Geochemical characteristics of primary halo and indication of deep prospecting in Xinfang gold deposit, Liaoning Province
-
摘要:
辽东半岛南部的新房金矿床由22、23、24、25、27号5条矿脉带组成,矿区内主要矿体已被发现,提能增储成为制约矿山持续服务的因素,矿床勘查过程中的钻探工程部署迫切需要科学、有效的成矿预测依据。以新房金矿床106线14个钻孔原生晕数据为研究对象,研究地球化学特征和元素分带规律,建立轴向分带序列,在研究原生晕地球化学特征基础上开展深部找矿预测。结果表明,新房金矿的前缘晕元素为As、Sb、Hg,近矿晕元素为Au、Ag、Cu、Pb、Zn,尾晕元素为W、Mo、Bi。采用分带指数法计算了22、23、24、25、27号5条矿脉带的轴向分带序列,指示5条矿脉带均出现“反分带”现象,可能是不同矿化阶段的矿体在空间上叠加导致正常的轴向分带序列出现错位。22、23、24、27号矿脉带的中下部出现较强的前缘晕和近矿晕,结合地球化学参数特征,这4条矿脉带的As/W、As/Mo、Sb/W、(As×Sb)/(Mo×W)评价指标出现多次振荡波动,并且在深部由降转升,指示深部有较好的找矿潜力。综合以上分析认为,新房金矿床经历多次成矿热液活动,在106勘探线东侧矿体还有一定的延伸。
Abstract:The Xinfang gold deposit is a large gold deposit on the southern edge of the Liaodong Peninsula, China. It consists of five vein belts including 22, 23, 24, 25 and 27.The main ore bodies in the study area have been discovered, and energy enhancement and storage have become the factors restricting the continuous service of the mines. There is an urgent need for the deployment of drilling works in the process of ore deposit exploration to be based on scientific and effective mineralization prediction. This paper analyzes the geochemical characteristics of primary halo and zoning pattern of mineralization halo elements from 14 drillings within No.106 exploration line section in Xinfang gold deposit. Based on geochemical characteristics of primary halo, establish the axial zoning sequence and make prospecting prediction in the depth of the No.106 exploration line section. The study shows that the frontal elements are As, Sb, Hg, the near-ore indicator elements are Au, Ag, Cu, Pb, Zn and the rear elements are W, Mo, Bi in the Xinfang gold deposit. Axial zonation sequence of five lodes (including lode 22, 23, 24, 25 and 27) derived from the Grigorian’s zoning index method all present reverse zoning phenomenon, which are probably caused by multiple phases of mineralization. Stronger frontal halos and near-ore halos appear in the middle and lower part of lode 22, 23, 24 and 27, and the axial geochemical parameters of As/W, As/Mo, Sb/W, (As×Sb)/(Mo×W) have multiple oscilation fluctuations and increasing in the depth, which indicate better prospecting potential for those lodes in the depth. These features suggested that the ore bodies formed by multiple hydrothermal mineralization stages and some ore bodies may extend to the depth on the east side of No.106 exploration line section.
-
新房金矿床是辽东半岛重要的大型金矿床。近年来,许多学者在成岩成矿年代、矿床成因、流体特征、物质来源等方面做了大量的工作(郭大招等,2005; Wei et al., 2007; Liu et al., 2021; Yu et al., 2021;仲米山等, 2021; Zhang et al., 2022, 2023)。研究表明,新房金矿属燕山期岩浆热液型金矿,成矿物质和成矿流体与深部岩浆有关,成矿温度为220~280℃,矿体产出受早白垩世(约128 Ma)变质核杂岩控制。然而,矿区勘查地球化学工作开展不足制约了找矿工作,加之开采年限已久,主要矿体已被发现,深部找矿成为目前矿山开发的重点。
原生晕地球化学找矿预测方法是迄今地球化学勘查领域研究时间最长、最具找矿效果的方法之一(邵跃, 1997; 刘崇民等, 2014)。前人对热液型金矿床进行了大量研究(谢学锦等, 1982; 邵跃, 1984, 1988, 1997; 王崇云, 1987; 李惠等, 1998, 1999),总结了金矿床元素的共生组合规律、地球化学异常特征和元素分带性,指出元素在轴向上的变化往往反映了热液的运移特征。金矿由于多期多阶段成矿的特点,不同成矿阶段形成的矿体(晕)在空间上的叠加会使分带序列出现反分带现象(李惠, 1998)。这种反分带现象可以作为深部找矿的标志,可以利用元素分带性和元素空间参数变化来指导找矿。矿床勘查过程中的钻探工程部署亟需科学、有效的成矿预测依据,因此利用原生晕进行矿区深边部找矿预测工作显得尤为迫切。
本文在详细研究新房金矿床地质特征的基础上,通过对新房金矿床106勘探线13个元素的分带性和内在联系研究,探讨新房金矿床5条主矿脉带原生晕的分带特征及其对深部找矿的指示意义。
1. 矿区地质特征
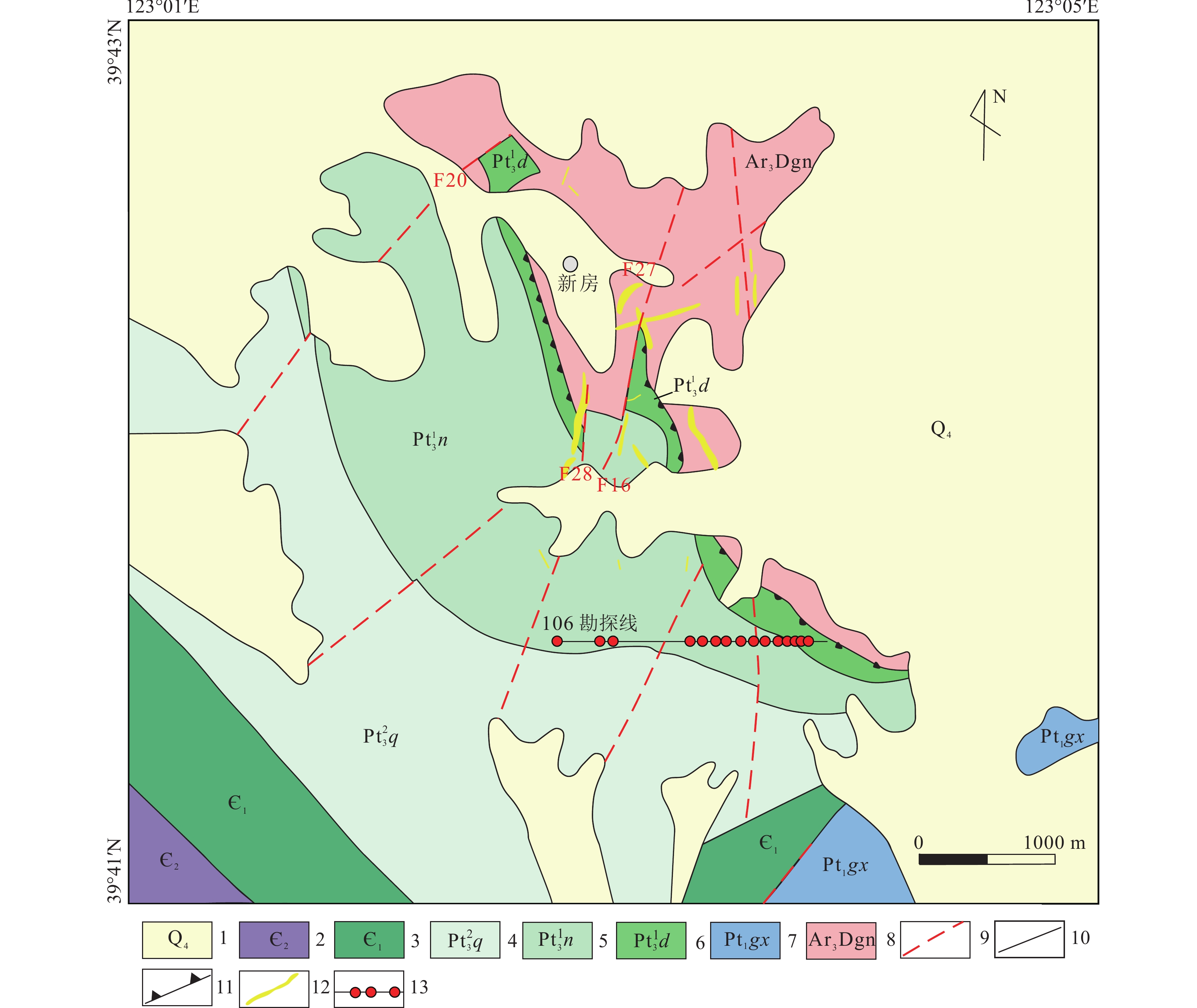
新房金矿地处华北克拉通东北缘,位于北东走向的庄(河)−桓(仁)区域断裂带上盘,地层主体由结晶基底和盖层组成(图1)。结晶基底主要由太古宇黑云母斜长角闪片麻岩组成。盖层由老到新为:古元古界辽河群盖县组绢云片岩和黑色钙质板岩,新元古界南华系桥头组灰色石英砂岩和灰绿色绢云母板岩,青白口系钓鱼台组灰白色变质砂岩、灰色石英砂岩及南芬组灰黑色钙质板岩,古生界中—下寒武统砂岩、页岩及新生界新近系。矿体主要赋存于太古宇片麻岩基底和钓鱼台组砂岩中。
![]() 图 1 新房金矿地质简图(据刘冰等,2020修改)1—新近系残积物; 2—中寒武统; 3—下寒武统; 4—南华系桥头组; 5—青白口系南芬组; 6—青白口系钓鱼台组; 7—古元古界盖县组; 8—太古宇结晶基底; 9—推测和实测断层; 10—地质界线; 11—拆离断层; 12—矿体; 13—106勘探线及钻孔位置Figure 1. Geological sketch map of the Xinfang gold deposit
图 1 新房金矿地质简图(据刘冰等,2020修改)1—新近系残积物; 2—中寒武统; 3—下寒武统; 4—南华系桥头组; 5—青白口系南芬组; 6—青白口系钓鱼台组; 7—古元古界盖县组; 8—太古宇结晶基底; 9—推测和实测断层; 10—地质界线; 11—拆离断层; 12—矿体; 13—106勘探线及钻孔位置Figure 1. Geological sketch map of the Xinfang gold deposit断裂是矿区发育的主要构造,包括北东向、北西向、近南北向、近东西向断裂,以及发育于新元古界盖层与太古宇变质岩接触带附近的拆离断层。其中拆离断层和北西向断裂控制了主要矿体(图1)。拆离断层总体走向300°~310°,倾向南西,倾角20°~40°。北西向断裂走向320°~335°,倾向北东,倾角25°~45°。22、23、24、25、27号等矿脉带赋存于这2类断裂中。矿区内岩浆岩不发育,主要出露脉岩,岩性主要为石英闪长玢岩、闪长岩、煌斑岩及辉绿岩。闪长岩与区内矿脉带关系密切,主要沿构造方向展布,以近南北向为主,倾向东,倾角30°~50°。
2. 矿体地质特征
截至2019年,新房金矿区发现了80余条金矿体,估算金资源量大于10 t,矿床Au平均品位3.09×10−6。
矿区106勘探线揭露5条金矿脉带:22、23、24、25、27号矿脉带。其中22号矿脉带走向330°,总体倾向60°,倾角29°~36°。其走向延长约260 m,倾向延深约120 m。22-1矿体与22矿体间距13~50 m,真厚度0.73~11.73 m。矿石类型主要为石英脉型,Au平均品位2.44×10−6。
23号矿脉带中主要矿体23走向300°~340°,倾向30°~70°,倾角20°~50°。其走向延长约1200 m,倾向延深约400 m。真厚度0.51~17.9 m。矿石类型主要为石英脉型,Au平均品位2.33×10−6。
24号矿脉带中主要矿体24走向325°,倾向55°,倾角24°~53°。其走向延长约500 m,最大倾向延深达340 m,真厚度0.51~8.92 m。矿石类型为石英脉型,Au平均品位2.42×10−6。
25号矿脉带中主要矿体25-1走向350°,总体倾向80°,倾角24°~44°。其走向延长约380 m,倾向延深约220 m,厚度0.47~2.68 m。矿石类型为石英脉型,Au平均品位5.38×10−6。
27号矿脉带内以27-1矿体为主,其是该矿区规模最大的矿体,走向30°,倾向120°,倾角25°~50°。矿体走向长660 m,真厚度0.59~9.87 m,平均2.23 m。矿石类型主要为石英脉型,有时见硅化钾化蚀变岩型,Au品位0.76×10−6~5.76×10−6,平均品位2.44×10−6。
根据矿石矿物的共生组合和穿切关系,结合前人研究成果(Liu et al., 2021; Yu et al., 2021)将新房矿区划分为4个矿化阶段:①硅化钾化热液蚀变阶段(图版Ⅰ−a),形成钾长石、石英、黄铁矿等矿物。钾长石呈不规则的宽板状,集合体呈不规则团块状,钾长石边部可见黄铁矿化、绢云母化、绿泥石化。石英见硅化,呈他形、粒状,受蚀变影响,石英颗粒增大,且聚集成不规则的团块状、脉状。黄铁矿多自形,呈浸染状分布,有的集合体呈细脉状沿硅化钾化蚀变岩裂隙分布。②石英−黄铁矿阶段(图版Ⅰ−b),主要形成石英、中粗粒黄铁矿等矿物。石英多为乳白色,呈他形粒状产出。黄铁矿呈立方体、半自形粒状或集合体出现,常见压碎结构(图版Ⅰ−e)。③石英−多金属硫化物阶段(图版Ⅰ−c、d),是主要成矿阶段,形成毒砂、石英、自然金、黄铁矿、黄铜矿、方铅矿、闪锌矿、银金矿、银黝铜矿等矿物。该阶段形成较多的硫化物,以黄铁矿、方铅矿为主,黄铁矿多为立方体(图版Ⅰ−f),少数为五角十二面体,常被包于方铅矿、闪锌矿中。该阶段发育不规则状、脉状黄铜矿(图版Ⅰ−g)。方铅矿呈不规则脉状、网脉状或团块状沿压碎黄铁矿裂隙分布(图版Ⅰ−h)。④石英−方解石阶段,主要形成方解石、石英和微量黄铁矿,常见方解石呈脉状穿切石英脉。主要围岩蚀变类型有硅化、钾长石化、黄铁矿化及碳酸盐化。
3. 样品采集与测试
本次研究样品采自新房金矿床106勘探线上的14个钻孔,采样点间距一般为10 m,在地层未蚀变区放稀至20 m,矿化带内视矿化强度加密至3~5 m。采样方法为连续拣块法,在采样点间距内均匀采集直径小于2 cm的5~8个子块组成一个样品,样品质量大于300 g,自上而下通孔取样,共采集575个样品。
邵跃(1984)指出,热液金矿床中Au的异常通常伴随Ag、Cu、Pb、Zn、As、Sb、F、Hg、Mo、W、Bi、Sn、Co、Ni等元素异常,结合本矿床地质特征和元素共生组合关系,选取Au、Ag、Cu、Pb、Zn、As、Sb、F、Hg、Mo、W、Bi、Sn共13个元素进行分析。其中,Au、Mo、Bi采用等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)测定,Pb、Cu采用X射线荧光光谱法(XRF),Ag、Sn采用发射光谱法(AES),Zn采用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES),As、Sb、Hg采用原子荧光光度法(AFS),W采用极谱法(POL),F采用离子选择性电极法(ISE)。测试分析在辽宁省第七地质大队实验测试中心完成,以国家标准物质和监控样进行质量控制,分析结果及分析质量指标达到《多目标区域地球化学调查规范(1∶250 000)》(中华人民共和国国土资源部, 2014a)样品分析的要求,其中标准物质和监控样的合格率为100%,内检的合格率达到95%以上,数据质量可靠。
4. 原生晕地球化学特征
本文对原始数据进行统计分析及标准化处理,使原始数据基本符合正态分布,统计过程由SPSS软件完成。
4.1 元素组合特征
4.1.1 矿区地质体元素含量统计
按照新房矿区内与矿体赋存状态有关的3种岩性,对各成晕成矿元素进行了统计(表1)。Bi、Hg、As、Sb等元素在3种岩石中的参数变化不明显,片麻岩和砂岩中成矿元素Au、Ag、Cu、W、Mo明显高于板岩,蚀变岩样中Au、Pb、Mo最富集,Au、Ag、Cu、Pb、W、Mo可作为矿床的指示元素。
表 1 新房金矿不同岩性元素平均含量Table 1. The average of elements in different lithologies of the Xinfang gold deposit岩性 样品数/个 几何平均值 Ag As Au Bi Cu F Hg Mo Pb Sb Sn W Zn 片麻岩 136 0.12 4.84 17.48 0.10 34.75 503.20 0.01 1.24 12.44 0.31 1.47 2.14 49.90 砂岩 142 0.18 4.64 20.47 0.21 16.51 634.53 0.01 1.54 25.17 0.37 2.47 3.31 59.13 板岩 72 0.08 4.30 2.06 0.41 12.30 772.88 0.01 0.85 19.87 0.38 3.77 2.04 81.24 蚀变岩样 169 0.25 2.65 28.73 0.11 27.93 534.91 0.01 1.69 35.82 0.33 1.70 2.27 49.64 注:Au含量单位为10−9,其他元素含量单位为10−6 4.1.2 相关性分析
相关性分析可以解释元素间的相关关系,常用相关系数表征相关性的强度(表2)。通过SPSS软件进行相关性分析,置信水平为0.05。
表 2 新房金矿床成矿成晕元素相关系数矩阵Table 2. Correlation coefficient matrix of mineralization elements halo in the Xinfang gold deposit元素 Ag As Au Bi Cu F Hg Mo Pb Sb Sn W Zn Ag 1 As 0.157 1 Au 0.830 0.030 1 Bi 0.222 0.420 0.069 1 Cu 0.469 0.009 0.534 0.032 1 F 0.106 0.026 0.133 0.085 0.023 1 Hg 0.205 0.123 0.204 0.076 0.208 0.017 1 Mo 0.228 0.013 0.106 0.073 0.025 0.093 0.093 1 Pb 0.711 0.013 0.717 0.072 0.908 0.052 0.229 0.084 1 Sb 0.296 0.502 0.231 0.195 0.134 0.089 0.240 0.079 0.231 1 Sn 0.106 0.159 0.117 0.161 0.040 0.578 0.107 0.077 0.053 0.132 1 W 0.143 0.067 0.128 0.068 0.018 0.148 0.038 0.103 0.013 0.043 0.201 1 Zn 0.236 0.248 0.242 0.128 0.346 0.081 0.643 0.072 0.354 0.186 0.084 0.029 1 Au与Ag、Cu、Pb呈现很好的正相关关系,这些元素可作为良好的近矿指示元素,同时也指示该矿床主要与中低温热液有关(刘英俊等, 1984; 尹志刚等, 2023)。Au、Ag、Cu、Pb、Zn之间较强的相关性指示Au与含Ag、Cu、Pb、Zn的硫化物相伴产出,这跟金与银金矿、方铅矿、闪锌矿及黄铜矿伴生产出的地质事实相符。活动性较强的As、Sb、Hg与Mo、Sn、W基本呈正相关,低温元素与高温元素叠加,暗示新房金矿至少经历了2次以上的热液活动叠加作用。
4.1.3 聚类分析
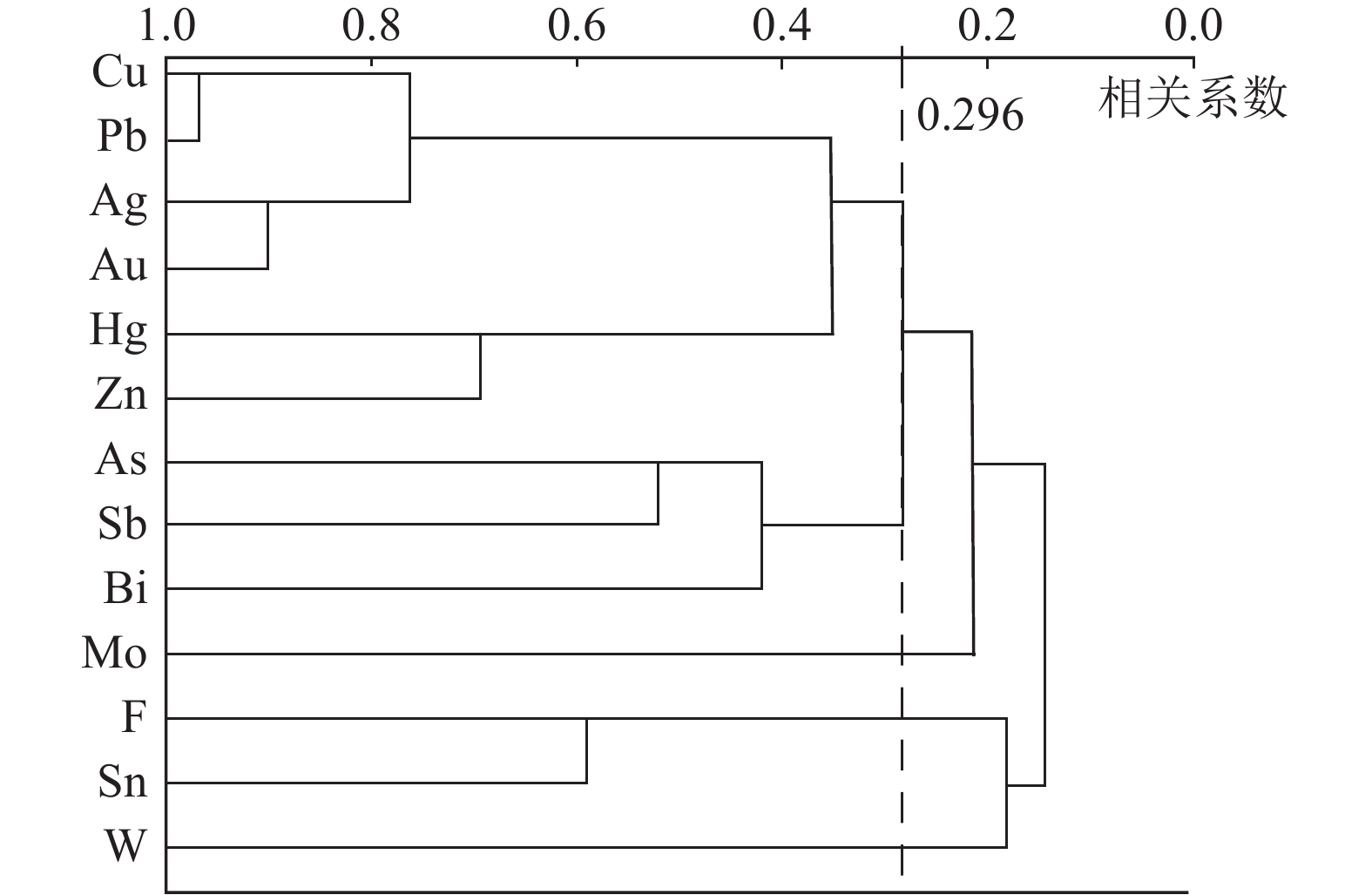
R型聚类分析是通过多个变量之间的相关系数定量研究元素之间的聚集和分离,在数理统计中多用于多变量的归类与分组(于俊博等, 2014)。对元素的R型聚类分析,不但可以了解元素间的亲疏关系,还可以进一步说明元素与成矿的关系(林成贵等, 2020)。对新房金矿床13个元素进行R型聚类分析,以相关系数0.296为界,可将元素分为5个组合(图2)。
与Au密切相关的元素主要有Cu、Pb、Ag、Au、Zn,这些元素是一套中低温元素,可作为金矿化的主要成矿成晕指示元素。Cu、Pb、Ag、Au、Zn均为亲硫元素,在一个群组出现,反映这些元素在成矿过程中可能以含S的络合物形式运移(刘英俊等, 1984; Yu et al., 2021),与金矿体中常见方铅矿、闪锌矿及黄铜矿一致。在更高的相关性水平上,将Hg、Zn归为一组,指示Zn的沉淀顺序与Cu、Pb、Ag、Au有差异。
4.1.4 因子分析
因子分析以变量间的相关性作为基础,通过降维将相关性高的变量聚在一起(钟海燕等, 2018),便于从关系复杂的众多变量中提取发挥主导作用的变量。利用SPSS对KMO进行检验,KMO为0.62,大于0.5,说明数据适合进行因子分析(张文彤, 2002)。
对13种元素的因子分析结果采用最大方差法进行旋转,得到正交旋转因子载荷矩阵(表3)。前5个因子的特征值大于1,且累计方差贡献率大于70%,使用因子分析对数据的提取较充分。
表 3 新房金矿床正交旋转因子载荷矩阵Table 3. Orthogonal rotation factor load matrix in the Xinfang gold deposit元素 成分 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 Ag 0.811 0.258 −0.115 0.031 0.288 As −0.048 0.861 0.044 0.125 −0.032 Au 0.855 0.095 −0.109 0.048 0.184 Bi 0.064 0.673 0.147 −0.048 0.086 Cu 0.838 −0.060 0.042 0.210 −0.181 F −0.047 −0.050 0.866 0.033 −0.019 Hg 0.110 0.086 0.027 0.887 0.087 Mo 0.032 0.023 −0.230 0.145 0.753 Pb 0.946 0.027 −0.004 0.175 −0.060 Sb 0.180 0.711 −0.075 0.175 0.011 Sn −0.084 0.182 0.836 0.082 0.018 W 0.078 0.038 0.369 −0.081 0.668 Zn 0.226 0.137 0.083 0.852 −0.009 特征值 3.104 1.844 1.702 1.673 1.184 累积方差贡献率/% 23.880 38.065 51.154 64.028 73.135 (1)F1主要载荷因子Ag、Au、Cu、Pb:反映了成矿元素Au形成的温度为中低温,代表以Ag、Au、Cu、Pb矿化为主的多金属硫化物阶段。
(2)F2主要载荷因子As、Bi、Sb:矿床中含 Sb 矿物有银黝铜矿,Sb元素在中—低温热液中的迁移能力较强; As与Sb一起出现,是中低温热液金矿床的指示元素。方铅矿是重要的含Bi矿物,其中Bi、Ag元素往往正相关,Bi、Ag含量可以指示方铅矿形成温度(代力, 2013)。相关性分析中,Bi与As关系最密切,其次是Ag。因此,F2代表一次中低温热液活动,可能与方铅矿的形成有关。
(3)F3主要载荷因子F、Sn,聚类分析中也将W、Sn、F元素划为一类,表明F3与含W、F、Sn矿化的脉岩有关,也反映出成矿与脉岩有关。
(4)F4主要载荷因子Hg、Zn,Zn在矿床中主要以闪锌矿的形式存在,闪锌矿在高温和中低温均可形成(代力, 2013)。考虑到Hg活动性较强,在相对低的温度下也可迁移,推测F4因子代表与Zn矿化有关的中低温热液成矿作用,与聚类分析结果一致。
(5)F5主要载荷因子有Mo、W,属于高温元素,指示与Mo、W富集有关的高温热液阶段。
4.2 原生晕分带特征
4.2.1 浓度分带特征
根据前人资料(章永梅等, 2010; 陈永清等, 2011; 郝迪等, 2021; 李彦强等, 2022)及新房金矿床研究成果,对所有元素进行包括基本统计分析、相关分析、聚类分析、因子分析在内的数理统计分析,结合元素地球化学特征,综合确定新房金矿床最佳指示元素组合为Au、Ag、Cu、Pb、As、Sb、W、Mo。本文采用迭代剔除法确定异常下限,将标准化处理的数据以均值¯X±3倍标准差S进行检验,若数据符合则进入下一轮计算,直至数据全部落入均值¯X±3倍标准差S范围内。将求得的平均值¯X作为背景值,¯X±3S作为异常下限。采用3级浓度分带标准,以异常下限的1倍、2倍、4倍作为各个元素的外带、中带、内带(表4),结合地质特征和矿体在空间上的分布确定浓度分带。
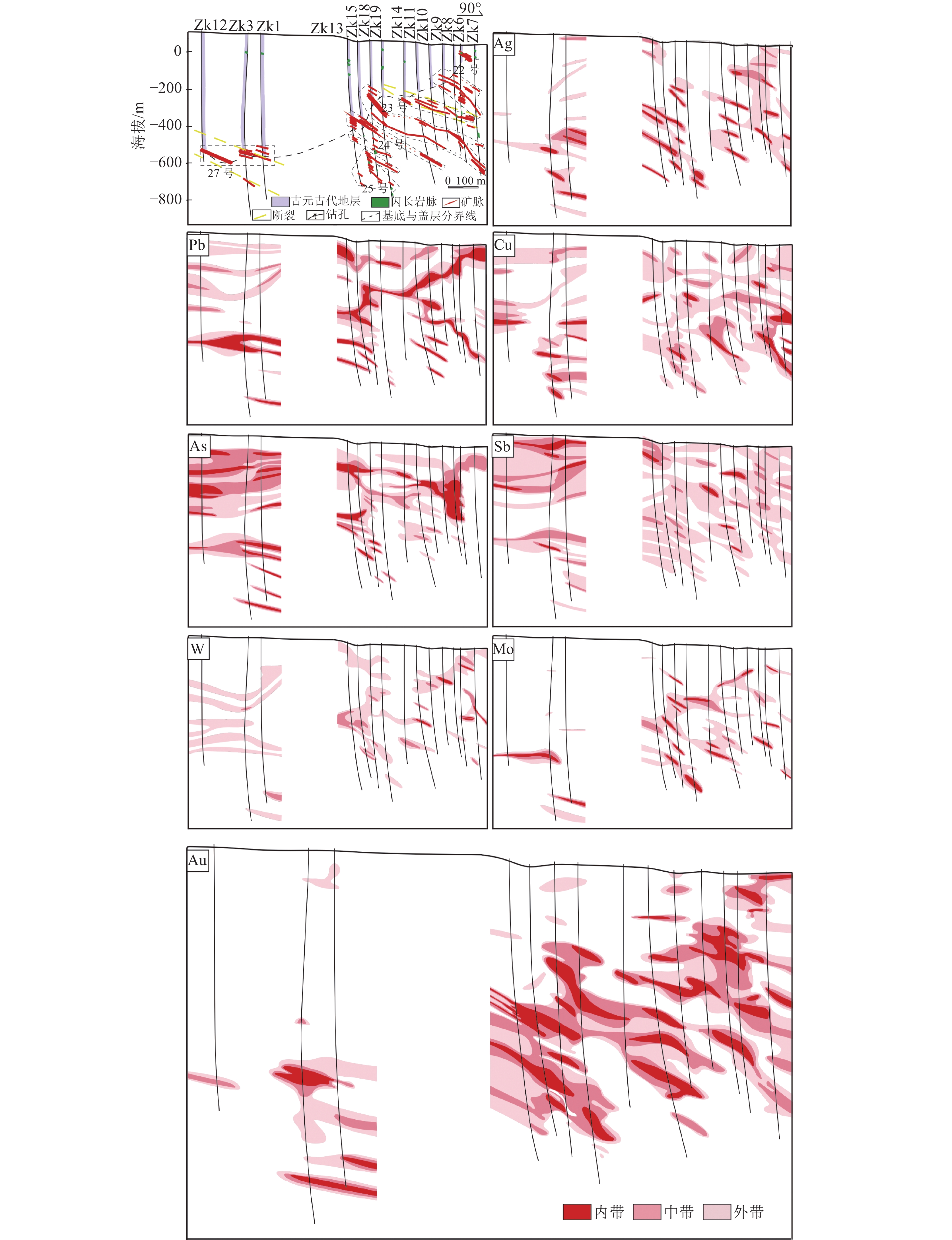
表 4 新房金矿床各元素浓度分带阈值Table 4. Concentration banding thresholds of elements in the Xinfang gold deposit元素 Ag As Au Cu Mo Pb Sb W 外带 0.2 3 6 35 2 20 0.3 3 中带 0.4 6 25 70 4 40 0.6 6 内带 0.8 12 100 140 8 80 1.2 12 注:Au含量单位为10−9,其他元素含量单位为10−6 通过分析原生晕分带特征,认为13个元素原生晕的外、中、内带分明,结构完整,原生晕形态在矿体周围与矿体产状一致,在远离矿体的地方原生晕形态与破裂带、侵入岩脉和盖层产状一致(图3)。
(1)Au、Ag、Cu、Pb成矿元素的原生晕结构完整,异常浓集中心突出。Au元素中带、外带分布范围广泛,内带异常与矿体形态最接近,在矿体中部、上部异常范围较大,矿体下部内带异常分散,在27号矿脉带800 m、22号矿脉带300 m深处内带范围逐渐扩大,有向东延伸的趋势。Ag元素的内带异常范围与矿体套合程度较好,且与Au元素的内带形态最接近,这与上述相关性分析、聚类分析结果一致,集中在矿体上部、中部。在矿体下部,Ag内带异常集中在27号矿脉带800 m,23号矿脉带500 m、700 m深处,异常范围呈现向东延伸的趋势。Pb元素集中在矿体中上部,在27号矿脉带600 m、900 m和25号矿脉带500 m、600 m深处内带有扩大的趋势。Cu元素内带异常与矿体走向基本一致,主要集中在矿体中部、下部,在22号矿脉带350 m、23号矿脉带650 m有向东继续延伸的趋势。矿体上部也存在内带异常,分布范围较窄。Au、Ag、Cu、Pb成矿元素可视为矿体的近矿晕元素。
(2)Sb、As成晕元素的异常范围广泛,内带、中带、外带分异明显。Sb外带异常范围较大,中带、内带异常范围相对较小且零散。内带异常出现在矿体上部、中部,矿体下部多为中带、外带异常。As在矿体的上部、中部出现大面积内带异常,在矿体下部零散分布内带异常,在27号矿脉带500 m以下内带有向深部延伸的趋势。As、Sb可被视为前缘晕元素。
(3)W、Mo整体以外带分布为主,零星分布有内带、中带异常。W、Mo内带异常在矿体中、下部范围较大,与矿体中下部套合较好,可视为尾晕元素。
4.2.2 组分分带特征
原生晕轴向分带序列计算方法有分带指数法(Grigoryan, 1974; 张鹰, 1984)、重心法(朴寿成等, 1996)、浓集系数法(解庆林, 1992)、概率法(邱德同, 1989)等。本文采用Grigoryan的分带指数法,分带指数法作为最早提出的指示元素轴向规律计算方法,是目前应用最广泛的一种方法。本文将控制矿脉带的钻孔见矿标高作为中段,矿体走向长度作为晕的宽度,以Au的异常下限数据为基础计算有异常的元素金属量,标准化之后进行分带指数计算,将每一元素分带指数的最大值所在分段作为该元素在序列中的位置。对于同一标高位置上出现多个元素分带指数最大值时,可根据变异性指数(G)和变异性指数梯度差(△G)原理确定同一中段的元素先后顺序(中华人民共和国国土资源部,2014b)。由此得出新房金矿106勘探线的轴向分带序列(表5)。
表 5 新房金矿轴向分带序列Table 5. Axial zonal sequence in the Xinfang gold deposit轴向分带序列 106勘探线整体 Au-Mo-F-Hg-Bi-Zn-Cu-Pb-Ag-W-Sn-As-Sb 22号矿脉带 Pb-W-Sn-Zn-Au-Bi-As-Sb-Mo-Ag-F-Hg-Cu 23号矿脉带 Bi-Ag-F-As-Sb-Pb-Au-Cu-Mo-W-Zn-Hg-Sn 24号矿脉带 F-W-Sn-Bi-Sb-Hg-Mo-As-Ag-Au-Zn-Pb-Cu 25号矿脉带 Zn-Au-Bi-As-Ag-Pb-F-Sb-Sn-Cu-Hg-W-Mo 27号矿脉带 Au-W-Sb-As-Bi-Mo-Sn-Hg-F-Pb-Zn-Ag-Cu 据李惠(李惠, 1996; 李惠等, 1998)总结的中国金矿床原生晕综合轴向分带B-I-As-Hg-F-Sb-Ba→Pb-Ag-Au-Zn-Cu→W-Bi-Mo-Mn-Ni-Cd-Co-V-Ti, 5条矿脉带分带序列整体叠加特征比较明显,呈现“反分带”现象,分带序列上部近矿晕、尾晕共存,暗示在剖面上应是一个矿体的尾部。分带序列中下部出现前缘晕元素及近矿晕元素Cu、Pb、Zn、Ag,暗示矿体中下部经历过多阶段热液成矿作用。具体来说,22号矿脉带中下部以铜矿化为主,Cu元素在浓度剖面图内带异常范围逐渐扩大,推测深部存在盲矿体;23号矿脉带中下部以Zn矿化为主;24号矿脉带中下部发生了以Ag、Au、Zn、Pb、Cu为主的成矿作用,结合浓度分带特征,在24号矿脉带下部几乎没有尾晕的中内带异常,而近矿晕元素异常面积增大,内带异常明显,显示矿体有继续延伸的可能;25号矿脉带发生以铜矿化为主的成矿作用,在浓度剖面图中出现尾晕元素Mo的内带异常,暗示已揭露的矿体接近中尾部;27号矿脉带中下部以铅、锌、银、铜矿化为主,且浓度剖面上近矿晕元素内带范围有扩大的趋势,暗示27号矿脉带深部存在盲矿体的潜力较大。
4.2.3 轴向地球化学参数
邵跃(1997)指出,地球化学参数中前缘元素与尾部元素的比值可以解释找矿工作中的一些地质地球化学问题。多阶段矿化形成的矿体(晕)地球化学参数在轴向上往往出现“转折”变化(李惠, 1996)。本文以前缘晕元素和尾晕元素衬度系数的比值作为地球化学参数评价指标,对深部成矿性进行预测。其中,衬度系数采用各元素几何平均值除各自背景值的方法,消除量级对结果的影响(张文彤, 2002)。考虑到27号矿脉带在矿区内只有2个钻孔控制,获取的数据较少,选择Au、Ag、Cu、Pb、Zn成矿元素的衬度系数作为参考(表6)。
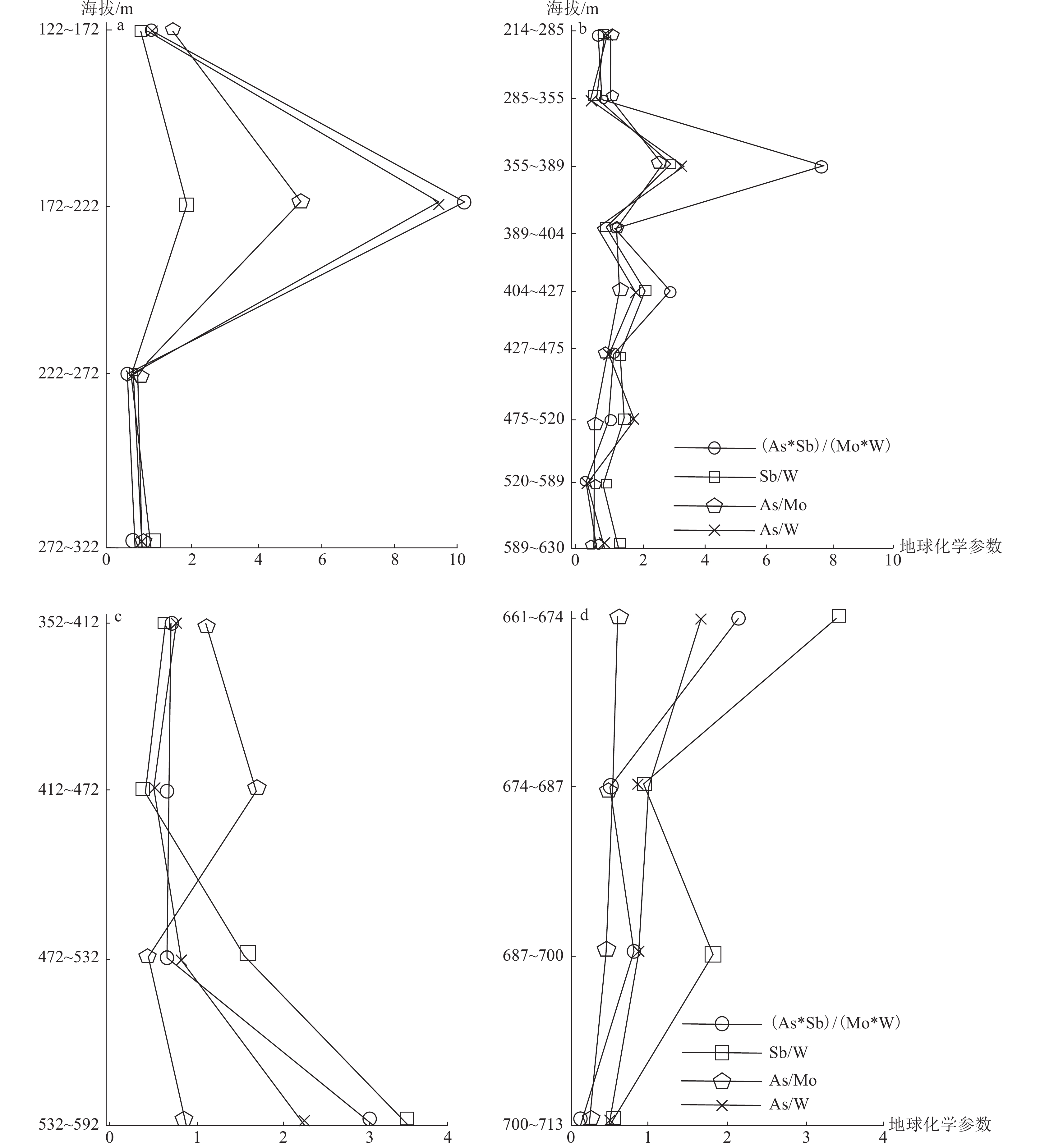
表 6 新房金矿床27号矿脉带地球化学参数Table 6. Geochemical parameters of the 27 ore vein in the Xinfang gold deposit钻孔 As/Mo As/W Sb/Mo Sb/W As*Sb/(Mo*W) Ag Au Cu Pb Zn ZK12 0.599 0.549 0.996 0.911 0.546 0.985 8.905 1.901 0.295 1.038 ZK3 0.432 0.950 0.455 1.000 0.432 1.592 3.432 3.359 0.503 2.519 注:Au含量单位为10−9,其他元素含量单位为10−6 从轴向地球化学参数变化看,整体从矿脉带头部至尾部振荡波动,有2种趋势:一种趋于升-降-升(-降-升)的波动,如 22、23、24、27 号矿脉带(图4−a~c;表6),与金矿床原生晕轴向地球化学参数理想模型中的 B 型、C 型相近(李惠等, 1998, 2015)。另一种“降-升-降”或“逐渐下降”,整体是下降的趋势,如 25 号矿脉带地球化学参数曲线(图 4−d)。
5. 讨 论
5.1 原生晕分带或反分带的推断
根据各矿化阶段矿物组成,结合元素地球化学性质,将矿体轴向分带序列(Au−Mo−F−Hg−Bi−Zn−Cu−Pb−Ag−W−Sn−As−Sb)与李惠等(1998,1999)总结的典型金矿床原生晕分带序列(B−I−As−Hg−F−Sb−Ba→Pb−Ag−Au−Zn−Cu→W−Bi−Mo−Mn−Ni−Cd−Co−V−Ti)对比可知,新房金矿床呈现明显的“反分带”现象,反映了多阶段矿化叠加成矿特征。
序列上部为Au-Mo组合,可能代表了石英−黄铁矿阶段/石英−方解石阶段的成矿成晕过程,形成了以黄铁矿为主的金属矿物,金以裂隙金、粒间金的形式赋存于黄铁矿中。序列中部代表石英−多金属硫化物阶段的成矿成晕过程。F、Hg 异常是由于F、Hg本身的挥发性强,作为成矿成晕过程中的前缘晕元素向上迁移。序列中部出现Bi,且排在Zn−Cu−Pb−Ag组合之前,相关性分析、聚类分析和因子分析中Bi与前缘晕、近矿晕元素关系密切,推测为Zn、Cu、Pb、Ag矿化成晕所致。Zn、Cu、Pb、Ag分别赋存在闪锌矿、黄铜矿、方铅矿和银金矿中。W、Sn是成矿过程中的尾晕元素,排在Zn−Cu−Pb−Ag组合之后。As主要赋存在含As的黄铁矿、毒砂矿物中,在序列下部与Sb一起出现,且在106勘探线成矿成晕元素浓度分带图(图3)中,As、Sb中内带异常多出现在矿体中上部,推测为深部盲矿体的成矿成晕迁移而来。
5条矿脉带清楚地显示了新房矿床多阶段矿化叠加成矿的特征,如24和27号矿脉带指示了主要成矿阶段的成矿成晕过程。24号矿脉带序列下部发生了以Ag、Au、Zn、Pb、Cu矿化为主的成矿成晕过程,金与黄铁矿、黄铜矿、方铅矿、闪锌矿、银金矿伴生产出。27号矿脉带上部是以Au矿化为主的石英−黄铁矿阶段或石英−方解石阶段;下部以Pb、Zn、Ag、Cu矿化为主,与方铅矿、闪锌矿、银金矿、黄铜矿在矿体中的富集部位基本一致。
5.2 原生晕地球化学对深部找矿的指示
通过对106勘探线元素异常特征的分析,发现元素异常总体出现在矿体或矿化带及断裂带附近,沿构造展布;多阶段成矿−晕在空间上显示出有部分同位叠加、矿尾晕与深部盲矿体叠加的多种叠加特征。
整体看,在新房金矿床上部和中部指示元素剖面浓度分带图中,主成矿元素 Au、Ag、Cu、Pb剖面特征形态相似,套合良好,发育面积较大的中内带异常。下部主成矿元素异常向下扩散,5条矿脉带基本未封闭。可分为3种情况:①在Au有外带异常的条件下,若前缘晕元素As、Sb有中、内带异常出现,则指示深部有盲矿体存在;②若再有Cu、Pb、Ag异常,为多金属硫化物矿化叠加部位,金成矿作用强烈,是很好的找矿靶区;③若Au为外带异常,而尾晕元素W、Mo为中、内带异常,前缘晕元素As、Sb只有外带异常,则深部无矿的可能性较大。矿体上部出现尾晕元素W、Mo或近矿晕Au、Ag、Cu、Pb,指示上部矿体可能已被剥蚀。
根据不同中段剖面上元素与矿体的关系,以及不同矿脉带、不同中段的轴向分带序列和轴向地球化学参数特征,识别出新房金矿床单一次成矿形成原生晕轴向分带序列,从上到下为:As、Sb→Au、Ag、Cu、Pb→W、Mo。事实上,5条矿脉带的分带序列整体上较混乱,出现“反分带”特征。矿体下部既出现尾晕元素W、Mo异常,又有前缘晕元素As、Sb中、内带异常叠加,推测为下部成矿过程的迁移所致,是深部盲矿体前缘晕叠加的结果,指示已知矿体深部有第二个盲矿体存在,如22、23、24、27号矿脉带深部可能有矿体延伸或盲矿体。
轴向地球化学参数的变化规律印证了分带序列特征。分带序列中近矿晕元素出现在中段,衬度系数变化趋势相似;尾晕元素出现在中段,衬度系数变化趋势相反,呈现下降趋势。参数尾部由降转为升,指示矿体向下延伸或为深部盲矿体的前缘晕,深部很可能存在一个未发现的成矿成晕过程(李惠等, 1998, 2015)。22、23、24号矿脉带具尖灭再现现象,轴向参数变化反映了矿化阶段形成下一个矿体前缘晕的叠加,深部仍存在金矿化。27 号矿脉带除 Au 外,Ag、Cu、Pb、Zn 元素衬度呈增大趋势,且在浓度剖面图中 27 号矿脉带下部显示 Ag、Cu、Pb元素内带异常,暗示在深部存在银、铜、铅、锌矿化。25 号矿脉带轴向参数变化则暗示该矿脉带下部为矿体的中尾部,深部成矿的可能性低于其他矿脉带。
5.3 新房金矿床原生晕叠加模式
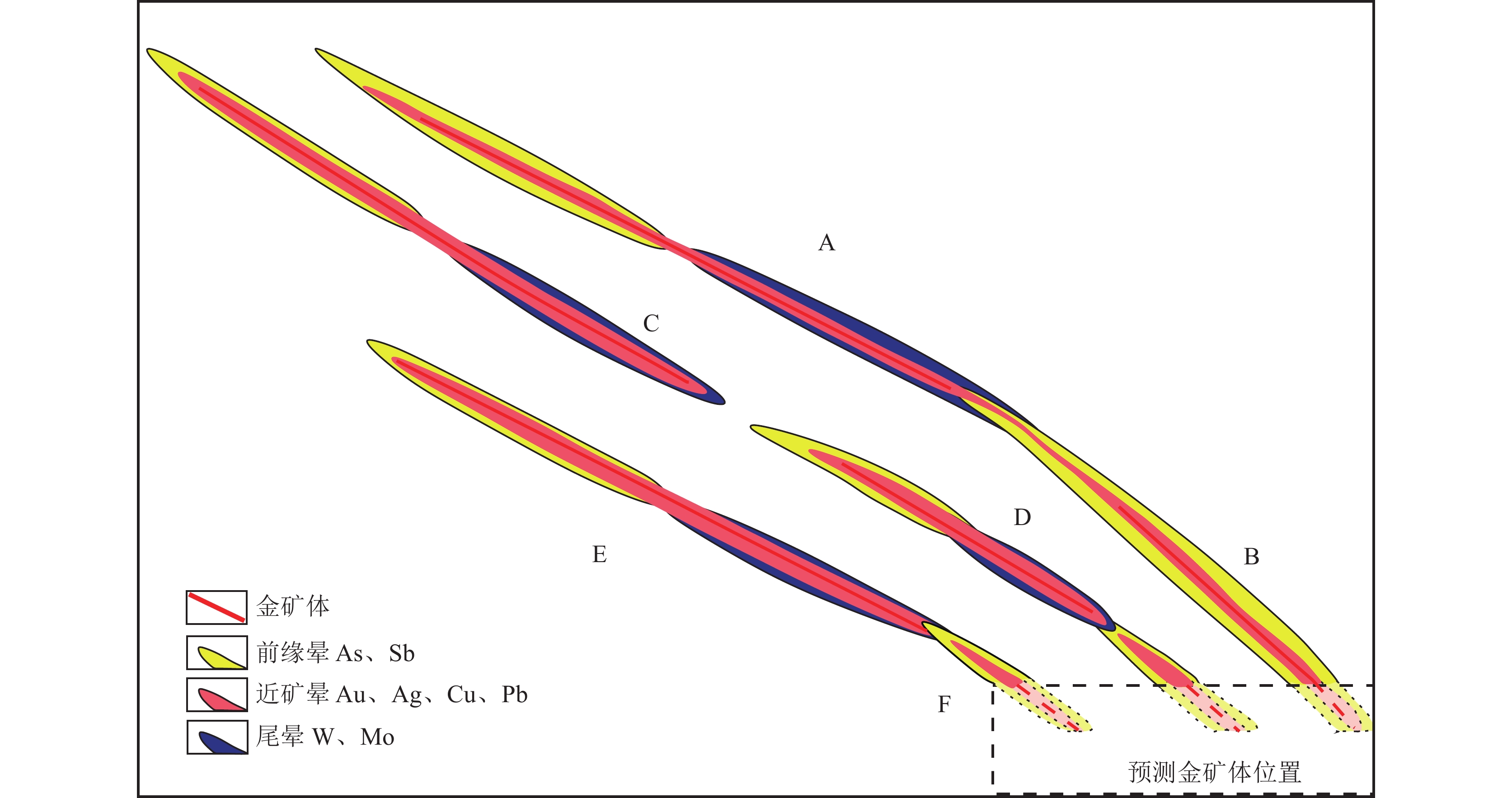
A-B、C-D、E-F模式(图5)为一次成矿过程形成矿体或是多阶段成矿过程分别形成的。A-B模式在上部矿体出现尾晕异常的同时又出现了前缘晕异常,即多个矿体首尾叠加,可分为2种情况:①一次成矿过程形成串珠状矿体,下部矿体B强度规模都比上部矿体A尾晕大;②A-B是多阶段成矿叠加的结果,部分同位或上下2个矿体前、尾晕叠加。可根据矿体尾部出现前缘晕、尾晕共存,推测深部存在盲矿体或矿体有向下延伸。C-D模式2个矿体首尾相距较大,没有叠加;下部盲矿体前缘晕与上部尾晕叠加。E-F模式是单一次成矿过程形成的矿体−原生晕或多阶段成矿形成的同位叠加矿体−晕,下部尾晕和前缘晕叠加,推测为盲矿体的前缘晕。
6. 结 论
(1)运用数理统计分析对矿区内13种元素分析得出,成矿元素Au与Ag、Cu、Hg、Pb、Sb、W、Zn有较好的相关性,可以作为新房金矿床的找矿指示元素。
(2)从各元素原生晕剖面特征得出,前缘晕元素为As、Sb、F、Hg,近矿晕元素为Ag、Au、Zn、Pb、Cu,尾晕元素为W、Mo、Sn、Bi。结合前缘晕、近矿晕、尾晕在空间上的叠加关系,推测在22、23、24号矿脉带中下部矿体有向深部延伸的可能。
(3)对106勘探线5个矿脉带分带序列的计算得出,整体上有“反分带”现象,推测为多阶段矿化造成原生晕叠加的结果。
(4)通过对地球化学参数轴向变化的评价得出,其变化趋势与矿体在空间上的位置基本吻合,同样指示22、23、24号矿脉带较25号矿脉带深部成矿的潜力更大;27号矿脉带下部可能发育有Ag、Cu、Pb、Zn为主的矿体。
致谢:文章撰写过程中得到中国地质调查局发展研究中心程志中高级工程师的支持和指导;审稿专家对本文提出了宝贵的修改意见,在此一并致以衷心的感谢。
-
图 1 新房金矿地质简图(据刘冰等,2020修改)
1—新近系残积物; 2—中寒武统; 3—下寒武统; 4—南华系桥头组; 5—青白口系南芬组; 6—青白口系钓鱼台组; 7—古元古界盖县组; 8—太古宇结晶基底; 9—推测和实测断层; 10—地质界线; 11—拆离断层; 12—矿体; 13—106勘探线及钻孔位置
Figure 1. Geological sketch map of the Xinfang gold deposit
表 1 新房金矿不同岩性元素平均含量
Table 1 The average of elements in different lithologies of the Xinfang gold deposit
岩性 样品数/个 几何平均值 Ag As Au Bi Cu F Hg Mo Pb Sb Sn W Zn 片麻岩 136 0.12 4.84 17.48 0.10 34.75 503.20 0.01 1.24 12.44 0.31 1.47 2.14 49.90 砂岩 142 0.18 4.64 20.47 0.21 16.51 634.53 0.01 1.54 25.17 0.37 2.47 3.31 59.13 板岩 72 0.08 4.30 2.06 0.41 12.30 772.88 0.01 0.85 19.87 0.38 3.77 2.04 81.24 蚀变岩样 169 0.25 2.65 28.73 0.11 27.93 534.91 0.01 1.69 35.82 0.33 1.70 2.27 49.64 注:Au含量单位为10−9,其他元素含量单位为10−6 表 2 新房金矿床成矿成晕元素相关系数矩阵
Table 2 Correlation coefficient matrix of mineralization elements halo in the Xinfang gold deposit
元素 Ag As Au Bi Cu F Hg Mo Pb Sb Sn W Zn Ag 1 As 0.157 1 Au 0.830 0.030 1 Bi 0.222 0.420 0.069 1 Cu 0.469 0.009 0.534 0.032 1 F 0.106 0.026 0.133 0.085 0.023 1 Hg 0.205 0.123 0.204 0.076 0.208 0.017 1 Mo 0.228 0.013 0.106 0.073 0.025 0.093 0.093 1 Pb 0.711 0.013 0.717 0.072 0.908 0.052 0.229 0.084 1 Sb 0.296 0.502 0.231 0.195 0.134 0.089 0.240 0.079 0.231 1 Sn 0.106 0.159 0.117 0.161 0.040 0.578 0.107 0.077 0.053 0.132 1 W 0.143 0.067 0.128 0.068 0.018 0.148 0.038 0.103 0.013 0.043 0.201 1 Zn 0.236 0.248 0.242 0.128 0.346 0.081 0.643 0.072 0.354 0.186 0.084 0.029 1 表 3 新房金矿床正交旋转因子载荷矩阵
Table 3 Orthogonal rotation factor load matrix in the Xinfang gold deposit
元素 成分 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 Ag 0.811 0.258 −0.115 0.031 0.288 As −0.048 0.861 0.044 0.125 −0.032 Au 0.855 0.095 −0.109 0.048 0.184 Bi 0.064 0.673 0.147 −0.048 0.086 Cu 0.838 −0.060 0.042 0.210 −0.181 F −0.047 −0.050 0.866 0.033 −0.019 Hg 0.110 0.086 0.027 0.887 0.087 Mo 0.032 0.023 −0.230 0.145 0.753 Pb 0.946 0.027 −0.004 0.175 −0.060 Sb 0.180 0.711 −0.075 0.175 0.011 Sn −0.084 0.182 0.836 0.082 0.018 W 0.078 0.038 0.369 −0.081 0.668 Zn 0.226 0.137 0.083 0.852 −0.009 特征值 3.104 1.844 1.702 1.673 1.184 累积方差贡献率/% 23.880 38.065 51.154 64.028 73.135 表 4 新房金矿床各元素浓度分带阈值
Table 4 Concentration banding thresholds of elements in the Xinfang gold deposit
元素 Ag As Au Cu Mo Pb Sb W 外带 0.2 3 6 35 2 20 0.3 3 中带 0.4 6 25 70 4 40 0.6 6 内带 0.8 12 100 140 8 80 1.2 12 注:Au含量单位为10−9,其他元素含量单位为10−6 表 5 新房金矿轴向分带序列
Table 5 Axial zonal sequence in the Xinfang gold deposit
轴向分带序列 106勘探线整体 Au-Mo-F-Hg-Bi-Zn-Cu-Pb-Ag-W-Sn-As-Sb 22号矿脉带 Pb-W-Sn-Zn-Au-Bi-As-Sb-Mo-Ag-F-Hg-Cu 23号矿脉带 Bi-Ag-F-As-Sb-Pb-Au-Cu-Mo-W-Zn-Hg-Sn 24号矿脉带 F-W-Sn-Bi-Sb-Hg-Mo-As-Ag-Au-Zn-Pb-Cu 25号矿脉带 Zn-Au-Bi-As-Ag-Pb-F-Sb-Sn-Cu-Hg-W-Mo 27号矿脉带 Au-W-Sb-As-Bi-Mo-Sn-Hg-F-Pb-Zn-Ag-Cu 表 6 新房金矿床27号矿脉带地球化学参数
Table 6 Geochemical parameters of the 27 ore vein in the Xinfang gold deposit
钻孔 As/Mo As/W Sb/Mo Sb/W As*Sb/(Mo*W) Ag Au Cu Pb Zn ZK12 0.599 0.549 0.996 0.911 0.546 0.985 8.905 1.901 0.295 1.038 ZK3 0.432 0.950 0.455 1.000 0.432 1.592 3.432 3.359 0.503 2.519 注:Au含量单位为10−9,其他元素含量单位为10−6 -
Grigoryan S V. 1974. Primary geochemical halos in prospecting and exploration of hydrothermal deposit[J]. International Geology Review, 16: 1, 12−25.
Liu S J, Chen B, Zheng J H, et al. 2021. Genesis of the Xinfang gold Deposit, Liaodong Peninsula: In−sights from Fluid Inclusions and S−Sr Isotopic Constrains[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 32(1): 68−80. doi: 10.1007/s12583-020-1074-7
Wei J H, Tan W J, Guo D Z, et al. 2007. Isotope systematics and metallogenetic age of Zhuanghe gold deposit, Liaoning Province, China[J]. Journal of central south university technology, 14(1): 104−110. doi: 10.1007/s11771-007-0021-4
Yu B, Zeng Q D, Frimmel H, et al. 2021. A magmatic−hydrothermal origin of the Xinfang gold deposit, Liaodong Peninsula, China, revealed by in−situ S−Pb isotopes and trace element analyses of pyrite[J]. Resource Geology, 71(2): 1−17.
Zhang P, Zhao Y, Kou L L, et al. 2022. Genesis of the Xinfang magmatic−hydrothermal gold deposit, Liaodong Peninsula, China: Constraints from pyrite Re−Os isotopes, C, O, S, Pb, Si, He and Ar isotopes[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, (148): 105025.
Zhang P, Zhao Y, Kou L L, et al. 2023. Genesis of the Xinfang gold deposit, Liaodong Peninsula: Constraints from fluid inclusions, H−O−S−Pb isotopes, pyrite trace element concentrations, and chronology[J]. Gondwana Research, (113): 210−231.
陈永清, 韩学林, 赵红娟, 等. 2011. 内蒙花敖包特Pb−Zn−Ag多金属矿床原生晕分带特征与深部矿体预测模型[J]. 地球科学, 36(2): 236−246. 代力. 2013. 四川夏塞银铅锌矿床I号矿体原生晕地球化学及深部预测[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文: 52−77. 郭大招, 魏俊浩, 张可清, 等. 2005. 辽东庄河金矿同位素地球化学特征及成矿时代[J]. 地质学报, (5): 671−678. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2005.05.012 郝迪, 孙彪, 孟菲蓉. 2021. 甘肃省寨上金矿床原生地球化学晕特征及其地质意义[J]. 西北地质, 54(4): 88−99. 李惠. 1996. 大型金矿盲矿的原生叠加晕和包裹体气晕、离子晕预测准则[J]. 贵金属地质, (4): 241−247, 278. 李惠, 张文华. 1998. 大型、特大型金矿盲矿预测的原生叠加晕模型[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社: 1−8. 李惠, 张文华, 刘宝林, 等. 1999. 中国主要类型金矿床的原生晕轴向分带序列研究及其应用准则[J]. 地质与勘探, 35(1): 32−35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.1999.01.009 李惠, 禹斌, 李德亮, 等. 2015. 不同类型金矿深部盲矿预测的构造叠加晕模型[J]. 矿产与地质, 29(5): 648−653, 658. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2015.05.018 李彦强, 段建华, 何学昭, 等. 2022. 青海白日其利金矿床构造叠加晕特征及深部找矿预测[J]. 西北地质, 55(4): 316−323. 刘崇民, 胡树起, 马生明. 2014. 热液多金属矿岩石地球化学勘查[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 1−6. 刘冰, 高巍, 王学强. 2020. 辽宁省庄河市新房金矿及外围专项地质填图课题[R]. 辽宁省第七地质大队有限责任公司, 16−24. 刘英俊, 曹励明, 李兆麟, 等. 1984. 元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 290−343. 林成贵, 程志中, 吕志成, 等. 2020. 甘肃省早子沟金矿原生晕分带特征及深部找矿预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 50(1): 70−84. 朴寿成, 杨永强, 连长云. 1996. 原生晕分带序列研究方法综述[J]. 世界地质, (1): 44−48, 53. 邱德同. 1989. 确定矿床原生晕指示元素分带序列的新方法[J]. 地质与勘探, (8): 51−53. 邵跃. 1984. 矿床元素原生分带的研究及其在地球化学找矿中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, (2): 47−55. 邵跃. 1988. 金矿化探异常评价的几个问题[J]. 中国地质, (5): 22−23. 邵跃. 1997. 热液矿床岩石测量(原生晕法)找矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 1−143. 王崇云. 1987. 地球化学找矿基础[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 39−43. 谢学锦, 欧阳宗昕. 1982. 中国的勘查地球化学的回顾与展望[J]. 地质论评, 28(6): 598−602. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1982.06.022 解庆林. 1992. 浓集指数法确定矿床原生晕元素轴向分带序列[J]. 地质与勘探, (6): 55. 于俊博, 宋云涛, 郭志娟, 等. 2014. R型聚类分析在区域化探元素分组中的作用探讨[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 36(6): 771−776. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2014.06.20 尹志刚, 姜然, 陈军典, 等. 2023. 黑龙江省木兰县六块地南土壤地球化学异常特征及成矿预测[J]. 地质通报, 42(12): 2015−2027. 张鹰. 1984. 应用格氏法确定元素分带序列具体问题的探讨[J]. 地质与勘探, (5): 58−61. 张文彤. 2002. SPSS11统计分析教程[M]. 北京: 希望电子出版社: 190−210. 章永梅, 顾雪祥, 程文斌, 等. 2010. 内蒙古柳坝沟金矿床原生晕地球化学特征及深部成矿远景评价[J]. 地学前缘, 17(2): 209−221. 中华人民共和国国土资源部. 2014a. 多目标区域地球化学调查规范(DZ/T 0258—2014)[S]. 中华人民共和国国土资源部. 2014b. 岩石地球化学测量技术规程(DZ-T 0248—2014) [S]. 钟海燕, 殷峰. 2018. IBM SPSS统计分析与应用[M]. 北京: 中国经济出版社: 136−151. 仲米山, 张国仁, 高福亮, 等. 2021. 辽南新房变质核杂岩的发现及地质意义[J]. 地质科学, 56(1): 272−287. doi: 10.12017/dzkx.2021.016 -
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: