Application of CSAMT and logging combined constrained inversion in oil shale identification in the southeast uplift area of Songliao Basin
-
摘要:
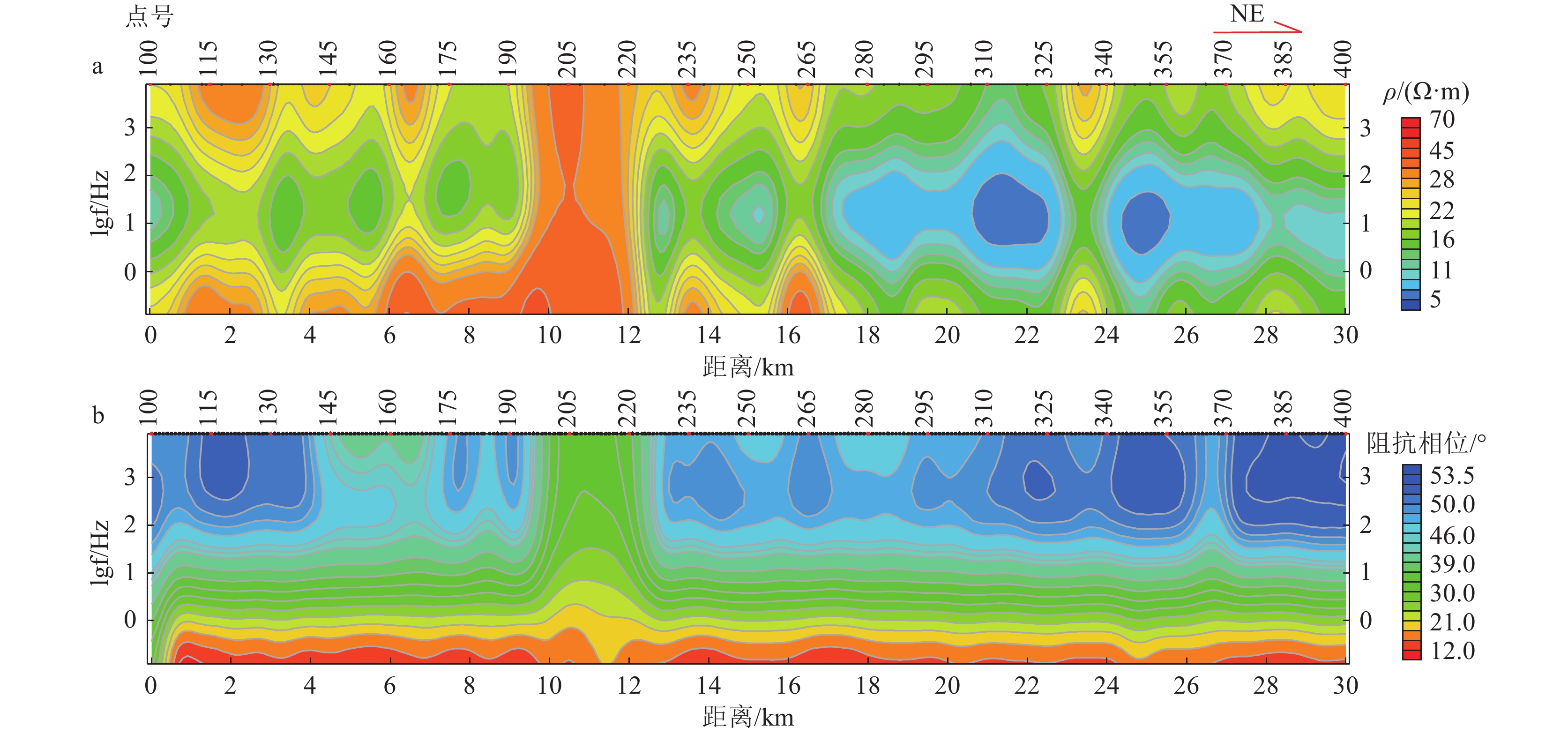
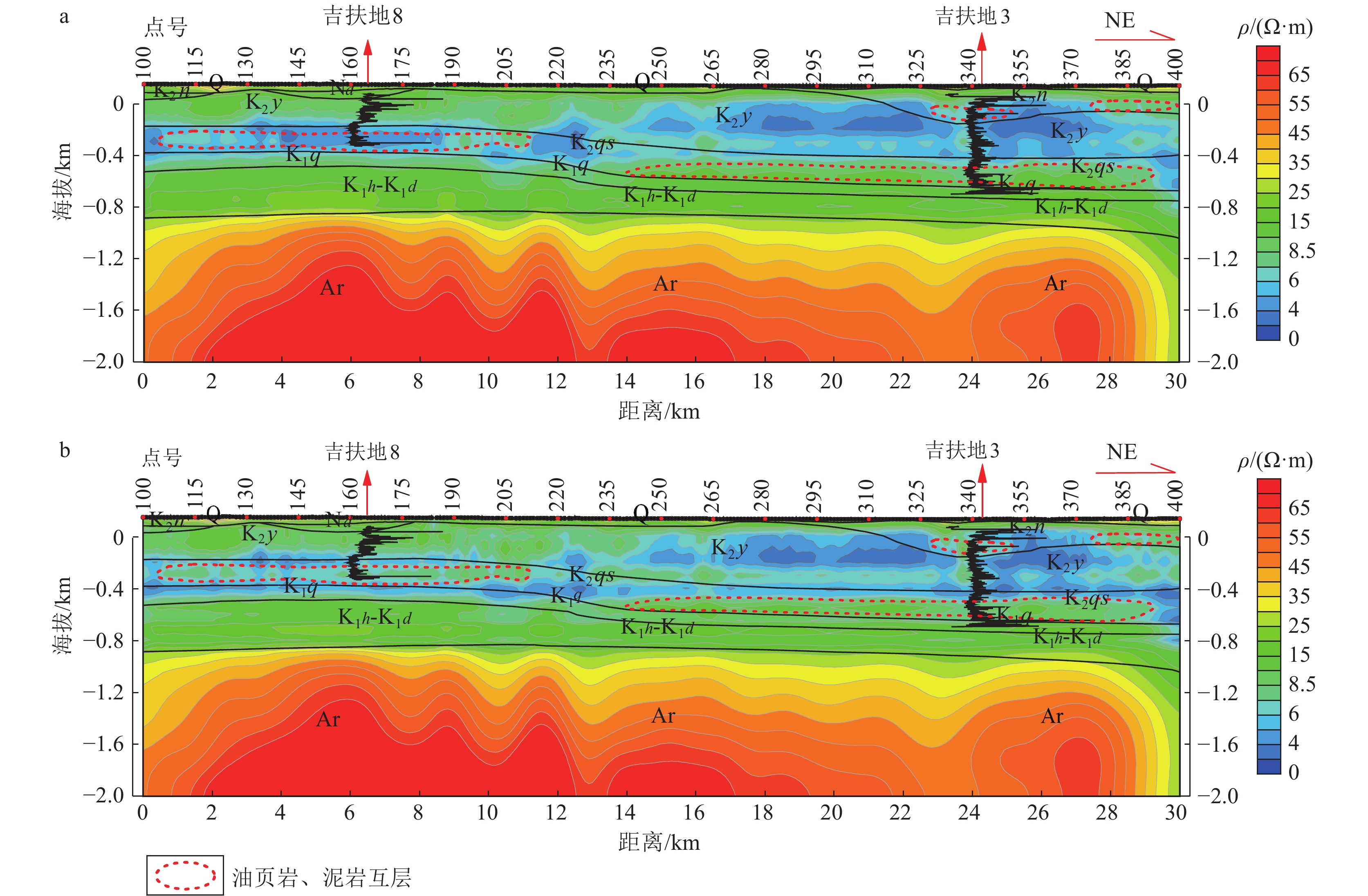
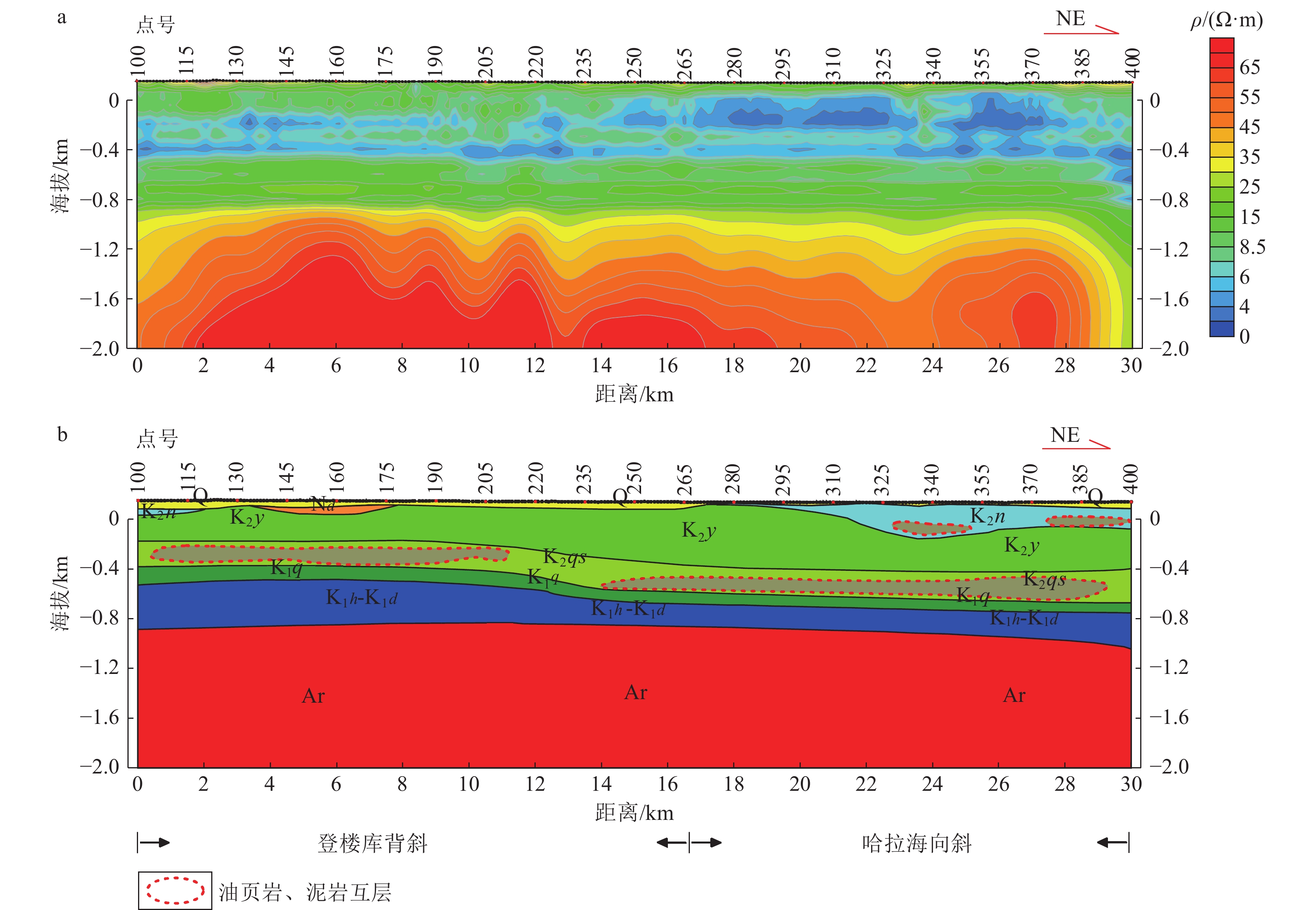
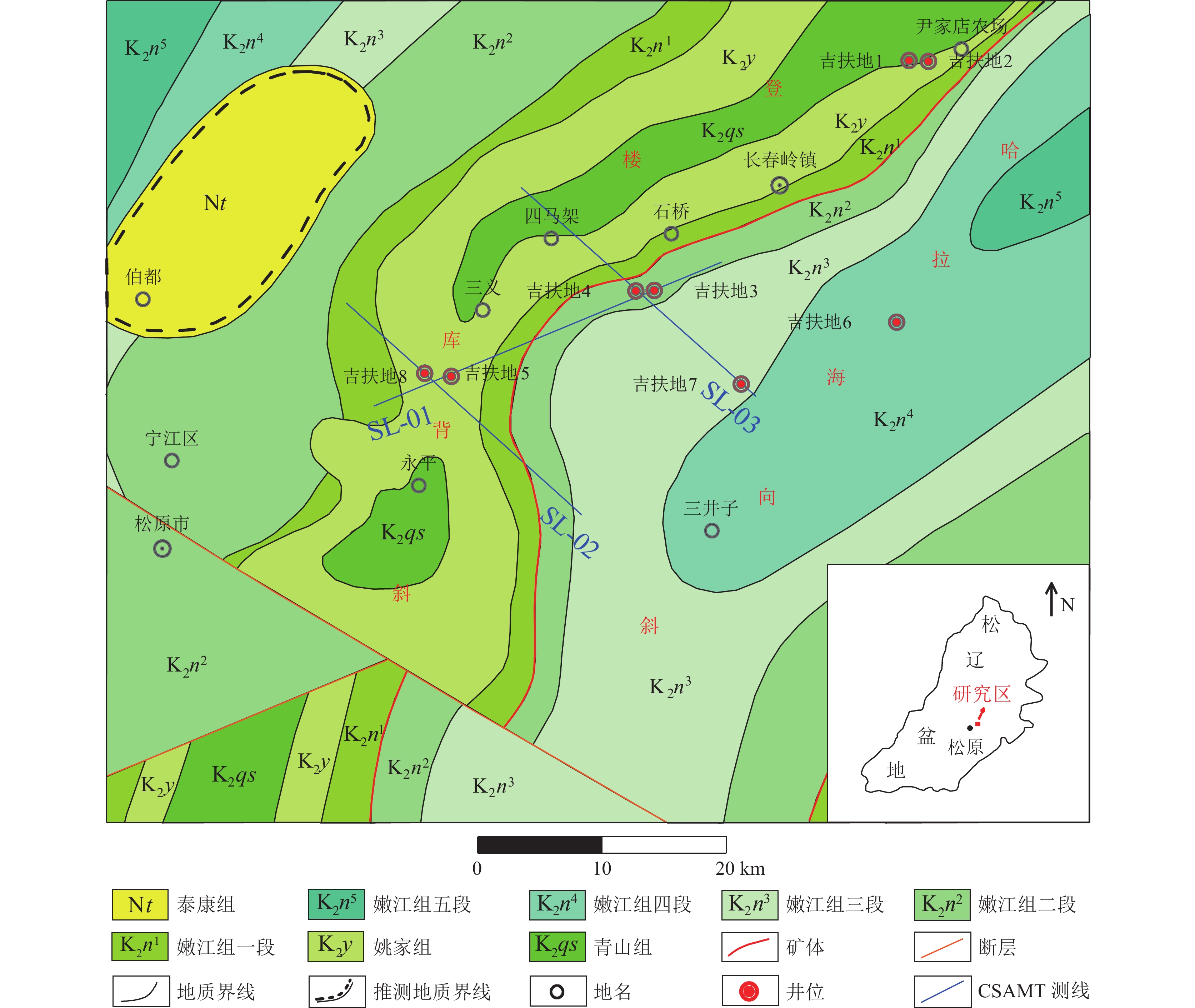
松辽盆地油页岩地震勘探难度大,为此在松辽盆地东南隆起区开展可控源音频大地电磁法(CSAMT)和测井联合约束反演技术应用研究。研究表明,联合约束反演技术可以将油页岩与泥页互层整体作为相对高阻层进行划分识别。利用该项技术查明研究区嫩江组油页岩主要分布在哈拉海向斜,仅在登楼库背斜西部局部沉积;青山口组油页岩在登楼库背斜、哈拉海向斜均有分布,整体呈沿登楼库背斜轴高、沿背斜轴两翼逐渐减薄的特征,为进一步勘探指明了有利方向。
Abstract:The seismic exploration of oil shale in Songliao Basin is difficult. Therefore, the application of controlled source audio magnetotelluric method and logging joint constrained inversion technology is carried out in the southeast uplift area of Songliao Basin. The research shows that the joint constraint inversion technology can divide and identify the oil shale and mud shale interbed as a relatively high resistance layer. Using this technology, it is found that the oil shale of the Nenjiang Formation in the study area is mainly distributed in the Halahai syncline, only locally deposited in the western part of the Denglouku anticline; the oil shale of the Qingshankou Formation is distributed in the Denglouku anticline and the Halahai syncline. The whole is characterized by the height along the Denglouku anticline axis and the gradual thinning along the two wings of the anticline axis, which points out the favorable direction for further exploration.
-
-
表 1 研究区及周缘地区岩层电性特征
Table 1 The electrical characteristics of rock strata in the study area and surrounding areas
系 统 组 符号 岩性特征 ρ/(Ω·m) 电性 第四系 Q 粘土、亚粘土、砂砾石 37.9 表层高阻 古近系—新近系 大安组 Nd 泥岩、粉砂质泥岩、泥质粉砂岩 3.2 低阻层 白垩系 上统 嫩江组 K2n 砂砾岩、粉砂岩、细砂岩、泥质粉砂岩、粉砂质泥岩、泥岩、油页岩 3.9 姚家组 K2y 泥岩、粉砂质泥岩、泥质粉砂岩、粉砂岩 6.8 青山口组 K2qs 质粉砂岩、粉砂岩、粉砂质泥岩、油页岩 22.8 下统 泉头组 K1q 粉砂质泥岩、泥岩、粉砂岩、泥质粉砂岩、细砂岩、砂岩 28.2 中阻层 登楼库组 K1d 砂砾岩夹泥岩 71.5 营城组 K1yc 泥岩与火山岩间互夹煤层 211.7 次高阻层 沙河子组 K1sh 火山岩、砂泥岩夹煤线 220.0 火石岭组 K1h 火山碎屑岩、火山喷发岩 240.0 石炭系—二叠系 293.0 基底高阻 表 2 研究区白垩系不同岩性测井曲线响应分布范围
Table 2 Logging response distribution range table of Cretaceous different lithology in the study area
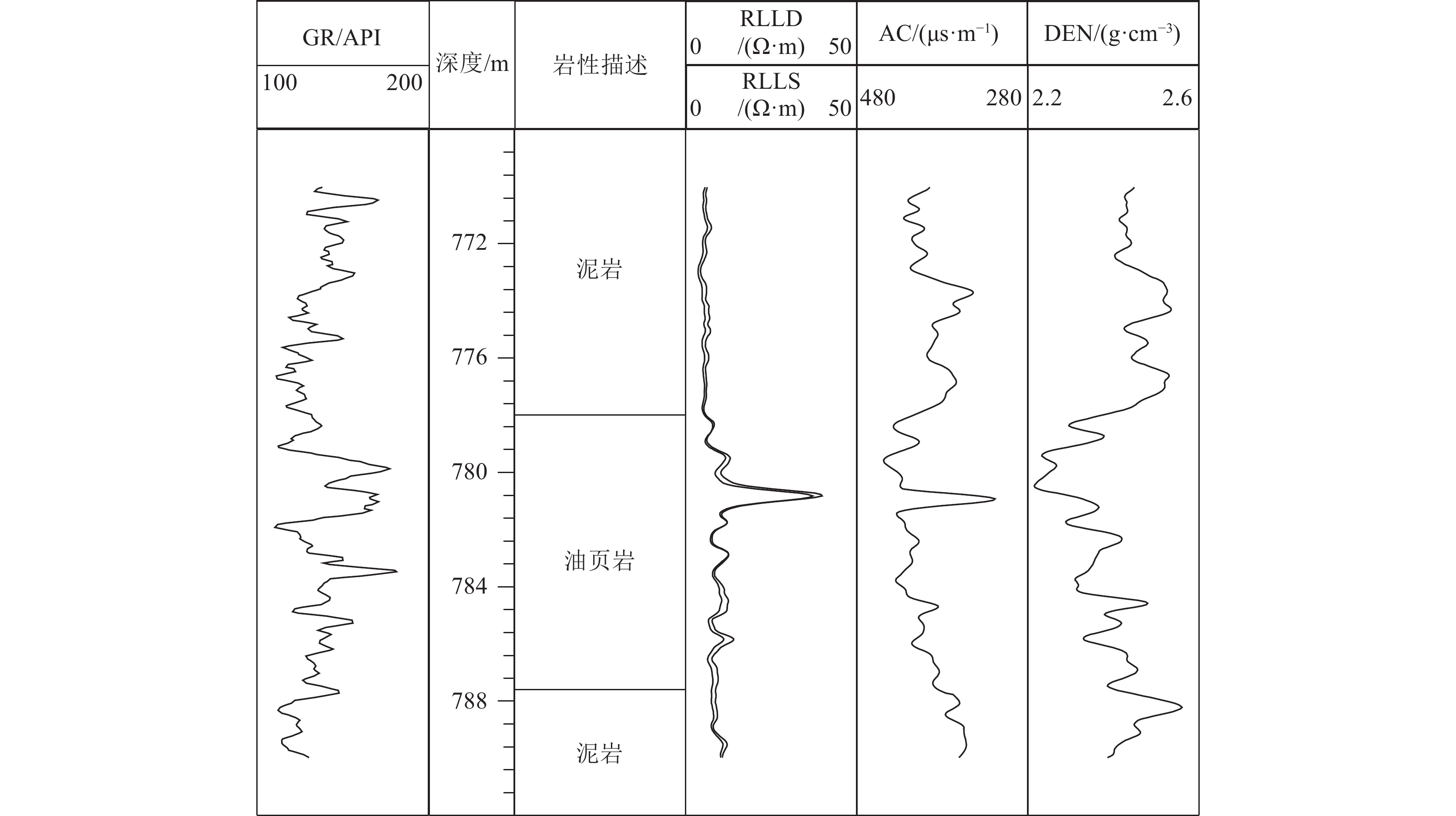
测井识别岩性 电阻率平均值/(Ω·m) 声波时差平均值/(μs·m−1) 补偿密度平均值/(g·cm−3) 自然伽马平均值/API 粉砂岩 10 ~ 13 250 ~ 430 2.15 ~ 2.62 50 ~ 115 泥质粉砂岩 6.5 ~ 17.5 240 ~ 450 2.20 ~ 2.50 75 ~ 140 粉砂质泥岩 5.5 ~ 12 275 ~ 500 2.25 ~ 2.55 90 ~ 135 泥岩 5 ~ 9 330 ~ 450 2.25 ~ 2.50 110 ~ 150 油页岩 7.5 ~ 15 ≥375 ≤2.35 ≥130 表 3 吉扶地3井油页岩及附近地层约束信息
Table 3 Constraint information of oil shale and nearby strata in Well Jifudi 3
序号 顶部深度/m 底部深度/m 厚度/m 电阻率/(Ω·m) 岩性 序号 顶部深度/m 底部深度/m 厚度/m 电阻率/(Ω·m) 岩性 1 258.2 268.6 10.4 9.19 泥岩 15 469.8 476.9 7.1 6.23 泥岩 2 268.6 281.4 12.8 10.70 粉砂质泥岩 16 476.9 478.0 1.1 6.99 油页岩 3 281.4 289.0 7.6 9.55 泥岩 17 478.0 483.2 5.2 5.70 泥岩 4 289.0 294.1 5.1 12.90 粉砂质泥岩 18 483.2 484.1 0.9 6.27 油页岩 5 294.1 298.3 4.2 9.44 泥岩 19 484.1 487.3 3.2 6.22 泥岩 6 298.3 306.6 8.3 11.61 粉砂质泥岩 20 487.3 489.5 2.2 8.38 粉砂质泥岩 7 306.6 312.4 5.8 9.55 泥岩 21 489.5 494.2 4.7 6.06 油页岩 8 312.4 341.0 28.6 10.92 粉砂质泥岩 22 494.2 503.2 9.0 5.25 泥岩 9 341.0 382.3 41.3 6.49 泥岩 23 503.2 507.1 3.9 12.73 油页岩 10 382.3 383.2 0.9 6.45 油页岩 24 507.1 514.0 6.9 7.19 泥岩 11 383.2 462.2 79.0 5.95 泥岩 25 514.0 519.3 5.3 11.22 油页岩 12 462.2 463.4 1.2 7.19 油页岩 26 519.3 523.1 3.8 5.91 泥岩 13 463.4 468.0 4.6 6.10 泥岩 27 523.1 524.0 0.9 10.72 油页岩 14 468.0 469.8 1.8 7.65 油页岩 28 524.0 528.7 4.7 8.34 粉砂质泥岩 表 4 吉扶地8井油页岩及附近地层约束信息
Table 4 Constraint information of oil shale and nearby strata in Well Jifudi 8
序号 顶部深度/m 底部深度/m 厚度/m 电阻率/(Ω·m) 岩性 序号 顶部深度/m 底部深度/m 厚度/m 电阻率/(Ω·m) 岩性 1 258.2 268.6 10.4 9.19 泥岩 15 469.8 476.9 7.1 6.23 泥岩 2 268.6 281.4 12.8 10.70 粉砂质泥岩 16 476.9 478.0 1.1 6.99 油页岩 3 281.4 289.0 7.6 9.55 泥岩 17 478.0 483.2 5.2 5.70 泥岩 4 289.0 294.1 5.1 12.90 粉砂质泥岩 18 483.2 484.1 0.9 6.27 油页岩 5 294.1 298.3 4.2 9.44 泥岩 19 484.1 487.3 3.2 6.22 泥岩 6 298.3 306.6 8.3 11.61 粉砂质泥岩 20 487.3 489.5 2.2 8.38 粉砂质泥岩 7 306.6 312.4 5.8 9.55 泥岩 21 489.5 494.2 4.7 6.06 油页岩 8 312.4 341.0 28.6 10.92 粉砂质泥岩 22 494.2 503.2 9.0 5.25 泥岩 9 341.0 382.3 41.3 6.49 泥岩 23 503.2 507.1 3.9 12.73 油页岩 10 382.3 383.2 0.9 6.45 油页岩 24 507.1 514.0 6.9 7.19 泥岩 11 383.2 462.2 79.0 5.95 泥岩 25 514.0 519.3 5.3 11.22 油页岩 12 462.2 463.4 1.2 7.19 油页岩 26 519.3 523.1 3.8 5.91 泥岩 13 463.4 468.0 4.6 6.10 泥岩 27 523.1 524.0 0.9 10.72 油页岩 14 468.0 469.8 1.8 7.65 油页岩 28 524.0 528.7 4.7 8.34 粉砂质泥岩 -
Brown V, Key K, Singh S. 2012. Seismically regularized controlled-source electromagnetic inversion[J]. Geophysics, 77(1): 57.
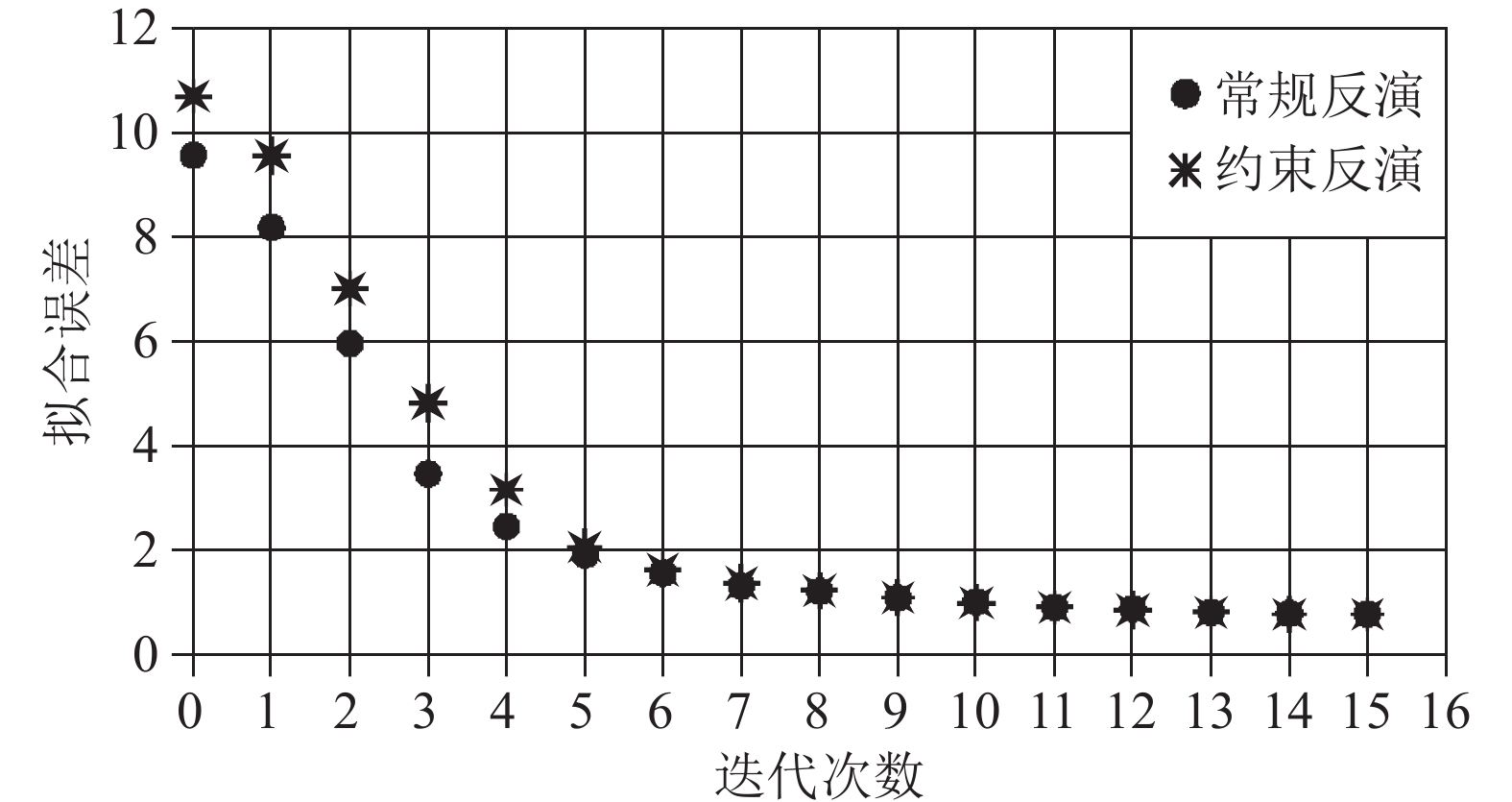
Constable S C, Parker R L, Constable C G. 1987. Occam's inversion: A practical algorithm for generating smooth models from electromagnetic sounding data[J]. Geophysics, 52(3): 289−300. doi: 10.1190/1.1442303
丰莉, 王石, 郭文建. 2016. 测井技术在泰安姚庄油页岩勘探中的识别应用[J]. 山东国土资源, 32(5): 75−78. 高立新. 2008. 中国松辽盆地构造环境及东北地区地震活动特征分析[J]. 地震, 28(4): 59−67. 何梅兴. 2006. 可控源音频大地电磁二维OCCAM反演研究[D]. 中国地质大学(武汉)博士学位论文. 贺君玲, 邓守伟, 陈文龙, 等. 2006. 利用测井技术评价松辽盆地南部油页岩[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 36(6): 909−914. 侯祥麟. 1994. 中国页岩油工业[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社: 156-158. 李宝毅, 王建鹏, 徐银波, 等. 2012. 断陷和坳陷盆地富有机质泥岩测试参数及研究意义[J]. 世界地质, 31(4): 778−784. 李翔, 刘招君, 孙平昌, 等. 2014. 松辽盆地东南隆起区青山口组一段泥页岩地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 世界地质, 33(4): 746−757,767. 李桂林. 2009. 现有技术条件下松辽盆地北部地区地震勘探分辨率潜力研究[D], 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文. 李致君, 李海艳, 李建国, 等. 2018. CSAMT在黄河沉降断裂带地热勘察中的应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 15(04): 509−513. 李英宾, 李毅, 魏滨, 等. 2019. CSAMT和浅层地震在松辽盆地西南部铀矿勘查中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 55(6): 1442−1451. 刘同庆. 2020. 吉木萨尔南油页岩测井识别及其含油率测算初探[J]. 山东煤炭科技, 236(4): 150−152, 156. 刘招君, 董清水, 叶松青, 等. 2006. 中国油页岩资源现状[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 36(6): 869−876. 刘招君, 杨虎林, 董清水, 等. 2009. 中国油页岩[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社: 38-116. 孟翠贤. 2003. 约束反演在金坛盆地CSAMT勘探中的应用[C]//中国国际地球电磁学术讨论会: 217-218. 秦伟. 2013. 可控源音频大地电磁法在地层识别中的研究[D]. 东北石油大学博士学位论文. 王永明, 郭建军, 刘宏. 2007. 陕北三叠纪煤田勘探中油页岩的地球物理测井效果[J]. 陕西地质, 25(1): 59−63. 王红岩, 李景明, 赵群, 等. 2009. 中国新能源资源基础及发展前景展望[J]. 石油学报, 30(3): 469−474. 余年, 李坚, 雷旭友, 等. 2012. 大地电磁约束反演在隧道勘探中的研究[J]. 铁道工程学报, 29(7): 41−46,61. 张凯飞. 2016. 基于电性约束的NLCG反演在CSAMT资料中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 40(3): 629−634. 张利. 2020. CSAMT法在地热法勘探中的应用[J]. 煤炭与化工, 43(9): 88−90. 赵政璋, 国干, 胡素云, 等. 2005. 全球油气勘探新进展[J]. 石油学报, 26(6): 119−126. 朱宇启, 裴建新, 段双敏, 等. 2021. 测井约束的海洋CSEM反演及其在南黄海中部隆起区勘探应用[J]. 中国海洋大学学报:自然科学版, 51(6): 70−77.



 下载:
下载: