过程讨论
北山造山带分布有多条蛇绿混杂岩带,其形成时代和构造背景各异,岩浆活动存在长期多期次的特点,说明北山造山带是典型的增生型造山带,经历了长期的大洋俯冲与陆缘增生拼贴过程。对于北山造山带的造山作用过程,前人提出了不同的大地构造模型。部分学者依据高级变质地体及泥盆纪粗碎屑沉积的分布,提出北山造山带是多个陆块在早古生代晚期发生碰撞形成的,晚古生代进入板内构造演化阶段(左国朝等, 1990, 2003)。Xiao et al. (2010)综合分析了岩浆岩、地层、蛇绿岩及构造变形等资料,提出北山造山带在古生代经历了多岛弧多重汇聚增生拼贴造山,增生造山过程持续至二叠纪。龚全胜等(2002)提出北山造山带为陆-增生弧碰撞造山带,二叠纪进入陆内演化阶段。He et al. (2018b)提出北山造山带起源于统一的前寒武纪微陆块(柳园微大陆),晚古生代俯冲板片后撤形成多个岛弧。本文根据北山造山带岩浆作用时空分布规律和蛇绿混杂岩的时代和构造背景,对北山造山带增生造山过程进行简要讨论。
北山造山带变质杂岩的来源与构造属性是理解北山增生造山过程的关键,特别是中高级变质的“北山杂岩”的形成时代和构造属性,长期以来受到诸多学者的关注,也是北山造山带构造演化研究中争议较多的问题。从近年来的同位素年代学研究进展来看,北山造山带最早的岩浆活动为约1.4 Ga的花岗质岩浆作用,零星出露于北山南带的旧井至穿山驯地区,其锆石具有亏损的Hf同位素组成(εHf(t) = +2.7~+12.4)和相对年轻的二阶段模式年龄(TDMC = 2.0~1.4 Ga)(He et al., 2018b; Yuan et al., 2019;Wang et al., 2024b),表明岩浆起源于新生地壳的熔融或存在幔源岩浆的注入,这暗示北山地区并不存在大量比约1.4 Ga更老的地壳。原被认为形成于早前寒武纪的“北山杂岩”,经过大量的年代学研究,大部分显示古生代的年龄(Song et al., 2013a, b, 2015, 2016)。现有年代学资料表明,北山造山带并不存在早前寒武纪(太古代—古元古代)结晶基底,也不存在大规模前寒武纪基底。北山约1.4 Ga的岩浆作用与地壳增生事件在中亚造山带南缘的吉尔吉斯北天山、中国中天山和阿拉善构造带、内蒙古锡林浩特地体等均有记录(He et al., 2018a),指示在中元古代早期经历了相似的地质过程。大量1.48~1.44 Ga的基性和长英质侵入体分布于波罗地克拉通的Fennoscandia地区,并可延续至劳伦大陆东南缘,处于哥伦比亚超大陆的外围增生边缘(Brander et al., 2007; Ulmius et al., 2015;He et al., 2018b)。这些花岗岩形成时代(1450~1360 Ma)显示了从造山到非造山的地球化学演变特征,指示构造环境从挤压到伸展的转换,可能与哥伦比亚超大陆外围从前进型增生造山作用到后撤型增生造山作用的构造转换,与俯冲板片的后撤有关(Yuan et al., 2019)。因此,北山南带可能最早起源于哥伦比亚超大陆的外围增生造山带。
新元古代岩浆作用在北山造山带分布较广泛,如北山北带标山地区约894 Ma的片麻状花岗岩(Wang et al., 2024b)、北山中部牛圈子地区765~756 Ma的辉长岩和安山岩(王二腾等, 2024)、北山南带古堡泉地区905~871 Ma的花岗质片麻岩(Liu et al., 2015; Yuan et al., 2015; Zong et al., 2017)及北山南带石板山地区881 Ma的斜长角闪岩和花岗质片麻岩(姜洪颖等, 2013)。这些新元古代片麻状花岗岩属于高钾钙碱性系列I型花岗岩,具有富集轻稀土元素和大离子亲石元素,亏损Nb、Ta、Ti、Sr的地球化学特征,锆石εHf(t)值(−16~+10)指示了古老地壳和幔源岩浆的贡献,这些特征表明,新元古代岩石很可能起源于安第斯型岩浆弧(Liu et al., 2015; Yuan et al., 2015)。北山南带旧井地区新元古代石榴子石片岩经历了麻粒岩相变质作用,锆石变质增生边的U−Pb年龄为约900 Ma,与该地区的新元古代弧岩浆作用时代接近,说明形成于大洋俯冲的增生造山过程(Zong et al., 2017)。北山造山带的新元古代岩浆和变质事件(900~750 Ma)明显晚于导致Rodinia超大陆聚合的格林威尔造山事件(1300-1050 Ma),且尚未在北山地区发现格林威尔期碰撞造山的构造和岩石记录,因此,新元古代地质记录说明北山当时位于Rodinia超大陆的外围,属于环超大陆俯冲-增生造山带的一部分(Liu et al., 2015; Zong et al., 2017)。
早古生代,北山造山带经历了复杂的俯冲-增生造山作用,在蛇绿混杂岩尤其是岩浆作用方面有很多地质记录。北山中部红柳河-牛圈子-洗肠井蛇绿混杂岩是北山造山带时代最古老的一条蛇绿混杂岩带,记录了早古生代俯冲-增生过程。红柳河蛇绿岩中辉长岩锆石U−Pb年龄为528~516 Ma (张元元等, 2008; Cleven et al., 2015; Shi et al., 2018),月牙山-洗肠井蛇绿岩中辉长岩和斜长花岗岩年龄分别为535~527 Ma和536~530 Ma (Ao et al., 2012;侯青叶等, 2012)。这些蛇绿混杂岩中的玄武岩和辉长岩显示大离子亲石元素相对富集、高场强元素相对亏损的地球化学特征,辉长岩具有正的εNd(t)值(+6.1~+8.5),指示它们起源于受俯冲流体交代的亏损地幔,形成于俯冲带之上的环境 (Shi et al., 2018)。这些SSZ型蛇绿岩的出现表明北山地区至少在早寒武世早期已经发生了洋内初始俯冲作用。马鬃山岛弧草呼勒哈德地区约526 Ma的片麻状花岗岩同样表明早寒武世存在俯冲作用(Song et al., 2015)。奥陶纪—志留纪岩浆作用广泛分布于北山造山带,包括雀儿山岛弧分布的咸水湖组火山岩(约462 Ma)、马鬃山岛弧公婆泉群火山岩(475~440 Ma)及双鹰山-花牛山岛弧分布的花牛山群火山岩(约455 Ma);此外,还有大量以中酸性岩石为主的奥陶纪—志留纪侵入体。这些岩浆岩均显示钙碱性弧岩浆作用的特征,形成于俯冲带环境( Song et al., 2015;谢建强等, 2018)。在北山造山带南部,古堡泉榴辉岩的主量、微量元素和Sm−Nd同位素组成表明,其原岩为洋壳玄武岩;锆石U−Pb和黑云母40Ar−39Ar定年揭示,榴辉岩相峰期变质和退变质时代分别为约467 Ma和约430 Ma;结合顺时针P-T轨迹,该榴辉岩代表了古亚洲洋洋壳在奥陶纪俯冲到榴辉岩相深度,随后在志留纪发生折返(Qu et al., 2011)。在北山造山带中部马鬃山岛弧,奥陶纪—志留纪火山-沉积岩及侵入体发生强烈的褶皱变形,发育透入性面理,揭示其总体形成于挤压构造背景(Song et al., 2014)。
从晚志留世—泥盆纪开始,北山造山带岩浆活动总体减弱,并且在北山中部和南部出现S型和A型花岗岩(李舢等, 2009; Wang et al., 2018b),指示构造环境由挤压向伸展转变。在双鹰山-花牛山岛弧、泥盆纪三个井组和墩墩山组火山-沉积岩发育粗碎屑沉积及中酸性火山喷发,曾长期被认为代表北山增生造山作用结束的“磨拉石建造”(左国朝等, 1995;何世平等, 2005; 赵泽辉等, 2007)。通过火山岩相和沉积相分析,发现墩墩山盆地泥盆纪火山-沉积层序指示伸展背景,与同造山期的磨拉石建造有显著的区别(牛亚卓等, 2020)。墩墩山组火山岩主量、微量元素和Nd−Hf同位素解耦的特征揭示,晚古生代发生了重要的地球动力学环境转换,由前进型俯冲转变为后撤型增生造山作用(Guo et al., 2014, 2017)。始于泥盆纪的俯冲板片回卷后撤,在石炭纪形成了大规模的裂解作用,北山北带早石炭世白山组和北山南带早石炭世红柳园组主体为双峰式火山岩组合和深水复理石建造,代表裂谷拉伸作用( Tian et al., 2017;陈超等, 2017)。强烈的岩石圈伸展最终形成了以芨芨台子-石板井-小黄山蛇绿混杂岩为代表的石炭纪裂解洋盆(杨合群等, 2010; Zheng et al., 2013)。晚石炭世—二叠纪,由于弧后洋盆的俯冲,北山总体构造-古地理面貌为多洋盆俯冲和多向汇聚过程,形成了大规模分布的石炭纪—二叠纪岩浆作用,这些岩浆岩大都具有正的εNd(t)和εHf(t)值,表明大量幔源物质的添加(Ao et al., 2010; Zheng et al., 2020)。同时,二叠纪期间北山造山带发育大量弧相关盆地,沉积了厚层的海相至海陆交互相砂岩,包括北带红岩井盆地及南带柳园-黑山口浊积岩(Guo et al., 2012; Tian et al., 2015)。柳园-后红泉蛇绿混杂岩是北山地区最年轻的大洋板片记录,辉长岩的形成时代为295~270 Ma ( Zhang et al., 2011;Mao et al., 2012),表明早二叠世尚存在大洋扩张过程。蛇绿混杂岩中最年轻砂岩基质的最大沉积年龄为234~222 Ma( Wang et al., 2017b;Mao et al., 2023),表明蛇绿岩在中—晚三叠世才最终与陆缘碎屑物质发生构造混杂,蛇绿岩的最终就位揭示了北山最晚的增生造山过程结束于中—晚三叠世。
自晚三叠世以来,北山造山带进入陆内构造演化的新阶段,由于北侧蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋和南侧特提斯洋汇聚过程远程效应的影响,北山造山带在中生代经历了复杂的陆内变形。野外构造观测和年代学研究发现,北山造山带在侏罗纪发生了大规模的逆冲推覆构造,使中元古代地层推覆至新元古代及更年轻的地层之上 (Zheng et al., 1996)。近年来的低温热年代学研究揭示了晚三叠世—早侏罗世(225~180 Ma)、早白垩世(130~95 Ma)及晚白垩世—早古近纪(75~60 Ma)3个阶段的剥露过程(Gillespie et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2024a)。
4. 结 语
北山造山带经历了长期的陆缘增生造山过程,最早的增生造山地质记录可以追溯到中元古代早期,约1.4 Ga的岩浆作用和地壳增生事件在北山南带及其相邻的天山、阿拉善和内蒙古地区均有分布,共同记录了哥伦比亚超大陆外围的增生造山过程。北山造山带0.9~0.8 Ga的岩浆作用在南带和北带都有分布,其同位素组成和同期麻粒岩相变质作用揭示了安第斯型增生造山过程,指示北山地区当时位于Rodinia大陆外围增生造山带。早古生代,北山造山带经历了复杂的增生过程,约530 Ma的SSZ型蛇绿混杂岩指示北山至少在早寒武世已经发生了洋内初始俯冲;奥陶纪—志留纪发生了大规模的俯冲-增生作用,形成大量钙碱性火山岩及侵入体,广泛分布的褶皱和透入性面理指示挤压构造背景。从泥盆纪开始,北山造山带由早古生代的挤压构造转变为伸展构造,在石炭纪早期形成大规模裂解和弧后洋盆,石炭纪—二叠纪北山为多重俯冲-汇聚的构造-古地理格局,造成显著的大陆增生。北山造山带最晚的增生造山作用发生在柳园—后红泉一带,蛇绿混杂岩中的基性岩形成时代和沉积岩基质的沉积时限共同限定了最晚的增生造山过程持续至中—晚三叠世,北山自此进入陆内构造演化阶段。
致谢:李春昱院士是中国板块构造研究先驱之一,也是中国和亚洲大地构造研究的早期开拓者之一。谨以此文献给李春昱先生诞辰120周年。感谢中国地质科学院地质研究所李锦轶和张进研究员在成文过程中的指导和帮助,以及审稿专家对本文提出的宝贵修改意见和建议。
-
表 1 白洋淀常见介质物性参数参考值
Table 1 Reference values of physical properties of common dielectrics in the deposition area
介质名称 相对介电常数(无量纲) 电磁波速度/(mm·ns−1) 电阻率/(Ω·m) 空气 1 300 ∞ 水 81 33 30 ~ 10000 耕种土 2.6 ~ 15 77 5 ~ 20 干砂 3 ~ 6 120 ~ 170 20 ~ 200 湿砂 25 ~ 30 55 ~ 60 15 ~ 50 粉质粘土 8 ~ 12 60 8 ~ 25 粘土 8 ~ 12 60 5 ~ 20 表 2 探地雷达水陆探测勘探能力对比结果
Table 2 Comparison of land and water detection capabilities of GPR
勘探方式 中心频率/MHz 模糊区 测程/ns 测深/m 垂直分辨率 地面探测(Er=9) 300 25 cm 150 ~ 300 2 ~ 3 15 cm 100 50 cm 300 ~ 500 20 40 cm 50 1 m 800 40 0.5~2 m 水上探测(Er=40) 300(沉水雷达) 水体,非勘探目标 150 ~ 300 2 20 cm 100 300 ~ 500 5 40~50 cm 50 800 15 0.5~2 m -
Ardekani M, Druyts P, Lambot S. 2014. Recovering the structure of a layered soil, including layer thickness and dielectric permittivity, using theinterfaces and objects backscatter detected in GPR b−scans[C]//Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR 2014), Brussels: 397–400.
Baek S, Kim S, Known J, et al. 2017. Ground penetrating radar for facture mapping in underground hazardous waste disposal sites: a case study from an underground research tunnel, South Korea[J]. Appl. Geophys., 141: 24−33. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2017.03.017
De Coster A, L Pérez J, Medina M. 2019. Towards an improvement of GPR−based detection of pipes and leaksin water distribution networks[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 162: 138−151. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2019.02.001
Filippo B, Lukas K, Bjørn K M, et al. 2023. Mapping inland water bathymetry with Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) on board Unmanned Aerial Systems (UASs)[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 616: 128789.
Goodman D. 1994. Ground−penetrating radar simulation in engineering and archaeology[J]. Geophysics, 59(2): 224−232. doi: 10.1190/1.1443584
Johnston B, Ruffell A, McKinley J, et al. 2018. Detecting voids within a historical building facade: a comparative study of three high frequency GPR antenna[J]. Cult. Herit., 32: 117–123.
Kämäri M, Alho P, Colpaert A, et al. 2017. Spatial variation of river−ice thickness in a meandering river[J]. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol., 137: 17–29.
Lambot S, André F. 2014. Full−wave modeling of near−field radar data for planar layered media reconstruction[J]. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 52 (5): 2295–2303.
Maas C, Schmalzl J. 2013. Using pattern recognition to automatically localize reflection hyperbolas in data from ground penetrating radar[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 58(2): 116−125.
Ruffell A, Parker R. 2021. Water penetrating radar[J]. Journal of Hydrology Journal of Hydrology, 597: 1−13.
Topp G C, Davis J L, Annna A P. 1980. Electromagnetic determination of soil water content: measurement in coaxial transmission lines[J]. Water Resource Research, 16(3): 574−582. doi: 10.1029/WR016i003p00574
蔡少峰. 2019. 探地雷达在河流水下地形及基岩探测中的试验研究[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 16(5): 680−685. 丁 凯, 查恩来, 周紧东, 等. 2005. 应用地质雷达进行水下抛石探测的试验研究[J]. 水利学报, 12(增刊): 560−565. 郭秀军, 王淼, 孙振水, 等. 2009. 基于探地雷达技术的水下淤泥层高分辨率探测研究[C]//山东省地球物理六十年学术交流会. 青岛: 中国海洋大学: 639−647. 欧阳, 张杰, 冯杰, 等. 2022. 地质-地球物理三维可视化建模及其应用——以雄安新区为例[J]. 华东地质, 43(3): 286−296. 王复明, 尚向阳, 钟燕辉. 2008. 探地雷达在河流水深探测中的应用研究[J]. 人民黄河, 30(4): 17−18. 王凯. 2022. 基于综合地球物理探测的雄安新区地热地质结构及深部热源机制研究[D]. 吉林大学博士学位论文. 袁国礼, 侯红星, 刘建宇, 等. 2023. 服务生态文明的生态地质调查工作方法浅析[J]. 西北地质, 56(3): 30−38. doi: 10.12401/j.nwg.2023065 赵永辉. 2019. 探地雷达在水下考古中的机遇与挑战[J]. 中国港口, S1: 125−133. 张杰, 杨毅, 王凯, 等. 2022. 综合地球物理在雄安新区三维地质结构探测中的应用与成果[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 44(6): 742−750. 张开伟, 吴园平, 王世淼, 等. 2019. 基于探地雷达技术的水下沉积地形探测应用研究[J]. 人民长江, 50(7): 117−122. 中共河北省委、河北省人民政府编制. 2018. 《河北雄安新区规划纲要》[R]. -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 邓乃尔,徐浩,周文,唐小川,王浩,闫晓闯,蒋柯. 基于深度学习的岩石矿物智能识别研究进展与发展趋势. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版). 2025(01): 64-93 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: